New Perspectives on Nutraceutical Insulin Sensitizing Agents in the Treatment of Psoriasis and Other Dermatological Diseases
Abstract
1. Introduction
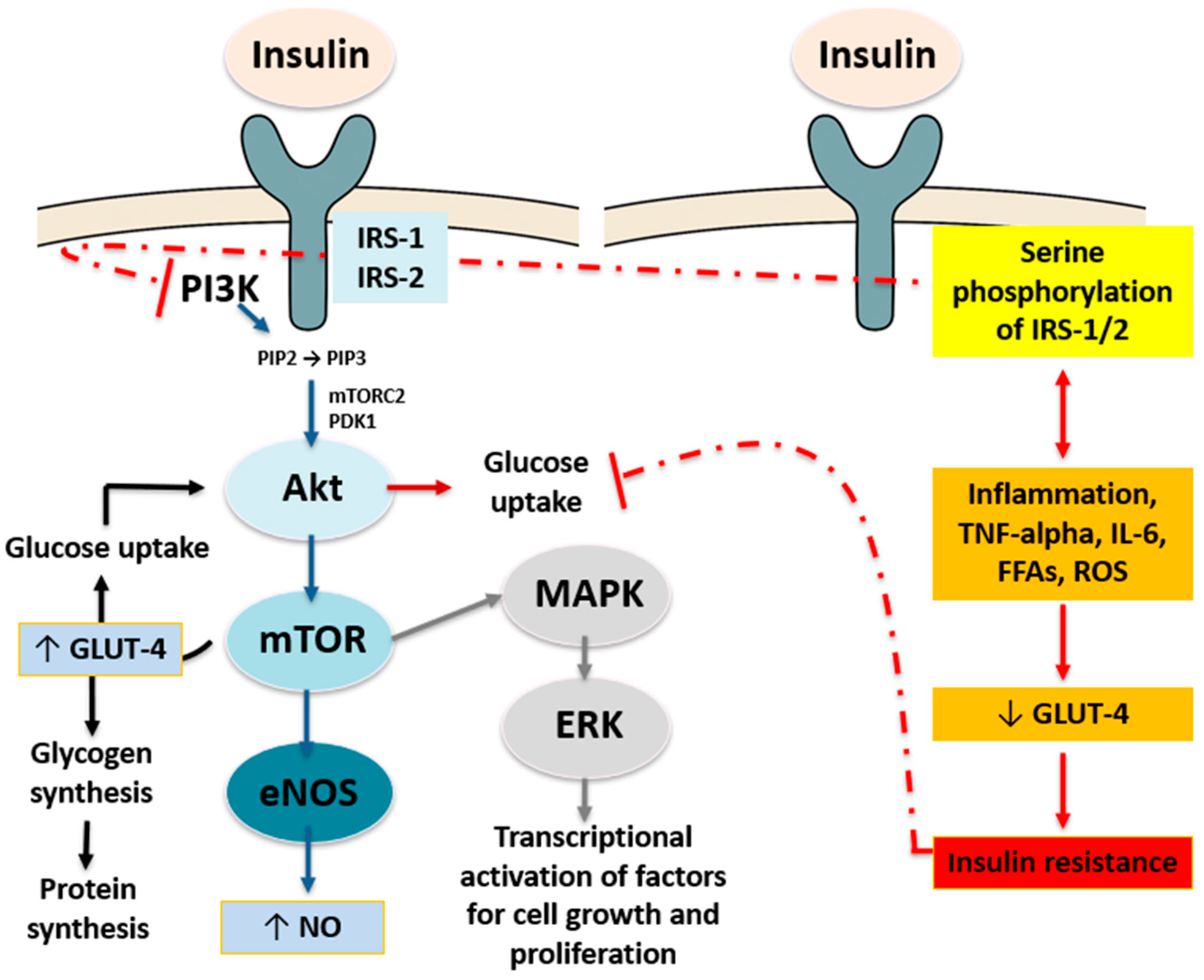
2. Overview of Insulin Signaling and Resistance Mechanisms
- ✓
- The phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) pathway, also known as the protein kinase B (PKB or Akt) pathway, facilitates GLUT-4 translocation to the membrane, glucose transport into the cell, and glycogen synthesis. This brings about the activation of PI3K by converting phosphatidyl inositol 4,5-biphosphate (PIP2) into phosphatidyl inositol 3,4,5-triphosphate (PIP3), the recruitment of Akt to the plasma membrane, and its phosphorylation by 3-phosphoinositide-dependent kinase-1 (PDK-1) and the mammalian target of rapamycin complex 2 (mTORC-2) [9]. This pathway results in the translocation of GLUT-4 in adipocytes and skeletal myocytes and the activation of glycogen synthase (GS) in skeletal myocytes, adipocytes, hepatocytes, and endothelial NO synthase (NOS) in endothelial cells, along with the phosphorylation of transcription factor forkhead box protein O1 (FoxO1) to suppress hepatic gluconeogenesis [9].
- ✓
- The MAPK pathway, also known as the extracellular signal regulated kinase (ERK) pathway, controls transcription factors involved in cell growth, differentiation, and proliferation, while entailing the activation of ERK and the synthesis of endothelin-1 in endothelial cells [10].
