Accurate Prediction of Protein Tertiary and Quaternary Stability Using Fine-Tuned Protein Language Models and Free Energy Perturbation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Predicting Mutational Impact on Protein Stability
2.2. Predicting Mutational Impact on Protein Function
2.3. Predicting Mutational Impact on Protein Complexes
3. Conclusions
4. Methods
4.1. Data Preprocessing: Protein Stability
4.2. Data Preprocessing: GFP Brightness
4.3. Data Preprocessing: Protein Quaternary Structure Stability
4.4. Model Training
4.5. Free Energy Perturbation
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Birhane, A.; Kasirzadeh, A.; Leslie, D.; Wachter, S. Science in the age of large language models. Nat. Rev. Phys. 2023, 5, 277–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.; Fu, C.; Zhao, S.; Li, K.; Sun, X.; Xu, T.; Chen, E. A Survey on Multimodal Large Language Models. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2024, 11, nwae403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.X.; Zhou, K.; Li, J.; Tang, T.; Wang, X.; Hou, Y.; Min, Y.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, J.; Dong, Z.; et al. A Survey of Large Language Models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.18223. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wolf, T.; Debut, L.; Sanh, V.; Chaumond, J.; Delangue, C.; Moi, A.; Cistac, P.; Rault, T.; Louf, R.; Funtowicz, M.; et al. Transformers: State-of-the-Art Natural Language Processing. In Proceedings of the 2020 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing: System Demonstrations: Association for Computational Linguistics, Punta Cana, Dominican Republic, 16–20 November 2020; pp. 38–45. [Google Scholar]
- Young, T.; Hazarika, D.; Poria, S.; Cambria, E. Recent Trends in Deep Learning Based Natural Language Processing. IEEE Comput. Intell. Mag. 2018, 13, 55–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaswani. Attention is all you need. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2017, 30, 5998–6008. [Google Scholar]
