The Neuroregenerative Effects of IncobotulinumtoxinA (Inco/A) in a Nerve Lesion Model of the Rat
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Inco/A Accelerated Functional Recovery in Rats Post CCI
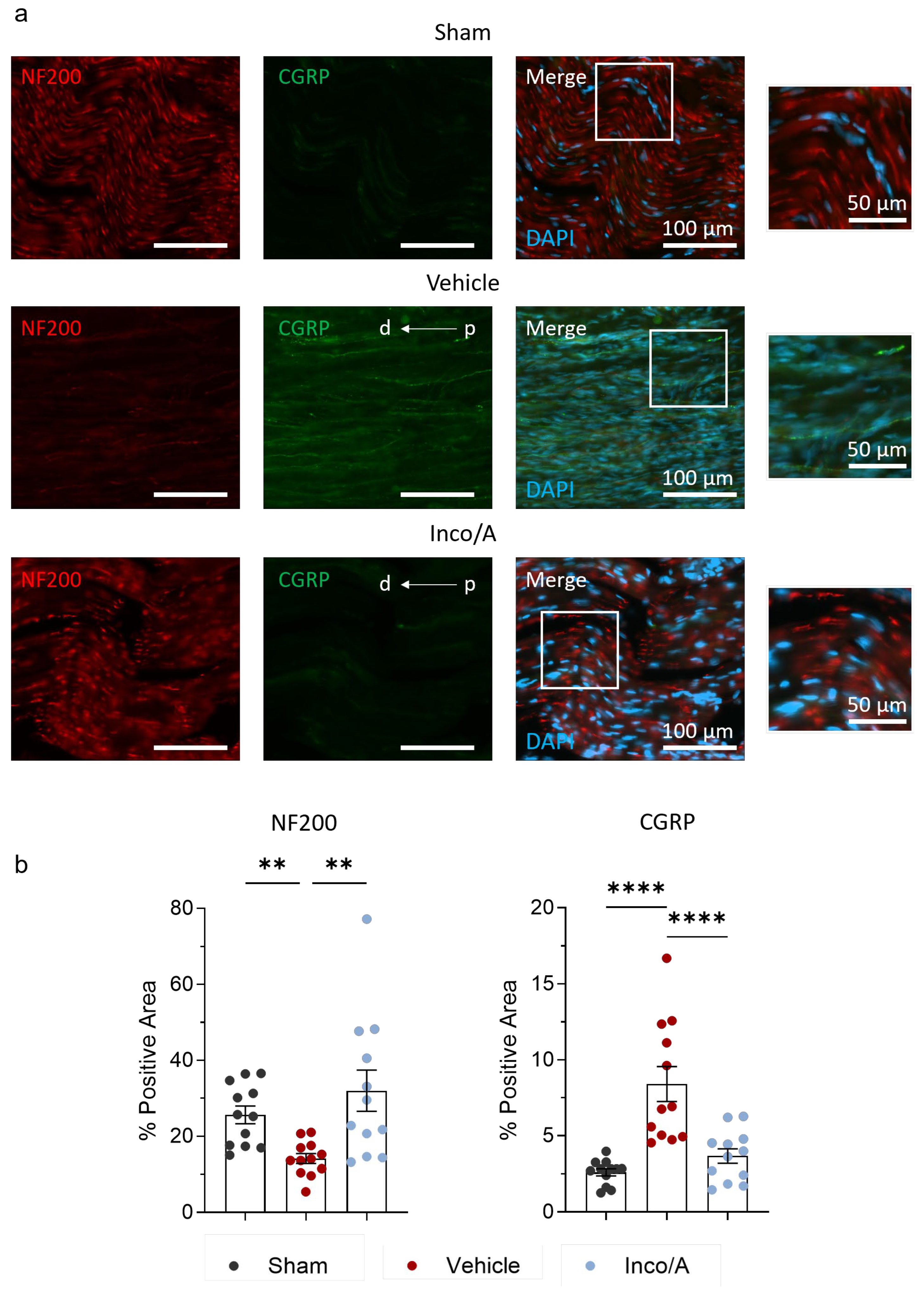
2.2. Inco/A Increased Nerve Myelinization and Diminished CGRP Expression
2.3. Inco/A Reduced Pro-Inflammatory Responses in Sciatic Nerves After CCI
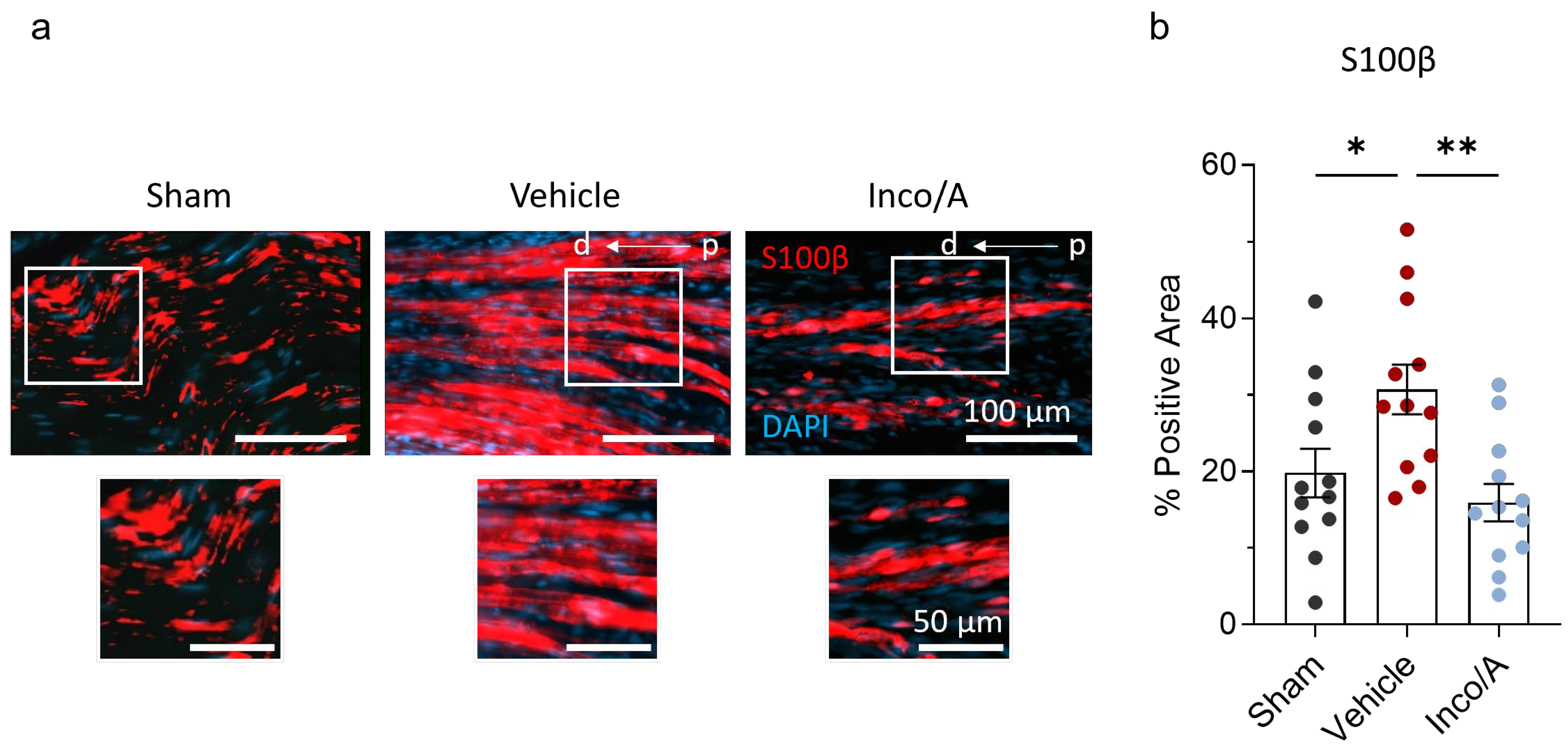
2.4. Inco/A Accelerated Schwann Cell (SC) Responses During Nerve Regeneration
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Chronic Constriction Injury (CCI) Surgery of the Sciatic Nerve
4.3. Drugs
4.4. Behavioral Tests
4.5. Sciatic Functional Index (SFI)
4.6. Compound Muscle Action Potential (CMAP)
4.7. Tissue Collection
4.8. Hematoxylin and Eosin Staining (H&E Staining)
4.9. Toluidine Blue Staining
4.10. Immunofluorescence Staining and Image Analysis
4.11. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BoNTA | Botulinum toxin A |
| Inco/A | IncobotulinumtoxinA |
| CCI | Chronic constriction injury |
| SFI | Sciatic Functional Index |
| CMAP | Compound Muscle Action Potential |
| AP | Action Potential |
| SC | Schwann cell |
| SSI | Sciatic Static Index |
References
- Attal, N.; de Andrade, D.C.; Adam, F.; Ranoux, D.; Teixeira, M.J.; Galhardoni, R.; Raicher, I.; Üçeyler, N.; Bouhassira, D. Safety and efficacy of repeated injections of botulinum toxin A in peripheral neuropathic pain (BOTNEP): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Neurol. 2016, 15, 555–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Hecke, O.; Austin, S.K.; Khan, R.A.; Smith, B.H.; Torrance, N. Neuropathic pain in the general population: A systematic review of epidemiological studies. Pain 2014, 155, 654–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scholz, J.; Finnerup, N.B.; Attal, N.; Aziz, Q.; Baron, R.; Bennett, M.I.; Benoliel, R.; Cohen, M.; Cruccu, G.; Davis, K.D.; et al. The IASP classification of chronic pain for ICD-11: Chronic neuropathic pain. Pain 2019, 160, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holds, J.B.; Alderson, K.; Fogg, S.G.; Anderson, R.L. Motor nerve sprouting in human orbicularis muscle after botulinum A injection. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1990, 31, 964–967. [Google Scholar]
- Marinelli, S.; Luvisetto, S.; Cobianchi, S.; Makuch, W.; Obara, I.; Mezzaroma, E.; Caruso, M.; Straface, E.; Przewlocka, B.; Pavone, F. Botulinum neurotoxin type A counteracts neuropathic pain and facilitates functional recovery after peripheral nerve injury in animal models. Neuroscience 2010, 171, 316–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobianchi, S.; Jaramillo, J.; Luvisetto, S.; Pavone, F.; Navarro, X. Botulinum neurotoxin A promotes functional recovery after peripheral nerve injury by increasing regeneration of myelinated fibers. Neuroscience 2017, 359, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, W.; Salles, A.G.; Faria, J.C.M.; Nepomuceno, A.C.; Salomone, R.; Krunn, P.; Gemperli, R. Contralateral Botulinum Toxin Improved Functional Recovery after Tibial Nerve Repair in Rats. