Serum Metabolomic Profiling Reveals Differences Between Systemic Sclerosis Patients with Polyneuropathy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Characteristics of the Study Cohort
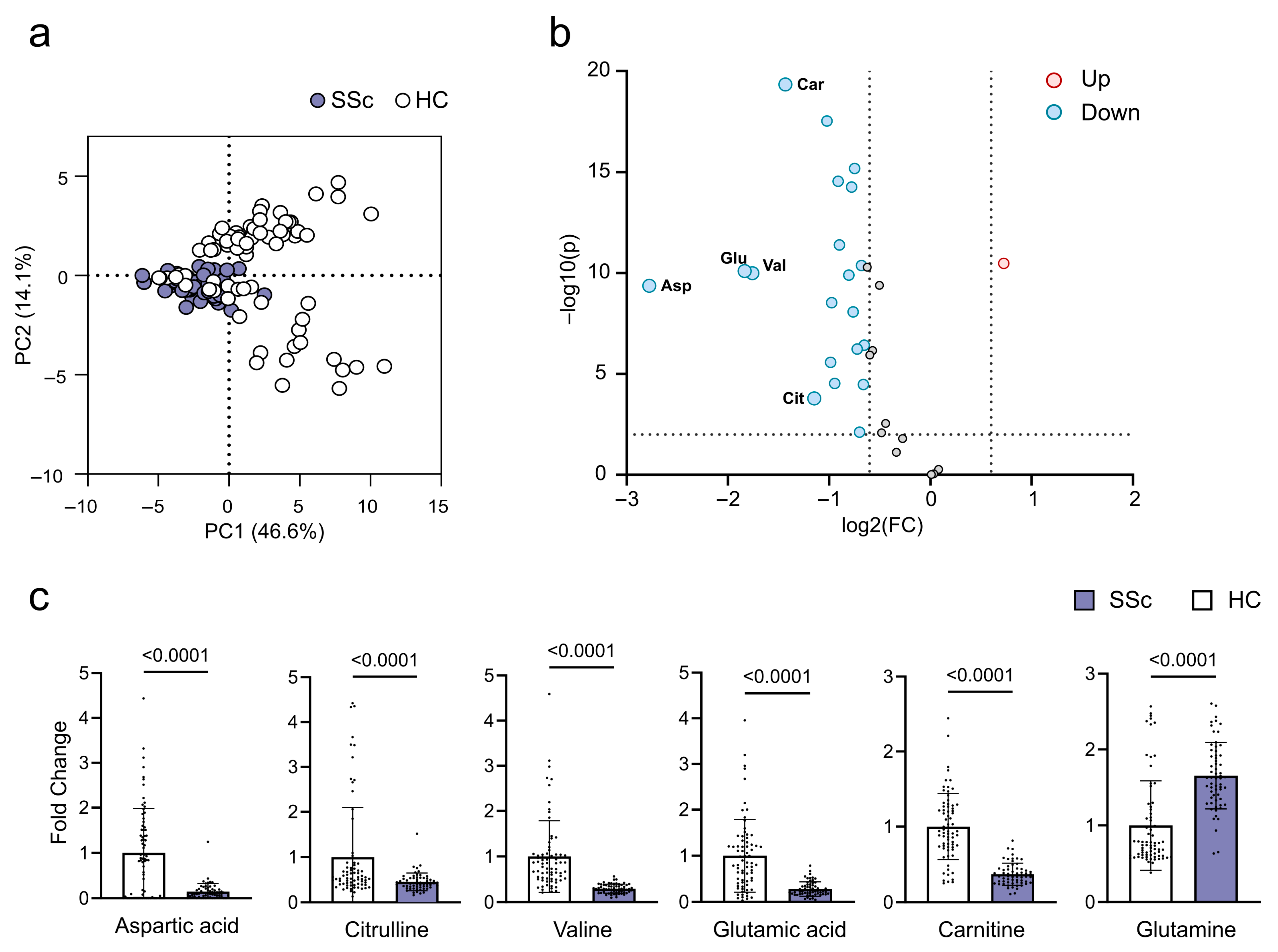
2.2. Metabolites in SSc Patients
2.3. Disease Prediction Models
2.4. Discrimination of SSc Patients with PNP
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Subjects
4.2. Methods
4.3. Sample Collection and Preparation
4.4. LC-MS Based Metabolomics
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SSc | Systemic sclerosis |
| PNP | Polyneuropathy |
| HC | Healthy control |
| ILD | Interstitial lung disease |
| mRSS | Modified Rodnan skin score |
| NS | Nervous system |
| NO | Nitric oxide |
| dcSSc | diffuse cutaneous Systemic sclerosis |
| lcSSc | limited cutaneous Systemic sclerosis |
| PAH | Pulmonary arterial hypertension |
| CNS | Central nervous system |
| DN | Diabetic neuropathy |
| DM | Diabetes mellitus |
| ARA | Anti-RNA-polymerase III |
| PNS | Peripheral nervous system |
| ACR | American College of Rheumatology |
| EULAR | European League Against Rheumatism |
| NCS | Nerve conduction study |
| EDTA | Ethylendiamine tetraacetic acid |
References
- Asano, Y. Systemic sclerosis. J. Dermatol. 2018, 45, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adigun, R.; Goyal, A.; Hariz, A. Systemic Sclerosis (Scleroderma). In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Morales-González, V.; Galeano-Sánchez, D.; Covaleda-Vargas, J.E.; Rodriguez, Y.; Monsalve, D.M.; Pardo-Rodriguez, D.; Cala, M.P.; Acosta-Ampudia, Y.; Ramírez-Santana, C. Metabolic fingerprinting of systemic sclerosis: A systematic review. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2023, 10, 1215039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jud, P.; Meinitzer, A.; Strohmaier, H.; Arefnia, B.; Wimmer, G.; Obermayer-Pietsch, B.; Foris, V.; Kovacs, G.; Odler, B.; Moazedi-Fürst, F.; et al. Association of amino acids and parameters of bone metabolism with endothelial dysfunction and vasculopathic changes in limited systemic sclerosis. Front. Med. 2023, 10, 1193121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murgia, F.; Svegliati, S.; Poddighe, S.; Lussu, M.; Manzin, A.; Spadoni, T.; Fischetti, C.; Gabrielli, A.; Atzori, L. Metabolomic profile of systemic sclerosis patients. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 7626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanova, K.; Žukovs, D.; Možeitoviča, E.; Rots, D.; Kurjāne, N.; Ķēniņa, V. Prevalence of polyneuropathies among systemic sclerosis patients and impact on health-related quality of life. Neurol. I Neurochir. Pol. 2023, 57, 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amaral, T.N.; Peres, F.A.; Lapa, A.T.; Marques-Neto, J.F.; Appenzeller, S. Neurologic involvement in scleroderma: A systematic review. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2013, 43, 335–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AlMehmadi, B.A.; To, F.Z.; Anderson, M.A.; Johnson, S.R. Epidemiology and treatment of peripheral neuropathy in systemic sclerosis. J. Rheumatol. 2021, 48, 1839–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, P.; Bruni, J.; Sukenik, S. Neurological manifestations in systemic sclerosis (scleroderma). J. Rheumatol. 1984, 11, 480–483. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Averbuch-Heller, L.; Steiner, I.; Abramsky, O. Neurologic manifestations of progressive systemic sclerosis. Arch. Neurol. 