Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor (GLP-1R) Signaling: Making the Case for a Functionally Gs Protein-Selective GPCR
Abstract
1. Introduction
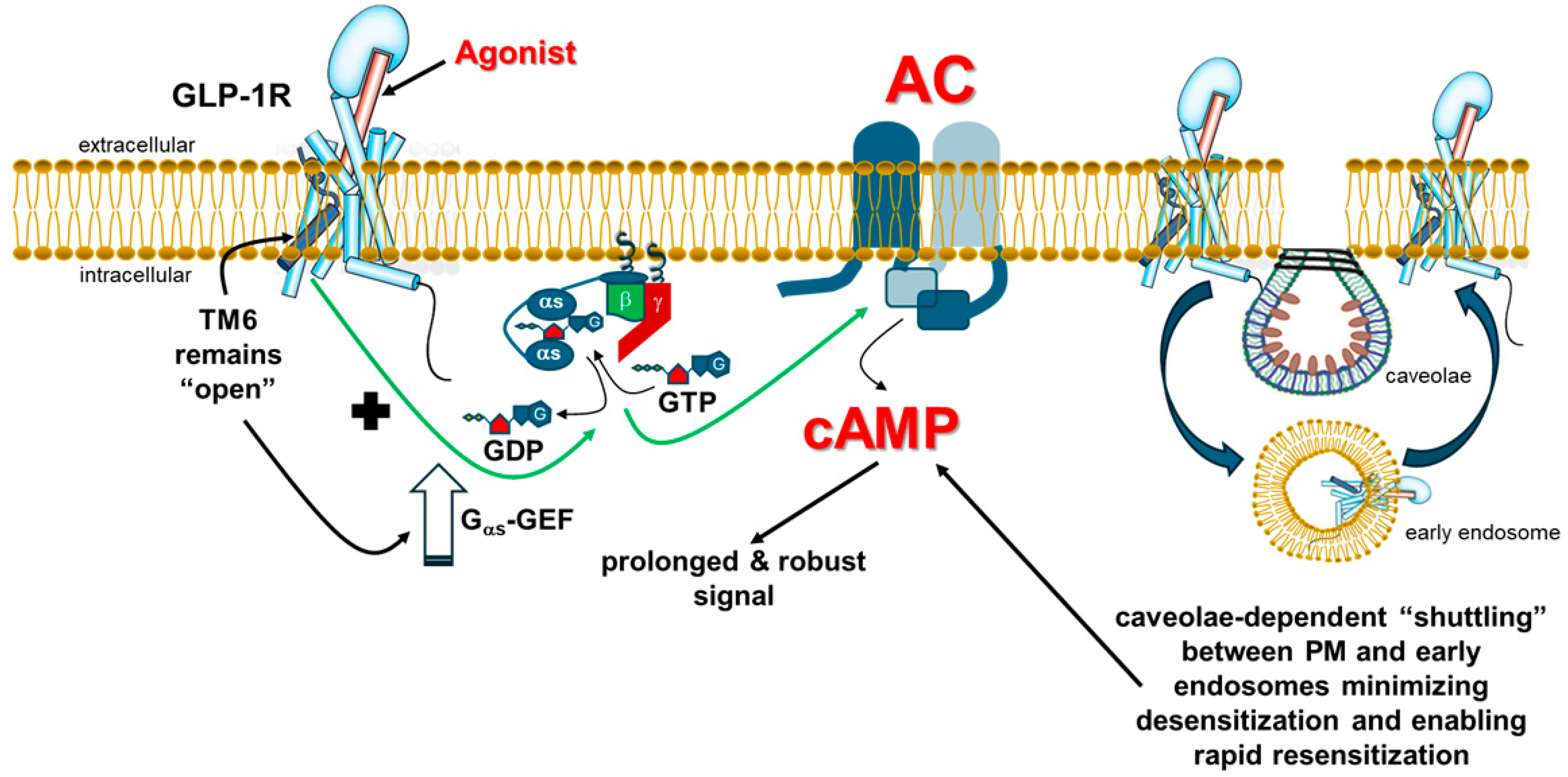
2. GLP-1R and Lack of Functional Desensitization In Vivo
3. GLP-1R vs. GIPR: Similar Receptors, Distinct Signaling Properties
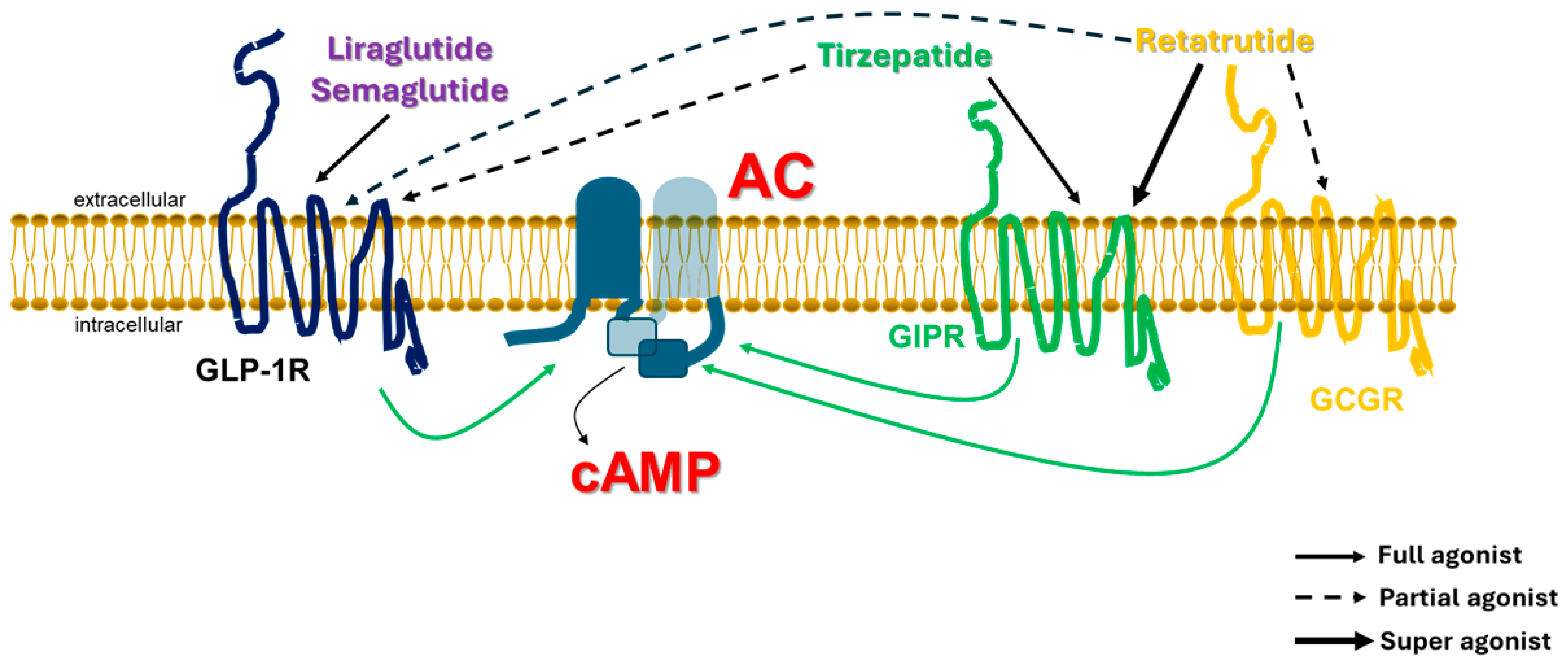
4. Implications for Glucagon Family Receptor Poly-Agonists: GLP-1R Agonism Is Sine Qua Non
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Enyew Belay, K.; Jemal, R.H.; Tuyizere, A. Innovative Glucagon-based Therapies for Obesity. J. Endocr. Soc. 2024, 8, bvae197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cifuentes, M.; Verdejo, H.E.; Castro, P.F.; Corvalan, A.H.; Ferreccio, C.; Quest, A.F.G.; Kogan, M.J.; Lavandero, S. Low-Grade Chronic Inflammation: A Shared Mechanism for Chronic Diseases. Physiology (Bethesda) 2025, 40, 4–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, P.B.; Larsen, P.J.; Karlsen, C.; Jensen, H.I.; Holst, J.J.; Madsen, O.D. Foetal proglucagon processing in relation to adult appetite control: Lessons from a transplantable rat glucagonoma with severe anorexia. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2011, 13 (Suppl. 1), 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaben, A.L.; Scherer, P.E. Adipogenesis and metabolic health. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 20, 242–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Choi, T.; Al-Aly, Z. Mapping the effectiveness and risks of GLP-1 receptor agonists. Nat. Med. 2025, 31, 951–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lymperopoulos, A.; Borges, J.I.; Stoicovy, R.A. Cyclic Adenosine Monophosphate in Cardiac and Sympathoadrenal GLP-1 Receptor Signaling: Focus on Anti-Inflammatory Effects. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilger, D.; Kumar, K.K.; Hu, H.; Pedersen, M.F.; O’Brien, E.S.; Giehm, L.; Jennings, C.; Eskici, G.; Inoue, A.; Lerch, M.; et al. Structural insights into differences in G protein activation by family A and family B GPCRs. Science 2020, 369, eaba3373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montrose-Rafizadeh, C.; Avdonin, P.; Garant, M.J.; Rodgers, B.D.; Kole, S.; Yang, H.; Levine, M.A.; Schwindinger, W.; Bernier, M. Pancreatic glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor couples to multiple G proteins and activates mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Endocrinology 1999, 140, 1132–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douros, J.D.; Novikoff, A.; DuBois, B.; Rohlfs, R.; Mokrosinski, J.; Hogendorf, W.F.J.; Augustin, R.; Merkestein, M.; Egaa Martini, L.B.; Linderoth, L.; et al. A GLP-1 analogue optimized for cAMP-biased signaling improves weight loss in obese mice. Mol. Metab. 2025, 2025, 102124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robichaux, W.G., 3rd; Cheng, X. Intracellular cAMP Sensor EPAC: Physiology, Pathophysiology, and Therapeutics Development. Physiol. Rev. 2018, 98, 919–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furness, S.G.B.; Liang, Y.L.; Nowell, C.J.; Halls, M.L.; Wookey, P.J.; Dal Maso, E.; Inoue, A.; Christopoulos, A.; Wootten, D.; Sexton, P.M. Ligand-Dependent Modulation of G Protein Conformation Alters Drug Efficacy. Cell 2016, 167, 739–749.