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2018, 142, 1511–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, M.; Hwang, S.; Lee, T.H.; Nam, K. Comparison of Neural Recovery Effects of Botulinum Toxin Based on Administration Timing in Sciatic Nerve-Injured Rats. Toxins 2024, 16, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdulahad, A.K.; Snijder, R.J.; Panni, M.K.; Riaz, F.K.; Karas, A.J. A novel standard to evaluate the impact of therapeutic agents on patient safety—The BURDEN OF THERAPY((c)*). Contemp. Clin. Trials Commun. 2016, 4, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.; Seo, M.; Lee, T.H.; Lee, H.J.; Park, J.W.; Kwon, B.S.; Nam, K. Comparison of the Effects of Botulinum Toxin Doses on Nerve Regeneration in Rats with Experimentally Induced Sciatic Nerve Injury. Toxins 2023, 15, 691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, M.; Pellett, S.; Sharma, S.K.; Lebeda, F.J.; Dembek, Z.F.; Mahan, M.A. Preclinical Evidence for the Role of Botulinum Neurotoxin A (BoNT/A) in the Treatment of Peripheral Nerve Injury. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerscher, M.; Wanitphakdeedecha, R.; Trinidade de Almedia, A.; Maas, C.; Frevert, J. IncobotulinumtoxinA: A Highly Purified and Precisely Manufactured Botulinum Neurotoxin Type A. J. Drugs Dermatol. 2019, 18, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- de Medinaceli, L.; Freed, W.J.; Wyatt, R.J. An index of the functional condition of rat sciatic nerve based on measurements made from walking tracks. Exp. Neurol. 1982, 77, 634–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baptista, A.F.; Gomes, J.R.; Oliveira, J.T.; Santos, S.M.; Vannier-Santos, M.A.; Martinez, A.M. A new approach to assess function after sciatic nerve lesion in the mouse—Adaptation of the sciatic static index. J. Neurosci. Methods 2007, 161, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollari, E.; Prior, R.; Robberecht, W.; Van Damme, P.; Van Den Bosch, L. In Vivo Electrophysiological Measurement of Compound Muscle Action Potential from the Forelimbs in Mouse Models of Motor Neuron Degeneration. J. Vis. Exp. 2018, 136, e57741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allgood, J.; James, S.; Laird, L.; Allotey, A.; Bushman, J. Electrode configurations for sensitive and specific detection of compound muscle action potentials to the tibialis anterior muscle after peroneal nerve injury in rats. J. Neurosci. Methods 2025, 415, 110335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghnenis, A.B.; Czaikowski, R.E.; Zhang, Z.J.; Bushman, J.S. Toluidine Blue Staining of Resin-Embedded Sections for Evaluation of Peripheral Nerve Morphology. J. Vis. Exp. 2018, 137, 58031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronchi, G.; Fregnan, F.; Muratori, L.; Gambarotta, G.; Raimondo, S. Morphological