Lycium barbarum Glycopeptide Inhibits Colorectal Cancer Cell Proliferation via Activating p53/p21 Pathway and Inducing Cellular Senescence
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
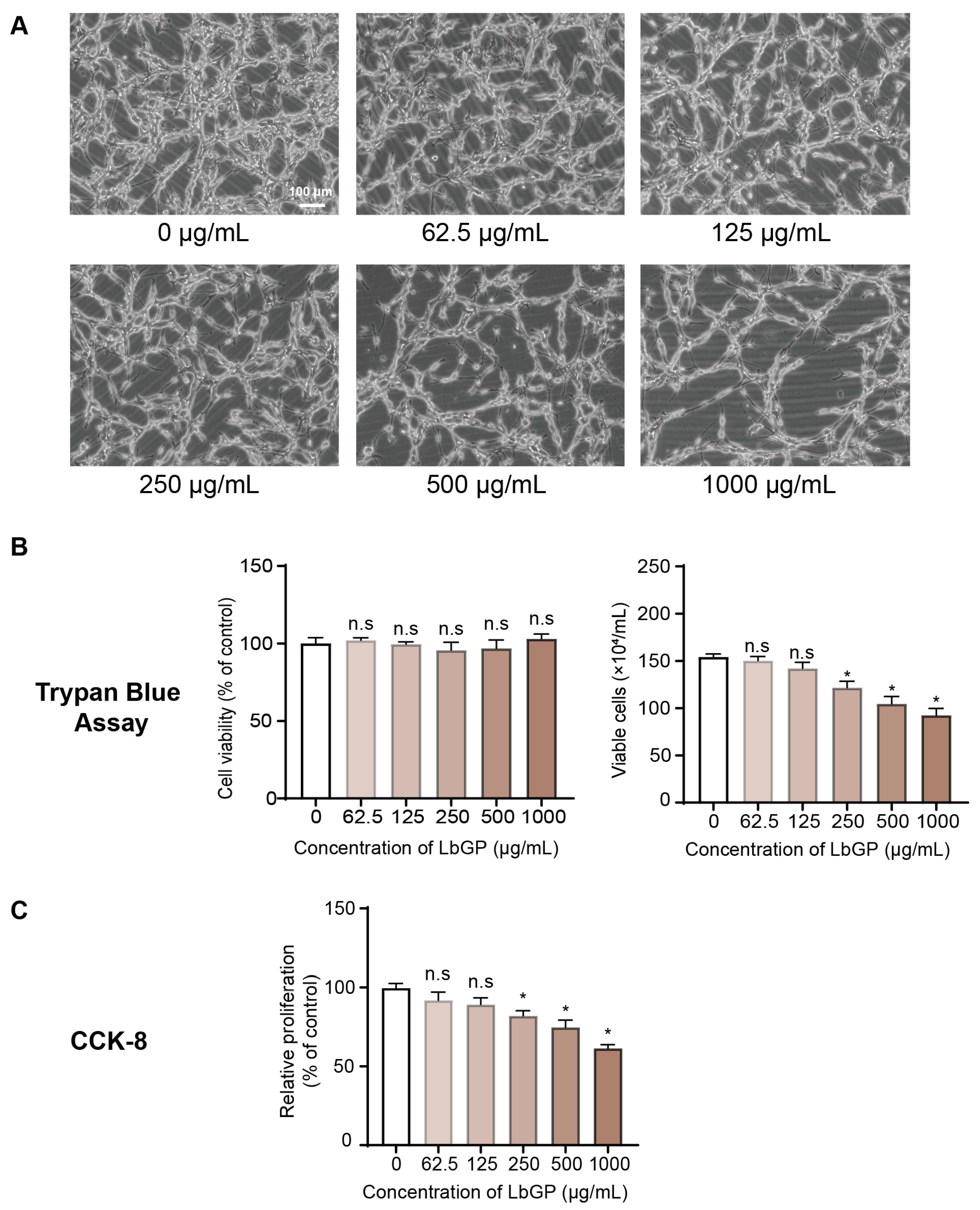
2.1. LbGP Inhibits CT26 Cell Proliferation
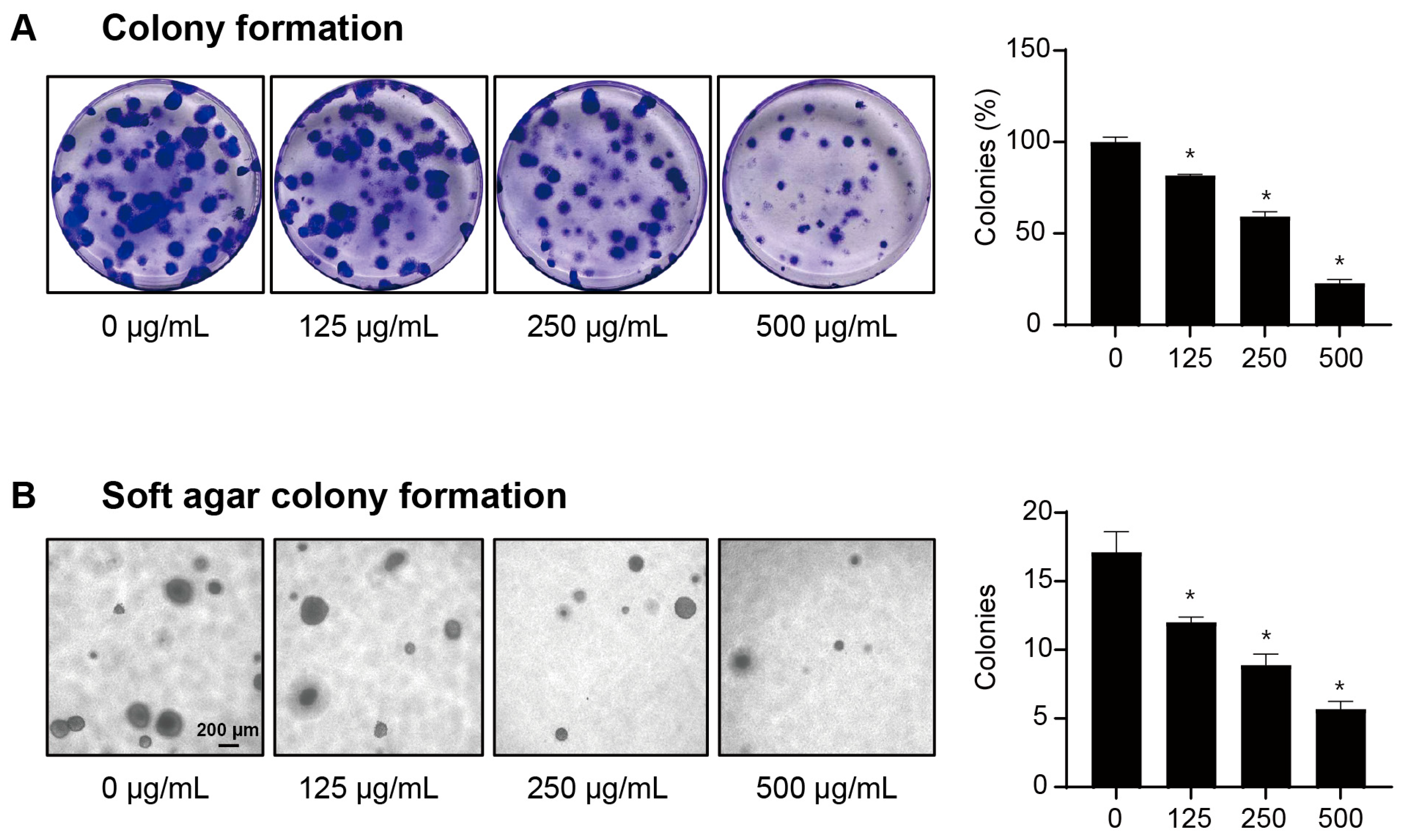
2.2. LbGP Reduces the Clonogenic Capacity of CT26 Cells
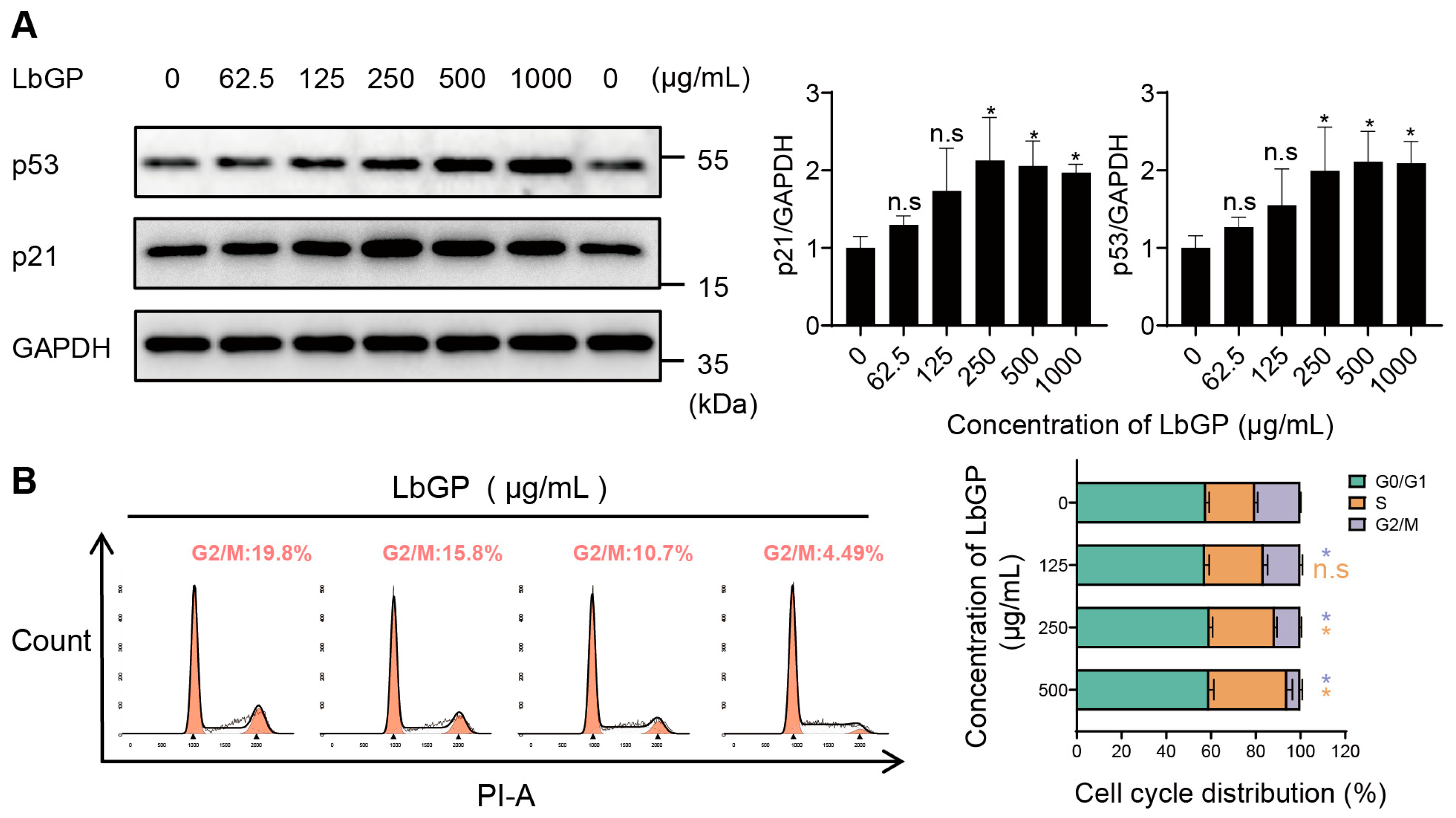
2.3. LbGP Arrests Cell Cycle of CT26 via Upregulating p53/p21
2.4. LbGP Promotes Cellular Senescence In Vitro
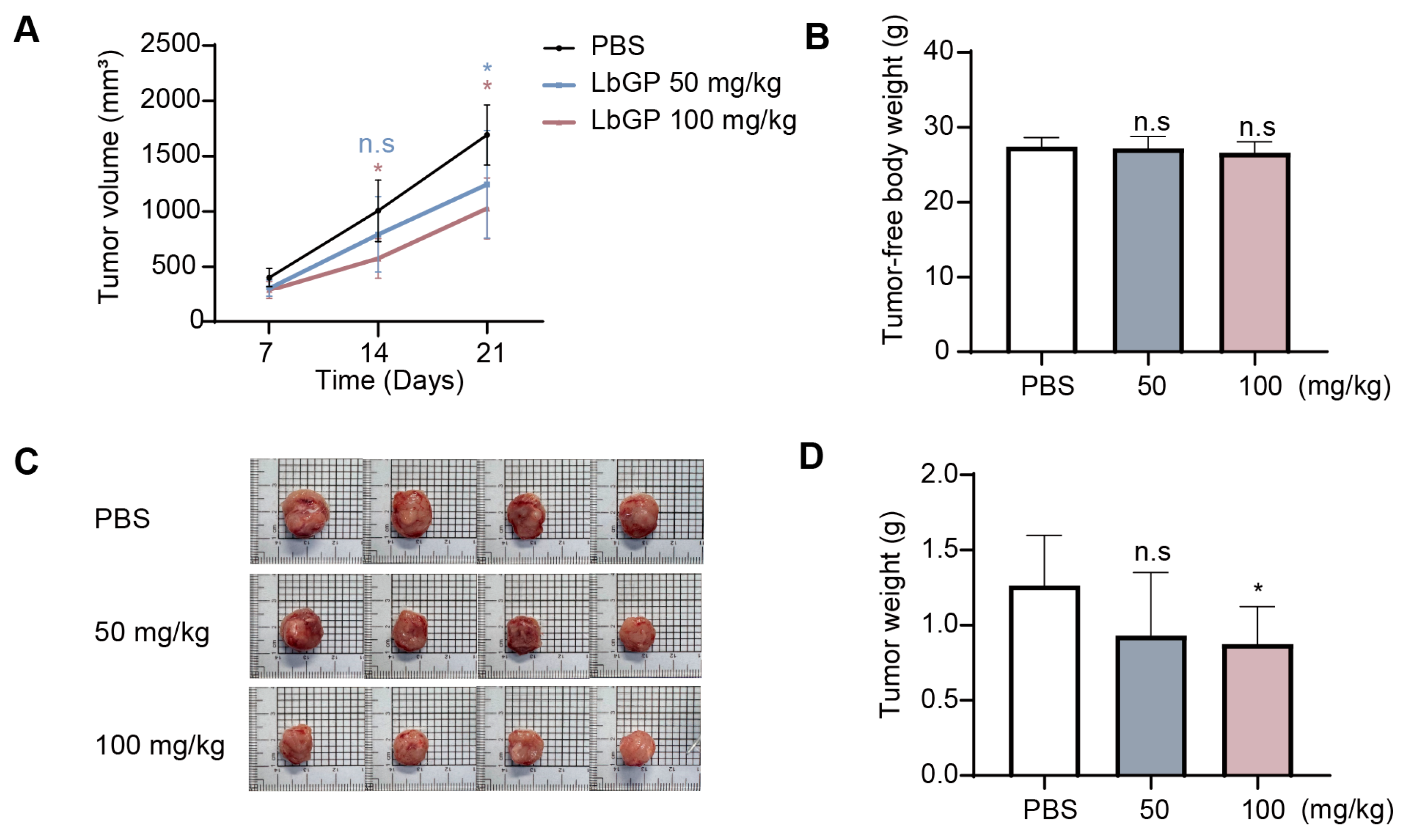
2.5. LbGP Suppresses Tumor Growth in CT26 Tumor-Bearing Mice
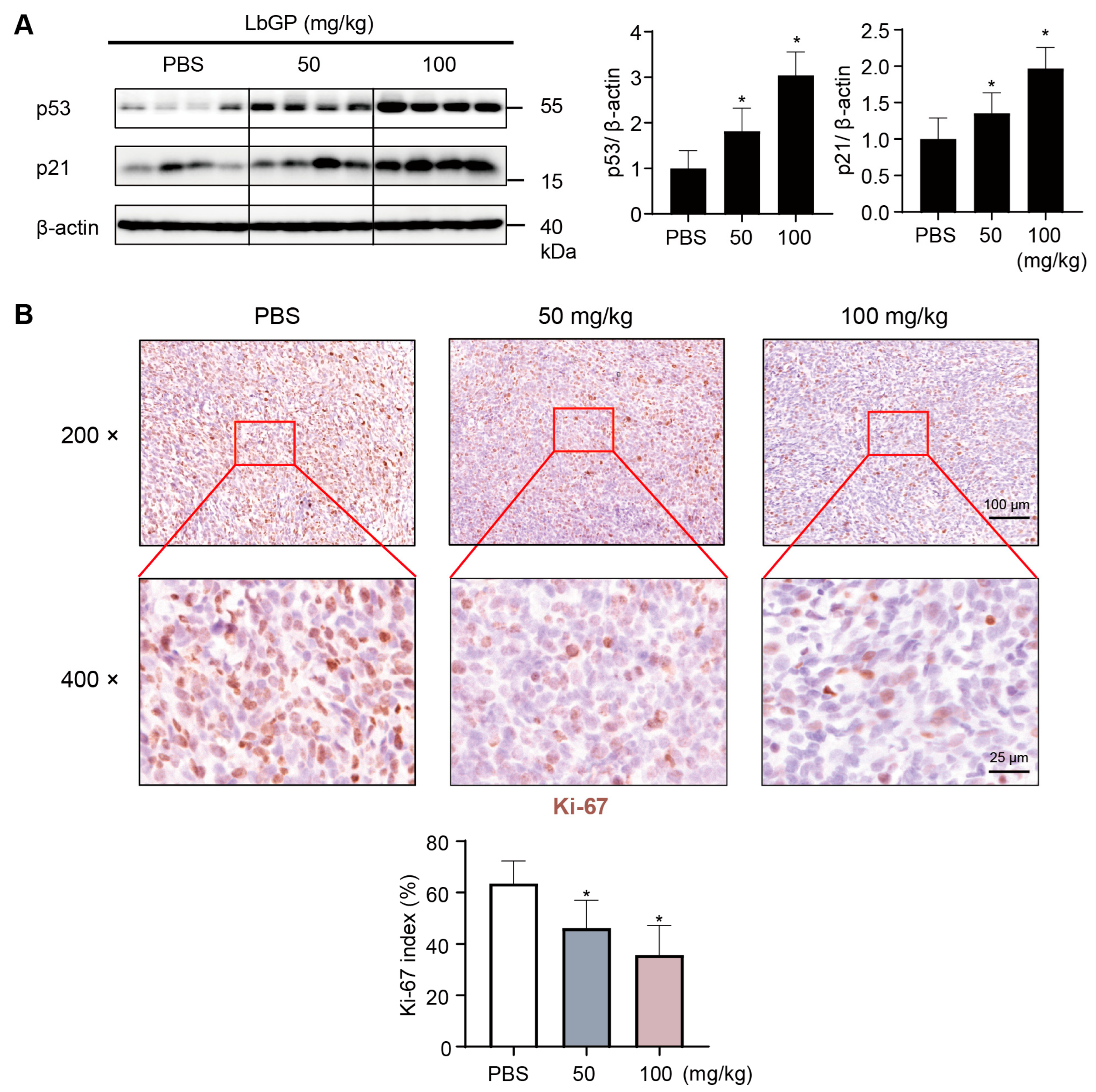
2.6. LbGP Inhibits Cell Proliferation in Tumor Tissues via Upregulating p53/p21
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Animal Experimentation
4.3. Cell Culture
4.4. CCK-8 Assay
4.5. Trypan Blue Assay
4.6. Colony Formation Assay
4.7. Soft Agar Colony Formation Assay
4.8. Cell Cycle Analysis
4.9. Senescence-Associated β-Galactosidase Staining
4.10. Western Blot Analysis
4.11. Immunohistochemistry
4.12. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CCK-8 | Cell counting kit-8 |
| CDKs | Cyclin-dependent kinases |
| CRC | Colorectal cancer |
| IHC | Immunohistochemistry |
| LbGP | Lycium barbarum glycopeptide |
| LBP | Lycium barbarum polysaccharide |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline |
| SA-β-gal | Senescence-associated β-galactosidase |
