Associations of Serum GIP, GLP-1, and DPP-4 with Metabolic and Hormonal Profiles and Tobacco Exposure in Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Results of Studied Parameters in the Group of Women with or Without PCOS
2.2. Results of Studied Parameters in the Group of Smoking and Non-Smoking Women with PCOS
2.3. The Studied Parameters in Women with PCOS Stratified According to Body Weight or IR
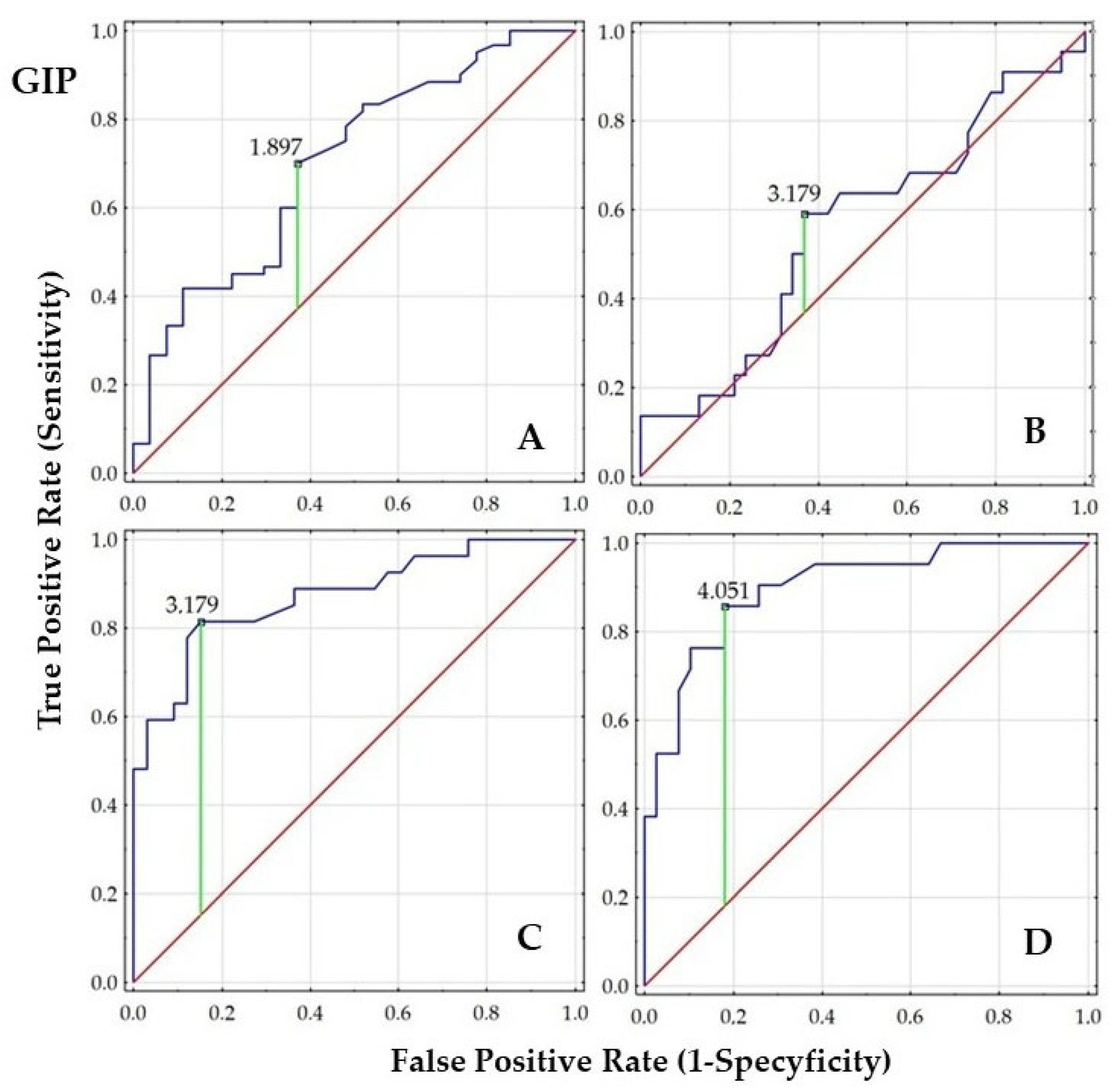
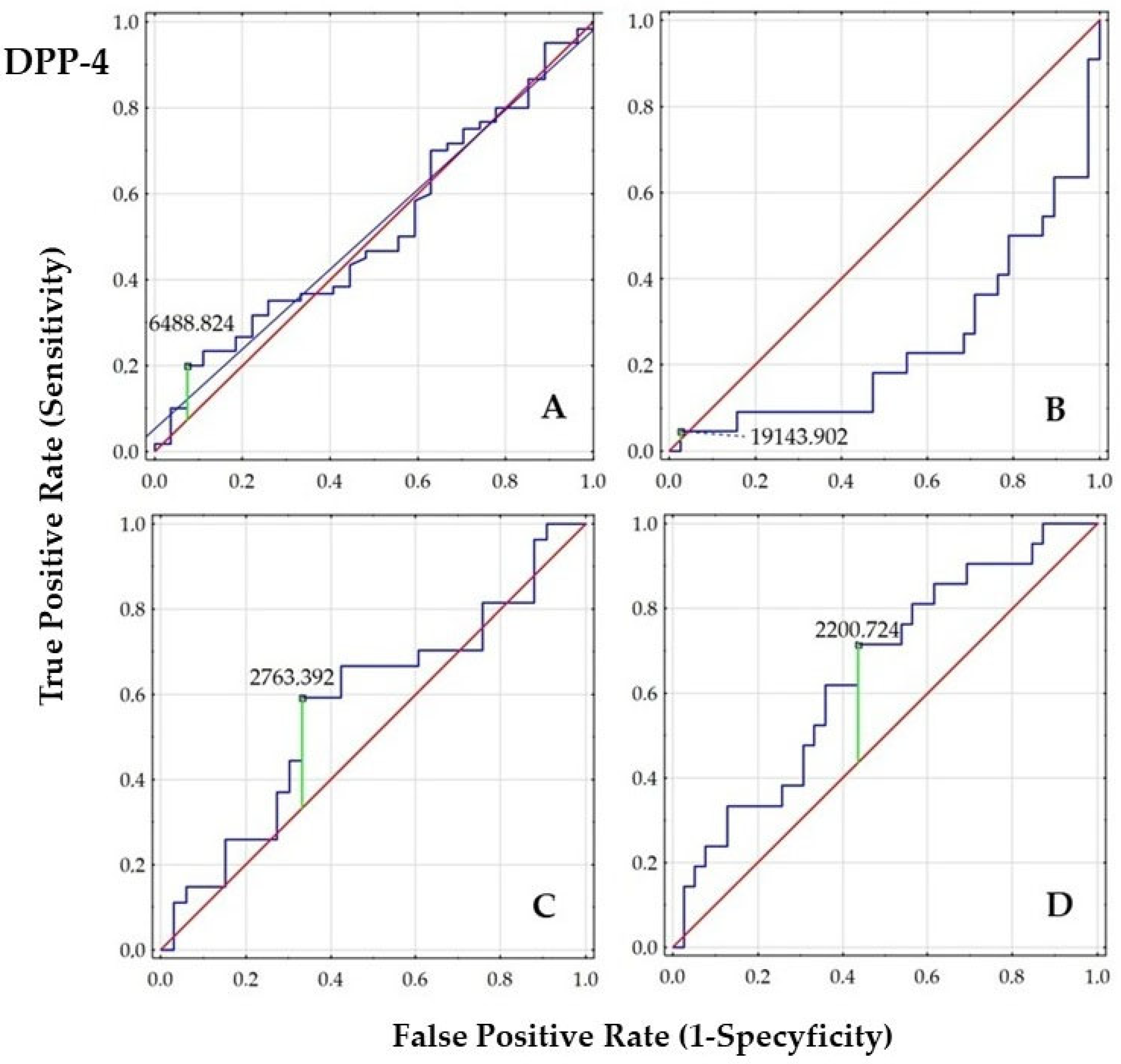
2.4. Diagnostic Value of GIP, GLP-1, and DPP-4
2.5. Correlations
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Methods
4.3. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PCOS | polycystic ovary syndrome |
| mFG | the modified Ferriman-Gallwey scale of hirsutism |
| G/I | glucose/insulin ratio |
| HOMA-IR | the Homeostatic Model Assessment for Insulin Resistance |
| QUICKI | the Quantitative Insulin Sensitivity Check Index |
| GIP | glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide |
| GLP-1 | glucagon-like-peptide-1 |
| DPP-4 | dipeptidyl peptidase-4 |
| LH/FSH | luteinizing hormone/follicle-stimulating hormone |
| DHEA-S | dehydroepiandrosterone sulphate |
| SHBG | sex hormone-binding globulin |
| tTest | total testosterone |
| fTest | free testosterone |
| AD | androstenedione |
| FAI | free androgen index |
| AMH | anti-Müllerian hormone |
| NA | not-applicable |
| NS | not-significant |
| BMI | body mass index |
| WHR | waist-to-hip ratio |
| WHtR | waist-to-height ratio |
| AUC | area under curve |
References
- Moran, L.J.; Misso, M.L.; Wild, R.A.; Norman, R.J. Impaired Glucose Tolerance, Type 2 Diabetes and Metabolic Syndrome in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Hum. Reprod. Update 2010, 16, 347–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, J.C.; Dunaif, A. Should All Women with PCOS Be Treated for Insulin Resistance? Fertil. Steril. 2012, 97, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Helden, J.; Evliyaoglu, O.; Küberl, A.; Weiskirchen, R. Disorders of the Glucose Metabolism Correlate with the Phenotype and the Severity in Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. Clin. Endocrinol. 2020, 93, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buggs, C.; Weinberg, F.; Kim, E.; Wolfe, A.; Radovick, S.; Wondisford, F. Insulin Augments GnRH-Stimulated LHbeta Gene Expression by Egr-1. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2006, 249, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawson, M.A.; Jain, S.; Sun, S.; Patel, K.; Malcolm, P.J.; Chang, R.J. Evidence for Insulin Suppression of Baseline Luteinizing Hormone in Women with Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome and Normal Women. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 93, 2089–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorn, C.; Mouillet, J.-F.; Yan, X.; Ou, Q.; Sadovsky, Y. Insulin Enhances the Transcription of Luteinizing Hormone-β Gene. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2004, 191, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, I.R.; McKinley, M.C.; Bell, P.M.; Hunter, S.J. Sex Hormone Binding Globulin and Insulin Resistance. Clin. Endocrinol. 2013, 78, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houston, E.J.; Templeman, N.M. Reappraising the Relationship between Hyperinsulinemia and Insulin Resistance in PCOS. J. Endocrinol. 