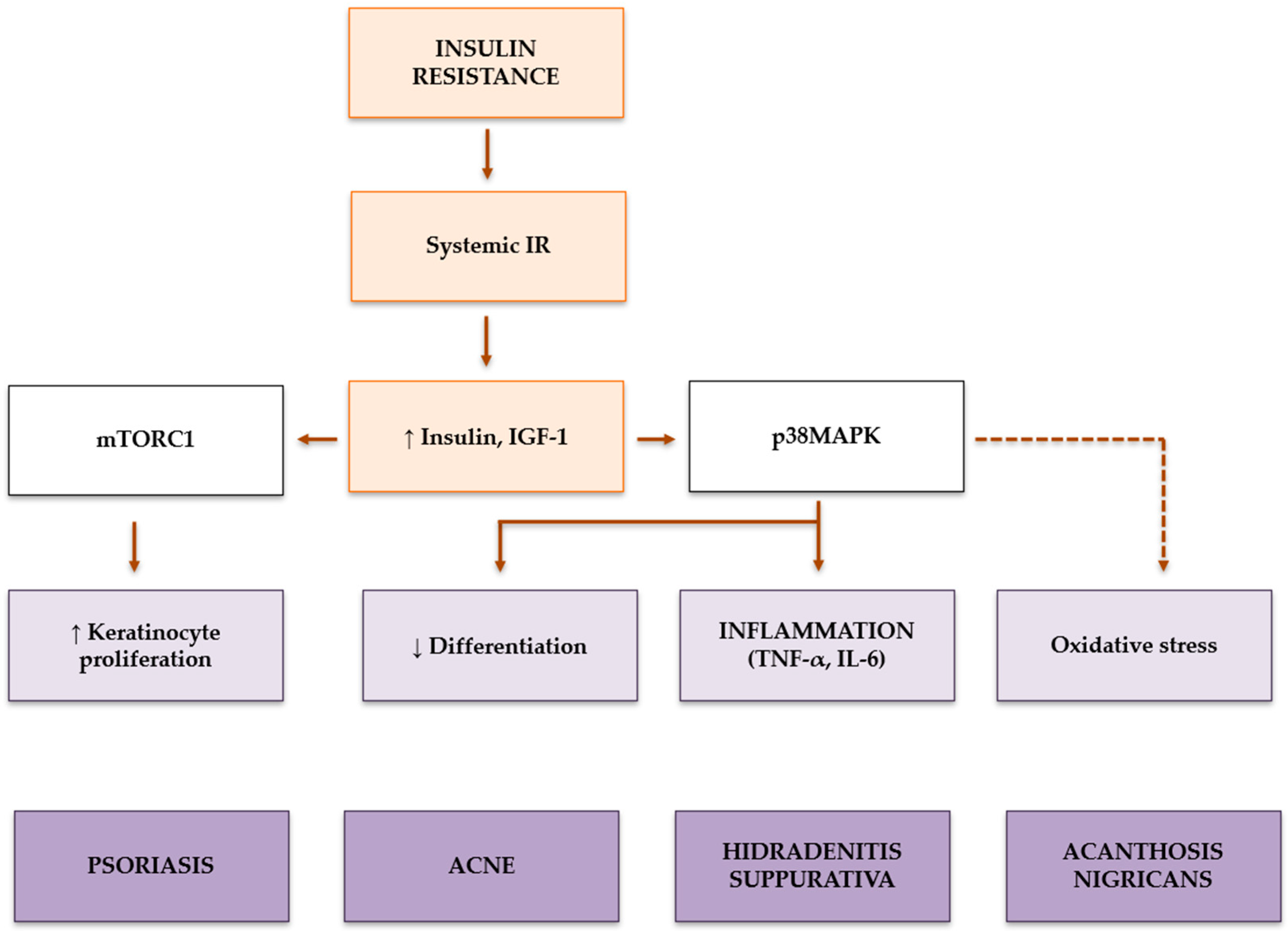
3. IR in Dermatological Conditions
3.1. Psoriasis
3.2. Acne
3.3. Acanthosis Nigricans
3.4. Hidradenitis Suppurativa
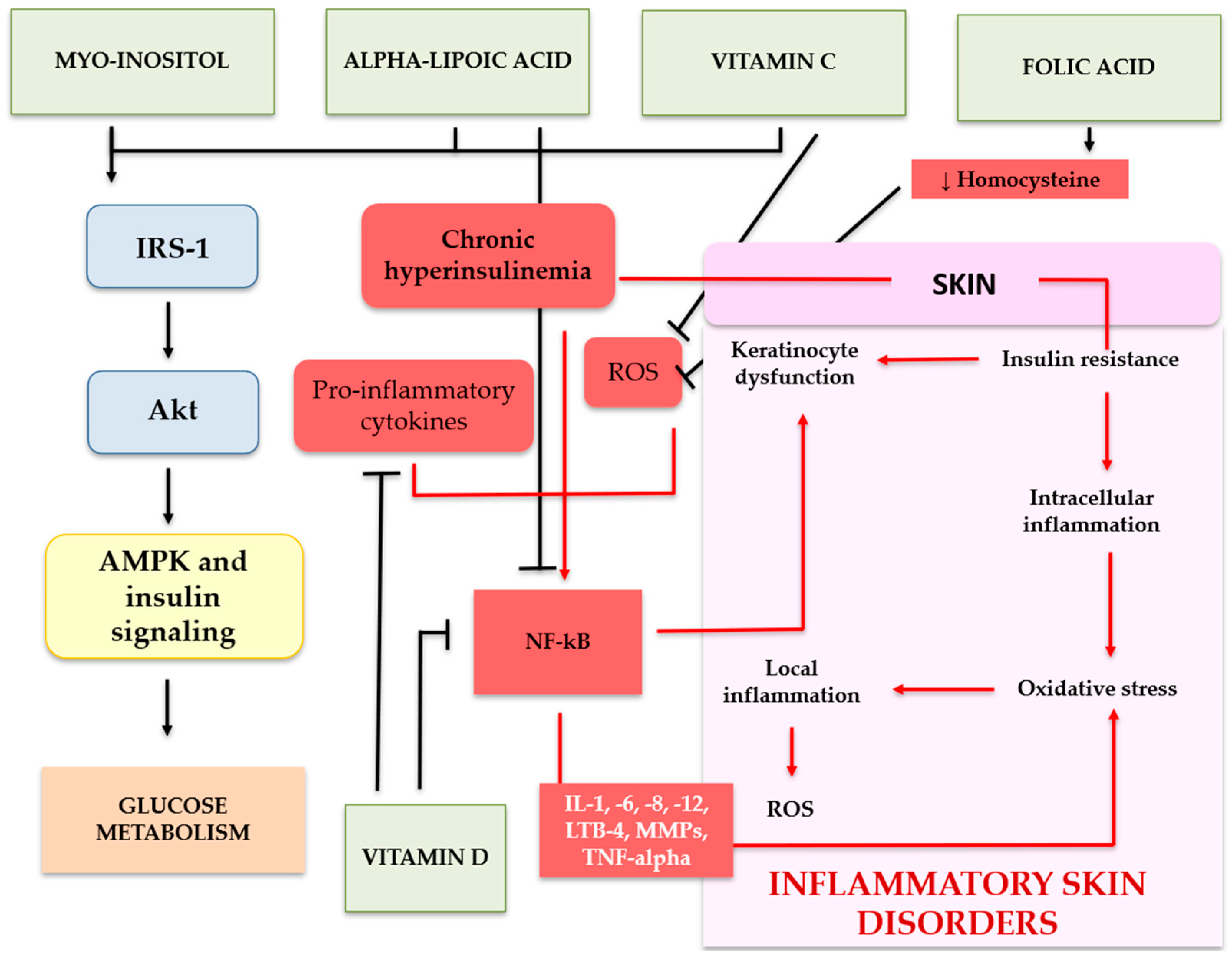
4. ISAs in IR-Related Conditions and Dermatoses
4.1. Vitamins
4.1.1. Folic Acid and Group B Vitamins
4.1.2. Vitamin C
4.1.3. Vitamin D
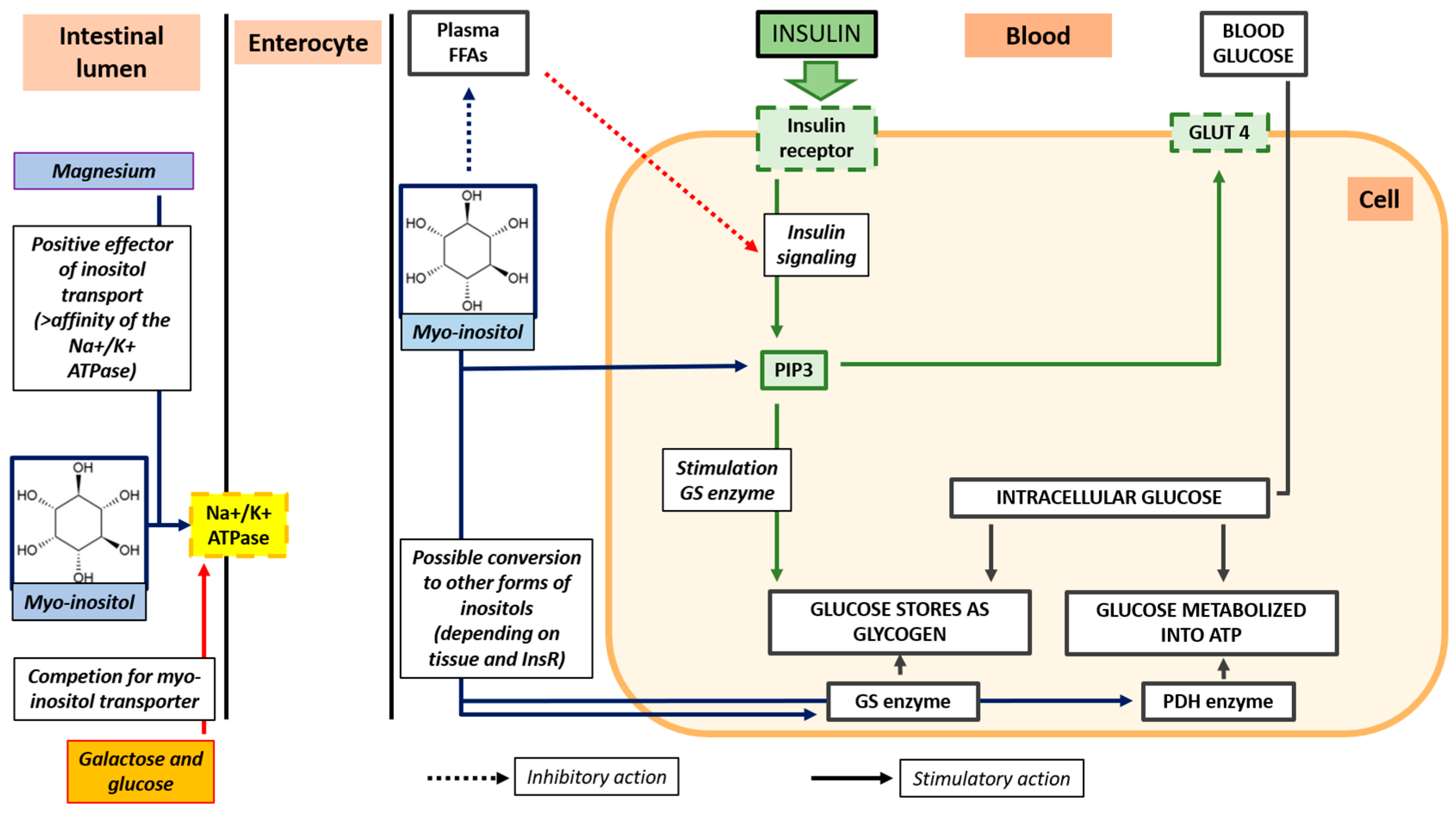
4.2. Inositol
4.3. Alpha Lipoic Acid
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Falcetta, P.; Aragona, M.; Bertolotto, A.; Bianchi, C.; Campi, F.; Garofolo, M.; Del Prato, S. Insulin discovery: A pivotal point in medical history. Metabolism 2022, 127, 154941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, G.F.; Brubaker, P.L. The discovery of insulin revisited: Lessons for the modern era. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 131, e142239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Niekerk, G.; Christowitz, C.; Conradie, D.; Engelbrecht, A.M. Insulin as an immunomodulatory hormone. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2020, 52, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buerger, C.; Richter, B.; Woth, K.; Salgo, R.; Malisiewicz, B.; Diehl, S.; Hardt, K.; Boehncke, S.; Boehncke, W.H. Interleukin-1Β interferes with epidermal homeostasis through induction of insulin resistance: Implications for psoriasis pathogenesis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2012, 132, 2206–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Natali, A.; Nesti, L. Vascular effects of insulin. Metabolism 2021, 124, 154891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posner, B.I. Insulin Signalling: The Inside Story. Can. J. Diabetes 2017, 41, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, S.M.; Hirschberg, P.R.; Sarkar, P.; Siegel, D.M.; Teegala, S.B.; Vail, G.M.; Routh, V.H. Insulin actions on hypothalamic glucose-sensing neurones. J. Neuroendocr. 2021, 33, e12937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Gao, Y.; Lieu, L.; Afrin, S.; Guo, H.; Williams, K.W. Acute effects of zinc and insulin on arcuate anorexigenic proopiomelanocortin neurons. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 176, 725–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norton, L.; Shannon, C.; Gastaldelli, A.; DeFronzo, R.A. Insulin: The master regulator of glucose metabolism. Metabolism 2022, 129, 155142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titchenell, P.M.; Lazar, M.A.; Birnbaum, M.J. Unraveling the Regulation of Hepatic Metabolism by Insulin. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 28, 497–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czech, M.P. Mechanisms of insulin resistance related to white, beige, and brown adipocytes. Mol. Metab. 2020, 34, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.S.; Hossain, K.S.; Das, S.; Kundu, S.; Adegoke, E.O.; Rahman, M.A.; Hannan, M.A.; Uddin, M.J.; Pang, M.G. Role of Insulin in Health and Disease: An Update. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Wang, J.; Li, M.; Li, J.; Pan, Y.; Liu, B.; Lip, G.Y.H.; Zhang, L. Association of Insulin Resistance with Cardiovascular Disease and All-Cause Mortality in Type 1 Diabetes: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Diabetes Care 2024, 47, 2266–2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Townsend, L.K.; Brunetta, H.S.; Mori, M.A.S. Mitochondria-associated ER membranes in glucose homeostasis and insulin resistance. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 319, e1053–e1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaribeygi, H.; Farrokhi, F.R.; Butler, A.E.; Sahebkar, A. Insulin resistance: Review of the underlying molecular mechanisms. J. Cell Physiol. 2019, 234, 8152–8161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fahed, G.; Aoun, L.; Bou Zerdan, M.; Allam, S.; Bou Zerdan, M.; Bouferraa, Y.; Assi, H.I. Metabolic Syndrome: Updates on Pathophysiology and Management in 2021. Int. J. Mol Sci. 2022, 23, 786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bungau, A.F.; Tit, D.M.; Stoicescu, M.; Moleriu, L.-C.; Muresan, M.; Radu, A.; Brisc, M.C.; Ghitea, T.C. Exploring a New Pathophysiological Association in Acne Vulgaris and Metabolic Syndrome: The Role of Biogenic Amines and Glutathione Peroxidase. Medicinal 2024, 60, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.; Donnelly, R. Sex Hormone-Binding Globulin (SHBG) as an Early Biomarker and Therapeutic Target in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armanini, D.; Boscaro, M.; Bordin, L.; Sabbadin, C. Controversies in the Pathogenesis, Diagnosis and Treatment of PCOS: Focus on Insulin Resistance, Inflammation, and Hyperandrogenism. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva Rosa, S.C.; Nayak, N.; Caymo, A.M.; Gordon, J.W. Mechanisms of muscle insulin resistance and the cross-talk with liver and adipose tissue. Physiol. Rep. 2020, 8, e14607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, L.P.W.; Sani, S.A.; Sabullah, M.K.; Gansau, J.A. The Prevalence of Insulin Resistance in Malaysia and Indonesia: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Medicinal 2022, 58, 826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saklayen, M.G. The Global Epidemic of the Metabolic Syndrome. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2018, 20, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giammò, A.; Sarzi-Puttini, P.; Favro, M.; De Pedrini, A.; Baj, G. Rationale of Insulin-Sensitizing Agents in the Treatment of Functional Bladder Disorders. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2023, 37, 4499–4510. [Google Scholar]