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dekker, E.; Tanis, P.J.; Vleugels, J.L.A.; Kasi, P.M.; Wallace, M.B. Colorectal cancer. Lancet 2019, 394, 1467–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Goding Sauer, A.; Fedewa, S.A.; Butterly, L.F.; Anderson, J.C.; Cercek, A.; Smith, R.A.; Jemal, A. Colorectal cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2020, 70, 145–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Lu, B.; Luo, C.; Cai, J.; Lu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, H.; Dai, M. Incidence, mortality, survival, risk factor and screening of colorectal cancer: A comparison among China, Europe, and northern America. Cancer Lett. 2021, 522, 255–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dronamraju, S.S.; Coxhead, J.M.; Kelly, S.B.; Burn, J.; Mathers, J.C. Cell kinetics and gene expression changes in colorectal cancer patients given resistant starch: A randomised controlled trial. Gut 2009, 58, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Lankhorst, L.; Bernards, R. Exploiting senescence for the treatment of cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2022, 22, 340–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, W.; Zender, L.; Miething, C.; Dickins, R.A.; Hernando, E.; Krizhanovsky, V.; Cordon-Cardo, C.; Lowe, S.W. Senescence and tumour clearance is triggered by p53 restoration in murine liver carcinomas. Nature 2007, 445, 656–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbas, T.; Dutta, A. p21 in cancer: Intricate networks and multiple activities. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 400–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strauss, R.; Hamerlik, P.; Lieber, A.; Bartek, J. Regulation of stem cell plasticity: Mechanisms and relevance to tissue biology and cancer. Mol. Ther. 2012, 20, 887–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Micco, R.; Krizhanovsky, V.; Baker, D.; d’Adda di Fagagna, F. Cellular senescence in ageing: From mechanisms to therapeutic opportunities. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2021, 22, 75–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, C.H.; Altschuler, S.J.; Wu, L.F. Patterns of Early p21 Dynamics Determine Proliferation-Senescence Cell Fate after Chemotherapy. Cell 2019, 178, 361–373.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griswold, D.P.; Corbett, T.H. A colon tumor model for anticancer agent evaluation. Cancer 1975, 36 (Suppl. 6), 2441–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castle, J.C.; Loewer, M.; Boegel, S.; de Graaf, J.; Bender, C.; Tadmor, A.D.; Boisguerin, V.; Bukur, T.; Sorn, P.; Paret, C.; et al. Immunomic, genomic and transcriptomic characterization of CT26 colorectal carcinoma. BMC Genomics 2014, 15, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, R.H.; Zhang, X.X.; Ni, Z.J.; Thakur, K.; Wang, W.; Yan, Y.M.; Cao, Y.L.; Zhang, J.G.; Rengasamy, K.R.R.; Wei, Z.J. Lycium barbarum (Goji) as functional food: A review of its nutrition, phytochemical structure, biological features, and food industry prospects. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 63, 10621–10635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, X.; Liang, T.; Liu, Y.; Ding, G.; Zhang, F.; Ma, Z. Extraction, Structural Characterization, and Biological Functions of Lycium barbarum Polysaccharides: A Review. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, F.; Xiao, B.; Jiang, Z.; Zhao, J.; Huang, X.; Guo, J. Anticancer effect of Lycium barbarum polysaccharides on colon cancer cells involves G0/G1 phase arrest. Med. Oncol. 2011, 28, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, X.M.; Huang, L.J.; Qi, C.H.; Zhang, Y.X.; Tian, G.Y. Studies on chemistry and immuno-modulating mechanism of a glycoconjugate from Lycium barbarum L. Chin. J. Chem. 2001, 19, 1190–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, G.; Liu, Q.; Deng, Y.; Dang, T.; Dai, W.; Liu, T.; Liu, Y.; Sun, J.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; et al. Arabinogalactan derived from Lycium barbarum fruit inhibits cancer cell growth via cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 149, 639–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, J.; Hui, J.W.; Chen, Y.J.; Luo, D.Y.; Yan, J.S.; Zhang, Y.F.; Lan, Y.X.; Yan, X.R.; Wang, Z.H.; Fan, H.; et al. Lycium barbarum glycopeptide targets PER2 to inhibit lipogenesis in glioblastoma by downregulating SREBP1c. Cancer Gene Ther. 2023, 30, 1084–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, G.; Dang, T.; Deng, Y.; Han, J.; Zou, Z.; Jing, S.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Huang, L.; Wang, Z. Physicochemical properties and biological activities of polysaccharides from Lycium barbarum prepared by fractional precipitation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 109, 611–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Yang, F.; Feng, Y.; Xu, K.; Wu, J.; Qu, S.; Yu, Z.; Fan, F.; Huang, L.; et al. Lycium barbarum Glycopeptide prevents the development and progression of acute colitis by regulating the composition and diversity of the gut microbiota in mice. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 921075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L.; Giaquinto, A.N.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2024. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 12–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guang, D.; Lu, L.; Jianguo, F. Experimental study on the enhancement of murine splenic lymphocyte proliferation by Lycium barbarum glycopeptide. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. Med. Sci. 2004, 24, 518–520, 527. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, L.; He, Q.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Cao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Sun, C.; Pan, Y.; Li, X.; Zhao, X. Polysaccharides in fruits: Biological activities, structures, and structure-activity relationships and influencing factors-A review. Food Chem. 2024, 451, 139408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.; Zhao, M.; Wang, X.; Tian, Y.; Wang, C.; Sun, J.; Wang, Z.; Gong, G.; Huang, L. Revisiting the structure of arabinogalactan from Lycium barbarum and the impact of its side chain on anti-ageing activity. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 286, 119282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, T.; Liu, S.; Ma, X.; Shuai, Y.; He, H.; Guo, T.; Huang, W.; Wang, Q.; Liu, S.; Wang, Z.; et al. Lycium barbarum arabinogalactan alleviates intestinal mucosal damage in mice by restoring intestinal microbes and mucin O-glycans. Carbohydr. Polym. 2024, 330, 121882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Peng, Y.; Wei, W. Cell cycle on the crossroad of tumorigenesis and cancer therapy. Trends Cell Biol. 2022, 32, 30–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, D.; Margolis, C.A.; Vokes, N.I.; Liu, D.; Taylor-Weiner, A.; Wankowicz, S.M.; Adeegbe, D.; Keliher, D.; Schilling, B.; Tracy, A.; et al. Genomic correlates of response to immune checkpoint blockade in microsatellite-stable solid tumors. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 1271–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Wang, W.; Wang, Z.; Li, X. Transcriptomic correlates of cell cycle checkpoints with distinct prognosis, molecular characteristics, immunological regulation, and therapeutic response in colorectal adenocarcinoma. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1291859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levine, A.J. p53: 800 million years of evolution and 40 years of discovery. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2020, 20, 471–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uxa, S.; Castillo-Binder, P.; Kohler, R.; Stangner, K.; Müller, G.A.; Engeland, K. Ki-67 gene expression. Cell Death Differ. 2021, 28, 3357–3370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, M.; Saha, S.; Li, J.; Montrose, D.C.; Martinez, L.A. p53 engages the cGAS/STING cytosolic DNA sensing pathway for tumor suppression. Mol. Cell 2023, 83, 266–280.