Pexidartinib and Nintedanib Combination Therapy Targets Macrophage Polarization to Reverse Pulmonary Fibrosis: A Preclinical Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
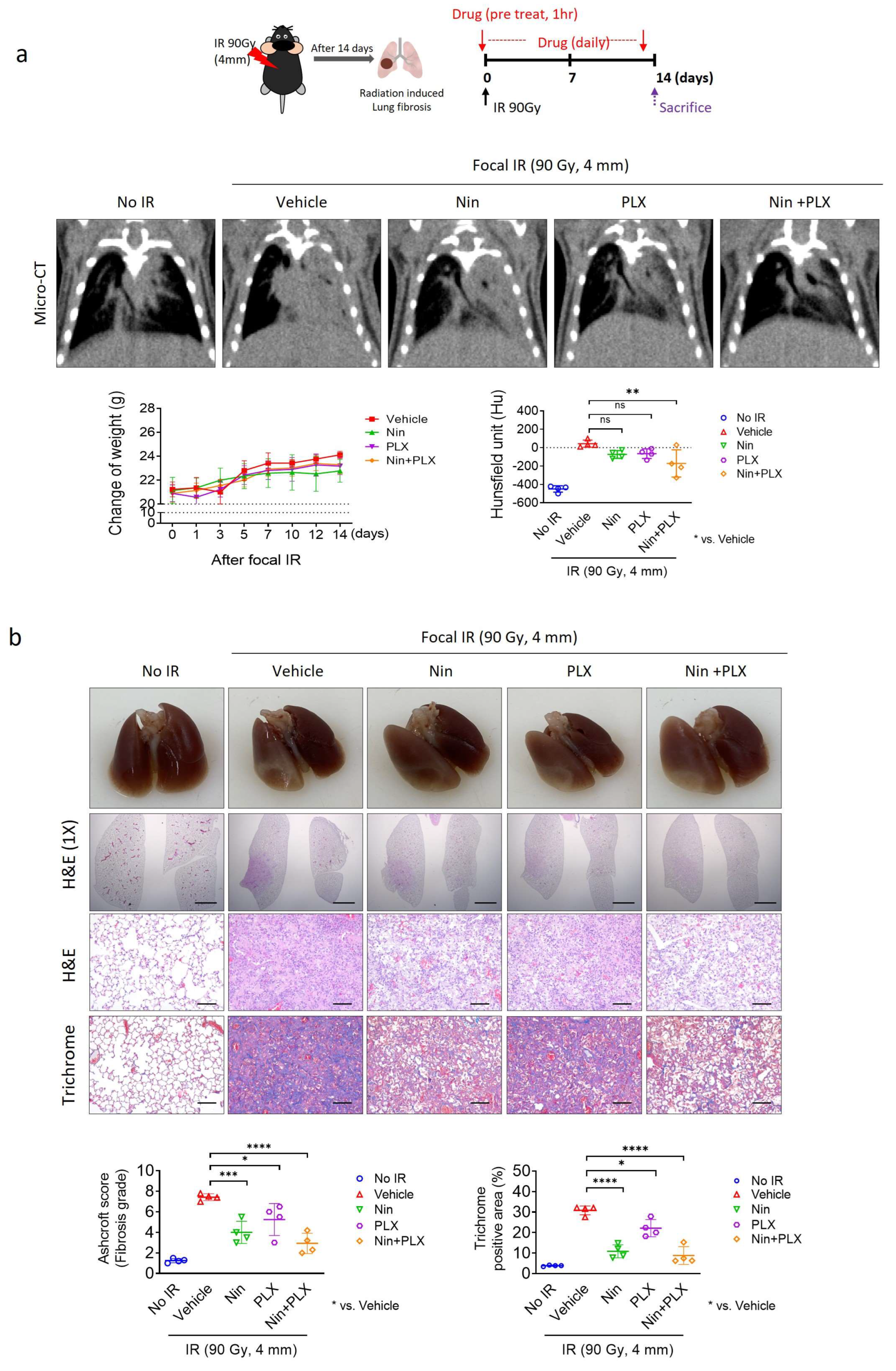
2.1. Enhanced Efficacy of Nintedanib in RIPF Through Combined Treatment with PLX3397
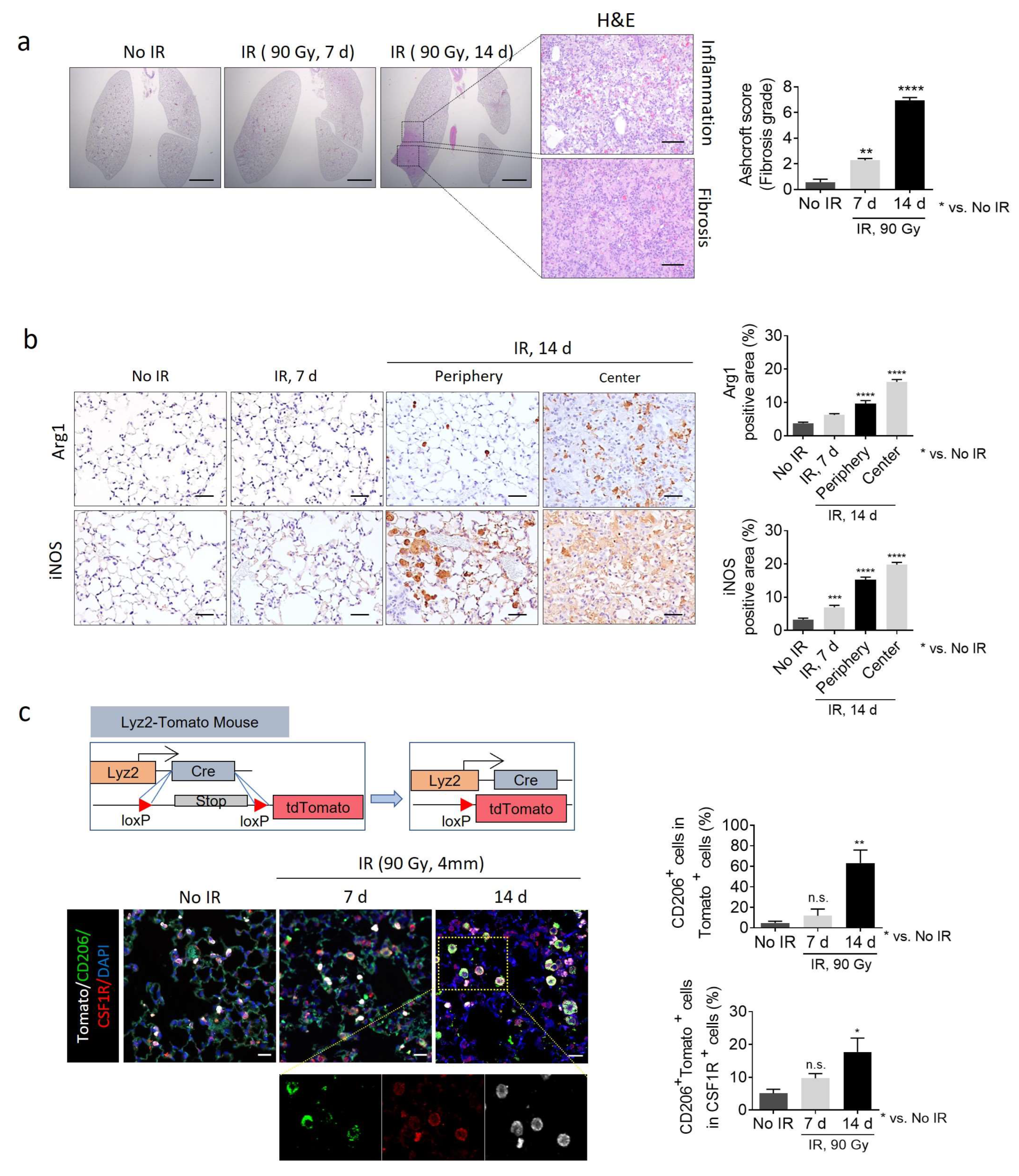
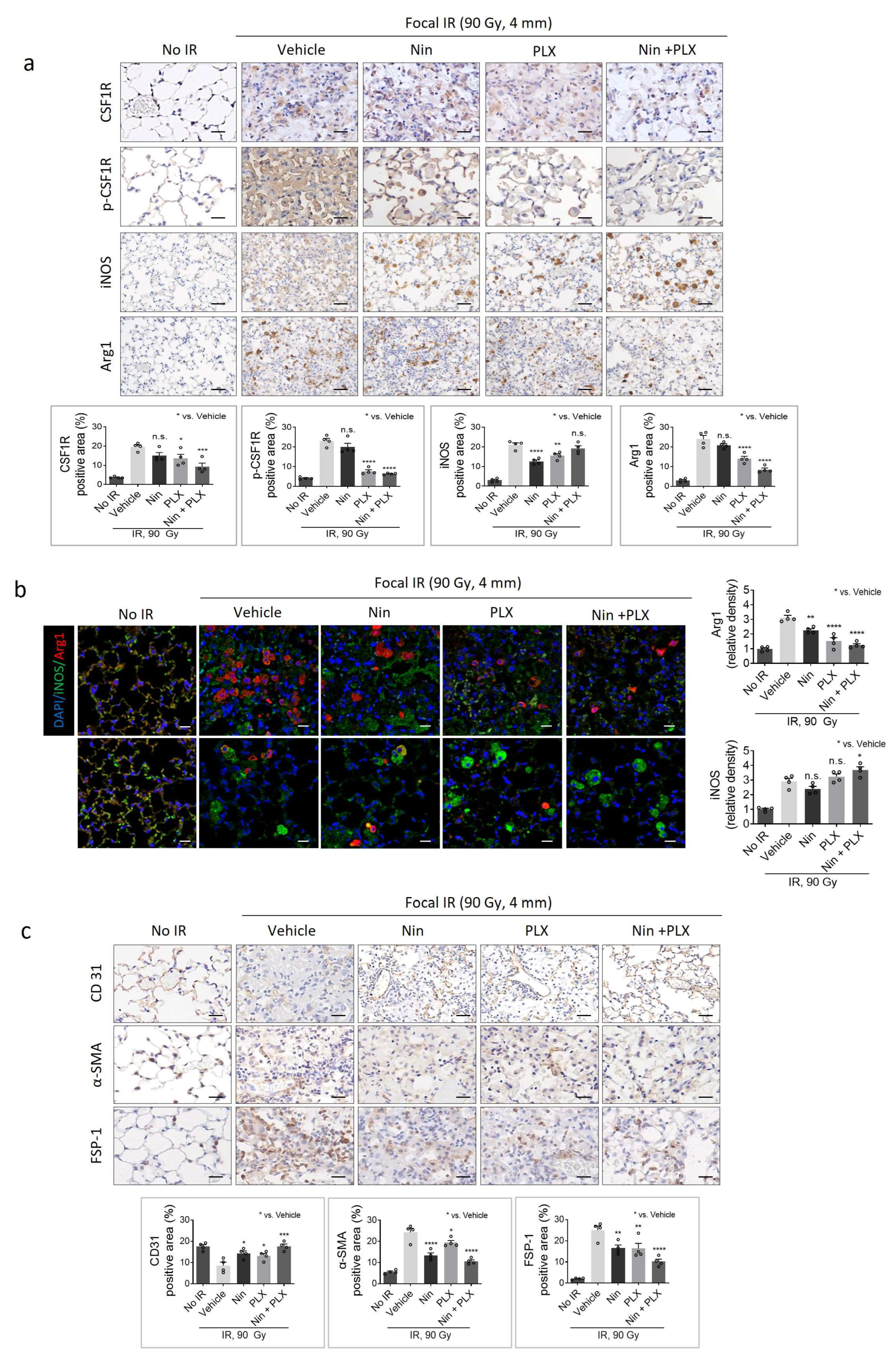
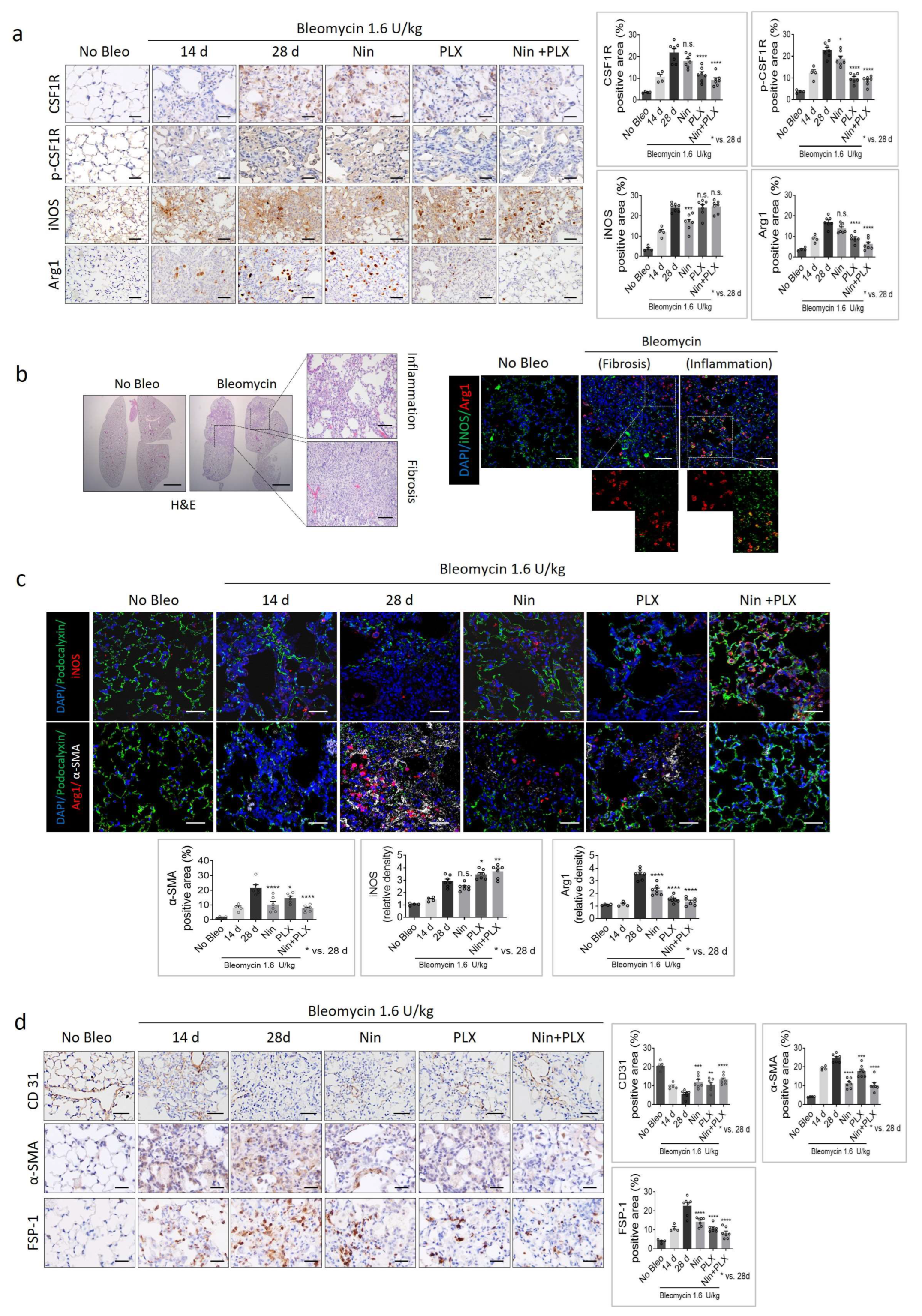
2.2. Effect of the PLX3397 and Nintedanib Combination Therapy on Macrophage Polarization During RIPF Development
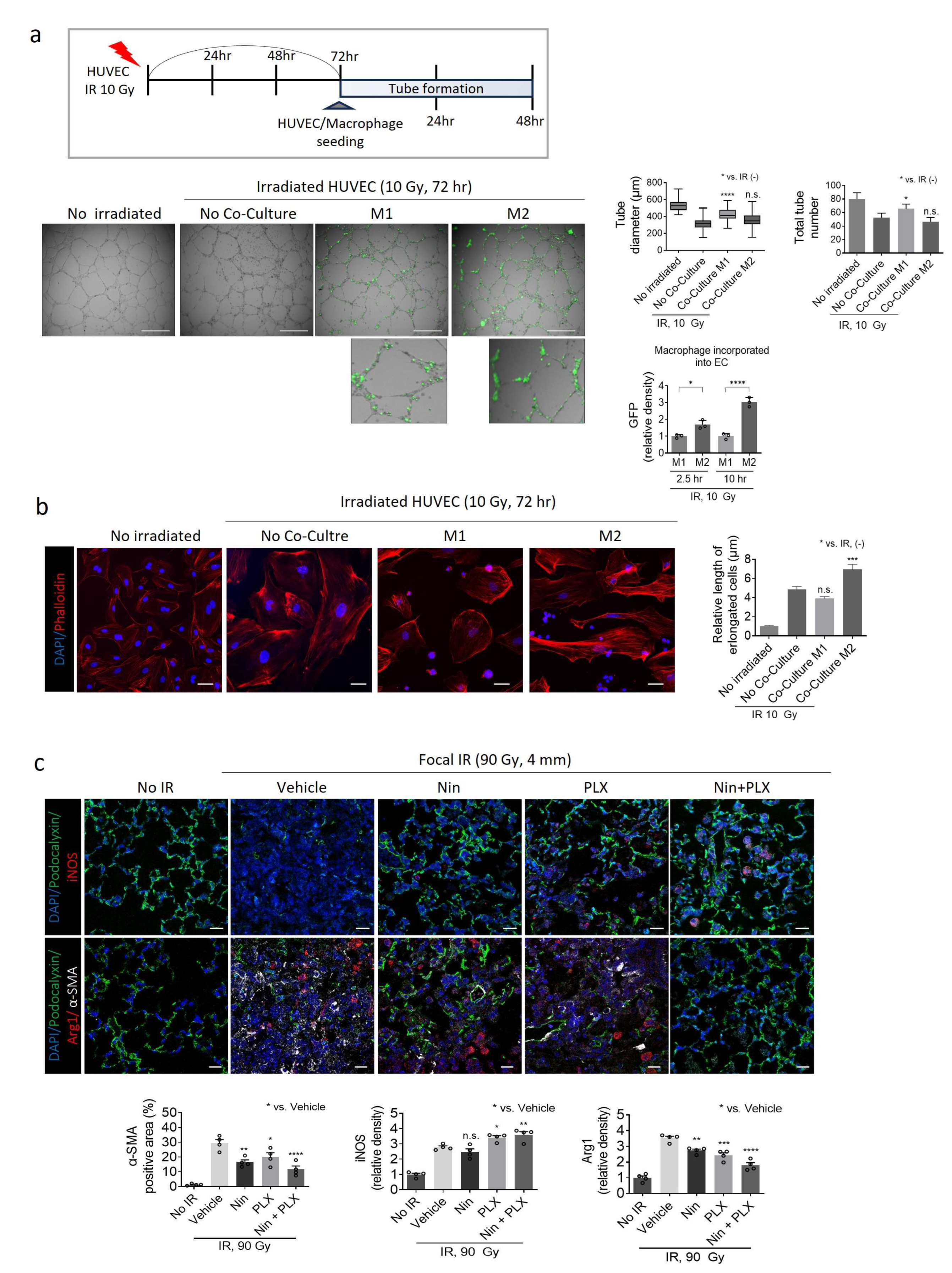
2.3. Modulation of Macrophage Polarization-Mediated Vascular Effects in RIPF
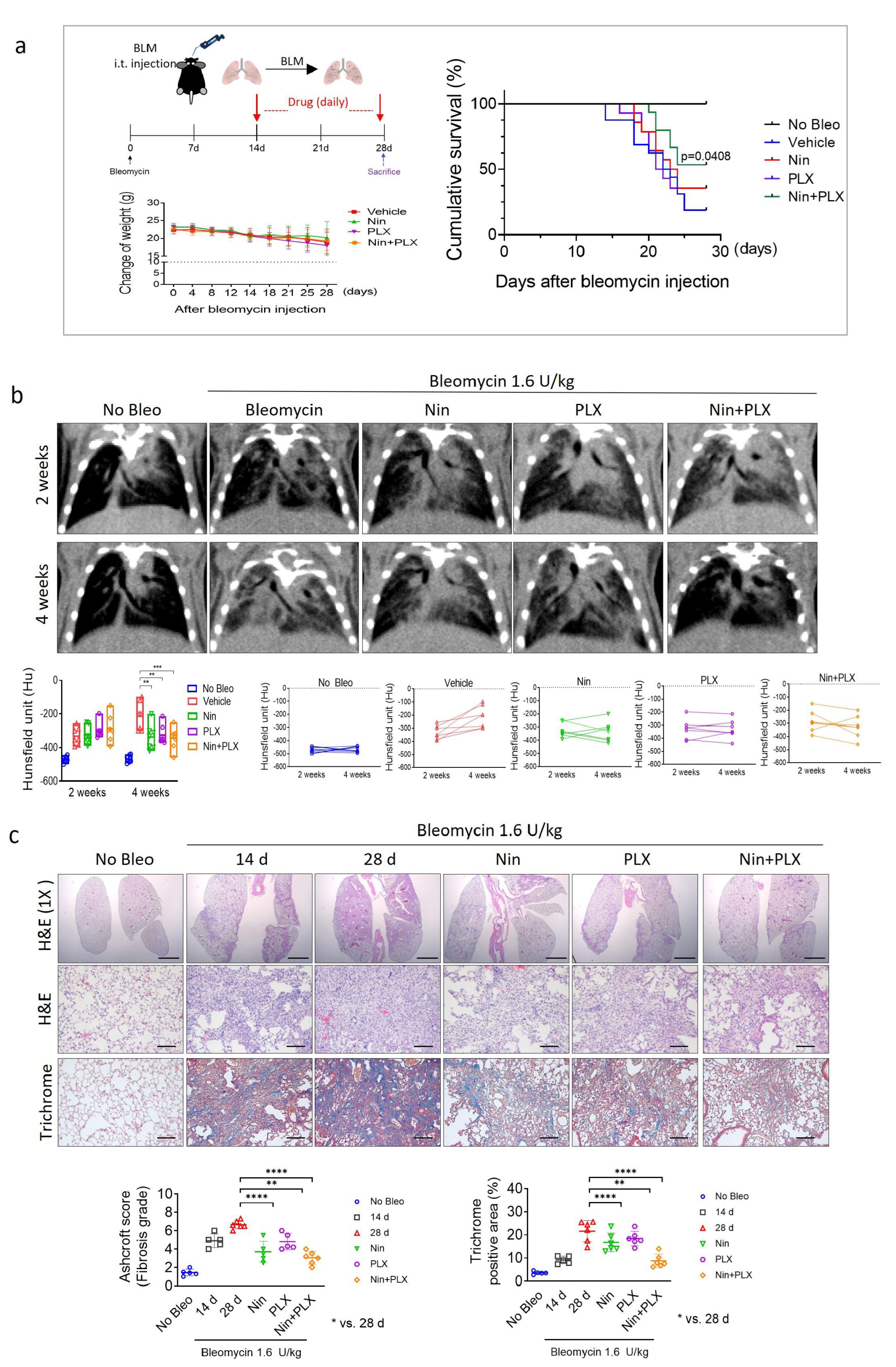
2.4. Synergistic Effects of Nintedanib and PLX3397 in Restoring BIPF and Prolonging Survival
2.5. Effects of M1/M2 Macrophage Polarization on Vascularization During BIPF
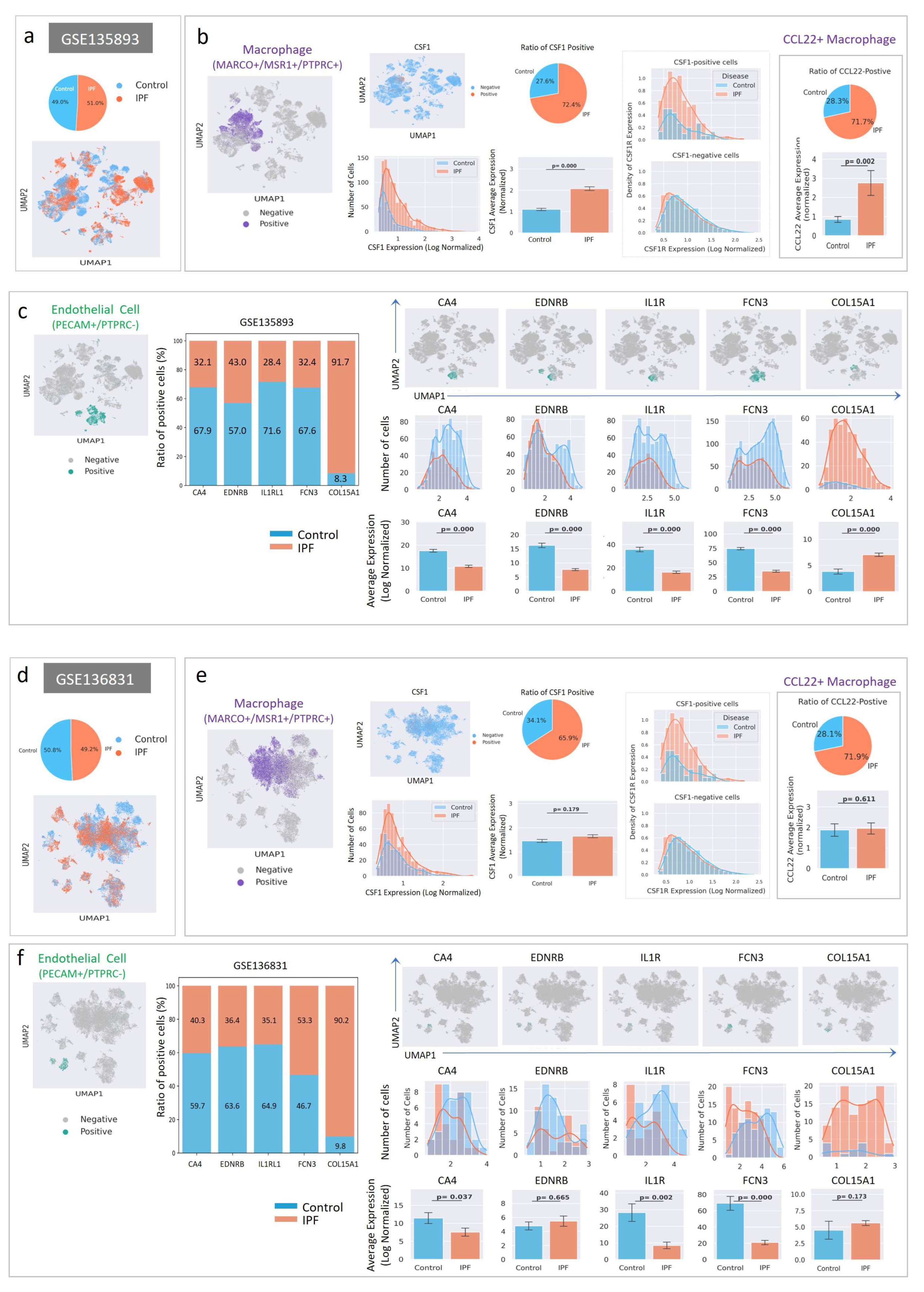
2.6. Cell-Level Characteristics of Patients with IPF Analyzed Using Single-Cell RNA Sequencing Data
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Mice and Ethical Approval
4.2. RIPF Model
4.3. Bleomycin-Induced PF (BIPF Model)
4.4. Immunohistochemistry and Immunofluorescence Staining
4.5. Microcone Beam CT (Micro-CBCT)
4.6. Cell Culture and Tube Formation Assay
4.7. Single-Cell RNA Sequencing Data Analysis
4.8. Antibodies for Immunofluorescence and Immunohistochemistry Staining
4.9. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Maher, T.M.; Strek, M.E. Antifibrotic therapy for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Time to treat. Respir Res. 2019, 20, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krauss, E.; Tello, S.; Wilhelm, J.; Schmidt, J.; Stoehr, M.; Seeger, W.; Dartsch, R.C.; Crestani, B.; Guenther, A. Assessing