- Dainichi, T.; Iwata, M. Inflammatory loops in the epithelial-immune microenvironment of the skin and skin appendages in chronic inflammatory diseases. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1274270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Napolitano, M.; Megna, M.; Monfrecola, G. Insulin resistance and skin diseases. Sci. World J. 2015, 2015, 479354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Lian, N.; Chen, M.; Bartke, A.; Yuan, R. Metabolic Syndrome and Skin Diseases. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alajroush, W.A.; Alrshid, A.I.; Alajlan, A.H.; Alsalamah, Y.B.; Alhumaidan, M.I.; Alhoumedan, A.I.; Alrasheed, M.I.; Alowairdhi, Y.A.; Alowirdi, F.; Aljoufi, A.Z.; et al. Psoriasis and Metabolic Disorders: A Comprehensive Meta-Analysis of Million Adults Worldwide. Cereus 2024, 16, e52099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, A.W.; Read, C. Pathophysiology, Clinical Presentation, and Treatment of Psoriasis: A Review. JAMA 2020, 323, 1945–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinić, M.; Zečević, R.D.; Hajduković, Z.; Mijušković, M.; Đurić, P.; Jović, Z.; Grdinić, A.; Petrović, M.; Terzić, B.; Pejović, J.; et al. Psoriasis is the independent factor for early atherosclerosis: A prospective study of cardiometabolic risk profile. Vojn. Pregl. 2016, 73, 1094–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, H.Y.; Hung, C.J.; Muo, C.H.; Fan, K.C.; Sung, F.C. The bidirectional association between type 2 diabetes and psoriasis: Two retrospective cohort studies. Indian J. Dermatol. Venereol. Leprol. 2020, 86, 366–374. [Google Scholar]
- Eder, L.; Chandran, V.; Cook, R.; Gladman, D.D. The risk of developing diabetes mellitus in patients with psoriatic arthritis: A cohort study. J. Rheumatol. 2017, 44, 286–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babalic, F.C.A.; Borza, C.; Ilie Rosca, C.; Gurban, C.V.; Banciu, C.D.; Mederle, O.A.; Popa, M.D.; Chelu, S.C.; Marius, P.; Sharma, A.; et al. Endothelial dysfunction in psoriatic arthritis patients: Correlations between insulin resistance and disease activity. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2022, 26, 6796–6804. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Wang, Y.; Kong, X.; Mu, J.; Wang, Z.; Yang, X.; Ye, J. Association between psoriasis and serum apolipoprotein A1 and B: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Heliyon 2023, 9, e21168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Słuczanowska-Głabowska, S. Adiponectin, Leptin and Resistin in Patients with Psoriasis. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiełbowski, K.; Bakinowska, E.; Ostrowski, P.; Pala, B.; Gromowska, E.; Gurazda, K.; Dec, P.; Modrzejewski, A.; Pawlik, A. The Role of Adipokines in the Pathogenesis of Psoriasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furue, K. Psoriasis and the TNF/IL23/IL17 axis. G. Ital. Dermatol. Venereol. 2019, 154, 418–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarandi, E.; Krueger-Krasagakis, S.; Tsoukalas, D.; Sidiropoulou, P.; Evangelou, G.; Sifaki, M.; Rudofsky, G.; Drakoulis, N.; Tsatsakis, A. Psoriasis immunometabolism: Progress on metabolic biomarkers and targeted therapy. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2023, 10, 1201912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polic, M.V.; Miskulin, M.; Smolic, M.; Kralik, K.; Miskulin, I.; Berkovic, M.C.; Curcic, I.B. Psoriasis Severity-A Risk Factor of Insulin Resistance Independent of Metabolic Syndrome. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, R. Metabolic influences on T cell in psoriasis: A literature review. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1279846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.H.; Wu, C.H.; Chen, M.L.; Yip, H.T.; Lee, C.I.; Lee, M.S.; Wei, J.C. Risk of Psoriasis in Patients with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: A National Population-Based Cohort Study. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeanes, Y.M.; Reeves, S. Metabolic consequences of obesity and insulin resistance in polycystic ovary syndrome: Diagnostic and methodological challenges. Nutr. Res. Rev. 2017, 30, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melnik, B.C. Acne vulgaris: The metabolic syndrome of the pilosebaceous follicle. Clin. Dermatol. 2018, 36, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.K.L.; Stein Gold, L.F.; Alexis, A.F.; Harper, J.C. Current Concepts in Acne Pathogenesis: Pathways to Inflammation. Semin. Cutan. Med. Surg. 2018, 37, S60–S62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadowska-Przytocka, A.; Gruszczyńska, M.; Ostałowska, A.; Antosik, P.; Czarnecka-Operacz, M.; Adamski, Z.; Łącka, K. Insulin resistance in the course of acne—Literature review. Postepy. Dermatol. Alergol. 2022, 39, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clayton, R.W.; Göbel, K.; Niessen, C.M.; Paus, R.; van Steensel, M.A.M.; Lim, X. Homeostasis of the sebaceous gland and mechanisms of acne pathogenesis. Br. J. Dermatol. 2019, 181, 677–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langan, E.A.; Hinde, E.; Paus, R. Prolactin as a candidate sebotrop(h)ic hormone? Exp. Dermatol. 2018, 27, 729–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Çerman, A.A.; Aktaş, E.; Altunay, İ.K.; Arıcı, J.E.; Tulunay, A.; Ozturk, F.Y. Dietary glycemic factors, insulin resistance, and adiponectin levels in acne vulgaris. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2016, 75, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, T.J.; Bazergy, C. Hormonal and dietary factors in acne vulgaris versus controls. Derm.-Endocrinol. 2018, 10, e1442160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snast, I.; Dalal, A.; Twig, G.; Astman, N.; Kedem, R.; Levin, D.; Erlich, Y.; Leshem, Y.A.; Lapidoth, M.; Hodak, E.; et al. Acne and obesity: A nationwide study of 600,404 adolescents. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2019, 81, 723–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balta, I.; Ekiz, O.; Ozuguz, P.; Ustun, I.; Karaca, S.; Dogruk Kacar, S.; Eksioglu, M. Insulin resistance in patients with post-adolescent acne. Int. J. Dermatol. 2015, 54, 662–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kartal, D.; Yildiz, H.; Ertas, R.; Borlu, M.; Utas, S. Association between isolated female acne and insulin resistance: A prospective study. G Ital. Dermatol. Venereol. 2016, 151, 353–357. [Google Scholar]
