Genomic and Cytotoxic Damage in Wistar Rats and Their Newborns After Transplacental Exposure to Hibiscus sabdariffa Hydroalcoholic Extract
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Mothers
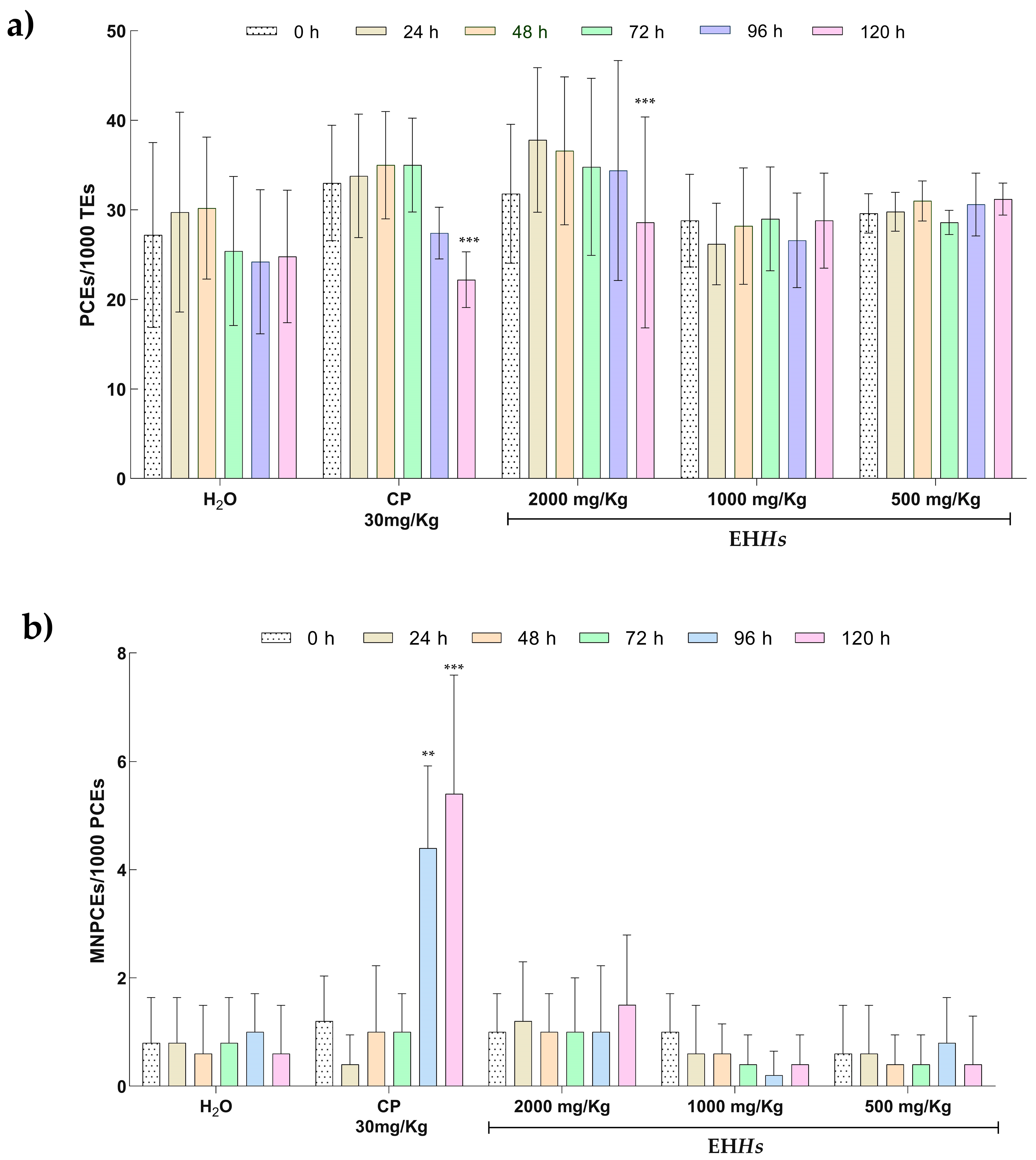
2.1.1. Genotoxic and Cytotoxic Evaluation of the EHHs with the Micronucleus Test in Peripheral Blood in Wistar Rats
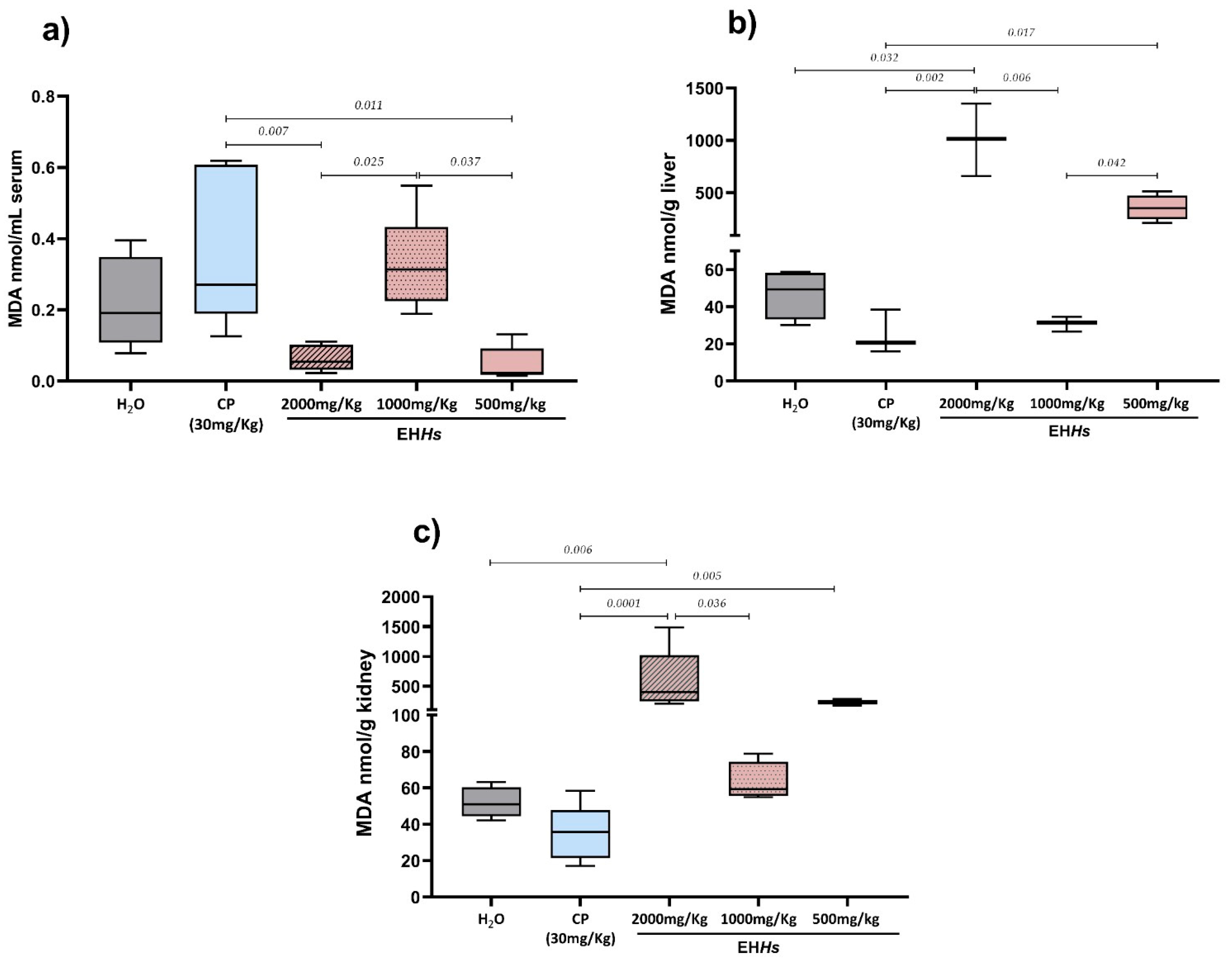
2.1.2. Cytotoxic Evaluation of the EHHs Through the Quantification of MDA in Mothers
2.2. Newborns
2.2.1. Morphometric Parameters in Newborns In Utero Exposed to the EHHs
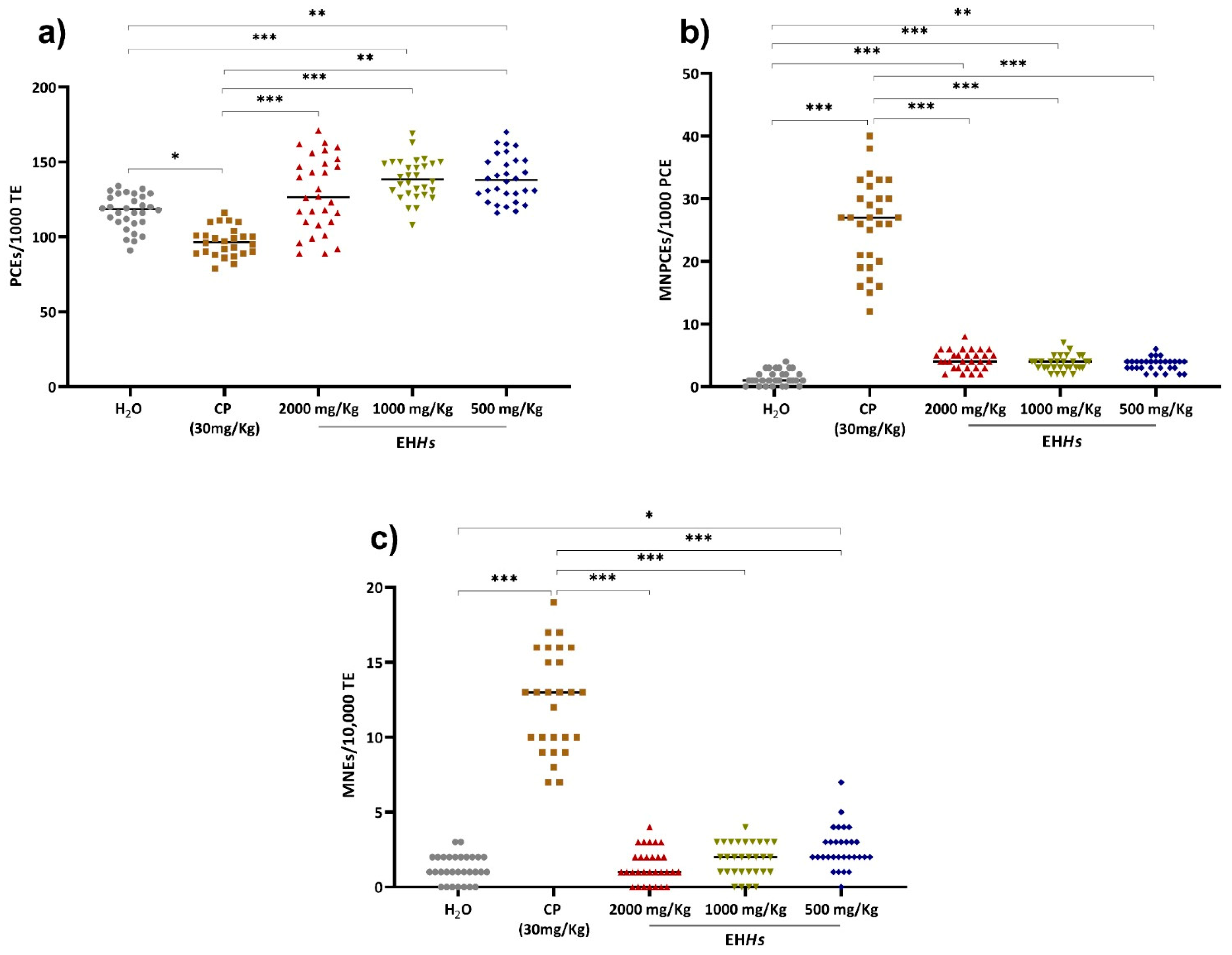
2.2.2. Genotoxic and Cytotoxic Evaluation in Newborns In Utero Exposed to EHHs