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roed, S.N.; Wismann, P.; Underwood, C.R.; Kulahin, N.; Iversen, H.; Cappelen, K.A.; Schäffer, L.; Lehtonen, J.; Hecksher-Soerensen, J.; Secher, A.; et al. Real-time trafficking and signaling of the glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2014, 382, 938–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Exton, J.H.; Robison, G.A.; Sutherland, E.W.; Park, C.R. Studies on the role of adenosine 3’,5’-monophosphate in the hepatic actions of glucagon and catecholamines. J. Biol. Chem. 1971, 246, 6166–6177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohl, S.L.; Birnbaumer, L.; Rodbell, M. The glucagon-sensitive adenyl cyclase system in plasma membranes of rat liver. I. Properties. J. Biol. Chem. 1971, 246, 1849–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagerström, M.C.; Schiöth, H.B. Structural diversity of G protein-coupled receptors and significance for drug discovery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2008, 7, 339–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, S.S. Evolving concepts in G protein-coupled receptor endocytosis: The role in receptor desensitization and signaling. Pharmacol. Rev. 2001, 53, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, P.Y.; Chuprun, J.K.; Schwartz, M.; Koch, W.J. The evolving impact of g protein-coupled receptor kinases in cardiac health and disease. Physiol. Rev. 2015, 95, 377–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefkowitz, R.J.; Shenoy, S.K. Transduction of receptor signals by beta-arrestins. Science 2005, 308, 512–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, Y.K.; Luttrell, L.M. The Diverse Roles of Arrestin Scaffolds in G Protein-Coupled Receptor Signaling. Pharmacol. Rev. 2017, 69, 256–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benovic, J.L. Historical Perspective of the G Protein-Coupled Receptor Kinase Family. Cells 2021, 10, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baggio, L.L.; Kim, J.G.; Drucker, D.J. Chronic exposure to GLP-1R agonists promotes homologous GLP-1 receptor desensitization in vitro but does not attenuate GLP-1R-dependent glucose homeostasis in vivo. Diabetes 2004, 53 (Suppl. 3), S205–S214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meneilly, G.S.; Greig, N.; Tildesley, H.; Habener, J.F.; Egan, J.M.; Elahi, D. Effects of 3 months of continuous subcutaneous administration of glucagon-like peptide 1 in elderly patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2003, 26, 2835–2841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fineman, M.S.; Bicsak, T.A.; Shen, L.Z.; Taylor, K.; Gaines, E.; Varns, A.; Kim, D.; Baron, A.D. Effect on glycemic control of exenatide (synthetic exendin-4) additive to existing metformin and/or sulfonylurea treatment in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2003, 26, 2370–2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baggio, L.; Adatia, F.; Bock, T.; Brubaker, P.L.; Drucker, D.J. Sustained expression of exendin-4 does not perturb glucose homeostasis, beta-cell mass, or food intake in metallothionein-preproexendin transgenic mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 34471–34477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zander, M.; Taskiran, M.; Toft-Nielsen, M.B.; Madsbad, S.; Holst, J.J. Additive glucose-lowering effects of glucagon-like peptide-1 and metformin in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2001, 24, 720–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szayna, M.; Doyle, M.E.; Betkey, J.A.; Holloway, H.W.; Spencer, R.G.; Greig, N.H.; Egan, J.M. Exendin-4 decelerates food intake, weight gain, and fat deposition in Zucker rats. Endocrinology 2000, 141, 1936–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolin, B.; Larsen, M.O.; Gotfredsen, C.F.; Deacon, C.F.; Carr, R.D.; Wilken, M.; Knudsen, L.B. The long-acting GLP-1 derivative NN2211 ameliorates glycemia and increases beta-cell mass in diabetic mice. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2002, 283, E745–E752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widmann, C.; Dolci, W.; Thorens, B. Desensitization and phosphorylation of the glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor by GLP-1 and 4-phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate. Mol. Endocrinol. 1996, 10, 62–75. [Google Scholar]
- Sonoda, N.; Imamura, T.; Yoshizaki, T.; Babendure, J.L.; Lu, J.C.; Olefsky, J.M. Beta-Arrestin-1 mediates glucagon-like peptide-1 signaling to insulin secretion in cultured pancreatic beta cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 6614–6619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabe, M.B.N.; van der Velden, W.J.C.; Gadgaard, S.; Smit, F.X.; Hartmann, B.; Bräuner-Osborne, H.; Rosenkilde, M.M. Enhanced agonist residence time, internalization rate and signalling of the GIP receptor variant [E354Q] facilitate receptor desensitization and long-term impairment of the GIP system. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2020, 126 (Suppl. 6), 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roed, S.N.; Nøhr, A.C.; Wismann, P.; Iversen, H.; Bräuner-Osborne, H.; Knudsen, S.M.; Waldhoer, M. Functional consequences of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor cross-talk and trafficking. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 1233–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nauck, M.A.; Heimesaat, M.M.; Orskov, C.; Holst, J.J.; Ebert, R.; Creutzfeldt, W. Preserved incretin activity of glucagon-like peptide 1 [7-36 amide] but not of synthetic human gastric inhibitory polypeptide in patients with type-2 diabetes mellitus. J. Clin. Investig. 1993, 91, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moo, E.V.; Møller, T.C.; Sørensen, F.A.; Inoue, A.; Bräuner-Osborne, H. Arrestin-independent internalization of the GLP-1 receptor is facilitated by a GRK, clathrin, and caveolae-dependent mechanism. FEBS J. 2025, 292, 1675–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNeill, S.M.; Lu, J.; Marion, C.; Carino, C.; Inoue, A.; Zhao, P.; Sexton, P.M.; Wootten, D. The role of G protein-coupled receptor kinases in GLP-1R β-arrestin recruitment and internalisation. Biochem Pharmacol. 2024, 222, 116119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syme, C.A.; Zhang, L.; Bisello, A. Caveolin-1 regulates cellular trafficking and function of the glucagon-like Peptide 1 receptor. Mol. Endocrinol. 2006, 20, 3400–3411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puddu, A.; Maggi, D. Emerging Role of Caveolin-1 in GLP-1 Action. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 668012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sabah, S.; Al-Fulaij, M.; Shaaban, G.; Ahmed, H.A.; Mann, R.J.; Donnelly, D.; Bünemann, M.; Krasel, C. The GIP receptor displays higher basal activity than the GLP-1 receptor but does not recruit GRK2 or arrestin3 effectively. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e106890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Møller, T.C.; Moo, E.V.; Inoue, A.; Pedersen, M.F.; Bräuner-Osborne, H. Characterization of the real-time internalization of nine GPCRs reveals distinct dependence on arrestins and G proteins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2024, 1871, 119584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Liu, L.; Huh, E.; Gbahou, F.; Cecon, E.; Oshima, M.; Houzé, L.; Katsonis, P.; Hegron, A.; Fan, Z.; et al. Human GLP1R variants affecting GLP1R cell surface expression are associated with impaired glucose control and increased adiposity. Nat. Metab. 2023, 5, 1673–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, L.B.; Blouin, M.J.; Le Gouill, C.; Picard, L.P.; Costa-Neto, C.M.; Bouvier, M.; Parreiras-E-Silva, L.T. Sustained Gαs signaling mediated by vasopressin type 2 receptors is ligand dependent but endocytosis and β-arrestin independent. Sci Signal. 2025, 18, eadf6206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamb, I.M.; White, A.D.; Willard, F.S.; Chalmers, M.J.; Xiao, J. Differential Role of Phosphorylation in Glucagon Family Receptor Signaling Revealed by Mass Spectrometry. J. Proteome Res. 2025, 24, 3367–3378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kizilkaya, H.S.; Sørensen, K.V.; Madsen, J.S.; Lindquist, P.; Douros, J.D.; Bork-Jensen, J.; Berghella, A.; Gerlach, P.A.; Gasbjerg, L.S.; Mokrosiński, J.; et al. Characterization of genetic variants of GIPR reveals a contribution of β-arrestin to metabolic phenotypes. Nat. Metab. 2024, 6, 1268–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Killion, E.A.; Chen, M.; Falsey, J.R.; Sivits, G.; Hager, T.; Atangan, L.; Helmering, J.; Lee, J.; Li, H.; Wu, B.; et al. Chronic glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide receptor (GIPR) agonism desensitizes adipocyte GIPR activity mimicking functional GIPR antagonism. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, S.; Patel, R.T.; Bruno, J.; Panhwar, M.S.; Wen, J.; McGraw, T.E. A naturally occurring GIP receptor variant undergoes enhanced agonist-induced desensitization, which impairs GIP control of adipose insulin sensitivity. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 34, 3618–3629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitsi, S.; El Eid, L.; Manchanda, Y.; Oqua, A.I.; Mohamed, N.; Hansen, B.; Suba, K.; Rutter, G.A.; Salem, V.; Jones, B.; et al. Divergent acute versus prolonged pharmacological GLP-1R responses in adult β cell-specific β-arrestin 2 knockout mice. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eadf7737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaïmia, N.; Obeid, J.; Varrault, A.; Sabatier, J.; Broca, C.; Gilon, P.; Costes, S.; Bertrand, G.; Ravier, M.A. GLP-1 and GIP receptors signal through distinct β-arrestin 2-dependent pathways to regulate pancreatic β cell function. Cell Rep. 2023, 42, 113326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, I.; Adriaenssens, A.E.; Scott, W.R.; Carling, D.; Murphy, K.G.; Minnion, J.S.; Bloom, S.R.; Jones, B.; Tan, T.M. Chronic GIPR agonism results in pancreatic islet GIPR functional desensitisation. Mol. Metab. 2025, 92, 102094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasbjerg, L.S.; Rasmussen, R.S.; Dragan, A.; Lindquist, P.; Melchiorsen, J.U.; Stepniewski, T.M.; Schiellerup, S.; Tordrup, E.K.; Gadgaard, S.; Kizilkaya, H.S.; et al. Altered desensitization and internalization patterns of rodent versus human glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) receptors. An important drug discovery challenge. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2025, 182, 3353–3370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, J.J.; Hucking, K.; Holst, J.J.; Deacon, C.F.; Schmiegel, W.H.; Nauck, M.A. Reduced insulinotropic effect of gastric inhibitory polypeptide in first-degree relatives of patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 2001, 50, 2497–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, S.A.; Brown, J.C.; Dupre, J. Hypersecretion of gastric inhibitory polypeptide following oral glucose in diabetes mellitus. Diabetes 1977, 26, 525–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, I.R.; Owens, D.R.; Luzio, S.; Williams, S.; Hayes, T.M. The glucose dependent insulinotropic polypeptide response to oral glucose and mixed meals is increased in patients with type 2 (non-insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia 1989, 32, 668–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Véniant, M.M.; Lu, S.C.; Atangan, L.; Komorowski, R.; Stanislaus, S.; Cheng, Y.; Wu, B.; Falsey, J.R.; Hager, T.; Thomas, V.A.; et al. A GIPR antagonist conjugated to GLP-1 analogues promotes weight loss with improved metabolic parameters in preclinical and phase 1 settings. Nat. Metab. 2024, 6, 290–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willard, F.S.; Douros, J.D.; Gabe, M.B.; Showalter, A.D.; Wainscott, D.B.; Suter, T.M.; Capozzi, M.E.; van der Velden, W.J.; Stutsman, C.; Cardona, G.R.; et al. Tirzepatide is an imbalanced and biased dual GIP and GLP-1 receptor agonist. JCI Insight 2020, 5, e140532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wean, J.; Kowalsky, A.H.; Laker, R.; Will, S.; Drucker, D.J.; Rhodes, C.J.; Seeley, R.J. Specific loss of GIPR signaling in GABAergic neurons enhances GLP-1R agonist-induced body weight loss. Mol. Metab. 2025, 95, 102074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Willard, F.S.; Feng, D.; Alsina-Fernandez, J.; Chen, Q.; Vieth, M.; Ho, J.D.; Showalter, A.D.; Stutsman, C.; Ding, L.; et al. Structural determinants of dual incretin receptor agonism by tirzepatide. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2116506119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coskun, T.; Urva, S.; Roell, W.C.; Qu, H.; Loghin, C.; Moyers, J.S.; O’Farrell, L.S.; Briere, D.A.; Sloop, K.W.; Thomas, M.K.; et al. LY3437943, a novel triple glucagon, GIP, and GLP-1 receptor agonist for glycemic control and weight loss: From discovery to clinical proof of concept. Cell Metab. 2022, 34, 1234–1247.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birnbaumer, L.; Rodbell, M. Adenyl cyclase in fat cells. II. Hormone receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 1969, 244, 3477–3482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moiz, A.; Filion, K.B.; Toutounchi, H.; Tsoukas, M.A.; Yu, O.H.Y.; Peters, T.M.; Eisenberg, M.J. Efficacy and Safety of Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists for Weight Loss Among Adults Without Diabetes: A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials. Ann. Intern. Med. 2025, 178, 199–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagnon, J.; Sauvé, M.; Zhao, W.; Stacey, H.M.; Wiber, S.C.; Bolz, S.S.; Brubaker, P.L. Chronic Exposure to TNFα Impairs