Hyaluronic Acid and Its Synthases—Current Knowledge
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Structure and Properties of HA
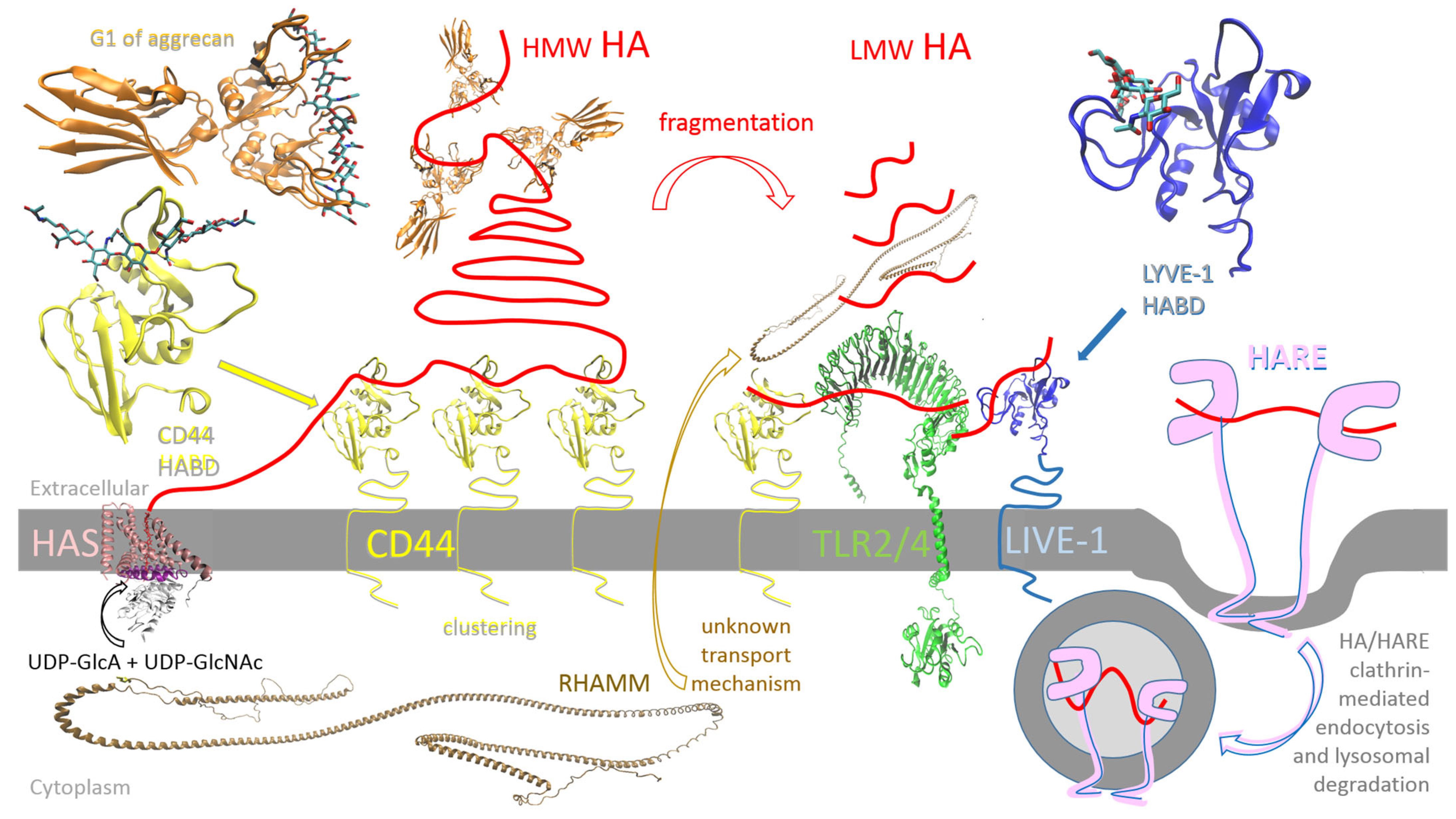
3. Biology of HA
4. Production of HA
4.1. Extraction from Animal Sources
4.2. Fermentation
4.3. In Vitro Synthesis
5. Hyaluronic Acid Synthases
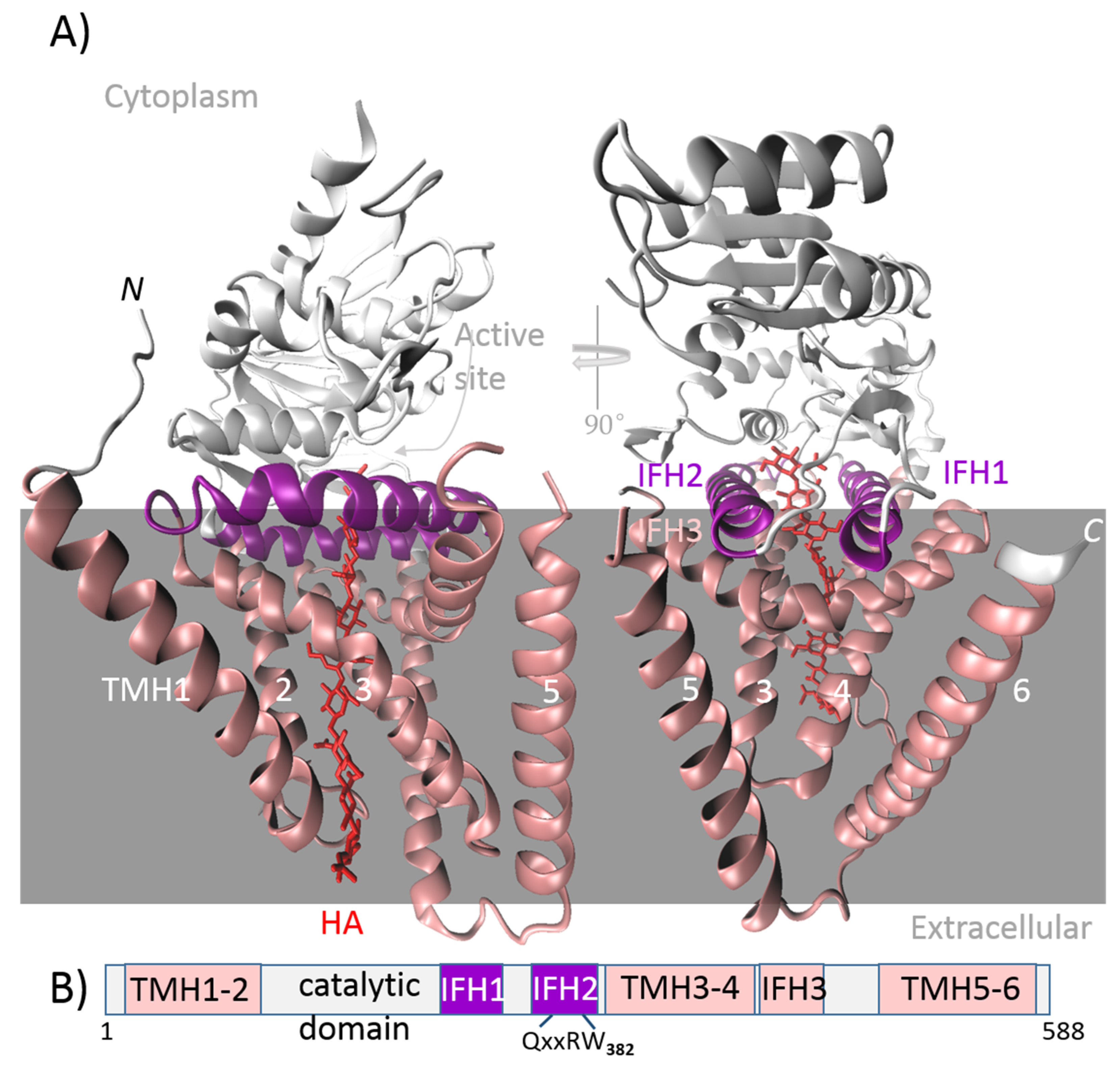
- Class I includes membrane-integrated proteins. As substrates are present in the cytosol, the catalytic domain is cytosolic and functionally integrated with the transmembrane region, which forms a channel. This intrinsic channel is used to secrete the HA directly out of the cell. Class I enzymes are characterized by a processive chain elongation mechanism; i.e., the enzyme retains the HA chain throughout biosynthesis, perhaps because of the close proximity of the GT active site with the channel. These enzymes contain