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basilicata, M.G.; Sommella, E.; Scisciola, L.; Tortorella, G.; Malavolta, M.; Giordani, C.; Barbieri, M.; Campiglia, P.; Paolisso, G. Multi-Omics Strategies to Decode the Molecular Landscape of Cellular Senescence. Ageing Res. Rev. 2025, 111, 102824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, J.; Chen, S.; Yi, Z.; Zhao, R.; Zhu, J.; Ding, S.; Wu, J. The role of p21 in cellular senescence and aging-related diseases. Mol. Cells 2024, 47, 100113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, L.; Jiang, Y.; Shen, J.; Ding, Z.; Xiang, Y.; Chen, G.; Tian, G. Wolfberry Glycopeptide Composition and Methods for Preparing and Using the Same. U.S. Patent 11,110,144 B2, 30 January 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Tominaga, H.; Ishiyama, M.; Ohseto, F.; Sasamoto, K.; Hamamoto, T.; Suzuki, K.; Watanabe, M. A water-soluble tetrazolium salt useful for colorimetric cell viability assay. Anal. Commun. 1999, 36, 47–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strober, W. Trypan Blue Exclusion Test of Cell Viability. Curr. Protoc. Immunol. 2015, 111, A3.B.1–A3.B.3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weng, M.-l.; Chen, W.-k.; Chen, X.-y.; Lu, H.; Sun, Z.-r.; Yu, Q.; Sun, P.-f.; Xu, Y.-j.; Zhu, M.-m.; Jiang, N.; et al. Fasting inhibits aerobic glycolysis and proliferation in colorectal cancer via the Fdft1-mediated AKT/mTOR/HIF1α pathway suppression. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borowicz, S.; Van Scoyk, M.; Avasarala, S.; Karuppusamy Rathinam, M.K.; Tauler, J.; Bikkavilli, R.K.; Winn, R.A. The soft agar colony formation assay. J. Vis. Exp. 2014, 92, e51998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimri, G.P.; Lee, X.; Basile, G.; Acosta, M.; Scott, G.; Roskelley, C.; Medrano, E.E.; Linskens, M.; Rubelj, I.; Pereira-Smith, O.; et