Assessment of Eotaxin Concentration in Children with Chronic Kidney Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Chronic Kidney Disease in Pediatric Population
1.2. Eotaxin
1.3. Aim
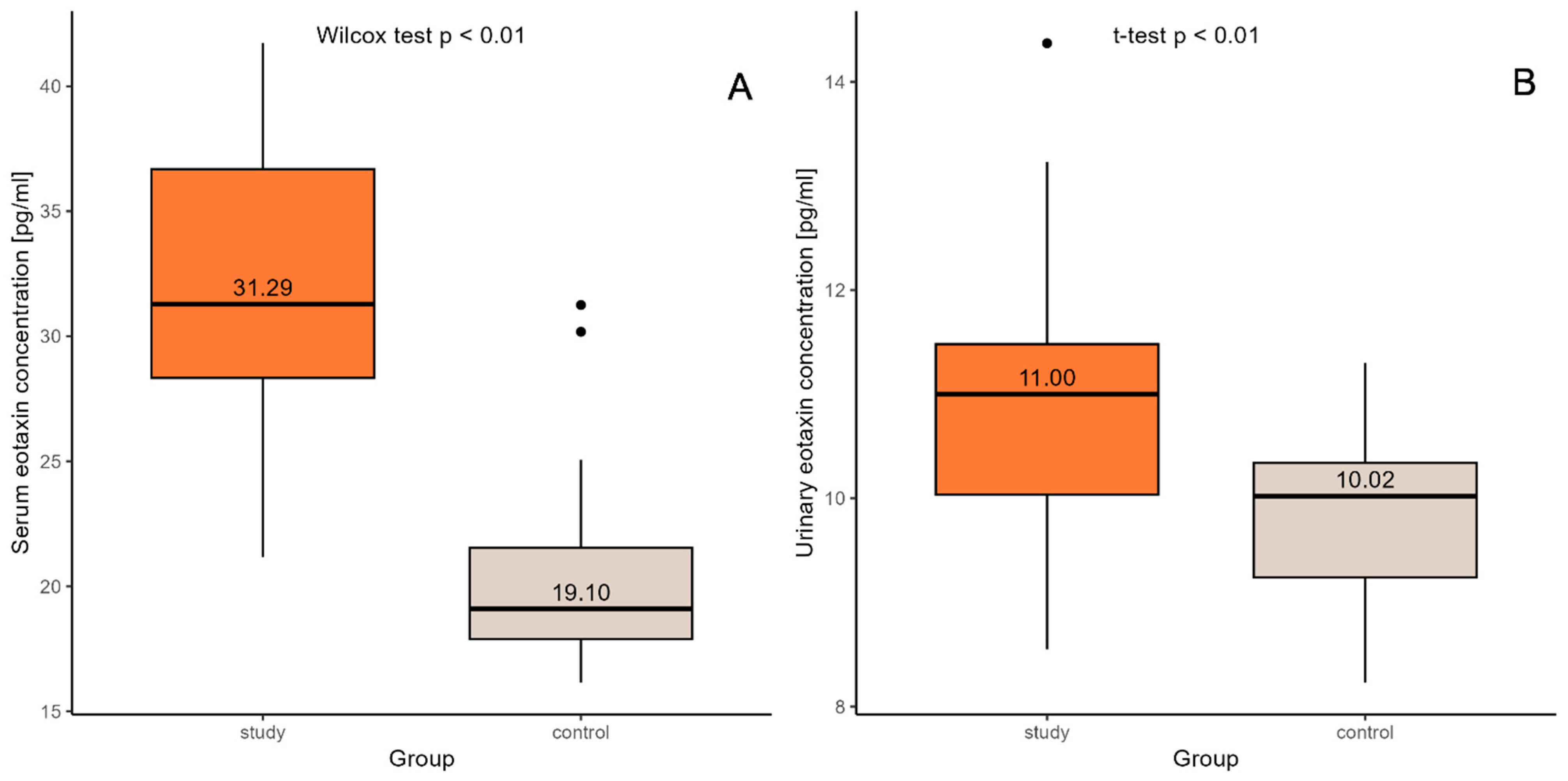
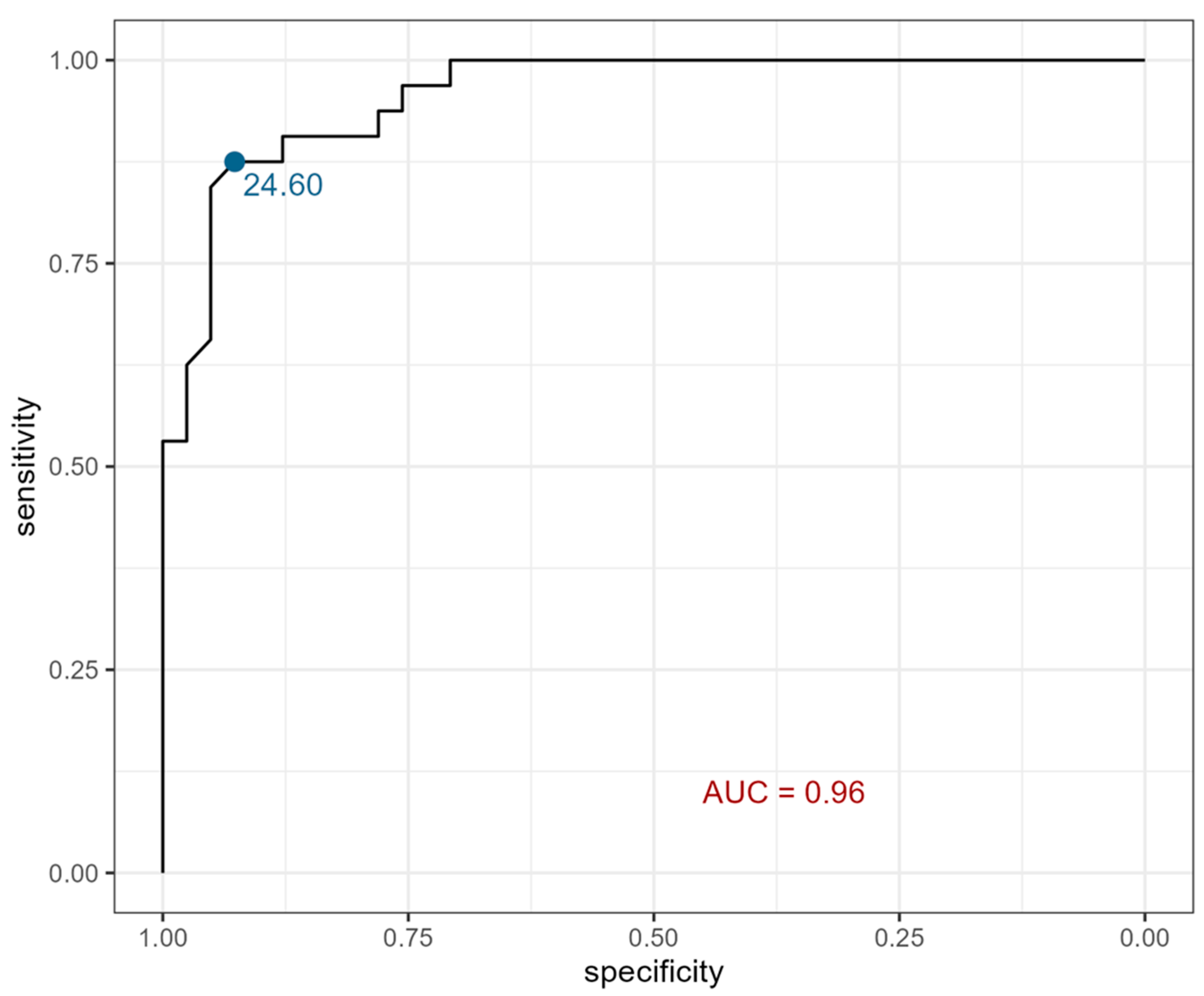
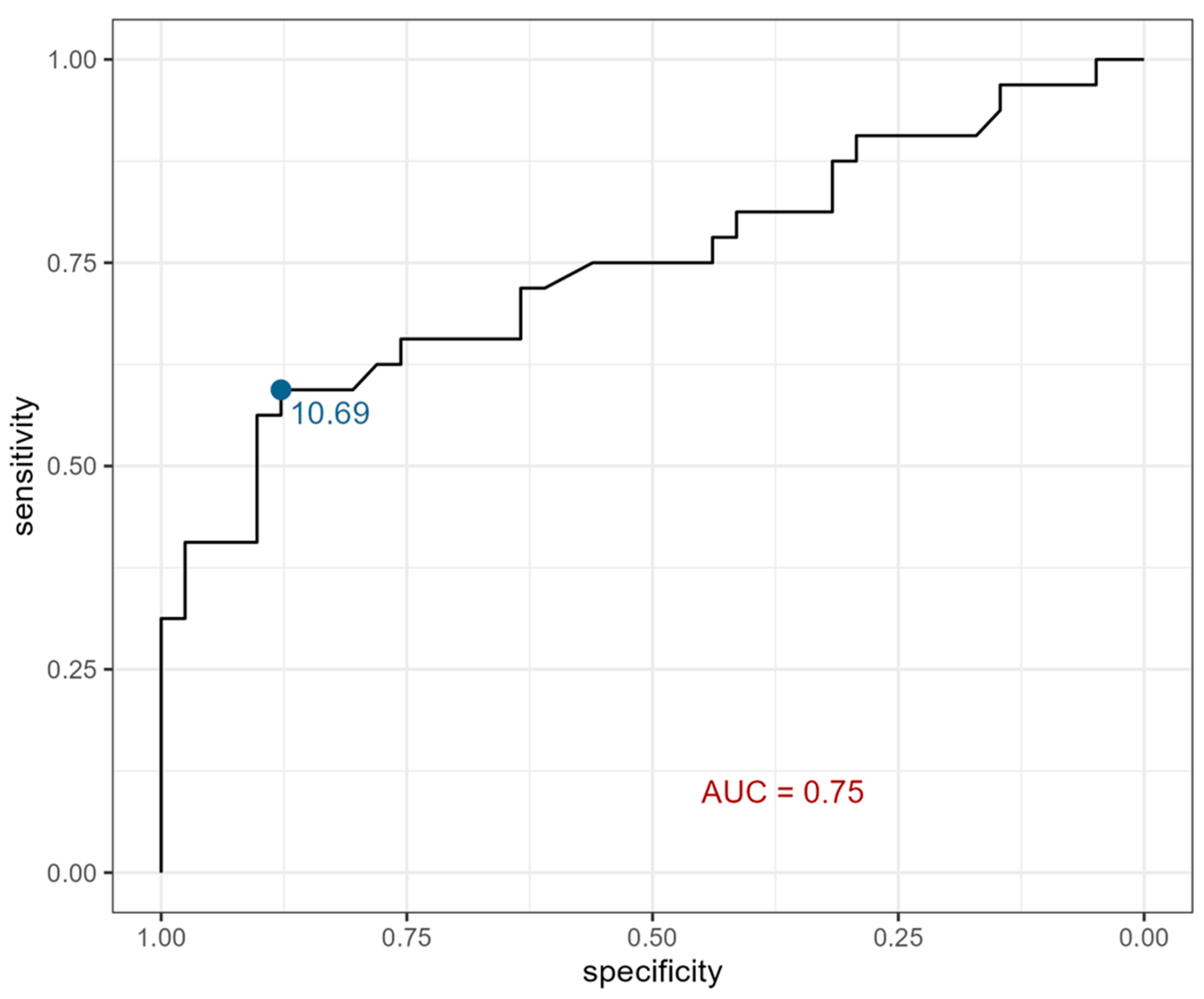
2. Results
3. Discussion
3.1. Diabetic Nephropathy
3.2. Eotaxin in Proliferative Disorders
3.3. Eotaxin in Acute Disorders
3.4. Eotaxin in Chronic Disorders
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Studied Groups
4.2. Laboratory Tests
4.3. Eotaxin Concentration
4.4. Anthropometric Measurements
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AKI | acute kidney injury |
| ALT | alanine transaminase level |
| BMI | body mass index |
| CAKUT | congenital anomalies of the kidneys and of the urinary tract |
| CKD | chronic kidney disease |
| CRP | c-reactive protein |
| DIA | diastolic arterial pressure |
| DM2 | type 2 diabetes mellitus |
| DN | diabetic nephropathy |
| eGFR | estimated glomerular filtration rate |
| ESRD | end-stage renal disease |
| FSGS | focal segmental glomerulosclerosis |
| HD | hemodialysis |
| HF | heart failure |
| HUS | hemolytic uremic syndrome |
| IRF | idiopathic retroperitoneal fibrosis |
| LN | lupus nephritis |
| MAP | mean arterial pressure |
| PCA | Principal Component Analysis |
| PTH | parathormone |
| PUV | posterior urethral valve |
| RA | rheumatoid arthritis |
| RCC | renal cell carcinoma |
| RII | renal ischemic injury |
| ROC | receiver operating characteristic |
| SDS | standard deviation score |
| SGLT2 | sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 |
| SLE | systemic lupus erythematosus |
| SYS | systolic arterial pressure |
| UPJ-O | congenital ureteropelvic junction obstruction |
| VC | vascular calcification |
| WNV | West Nile Virus |
References
- Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) CKD Work Group. KDIGO 2024 Clinical Practice Guideline for the Evaluation and Management of Chronic Kidney Disease. Kidney Int. 2024, 105, 117–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, R.; Hamasaki, Y.; Okuda, Y.; Hamada, R.; Ishikura, K. Epidemiology of pediatric chronic kidney disease/kidney failure: Learning from registries and cohort studies. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2022, 37, 1215–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romagnani, P.; Agarwal, R.; Chan, J.C.N.; Levin, A.; Kalyesubula, R.; Karam, S.; Nangaku, M.; Rodríguez-Iturbe, B.; Anders, H.J. Chronic kidney disease. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers. 2025, 11, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedin, E.; Tungsanga, S.; Ye, F.; Kung, J.Y.; Okpechi, I.; Dart, A.B.; Thompson, S.; Morgan, C.; Erickson, R.; Chaturvedi, S.; et al. Global prevalence of chronic kidney disease and associated risk factors in children and adolescents: Protocol for a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open 2025, 15, e090615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panzarino, V.; Lesser, J.; Cassani, F.A. Pediatric Chronic Kidney Disease. Adv. Pediatr. 2022, 69, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacob, Z.; Plumb, L.; Oni, L.; Mitra, S.; Reynolds, B. A systematic review of symptoms experienced by children and young people with kidney failure. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2025, 40, 53–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karava, V.; Dotis, J.; Kondou, A.; Printza, N. Malnutrition Patterns in Children with Chronic Kidney Disease. Life 2023, 13, 713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitaura, M.; Suzuki, N.; Imai, T.; Takagi, S.; Suzuki, R.; Nakajima, T.; Hirai, K.; Nomiyama, H.; Yoshie, O. Molecular cloning of a novel human CC chemokine (Eotaxin-3) that is a functional ligand of CC chemokine receptor 3. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 27975–27980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Huang, Y.; Ji, X.; Wu, T.; Xiao, P. CCL11 (Eotaxin) Promotes the Advancement of Aging-Related Cardiovascular Diseases. RCM 2025, 26, 26020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghuraman, G.; Hsiung, J.; Zuniga, M.C.; Baughman, B.D.; Hitchner, E.; Guzman, R.J.; Zhou, W. Eotaxin Augments Calcification in Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells. J. Cell. Biochem. 2017, 118, 647–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.L.; Sen, A.I.; Kitaura, M.; Yoshie, O.; Rothenberg, M.E.; Murphy, P.M.; Luster, A.D. Identification of a mouse eosinophil receptor for the CC chemokine eotaxin. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1996, 223, 679–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Starr, L.M.; Scott, M.E.; Koski, K.G. Protein deficiency and intestinal nematode infection in pregnant mice differentially impact fetal growth through specific stress hormones, growth factors, and cytokines. J. Nutr. 2015, 145, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szulimowska, J.; Zalewska, A.; Taranta-Janusz, K.; Marczuk-Kolada, G.; Żendzian-Piotrowska, M.; Maciejczyk, M. Association Between Salivary Cytokines, Chemokines and Growth Factors and Salivary Gland Function in Children with Chronic Kidney Disease. J. Inflamm. Res. 2023, 16, 1103–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiou, Y.Y.; Shieh, C.C.; Cheng, H.L.; Tang, M.J. Intrinsic expression of Th2 cytokines in urothelium of congenital ureteropelvic junction obstruction. Kidney Int. 2005, 67, 638–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, M.S.; Janal, M.N.; Crosby, J.; Donnelly, R. Markers of endothelial dysfunction and inflammation predict progression of diabetic nephropathy in African Americans with type 1 diabetes. Kidney Int. 2015, 87, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landis, R.C.; Quimby, K.R.; Greenidge, A.R. M1/M2 Macrophages in Diabetic Nephropathy: Nrf2/HO-1 as Therapeutic Targets. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2018, 24, 2241–2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, L.S.; Torquato, B.G.S.; da Silva, C.A.; Dos Reis Monteiro, M.L.G.; Dos Santos Martins, A.L.M.; da Silva, M.V.; Dos Reis, M.A.; Machado, J.R. Renal expression of cytokines and chemokines in diabetic nephropathy. BMC Nephrol. 2020, 21, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perlman, A.S.; Chevalier, J.M.; Wilkinson, P.; Liu, H.; Parker, T.; Levine, D.M.; Sloan, B.J.; Gong, A.; Sherman, R.; Farrell, F.X. Serum Inflammatory and Immune Mediators Are Elevated in Early-Stage Diabetic Nephropathy. Ann. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2015, 45, 256–263. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Sridhar, V.S.; Lovblom, L.E.; Lytvyn, Y.; Burger, D.; Burns, K.; Brinc, D.; Lawler, P.R.; Cherney, D.Z.I. Markers of Kidney Injury, Inflammation, and Fibrosis Associated With Ertugliflozin in Patients With CKD and Diabetes. Kidney Int. Rep. 2021, 6, 2095–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Har, R.; Scholey, J.W.; Daneman, D.; Mahmud, F.H.; Dekker, R.; Lai, V.; Elia, Y.; Fritzler, M.L.; Sochett, E.B.; Reich, H.N.; et