2025, 265, e240269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brutocao, C.; Zaiem, F.; Alsawas, M.; Morrow, A.S.; Murad, M.H.; Javed, A. Psychiatric Disorders in Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Endocrine 2018, 62, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holst, J.J.; Gasbjerg, L.S.; Rosenkilde, M.M. The Role of Incretins on Insulin Function and Glucose Homeostasis. Endocrinology 2021, 162, bqab065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasbjerg, L.S.; Bergmann, N.C.; Stensen, S.; Christensen, M.B.; Rosenkilde, M.M.; Holst, J.J.; Nauck, M.; Knop, F.K. Evaluation of the Incretin Effect in Humans Using GIP and GLP-1 Receptor Antagonists. Peptides 2020, 125, 170183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Zhao, F.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, D.; Wang, M.-W. Structural Pharmacology and Mechanisms of GLP-1R Signaling. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2025, 46, 422–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfe, M.M.; Boylan, M.O.; Chin, W.W. Glucose-Dependent Insulinotropic Polypeptide in Incretin Physiology: Role in Health and Disease. Endocr. Rev. 2025, 46, 479–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamane, S.; Harada, N.; Inagaki, N. Physiology and Clinical Applications of GIP. Endocr. J. 2025, 72, 751–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horton, E.S.; Silberman, C.; Davis, K.L.; Berria, R. Weight Loss, Glycemic Control, and Changes in Cardiovascular Biomarkers in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Receiving Incretin Therapies or Insulin in a Large Cohort Database. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 1759–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razavi, M.; Wei, Y.-Y.; Rao, X.-Q.; Zhong, J.-X. DPP-4 Inhibitors and GLP-1RAs: Cardiovascular Safety and Benefits. Mil. Med. Res. 2022, 9, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Creanga, A.A.; Bradley, H.M.; McCormick, C.; Witkop, C.T. Use of Metformin in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: A Meta-Analysis. Obstet. Gynecol. 2008, 111, 959–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Qu, H.; Yang, L.; Shou, L. Effects of GLP1RAs on Pregnancy Rate and Menstrual Cyclicity in Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: A Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2023, 23, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grøndahl, M.F.; Bagger, J.I.; Lund, A.; Faurschou, A.; Rehfeld, J.F.; Holst, J.J.; Vilsbøll, T.; Knop, F.K. Effects of Smoking Versus Nonsmoking on Postprandial Glucose Metabolism in Heavy Smokers Compared with Nonsmokers. Diabetes Care 2018, 41, 1260–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piatti, P.; Setola, E.; Galluccio, E.; Costa, S.; Fontana, B.; Stuccillo, M.; Crippa, V.; Cappelletti, A.; Margonato, A.; Bosi, E.; et al. Smoking Is Associated with Impaired Glucose Regulation and a Decrease in Insulin Sensitivity and the Disposition Index in First-Degree Relatives of Type 2 Diabetes Subjects Independently of the Presence of Metabolic Syndrome. Acta Diabetol. 2014, 51, 793–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artese, A.; Stamford, B.A.; Moffatt, R.J. Cigarette Smoking: An Accessory to the Development of Insulin Resistance. Am. J. Lifestyle Med. 2019, 13, 602–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, A.; Mirahmad, M.; Mohajeri-Tehrani, M.R.; Jamalizadeh, M.; Hosseinimousa, S.; Rashidi, F.; Asili, P.; Sajjadi-Jazi, S.M. Risk Factors for Insulin Resistance Related to Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome in Iranian Population. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 10269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassar, S.; Misso, M.L.; Hopkins, W.G.; Shaw, C.S.; Teede, H.J.; Stepto, N.K. Insulin Resistance in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Euglycaemic–Hyperinsulinaemic Clamp Studies. Hum. Reprod. 2016, 31, 2619–2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gieroba, B.; Kryska, A.; Sroka-Bartnicka, A. Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus-Conventional Therapies and Future Perspectives in Innovative Treatment. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2025, 42, 102037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aydin, K.; Arusoglu, G.; Koksal, G.; Cinar, N.; Aksoy, D.Y.; Yildiz, B.O. Fasting and Post-Prandial Glucagon like Peptide 1 and Oral Contraception in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. Clin. Endocrinol. 2014, 81, 588–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robeva, R.; Kirilov, G.; Elenkova, A.; Zacharieva, S. Fasting GLP-1 Levels in Women with PCOS and CAH. Acta Medica Bulg. 2024, 51, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milewicz, T.; Migacz, K.; Kiałka, M.; Rogatko, I.; Kowalczuk, A.; Spalkowska, M.; Mrozińska, S.; Czajkowska, Z.; Sztefko, K. Basic and Meal Stimulated Plasma GIP Levels Are Higher in Lean PCOS Women with FAI over 5. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2016, 124, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seon, M.J.; Hwang, S.Y.; Son, Y.; Song, J.; Kim, O.Y. Circulating GLP-1 Levels as a Potential Indicator of Metabolic Syndrome Risk in Adult Women. Nutrients 2021, 13, 865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.L.; Huang, S.Y.; Soong, Y.K.; Cheng, P.J.; Wang, C.-J.; Liang, I.T. Circulating Irisin and Glucose-Dependent Insulinotropic Peptide Are Associated with the Development of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 99, E2539–E2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moffett, R.C.; Naughton, V. Emerging Role of GIP and Related Gut Hormones in Fertility and PCOS. Peptides 2020, 125, 170233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontikis, C.; Yavropoulou, M.P.; Toulis, K.A.; Kotsa, K.; Kazakos, K.; Papazisi, A.; Gotzamani-Psarakou, A.; Yovos, J.G. The Incretin Effect and Secretion in Obese and Lean Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: A Pilot Study. J. Womens Health 2011, 20, 971–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nauck, M.A.; Meier, J.J. Incretin Hormones: Their Role in Health and Disease. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2018, 20 (Suppl. 1), 5–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrbikova, J.; Hill, M.; Bendlova, B.; Grimmichova, T.; Dvorakova, K.; Vondra, K.; Pacini, G. Incretin Levels in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2008, 159, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krisai, P.; Aeschbacher, S.; Ruperti Repilado, F.J.; Schoen, T.; Reusser, A.; Meier, M.; Todd, J.; Estis, J.; Risch, M.; Risch, L.; et al. Healthy Lifestyle and Glucagon-like Peptide-1 in Young and Healthy Adults: A Population-Based Study. Prev. Med. 2017, 101, 72–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pankova, A.; Kralikova, E.; Kavalkova, P.; Stepankova, L.; Zvolska, K.; Haluzik, M. No Change in Serum Incretins Levels but Rise of Leptin Levels after Smoking Cessation: A Pilot Study. Physiol. Res. 2016, 65, 651–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stadler, M.; Tomann, L.; Storka, A.; Wolzt, M.; Peric, S.; Bieglmayer, C.; Pacini, G.; Dickson, S.L.; Brath, H.; Bech, P.; et al. Effects of Smoking Cessation on β-Cell Function, Insulin Sensitivity, Body Weight, and Appetite. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2014, 170, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Driva, S.; Korkontzelou, A.; Tonstad, S.; Tentolouris, N.; Litsiou, E.; Vasileiou, V.; Vassiliou, A.G.; Saltagianni, V.; Katsaounou, P. Metabolic Changes Following Smoking Cessation in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waylen, A.L.; Jones, G.L.; Ledger, W.L. Effect of Cigarette Smoking upon Reproductive Hormones in Women of Reproductive Age: A Retrospective Analysis. Reprod. Biomed. Online 2010, 20, 861–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chia, C.W.; Egan, J.M.; Ferrucci, L. Age-Related Changes in Glucose Metabolism, Hyperglycemia, and Cardiovascular Risk. Circ. Res. 2018, 123, 886–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalyani, R.R.; Egan, J.M. Diabetes and Altered Glucose Metabolism with Aging. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. N. Am. 2013, 42, 333–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClean, P.L.; Irwin, N.; Cassidy, R.S.; Holst, J.J.; Gault, V.A.; Flatt, P.R. GIP Receptor Antagonism Reverses Obesity, Insulin Resistance, and Associated Metabolic Disturbances Induced in Mice by Prolonged Consumption of High-Fat Diet. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 293, E1746–E1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosman, G.G.; Katcher, H.I.; Legro, R.S. Obesity and the Role of Gut and Adipose Hormones in Female Reproduction. Hum. Reprod. Update 2006, 12, 585–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishiyama, Y.; Hasegawa, T.; Fujita, S.; Iwata, N.; Nagao, S.; Hosoya, T.; Inagaki, K.; Wada, J.; Otsuka, F. Incretins Modulate Progesterone Biosynthesis by Regulating Bone Morphogenetic Protein Activity in Rat Granulosa Cells. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2018, 178, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Li, Y.; He, B. GLP-1 Receptor Agonists versus Metformin in PCOS: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Reprod. Biomed. Online 2019, 39, 332–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tzotzas, T.; Karras, S.N.; Katsiki, N. Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 (GLP-1) Receptor Agonists in the Treatment of Obese Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. Curr. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2017, 15, 218–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farkas, I.; Vastagh, C.; Farkas, E.; Bálint, F.; Skrapits, K.; Hrabovszky, E.; Fekete, C.; Liposits, Z. Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Excites Firing and Increases GABAergic Miniature Postsynaptic Currents (mPSCs) in Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone (GnRH) Neurons of the Male Mice via Activation of Nitric Oxide (NO) and Suppression of Endocannabinoid Signaling Pathways. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, S.; Yang, H.; Ji, Y.; Wu, W.; Dong, Y.; Fu, H.; Tang, N.; Hou, Z.; Wang, F. Liraglutide Improves PCOS Symptoms in Rats by Targeting FDX1. Reprod. Sci. Thousand Oaks Calif 2024, 31, 2049–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferjan, S.; Janez, A.; Jensterle, M. DPP4 inhibitor sitagliptin as a potential treatment option in metformin-intolerant obese women with polycystic ovary syndrome: A pilot randomized study. Endocr. Pract. 