- Emiroğlu, N.; Cengiz, F.P.; Kemeriz, F. Insulin resistance in severe acne vulgaris. Adv. Dermatol. Allergol. 2015, 32, 281–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bungau, A.F.; Radu, A.F.; Bungau, S.G.; Vesa, C.M.; Tit, D.M.; Endres, L.M. Oxidative stress and metabolic syndrome in acne vulgaris: Pathogenetic connections and potential role of dietary supplements and phytochemicals. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 164, 115003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.-M.; Cheng, M.-Y.; Xun, M.-H.; Zhao, Z.-W.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, W.; Cheng, J.; Ni, J.; Wang, W. Possible Mechanisms of Oxidative Stress-Induced Skin Cellular Senescence, Inflammation, and Cancer and the Therapeutic Potential of Plant Polyphenols. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreno, B.; Dagnelie, M.A.; Khammari, A.; Corvec, S. The Skin Microbiome: A New Actor in Inflammatory Acne. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2020, 21, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Datta, D.; Kassir, M.; Wollina, U.; Galadari, H.; Lotti, T.; Jafferany, M.; Grabbe, S.; Goldust, M. Acanthosis nigricans: A review. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2020, 19, 1857–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, A.K.C.; Lam, J.M.; Barankin, B.; Leong, K.F.; Hon, K.L. Acanthosis Nigricans: An Updated Review. Curr. Pediatr. Rev. 2022, 19, 68–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, H.Y. Acanthosis nigricans in obese adolescents: Prevalence, impact, and management challenges. Adolesc. Health Med. Ther. 2016, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banti, S.; Sumathy, T.K.; Pramila, K. Insulin resistance in various grades of acanthosis nigricans. Acta Dermatovenerol. Alp. Pannonica Adriat. 2022, 31, 101–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radu, A.M.; Carsote, M.; Dumitrascu, M.C.; Sandru, F. Acanthosis Nigricans: Pointer of Endocrine Entities. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philip, N.E.; Girisha, B.S.; Shetty, S.; Pinto, A.M.; Noronha, T.M. Estimation of Metabolic Syndrome in Acanthosis Nigricans—A Hospital Based Cross-Sectional Study. Indian J. Dermatol. 2022, 67, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velazquez-Bautista, M.; López-Sandoval, J.J.; González-Hita, M.; Vázquez-Valls, E.; Cabrera-Valencia, I.Z.; Torres-Mendoza, B.M. Association of metabolic syndrome with low birth weight, intake of high-calorie diets and acanthosis nigricans in children and adolescents with overweight and obesity. Endocrinol. Diabetes Nutr. 2017, 64, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.Y.; Manne, V.; Manne, R.; Himani, C. Neurofibromatosis, Down’s syndrome, and acquired abnormalities. Indian Dermatol. Online J. 2016, 7, 198–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, B.; Dahiya, R.; Kimble, R. Hyperandrogenism, insulin resistance and acanthosis nigricans (HAIR-AN syndrome): An extreme subphenotype of polycystic ovary syndrome. BMJ Case Rep. 2020, 13, e231749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maguolo, A.; Maffeis, C. Acanthosis nigricans in childhood: A cutaneous marker that should not be underestimated, especially in obese children. Acta Paediatr. 2020, 109, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abu Rached, N.; Gambichler, T.; Dietrich, J.W.; Ocker, L.; Seifert, C.; Stockfleth, E.; Bechara, F.G. The Role of Hormones in Hidradenitis Suppurativa: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Özkur, E.; Erdem, Y.; Altunay, İ.K.; Demir, D.; Dolu, N.Ç.; Serin, E.; Çerman, A.A. Serum irisin level, insulin resistance, and lipid profiles in patients with hidradenitis suppurativa: A case-control study. An. Bras. Dermatol. 2020, 95, 708–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, A.S.; Johnson, J.S.; Kerns, M.L. Dietary Factors and Hidradenitis Suppurativa. Dermatol. Ther. 2023, 13, 3007–3017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mintoff, D.; Agius, R.; Fava, S.; Pace, N.P. Investigating Adiposity-Related Metabolic Health Phenotypes in Patients with Hidradenitis Suppurativa: A Cross-Sectional Study. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 4847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hambly, R.; Kearney, N.; Hughes, R.; Fletcher, J.M.; Kirby, B. Metformin Treatment of Hidradenitis Suppurativa: Effect on Metabolic Parameters, Inflammation, Cardiovascular Risk Biomarkers, and Immune Mediators. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zouboulis, C.C.; Benhadou, F.; Byrd, A.S.; Chandran, N.S.; Giamarellos-Bourboulis, E.J.; Fabbrocini, G. What causes hidradenitis suppurativa?-15 years after. Exp. Dermatol. 2020, 29, 1154–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knowles, J.P.; Shuster, S.; Wells, G.C. Folic-acid deficiency in patients with skin disease. Lancet 1963, 1, 1138–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shuster, S.; Marks, J.; Chanarin, I. Folic acid deficiency in patients with skin disease. Br. J. Dermatol. 1967, 79, 398–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asbaghi, O.; Ashtary-Larky, D.; Bagheri, R.; Moosavian, S.P.; Olyaei, H.P.; Nazarian, B.; Rezaei Kelishadi, M.; Wong, A.; Candow, D.G.; Dutheil, F.; et al. Folic Acid Supplementation Improves Glycemic Control for Diabetes Prevention and Management: A Systematic Review and Dose-Response Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setola, E.; Monti, L.D.; Galluccio, E.; Palloshi, A.; Fragasso, G.; Paroni, R.; Magni, F.; Sandoli, E.P.; Lucotti, P.; Costa, S.; et al. Insulin resistance and endothelial function are improved after folate and vitamin B12 therapy in patients with metabolic syndrome: Relationship between homocysteine levels and hyperinsulinemia. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2004, 151, 483–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaçil Ermumcu, M.Ş.; Acar Tek, N. Effects of High-dose Folic Acid Supplementation on Maternal/Child Health Outcomes: Gestational Diabetes Mellitus in Pregnancy and Insulin Resistance in Offspring. Can. J. Diabetes 2023, 47, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brazzelli, V.; Grasso, V.; Fornara, L.; Moggio, E.; Gamba, G.; Villani, S.; Borroni, G. Homocysteine, vitamin B12 and folic acid levels in psoriatic patients and correlation with disease severity. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2010, 23, 911–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghiasi, M.; Mortazavi, H.; Jafari, M. Efficacy of Folic Acid and Vitamin B12 Replacement Therapies in the Reduction of Adverse Effects of Isotretinoin: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Skinmed 2018, 16, 239–245. [Google Scholar]
- Villagran, M.; Ferreira, J.; Martorell, M.; Mardones, L. The Role of Vitamin C in Cancer Prevention and Therapy: A Literature Review. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellulu, M.S.; Rahmat, A.; Patimah, I.; Khaza’ai, H.; Abed, Y. Effect of vitamin C on inflammation and metabolic markers in hypertensive and/or diabetic obese adults: A randomized controlled trial. Drug. Des. Devel. Ther. 2015, 9, 3405–3412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Ahn, J.; Shin, S.S.; Yoon, M. Ascorbic acid inhibits visceral obesity and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease by activating peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α in high-fat-diet fed C57BL/6J mice. Int. J. Obes. 2019, 43, 1620–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Jiang, H.; Li, W.; Qiang, M.; Dong, T.; Li, H. Role of Vitamin C in Skin Diseases. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, K.E. Porphyria cutanea tarda: A possible role for ascorbic acid. Hepatology 2007, 45, 6–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinclair, P.R.; Gorman, N.; Shedlofsky, S.I.; Honsinger, C.P.; Sinclair, J.F.; Karagas, M.R.; Anderson, K.E. Ascorbic acid deficiency in porphyria cutanea tarda. J. Lab Clin. Med. 1997, 130, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maretzke, F.; Bechthold, A.; Egert, S.; Ernst, J.B.; Melo van Lent, D.; Pilz, S.; Reichrath, J.; Stangl, G.I.; Stehle, P.; Volkert, D.; et al. Role of Vitamin D in Preventing and Treating Se- 12 lected Extraskeletal Diseases-An Umbrella Review. Nutrients 2020, 12, 969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cefalo, C.M.A.; Conte, C.; Sorice, G.P.; Moffa, S.; Sun, V.A.; Cinti, F.; Salomone, E.; Muscogiuri, G.; Brocchi, A.A.G.; Pontecorvi, A.; et al. Effect of Vitamin D Supplementation on Obesity-Induced Insulin Resistance: A Double-Blind, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Obesity 2018, 26, 651–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamilian, M.; Samimi, M.; Ebrahimi, F.A.; Hashemi, T.; Taghizadeh, M.; Razavi, M. The effects of vitamin D and omega-3 fatty acid co-supplementation on glycemic control and lipid concentrations in patients with gestational diabetes. J. Clin. Lipidol. 2017, 11, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imga, N.N.; Karci, A.C.; Oztas, D.; Berker, D.; Guler, S. Effects of vitamin D supplementation on insulin resistance and dyslipidemia in overweight and obese premenopausal women. AMS 2019, 15, 598–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łagowska, K.; Bajerska, J.; Jamka, M. The Role of Vitamin D Oral Supplementation in Insulin Resistance in Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzal, S.; Bojesen, S.E.; Nordestgaard, B.G. Low 25- hydroxyvitamin D and risk of type 2 diabetes: A prospective cohort study and metaanalysis. Clin. Chem. 2013, 59, 381–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Wang, L.; Pittas, A.G.; Del Gobbo, L.; Zhang, C.; Manson, J.E.; Hu, F.B. Blood 25-hydroxy vitamin D levels and incident type 2 diabetes: A meta-analysis of prospective studies. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 1422–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bikle, D.D. Vitamin D and the skin: Physiology and pathophysiology. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2012, 13, 3–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gisondi, P.; Rossini, M.; Di Cesare, A.; Idolazzi, L.; Farina, S.; Beltrami, G.; Peris, K.; Girolomoni, G. Vitamin D status in patients with chronic plaque psoriasis. Br. J. Dermatol. 2012, 166, 505–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, P.B. Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D status in individuals with psoriasis in the general population. Endocrine 2013, 44, 537–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finamor, D.C.; Sinigaglia-Coimbra, R.; Neves, L.C.; Gutierrez, M.; Silva, J.J.; Torres, L.D.; Surano, F.; Neto, D.J.; Novo, N.F.; Juliano, Y.; et al. A pilot study assessing the effect of prolonged administration of high daily doses of vitamin D on the clinical course of vitiligo and psoriasis. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2013, 68, 511–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mutairi, N.; Shaaban, D. Effect of narrow-band ultraviolet B therapy on serum vitamin D and cathelicidin (LL-37) in patients with chronic plaque psoriasis. J. Cutan. Med. Surg. 2014, 18, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattozzi, C.; Paolino, G.; Salvi, M.; Macaluso, L.; Luci, C.; Morrone, S.; Calvieri, S.; Richetta, A.G. Importance of regulatory T cells in the pathogenesis of psoriasis: Review of the literature. Dermatology 2013, 227, 134–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dall’Ara, F.; Riccio, L.; Santoro, A.; Di Mattia, D.; Di Pietro, C.; Chiricozzi, A.; Calzavara-Pinton, P.; Girolomoni, G. The association between serum vitamin D levels and the severity of atopic dermatitis in children and adults: A systematic review. Dermatitis 2014, 25, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Ooi, H.S.; Kamal, S.M.; Yeo, J.F.; Thng, T.G.S.; Giam, Y.C. A systematic review of the effect of vitamin D supplementation on atopic dermatitis. Dermatology 2017, 233, 356–361. [Google Scholar]