al. The effect of renal hyperfiltration on urinary inflammatory cytokines/chemokines in patients with uncomplicated type 1 diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia 2013, 56, 1166–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, S.; Lin, Y.; Huang, S.; Lin, S.; Jin, K.; Chen, H. Circulating inflammatory cytokines in relation to the risk of renal cell carcinoma: A gender-specific two-sample Mendelian randomization study. Cancer Med. 2023, 12, 21013–21021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jöhrer, K.; Zelle-Rieser, C.; Perathoner, A.; Moser, P.; Hager, M.; Ramoner, R.; Gander, H.; Höltl, L.; Bartsch, G.; Greil, R.; et al. Up-regulation of functional chemokine receptor CCR3 in human renal cell carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 2459–2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andres-Hernando, A.; Dursun, B.; Altmann, C.; Ahuja, N.; He, Z.; Bhargava, R.; Edelstein, C.E.; Jani, A.; Hoke, T.S.; Klein, C.; et al. Cytokine production increases and cytokine clearance decreases in mice with bilateral nephrectomy. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2012, 27, 4339–4347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabadi, M.M.; Ghaly, T.; Goligorksy, M.S.; Ratliff, B.B. HMGB1 in renal ischemic injury. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2012, 303, F873–F885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuda, K.; Vasko, R.; Hayek, P.; Ratliff, B.; Bicer, H.; Mares, J.; Maruyama, S.; Bertuglia, S.; Mascagni, P.; Goligorsky, M.S. Functional consequences of inhibiting exocytosis of Weibel-Palade bodies in acute renal ischemia. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2012, 302, F713–F721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pereira, R.L.; Reis, V.O.; Semedo, P.; Buscariollo, B.N.; Donizetti-Oliveira, C.; Cenedeze, M.A.; Soares, M.F.; Pacheco-Silva, A.; Savage, P.B.; Câmara, N.O.; et al. Invariant natural killer T cell agonist modulates experimental focal and segmental glomerulosclerosis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e32454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raglianti, V.; Rossi, G.M.; Vaglio, A. Idiopathic retroperitoneal fibrosis: An update for nephrologists. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2021, 36, 1773–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perna, A.F.; Russo, L.; D'Esposito, V.; Formisano, P.; Bruzzese, D.; Vigorito, C.; Coppola, A.; Lombari, P.; Russo, D.; Ingrosso, D. Lanthionine, a Novel Uremic Toxin, in the Vascular Calcification of Chronic Kidney Disease: The Role of Proinflammatory Cytokines. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, M.; Nolan, M.S.; Gorchakov, R.; Hasbun, R.; Murray, K.O.; Ronca, S.E. Unique Cytokine Response in West Nile Virus Patients Who Developed Chronic Kidney Disease: A Prospective Cohort Study. Viruses 2021, 13, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, B.; Wang, Z.; Suo, Y.; Shao, S.; Yuan, M.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, G.; Bao, Q. IL-2Rα is a potential biomarker for heart failure diagnosis of patients with end-stage renal disease and haemodialysis. ESC Heart Fail. 2025, 12, 118–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansouri, L.; Paulsson, J.M.; Moshfegh, A.; Jacobson, S.H.; Lundahl, J. Leukocyte proliferation and immune modulator production in patients with chronic kidney disease. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacheco-Lugo, L.; Sáenz-García, J.; Navarro Quiroz, E.; González Torres, H.; Fang, L.; Díaz-Olmos, Y.; Garavito de Egea, G.; Egea Bermejo, E.; Aroca Martínez, G. Plasma cytokines as potential biomarkers of kidney damage in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 2019, 28, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, É.L.M.; Pessoa Rocha, N.; Macedo Bastos, F.; da Silveira, K.D.; Pereira, A.K.; Araújo Oliveira, E.; Marques de Miranda, D.; Simões e Silva, A.C. Posterior urethral valve in fetuses: Evidence for the role of inflammatory molecules. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2017, 32, 1391–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kułaga, Z.; Różdżyńska, A.; Palczewska, I.; Grajda, A.; Gurzkowska, B.; Napieralska, E.; Litwin, M. Percentile charts of height, body mass and body mass index in children and adolescents in Poland—Results of the OLAF study. Stand. Med. Pediatr. 2010, 7, 690–700. [Google Scholar]
- Kułaga, Z.; Litwin, M.; Grajda, A.; Gurzkowska, B.; Napieralska, E.; Kułaga, K. Distribution of blood pressure in school-aged children and adolescents reference population. Stand. Med. Pediatr. 2010, 7, 100–111. [Google Scholar]