- Khurana, D.; Koli, A.; Khatter, K.; Singh, S. Natural language processing: State of the art, current trends and challenges. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2023, 82, 3713–3744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- OpenAI. ChatGPT: Optimizing Language Models for Dialogue 2022. Available online: https://openai.com/blog/chatgpt (accessed on 30 November 2022).
- Tiwari, D.; Nagpal, B.; Bhati, B.S.; Mishra, A.; Kumar, M. A systematic review of social network sentiment analysis with comparative study of ensemble-based techniques. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2023, 55, 13407–13461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandes, N.; Ofer, D.; Peleg, Y.; Rappoport, N.; Linial, M. ProteinBERT: A universal deep-learning model of protein sequence and function. Bioinformatics 2022, 38, 2102–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elnaggar, A.; Heinzinger, M.; Dallago, C.; Rehawi, G.; Wang, Y.; Jones, L.; Gibbs, T.; Feher, T.; Angerer, C.; Steinegger, M.; et al. ProtTrans: Toward Understanding the Language of Life Through Self-Supervised Learning. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2022, 44, 7112–7127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verkuil, R.; Kabeli, O.; Du, Y.; Wicky, B.I.M.; Milles, L.F.; Dauparas, J.; Baker, D.; Ovchinnikov, S.; Sercu, T.; Rives, A. Language models generalize beyond natural proteins. bioRxiv 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, R.; Bhattacharya, N.; Thomas, N.; Duan, Y.; Chen, X.; Canny, J.; Abbeel, P.; Song, Y.S. Evaluating Protein Transfer Learning with TAPE. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1906.08230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisby, T.S.; Langmead, C.J. Identifying promising sequences for protein engineering using a deep transformer protein language model. Proteins 2023, 91, 1471–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferruz, N.; Hocker, B. Controllable protein design with language models. Nat. Mach. Intell. 2022, 4, 521–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferruz, N.; Schmidt, S.; Hocker, B. ProtGPT2 is a deep unsupervised language model for protein design. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandra, A.; Tunnermann, L.; Lofstedt, T.; Gratz, R. Transformer-based deep learning for predicting protein properties in the life sciences. eLife 2023, 12, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morozov, V.; Rodrigues, C.H.M.; Ascher, D.B. CSM-Toxin: A Web-Server for Predicting Protein Toxicity. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sergeeva, A.P.; Katsamba, P.S.; Liao, J.; Sampson, J.M.; Bahna, F.; Mannepalli, S.; Morano, N.C.; Shapiro, L.; Friesner, R.A.; Honig, B. Free Energy Perturbation Calculations of Mutation Effects on SARS-CoV-2 RBD::ACE2 Binding Affinity. J. Mol. Biol. 2023, 435, 168187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Clark, A.J.; Negron, C.; Hauser, K.; Sun, M.; Wang, L.; Abel, R.; Friesner, R.A. Relative Binding Affinity Prediction of Charge-Changing Sequence Mutations with FEP in Protein–Protein Interfaces. J. Mol. Biol. 2019, 431, 1481–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Tsuboyama, K.; Dauparas, J.; Chen, J.; Laine, E.; Behbahani, Y.M.; Weinstein, J.J.; Mangan, N.M.; Ovchinnikov, S.; Rocklin, G.J. Mega-scale experimental analysis of protein folding stability in biology and design. Nature 2023, 31, 434–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colloch, N.; Etchebest, C.; Thoreau, E.; Henrissat, B.; Mornon, J.P. Comparison of 3 algorithms for the assignment of secondary structure in proteins—The advantages of a consensus assignment. Protein Eng. 1993, 6, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, S.K.S.; Narang, K.; Siegel, J.B. Protein stability prediction by fine-tuning a protein language model on a mega-scale dataset. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2024, 20, e1012248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cagiada, M.; Ovchinnikov, S.; Lindorff-Larsen, K. Predicting absolute protein folding stability using generative models. Protein Sci. 2025, 