the Effectiveness of Pirfenidone in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Long-Term, Real-World Data from European IPF Registry (eurIPFreg). J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, F.; Hong, Y.; Luo, F. Bibliometric analysis of the pirfenidone and nintedanib in interstitial lung diseases. Heliyon 2024, 10, e29266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangarajan, S.; Kurundkar, A.; Kurundkar, D.; Bernard, K.; Sanders, Y.Y.; Ding, Q.; Antony, V.B.; Zhang, J.; Zmijewski, J.; Thannickal, V.J. Novel Mechanisms for the Antifibrotic Action of Nintedanib. Am. J Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2016, 54, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Libra, A.; Sciacca, E.; Muscato, G.; Sambataro, G.; Spicuzza, L.; Vancheri, C. Highlights on Future Treatments of IPF: Clues and Pitfalls. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaefer, C.J.; Ruhrmund, D.W.; Pan, L.; Seiwert, S.D.; Kossen, K. Antifibrotic activities of pirfenidone in animal models. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2011, 20, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chianese, M.; Screm, G.; Salton, F.; Confalonieri, P.; Trotta, L.; Barbieri, M.; Ruggero, L.; Mari, M.; Reccardini, N.; Geri, P.; et al. Pirfenidone and Nintedanib in Pulmonary Fibrosis: Lights and Shadows. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenzuela, C.; Torrisi, S.E.; Kahn, N.; Quaresma, M.; Stowasser, S.; Kreuter, M. Ongoing challenges in pulmonary fibrosis and insights from the nintedanib clinical programme. Respir. Res. 2020, 21, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wuyts, W.A.; Antoniou, K.M.; Borensztajn, K.; Costabel, U.; Cottin, V.; Crestani, B.; Grutters, J.C.; Maher, T.M.; Poletti, V.; Richeldi, L.; et