2018, 24, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, Y.; Zhao, J.; Liu, C.; Yu, T. Comparative Efficacy of Pharmacological Interventions on Metabolic and Hormonal Outcomes in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: A Network Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. BMC Womens Health 2025, 25, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.K. Mechanisms of Action and Therapeutic Applications of GLP-1 and Dual GIP/GLP-1 Receptor Agonists. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1431292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotterdam ESHRE/ASRM-Sponsored PCOS consensus workshop group. Revised 2003 Consensus on Diagnostic Criteria and Long-Term Health Risks Related to Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS). Hum. Reprod. 2004, 19, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niepsuj, J.; Piwowar, A.; Franik, G.; Bizoń, A. The Concentration of Follistatin and Activin A in Serum and Selected Biochemical Parameters in Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: Stratification by Tobacco Smoke Exposure, Insulin Resistance, and Overweight/Obesity. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 5316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duque, A.; Martínez, P.-J.; Giraldo, A.; Gualtero, D.-F.; Ardila, C.-M.; Contreras, A.; Duarte, S.; Lafaurie, G.-I. Accuracy of Cotinine Serum Test to Detect the Smoking Habit and Its Association with Periodontal Disease in a Multicenter Study. Med. Oral Patol. Oral Cir. Bucal 2017, 22, e425–e431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biernacka-Bartnik, A.; Kocełak, P.; Owczarek, A.J.; Choręza, P.S.; Markuszewski, L.; Madej, P.; Puzianowska-Kuźnicka, M.; Chudek, J.; Olszanecka-Glinianowicz, M. The Cut-off Value for HOMA-IR Discriminating the Insulin Resistance Based on the SHBG Level in Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. Front. Med. 2023, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.A. Comparison of Insulin Resistance Scoring System with Indirect Methods of Estimating Insulin Resistance in Indian Type 2 Diabetes Subjects. Int. J. Med. Res. Rev. 2019, 7, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flegal, K.M.; Shepherd, J.A.; Looker, A.C.; Graubard, B.I.; Borrud, L.G.; Ogden, C.L.; Harris, T.B.; Everhart, J.E.; Schenker, N. Comparisons of Percentage Body Fat, Body Mass Index, Waist Circumference, and Waist-Stature Ratio in Adults. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 89, 500–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franik, G.; Bizoń, A.; Włoch, S.; Pluta, D.; Blukacz, Ł.; Milnerowicz, H.; Madej, P. The Effect of Abdominal Obesity in Patients with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome on Metabolic Parameters. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2017, 21, 4755–4761. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ashwell, M.; Gibson, S. A Proposal for a Primary Screening Tool: “Keep Your Waist Circumference to Less than Half Your Height. ” BMC Med. 2014, 12, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Parameters | PCOS Women | Women without PCOS | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| n = 60 | n = 28 | ||
| Age (years) | 25.50 ± 3.83 24.50 (22.00–28.00) | 26.71 ± 5.87 27.00 (22.00–31.00) | 0.480 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 26.13 ± 6.74 23.93 (20.76–30.86) | 22.62 ± 4.58 21.63 (20.57–23.03) | 0.21 |