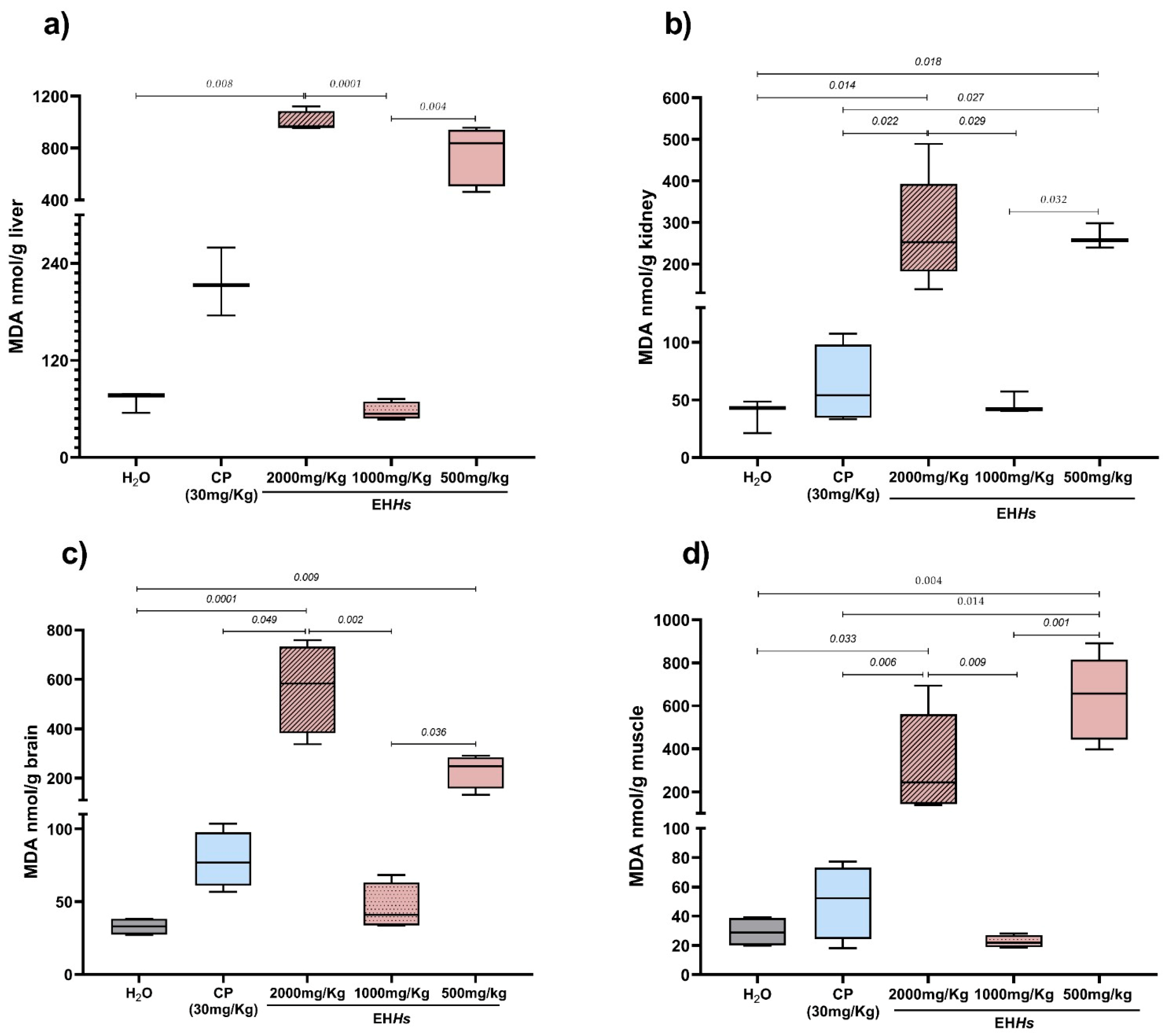
2.2.3. MDA as a Marker of Cytotoxicity in Newborns In Utero Exposed to EHHs and CP
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Hibiscus Sabdariffa Hydroalcoholic Extract
4.1.1. Preparation
4.1.2. Experimental Design
4.1.3. Gestation Induction
4.1.4. Sample Collection
4.1.5. Sacrifice
4.1.6. Morphometric Parameters
4.1.7. Determination of Genotoxic and Cytotoxic Damage by Micronucleus Assay in Pregnant Rats and Their Newborns
4.1.8. Quantification of MDA in Different Organs as a Marker of Cytotoxicity
4.1.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PCMNEs | Polychromatic micronucleated erythrocytes |
