Selective MicroRNA Packaging Reveals Distinct Core Signatures in Human Mesenchymal-Stromal-Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
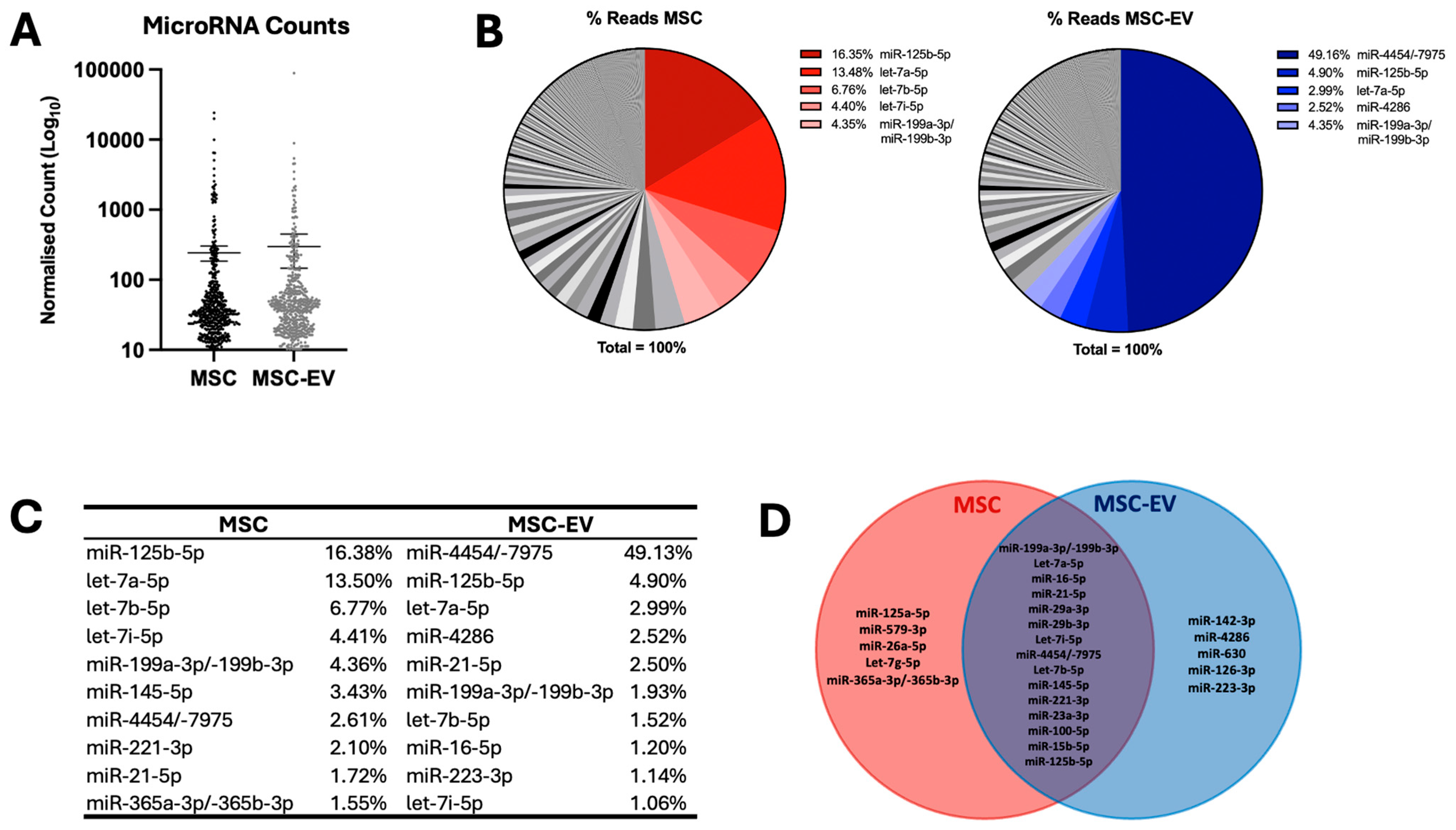
2.1. MSC and MSC-EV Demonstrate High Expression of Selected MicroRNAs
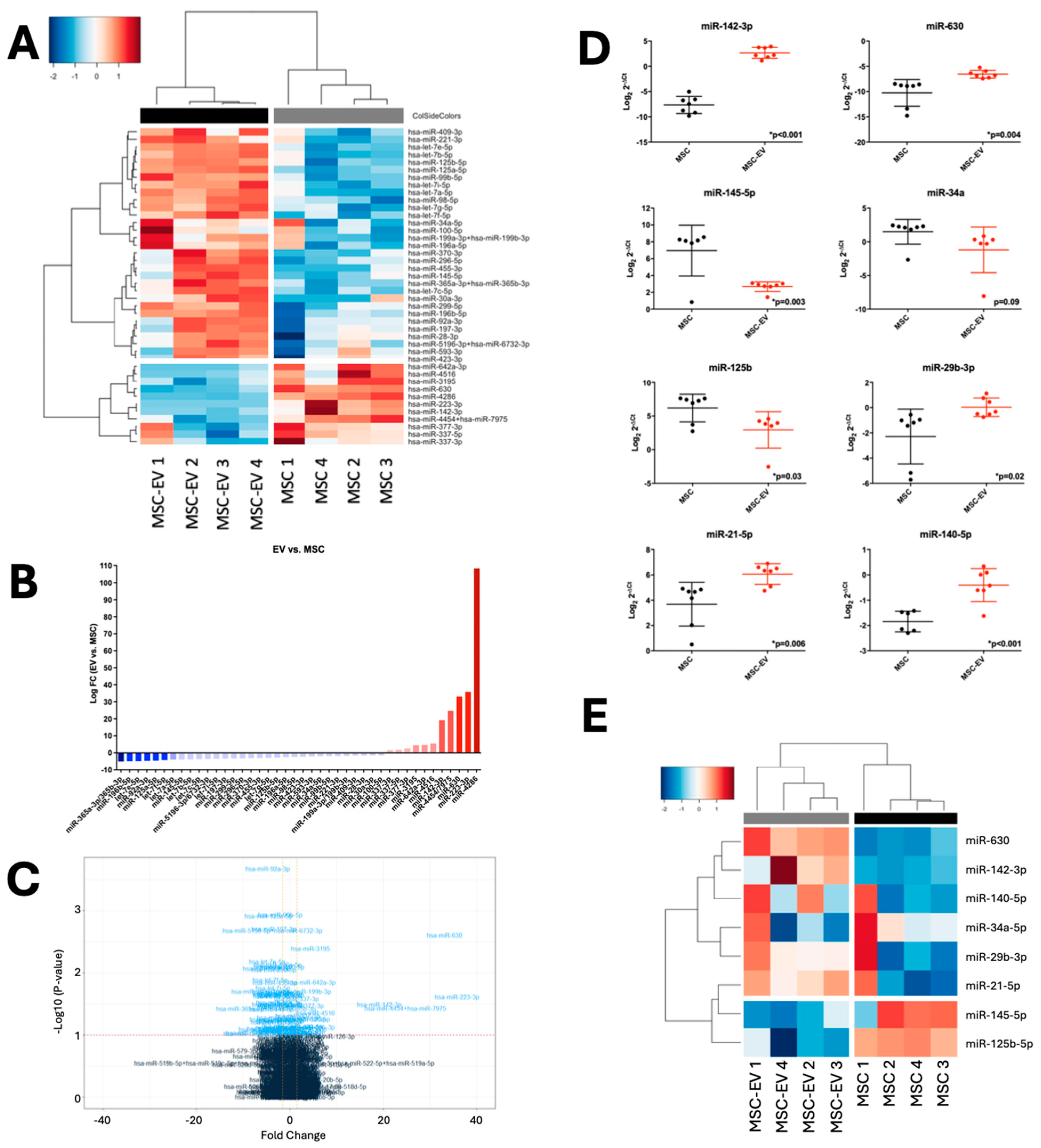
2.2. MSC-EVs Demonstrate Distinct MicroRNA Profiles from Parental MSCs
2.3. MSC and MSC-EV MicroRNA Profiles Can Be Validated in Independent Cohorts
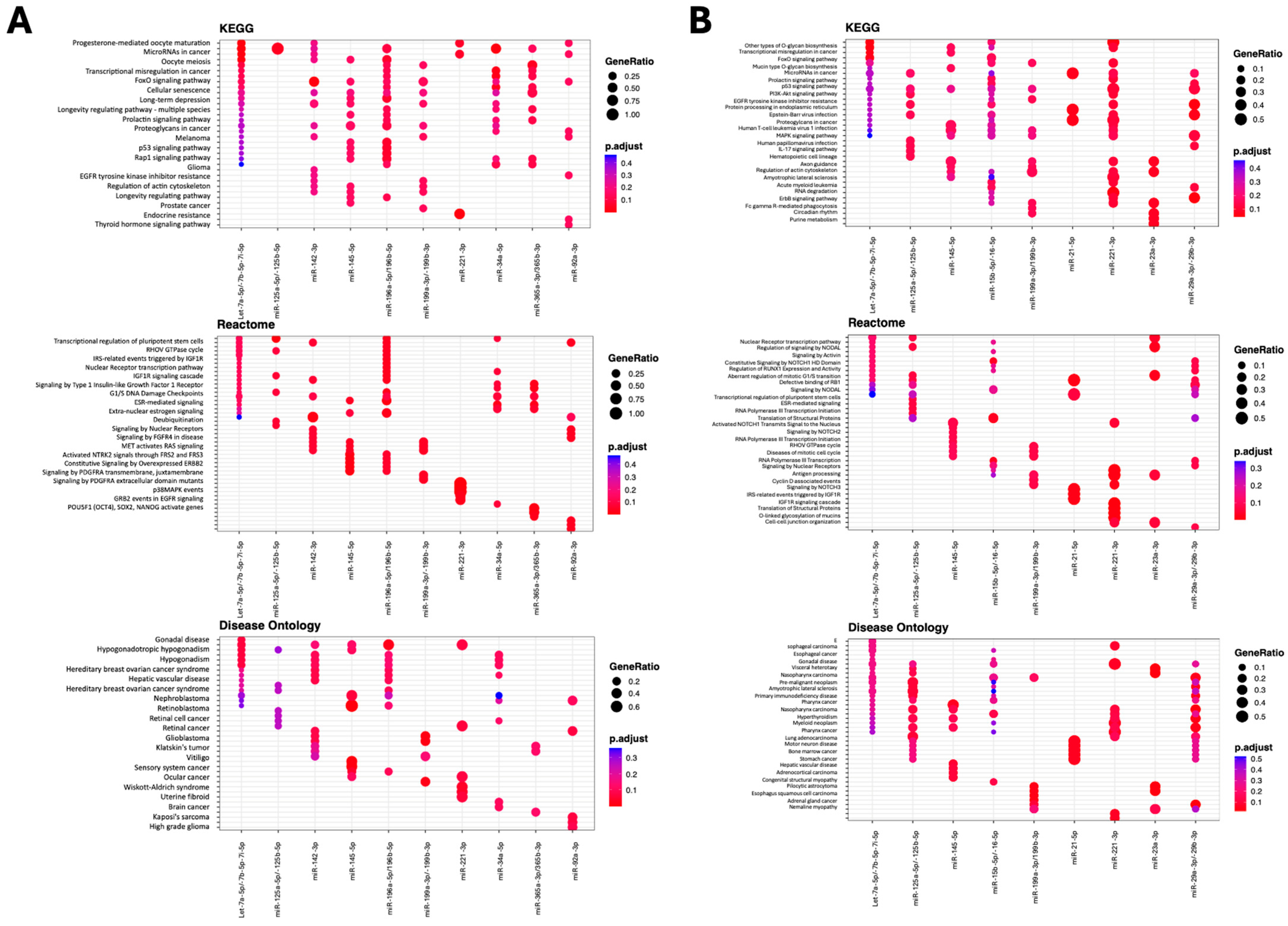
2.4. MSC-EV MicroRNAs Are Predicted to Target Fundamental Pathways
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
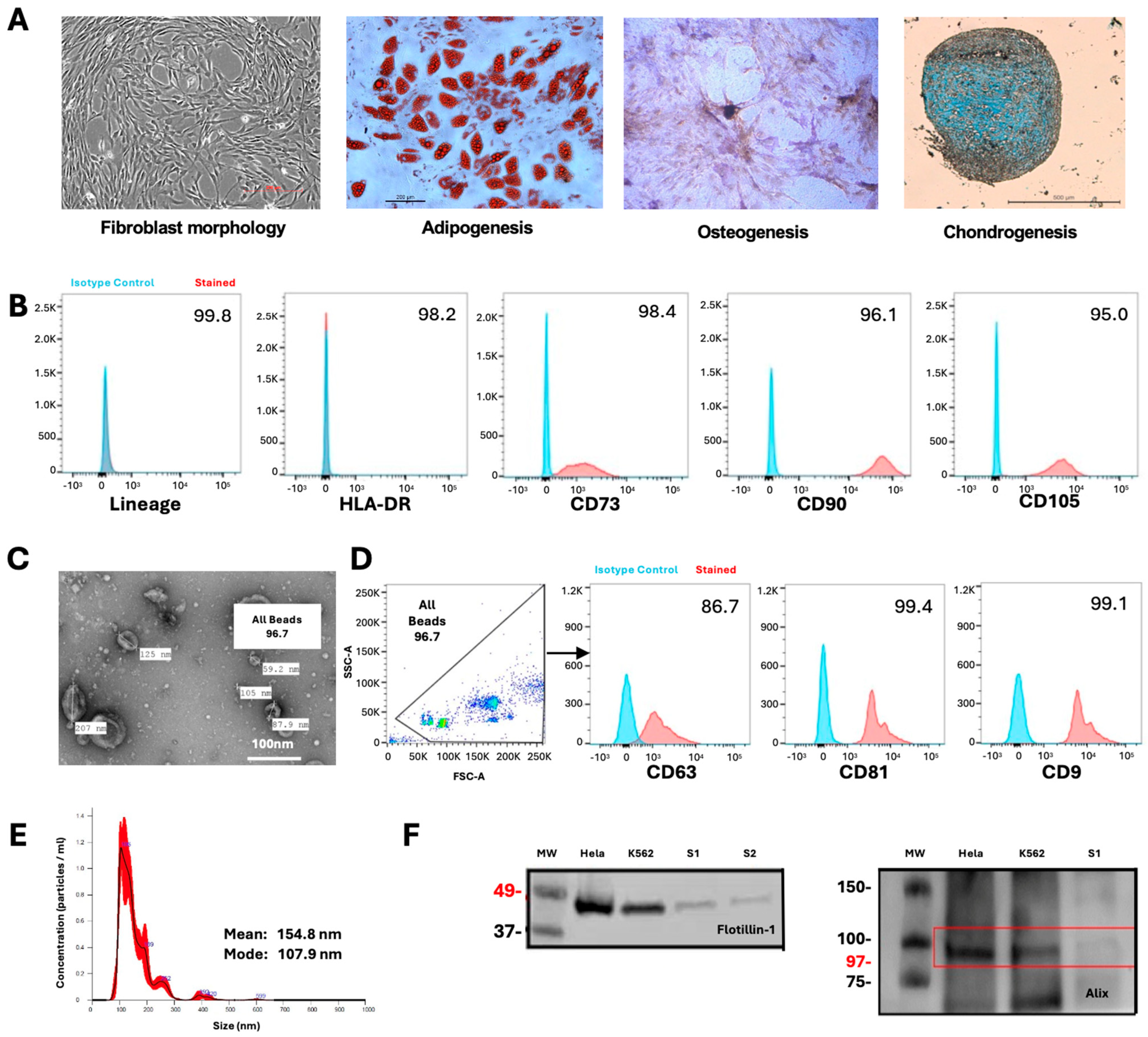
4.1. MSC Culture and Characterization
4.2. MSC-EV Isolation
4.3. MSC-EV Characterization
4.3.1. Transmission Electron Microscopy
4.3.2. Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis
4.3.3. Western Blot
4.3.4. Flow Cytometry
4.4. RNA Isolation and Quantification
4.5. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
4.6. NanoString
4.7. Pathway and Gene Enrichment Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Uccelli, A.; Moretta, L.; Pistoia, V. Mesenchymal stem cells in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 8, 726–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuk, P.A.; Zhu, M.; Mizuno, H.; Huang, J.; Futrell, J.W.; Katz, A.J.; Benhaim, P.; Lorenz, H.P.; Hedrick, M.H. Multilineage cells from human adipose tissue: Implications for cell-based therapies. Tissue Eng. 2001, 7, 211–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffiths, M.J.; Bonnet, D.; Janes, S.M. Stem cells of the alveolar epithelium. Lancet 2005, 366, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beltrami, A.P.; Barlucchi, L.; Torella, D.; Baker, M.; Limana, F.; Chimenti, S.; Kasahara, H.; Rota, M.; Musso, E.; Urbanek, K.; et al. Adult cardiac stem cells are multipotent and support myocardial regeneration. Cell 2003, 114, 763–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, M.S.; Lee, J.L.; Chang, Y.J.; Hwang, S. Isolation of human multipotent mesenchymal stem cells from second-trimester amniotic fluid using a novel two-stage culture protocol. Hum. Reprod. 