| mFG score of hirsutism | 5.87 ± 4.63 6.00 (1.50–9.00) | NA | NA |
| Glucose 0′ (mg/dL) | 85.31 ± 6.75 84.35 (80.80–89.30) | 81.65 ± 5.19 80.50 (78.50–86.80) | 0.049 |
| Glucose 120′ (mg/dL) | 118.41 ± 41.95 111.77 (89.20–130.00) | 94.40 ± 27.06 93.50 (80.20–103.00) | 0.066 |
| Insulin 0′ (mU/mL) | 9.50 ± 6.86 7.14 (5.18–12.15) | 5.34 ± 2.52 5.93 (3.49–6.77) | 0.002 |
| G/I ratio | 12.55 ± 6.83 11.78 (7.42–16.09) | 20.95 ± 13.52 14.15 (11.86–26.46) | 0.003 |
| HOMA-IR | 2.06 ± 1.70 1.51 (1.04–2.68) | 1.09 ± 0.52 1.18 (0.70–1.41) | 0.002 |
| QUICKI | 0.36 ± 0.03 0.36 (0.33–0.38) | 0.39 ± 0.04 0.37 (0.36–0.42) | 0.002 |
| GIP (ng/mL) | 6.75 ± 17.75 2.46 (1.67–6.67) | 2.70 ± 4.18 1.54 (1.03–2.80) | 0.003 |
| GLP-1 (ng/mL) | 1.49 ± 2.44 0.66 (0.41–1.41) | 0.65 ± 0.94 0.43 (0.27–0.69) | 0.005 |
| DPP-4 (µg/mL) | 4.31 ± 5.53 2.37 (1.15–4.56) | 3.86 ± 5.10 2.64 (1.23–4.22) | 0.819 |
| LH/FSH ratio | 1.44 ± 0.70 1.26 (1.00–1.65) | 0.98 ± 0.83 0.79 (0.54–1.18) | 0.001 |
| Cortisol (µg/dL) | 12.84 ± 3.91 12.65 (9.86–16.00) | 14.31 ± 5.66 13.75 (10.80–17.50) | 0.381 |
| DHEA-S (µg/mL) | 320.63 ± 135.59 294.00 (222.00–386.50) | 252.51 ± 143.42 230.00 (164.00–295.00) | 0.015 |
| SHBG (nmol/L) | 56.54 ± 35.99 39.95 (28.40–55.50) | 68.91 ± 37.07 62.50 (50.20–71.60) | 0.118 |
| tTest (ng/mL) | 0.41 ± 0.16 0.36 (0.30–0.53) | 0.30 ± 0.22 0.26 (0.16–0.32) | 0.004 |
| fTest (pg/mL) | 3.20 ± 2.78 2.11 (1.46–4.00) | 2.22 ± 2.25 1.45 (0.71–2.06) | 0.042 |
| AD (ng/mL) | 2.48 ± 0.90 2.33 (1.89–2.83) | 2.06 ± 0.73 1.86 (1.59–2.20) | 0.085 |
| FAI | 3.74 ± 3.15 2.78 (1.60–4.40) | 1.83 ± 1.54 1.2 (0.72–2.61 | 0.005 |
| AMH (ng/mL) | 6.28 ± 3.06 5.98 (3.93–7.78) | 3.18 ± 2.18 2.47 (1.63–4.49) | 0.001 |
| Parameters | Smoking with PCOS | Non-Smoking with PCOS | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| n = 23 | n = 37 | ||
| Age (years) | 26.46 ± 4.47 25.50 (23.00–29.00) | 24.51 ± 4.79 24.50 (22.00–27.00) | 0.262 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 27.30 ± 7.57 25.55 (21.01–31.25) | 25.15 ± 7.14 23.66 (20.42–29.49) | 0.381 |
| mFG score of hirsutism | 5.48 ± 3.93 6.00 (2.00–8.00) | 6.02 ± 5.23 5.00 (1.50–9.00) | 0.837 |
| Glucose 0′ (mg/dL) | 87.96 ± 7.96 86.65 (81.00–92.00) | 83.45 ± 5.20 83.50 (79.80–87.50) | 0.040 |
| Glucose 120′ (mg/dL) | 118.41 ± 41.95 111.00 (95.50–133.00) | 106.67 ± 33.41 96.65 (85.40–125.00) | 0.289 |
| Insulin 0′ (mU/mL) | 9.55 ± 7.76 7.52 (5.37–11.40) | 9.72 ± 7.00 6.97 (4.98–12.50) | 0.958 |
| G/I ratio | 13.61 ± 8.61 11.44 (7.52–16.65) | 11.93 ± 5.59 11.91 (7.40–16.03) | 0.790 |
| HOMA-IR | 2.17 ± 2.11 1.54 (1.09–2.41) | 2.07 ± 1.60 1.50 (0.98–2.76) | 0.885 |
| QUICKI | 0.36 ± 0.04 0.36 (0.34–0.38) | 0.36 ± 0.03 0.36 (0.33–0.39) | 0.897 |
| GIP (ng/mL) | 9.75 ± 17.77 3.64 (1.69–7.03) | 5.00 ± 5.69 2.41 (1.64–6.31) | 0.460 |
| GLP-1 (ng/mL) | 2.11 ± 3.69 0.83 (0.42–1.42) | 1.13 ± 1.20 0.63 (0.40–1.41) | 0.527 |
| DPP-4 (µg/mL) | 2.52 ± 4.12 1.37 (0.62–2.20) | 5.34 ± 6.02 3.06 (1.81–6.49) | 0.001 |
| LH/FSH ratio | 1.51 ± 0.84 1.19 (0.96–1.79) | 1.40 ± 0.60 1.28 (1.00–1.58) | 0.958 |
| Cortisol (µg/dL) | 11.43 ± 3.80 11.00 (8.99–13.70) | 13.65 ± 3.78 14.40 (11.00–17.00) | 0.036 |
| DHEA-S (µg/mL) | 306.14 ± 161.93 252.00 (192.00–362.00) | 326.50 ± 127.11 301.00 (223.00–397.00) | 0.176 |
| SHBG (nmol/L) | 49.56 ± 34.26 39.95 (28.40–55.50) | 62.85 ± 43.64 58.55 (34.40–74.70) | 0.103 |
| tTest (ng/mL) | 0.39 ± 0.17 0.35 (0.29–0.57) | 0.41 ± 0.17 0.38 (0.31–0.51) | 0.549 |