| PCEs | Polychromatic erythrocytes |
| MNEs | Micronucleated erythrocytes |
| OECD | Organization for economic cooperation and development |
| WHO | World health organization |
| DNA | Deoxyribonucleic acid |
| EHHs | Hydroalcoholic extract of Hibiscus sabdariffa |
| Hs | Hibiscus sabdariffa |
| PM | Phosphoramide mustard |
| AC | Acrolein |
| 4OHCP | 4-hydroxycyclophosphamide |
| LI | Lee index |
| CP | Cyclophosphamide |
References
- Organización Mundial de la Salud. Situación Reglamentaria de los Medicamentos Herbarios: Una Reseña Mundial. 2000. Available online: https://iris.who.int/handle/10665/66629 (accessed on 13 May 2025).
- Organización Mundial de la Salud. Medicina Tradicional: Preguntas y Respuestas. 2023. Available online: https://www.who.int/es/news-room/questions-and-answers/item/traditional-medicine (accessed on 13 May 2025).
- Secretaría de Salud. Medicinas Complementarias. Gobierno de México. 2024. Available online: https://www.gob.mx/salud/acciones-y-programas/medicinas-complementarias-313623 (accessed on 12 May 2025).
- Secretaría de Agricultura y Desarrollo Rural. Flor de Jamaica, Una Opción de la Bioeconomía Agrícola. Gobierno de México. 2024. Available online: https://www.gob.mx/agricultura/articulos/flor-de-jamaica-una-opcion-de-la-bioeconomia-agricola (accessed on 16 May 2025).