a single GT-2 module that adds both monosaccharide units to the synthesized chain, either to a reducing or non-reducing end. The following are the criteria for subdivision of this class into two subclasses:
- Class I-NR elongates the HA chain at the non-reducing end and can be found in vertebrates and algal viruses.
- Class I-R elongates the HA chain at the reducing end and is found in the bacterial genus Streptococcus.
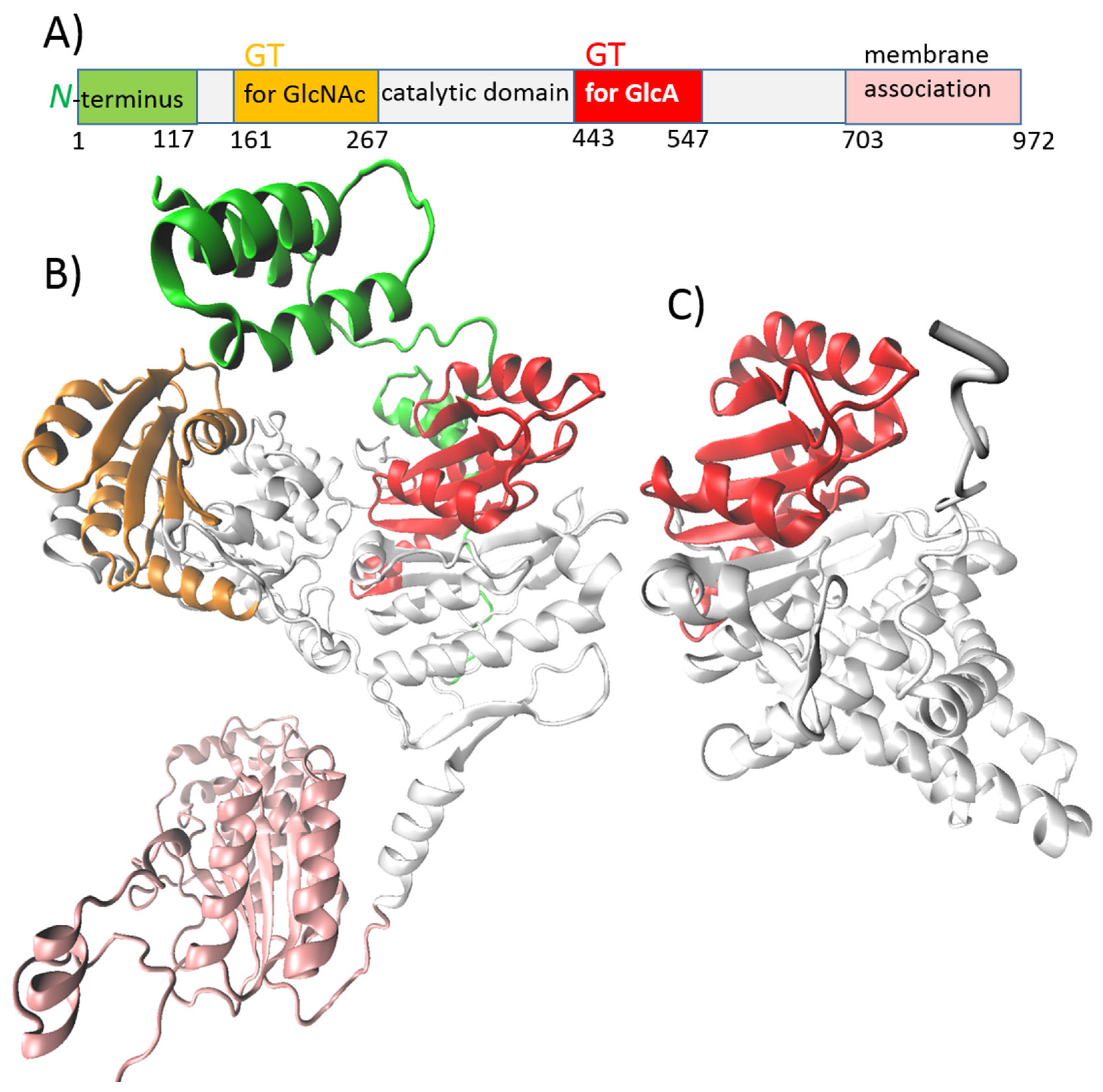
- Class II-NR includes membrane-associated peripheral proteins that require a separate secretion system for HA export. They elongate the chain through a non-processive mechanism. There are two independent GT-2 modules in their structure, one for each type of monosaccharide unit, which are added to the non-reducing end of the synthesized chain. This class is represented by HAS from P. multocida (pmHAS) [49,51].