Methods to Evaluate Peripheral Nerve Fiber Regeneration: A Comprehensive Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, M.; Khanijou, S.; Rubino, J.; Aoki, K.R. Subcutaneous administration of botulinum toxin A reduces formalin-induced pain. Pain 2004, 107, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durham, P.L.; Cady, R.; Cady, R. Regulation of calcitonin gene-related peptide secretion from trigeminal nerve cells by botulinum toxin type A: Implications for migraine therapy. Headache 2004, 44, 35–42; discussion 42–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Bennett, D.L.H.; Querol, L.A.; Wu, L.J.; Irani, S.R.; Watson, J.C.; Pittock, S.J.; Klein, C.J. Pain and the immune system: Emerging concepts of IgG-mediated autoimmune pain and immunotherapies. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2020, 91, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wedel, S.; Mathoor, P.; Rauh, O.; Heymann, T.; Ciotu, C.I.; Fuhrmann, D.C.; Fischer, M.J.M.; Weigert, A.; de Bruin, N.; Hausch, F.; et al. SAFit2 reduces neuroinflammation and ameliorates nerve injury-induced neuropathic pain. J. Neuroinflamm. 2022, 19, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iyengar, S.; Ossipov, M.H.; Johnson, K.W. The role of calcitonin gene-related peptide in peripheral and central pain mechanisms including migraine. Pain 2017, 158, 543–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marinelli, S. BoNT/Action beyond neurons. Toxicon 2025, 255, 108250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toth, C.C.; Willis, D.; Twiss, J.L.; Walsh, S.; Martinez, J.A.; Liu, W.-Q.; Midha, R.; Zochodne, D.W. Locally Synthesized Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide Has a Critical Role in Peripheral Nerve Regeneration. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2009, 68, 326–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caillaud, M.; Richard, L.; Vallat, J.M.; Desmouliere, A.; Billet, F. Peripheral nerve regeneration and intraneural revascularization. Neural Regen. Res. 2019, 14, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Chen, P.; Lin, D.; Chen, Y.; Lv, B.; Zheng, K.; Lin, X.; Wu, Z. Effects of varying degrees of ligation in a neuropathic pain model induced by chronic constriction injury. Life Sci. 2021, 276, 119441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranoux, D.; Attal, N.; Morain, F.; Bouhassira, D. Botulinum toxin type A induces direct analgesic effects in chronic neuropathic pain. Ann. Neurol. 2008, 64, 274–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastrorilli, V.; De Angelis, F.; Vacca, V.; Pavone, F.; Luvisetto, S.; Marinelli, S. Xeomin((R)), a Commercial Formulation of Botulinum Neurotoxin Type A, Promotes Regeneration in a Preclinical Model of Spinal Cord Injury. Toxins 2023, 15, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irintchev, M.; Guntinas-Lichius, O.; Irintchev, A. Botulinum Neurotoxin Application to the Severed Femoral Nerve Modulates Spinal Synaptic Responses to Axotomy and Enhances Motor Recovery in Rats. Neural Plast. 