- Lin, H.H.; Chen, J.H.; Wang, C.J. Chemopreventive properties and molecular mechanisms of the bioactive compounds in Hibiscus sabdariffa Linne. Curr. Med. Chem. 2011, 18, 1245–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izquierdo-Vega, J.A.; Arteaga-Badillo, D.A.; Sánchez-Gutiérrez, M.; Morales-González, J.A.; Vargas-Mendoza, N.; Gómez-Aldapa, C.A.; Castro-Rosas, J.; Delgado-Olivares, L.; Madrigal-Bujaidar, E.; Madrigal-Santillán, E. Organic Acids from Roselle (Hibiscus sabdariffa L.)-A Brief Review of Its Pharmacological Effects. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelmonem, M.; Ebada, M.A.; Diab, S.; Ahmed, M.M.; Zaazouee, M.S.; Essa, T.M.; ElBaz, Z.S.; Ghaith, H.S.; Abdella, W.S.; Ebada, M.; et al. Efficacy of Hibiscus sabdariffa on Reducing Blood Pressure in Patients With Mild-to-Moderate Hypertension: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Published Randomized Controlled Trials. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2022, 79, e64–e74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suárez-Diéguez, T.; Palma-Morales, M.; Bernal, G.I.C.; López, E.N.V.; Rodríguez-Pérez, C.; Cruz-Cansino, N.d.S.; Nieto, J.A. Modulation of the Hyperglycemia Condition in Diabetic Lab Rats with Extracts of the Creole Jamaica Flower (Hibiscus sabdariffa L.) from the Morelia Region (Mexico). Antioxidants 2024, 13, 1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciel, L.G.; Do Carmo, M.A.V.; Azevedo, L.; Daguer, H.; Molognoni, L.; de Almeida, M.M.; Granato, D.; Rosso, N.D. Hibiscus sabdariffa anthocyanins-rich extract: Chemical stability, in vitro antioxidant and antiproliferative activities. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 113, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojulari, O.V.; Lee, S.G.; Nam, J.O. Beneficial Effects of Natural Bioactive Compounds from Hibiscus sabdariffa L. on Obesity. Molecules 2019, 24, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanou, A.; Konaté, K.; Belemnaba, L.; Sama, H.; Kaboré, K.; Dakuyo, R.; Nitiéma, M.; Dicko, M.H. In Vivo Diuretic Activity and Anti-Hypertensive Potential of Hibiscus sabdariffa Extract by Inhibition of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme and Hypertension Precursor Enzymes. Foods 2024, 13, 534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subhaswaraj, P.; Sowmya, M.; Bhavana, V.; Dyavaiah, M.; Siddhardha, B. Determination of antioxidant activity of Hibiscus sabdariffa and Croton caudatus in Saccharomyces cerevisiae model system. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 54, 2728–2736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da-Costa-Rocha, I.; Bonnlaender, B.; Sievers, H.; Pischel, I.; Heinrich, M. Hibiscus sabdariffa L.—A phytochemical and pharmacological review. Food Chem. 2014, 165, 424–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, N.; Wang, T.; Gan, Q.; Liu, S.; Wang, L.; Jin, B. Plant flavonoids: Classification, distribution, biosynthesis, and antioxidant activity. Food Chem. 2022, 383, 132531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruilope, L.M.; Nunes Filho, A.C.B.; Nadruz, W., Jr.; Rodríguez Rosales, F.F.; Verdejo-Paris, J. Obesity and hypertension in Latin America: Current perspectives. Hipertens. Y Riesgo Vasc. 2018, 35, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Arruda, A.; Cardoso, C.A.L.; Vieira, M.D.C.; Arena, A.C. Safety assessment of Hibiscus sabdariffa after maternal exposure on male reproductive parameters in rats. Drug Chem. Toxicol. 2016, 39, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, Y.I. Effect of extract of Hibiscus on the ultrastructure of the testis in adult mice. Acta Histochem. 2012, 114, 342–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orisakwe, O.E.; Husaini, D.C.; Afonne, O.J. Testicular effects of sub-chronic administration of Hibiscus sabdariffa calyx aqueous extract in rats. Reprod. Toxicol. 2004, 18, 295–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akindahunsi, A.A.; Olaleye, M.T. Toxicological investigation of aqueous-methanolic extract of the calyces of Hibiscus sabdariffa L. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2003, 89, 161–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Njinga, N.S.; Kola-Mustapha, A.T.; Quadri, A.L.; Atolani, O.; Ayanniyi, R.O.; Buhari, M.O.; Amusa, T.O.; Ajani, E.O.; Folaranmi, O.O.; Bakare-Odunola, M.T.; et al. Toxicity assessment of sub-acute and sub-chronic oral administration and diuretic potential of aqueous extract of Hibiscus sabdariffa calyces. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sireeratawong, S.; Itharat, A.; Khonsung, P.; Lertprasertsuke, N.; Jaijoy, K. Toxicity studies of the water extract from the calyces of Hibiscus sabdariffa L. in rats. Afr. J. Tradit. Complement. Altern. Med. AJTCAM 2013, 10, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. Guidance Document on the Recognition, Assessment, and Use of Clinical Signs as Humane Endpoints for Experimental Animals Used in Safety Evaluation (ENV/JM/MONO(2000)7); Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development: Paris, France, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Lucía, C.A.; Jacqueline, B.R.; Alberto, B.L.; David, B.A.; Beatriz, R.A. Actualized inventory of medicinal plants used in traditional medicine in Oaxaca, Mexico. J. Ethnobiol. Ethnomed. 2021, 17, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garima, S.; Ajit Kumar, P.; Marcy, D.M.; Sakthivel, R.; Bhim Pratap, S.; Nachimuthu Senthil, K. Ethnobotanical survey of medicinal plants used in the management of cancer and diabetes. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2020, 40, 1007–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macías-Peacok, B.; Pérez-Jackson, L.; Suárez-Crespo, M.F.; Fong-Domínguez, C.O.; Pupo-Perera, E. Consumo de plantas medicinales por mujeres embarazadas. Rev. Médica Inst. Mex. Seguro Soc. 2009, 47, 331–334. [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez Lamar, Á.; Fonseca López, G.; Capiro Trujillo, N.; Fernández Fuentes, D. Propuesta de ruta crítica para la evaluación genotóxica de lantas medicinales en Cuba. Rev. Cuba. Farm. 2000, 34, 34–43. Available online: http://scielo.sld.cu/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0034-75152000000100005&lng=es&tlng=es (accessed on 28 May 2025).
