Clinical, Immunological, Radiographic, and Pathologic Improvements in a Patient with Long-Standing Crohn’s Disease After Receiving Stem Cell Educator Therapy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Medical History and Diagnosis of Crohn’s Disease
2.2. Clinical Safety and Improvements of Symptoms After Stem Cell Educator Therapy
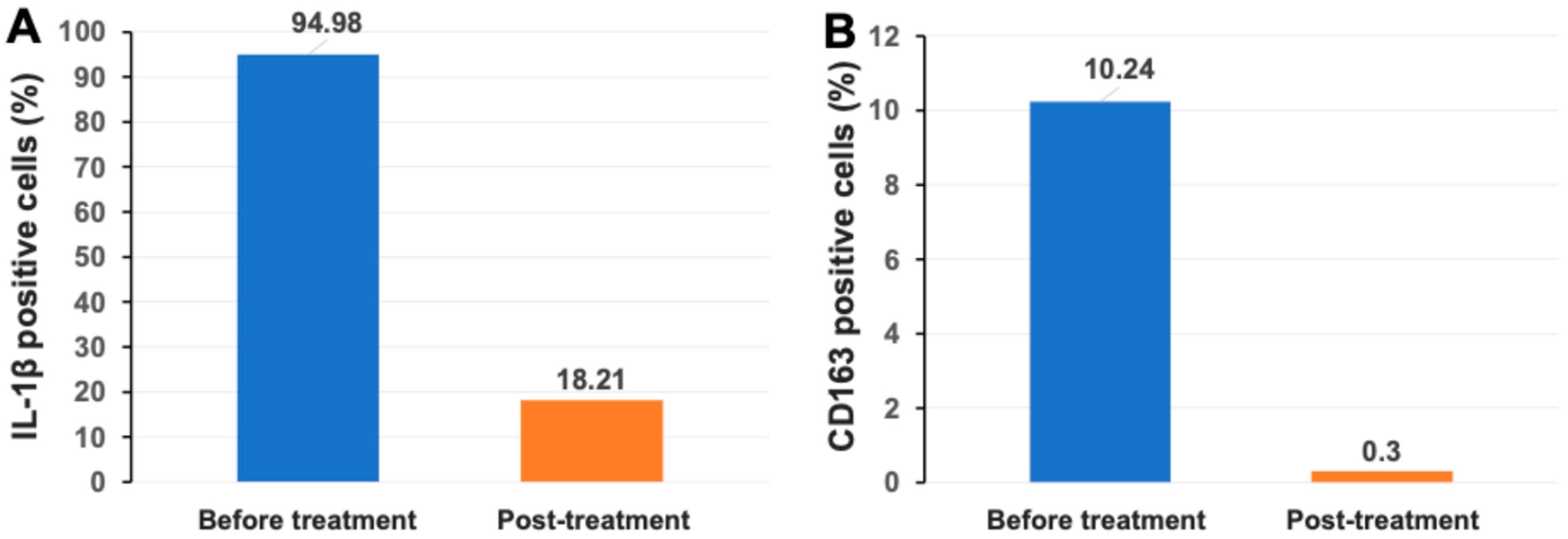
2.3. Markedly Reduced Monocyte/Macrophage-Associated Inflammatory Markers IL-1β and CD163 After Stem Cell Educator Therapy
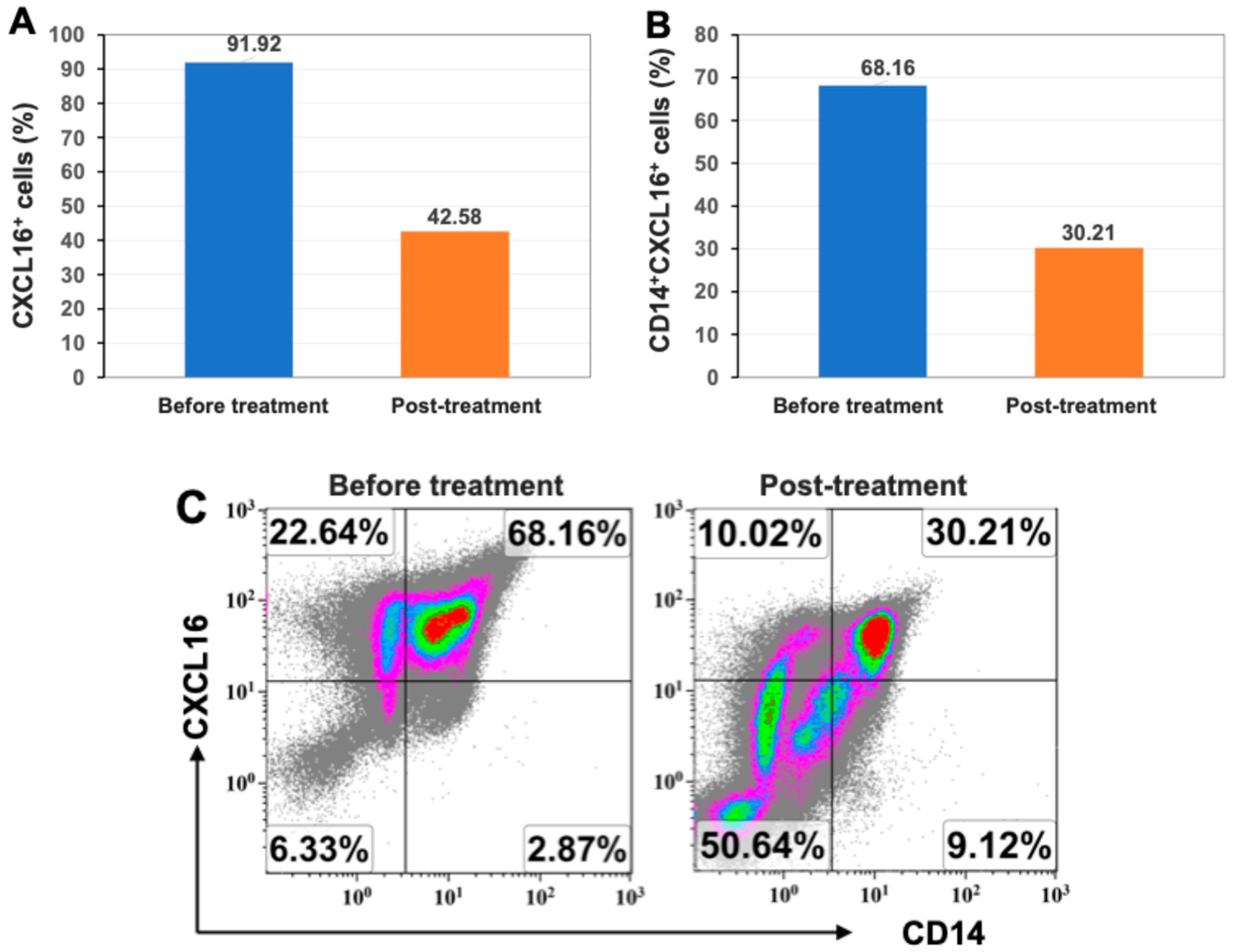
2.4. Markedly Reduced Expression of Inflammatory Chemokine CXCL16 After Stem Cell Educator Therapy
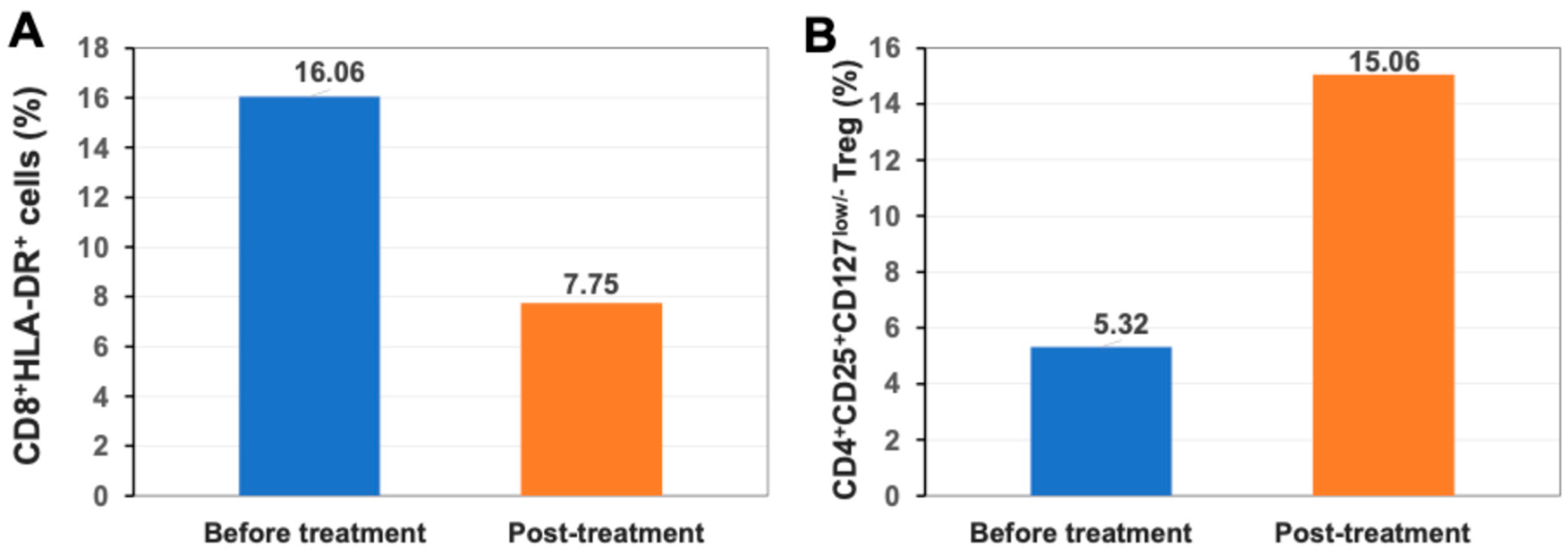
2.5. Up-Regulation of Percentage of Regulatory T Cells (Treg) After Stem Cell Educator Therapy
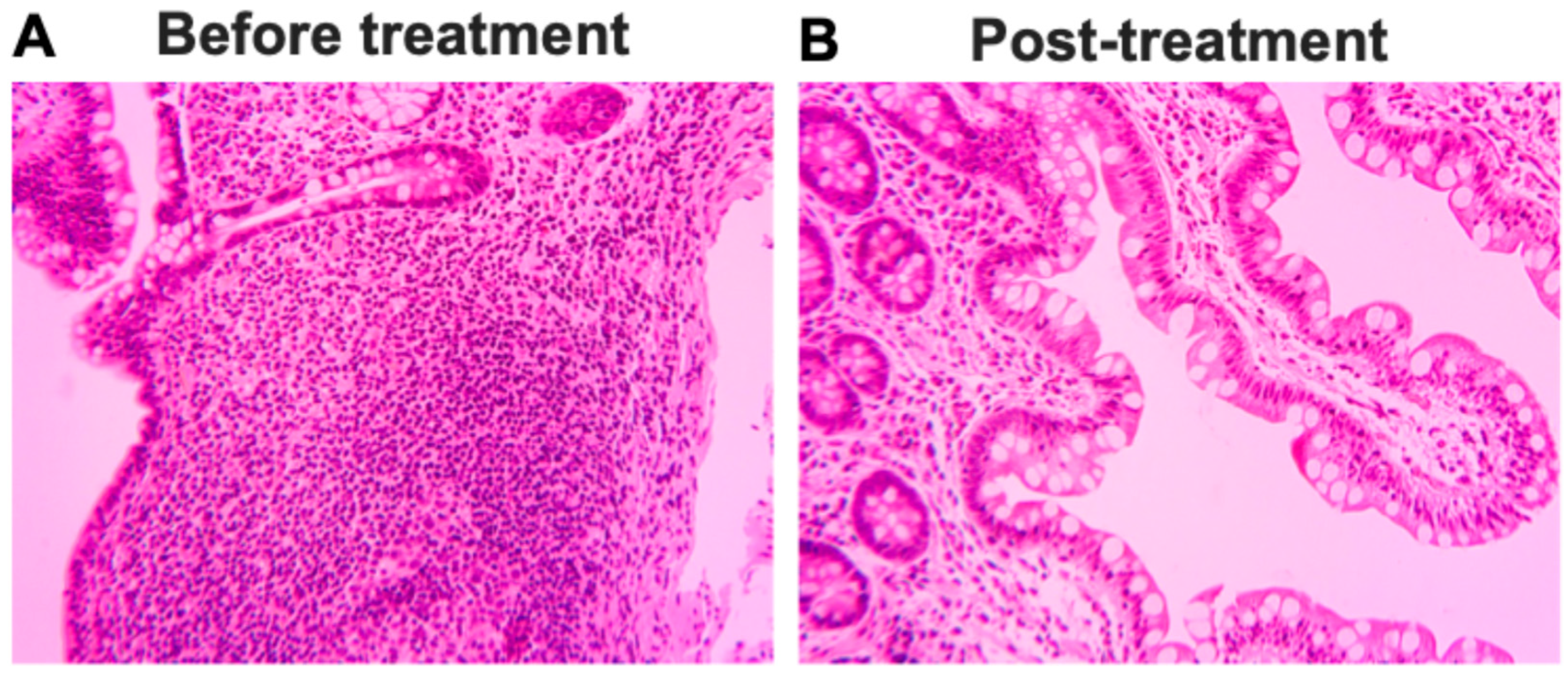
2.6. Pathologic and Radiographic Improvements After Stem Cell Educator Therapy
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patient and Treatment with Stem Cell Educator Therapy
4.2. Flow Cytometry
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Dolinger, M.; Torres, J.; Vermeire, S. Crohn’s disease. Lancet 2024, 403, 1177–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neurath, M.F. Strategies for targeting cytokines in inflammatory bowel disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2024, 24, 559–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettenworth, D.; Baker, M.E.; Fletcher, J.G.; Jairath, V.; Lu, C.; Bemelman, W.; d’Haens, G.; d’Hoore, A.; Dignass, A.; Dotan, I.; et al. A global consensus on the definitions, diagnosis and management of fibrostenosing small bowel Crohn’s disease in clinical practice. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, 21, 572–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Annese, V. Genetics and epigenetics of IBD. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 159, 104892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvez, V.; Puca, P.; Di Vincenzo, F.; Del Gaudio, A.; Bartocci, B.; Murgiano, M.; Iaccarino, J.; Parand, E.; Napolitano, D.; Pugliese, D.; et al. Novel Insights into the Pathogenesis of Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.H.; Ju, H.J.; Han, J.H.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, W.S.; Bae, J.M.; Lee, S. Autoimmune and Autoinflammatory Connective Tissue Disorders Following COVID-19. JAMA Netw. Open. 2023, 6, e2336120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, Y.W.; Jeon, J.J.; Ha, M.C.; Kim, Y.H.; Lee, S. Long-Term Risk of Autoimmune and Autoinflammatory Connective Tissue Disorders Following COVID-19. JAMA Dermatol. 2024, 160, 1278–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Lau, L.H.; Chanchlani, N.; Kennedy, N.A.; Ng, S.C. Recent advances in clinical practice: Management of inflammatory bowel disease during the COVID-19 pandemic. Gut 2022, 71, 1426–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, J.; Mehandru, S.; Colombel, J.F.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L. Crohn’s disease. Lancet 2017, 389, 1741–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Zhao, T.; Ye, M.; Hu, C.; Yin, Z.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Diao, Y.; Li, Y.; et al. Reversal of type 1 diabetes via islet beta cell regeneration following immune modulation by cord blood-derived multipotent stem cells. BMC Med. 2012, 10, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yan, B.; Wang, H.; Li, H.; Li, Q.; Zhao, D.