5.1. HASs from Vertebrates and the Chlorella algae Virus
5.2. Streptococcal HASs
5.3. pmHAS
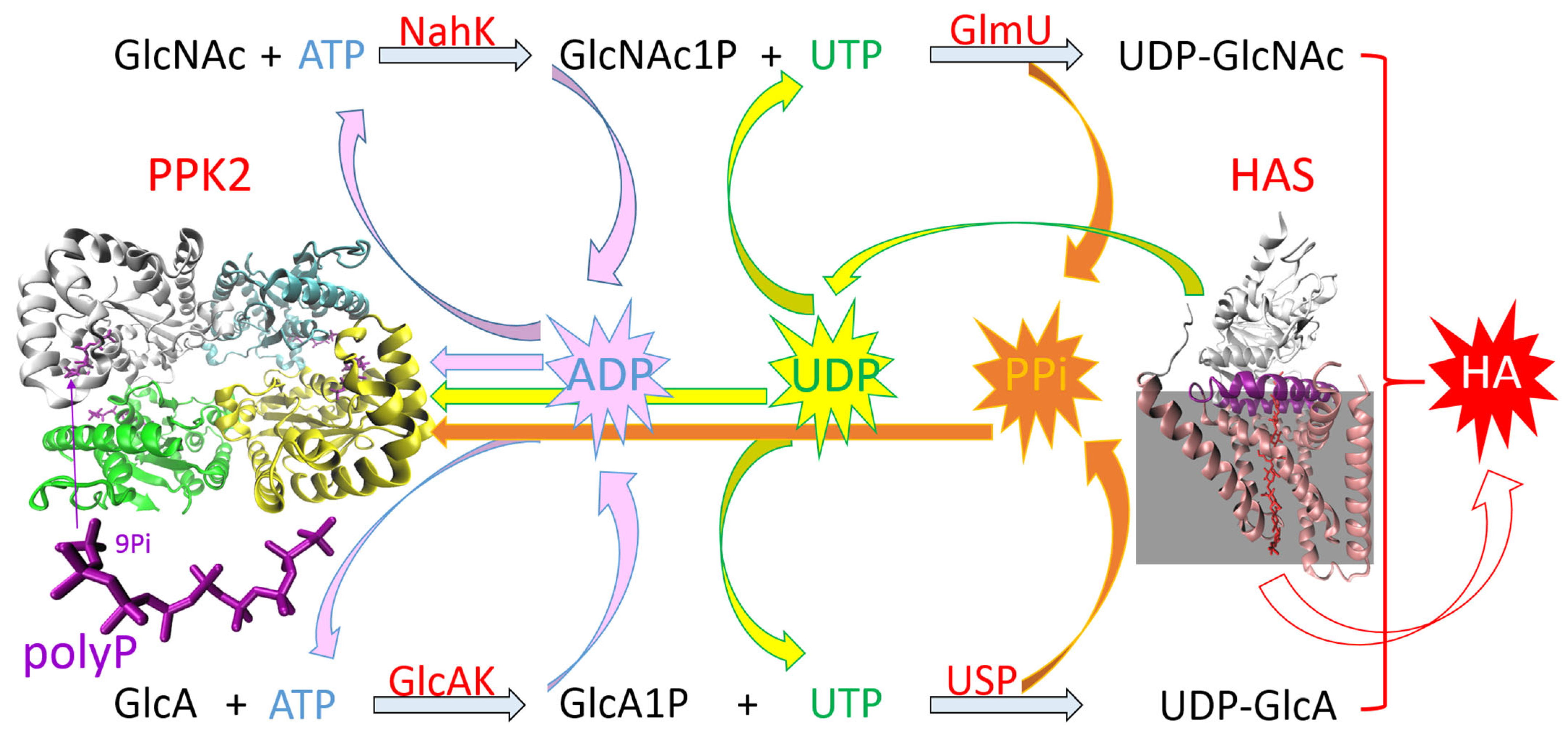
5.4. One-Pot Synthesis of HA
ATP/UTP Regeneration System
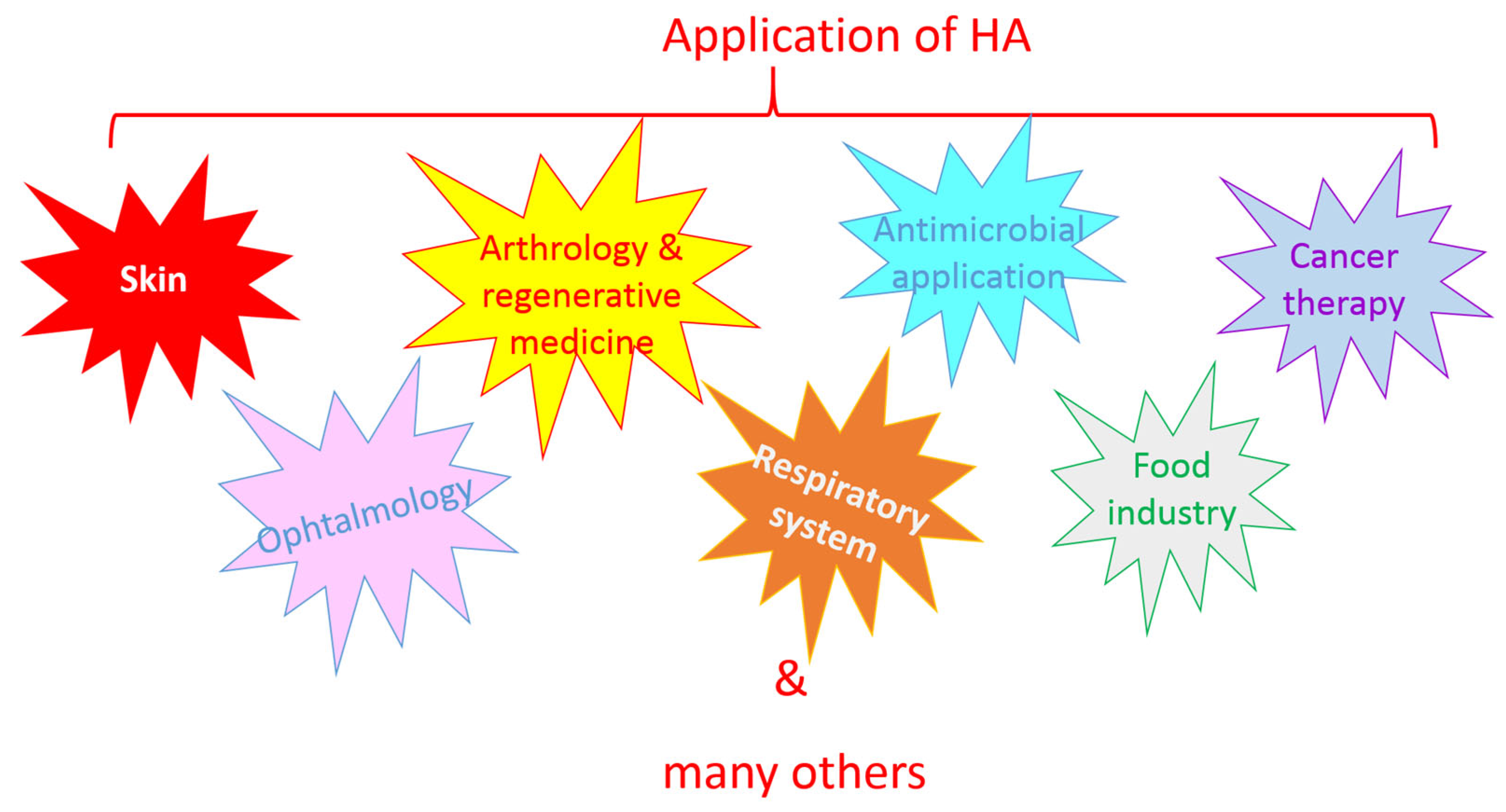
6. Application of HA
6.1. Skin
6.2. Ophthalmology
6.3. Arthrology and Regenerative Medicine
6.4. Respiratory System
6.5. Antimicrobial Application
6.6. Cancer Therapy
6.7. Food Industry
7. Conclusions and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CD44 | Cluster of differentiation 44 |
| CP | Creatine phosphate |
| GlcA | D-glucuronic acid |
| GlcNAc | N-acetyl-D-glucosamine |
| GT | Glycosyltransferase |
| HA | Hyaluronic acid |
| HARE | Hyaluronan receptor for endocytosis |
| HAS | Hyaluronic acid synthase |
| HMW HA | High-molecular-weight hyaluronic acid |
| IFH | Interfacial helix |
| LMW HA | Low-molecular-weight hyaluronic acid |
| LYVE1 | Lymphatic vessel endothelial hyaluronan receptor 1 |
| MW | Molecular weight |
| NDP | Nucleotide diphosphate |
| NTP | Nucleotide triphosphate |
| o-HAs | Oligosaccharides of hyaluronic acid |
| PEP | Phosphoenolpyruvate |
| Pi | Phosphate |
| polyP | Polyphosphate |
| PPi | Pyrophosphate |
| PPK | Polyphosphate kinase |
| RMAHH | Receptor for HA-mediated cell motility |
| TLR | Toll-like receptor |
| TMH | Transmembrane helix |
| vHMW HA | Very-high-molecular-weight hyaluronic acid |
References
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, X.; Bai, Q.; Liang, L.; Wang, S.; Guo, L. Structure–effect relationship studies of polysaccharides based on receptor–active centres: An alternative view. Food Funct. 2023, 14, 4981–5000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, B.W.; Li, S.S.; Ding, W.L.; Zhang, C.; Rehman, M.U.; Tareen, M.F.; Wang, L.; Huang, S.C. From structure to function: A comprehensive overview of polysaccharide roles and applications. Food Front. 