al. Combination therapy: The future of management for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis? Lancet Respir. Med. 2014, 2, 933–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Clinical Research Network; Raghu, G.; Anstrom, K.J.; King, T.E., Jr.; Lasky, J.A.; Martinez, F.J. Prednisone, azathioprine, and N-acetylcysteine for pulmonary fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 1968–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vancheri, C.; Kreuter, M.; Richeldi, L.; Ryerson, C.J.; Valeyre, D.; Grutters, J.C.; Wiebe, S.; Stansen, W.; Quaresma, M.; Stowasser, S.; et al. Nintedanib with Add-on Pirfenidone in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Results of the INJOURNEY Trial. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 197, 356–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogura, T.; Taniguchi, H.; Azuma, A.; Inoue, Y.; Kondoh, Y.; Hasegawa, Y.; Bando, M.; Abe, S.; Mochizuki, Y.; Chida, K.; et al. Safety and pharmacokinetics of nintedanib and pirfenidone in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Eur. Respir. J. 2015, 45, 1382–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Geffen, C.; Deissler, A.; Quante, M.; Renz, H.; Hartl, D.; Kolahian, S. Regulatory Immune Cells in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Friends or Foes? Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 663203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbons, M.A.; MacKinnon, A.C.; Ramachandran, P.; Dhaliwal, K.; Duffin, R.; Phythian-Adams, A.T.; van Rooijen, N.; Haslett, C.; Howie, S.E.; Simpson, A.J.; et al. Ly6Chi monocytes direct alternatively