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, W.; Zhang, J.; et al. Hair regrowth in alopecia areata patients following Stem Cell Educator therapy. BMC Med. 2015, 13, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Veysman, B.; Antolijao, K.; Zhao, Y.; Papagni, Y.; Wang, H.; Ross, R.; Tibbot, T.; Povrzenic, D.; Fox, R. Increase in the Expression of Glucose Transporter 2 (GLUT2) on the Peripheral Blood Insulin-Producing Cells (PB-IPC) in Type 1 Diabetic Patients after Receiving Stem Cell Educator Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 8337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamada, N.; Rogler, G. The Innate Immune System: A Trigger for Many Chronic Inflammatory Intestinal Diseases. Inflamm. Intest. Dis. 2016, 1, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, N.; Fu, B.; Zhong, X.; Jia, S.; Ren, Z.; Wang, H.; Wang, W.; Shi, H.; Li, J.; Ge, F.; et al. Role of the CXCR6/CXCL16 axis in autoimmune diseases. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2023, 121, 110530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, A.M.; Farghal, N.M.A.; Hegab, D.S.; Mohamed, W.S.; Abd-Elnabi, H.H. Serum-soluble CXCL16 in juvenile systemic lupus erythematosus: A promising predictor of disease severity and lupus nephritis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2018, 37, 3025–3032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connor, R.A.; Li, X.; Blumerman, S.; Anderton, S.M.; Noelle, R.J.; Dalton, D.K. Adjuvant immunotherapy of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis: Immature myeloid cells expressing CXCL10 and CXCL16 attract CXCR3+CXCR6+ and myelin-specific T cells to the draining lymph nodes rather than the central nervous system. J. Immunol. 