2025, 6, 15–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lierova, A.; Kasparova, J.; Filipova, A.; Cizkova, J.; Pekarova, L.; Korecka, L.; Mannova, N.; Bilkova, Z.; Sinkorova, Z. Hyaluronic acid: Known for almost a century, but still in vogue. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fallacara, A.; Baldini, E.; Manfredini, S.; Vertuani, S. Hyaluronic acid in the third millennium. Polymers 2018, 10, 701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jabbari, F.; Babaeipour, V.; Saharkhiz, S. Comprehensive review on biosynthesis of hyaluronic acid with different molecular weights and its biomedical applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 240, 124484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Liu, X.; Li, C.; Li, J.; Qiu, M.; Wang, Y.; Han, W. Effects of molecular weights on the bioactivity of hyaluronic acid: A review. Carbohydr. Res. 2025, 552, 109472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Z.Y.; Qin, J.; Gong, J.S.; Ye, Y.H.; Qian, J.Y.; Li, H.; Xu, Z.H.; Shi, J.S. Versatile strategies for bioproduction of hyaluronic acid driven by synthetic biology. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 264, 118015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saadati, F.; Bahrulolum, H.; Talebi, M.; Karimi, M.; Bozorgchami, N.; Ghale, R.A.; Zafar, S.; Aghighi, Y.; Asiaei, E.; Tabandeh, F. Advances and principles of hyaluronic acid production, extraction, purification, and its applications: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 312, 143839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Precedence Research. Hyaluronic Acid Market Expands with Demand for Skincare and Medical Solutions. Available online: https://www.precedenceresearch.com/hyaluronic-acid-market (accessed on 16 June 2025).