- Gilaberte, Y.; Rojas-Hernandez, C.; Ramos, L.; Granizo, C.; Bardají, M.; Herranz, P.; Burgos, F.J. Efficacy of vitamin D supplementation in atopic dermatitis patients with low vitamin D levels: Results of a randomized controlled trial. Eur. J. Dermatol. 2017, 27, 372–377. [Google Scholar]
- Drozdenko, G.; Heine, G.; Worm, M. Oral vitamin D increases the frequencies of CD38+ human B cells and ameliorates IL-17-producing T cells. Exp Dermatol. 2014, 23, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanda, N.; Hau, C.S.; Tada, Y.; Sato, S.; Watanabe, S. Decreased serum LL-37 and vitamin D3 levels in atopic dermatitis: Relationship between IL-31 and oncostatin M. Allergy 2012, 67, 804–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilaberte, Y.; Sanmartín, R.; Aspiroz, C.; Hernandez-Martin, A.; Benito, D.; Sanz-Puertolas, P.; Alonso, M.; Torrelo, A.; Torres, C. Correlation Between Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D and Virulence Genes of Staphylococcus aureus Isolates Colonizing Children with Atopic Dermatitis. Pediatr Dermatol. 2015, 32, 506–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Nicolantonio, J.J.; O’Keefe, J. Myo-inositol for insulin resistance, metabolic syndrome, polycystic ovary syndrome and gestational diabetes. Open Heart 2022, 9, e001989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonowski, T.; Osowski, A.; Lahuta, L.; Górecki, R.; Rynkiewicz, A.; Wojtkiewicz, J. Health-Promoting Properties of Selected Cyclitols for Metabolic Syndrome and Diabetes. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Gambero, A.J.; Sanjuan, C.; Serrano-Castro, P.J.; Suárez, J.; Rodríguez de Fonseca, F. The Biomedical Uses of Inositols: A Nutraceutical Approach to Metabolic Dysfunction in Aging and Neurodegenerative Diseases. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grafton, G.; Bunce, C.M.; Sheppard, M.C.; Brown, G.; Baxter, M.A. Effect of Mg2+ on Na(+)-dependent inositol transport. Role for Mg2+ in etiology of diabetic complications. Diabetes 1992, 41, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamenov, Z.; Gateva, A.; Dinicola, S.; Unfer, V. Comparing the Efficacy of Myo-Inositol Plus α-Lactalbumin vs. Myo-Inositol Alone on Reproductive and Metabolic Disturbances of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. Metabolites 2023, 13, 717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarezadeh, M.; Dehghani, A.; Faghfouri, A.H.; Radkhah, N.; Naemi Kermanshahi, M.; Hamedi Kalajahi, F.; Mohammadzadeh Honarvar, N.; Ghoreishi, Z.; Ostadrahimi, A.; Ebrahimi Mamaghani, M. Inositol supplementation and body mass index: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Obes. Sci. Pract. 2021, 8, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandraki, K.I.; Kandaraki, E.A.; Poulia, K.A.; Piperi, C.; Papadimitriou, E.; Papaioannou, T.G. Assessment of Early Markers of Cardiovascular Risk in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. Touch Rev. Endocrinol. 2021, 17, 37–53. [Google Scholar]
- Genazzani, A.D.; Lanzoni, C.; Ricchieri, F.; Jasonni, V.M. Myoinositol administration positively affects hyperinsulinemia and hormonal parameters in overweight patients with polycystic ovary syndrome. Gynecol. Endocrinol. 2008, 24, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shokrpour, M.; Foroozanfard, F.; Afshar Ebrahimi, F.; Vahedpoor, Z.; Aghadavod, E.; Ghaderi, A.; Asemi, Z. Comparison of myo-inositol and metformin on glycemic control, lipid profiles, and gene expression related to insulin and lipid metabolism in women with polycystic ovary syndrome: A randomized controlled clinical trial. Gynecol. Endocrinol. 2019, 35, 406–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minozzi, M.; Costantino, D.; Guaraldi, C.; Unfer, V. The effect of a combination therapy with myo-inositol and a combined oral contraceptive pill versus a combined oral contraceptive pill alone on metabolic, endocrine, and clinical parameters in polycystic ovary syndrome. Gynecol. Endocrinol. 2011, 27, 920–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regidor, P.A.; Schindler, A.E. Myoinositol as a Safe and Alternative Approach in the Treatment of Infertile PCOS Women: A German Observational Study. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2016, 2016, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santamaria, A.; Alibrandi, A.; Di Benedetto, A.; Pintaudi, B.; Corrado, F.; Facchinetti, F.; D’Anna, R. Clinical and metabolic outcomes in pregnant women at risk for gestational diabetes mellitus supplemented with myo-inositol: A secondary analysis from 3 RCTs. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2018, 219, 300.e1–300.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, B.; Kondeti, V.K.; Xie, P.; Lin, S.; Viswakarma, N.; Raparia, K.; Kanwar, Y.S. Transcriptional and post-translational modulation of myo-inositol oxygenase by high glucose and related pathobiological stresses. J. Biol. Chemi. 2011, 286, 27594–27611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quach, M.; Chang, Y.F.; Lee, I.; Tai, L.; Choi, F.; Bodemer, A. Inositol for Treating Dermatological Disorders: A Systematic Review. J. Integr. Dermatol. 2024. Available online: https://www.jintegrativederm.org/article/122716 (accessed on 18 May 2025).