| fTest (pg/mL) | 3.26 ± 3.18 1.98 (1.47–4.11) | 3.14 ± 2.58 2.18 (1.51–3.88) | 0.825 |
| AD (ng/mL) | 2.11 ± 0.60 2.13 (1.65–2.57) | 2.66 ± 1.04 2.48 (1.90–3.39) | 0.048 |
| FAI | 4.28 ± 3.57 3.48 (1.54–5.67) | 3.55 ± 3.12 2.73 (1.74–3.95) | 0.414 |
| AMH (ng/mL) | 5.12 ± 2.64 5.20 (3.19–6.39) | 6.95 ± 3.53 6.66 (3.98–9.34) | 0.029 |
| Variables | Normal Weight Women with PCOS | Elevated Weight Women with PCOS | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-Smoking | Smoking | Non-Smoking | Smoking | |
| n = 23 | n = 10 | n = 15 | n = 12 | |
| Glucose 0′ (mg/dL) | 83.43 ± 5.57 83.45 (79.65–86.75) | 85.14 ± 5.09 86.250 (80.90–87.60) | 85.34 ± 5.83 86.10 (80.85–90.20) | 90.31 ± 9.29 88.50 (82.25–96.85) |
| Glucose 120′ (mg/dL) | 100.61 ± 22.87 95.40 (84.75–113.50) | 110.06 ± 21.53 111.00 (95.50–124.00) | 122.83 ± 38.47 118.00 (90.85–148.50) 2 | 125.36 ± 53.52 111.00 (91.65–137.00) |
| Insulin 0′ (mU/mL) | 6.44 ± 2.56 6.11 (4.33–7.29) | 5.66 ± 2.92 5.02 (3.52–7.38) | 14.40 ± 7.14 12.85 (9.66–18.50) 1 | 12.71 ± 9.10 10.65 (7.11–14.75) 3 |
| G/I ratio | 14.86 ± 4.51 13.74 (11.75–18.03) | 19.06 ± 9.75 17.63 (11.74–26.99) | 7.45 ± 3.88 6.53 (4.48–10.24) 1 | 9.07 ± 3.78 8.89 (6.61–12.35) 3 |
| HOMA-IR | 1.35 ± 0.62 1.26 (0.85–1.56) | 1.18 ± 0.58 1.09 (0.81–1.50) | 3.07 ± 1.63 2.76 (2.00–3.85) 1 | 2.99 ± 2.56 2.35 (1.55–3.26) 3 |
| QUICKI | 0.37 ± 0.02 0.37 (0.36–0.40) | 0.38 ± 0.03 0.38 (0.36–0.40) | 0.33 ± 0.03 0.33 (0.31–0.35) 1 | 0.34 ± 0.03 0.34 (0.32–0.36) 3 |
| GIP (ng/mL) | 2.20 ± 1.46 2.05 (1.23–2.41) | 2.40 ± 1.53 1.92 (1.33–3.18) | 9.30 ± 7.04 7.44 (4.05–13.85) 1 | 15.89 ± 22.59 5.95 (3.64–22.08) 3 |
| GLP-1 (ng/mL) | 0.54 ± 0.33 0.50 (0.30–0.62) | 0.55 ± 0.33 0.45 (0.33–0.78) | 2.04 ± 1.47 1.69 (0.82–3.00) 1 | 3.41 ± 4.67 1.31 (0.80–4.85) 3 |
| DPP-4 (µg/mL) | 4.87 ± 6.66 2.42 (1.34–5.69) | 1.88 ± 2.40 1.55 (0.51–1.93) * | 6.08 ± 5.00 4.13 (2.76–7.68) | 3.05 ± 5.20 1.13 (0.65–3.14) ** |
| Variables | HOMA-IR < 2.0 in Women with PCOS | HOMA-IR ≥2.0 in Women with PCOS | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-Smoking | Smoking | Non-Smoking | Smoking | |
| n = 25 | n = 14 | n = 13 | n = 8 | |
| Glucose 0′ (mg/dL) | 81.78 ± 4.80 82.30 (77.60–84.40) | 85.19 ± 4.64 86.25 (81.00–87.60) | 87.59 ± 4.80 88.90 (83.70–91.00) 2 | 92.80 ± 10.38 92.85 (83.30–100.00) |
| Glucose 120′ (mg/dL) | 99.85 ± 24.57 92.90 (83.50–115.00) | 105.90 ± 23.12 107.50 (77.60–124.00) | 123.47 ± 34.17 108.00 (95.90–148.00) 2 | 140.23 ± 58.54 125.00 (105.50–154.50) |
| Insulin 0′ (mU/mL) | 5.90 ± 1.76 6.08 (4.38–6.89) | 5.69 ± 2.07 5.79 (4.10–7.38) | 16.36 ± 6.44 13.40 (12.50–18.70) 1 | 16.31 ± 9.53 12.75 (11.30–16.60) 3 |
| G/I ratio | 14.98 ± 4.19 13.74 (12.01–17.92) | 17.60 ± 8.38 14.51 (11.74–19.21) | 6.07 ± 2.17 6.05 (4.48–7.40) 1 | 6.63 ± 2.10 6.85 (5.46–8.23) 3 |
| HOMA-IR | 1.20 ± 0.38 1. 17 (0.86–1.48) | 1.19 ± 0.43 1.22 (0.83–1.50) | 3.53 ± 1.46 2.91 (2.76–3.87) 1 | 3.87 ± 2.79 2.95 (2.41–3.68) 3 |
| QUICKI | 0.38 ± 0.02 0.37 (0.36–0.94) | 0.38 ± 0.03 0.37 (0.36–0.40) | 0.32 ± 0.02 0.33 (0.31–0.33) 1 | 0.32 ± 0.02 0.33 (0.32–0.34) 3 |
| GIP (ng/mL) | 2.24 ± 1.47 2.05 (1.28–2.41) | 3.34 ± 3.00 2.31 (1.59–4.15) | 10.32 ± 7.00 8.87 (5.64–13.85) 1 | 20.97 ± 26.53 6.23 (4.49–33.28) 4 |
| GLP-1 (ng/mL) | 0.55 ± 0.33 0.50 (0.32–0.66) | 0.78 ± 0.70 0.55 (0.34–0.89) | 2.25 ± 1.45 1.81 (1.25–3.00) 1 | 4.45 ± 5.49 1.31 (1.05–7.22) 4 |
| DPP-4 (µg/mL) | 5.10 ± 6.34 3.19 (1.89–5.69) | 1.04 ± 0.65 * 1.05 (0.51–1.58) | 5.81 ± 5.55 2.93 (1.81–7.15) | 5.11 ± 6.17 3.14 (1.44–6.00) 4 |