2012, 188, 2093–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yip, J.L.K.; Balasuriya, G.K.; Spencer, S.J.; Hill-Yardin, E.L. The Role of Intestinal Macrophages in Gastrointestinal Homeostasis: Heterogeneity and Implications in Disease. Cell Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 12, 1701–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegarty, L.M.; Jones, G.R.; Bain, C.C. Macrophages in intestinal homeostasis and inflammatory bowel disease. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 20, 538–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Zhu, Q.; Pan, L.L.; Sun, J. Macrophage immunometabolism in inflammatory bowel diseases: From pathogenesis to therapy. Pharmacol. Ther. 2022, 238, 108176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saez, A.; Herrero-Fernandez, B.; Gomez-Bris, R.; Sanchez-Martinez, H.; Gonzalez-Granado, J.M. Pathophysiology of Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Innate Immune System. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, N.; Kurata, M.; Yamamoto, T.; Morikawa, S.; Masumoto, J. The role of interleukin-1 in general pathology. Inflamm. Regen. 2019, 39, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Song, X.; Yu, H.; Sun, J.; Zhao, Y. Released Exosomes Contribute to the Immune Modulation of Cord Blood-Derived Stem Cells. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Bris, R.; Saez, A.; Herrero-Fernandez, B.; Rius, C.; Sanchez-Martinez, H.; Gonzalez-Granado, J.M. CD4 T-Cell Subsets and the Pathophysiology of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalan-Serra, I.; Sandvik, A.K.; Bruland, T.; Andreu-Ballester, J.C. Gammadelta T Cells in Crohn’s Disease: A New Player in the Disease Pathogenesis? J. Crohns. Colitis 2017, 11, 1135–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplanski, G. Interleukin-18: Biological properties and role in disease pathogenesis. Immunol. Rev. 2018, 281, 