- Salomone, S.; Carruba, M.; Drago, F. Gli Inositoli Nella sindrome Dell’ovaio Policistico: Evidenze Cliniche e Razionali D’impiego; Opinion Papers; Italian Society of Pharmacology: Milan, Italy, 2017; pp. 1–22. Available online: https://www.sifweb.org/pubblicazioni/position-papers/position-papers-gli-inositoli-nella-sindrome-dell-ovaio-policistico-evidenze-cliniche-e-razionale-d-impiego-2017-03-01 (accessed on 18 May 2025).
- Bevilacqua, A.; Dragotto, J.; Lucarelli, M.; Di Emidio, G.; Monastra, G.; Tatone, C. High Doses of D-Chiro-Inositol Alone Induce a PCO-Like Syndrome and Other Alterations in Mouse Ovaries. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monastra, G.; Vazquez-Levin, M.; Bezerra Espinola, M.S.; Bilotta, G.; Laganà, A.S.; Unfer, V. D-chiro-inositol, an aromatase down-modulator, increases androgens and reduces estrogens in male volunteers: A pilot study. Basic Clin. Androl. 2021, 31, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pezza, M.; Carlomagno, V.; Casucci, G. Inositol and acne. G Ital. Dermatol. Venereol. 2015, 150, 649–653. [Google Scholar]
- Pezza, M.; Carlomagno, V.; Sammarco, E.; Trischitta, A.; Ceddia, C.; Vitiello, A.; Baj, G.; Citi, V.; Colletti, A. Association of Myo-Inositol and Microlipodispersed Magnesium in Androgen-Dependent Dermatological Diseases: A Retrospective Study. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fruzzetti, F.; Perini, D.; Russo, M.; Bucci, F.; Gadducci, A. Comparison of two insulin sensitizers, metformin and myo-inositol, in women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). Gynecol. Endocrinol. 2016, 33, 39–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minozzi, M.; D’Andrea, G.; Unfer, V. Treatment of hirsutism with myo-inositol: A prospective clinical study. Reprod. Biomed. Online 2008, 17, 579–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Advani, K.; Batra, M.; Tajpuriya, S.; Gupta, R.; Saraswat, A.; Nagar, H.D.; Makwana, L.; Kshirsagar, S.; Kaul, P.; Ghosh, A.K.; et al. Efficacy of combination therapy of inositols, antioxidants and vitamins in obese and non-obese women with polycystic ovary syndrome: An observational study. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2020, 40, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramanan, E.A.; Ravi, S.; Anbu, K.R.R.; Michael, M. Efficacy and Safety of Tracnil™ Administration in Patients with Dermatological Manifestations of PCOS: An Open-Label Single-Arm Study. Dermatol. Res. Pract. 2020, 2020, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allan, S.; Kavanagh, G.; Herd, R.; Savin, J. The effect of inositol supplements on the psoriasis of patients taking lithium: A randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Br. J. Dermatol. 2004, 150, 966–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnarumma, M.; Marasca, C.; Palma, M.; Vastarella, M.; Annunziata, M.C.; Fabbrocini, G. An oral supplementation based on myo-inositol, folic acid and liposomal magnesium may act synergistically with antibiotic therapy and can improve metabolic profile in patients affected by Hidradenitis suppurativa: Our experience. G Ital. Dermatol. Venereol. 2020, 155, 749–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abubaker, S.A.; Alonazy, A.M.; Abdulrahman, A. Effect of Alpha-Lipoic Acid in the Treatment of Diabetic Neuropathy: A Systematic Review. Cureus 2022, 14, e25750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shay, K.P.; Moreau, R.F.; Smith, E.J.; Smith, A.R.; Hagen, T.M. Alpha-lipoic acid as a dietary supplement: Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic potential. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009, 1790, 1149–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.J.; Eun, D.H.; Kim, S.M.; Kim, J.Y.; Jang, Y.H.; Lee, S.J. Anti-Inflammatory and Antioxidative Effects of Alpha Lipoic Acid on Cultured Human Sebocytes. Ann. Dermatol. 2019, 31, 84–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Bengy, A.-F.; Decorps, J.; Martin, L.S.; Pagnon, A.; Chevalier, F.P.; Sigaudo-Roussel, D.; Fromy, B. Alpha-Lipoic Acid Supplementation Restores Early Age-Related Sensory and Endothelial Dysfunction in the Skin. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jibril, A.T.; Jayedi, A.; Shab-Bidar, S. Efficacy and safety of oral alpha-lipoic acid supplementation for type 2 diabetes management: A systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of randomized trials. Endocr. Connect. 2022, 11, e220322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA Panel on Nutrition, Novel Foods and Food Allergens (NDA); Turck, D.; Castenmiller, J.; de Henauw, S.; Hirsch-Ernst, K.I.; Kearney, J.; Knutsen, H.K.; Mangelsdorf, I.; McArdle, H.J.; Naska, A.; et al. Scientific opinion on the relationship between intake of alpha-lipoic acid (thioctic acid) and the risk of insulin autoimmune syndrome. EFSA J. 2021, 19, e06577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rendon, A.; Schäkel, K. Psoriasis Pathogenesis and Treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruszczyńska, M.; Sadowska-Przytocka, A.; Szybiak, W.; Więckowska, B.; Lacka, K. Insulin Resistance in Patients with Acne Vulgaris. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monte-Serrano, J.; Villagrasa-Boli, P.; Cruañes-Monferrer, J.; Arbués-Espinosa, P.; Martínez-Cisneros, S.; García-Gil, M.F. Metformina en el tratamiento de enfermedades dermatológicas: Una revisión narrativa [The role of metformin in the treatment of dermatological diseases: A narrative review]. Aten. Primaria 2022, 54, 102354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadati, M.S.; Yazdanpanah, N.; Shahriarirad, R.; Javaheri, R.; Parvizi, M.M. Efficacy of metformin vs. doxycycline in treating acne vulgaris: An assessor-blinded, add-on, randomized, controlled clinical trial. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2023, 22, 2816–2823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreadi, A.; Muscoli, S.; Tajmir, R.; Meloni, M.; Minasi, A.; Muscoli, C.; Ilari, S.; Mollace, V.; Della Morte, D.; Bellia, A.; et al. Insulin Resistance and Acne: The Role of Metformin as Alternative Therapy in Men. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 16, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, H.T.X.; Thuy, L.N.D.; Vinh, N.M.; Anh, T.N.; Van, B.T. The Combined Use of Metformin and Methotrexate in Psoriasis Patients with Metabolic Syndrome. Dermatol. Res. Pract. 