1992, 49, 1292–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bignotti, B.; Ghio, M.; Panico, N.; Tagliafico, G.; Martinoli, C.; Tagliafico, A. High-resolution ultrasound of peripheral nerves in systemic sclerosis: A pilot study of computer-aided quantitative assessment of nerve density. Skelet. Radiol. 2015, 44, 1761–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campello Morer, I.; Velilla Marco, J.; Hortells Aznar, J.L.; Almárcegui Lafita, C.; Barrena Caballo, R.; Oliveros Juste, A. Manifestaciones neurológicas en la esclerosis sistémica [Neurological involvement in systemic sclerosis]. Rev. Clin. Esp. 2003, 203, 373–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bandinelli, F.; Kaloudi, O.; Candelieri, A.; Conforti, M.L.; Casale, R.; Cammarata, S.; Grassiri, G.; Miniati, I.; Melchiorre, D.; Matucci-Cerinic, M. Early detection of median nerve syndrome at the carpal tunnel with high-resolution 18 MHz ultrasonography in systemic sclerosis patients. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2010, 28, S15–S18. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Barr, W.G.; Blair, S.J. Carpal tunnel syndrome as the initial manifestation of scleroderma. J. Hand Surg. 1988, 13, 366–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chammas, M.; ZU Reckendorf, G.M.; Allieu, Y. Compression of the ulnar nerve in Guyon’s canal by pseudotumoral calcinosis in systemic scleroderma. J. Hand Surg. 1995, 20, 794–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dyck, P.J.; Hunder, G.G.; Dyck, P.J. A case-control and nerve biopsy study of CREST multiple mononeuropathy. Neurology 1997, 49, 1641–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leichenko, T.; Herrick, A.; Alani, S.M.; Hilton, R.C.; Jayson, M.I.V. Mononeuritis in two patients with limited cutaneous systemic sclerosis. Br. J. Rheumatol. 1994, 33, 594–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mouthon, L.; Halimi, C.; Muller, G.P.; Cayre-Castel, M.; Bégué, T.; Masquelet, A.C.; Guillevin, L. Systemic scleroderma associated with bilateral ulnar nerve entrapment at the elbow. Rheumatology 2000, 39, 682–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nitta, Y.; Sobue, G. Progressive systemic sclerosis associated with multiple mononeuropathy. Dermatology 1996, 193, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tagliafico, A.; Panico, N.; Resmini, E.; Derchi, L.E.; Ghio, M.; Martinoli, C. The role of ultrasound imaging in the evaluation of peripheral nerve in systemic sclerosis (scleroderma). Eur. J. Radiol. 2011, 77, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, M.; Liu, D.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, W.; Zhao, L.; Bao, D.; Li, Y.; Distler, J.H.; Zhu, H. Serum metabolomic profiling reveals potential biomarkers in systemic sclerosis. Metabolism 2023, 144, 155587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, A.; Sun, H.; Yan, G.; Wang, P.; Wang, X. Metabolomics for Biomarker Discovery: Moving to the Clinic. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 1, 354671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, S.; Cai, Y.; Yao, H.; Lin, C.; Xie, Y.; Tang, S.; Zhang, A. Small molecule metabolites: Discovery of biomarkers and therapeutic targets. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bögl, T.; Mlynek, F.; Himmelsbach, M.; Sepp, N.; Buchberger, W.; Geroldinger-Simić, M. Plasma Metabolomic Profiling Reveals Four Possibly Disrupted Mechanisms in Systemic Sclerosis. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smolenska, Z.; Zabielska-Kaczorowska, M.; Wojteczek, A.; Kutryb-Zajac, B.; Zdrojewski, Z. Metabolic Pattern of Systemic Sclerosis: Association of Changes in Plasma Concentrations of Amino Acid-Related Compounds With Disease Presentation. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2020, 7, 585161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bengtsson, A.A.; Trygg, J.; Wuttge, D.M.; Sturfelt, G.; Theander, E.; Donten, M.; Moritz, T.; Sennbro, C.-J.; Torell, F.; Lood, C.; et al. Metabolic Profiling of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Comparison with Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome and Systemic Sclerosis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0159384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ottria, A.; Hoekstra, A.T.; Zimmermann, M.; van der Kroef, M.; Vazirpanah, N.; Cossu, M.; Chouri, E.; Rossato, M.; Beretta, L.; Tieland, R.G.; et al. Fatty Acid and Carnitine Metabolism Are Dysregulated in Systemic Sclerosis Patients. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Zheng, X.; Liu, B.; Xia, Y.; Xin, Z.; Deng, B.; He, L.; Deng, J.; Ren, W. Aspartate Metabolism Facilitates IL-1β Production in Inflammatory Macrophages. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 753092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Funes, S.C.; Rios, M.; Escobar-Vera, J.; Kalergis, A.M. Implications of macrophage polarization in autoimmunity. Immunology 2018, 154, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soldano, S.; Pizzorni, C.; Paolino, S.; Trombetta, A.C.; Montagna, P.; Brizzolara, R.; Ruaro, B.; Sulli, A.; Cutolo, M. Alternatively Activated (M2) Macrophage Phenotype Is Inducible by Endothelin-1 in Cultured Human Macrophages. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0166433, Erratum in PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0175238. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0175238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christmann, R.B.; Lafyatis, R. The cytokine language of monocytes and macrophages in systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2010, 12, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaore, S.N.; Amane, H.S.; Kaore, N.M. Citrulline: Pharmacological perspectives and its role as an emerging biomarker in future. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2013, 27, 35–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Jasmi, F.; Al Zaabi, N.; Al-Thihli, K.; Al Teneiji, A.M.; Hertecant, J.; El-Hattab, A.W. Endothelial Dysfunction and the Effect of Arginine and Citrulline Supplementation in Children and Adolescents With Mitochondrial Diseases. J. Cent. Nerv. Syst. Dis. 2020, 12, 1179573520909377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bratoiu, I.; Burlui, A.M.; Cardoneanu, A.; Macovei, L.A.; Richter, P.; Rusu-Zota, G.; Rezus, C.; Badescu, M.C.; Szalontay, A.; Rezus, E. The Involvement of Smooth Muscle, Striated Muscle, and the Myocardium in Scleroderma: A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sari, A.; Esme, M.; Aycicek, G.S.; Armagan, B.; Kilic, L.; Ertenli, A.I.; Halil, M.G.; Akdogan, A. Evaluating skeletal muscle mass with ultrasound in patients with systemic sclerosis. Nutrition 2021, 84, 110999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.; Zhang, X.; Azhar, G.; Patyal, P.; Verma, A.; Kc, G.; Wei, J.Y. Valine improves mitochondrial function and protects against oxidative stress. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2024, 88, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haroon, E.; Miller, A.H.; Sanacora, G. Inflammation, Glutamate, and Glia: A Trio of Trouble in Mood Disorders. Neuropsychopharmacology 2017, 42, 193–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ardawi, M.S.M. Glutamine and glucose metabolism in human peripheral lymphocytes. Metabolism 1988, 37, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henderson, J.; Duffy, L.; Stratton, R.; Ford, D.; O’Reilly, S. Metabolic reprogramming of glycolysis and glutamine metabolism are key events in myofibroblast transition in systemic sclerosis pathogenesis. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 14026–14038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ung, C.Y.; Onoufriadis, A.; Parsons, M.; McGrath, J.A.; Shaw, T.J. Metabolic perturbations in fibrosis disease. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2021, 139, 106073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kay, E.J.; Koulouras, G.; Zanivan, S. Regulation of extracellular matrix production in activated fibroblasts: Roles of amino acid metabolism in collagen synthesis. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 719922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, M.A.; Baba, S.K.; Khan, I.R.; Khan, M.S.; Husain, F.M.; Ahmad, S.; Haris, M.; Singh, M.; Akil, A.S.A.; Macha, M.A.; et al. Glutamine Metabolism: Molecular Regulation, Biological Functions, and Diseases. MedComm 2025, 6, e70120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staats Pires, A.; Heng, B.; Tan, V.X.; Latini, A.; Russo, M.A.; Santarelli, D.M.; Bailey, D.; Wynne, K.; O’Brien, A.J.; Guillemin, G.J.; et al. Kynurenine, Tetrahydrobiopterin, and Cytokine Inflammatory Biomarkers in Individuals Affected by Diabetic Neuropathic Pain. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, M.-M.; Xiang, H.-J.; Lu, H.; Yin, P.-H.; Li, G.-W.; Wang, Y.-M.; Chen, L.; Chen, Q.-G.; Zhao, C.; Lu, Q.; et al. Candidate metabolite markers of peripheral neuropathy in Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2022, 14, 5420–5440. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Davis, I.; Liu, A. What is the tryptophan kynurenine pathway and why is it important to neurotherapeutics? Expert Rev. Neurother. 2015, 15, 719–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campochiaro, C.; Lytton, S.; Nihtyanova, S.; Fuchs, D.; Ong, V.H.; Denton, C.P. Elevated kynurenine levels in diffuse cutaneous and anti-RNA polymerase III positive systemic sclerosis. Clin. Immunol. 2019, 199, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace, N.; Gaboyan, S.; Nichols, W.; Pauciulo, M.; Cheng, S.; Chan, S.; Jain, M.; Alotaibi, M. Metabolites of the Kynurenine Pathway Are Significantly Altered in Systemic Sclerosis Associated PAH Compared to Other Subgroups of PAH (abstract). Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2023, 207, A2517. [Google Scholar]