Secretion of Glucagon-Like Peptide-1. Endocrinology 2015, 156, 3950–3960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoicovy, R.A.; Cora, N.; Perez, A.; Nagliya, D.; Del Calvo, G.; Lopez, T.B.; Weinstein, E.C.; Borges, J.I.; Maning, J.; Lymperopoulos, A. Cyclic adenosine monophosphate critically modulates cardiac GLP-1 receptor’s anti-inflammatory effects. Inflamm. Res. 2024, 73, 2043–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Mei, A.; Liu, X.; Braunstein, Z.; Wei, Y.; Wang, B.; Duan, L.; Rao, X.; Rajagopalan, S.; Dong, L.; et al. Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Regulates Macrophage Migration in Monosodium Urate-Induced Peritoneal Inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 772446. [Google Scholar]
- Malbert, C.H.; Chauvin, A.; Horowitz, M.; Jones, K.L. Pancreatic GLP-1r binding potential is reduced in insulin-resistant pigs. BMJ Open Diabetes Res. Care 2020, 8, e001540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ejarque, M.; Guerrero-Pérez, F.; de la Morena, N.; Casajoana, A.; Virgili, N.; López-Urdiales, R.; Maymó-Masip, E.; Pujol Gebelli, J.; Garcia Ruiz de Gordejuela, A.; Perez-Maraver, M.; et al. Role of adipose tissue GLP-1R expression in metabolic improvement after bariatric surgery in patients with type 2 diabetes. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 6274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vendrell, J.; El Bekay, R.; Peral, B.; García-Fuentes, E.; Megia, A.; Macias-Gonzalez, M.; Fernández Real, J.; Jimenez-Gomez, Y.; Escoté, X.; Pachón, G.; et al. Study of the potential association of adipose tissue GLP-1 receptor with obesity and insulin resistance. Endocrinology 2011, 152, 4072–4079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, T.; Obata, A.; Shimoda, M.; Shimizu, I.; da Silva Xavier, G.; Okauchi, S.; Hirukawa, H.; Kohara, K.; Mune, T.; Moriuchi, S.; et al. Down-regulation of vascular GLP-1 receptor expression in human subjects with obesity. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, R.; Hergarden, A.; Krishnan, S.; Morales, M.; Lam, D.; Tracy, T.; Tang, T.; Patton, A.; Lee, C.; Pant, A.; et al. Biased agonism of GLP-1R and GIPR enhances glucose lowering and weight loss, with dual GLP-1R/GIPR biased agonism yielding greater efficacy. Cell Rep. Med. 2025, 6, 102156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, T.; Sun, B.; Yoshino, H.; Feng, D.; Suzuki, Y.; Fukazawa, M.; Nagao, S.; Wainscott, D.B.; Showalter, A.D.; Droz, B.A.; et al. Structural basis for GLP-1 receptor activation by LY3502970, an orally active nonpeptide agonist. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 29959–29967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lincoff, A.M.; Brown-Frandsen, K.; Colhoun, H.M.; Deanfield, J.; Emerson, S.S.; Esbjerg, S.; Hardt-Lindberg, S.; Hovingh, G.K.; Kahn, S.E.; Kushner, R.F.; et al. Semaglutide and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Obesity without Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 2221–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lähteenvuo, M.; Tiihonen, J.; Solismaa, A.; Tanskanen, A.; Mittendorfer-Rutz, E.; Taipale, H. Repurposing Semaglutide and Liraglutide for Alcohol Use Disorder. JAMA Psychiatry 2025, 82, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wang, Q.; Qi, X.; Gurney, M.; Perry, G.; Volkow, N.D.; Davis, P.B.; Kaelber, D.C.; Xu, R. Associations of semaglutide with first-time diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease in patients with type 2 diabetes: Target trial emulation using nationwide real-world data in the, U.S. Alzheimers Dement. 