2018, 2018, 7975013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Sun, Y.; Yang, W.; Lindo, P.; Singh, B.R. Type A botulinum neurotoxin complex proteins differentially modulate host response of neuronal cells. Toxicon 2014, 82, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.J.; Wei, X.M.; Wu, M.L.; Song, Z.B.; Jiang, L.; Zhang, W.X. Analgesic Effect of Perineural Injection of BoNT/A on Neuropathic Pain Induced by Chronic Constriction Injury of Sciatic Nerve in Rats. Neurochem. Res. 2023, 48, 2161–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vacca, V.; Madaro, L.; De Angelis, F.; Proietti, D.; Cobianchi, S.; Orsini, T.; Puri, P.L.; Luvisetto, S.; Pavone, F.; Marinelli, S. Revealing the Therapeutic Potential of Botulinum Neurotoxin Type A in Counteracting Paralysis and Neuropathic Pain in Spinally Injured Mice. Toxins 2020, 12, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangadharan, V.; Zheng, H.; Taberner, F.J.; Landry, J.; Nees, T.A.; Pistolic, J.; Agarwal, N.; Mannich, D.; Benes, V.; Helmstaedter, M.; et al. Neuropathic pain caused by miswiring and abnormal end organ targeting. Nature 2022, 606, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.Z.; Nayer, B.; Singh, S.K.; Alshoubaki, Y.K.; Yuan, E.; Park, A.J.; Maruyama, K.; Akira, S.; Martino, M.M. CGRP sensory neurons promote tissue healing via neutrophils and macrophages. Nature 2024, 628, 604–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.H.; Son, J.Y.; Ju, J.S.; Kim, Y.M.; Ahn, D.K. Cellular Mechanisms Mediating the Antinociceptive Effect of Botulinum Toxin A in a Rodent Model of Trigeminal Irritation by a Foreign Body. J. Pain 2022, 23, 2070–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiguchi, N.; Kobayashi, D.; Saika, F.; Matsuzaki, S.; Kishioka, S. Pharmacological Regulation of Neuropathic Pain Driven by Inflammatory Macrophages. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.A.; Yu, J.; Cheung, C.W. Immune Actions on the Peripheral Nervous System in Pain. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jessen, K.R.; Mirsky, R. The Success and Failure of the Schwann Cell Response to Nerve Injury. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2019, 13, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tofaris, G.K.; Patterson, P.H.; Jessen, K.R.; Mirsky, R. Denervated Schwann Cells Attract Macrophages by Secretion of Leukemia Inhibitory Factor (LIF) and Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 in a Process Regulated by Interleukin-6 and LIF. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 6696–6703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zigmond, R.E.; Echevarria, F.D. Macrophage biology in the peripheral nervous system after injury. Prog. Neurobiol. 