| Parameter | Children with Chronic Kidney Disease (n = 32) | Control Group (n = 41) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Whole Group | Female | Male | Whole Group | Female | Male | |
| Age (year) | 10.23 ± 5.62 (1.17–17.90) | 12.38 ± 4.23 * (6.50–17.90) | 9.25 ± 5.98 (1.17–17.90) | 9.29 ± 4.19 (2.00–17.50) | 8.18 ± 4.01 (2.00–17.00) | 10.08 ± 4.21 (4.50–17.50) |
| Height (cm) | 131.86 ± 29.73 (75.00–171.00) | 144.30 ± 19.59 * (113.00–165.00) | 126.21 ± 32.14 * (75.00–171.00) | 136.37 ± 25.28 (82.00–197.00) | 125.97 ± 21.23 (82.00–170.00) | 143.73 ± 25.72 (110.00–197.00) |
| SDS for Height | −1.14 ± 1.70 * (−5.69–4.00) | −0.66 ± 0.67 (−1.85–37.29) | −1.36 ± 1.98 (−5.69–4.00) | 0.19 ± 1.11 (−1.53–3.00) | −0.17 ± 1.11 (−1.53–2.35) | 0.44 ± 1.07 (−1.34–3.00) |
| Body Weight (kg) | 33.13 ± 16.56 (10.00–68.70) | 39.06 ± 15.46 (21.70–68.70) | 30.44 ± 16.67 * (10.00–65.70) | 35.51 ± 19.26 (9.70–87.50) | 29.67 ± 15.20 (9.70–71.00) | 39.64 ± 21.01 (15.00–87.50) |
| SDS for Body Weight | −0.72 ± 1.91 * (−3.40–7.33) | −0.51 ± 1.39 (−2.76–2.57) | −0.81 ± 2.13 * (−3.40–7.33) | 0.10 ± 1.13 (−2.34–2.12) | 0.08 ± 1.27 (−1.87–2.11) | 0.11 ± 1.05 (−2.34–2.12) |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 17.72 ± 2.93 (14.30–27.20) | 18.20 ± 3.76 (15.50–27.20) | 17.50 ± 2.55 (14.30–22.70) | 17.63 ± 3.53 (12.40–26.50) | 17.51 ± 3.21 (13.90–24.60) | 17.72 ± 3.81 (12.40–26.50) |
| SDS for BMI | −0.12 ± 1.59 (−2.47–5.22) | −0.18 ± 1.63 (−2.47–2.85) | −0.10 ± 1.62 * (−2.37–5.22) | −0.01 ± 1.22 (−2.97–2.29) | 0.27 ± 1.07 (−1.38–2.29) | −0.22 ± 1.29 (−2.97–2.02) |
| SYS (mmHg) | 106.81 ± 13.58 (83.00–133.00) | 106.10 ± 13.54 (88.00–123.00) | 107.14 ± 13.91 (83.00–133.00) | 111.85 ± 11.35 (85.00–134.00) | 107.41 ± 8.73 (89.00–122.00) | 115.00 ± 12.08 (85.00–134.00) |
| DIA (mmHg) | 66.38 ± 10.26 (49.00–88.00) | 64.10 ± 11.03 (49.00–77.00) | 67.41 ± 9.98 * (53.00–88.00) | 75.00 ±11.56 (45.00–107.00) | 66.82 ± 11.81 (45.00–96.00) | 71.38 ± 11.24 (57.00–107.00) |
| MAP (mmHg) | 79.85 ± 10.39 (63.33–103.00) | 78.10 ± 11.49 (63.33–91.00) | 80.65 ± 10.03 * (67.67–103.00) | 83.61 ± 10.33 (62.33–115.70) | 80.36 ± 9.83 (62.33–102.33) | 85.92 ± 10.25 (70.00–115.70) |
| Serum creatinine (µmol/L) | 210.47 ± 150.21 * (51.00–629.00) | 239.80 ± 189.41 * (56.00–629.00) | 197.14 ± 131.66 * (51.00–580.00) | 49.29 ± 10.03 (32.00–80.00) | 45.82 ± 8.88 (32.00–72.00) | 51.75 ± 10.25 (39.00–80.00) |