- Eisele, A.; Zaun, H.; Kuballa, J.; Elling, L. In vitro one-pot enzymatic synthesis of hyaluronic acid from sucrose and N-acetylglucosamine: Optimization of the enzyme module system and nucleotide sugar regeneration. ChemCatChem 2018, 10, 2969–2981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottschalk, J.; Elling, L. Current state on the enzymatic synthesis of glycosaminoglycans. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2021, 61, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Zhao, S.; Wang, J.; Chen, Y.; Li, H.; Li, J.P.; Kan, Y.; Zhang, T. Methods for determining the structure and physicochemical properties of hyaluronic acid and its derivatives: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 282, 137603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Dong, J.; Pan, R.; Xu, Z.; Li, M.; Zang, R. Structures, properties, and bioengineering applications of alginates and hyaluronic acid. Polymers 2023, 15, 2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Qiao, M.; Ji, Y.; Lin, L.; Zhang, X.; Linhardt, R.J. Chemical, enzymatic and biological synthesis of hyaluronic acids. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 152, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, L.; Li, M.; Xu, A.; Zhuo, F. Recent applications and molecular mechanisms of hyaluronic acid in skin aging and wound healing. Med. Nov. Technol. Devices 2024, 23, 100320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamer, T.M. Hyaluronan and synovial joint: Function, distribution and healing. Interdiscip. Toxicol. 2013, 6, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marinho, A.; Nunes, C.; Reis, S. Hyaluronic acid: A key ingredient in the therapy of inflammation. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hynnekleiv, L.; Magno, M.; Vernhardsdottir, R.R.; Moschowits, E.; Tønseth, K.A.; Dartt, D.A.; Vehof, J.; Utheim, T.P. Hyaluronic acid in the treatment of dry eye disease. Acta Ophthalmol. 2022, 100, 844–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Day, A.J. Hyaluronan-protein interactions: Lilliput revisited. Proteoglycan Res. 2024, 2, e70007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowman, M.K.; Turley, E.A. Functional organization of extracellular hyaluronan, CD44, and RHAMM. Proteoglycan Res. 2023, 1, e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evanko, S.P.; Parks, W.T.; Wight, T.N. Intracellular hyaluronan in arterial smooth muscle cells: Association with microtubules, RHAMM, and the mitotic spindle. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2004, 52, 1525–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavianatou, A.G.; Caon, I.; Franchi, M.; Piperigkou, Z.; Galesso, D.; Karamanos, N.K. Hyaluronan: Molecular size-dependent signaling and biological functions in inflammation and cancer. FEBS J. 2019, 286, 2883–2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volpi, N.; Maccari, F. Purification and characterization of hyaluronic acid from the mollusc bivalve Mytilus galloprovincialis. Biochimie 2003, 85, 619–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanchana, S.; Arumugam, M.; Giji, S.; Balasubramanian, T. Isolation, characterization and antioxidant activity of hyaluronic acid from marine bivalve mollusc Amussium pleuronectus (Linnaeus, 1758). Bioact. Carbohydr. Diet. Fibre 2013, 2, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurst, J.R.; Shannon, B.A.; Craig, H.C.; Rishi, A.; Tuffs, S.W.; McCormick, J.K. The Streptococcus pyogenes hyaluronic acid capsule promotes experimental nasal and skin infection by preventing neutrophil-mediated clearance. PLoS Pathog. 2022, 18, e1011013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Huthaifi, A.M.; Radman, B.A.; Al-Alawi, A.A.; Mahmood, F.; Liu, T.B. Mechanisms and virulence factors of Cryptococcus neoformans dissemination to the central nervous system. J. Fungi 2024, 10, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamboni, F.; Wong, C.K.; Collins, M.N. Hyaluronic acid association with bacterial, fungal and viral infections: Can hyaluronic acid be used as an antimicrobial polymer for biomedical and pharmaceutical applications? Bioact. Mater. 2023, 19, 458–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeAngelis, P.L.; Jing, W.; Graves, M.V.; Burbank, D.E.; Van Etten, J.L. Hyaluronan synthase of chlorella virus PBCV-1. Science 1997, 278, 1800–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rakkhumkaew, N.; Kawasaki, T.; Fujie, M.; Yamada, T. Prolonged synthesis of hyaluronan by Chlorella cells infected with chloroviruses. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2013, 115, 527–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, M.; Huang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Qiao, Y.; Xiao, N.; Jin, M.; Gao, H.; Huang, Y.; Hu, X.; Li, O. Advances in hyaluronic acid production: Biosynthesis and genetic engineering strategies based on Streptococcus—A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 270, 132334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Marquez, C.D.; Arteaga-Marin, S.; Rivas-Sánchez, A.; Autrique-Hernández, R.; Castro-Muñoz, R. A review on current strategies for extraction and purification of hyaluronic acid. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graciela, C.Q.; José Juan, E.C.; Gieraldin, C.L.; Xóchitl Alejandra, P.M.; Gabriel, A.Á. Hyaluronic Acid—Extraction methods, sources and applications. Polymers 2023, 15, 3473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shikina, E.V.; Kovalevsky, R.A.; Shirkovskaya, A.I.; Toukach, P.V. Prospective bacterial and fungal sources of hyaluronic acid: A review. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2022, 20, 6214–6236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marwan-Abdelbaset, E.; Samy-Kamal, M.; Tan, D.; Lu, X. Microbial Production of Hyaluronic Acid: The Current Advances, Engineering Strategies and Trends. J. Biotechnol. 2025, 403, 52–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Hu, L.; Xu, R.; Zhang, W.; Xiong, H.; Wang, Y.; Du, G.; Kang, Z. Production of different molecular weight glycosaminoglycans with microbial cell factories. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2023, 171, 110324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, R.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Pei, X.; Di, J.; Xie, Z.; Liu, H.; Gao, W. Inducible engineering precursor metabolic flux for synthesizing hyaluronic acid of customized molecular weight in Streptococcus zooepidemicus. Microb. Cell Factories 2025, 24, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Shi, Z.; Shao, Y.; Wu, M.; Li, G.; Ma, T. Temperature-controlled molecular weight of hyaluronic acid produced by engineered Bacillus subtilis. Biotechnol. Lett. 2021, 43, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Q.; Shi, X.; Song, Y.; Lei, P.; Xu, X.; Xu, H.; Qiu, Y.; Li, S. De novo synthesis of hyaluronic acid with tailored molecular weights using a new hyaluronidase SthHL. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 293, 139381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Dong, J.; Xu, G.; Han, R.; Zhou, J.; Ni, Y. Efficient production of hyaluronic acid by Streptococcus zooepidemicus using two-stage semi-continuous fermentation. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 377, 128896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di, J.; Pei, X.; Hu, S.; Zuo, M.; Liu, H.; Gao, W. Effect of cysteine transport on the molecular weight and synthesis of hyaluronic acid in Streptococcus zooepidemicus. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 306, 141060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Han, Y.; Sun, H.Y.; Hilborn, J.; Shi, L. Click chemistry-based biopolymeric hydrogels for regenerative medicine. Biomed. Mater. 2021, 16, 022003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hintze, V.; Schnabelrauch, M.; Rother, S. Chemical modification of hyaluronan and their biomedical applications. Front. Chem. 2022, 10, 830671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.C.; Huang, K.Y.; Lew, W.Z.; Fan, K.H.; Chang, W.J.; Huang, H.M. Gamma-irradiation-prepared low molecular weight hyaluronic acid promotes skin wound healing. Polymers 2019, 11, 1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.T.; Chou, P.C.; Wu, P.H.; Lee, C.M.; Fan, K.H.; Chang, W.J.; Lee, S.Y.; Huang, H.M. Physical and biological evaluation of low-molecular-weight hyaluronic Acid/Fe3O4 nanoparticle for targeting MCF7 breast cancer cells. Polymers 2020, 12, 1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stern, R.; Kogan, G.; Jedrzejas, M.J.; Šoltés, L. The many ways to cleave hyaluronan. Biotechnol. Adv. 2007, 25, 537–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebrahimi, T.; Keramati, M.; Khodabakhsh, F.; Cohan, R.A. Enzyme variants in biosynthesis and biological assessment of different molecular weight hyaluronan. AMB Express 2024, 14, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gottschalk, J.; Aßmann, M.; Kuballa, J.; Elling, L. Repetitive Synthesis of High-Molecular-Weight Hyaluronic Acid with Immobilized Enzyme Cascades. ChemSusChem 2022, 15, e202101071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, G.; Krishnan, K.V.; Prasad, S.B.; Bhaduri, A.; Jayaraman, G. Biosynthesis of hyaluronic acid polymer: Dissecting the role of sub structural elements of hyaluronan synthase. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 12510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeAngelis, P.L.; Zimmer, J. Hyaluronan synthases; mechanisms, myths, & mysteries of three types of unique bifunctional glycosyltransferases. Glycobiology 2023, 33, 1117–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durin, Z.; Houdou, M.; Legrand, D.; Foulquier, F. Metalloglycobiology: The power of metals in regulating glycosylation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Gen. Subj. 2023, 1867, 130412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeAngelis, P.L. Chemoenzymatic synthesis with the Pasteurella hyaluronan synthase; production of a multitude of defined authentic, derivatized, and analog polymers. Proteoglycan Res. 2024, 2, e70000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Wu, Z.; Cao, L.; Long, F. Differential Regulation of Hyaluronan Synthesis by Three Isoforms of Hyaluronan Synthases in Mammalian Cells. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Górniak, I.; Stephens, Z.; Erramilli, S.K.; Gawda, T.; Kossiakoff, A.A.; Zimmer, J. Structural insights into translocation and tailored synthesis of hyaluronan. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2025, 32, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maloney, F.P.; Kuklewicz, J.; Corey, R.A.; Bi, Y.; Ho, R.; Mateusiak, L.; Pardon, E.; Steyaert, J.; Stansfeld, P.J.; Zimmer, J. Structure, substrate recognition and initiation of hyaluronan synthase. Nature 2022, 604, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heldermon, C.; DeAngelis, P.L.; Weigel, P.H. Topological organization of the hyaluronan synthase from Streptococcus pyogenes. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 2037–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohan, R.A.; Keramati, M.; Afshari, E.; Parsian, P.; Ahani, R.; Ebrahimi, T. Evaluation of transmembrane domain deletions on hyaluronic acid polymerization of hyaluronan synthase isolated from Streptococcus equisimilis group G. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2023, 39, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baggenstoss, B.A.; Harris, E.N.; Washburn, J.L.; Medina, A.P.; Nguyen, L.; Weigel, P.H. Hyaluronan synthase control of synthesis rate and hyaluronan product size are independent functions differentially affected by mutations in a conserved tandem B-X7-B motif. Glycobiology 2017, 27, 154–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, W.; DeAngelis, P.L. Analysis of the two active sites of the hyaluronan synthase and the chondroitin synthase of Pasteurella multocida. Glycobiology 2003, 13, 661–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandawe, J.; Infanzon, B.; Eisele, A.; Zaun, H.; Kuballa, J.; Davari, M.D.; Jakob, F.; Elling, L.; Schwaneberg, U. Directed evolution of hyaluronic acid synthase from Pasteurella multocida towards high-molecular-weight hyaluronic acid. ChemBioChem 2018, 19, 1414–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kooy, F.K.; Beeftink, H.H.; Eppink, M.H.; Tramper, J.; Eggink, G.; Boeriu, C.G. Kinetic and structural analysis of two transferase domains in Pasteurella multocida hyaluronan synthase. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2014, 102, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, W.; DeAngelis, P.L. Dissection of the two transferase activities of the Pasteurella multocida hyaluronan synthase: Two active sites exist in one polypeptide. Glycobiology 2000, 10, 883–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.Y.; Deng, J.Q.; Du, R.R.; Xin, S.Y.; Cao, Y.L.; Lu, Z.; Guo, X.P.; Wang, F.S.; Sheng, J.Z. Novel β1, 4 N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase in de novo enzymatic synthesis of hyaluronic acid oligosaccharides. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2023, 107, 5119–5129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, T.; Hirose, A.; Hagiwara, T.; Ohtsuka, M.; Kakuta, Y.; Kimata, K.; Okahata, Y. Single-molecular enzymatic elongation of hyaluronan polymers visualized by high-speed atomic force microscopy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 20254–20257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeAngelis, P.L.; Oatman, L.C.; Gay, D.F. Rapid chemoenzymatic synthesis of monodisperse hyaluronan oligosaccharides with immobilized enzyme reactors. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 35199–35203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, M.; Zhang, J.; Li, J.; Xing, L.; Zhou, X.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, X. Self-assembly immobilization of a universal catalytic microreactor for glycosyltransferases. Process Biochem. 2023, 133, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommerfeld, I.K.; Dälken, E.M.; Elling, L.; Pich, A. Nitrilotriacetic Acid Functionalized Microgels for Efficient Immobilization of Hyaluronan Synthase. Macromol. Biosci. 2024, 24, 2400075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Luca, C.; Lansing, M.; Martini, I.; Crescenzi, F.; Shen, G.J.; O’Regan, M.; Wong, C.H. Enzymic synthesis of hyaluronic acid with regeneration of sugar nucleotides. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1995, 117, 5869–5870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wang, S.; Fu, X.; Liu, X.W.; Wang, P.G.; Fang, J. Sequential one-pot multienzyme synthesis of hyaluronan and its derivative. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 178, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iaconisi, G.N.; Lunetti, P.; Gallo, N.; Cappello, A.R.; Fiermonte, G.; Dolce, V.; Capobianco, L. Hyaluronic acid: A powerful biomolecule with wide-ranging applications—A comprehensive review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andexer, J.N.; Richter, M. Emerging enzymes for ATP regeneration in biocatalytic processes. ChemBioChem 2015, 16, 380–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siedentop, R.; Prenzel, T.; Waldvogel, S.R.; Rosenthal, K.; Lütz, S. Reaction engineering and comparison of electroenzymatic and enzymatic ATP regeneration systems. ChemElectroChem 2023, 10, e202300332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achbergerová, L.; Nahálka, J. Polyphosphate-an ancient energy source and active metabolic regulator. Microb. Cell Factories 2011, 10, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nahálka, J.; Pätoprstý, V. Enzymatic synthesis of sialylation substrates powered by a novel polyphosphate kinase (PPK3). Org. Biomol. Chem. 2009, 7, 1778–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuge, M.; Keppler, M.; Friedrich, F.; Saleem-Batcha, R.; Winter, J.; Prucker, I.; Germer, P.; Gerhardt, S.; Einsle, O.; Jung, M.; et al. Structural Insights into Broad-Range Polyphosphate Kinase 2-II Enzymes Applicable for Pyrimidine Nucleoside Diphosphate Synthesis. ChemBioChem 2025, 26, e202400970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gottschalk, J.; Blaschke, L.; Aßmann, M.; Kuballa, J.; Elling, L. Integration of a Nucleoside Triphosphate Regeneration System in the One-pot Synthesis of UDP-sugars and Hyaluronic Acid. ChemCatChem 2021, 13, 3074–3083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Hu, L.; Xu, R.; Zhang, W.; Hu, S.; Wang, Y.; Du, G.; Kang, Z. Construction of immobilized enzyme cascades for the biosynthesis of nucleotide sugars UDP-N-acetylglucosamine and UDP-glucuronic acid. Syst. Microbiol. Biomanufacturing 2024, 4, 895–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Wang, Y.; Huang, H.; Jin, X.; Li, J.; Du, G.; Kang, Z. Closed-loop system driven by ADP phosphorylation from pyrophosphate affords equimolar transformation of ATP to 3′-phosphoadenosine-5′-phosphosulfate. ACS Catal. 2021, 11, 10405–10415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chylińska, N.; Maciejczyk, M. Hyaluronic Acid and Skin: Its Role in Aging and Wound-Healing Processes. Gels 2025, 11, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toprangkobsin, P.; Teepakakorn, A.; Ampawa, S.; Efendi, A.; Limcharoen, B.; Banlunara, W.; Asawanonda, P.; Wanichwecharungruang, S. Detachable Microneedles With Crosslinked Hyaluronic Acid as Superficial Skin Filler. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2025, 113, e37933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Xue, J.; Huang, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, H.; Du, L.; Zhai, D.; Huan, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Wu, C. An injectable hyaluronic acid/lithium calcium silicate soft tissue filler with vascularization and collagen regeneration. Bioact. Mater. 2025, 44, 256–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murugesan, M.; Mathiyalagan, R.; Ramadhania, Z.M.; Nahar, J.; Luu, C.H.; Phan, V.G.; Yang, D.C.; Zhou, Q.; Kang, S.C.; Thambi, T. Tailoring hyaluronic acid hydrogels: Impact of cross-linker length and density on skin rejuvenation as injectable dermal fillers and their potential effects on the MAPK signaling pathway suppression. Bioact. Mater. 2025, 49, 154–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Lee, K.; Kim, M.; Kwon, Y.; Yun, J.; Choi, J.H.; Youn, H.J. Synergistic moisturizing effect of a cellulose nanofibril/hyaluronic acid/poly-γ-glutamic acid blend system. Cellulose 2025, 32, 4781–4796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmal, S.; Subbappa, P.; Nikam, V.; Tarwate, Y.; Barhate, K.; Wagh, S.; Gholap, A.; Dua, K.; Singh, S.K.; Parikh, D.; et al. Hyaluronic acid based approaches for wound healing: A comprehensive review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 306, 141625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, W.; Huang, C.; Deng, W.; Lai, J.; Chen, J.; Jie, J.; Wu, Y.; You, T.; Wu, L.P. Hyaluronic acid methacryloyl/chitosan methacryloyl/3-methacrylamidophenylboronic acid multifunctional hydrogel loading exosome for diabetic wound healing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 280, 135562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Y.P.; Jin, M.Y.; Huang, S.; Zhuang, Z.M.; Zhang, T.; Cao, L.L.; Lin, X.Y.; Chen, J.; et al. Versatile dopamine-functionalized hyaluronic acid-recombinant human collagen hydrogel promoting diabetic wound healing via inflammation control and vascularization tissue regeneration. Bioact. Mater. 2024, 35, 330–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proietti, I.; Kus, S.; Amore, E.; Svara, F.; Battilotti, C.; Potenza, C.; Ogilvie, P. Integrative Rosacea Treatment: Combination of a Low Crosslinked Injectable Hyaluronic Acid Filler With Standard Therapeutical Interventions—An International Real World Case Series. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2025, 24, e70199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, W.H.; Liu, P.Y.; Lin, M.H.; Lu, C.J.; Chou, H.Y.; Nian, C.Y.; Jiang, Y.T.; Hsu, Y.H.H. Applications of hyaluronic acid in ophthalmology and contact lenses. Molecules 2021, 26, 2485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chauchat, L.; Guerin, C.; Sahyoun, M.; Guillon, M.; Calonge, M. Management of Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Patients with Symptomatic Dry Eye Disease Treated with a Preservative-Free Ophthalmic Emulsion Combining Alpha-Lipoic Acid and High Molecular Weight Sodium Hyaluronate. Adv. Ther. 2025, 42, 2219–2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.; Xu, Z. Hyaluronic acid-based nanoparticles to deliver drugs to the ocular posterior segment. Drug Deliv. 2023, 30, 2204206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, A.; Halder, J.; Saha, I.; Rai, V.K.; Mahanty, R.; Pradhan, D.; Dash, P.; Das, C.; Rajwar, T.K.; Satpathy, B.; et al. Biogenic Amino Acid Cross-Linked Hyaluronic Acid Nanoparticles Containing Dexamethasone for the Treatment of Dry Eye Syndrome. AAPS PharmSciTech 2025, 26, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohani, Z.; Jamshidi, S.; Koohi, M.K.; Malakootikhah, J.; Abarkar, M.; Golchin, D.; Roshani, S.; Naghdi, H.; Aghajanpour-Moghaddam-Gazafroudi, N.; Gazafroudi; et al. Novel ophthalmic hyaluronic acid-hydrogel with curcumin nanoparticles for enhanced healing of ulcerative keratitis in rabbit model. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 23046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walvekar, P.; Lulinski, P.; Kumar, P.; Aminabhavi, T.M.; Choonara, Y.E. A review of hyaluronic acid-based therapeutics for the treatment and management of arthritis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 264, 130645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Ma, M.; Gao, R.