138–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bushara, O.; Escobar, D.J.; Weinberg, S.E.; Sun, L.; Liao, J.; Yang, G.Y. The Possible Pathogenic Role of IgG4-Producing Plasmablasts in Stricturing Crohn’s Disease. Pathobiology 2022, 89, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bashford-Rogers, R.J.M.; Bergamaschi, L.; McKinney, E.F.; Pombal, D.C.; Mescia, F.; Lee, J.C.; Thomas, D.C.; Flint, S.M.; Kellam, P.; Jayne, D.R.W.; et al. Analysis of the B cell receptor repertoire in six immune-mediated diseases. Nature 2019, 574, 122–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.; Gu, J.; Wang, Z. B cells in Crohn’s patients presented reduced IL-35 expression capacity. Mol. Immunol. 2020, 118, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.W.; Park, H.J.; Van Kaer, L.; Hong, S. Role of CD1d and iNKT cells in regulating intestinal inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1343718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosati, E.; Rios Martini, G.; Pogorelyy, M.V.; Minervina, A.A.; Degenhardt, F.; Wendorff, M.; Sari, S.; Mayr, G.; Fazio, A.; Dowds, C.M.; et al. A novel unconventional T cell population enriched in Crohn’s disease. Gut 2022, 71, 2194–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potdar, A.A.; Li, D.; Haritunians, T.; VanDussen, K.L.; Fiorino, M.F.; Liu, T.C.; Stappenbeck, T.S.; Fleshner, P.; Targan, S.R.; McGovern, D.P.B.; et al. Ileal Gene Expression Data from Crohn’s Disease Small Bowel Resections Indicate Distinct Clinical Subgroups. J. Crohns. Colitis 2019, 13, 1055–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, W.; Song, X.; Yu, H.; Fan, S.; Shi, A.; Sun, J.; Wang, H.; Zhao, L.; Zhao, Y. Suppression of B-Cell Activation by Human Cord Blood-Derived Stem Cells (CB-SCs) through the Galectin-9-Dependent Mechanism. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fox, R.; Veysman, B.; Antolijao, K.; Mendoza, N.; Lorenzo, R.A.; Wang, H.; Huang, Z.H.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Tibbot, T.; et al. Clinical, Immunological, Radiographic, and Pathologic Improvements in a Patient with Long-Standing Crohn’s Disease After Receiving Stem Cell Educator Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 7292. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157292
Fox R, Veysman B, Antolijao K, Mendoza N, Lorenzo RA, Wang H, Huang ZH, Zhao Y, Zhao Y, Tibbot T, et al. Clinical, Immunological, Radiographic, and Pathologic Improvements in a Patient with Long-Standing Crohn’s Disease After Receiving Stem Cell Educator Therapy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(15):7292. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157292
Chicago/Turabian StyleFox, Richard, Boris Veysman, Kristine Antolijao, Noelle Mendoza, Ruby Anne Lorenzo, Honglan Wang, Zhi Hua Huang, Yelu Zhao, Yewen Zhao, Terri Tibbot, and et al. 2025. "Clinical, Immunological, Radiographic, and Pathologic Improvements in a Patient with Long-Standing Crohn’s Disease After Receiving Stem Cell Educator Therapy" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 15: 7292. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157292
APA StyleFox, R., Veysman, B., Antolijao, K., Mendoza, N., Lorenzo, R. A., Wang, H., Huang, Z. H., Zhao, Y., Zhao, Y., Tibbot, T., Povrzenic, D., Bayawa, M. L., Kung, S., Saffouri, B., & Zhao, Y. (2025). Clinical, Immunological, Radiographic, and Pathologic Improvements in a Patient with Long-Standing Crohn’s Disease After Receiving Stem Cell Educator Therapy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(15), 7292. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157292