2019, 173, 102–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.P.; Shan, X.F.; Qiu, J.X.; Wang, L.N.; Xiang, R.L.; Cai, Z.G. Botulinum toxin type A inhibits M1 macrophage polarization by deactivation of JAK2/STAT1 and IkappaB/NFkappaB pathway and contributes to scar alleviation in aseptic skin wound healing. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 174, 116468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, D.; Xia, Y.; Ding, Z.; Qian, J.; Gu, X.; Bai, H.; Jiang, M.; Yao, D. Inflammation in the Peripheral Nervous System after Injury. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinski, A.L.; Yoon, C.; Huffman, L.D.; Duncker, P.C.; Kohen, R.; Passino, R.; Hafner, H.; Johnson, C.; Kawaguchi, R.; Carbajal, K.S.; et al. Analysis of the immune response to sciatic nerve injury identifies efferocytosis as a key mechanism of nerve debridement. Elife 2020, 9, e60223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fregnan, F.; Muratori, L.; Simoes, A.R.; Giacobini-Robecchi, M.G.; Raimondo, S. Role of inflammatory cytokines in peripheral nerve injury. Neural Regen. Res. 2012, 7, 2259–2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jessen, K.R.; Mirsky, R. The repair Schwann cell and its function in regenerating nerves. J. Physiol. 2016, 594, 3521–3531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pieretti, S.; Di Giannuario, A.; Di Giovannandrea, R.; Marzoli, F.; Piccaro, G.; Minosi, P.; Aloisi, A.M. Gender differences in pain and its relief. Ann. Ist. Super. Sanita 2016, 52, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco-Enzastiga, U.; Inturi, N.N.; Natarajan, K.; Mwirigi, J.M.; Mazhar, K.; Schlachetzki, J.C.M.; Schumacher, M.; Price, T.J. Epigenomic landscape of the human dorsal root ganglion: Sex differences and transcriptional regulation of nociceptive genes. bioRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenspan, J.D.; Craft, R.M.; LeResche, L.; Arendt-Nielsen, L.; Berkley, K.J.; Fillingim, R.B.; Gold, M.S.; Holdcroft, A.; Lautenbacher, S.; Mayer, E.A.; et al. Studying sex and gender differences in pain and analgesia: A consensus report. Pain 2007, 132 (Suppl. 1), S26–S45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsang, A.; Von Korff, M.; Lee, S.; Alonso, J.; Karam, E.; Angermeyer, M.C.; Borges, G.L.; Bromet, E.J.; Demytteneare, K.; de Girolamo, G.; et al. Common chronic pain conditions in developed and developing countries: Gender and age differences and comorbidity with depression-anxiety disorders. J. Pain 2008, 9, 883–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soliman, N.; Moisset, X.; Ferraro, M.C.; de Andrade, D.C.; Baron, R.; Belton, J.; Bennett, D.L.H.; Calvo, M.; Dougherty, P.; Gilron, I.; et al. Pharmacotherapy and non-invasive neuromodulation for neuropathic pain: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Neurol. 2025, 24, 413–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdo, H.; Calvo-Enrique, L.; Lopez, J.M.; Song, J.; Zhang, M.