34, e5233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkisyan, K.S.; Bolotin, D.A.; Meer, M.V.; Usmanova, D.R.; Mishin, A.S.; Sharonov, G.V.; Ivankov, D.N.; Bozhanova, N.G.; Baranov, M.S.; Soylemez, O.; et al. Local fitness landscape of the green fluorescent protein. Nature 2016, 533, 397–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jankauskaite, J.; Jimenez-Garcia, B.; Dapkunas, J.; Fernandez-Recio, J.; Moal, I.H. SKEMPI 2.0: An updated benchmark of changes in protein-protein binding energy, kinetics and thermodynamics upon mutation. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 462–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sampson, J.M.; Cannon, D.A.; Duan, J.; Epstein, J.C.; Sergeeva, A.P.; Katsamba, P.S.; Mannepalli, S.M.; Bahna, F.A.; Adihou, H.; Guéret, S.M.; et al. Robust prediction of relative binding energies for protein-protein complex mutations using free energy perturbation calculations. J. Mol. Biol. 2024, 16, 168640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akiba, T.; Sano, S.; Yanase, T.; Ohta, T.; Koyama, M. Optuna: A Next-generation Hyperparameter Optimization Framework. In Proceedings of the KDD 2019 Applied Data Science Track, Anchorage, AK, USA, 4–8 August 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Abraham, M.J.; Murtola, T.; Schulz, R.; Páll, S.; Smith, J.C.; Hess, B.; Lindahl, E. GROMACS: High performance molecular simulations through multi-level parallelism from laptops to supercomputers. SoftwareX 2015, 1, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Friesner, R.A.; Berne, B.J. Replica Exchange with Solute Scaling: A more efficient version of Replica Exchange with Solute Tempering (REST2). J. Phys. Chem. B 2011, 115, 9431–9438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wang, L.; Chambers, J.; Abel, R. Protein–Ligand Binding Free Energy Calculations with FEP. Methods Mol. Biol. 2022, 2019, 201–232. [Google Scholar]
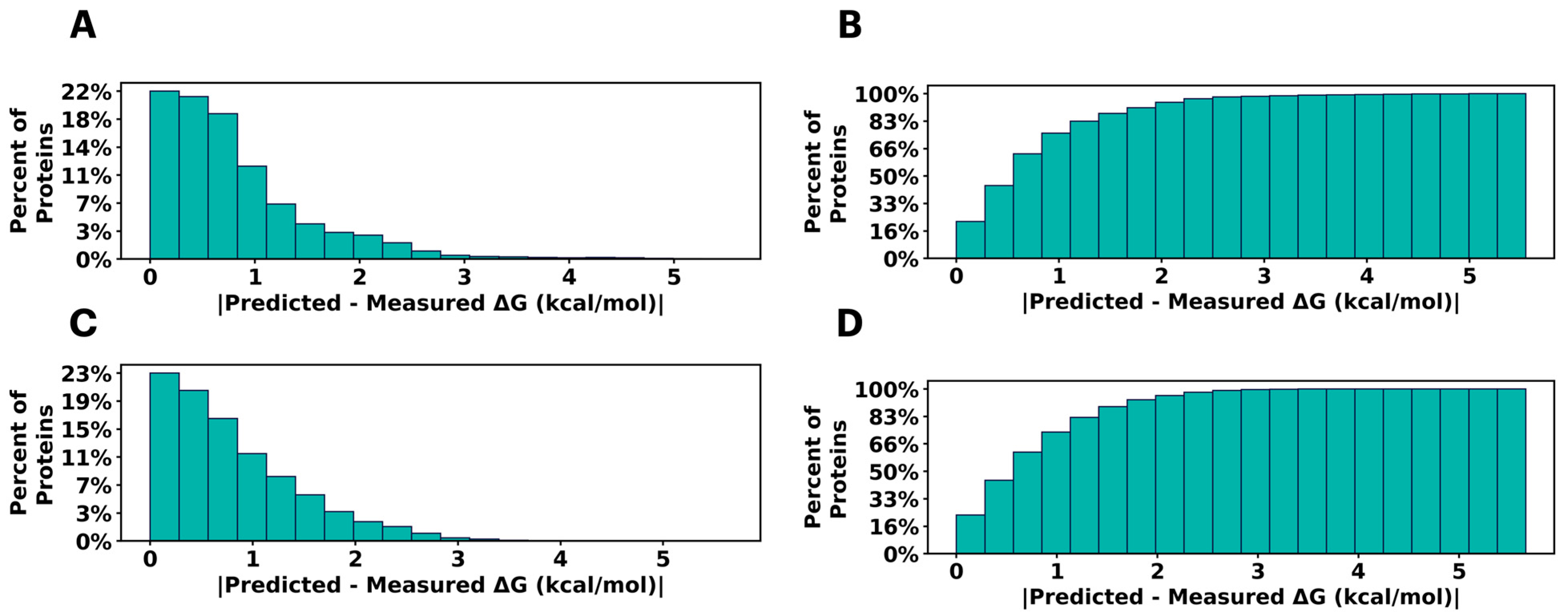
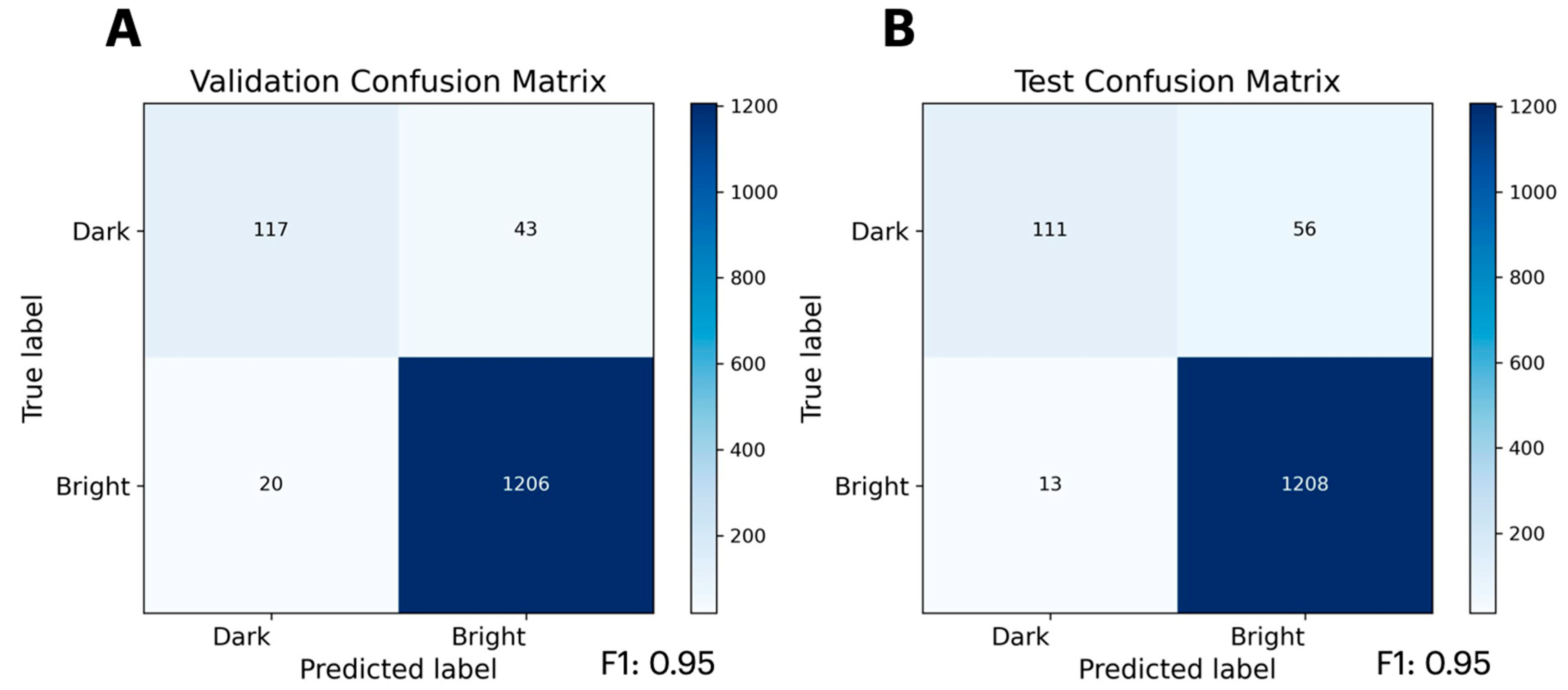
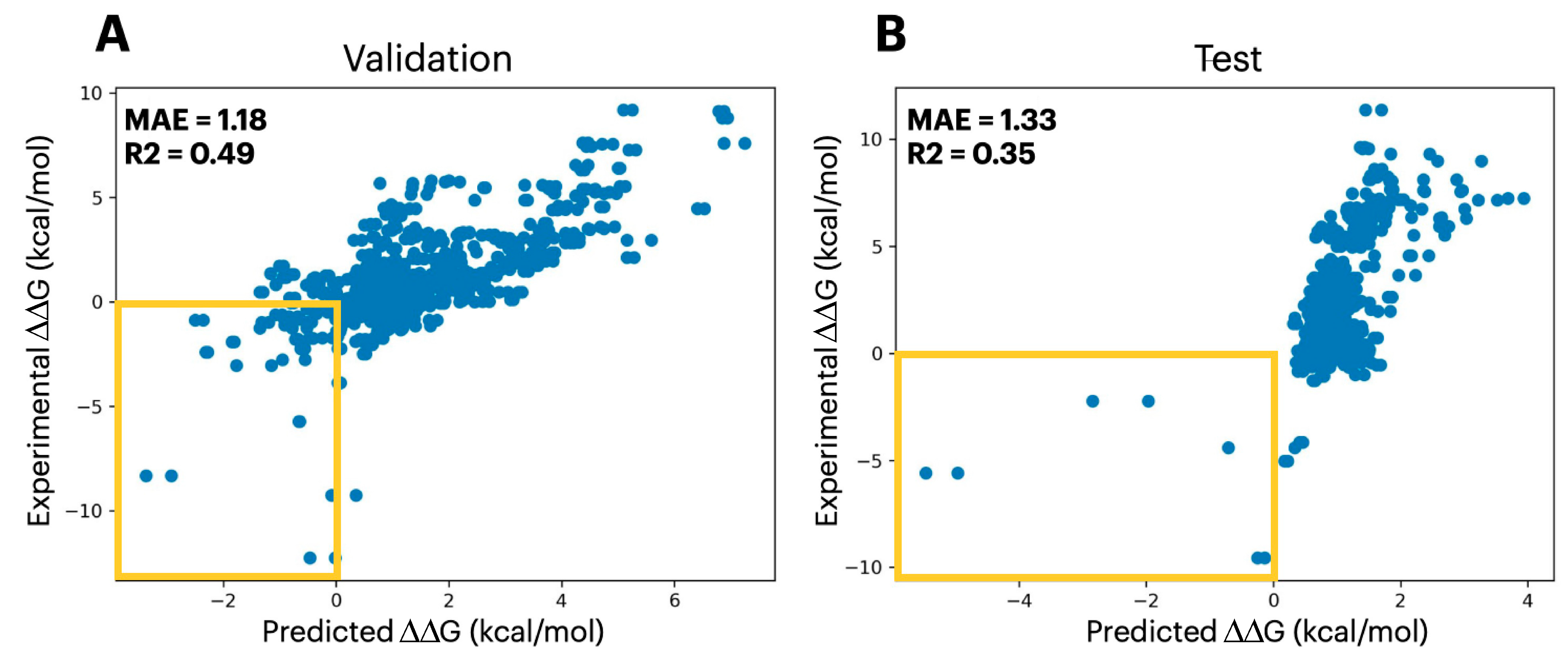