2024, 20, 8661–8672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Volkow, N.D.; Wang, Q.; Berger, N.A.; Davis, P.B.; Kaelber, D.C.; Xu, R. Semaglutide and Opioid Overdose Risk in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Opioid Use Disorder. JAMA Netw. Open. 2024, 7, e2435247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Volkow, N.D.; Berger, N.A.; Davis, P.B.; Kaelber, D.C.; Xu, R. Association of Semaglutide with Tobacco Use Disorder in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: Target Trial Emulation Using Real-World Data. Ann. Intern. Med. 2024, 177, 1016–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klausen, M.K.; Thomsen, M.; Wortwein, G.; Fink-Jensen, A. The role of glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) in addictive disorders. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2022, 179, 625–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Garrido, M.A.; Serrano-López, V.; Ruiz-Pino, F.; Vázquez, M.J.; Rodríguez-Martín, A.; Torres, E.; Velasco, I.; Rodríguez, A.B.; Chicano-Gálvez, E.; Mora-Ortiz, M.; et al. Superior metabolic improvement of polycystic ovary syndrome traits after GLP1-based multi-agonist therapy. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 8498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muayad, J.; Loya, A.; Hussain, Z.S.; Chauhan, M.Z.; Alsoudi, A.F.; De Francesco, T.; Ahmed, I.I.K. Comparative Effects of Glucagon-like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonists and Metformin on Glaucoma Risk in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Ophthalmology 2024, 132, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.C.; Hum, R.M.; Rogers, K.; Maglio, C.; Alam, U.; Zhao, S.S. Metabolic syndrome and psoriatic arthritis: The role of weight loss as a disease-modifying therapy. Ther. Adv. Musculoskelet. Dis. 2024, 16, 1759720X241271886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cencioni, C.; Malatesta, S.; Vigiano Benedetti, V.; Licursi, V.; Perfetto, L.; Conte, F.; Ranieri, D.; Bartolazzi, A.; Kunkl, M.; Tuosto, L.; et al. The GLP-1R agonist semaglutide reshapes pancreatic cancer associated fibroblasts reducing collagen proline hydroxylation and favoring T lymphocyte infiltration. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2025, 44, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
 indicates no effect of βarrestin; “+” symbol next to the black arrow indicates potentiation; “?”: Exact effect of βarrestin on Gs coupling not known; “++” symbol indicates higher potency than “+” symbol. Abbreviations: αs: Gas subunit; βγ: The Gβγ subunit dimer of heterotrimeric G proteins.
indicates no effect of βarrestin; “+” symbol next to the black arrow indicates potentiation; “?”: Exact effect of βarrestin on Gs coupling not known; “++” symbol indicates higher potency than “+” symbol. Abbreviations: αs: Gas subunit; βγ: The Gβγ subunit dimer of heterotrimeric G proteins.
 indicates no effect of βarrestin; “+” symbol next to the black arrow indicates potentiation; “?”: Exact effect of βarrestin on Gs coupling not known; “++” symbol indicates higher potency than “+” symbol. Abbreviations: αs: Gas subunit; βγ: The Gβγ subunit dimer of heterotrimeric G proteins.