-D.; Usoskin, D.; El Manira, A.; Adameyko, I.; Hjerling-Leffler, J.; Ernfors, P. Specialized cutaneous Schwann cells initiate pain sensation. Science 2019, 365, 695–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer Zu Reckendorf, S.; Brand, C.; Pedro, M.T.; Hegler, J.; Schilling, C.S.; Lerner, R.; Bindila, L.; Antoniadis, G.; Knoll, B. Lipid metabolism adaptations are reduced in human compared to murine Schwann cells following injury. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilcox, M.B.; Laranjeira, S.G.; Eriksson, T.M.; Jessen, K.R.; Mirsky, R.; Quick, T.J.; Phillips, J.B. Characterising cellular and molecular features of human peripheral nerve degeneration. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2020, 8, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klee, M.; Hormann Thomsen, T.; Enggaard, T.P.; Bitsch, M.S.; Simonsen, L.; Jensen, R.H.; Biering-Sorensen, B. Perineural injections of incobotulinumtoxin-A for diabetic neuropathic pain of the lower extremities: Protocol for a phase II, single-centre, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled trial (the PINBOT study). BMJ Open 2024, 14, e074372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, G.J.; Xie, Y.-K. A peripheral mononeuropathy in rat that produces disorders of pain sensation like those seen in man. Pain 1988, 33, 87–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagel, J.; Danysz, W.; Fink, K.; Ruitenberg, M.; Gravius, A. Neuroregenerative Effects in a Chronic Constriction Injury (CCI) Model of the Rat Observed After Administration of Botulinum Neurotoxin A (BoNT-A). Toxicon 2024, 237, 107462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sánchez-Carranza, O.; Danysz, W.; Fink, K.; Ruitenberg, M.; Gravius, A.; Nagel, J. The Neuroregenerative Effects of IncobotulinumtoxinA (Inco/A) in a Nerve Lesion Model of the Rat. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 7482. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157482
Sánchez-Carranza O, Danysz W, Fink K, Ruitenberg M, Gravius A, Nagel J. The Neuroregenerative Effects of IncobotulinumtoxinA (Inco/A) in a Nerve Lesion Model of the Rat. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(15):7482. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157482
Chicago/Turabian StyleSánchez-Carranza, Oscar, Wojciech Danysz, Klaus Fink, Maarten Ruitenberg, Andreas Gravius, and Jens Nagel. 2025. "The Neuroregenerative Effects of IncobotulinumtoxinA (Inco/A) in a Nerve Lesion Model of the Rat" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 15: 7482. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157482
APA StyleSánchez-Carranza, O., Danysz, W., Fink, K., Ruitenberg, M., Gravius, A., & Nagel, J. (2025). The Neuroregenerative Effects of IncobotulinumtoxinA (Inco/A) in a Nerve Lesion Model of the Rat. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(15), 7482. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157482