| Set | Datapoints | Domains | Bin 1 | Bin 2 | Bin 3 | Bin 4 | Bin 5 | Bin 6 | Bin 7 | Bin 8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Training (~80%) | 546,550 | 432 | 5.41 | 6.58 | 18.53 | 22.54 | 22.02 | 16.27 | 7.51 | 1.14 |
| Validation (~10%) | 74,169 | 55 | 6.92 | 6.47 | 16.82 | 24.50 | 22.81 | 14.41 | 7.33 | 0.74 |
| Testing (~10%) | 79,074 | 55 | 8.33 | 9.28 | 17.02 | 20.64 | 21.36 | 15.13 | 7.46 | 0.78 |
| Mutant | Experimental (kcal/mol) | FEP (kcal/mol) | PLM (kcal/mol) | FEP Error (kcal/mol) | PLM Error (kcal/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1B2U_A_A27K | −5.03 | −6.68 | 0.194 | 1.65 | 5.22 |
| 1B2U_A_A27K_D_A36D | −9.56 | −10.90 | −0.195 | 1.34 | 9.37 |
| 1CSO_I_I_18_L | −4.41 | −0.40 | −0.189 | 4.01 | 4.22 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Perez, R.; Ferrie, J.J.; Petersson, E.J.; Giannakoulias, S. Accurate Prediction of Protein Tertiary and Quaternary Stability Using Fine-Tuned Protein Language Models and Free Energy Perturbation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 7125. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157125
Li X, Perez R, Ferrie JJ, Petersson EJ, Giannakoulias S. Accurate Prediction of Protein Tertiary and Quaternary Stability Using Fine-Tuned Protein Language Models and Free Energy Perturbation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(15):7125. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157125
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xinning, Ryann Perez, John J. Ferrie, E. James Petersson, and Sam Giannakoulias. 2025. "Accurate Prediction of Protein Tertiary and Quaternary Stability Using Fine-Tuned Protein Language Models and Free Energy Perturbation" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 15: 7125. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157125
APA StyleLi, X., Perez, R., Ferrie, J. J., Petersson, E. J., & Giannakoulias, S. (2025). Accurate Prediction of Protein Tertiary and Quaternary Stability Using Fine-Tuned Protein Language Models and Free Energy Perturbation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(15), 7125. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157125