activated profibrotic macrophage regulation of lung fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 184, 569–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Cai, R.; Huang, Y.; Zhu, L.; Xiao, L.; Wang, C.; Wang, L. Macrophages in organ fibrosis: From pathogenesis to therapeutic targets. Cell Death Discov. 2024, 10, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Saeed, A.; Liu, Q.; Jiang, Q.; Xu, H.; Xiao, G.G.; Rao, L.; Duo, Y. Macrophages in immunoregulation and therapeutics. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, N.; Watanabe, S.; Verma, R.; Jablonski, R.P.; Chen, C.I.; Cheresh, P.; Markov, N.S.; Reyfman, P.A.; McQuattie-Pimentel, A.C.; Sichizya, L.; et al. A spatially restricted fibrotic niche in pulmonary fibrosis is sustained by M-CSF/M-CSFR signalling in monocyte-derived alveolar macrophages. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 55, 1900646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meziani, L.; Mondini, M.; Petit, B.; Boissonnas, A.; Thomas de Montpreville, V.; Mercier, O.; Vozenin, M.C.; Deutsch, E. CSF1R inhibition prevents radiation pulmonary fibrosis by depletion of interstitial macrophages. Eur. Respir. J. 2018, 51, 1702120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wynn, T.A.; Vannella, K.M. Macrophages in Tissue Repair, Regeneration, and Fibrosis. Immunity 2016, 44, 450–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanumegowda, C.; Farkas, L.; Kolb, M. Angiogenesis in pulmonary fibrosis: Too much or not enough? Chest 2012, 142, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.H.; Hong, Z.Y.; Nam, J.K.; Lee, H.J.; Jang, J.; Yoo, R.J.; Lee, Y.J.; Lee, C.Y.; Kim, K.H.; Park, S.; et al. A Hypoxia-Induced Vascular Endothelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition in Development of Radiation-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 3716–3726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michiels, C. Endothelial cell functions. J. Cell Physiol. 2003, 196, 430–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, R.C. Preferential PDE4B Inhibition—A Step toward a New Treatment for Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 2235–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, J.; Mitchell, J.A.; Jenkins, R.G. Beyond epithelial damage: Vascular and endothelial contributions to idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2023, 133, e172058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Wu, G.; Xiong, W.; Gu, W.; Wang, C.Y. Macrophages: Friend or foe in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis? Respir. Res. 2018, 19, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nam, J.K.; Kim, A.R.; Choi, S.H.; Kim, J.H.; Han, S.C.; Park, S.; Lee, Y.J.; Kim, J.; Cho, J.; Lee, H.J.; et al. Pharmacologic Inhibition of HIF-1alpha Attenuates Radiation-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis in a Preclinical Image Guided Radiation Therapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2021, 109, 553–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della Latta, V.; Cecchettini, A.; Del Ry, S.; Morales, M.A. Bleomycin in the setting of lung fibrosis induction: From biological mechanisms to counteractions. Pharmacol. Res. 2015, 97, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habermann, A.C.; Gutierrez, A.J.; Bui, L.T.; Yahn, S.L.; Winters, N.I.; Calvi, C.L.; Peter, L.; Chung, M.I.; Taylor, C.J.; Jetter, C.; et al. Single-cell RNA sequencing reveals profibrotic roles of distinct epithelial and mesenchymal lineages in pulmonary fibrosis. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaba1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ushio, A.; Arakaki, R.; Otsuka, K.; Yamada, A.; Tsunematsu, T.; Kudo, Y.; Aota, K.; Azuma, M.; Ishimaru, N. CCL22-Producing Resident Macrophages Enhance T Cell Response in Sjogren′s Syndrome. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, C.K.; Schloesser, D.; Fundel-Clemens, K.; Lerner, C.; Gabler, S.; Baskaran, P.; Wohnhaas, C.T.; Dichtl, S.; Huber, H.J.; Ask, K.; et al. Antifibrotic Drug Nintedanib Inhibits CSF1R to Promote IL-4-associated Tissue Repair Macrophages. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2023, 68, 366–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Q.; Zhang, P.; Lei, X.; Du, L.; Qu, B. Insights into CSF-1/CSF-1R signaling: The role of macrophage in radiotherapy. Front. Immunol. 2025, 16, 1530890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.; Priya, A.; Borade, D.R.; Agrawal-Rajput, R. Macrophage subsets and their role: Co-relation with colony-stimulating factor-1 receptor and clinical relevance. Immunol. Res. 2023, 71, 130–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Probst, C.K.; Montesi, S.B.; Medoff, B.D.; Shea, B.S.; Knipe, R.S. Vascular permeability in the fibrotic lung. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 56, 1900100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackermann, M.; Kim, Y.O.; Wagner, W.L.; Schuppan, D.; Valenzuela, C.D.; Mentzer, S.J.; Kreuz, S.; Stiller, D.; Wollin, L.; Konerding, M.A. Effects of nintedanib on the microvascular architecture in a lung fibrosis model. Angiogenesis 2017, 20, 359–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajagopal, K.; Bryant, A.J.; Sahay, S.; Wareing, N.; Zhou, Y.; Pandit, L.M.; Karmouty-Quintana, H. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and pulmonary hypertension: Heracles meets the Hydra. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 178, 172–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Z.Y.; Lee, H.J.; Choi, W.H.; Lee, Y.J.; Eun, S.H.; Lee, J.I.; Park, K.; Lee, J.M.; Cho, J. A preclinical rodent model of acute radiation-induced lung injury after ablative focal irradiation reflecting clinical stereotactic body radiotherapy. Radiat. Res. 2014, 182, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolb, P.; Upagupta, C.; Vierhout, M.; Ayaub, E.; Bellaye, P.S.; Gauldie, J.; Shimbori, C.; Inman, M.; Ask, K.; Kolb, M.R.J. The importance of interventional timing in the bleomycin model of pulmonary fibrosis. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 55, 1901105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashcroft, T.; Simpson, J.M.; Timbrell, V. Simple method of estimating severity of pulmonary fibrosis on a numerical scale. J. Clin. Pathol. 1988, 41, 467–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeCicco-Skinner, K.L.; Henry, G.H.; Cataisson, C.; Tabib, T.; Gwilliam, J.C.; Watson, N.J.; Bullwinkle, E.M.; Falkenburg, L.; O′Neill, R.C.; Morin, A.; et al. Endothelial cell tube formation assay for the in vitro study of angiogenesis. J. Vis. Exp. 2014, 91, e51312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, T.S.; Schupp, J.C.; Poli, S.; Ayaub, E.A.; Neumark, N.; Ahangari, F.; Chu, S.G.; Raby, B.A.; DeIuliis, G.; Januszyk, M.; et al. Single-cell RNA-seq reveals ectopic and aberrant lung-resident cell