| AUC | SE | AUC Lower 95% | AUC Upper 95% | z = (v1–0.5)/v2 | p-Value | |
| Entire Cohort: PCOS vs. Controls (A) | ||||||
| GIP (ng/mL) | 0.699 | 0.061 | 0.58 | 0.818 | 3.278 | 0.001 |
| GLP-1 (ng/mL) | 0.688 | 0.06 | 0.571 | 0.804 | 3.152 | 0.002 |
| DPP-4 (µg/mL) | 0.516 | 0.066 | 0.387 | 0.646 | 0.243 | 0.808 |
| PCOS Group Stratified by Smoking Status (B) | ||||||
| GIP (ng/mL) | 0.559 | 0.079 | 0.404 | 0.713 | 0.744 | 0.457 |
| GLP-1 (ng/mL) | 0.55 | 0.079 | 0.394 | 0.705 | 0.625 | 0.532 |
| DPP-4 (µg/mL) | 0.244 | 0.067 | 0.112 | 0.376 | −3.798 | 0.001 |
| PCOS Group Stratified by Body Weight (C) | ||||||
| GIP (ng/mL) | 0.939 | 0.035 | 0.871 | 1 | 12.705 | 0.001 |
| GLP-1 (ng/mL) | 0.942 | 0.036 | 0.871 | 1 | 12.194 | 0.001 |
| DPP-4 (µg/mL) | 0.579 | 0.078 | 0.426 | 0.731 | 1.011 | 0.312 |
| PCOS Group Stratified by Insulin Resistance (HOMA-IR <2.0 or ≥2.0) (D) | ||||||
| GIP (ng/mL) | 0.899 | 0.042 | 0.818 | 0.981 | 9.573 | 0.001 |
| GLP-1 (ng/mL) | 0.893 | 0.045 | 0.805 | 0.981 | 8.729 | 0.001 |
| DPP-4 (µg/mL) | 0.648 | 0.073 | 0.505 | 0.792 | 2.023 | 0.043 |
| GIP (ng/mL) | GLP-1 (ng/mL) | DPP-4 (µg/mL) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| GIP (ng/mL) | - | 0.99; p < 0.000 | NS |
| GLP-1 (ng/mL) | 0.99; p < 0.001 | - | NS |
| DPP-4 (µg/mL) | NS | NS | - |
| Age (years) | NS | NS | NS |
| Cotinine (ng/mL) | NS | NS | −0.41; p < 0.001 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 0.64; p < 0.001 | 0.65; p < 0.001 | NS |
| WHR | 0.55; p < 0.001 | 0.56; p < 0.001 | 0.35; p < 0.007 |
| WHtR | 0.66; p < 0.001 | 0.67; p < 0.001 | NS |
| Glucose 0′ (mg/dL) | 0.35; p < 0.006 | 0.36; p < 0.005 | NS |
| Glucose 120′ (mg/dL) | 0.29; p < 0.022 | 0.31; p < 0.015 | NS |
| Insulin 0′ (mU/mL) | 0.82; p < 0.001 | 0.79; p < 0.001 | NS |
| G/I | −0.82; p < 0.001 | −0.79; p < 0.001 | NS |
| HOMA-IR | 0.80; p < 0.001 | 0.79; p < 0.001 | NS |
| QUICKI | −0.80; p < 0.001 | −0.79; p < 0.001 | NS |
| LH/FSH | NS | NS | NS |
| Cortisol (µg/dL) | NS | NS | NS |
| DHEA-S (µg/mL) | NS | NS | NS |
| SHBG (nmol/L) | −0.72; p < 0.001 | −0.71; p < 0.001 | NS |
| tTest (ng/mL) | NS | NS | NS |
| fTest (pg/mL) | 0.41; 0.001 | 0.42; p < 0.001 | NS |
| AD (ng/mL) | NS | NS | NS |
| FAI | 0.65; p < 0.001 | 0.65; p < 0.001 | NS |
| AMH (ng/mL) | NS | NS | NS |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bizoń, A.; Borkowska, J.; Franik, G.; Piwowar, A. Associations of Serum GIP, GLP-1, and DPP-4 with Metabolic and Hormonal Profiles and Tobacco Exposure in Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 7097. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157097
Bizoń A, Borkowska J, Franik G, Piwowar A. Associations of Serum GIP, GLP-1, and DPP-4 with Metabolic and Hormonal Profiles and Tobacco Exposure in Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(15):7097. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157097
Chicago/Turabian StyleBizoń, Anna, Julia Borkowska, Grzegorz Franik, and Agnieszka Piwowar. 2025. "Associations of Serum GIP, GLP-1, and DPP-4 with Metabolic and Hormonal Profiles and Tobacco Exposure in Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 15: 7097. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157097
APA StyleBizoń, A., Borkowska, J., Franik, G., & Piwowar, A. (2025). Associations of Serum GIP, GLP-1, and DPP-4 with Metabolic and Hormonal Profiles and Tobacco Exposure in Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(15), 7097. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157097