2022, 2022, 9838867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malavazos, A.E.; Meregalli, C.; Sorrentino, F.; Vignati, A.; Dubini, C.; Scravaglieri, V.; Basilico, S.; Boniardi, F.; Spagnolo, P.; Malagoli, P.; et al. Semaglutide therapy decreases epicardial fat inflammation and improves psoriasis severity in patients affected by abdominal obesity and type-2 diabetes. Endocrinol. Diabetes Metab. Case Rep. 2023, 2023, 23-0017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, H.; Chang, Y.T.; Yee, F.J.; Huang, Y.C. Metformin Therapy for Acne in Patients with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2021, 22, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Ahn, C.W.; Fang, S.; Lee, H.S.; Park, J.S. Association between metformin dose and vitamin B12 deficiency in patients with type 2 diabetes. Medicine 2019, 98, e17918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zacchè, M.M.; Caputo, L.; Filippis, S.; Zacchè, G.; Dindelli, M.; Ferrari, A. Efficacy of myo-inositol in the treatment of cutaneous disorders in young women with polycystic ovary syndrome. Gynecol. Endocrinol. 2009, 25, 508–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radu, A.; Tit, D.M.; Endres, L.M.; Radu, A.F.; Vesa, C.M.; Bungau, S.G. Naturally derived bioactive compounds as precision modulators of immune and inflammatory mechanisms in psoriatic conditions. Inflammopharmacology 2025, 33, 527–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, J.; Xing, H.; Ye, J. Efficacy of berberine in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Metabolism 2008, 57, 712–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, P.V.; Gan, S.H. Cinnamon: A multifaceted medicinal plant. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2014, 2014, 642942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickenberg, J.; Ingemansson, S.L.; Hlebowicz, J. Effects of green tea and its polyphenols on insulin sensitivity. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 64, 1243–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Xiao, X.; Li, M. Berberine moderates glucose and lipid metabolism through multi-target regulation. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2011, 2011, 924851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Gong, Z.; Huang, C.; Zang, Y.Q. Improved Insulin Resistance and Lipid Metabolism by Cinnamon Extract through Activation of Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptors. PPAR Res. 2008, 2008, 581348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posadzki, P.; Watson, L.; Ernst, E. Herb-drug interactions: An overview of systematic reviews. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2013, 75, 603–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colletti, A.; Fratter, A.; Pellizzato, M.; Cravotto, G. Nutraceutical Approaches to Dyslipidaemia: The Main Formulative Issues Preventing Efficacy. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Author(s), Year | Study Design | Participants | Intervention | Primary Outcome | Adverse Events | Follow-Up (Weeks) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pezza et al., 2015 [121] | RCT | 50 women with PCOS and acne | LEVIGON™ MI 2 g, microlipodispersed magnesium 56.25 mg, folic acid 200 mcg BID | Decreased number of papulopustular lesions | None | 6 |
| Pezza et al., 2025 [122] | Retrospective study | 200 women with PCOS and acne | LEVIGON™ MI 2 g, microlipodispersed magnesium 56.25 mg, folic acid 200 mcg BID | Reduction in BMI, testosterone, free testosterone, and DHEAS levels, Improvement of quality of life (Cardiff Acne Disability Index and Dermatology Life Quality Index) and Ferriman–Gallwey score | None | 24 |
| Fruzzetti et al., 2017 [123] | RCT | 50 women with PCOS | MI 4 g, folic acid 400 mcg | Reduction in BMI, 20% felt improvement in hirsutism; 38% in acne | None | 6 |
| Minozzi et al., 2008 [124] | Uncontrolled clinical trial | 46 women with mild to moderate hirsutism | MI 2 g, BID | Hirsutism score decreased by −2.3 ± 0.9 (p < 0.001) | None | 6 |
| Advani et al., 2019 [125] | Retrospective trial | 51 women (35 obese, 16 lean) with PCOS | Trazer F Forte, BID (inositol MI:DCI 600 mg, NAC 300 mg, Biotin 5 mg, Lycopene 5 mg, vitamin D 400IU) | Acne scores decreased significantly in obese patients and in lean patients) | None | 3 |
| Ramanan et al., 2020 [126] | Uncontrolled clinical trial | 32 women with mild to moderate acne and hirsutism | Tracnil, BID (MI 2 g, folic acid 1 mg, vit D3 1000 IU) | Significant improvement in GA and hirsutism scores (p < 0.05) | Mild GI distress in some patients | 6 |
| Allan et al., 2004 [127] | Crossover RCT | 23 patients with psoriasis | Inositol 6 g, QD | Patients on lithium: PASI scores improved (p > 0.05); patients not on lithium: PASI scores improved significantly (p = 0.015) | None | 2.5 |
| Donnarumma et al., 2020 [128] | RCT | 10 patients with HS | Antibiotics + MI 2 g, liposomal magnesium, folic acid, BID | Reduction in Sartorius scores (p < 0.04) | None | 6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Morrone, P.; Caroppo, F.; De Pedrini, A.; Colletti, A.; Baj, G. New Perspectives on Nutraceutical Insulin Sensitizing Agents in the Treatment of Psoriasis and Other Dermatological Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 7538. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157538
Morrone P, Caroppo F, De Pedrini A, Colletti A, Baj G. New Perspectives on Nutraceutical Insulin Sensitizing Agents in the Treatment of Psoriasis and Other Dermatological Diseases. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(15):7538. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157538
Chicago/Turabian StyleMorrone, Pietro, Francesca Caroppo, Alberto De Pedrini, Alessandro Colletti, and Germano Baj. 2025. "New Perspectives on Nutraceutical Insulin Sensitizing Agents in the Treatment of Psoriasis and Other Dermatological Diseases" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 15: 7538. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157538
APA StyleMorrone, P., Caroppo, F., De Pedrini, A., Colletti, A., & Baj, G. (2025). New Perspectives on Nutraceutical Insulin Sensitizing Agents in the Treatment of Psoriasis and Other Dermatological Diseases. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(15), 7538. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157538