populations in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaba1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, F.A.; Angerer, P.; Theis, F.J. SCANPY: Large-scale single-cell gene expression data analysis. Genome Biol. 2018, 19, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, J.-H.; Nam, J.-K.; Park, M.-S.; Seo, S.; Ryu, H.C.; Lee, H.-J.; Lee, J.; Lee, Y.-J. Pexidartinib and Nintedanib Combination Therapy Targets Macrophage Polarization to Reverse Pulmonary Fibrosis: A Preclinical Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 7570. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157570
Kim J-H, Nam J-K, Park M-S, Seo S, Ryu HC, Lee H-J, Lee J, Lee Y-J. Pexidartinib and Nintedanib Combination Therapy Targets Macrophage Polarization to Reverse Pulmonary Fibrosis: A Preclinical Study. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(15):7570. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157570
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Ji-Hee, Jae-Kyung Nam, Min-Sik Park, Seungyoul Seo, Hyung Chul Ryu, Hae-June Lee, Jeeyong Lee, and Yoon-Jin Lee. 2025. "Pexidartinib and Nintedanib Combination Therapy Targets Macrophage Polarization to Reverse Pulmonary Fibrosis: A Preclinical Study" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 15: 7570. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157570
APA StyleKim, J.-H., Nam, J.-K., Park, M.-S., Seo, S., Ryu, H. C., Lee, H.-J., Lee, J., & Lee, Y.-J. (2025). Pexidartinib and Nintedanib Combination Therapy Targets Macrophage Polarization to Reverse Pulmonary Fibrosis: A Preclinical Study. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(15), 7570. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157570