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) | 34.66 ± 22.55 * (9.40–80.90) | 38.17 ± 26.77 * (9.40–78.00) | 33.06 ± 20.85 * (10.48–80.90) | 101.90 ± 12.32 (81.69–138.27) | 101.11 ± 10.35 (86.20–117.93) | 102.46 ± 13.73 (81.69–138.27) |
| Serum eotaxin (pg/mL) | 31.87± 5.70 * (21.17–41.72) | 32.16 ± 6.29 (21.75–41.72) | 31.74 ± 5.57 * (21.17–40.54) | 20.28± 3.37 (16.15–31.25) | 19.84 ± 3.73 (16.15–31.25) | 20.58 ± 3.14 (17.03–30.18) |
| Urine eotaxin (pg/mL) | 10.83 ± 1.25 (8.55–14.37) | 10.54 ± 1.03 (8.92–12.47) | 10.97 ± 1.34 * (8.55–14.37) | 9.86± 0.79 (8.23–11.3) | 9.71 ± 0.98 (8.23–11.30) | 9.97 ± 0.63 (8.79–11.20) |
| Parameter | Children with Chronic Kidney Disease | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Whole Group (n = 32) | Female (n = 10) | Male (n = 22) | |
| Serum urea (mmol/L) | 13.47 ± 6.43 (4.10–26.00) | 12.19 ± 7.14 (5.20–26.00) | 14.05 ± −6.16 (4.10–25.60) |
| Serum uric acid (umol/L) | 371.09 ± 104.52 (120.00–617.00) | 375.60 ± 95.63 (234.00–475.00) | 369.05 ± −110.41 (120.00–617.00) |
| Serum total protein (g/L) | 68.43 ± 8.25 (43.30–81.30) | 69.12 ± 10.67 (43.30–81.30) | 68.12 ± −7.16 (47.90–77.00) |
| Serum albumin (g/L) | 44.62 ± 6.21 (18.90–54.00) | 43.83 ± 9.64 (18.90–54.00) | 44.98 ± −4.08 (34.20–50.38) |
| Cholesterol (mmol/L) | 4.57 ± 1.18 (2.90–8.94) | 4.81 ± 1.65 (3.60–8.94) | 4.46 ± −0.93 (2.90–6.19) |
| Triglycerides (mmol/L) | 1.61 ± 1.05 (0.52–4.15) | 1.38 ± 1.09 (0.52–4.15) | 1.71 ± −1.03 (0.59–3.84) |
| High-density lipoprotein (mmol/L) | 1.43 ± 0.39 (0.59–2.20) | 1.47 ± 0.35 (0.71–1.80) | 1.40 ± −0.42 (0.59–2.20) |
| Serum hemoglobin (g/dL) | 11.82 ± 1.76 (8.60–15.60) | 11.77 ± 1.69 (8.60–14.00) | 11.85 ± −1.83 (9.70–15.60) |
| Hematocrit (%) | 34.41 ± 5.15 (25.00–46.40) | 34.52 ± 4.69 (25.00–41.00) | 34.36 ± −5.44 (27.50–46.40) |
| White blood count (103/uL) | 7.22 ± 2.11 (3.96–11.97) | 7.60 ± 2.02 (5.00–11.21) | 7.05 ± −2.17 (3.96–11.97) |
| Platelet count (103/uL) | 255.03 ± 58.47 (165.00–424.00) | 270.80 ± 61.16 (169.00–372.00) | 247.86 ± −57.20 (165.00–424.00) |
| Granulocytes (103/uL) | 3.34 ± 1.74 (1.24–8.43) | 4.29 ± 1.85 (2.06–8.43) | 2.91 ± −1.54 (1.24–7.65) |
| C-reactive protein (mg/L) | 2.51 ± 6.17 (0.01–34.70) | 1.59 ± 1.47 (0.42–4.72) | 2.93 ± −7.40 (0.01–34.70) |