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Huang, P.; Wang, W.; Feng, Z.; Gao, J. Hyaluronic-Acid-Nanomedicine Hydrogel for Enhanced Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis by Mediating Macrophage–Synovial Fibroblast Cross-Talk. Biomater. Res. 2024, 28, 0046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Sun, J. A mini-invasive injectable hydrogel for temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis: Its pleiotropic effects and multiple pathways in cartilage regeneration. Biomater. Adv. 2025, 169, 214162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assi, M.M.; Grawish, M.E.; Elsabaa, H.M.; Helal, M.E.; Ezzat, S.K. Therapeutic potential of hyaluronic acid hydrogel combined with bone marrow stem cells-conditioned medium on arthritic rats’ TMJs. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 26828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, D.W.; Gilbert, R.J. Extracellular matrix-mimetic hydrogels for treating neural tissue injury: A focus on fibrin, hyaluronic acid, and elastin-like polypeptide hydrogels. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2021, 10, 2101329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranjan, S.; Choudhary, P.; Shivalkar, S.; Dwivedi, S.; Singh, S. Potential of hyaluronic acid and collagen-based scaffolds in promoting stem cell neuronal differentiation for neuroregenerative therapies: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 309, 142981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos Ferrer, P.; Vardhan, S.; Sakiyama-Elbert, S. Sustained neurotrophin-3 delivery from hyaluronic acid hydrogels for neural tissue regeneration. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2024, 112, 1188–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajic, A.; Andersson, B.; Ossinger, A.; Tavakoli, S.; Varghese, O.P.; Schizas, N. Physically and Chemically Crosslinked Hyaluronic Acid-Based Hydrogels Differentially Promote Axonal Outgrowth from Neural Tissue Cultures. Biomimetics 2024, 9, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Xue, H.; Zeng, H.; Dai, M.; Tang, C.; Liu, L. 3D printed scaffolds based on hyaluronic acid bioinks for tissue engineering: A review. Biomater. Res. 2023, 27, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, P.J.; Yen, H.J.; Lin, C.Y.; Lai, H.Y.; Chen, C.H.; Wang, S.H.; Chang, W.J.; Lee, S.Y.; Huang, H.M. Estimation of the effect of accelerating new bone formation of high and low molecular weight hyaluronic acid hybrid: An animal study. Polymers 2021, 13, 1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.Y.; Kuo, P.J.; Lin, Y.H.; Lin, C.Y.; Lin, J.C.Y.; Chiu, H.C.; Hung, T.F.; Lin, H.Y.; Huang, H.M. Fabrication of low-molecular-weight hyaluronic acid–carboxymethyl cellulose hybrid to promote bone growth in guided bone regeneration surgery: An animal study. Polymers 2022, 14, 3211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Máiz Carro, L.; Martínez-García, M.A. Use of hyaluronic acid (HA) in chronic airway diseases. Cells 2020, 9, 2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, E.Y.; Tan, B.K.J.; Teo, J.Y.Y.; He, G.S.; Tan, C.J.W.; Yeo, B.S.Y.; Chua, A.J.K. Hyaluronic Acid for Sinonasal Surgery: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2025, 15, 616–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galdi, F.; Pedone, C.; McGee, C.A.; George, M.; Rice, A.B.; Hussain, S.S.; Vijaykumar, K.; Boitet, E.R.; Tearney, G.J.; McGrath, J.A.; et al. Inhaled high molecular weight hyaluronan ameliorates respiratory failure in acute COPD exacerbation: A pilot study. Respir. Res. 2021, 22, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magi, M.S.; de Lafuente, Y.; Quarta, E.; Palena, M.C.; Ardiles, P.D.R.; Páez, P.L.; Sonvico, F.; Buttini, F.; Jimenez-Kairuz, A.F. Novel Dry Hyaluronic Acid–Vancomycin Complex Powder for Inhalation, Useful in Pulmonary Infections Associated with Cystic Fibrosis. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camara, C.I.; Bertocchi, L.; Ricci, C.; Bassi, R.; Bianchera, A.; Cantu’, L.; Bettini, R.; Del Favero, E. Hyaluronic acid—Dexamethasone nanoparticles for local adjunct therapy of lung inflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.J.; Kim, J.A.; Lee, Y.; Lim, S.; Chun, Y.H. Allergic-Specific Immunotherapy Using Injectable In Situ Crosslinked Hyaluronic Acid Hydrogels Ameliorates Allergic Response in Murine Allergic Rhinitis Model. Allergy Asthma Immunol. Res. 2024, 17, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamboni, F.; Okoroafor, C.; Ryan, M.P.; Pembroke, J.T.; Strozyk, M.; Culebras, M.; Collins, M.N. On the bacteriostatic activity of hyaluronic acid composite films. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 260, 117803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gagneja, S.; Capalash, N.; Sharma, P. Hyaluronic acid as a tumor progression agent and a potential chemotherapeutic biomolecule against cancer: A review on its dual role. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 275, 133744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Pang, S.; Liu, X.; Dong, Z.; Tian, Y.; Ashrafizadeh, M.; Rabiee, N.; Ertas, Y.N.; Mao, Y. Chitosan-and hyaluronic acid-based nanoarchitectures in phototherapy: Combination cancer chemotherapy, immunotherapy and gene therapy. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 273, 132579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, X.; Yin, Y.; Wang, C.; Xu, H. Hyaluronic acid regulated facile synthesis of size-tunable multifunctional nanomedicine for effective cancer therapy. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 288, 138668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Zhang, H.; Han, J.; Yang, L.; Li, S.; Jia, Q.; Fang, J.; Ling, P.; Wang, S. Synthesis and antitumor activity of ultra-low molecular weight hyaluronic acid-decorated camptothecin conjugates. Carbohydr. Polym. 2025, 351, 123144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kousar, K.; Naseer, F.; Abduh, M.S.; Kakar, S.; Gul, R.; Anjum, S.; Ahmad, T. Green synthesis of hyaluronic acid coated, thiolated chitosan nanoparticles for CD44 targeted delivery and sustained release of Cisplatin in cervical carcinoma. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 13, 1073004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, C.P.; Cai, X.Y.; Chen, S.L.; Yu, H.W.; Fang, Y.; Feng, X.C.; Zhang, L.M.; Li, C.Y. Hyaluronic acid-based nanocarriers for anticancer drug delivery. Polymers 2023, 15, 2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Q.; Liu, C.; Zhao, J.; Li, W.; Guo, F.; Qin, J.; Wang, Y. Unlocking the potential of hyaluronic acid: Exploring its physicochemical properties, modification, and role in food applications. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 142, 104218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Palenčárová, K.; Köszagová, R.; Nahálka, J. Hyaluronic Acid and Its Synthases—Current Knowledge. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 7028. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157028
Palenčárová K, Köszagová R, Nahálka J. Hyaluronic Acid and Its Synthases—Current Knowledge. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(15):7028. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157028
Chicago/Turabian StylePalenčárová, Klaudia, Romana Köszagová, and Jozef Nahálka. 2025. "Hyaluronic Acid and Its Synthases—Current Knowledge" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 15: 7028. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157028
APA StylePalenčárová, K., Köszagová, R., & Nahálka, J. (2025). Hyaluronic Acid and Its Synthases—Current Knowledge. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(15), 7028. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157028