- Simpson, C.E.; Ambade, A.S.; Harlan, R.; Roux, A.; Aja, S.; Graham, D.; Shah, A.A.; Hummers, L.K.; Hemnes, A.R.; Leopold, J.A.; et al. Kynurenine pathway metabolism evolves with development of preclinical and scleroderma-associated pulmonary arterial hypertension. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2023, 325, L617–L627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dantzer, R.; O’COnnor, J.C.; Freund, G.G.; Johnson, R.W.; Kelley, K.W. From inflammation to sickness and depression: When the immune system subjugates the brain. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2008, 9, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavlova, N.N.; Hui, S.; Ghergurovich, J.M.; Fan, J.; Intlekofer, A.M.; White, R.M.; Rabinowitz, J.D.; Thompson, C.B.; Zhang, J. As Extracellular Glutamine Levels Decline, Asparagine Becomes an Essential Amino Acid. Cell Metab. 2018, 27, 428–438.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Vandekeere, S.; Kalucka, J.; Bierhansl, L.; Zecchin, A.; Brüning, U.; Visnagri, A.; Yuldasheva, N.; Goveia, J.; Cruys, B.; et al. Role of glutamine and interlinked asparagine metabolism in vessel formation. EMBO J. 2017, 36, 2334–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jong, C.J.; Ito, T.; Mozaffari, M.; Azuma, J.; Schaffer, S. Effect of beta-alanine treatment on mitochondrial taurine level and 5-taurinomethyluridine content. J. Biomed. Sci. 2010, 17 (Suppl 1), S25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shetewy, A.; Shimada-Takaura, K.; Warner, D.; Jong, C.J.; Al Mehdi, A.-B.; Alexeyev, M.; Takahashi, K.; Schaffer, S.W. Mitochondrial defects associated with β-alanine toxicity: Relevance to hyper-beta-alaninemia. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2016, 416, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaffer, S.W.; Shimada-Takaura, K.; Jong, C.J.; Ito, T.; Takahashi, K. Impaired energy metabolism of the taurine deficient heart. Amino Acids 2016, 48, 549–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van den Hoogen, F.; Khanna, D.; Fransen, J.; Johnson, S.R.; Baron, M.; Tyndall, A.; Matucci-Cerinic, M.; Naden, R.P.; Medsger, T.A., Jr.; Carreira, P.E.; et al. 2013 classification criteria for systemic sclerosis: An American college of rheumatology/European league against rheumatism collaborative initiative. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2013, 72, 1747–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tankisi, H.; Pugdahl, K.; Beniczky, S.; Andersen, H.; Fuglsang-Frederiksen, A. Evidence-based recommendations for examination and diagnostic strategies of polyneuropathy electrodiagnosis. Clin. Neurophysiol. Pract. 2019, 4, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valentini, G.; Iudici, M.; Walker, U.A.; Jaeger, V.K.; Baron, M.; Carreira, P.; Czirják, L.; Denton, C.P.; Distler, O.; Hachulla, E.; et al. The European Scleroderma Trials and Research group (EUSTAR) task force for the development of revised activity criteria for systemic sclerosis: Derivation and validation of a preliminarily revised EUSTAR activity index. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, R.; Wang, J.; Su, M.; Jia, E.; Chen, S.; Chen, T.; Ni, Y. Missing Value Imputation Approach for Mass Spectrometry-based Metabolomics Data. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Variable | SSc Without PNP | SSc with PNP | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex, n (%) | 0.35 | ||
| Male | 5 (45.5%) | 6 (54.5%) | |
| Female | 31 (60.8%) | 20 (39.2%) | |
| Mean age in years (standard deviation) | 54.94 (12.533) | 69.95 (7.893) | <0.05 |
| Mean disease duration in years (standard deviation) | 10.44 (6.596) | 18.08 (10.476) | <0.05 |
| Mean modified Rodnan skin score (standard deviation) | 7.26 (9.053) | 7.65 (8.158) | 0.86 |
| Raynaud’s phenomenon, % | 86 | 92 | 0.45 |
| Variable | SSc | HC | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex, n (%) | 0.77 | ||
| Male | 11 (17.74%) | 14 (19.72%) | |