| Parathormone (pg/mL) | 163.54 ± 187.57 (23.67–835.00) | 251.41 ± 291.48 (30.67–835.00) | 123.60 ± −100.88 (23.67–337.80) |
| Serum phosphate (mmol/L) | 1.60 ± 0.39 (1.04–2.57) | 1.74 ± 0.48 (1.22–2.57) | 1.53 ± −0.33 (1.04–2.40) |
| Serum sodium (mmol/L) | 139.00 ± 2.64 (132.00–145.00) | 139.10 ± 2.85 (132.00–142.00) | 138.95 ± −2.61 (133.00–145.00) |
| Total serum calcium (mmol/L) | 2.46 ± 0.18 (3.20–6.13) | 2.42 ± 0.21 (2.05–2.62) | 2.47 ± −0.17 (2.06–2.80) |
| Serum potassium (mmol/L) | 4.60 ± 0.67 (3.20–6.13) | 4.41 ± 0.57 (3.79–5.70) | 4.67 ± −0.70 (3.20–6.13) |
| D3 vitamin (ng/mL) | 37.96 ± 13.77 (7.62–63.84) | 34.91 ± 14.39 (7.62–55.00) | 39.35 ± −13.59 (13.11–63.84) |
| Transferrin (umol/L) | 25.78 ± 11.50 (9.00–60.00) | 32.19 ± 14.04 (11.50–60.00) | 22.39 ± −8.53 (9.00–36.60) |
| Alanine Transaminase (U/L) | 18.60 ± 12.04 (6.20–69.70) | 12.68 ± 4.39 (6.20–21.10) | 21.29 ± −13.47 (8.80–69.70) |
| Serum bicarbonate (mmol/L) | 23.17 ± 3.55 (16.40–30.00) | 23.11 ± 3.29 (18.50–28.00) | 23.19 ± −3.73 (16.40–30.00) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Badeńska, M.; Badeński, A.; Świętochowska, E.; Janek, A.; Marczak, K.; Gliwińska, A.; Szczepańska, M. Assessment of Eotaxin Concentration in Children with Chronic Kidney Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 7260. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157260
Badeńska M, Badeński A, Świętochowska E, Janek A, Marczak K, Gliwińska A, Szczepańska M. Assessment of Eotaxin Concentration in Children with Chronic Kidney Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(15):7260. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157260
Chicago/Turabian StyleBadeńska, Marta, Andrzej Badeński, Elżbieta Świętochowska, Artur Janek, Karolina Marczak, Aleksandra Gliwińska, and Maria Szczepańska. 2025. "Assessment of Eotaxin Concentration in Children with Chronic Kidney Disease" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 15: 7260. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157260
APA StyleBadeńska, M., Badeński, A., Świętochowska, E., Janek, A., Marczak, K., Gliwińska, A., & Szczepańska, M. (2025). Assessment of Eotaxin Concentration in Children with Chronic Kidney Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(15), 7260. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157260