- Guardiola, S.; Mach, N. Potencial terapéutico del Hibiscus sabdariffa: Una revisión de las evidencias científicas [Therapeutic potential of Hibiscus sabdariffa: A review of the scientific evidence]. Endocrinol. Y Nutr. 2014, 61, 274–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyas, U.K.; Katare, D.P.; Aeri, V. Comparative evaluation of standardized alcoholic, hydroalcoholic, and aqueous extracts of Phyllanthus maderaspatensis Linn. against galactosamine-induced hepatopathy in albino rats. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2015, 11, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Research Council. Mechanisms of Developmental Toxicity. In Scientific Frontiers in Developmental Toxicology and Risk Assessment; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2000; pp. 29–60. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK225674/ (accessed on 30 May 2025).
- OCDE. Prueba n. 474: Prueba de micronúcleos de eritrocitos de mamíferos. In Directrices de la OCDE Para el Ensayo de Sustancias Químicas, Sección 4; Publicaciones de la OCDE: Paris, France, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirkes, P.E. Cyclophosphamide teratogenesis: A review. Teratog. Carcinog. Mutagen. 1985, 5, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, R.; Yu, H.L.; Zhao, H.F.; Liang, J.; Feng, J.F.; Wang, W. Developmental neurotoxicity role of cyclophosphamide on post-neural tube closure of rodents in vitro and in vivo. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 2007, 25, 531–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashby, R.; Davis, L.; Dewhurst, B.B.; Espinal, R.; Penn, R.N.; Upshall, D.G. Aspects of the teratology of cyclophosphamide (NSC-26271). Cancer Treat. Rep. 1976, 60, 477–482. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, H.; Rosenbaum, S. Developmental pharmacokinetics in pediatric populations. J. Pediatr. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 19, 262–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renwick, A.G. Toxicokinetics in infants and children in relation to the ADI and TDI. Food Addit. Contam. 1998, 15 (Suppl. 1), 17–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orkin, S.H.; Zon, L.I. Hematopoiesis: An evolving paradigm for stem cell biology. Cell 2008, 132, 631–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, N.; Yasui, Y. Identification of mutagenic substances in roselle color, elderberry color and safflower yellow. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1985, 49, 1851–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tazoho, G.M.; Gouado, I.; Ndomou, M.; Bonsi, S.T.; Wamba, Y.M.; Agbor, E.E. Clinical, hematological and biochemical health benefit effects of Hibiscus sabdariffa Lin dried calyces beverage in human. Food Nutr. Sci. 2016, 7, 383–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peter, E.L.; Rumisha, S.F.; Mashoto, K.O.; Minzi, O.M.; Mfinanga, S. Efficacy of standardized extract of Hibiscus sabdariffa L.(Malvaceae) in improving iron status of adults in malaria endemic area: A randomized controlled trial. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2017, 209, 288–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olvera-García, V.; Castaño-Tostado, E.; Rezendiz-Lopez, R.I.; Reynoso-Camacho, R.; de Mejía, E.G.; Elizondo, G.; Loarca-Piña, G. Hibiscus sabdariffa L. extracts inhibit the mutagenicity in microsuspension assay and the proliferation of HeLa cells. J. Food Sci. 2008, 73, T75–T81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gheller, A.C.; Kerkhoff, J.; Vieira Júnior, G.M.; de Campos, K.E.; Sugui, M.M. Antimutagenic Effect of Hibiscus sabdariffa L. Aqueous Extract on Rats Treated with Monosodium Glutamate. Sci. World J. 2017, 2017, 9392532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Ma, H.; Lu, S.; Shi, X.; Liu, J.; Yang, C.; Zhang, R. Effects of bamboo leaf flavonoids on growth performance, antioxidants, immune function, intestinal morphology, and cecal microbiota in broilers. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2024, 104, 7656–7667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, H.; Changchun, T.; Qiren, H.; Ping, L.; Xiaoyu, L.; Weijie, P. Approach on exerting Lee’s index to evaluate the obese degree of mature rats. Chin. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 1997, 2, 177. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, V. The structure and function of brown adipose tissue in the neonate. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Neonatal Nurs. 1980, 9, 368–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valko, M.; Leibfritz, D.; Moncol, J.; Cronin, M.T.; Mazur, M.; Telser, J. Free radicals and antioxidants in normal physiological functions and human disease. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2007, 39, 44–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marnett, L.J. Chemistry and biology of DNA damage by malondialdehyde. IARC Sci. Publ. 1999, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sienes Bailo, P.; Llorente Martín, E.; Calmarza, P.; Montolio Breva, S.; Bravo Gómez, A.; Pozo Giráldez, A.; Sánchez-Pascuala Callau, J.J.; Vaquer Santamaría, J.M.; Dayaldasani Khialani, A.; Cerdá Micó, C.; et al. Implicación del estrés oxidativo en las enfermedades neurodegenerativas y posibles terapias antioxidantes. Adv. Lab. Med. 2022, 3, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eghbaliferiz, S.; Iranshahi, M. Prooxidant Activity of Polyphenols, Flavonoids, Anthocyanins and Carotenoids: Updated Review of Mechanisms and Catalyzing Metals. Phytother. Res. PTR 2016, 30, 1379–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yen, G.C.; Duh, P.D.; Tsai, H.L.; Huang, S.L. Pro-oxidative properties of flavonoids in human lymphocytes. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2003, 67, 1215–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guneidy, R.A.; Zaki, E.R.; Gad, A.A.M.; Saleh, N.S.E.; Shokeer, A. Evaluation of Phenolic Content Diversity along with Antioxidant/Pro-Oxidant, Glutathione Transferase Inhibition, and Cytotoxic Potential of Selected Commonly Used Plants. Prev. Nutr. Food Sci. 2022, 27, 282–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukhari, S.N.A.; Duncan, R.; Prasad, K. Binding of dietary flavonoids to human serum albumin: Implications for bioavailability and pharmacokinetics. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 108, 1438–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrese, E.J. Hormesis: Redefining toxicology’s central belief—How low doses of familiar agents cause stimulation, not inhibition. Toxicol. Sci. 2008, 104, 973–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernstein, N.; Akram, M.; Yaniv-Bachrach, Z.; Daniyal, M. Is it safe to consume traditional medicinal plants during pregnancy? Phytother. Res. PTR 2021, 35, 1908–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escalante Bencomo, N.B. Enfermedades hepáticas propias del embarazo. Gen 2010, 64, 373–380. Available online: http://ve.scielo.org/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0016-35032010000400025&lng=es&tlng=es (accessed on 28 May 2025).
- Sociedad Española de Fitoterapia (SEFIT). Fitoterapia Durante el Embarazo y la Lactancia. 2017. Available online: https://www.sefit.es/fitoterapia-durante-embarazo-lactancia/ (accessed on 28 May 2025).
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Guidance for Industry: Estimating the Maximum Safe Starting Dose in Initial Clinical Trials for Therapeutics in Adult Healthy Volunteers; U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER): Washington, DC, USA, 2005. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/72309/download (accessed on 30 May 2025).
- Rodriguez-Saona, L.E.; Wrolstad, R.E. Extraction, Isolation, and Purification of Anthocyanins. Curr. Protoc. Food Anal. Chem. 2001, F1.1.1–F1.1.11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals; Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development: Paris, France, 2023; Available online: https://www.oecd-ilibrary.org/environment/oecd-guidelines-for-the-testing-of-chemicals_chem_guide_pkg-en (accessed on 30 May 2025).