| Female | 51 (82.26%) | 57 (80.28%) | |
| Mean age in years (standard deviation) | 61.19 (13.06) | 53.18 (18.65) | <0.05 |
| Metabolite | Our Study | Murgia et al. 2018 [5] | Jud et al. 2023 [4] | Guo et al. 2023 [21] | Bögl et al. 2022 [24] | Smolenska et al. 2019 [25] | Bengtsson et al. 2016 [26] | Ottria et al. 2020 [27] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aspartic acid or aspartate | ↓ | ↓ | ↑ with higher mRSS | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | ↑ | N.A. |
| Citrulline | ↓ | N.A. | correlated with other amino acids | N.A. | ↑ | ↓ with scleroderma | N.A. | N.A. |
| Carnitine | ↓ | N.A. | N.A. | ↑ with higher mRSS | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | ↑ |
| Valine | ↓ | ↑ in dsSSc | ↑ with a higher DETECT score | N.A. | N.A. | ↑ in lung involvement | N.A. | N.A. |
| Glutamic acid | ↓ | ↓ (↑ in dsSSc) | ↑ with higher mRSS | ↓ | N.A. | ↑ in calcinosis and telangiectasia | N.A. | N.A. |
| Glutamine | ↑ | ↑ | ↓ with higher mRSS | N.A. | N.A. | ↑ | N.A. | N.A. |
| Metabolite | Our Study | Murgia et al. 2018 [5] | Jud et al. 2023 [4] | Guo et al. 2023 [21] | Bögl et al. 2022 [24] | Smolenska et al. 2019 [25] | Bengtsson et al. 2016 [26] | Ottria et al. 2020 [27] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kynurenine | ↑ | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | ↑ in dcSSc | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. |
| Asparagine | ↑ | N.A. | ↓ with higher mRSS | N.A. | N.A. | ↓ with scleroderma | N.A. | N.A. |
| Alanine | ↑ | ↓ | ↑ in lcSSc | N.A. | reduced concentration | ↑ in dcSSc | ↓ | N.A. |
| Metabolite | Our Study | Staats Pires et al. 2020 [43] | Shao MM et al. 2022 [44] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kynurenine | ↑ | ↑ in DM Type 1 patients with neuropathic pain compared to diabetic controls | ↑ in patients with severe DN compared to patients with mild DN; and without DN |
| Asparagine | ↑ | N.A. | ↑ in DM Type 2 patients with PNP compared to DM Type 2 patients without DN |
| Alanine | ↑ | N.A. | ↑ in patients with severe DN compared to patients with mild DN; significantly. ↑ compared to DM Type 2 patients without DN |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ivanova, K.; Schiemer, T.; Vaska, A.; Kurjāne, N.; Kenina, V.; Klavins, K. Serum Metabolomic Profiling Reveals Differences Between Systemic Sclerosis Patients with Polyneuropathy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 7133. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157133
Ivanova K, Schiemer T, Vaska A, Kurjāne N, Kenina V, Klavins K. Serum Metabolomic Profiling Reveals Differences Between Systemic Sclerosis Patients with Polyneuropathy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(15):7133. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157133
Chicago/Turabian StyleIvanova, Kristine, Theresa Schiemer, Annija Vaska, Nataļja Kurjāne, Viktorija Kenina, and Kristaps Klavins. 2025. "Serum Metabolomic Profiling Reveals Differences Between Systemic Sclerosis Patients with Polyneuropathy" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 15: 7133. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157133
APA StyleIvanova, K., Schiemer, T., Vaska, A., Kurjāne, N., Kenina, V., & Klavins, K. (2025). Serum Metabolomic Profiling Reveals Differences Between Systemic Sclerosis Patients with Polyneuropathy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(15), 7133. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157133