al. A biomarker that identifies senescent human cells in culture and in aging skin in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 9363–9367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yuan, M.; Wo, D.; Gong, Y.; Lin, M.; Ma, E.; Zhu, W.; Ren, D.-n. Lycium barbarum Glycopeptide Inhibits Colorectal Cancer Cell Proliferation via Activating p53/p21 Pathway and Inducing Cellular Senescence. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 7091. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157091
Yuan M, Wo D, Gong Y, Lin M, Ma E, Zhu W, Ren D-n. Lycium barbarum Glycopeptide Inhibits Colorectal Cancer Cell Proliferation via Activating p53/p21 Pathway and Inducing Cellular Senescence. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(15):7091. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157091
Chicago/Turabian StyleYuan, Meng, Da Wo, Yuhang Gong, Ming Lin, En Ma, Weidong Zhu, and Dan-ni Ren. 2025. "Lycium barbarum Glycopeptide Inhibits Colorectal Cancer Cell Proliferation via Activating p53/p21 Pathway and Inducing Cellular Senescence" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 15: 7091. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157091
APA StyleYuan, M., Wo, D., Gong, Y., Lin, M., Ma, E., Zhu, W., & Ren, D.-n. (2025). Lycium barbarum Glycopeptide Inhibits Colorectal Cancer Cell Proliferation via Activating p53/p21 Pathway and Inducing Cellular Senescence. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(15), 7091. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157091