- Cole, R.J.; Taylor, N.A.; Cole, J.; Arlett, C.F. Transplacental effects of chemical mutagens detected by the micronucleus test. Nature 1979, 277, 317–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, M.; Morita, T.; Kodama, Y.; Sofuni, T.; Ishidate, M., Jr. The micronucleus assay with mouse peripheral blood reticulocytes using acridine orange-coated slides. Mutat. Res. Lett. 1990, 245, 245–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanparys, P.; Deknudt, G.; Vermeiren, F.; Sysmans, M.; Marsboom, R. Sampling times in micronucleus testing. Mutat. Res. 1992, 282, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Meda, B.C.; Zúñiga-González, G.M.; Zamora-Perez, A.; Ramos-Ibarra, M.L.; Batista-González, C.M.; Torres-Mendoza, B.M. Folate supplementation of cyclophosphamide-treated mothers diminishes micronucleated erythrocytes in peripheral blood of newborn rats. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 2004, 44, 174–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.O. Determination of the Surface Area of the White Rat. Am. J. Physiol. 1928, 89, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, S.; Buraczewska, I.; Kruszewski, M. Micronucleus Assay: The State of Art, and Future Directions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, M.; MacGregor, J.T.; Gatehouse, D.G.; Adler, I.D.; Blakey, D.H.; Dertinger, S.D.; Krishna, G.; Morita, T.; Russo, A.; Sutou, S. In vivo rodent erythrocyte micronucleus assay. II. Some aspects of protocol design including repeated treatments, integration with toxicity testing, and automated scoring. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 2000, 35, 234–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rencüzoğulları, E.; Aydın, M. Genotoxic and mutagenic studies of teratogens in developing rat and mouse. Drug Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 42, 409–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihara, M.; Uchiyama, M. Determination of malonaldehyde precursor in tissues by thiobarbituric acid test. Anal. Biochem. 1978, 86, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Groups of Study | H2O | CP 30 mg/Kg | EHHs 500 mg/Kg | EHHs 1000 mg/Kg | EHHs 2000 mg/Kg |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weight (g) | 6.20 (4.6–6.9) | 4.95 (3.8–5.8) | 6.45 (4.0–7.1) | 5.85 (5.25–7.10) | 6.35 (4.22–7.40) |
| p-value | b *** | d *** | b *** | ||
| Height (mm) | 44.15 (37.80–50.40) | 34.90 (30.50–40.20) | 38.30 (31.90–45.60) | 44.20 (39.30–48.60) | 42.60 (38.40–53.40) |
| p-value | b *** | c * | b *** | b *** | |
| Abdominal length (mm) | 13.0 (11.40–14.10) | 12.25 (10.20–13.70) | 12.60 (10.20–13.90) | 13.10 (11.60–15.70) | 12.65 (10.30–17.30) |
| p-value | d ** | ||||
| Lee index | 0.5154 (0.48–0.54) | 0.5223 (0.49–0.55) | 0.5404 (0.50–0.56) | 0.5153 (0.49–0.55) | 0.5243 (0.43–0.56) |
| p-value | c *** | c * | d *** | c * |
| Group | Treatment | Dose | Administration Route | Administration Time | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | EHHs | 2000 mg/Kg. | Orally | 5 days | Each 24 h from gestational day 16 to 20. |
| 2 | 1000 mg/Kg. | ||||
| 3 | 500 mg/Kg. | ||||
| 4 | Tridistilled H2O (Negative Control) | 0.1 mL/10 g of weight. | |||
| 5 | Cyclophosphamide (Positive control) | 30 mg/Kg. | 2 days | Gestational day 19 and 20. | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tobanche Mireles, Y.; Zamora-Pérez, A.L.; Galván Valencia, M.; Sánchez de la Rosa, S.V.; Reyes Escobedo, F.d.R.; Lazalde-Ramos, B.P. Genomic and Cytotoxic Damage in Wistar Rats and Their Newborns After Transplacental Exposure to Hibiscus sabdariffa Hydroalcoholic Extract. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 7448. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157448
Tobanche Mireles Y, Zamora-Pérez AL, Galván Valencia M, Sánchez de la Rosa SV, Reyes Escobedo FdR, Lazalde-Ramos BP. Genomic and Cytotoxic Damage in Wistar Rats and Their Newborns After Transplacental Exposure to Hibiscus sabdariffa Hydroalcoholic Extract. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(15):7448. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157448
Chicago/Turabian StyleTobanche Mireles, Yelin, Ana Lourdes Zamora-Pérez, Marisol Galván Valencia, Susana Vanessa Sánchez de la Rosa, Fuensanta del Rocío Reyes Escobedo, and Blanca Patricia Lazalde-Ramos. 2025. "Genomic and Cytotoxic Damage in Wistar Rats and Their Newborns After Transplacental Exposure to Hibiscus sabdariffa Hydroalcoholic Extract" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 15: 7448. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157448
APA StyleTobanche Mireles, Y., Zamora-Pérez, A. L., Galván Valencia, M., Sánchez de la Rosa, S. V., Reyes Escobedo, F. d. R., & Lazalde-Ramos, B. P. (2025). Genomic and Cytotoxic Damage in Wistar Rats and Their Newborns After Transplacental Exposure to Hibiscus sabdariffa Hydroalcoholic Extract. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(15), 7448. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157448