indicates no effect of βarrestin; “+” symbol next to the black arrow indicates potentiation; “?”: Exact effect of βarrestin on Gs coupling not known; “++” symbol indicates higher potency than “+” symbol. Abbreviations: αs: Gas subunit; βγ: The Gβγ subunit dimer of heterotrimeric G proteins.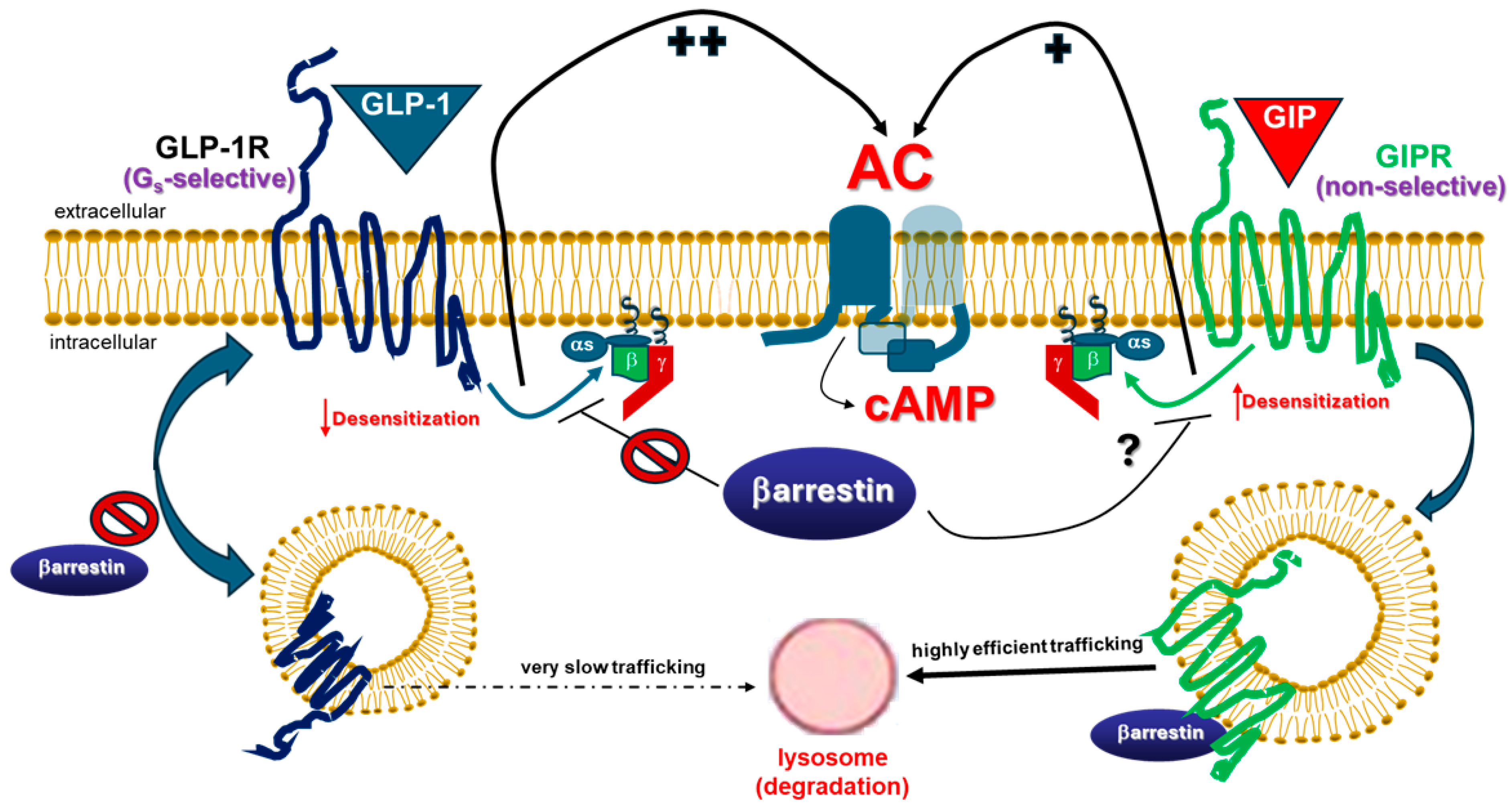
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lymperopoulos, A.; Altsman, V.L.; Stoicovy, R.A. Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor (GLP-1R) Signaling: Making the Case for a Functionally Gs Protein-Selective GPCR. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 7239. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157239
Lymperopoulos A, Altsman VL, Stoicovy RA. Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor (GLP-1R) Signaling: Making the Case for a Functionally Gs Protein-Selective GPCR. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(15):7239. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157239
Chicago/Turabian StyleLymperopoulos, Anastasios, Victoria L. Altsman, and Renee A. Stoicovy. 2025. "Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor (GLP-1R) Signaling: Making the Case for a Functionally Gs Protein-Selective GPCR" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 15: 7239. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157239
APA StyleLymperopoulos, A., Altsman, V. L., & Stoicovy, R. A. (2025). Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor (GLP-1R) Signaling: Making the Case for a Functionally Gs Protein-Selective GPCR. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(15), 7239. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157239