2004, 19, 1450–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igura, K.; Zhang, X.; Takahashi, K.; Mitsuru, A.; Yamaguchi, S.; Takahashi, T. Isolation and characterization of mesenchymal progenitor cells from chorionic villi of human placenta. Cytotherapy 2004, 6, 543–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.S.; Hung, S.C.; Peng, S.T.; Huang, C.C.; Wei, H.M.; Guo, Y.J.; Fu, Y.S.; Lai, M.C.; Chen, C.C. Mesenchymal stem cells in the Wharton’s jelly of the human umbilical cord. Stem Cells 2004, 22, 1330–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominici, M.; Le Blanc, K.; Mueller, I.; Slaper-Cortenbach, I.; Marini, F.; Krause, D.; Deans, R.; Keating, A.; Prockop, D.; Horwitz, E. Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy 2006, 8, 315–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Manrreza, M.E.; Montesinos, J.J. Immunoregulation by mesenchymal stem cells: Biological aspects and clinical applications. J. Immunol. Res. 2015, 2015, 394917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Carrasco, R.; Sanchez-Abarca, L.; Nieto-Gomez, C.; García, E.M.; Sánchez-Guijo, F.; Argüeso, P.; Aijón, J.; Hernández-Galilea, E.; Velasco, A. Subconjunctival injection of mesenchymal stromal cells protects the cornea in an experimental model of GVHD. Ocul. Surf. 2019, 17, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartunek, J.; Behfar, A.; Dolatabadi, D.; Vanderheyden, M.; Ostojic, M.; Dens, J.; El Nakadi, B.; Banovic, M.; Beleslin, B.; Vrolix, M.; et al. Cardiopoietic stem cell therapy in heart failure: The C-CURE (Cardiopoietic stem Cell therapy in heart failURE) multicenter randomized trial with lineage-specified biologics. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2013, 61, 2329–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, R.; Lin, H.; Fu, J.; Zou, Z.; Zhang, A.; Shi, J.; Chen, L.; Lv, S.; et al. Human mesenchymal stem cell transfusion is safe and improves liver function in acute-on-chronic liver failure patients. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2012, 1, 725–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, C.W.; Lee, S.H. Potential and Therapeutic Efficacy of Cell-based Therapy Using Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Acute/chronic Kidney Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ankrum, J.A.; Ong, J.F.; Karp, J.M. Mesenchymal stem cells: Immune evasive, not immune privileged. Nat. Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.B.; Ha, C.W.; Lee, C.H.; Yoon, Y.C.; Park, Y. Cartilage Regeneration in Osteoarthritic Patients by a Composite of Allogeneic Umbilical Cord Blood-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Hyaluronate Hydrogel: Results from a Clinical Trial for Safety and Proof-of-Concept with 7 Years of Extended Follow-Up. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2017, 6, 613–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volarevic, V.; Arsenijevic, N.; Lukic, M.L.; Stojkovic, M. Concise review: Mesenchymal stem cell treatment of the complications of diabetes mellitus. Stem Cells 2011, 29, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.J.; Moon, G.J.; Chang, W.H.; Kim, Y.-H.; Bang, O.Y. Intravenous transplantation of mesenchymal stem cells preconditioned with early phase stroke serum: Current evidence and study protocol for a randomized trial. Trials 2013, 14, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, R.; Yajima, T.; Yamazaki, M.; Kanai, T.; Mukai, M.; Okamoto, S.; Ikeda, Y.; Hibi, T.; Inazawa, J.; Watanabe, M. Damaged epithelia regenerated by bone marrow-derived cells in the human gastrointestinal tract. Nat. Med. 2002, 8, 1011–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, Y.; Zhang, M.; Tao, E.; Wang, J.; Wei, N.; Lu, Y.; Liu, Q.; Hao, K.; Zhou, F.; Wang, G. Pharmacokinetic characteristics of mesenchymal stem cells in translational challenges. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, D.; Zhao, F. Updates on clinical trials evaluating the regenerative potential of allogenic mesenchymal stem cells in COVID-19. npj Regen. Med. 2021, 6, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, D.J.; Rolandsson Enes, S. MSC-Based Cell Therapy for COVID-19-Associated ARDS and Classical ARDS: Comparative Perspectives. Curr. Stem Cell Rep. 2024, 10, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casiraghi, F.; Noris, M.; Remuzzi, G. Immunomodulatory effects of mesenchymal stromal cells in solid organ transplantation. Curr. Opin. Organ Transplant. 2010, 15, 731–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, S.; Horwood, N.; Cope, A.; Dazzi, F. The antiproliferative effect of mesenchymal stem cells is a fundamental property shared by all stromal cells. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 2824–2831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corcione, A.; Benvenuto, F.; Ferretti, E.; Giunti, D.; Cappiello, V.; Cazzanti, F.; Risso, M.; Gualandi, F.; Mancardi, G.L.; Pistoia, V.; et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells modulate B-cell functions. Blood 2006, 107, 367–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glennie, S.; Soeiro, I.; Dyson, J.; Lam, E.; Dazzi, F. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells induce division arrest anergy of activated T cells. Blood 2005, 105, 2821–2827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nauta, A.J.; Kruisselbrink, A.B.; Lurvink, E.; Willemze, R.; Fibbe, W.E. Mesenchymal stem cells inhibit generation and function of both CD34+-derived and monocyte-derived dendritic cells. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 2080–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, S.; Grange, C.; Deregibus, M.C.; Calogero, R.A.; Saviozzi, S.; Collino, F.; Morando, L.; Busca, A.; Falda, M.; Bussolati, B.; et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived microvesicles protect against acute tubular injury. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 20, 1053–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.J.; Moon, G.J.; Cho, Y.H.; Kang, H.Y.; Hyung, N.K.; Kim, D.; Lee, J.H.; Nam, J.Y.; Bang, O.Y.; Rameshwar, P. Circulating mesenchymal stem cells microparticles in patients with cerebrovascular disease. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e37036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, R.C.; Arslan, F.; Tan, S.S.; Tan, B.; Choo, A.; Lee, M.M.; Chen, T.S.; Teh, B.J.; Eng, J.K.L.; Sidik, H.; et al. Derivation and characterization of human fetal MSCs: An alternative cell source for large-scale production of cardioprotective microparticles. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2010, 48, 1215–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keerthikumar, S.; Chisanga, D.; Ariyaratne, D.; Al Saffar, H.; Anand, S.; Zhao, K.; Samuel, M.; Pathan, M.; Jois, M.; Chilamkurti, N.; et al. ExoCarta: A Web-Based Compendium of Exosomal Cargo. J. Mol. Biol. 2016, 428, 688–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, R.C.; Yeo, R.W.; Lim, S.K. Mesenchymal stem cell exosomes. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2015, 40, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Yin, Y.; Lai, R.C.; Tan, S.S.; Choo, A.B.H.; Lim, S.K. Mesenchymal stem cells secrete immunologically active exosomes. Stem Cells Dev. 2014, 23, 1233–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stawarska, A.; Bamburowicz-Klimkowska, M.; Runden-Pran, E.; Dusinska, M.; Cimpan, M.R.; Rios-Mondragon, I.; Grudzinski, I.P. Extracellular Vesicles as Next-Generation Diagnostics and Advanced Therapy Medicinal Products. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 6533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Milbank, E.; Cragano, N.R.V.; Gonzalez-Garcia, I.; Garcia, M.R.; Rivas-Limeres, V.; Perdomo, L.; Hilairet, G.; Ruiz-Pino, F.; Mallegol, P.; Morgan, D.A.; et al. Small extracellular vesicle-mediated targeting of hypothalamic AMPKα1 corrects obesity through BAT activation. Nat. Metab. 2021, 3, 1415–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, Y.; Tsuchiya, A.; Terai, S. The development of mesenchymal stem cell therapy in the present, and the perspective of cell-free therapy in the future. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2021, 27, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, I.K.; Wood, M.J.A.; Fuhrmann, G. Extracellular vesicles as a next-generation drug delivery platform. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2021, 16, 748–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phinney, D.G.; Di Giuseppe, M.; Njah, J.; Sala, E.; Shiva, S.; St Croix, C.M.; Stolz, D.B.; Watkins, S.C.; Di, Y.P.; Leikauf, G.D.; et al. Mesenchymal stem cells use extracellular vesicles to outsource mitophagy and shuttle microRNAs. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baglio, S.R.; Rooijers, K.; Koppers-Lalic, D.; Verweij, F.J.; Pérez Lanzón, M.; Zini, N.; Naaijkens, B.; Perut, F.; Niessen, H.W.M.; Baldini, N.; et al. Human bone marrow- and adipose-mesenchymal stem cells secrete exosomes enriched in distinctive miRNA and tRNA species. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2015, 6, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jothimani, G.; Pathak, S.; Dutta, S.; Duttaroy, A.K.; Banerjee, A. A Comprehensive Cancer-Associated MicroRNA Expression Profiling and Proteomic Analysis of Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2022, 19, 1013–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soni, N.; Gupta, S.; Rawat, S.; Krishnakumar, V.; Mohanty, S.; Banerjee, A. MicroRNA-Enriched Exosomes from Different Sources of Mesenchymal Stem Cells Can Differentially Modulate Functions of Immune Cells and Neurogenesis. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, Y.; Miyaki, S.; Ishitobi, H.; Matsuyama, S.; Nakasa, T.; Kamei, N.; Akimoto, T.; Higashi, Y.; Ochi, M. Mesenchymal-stem-cell-derived exosomes accelerate skeletal muscle regeneration. FEBS Lett. 2015, 589, 1257–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zou, R.; Wang, Z.; Wen, C.; Zhang, F.; Lin, F. Exosomal KLF3-AS1 from hMSCs promoted cartilage repair and chondrocyte proliferation in osteoarthritis. Biochem. J. 2018, 475, 3629–3638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Lan, B.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Xiao, P.; Meng, Q.; Geng, Y.-j.; Yu, X.-y.; et al. MiRNA-Sequence Indicates That Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Exosomes Have Similar Mechanism to Enhance Cardiac Repair. BioMed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 4150705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemeda, H.; Giebel, B.; Wagner, W. Evaluation of human platelet lysate versus fetal bovine serum for culture of mesenchymal stromal cells. Cytotherapy 2014, 16, 170–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haque, N.; Kasim, N.H.; Rahman, M.T. Optimization of pre-transplantation conditions to enhance the efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2015, 11, 324–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spees, J.L.; Gregory, C.A.; Singh, H.; Tucker, H.A.; Peister, A.; Lynch, P.J.; Hsu, S.-C.; Smith, J.; Prockop, D.J. Internalized antigens must be removed to prepare hypoimmunogenic mesenchymal stem cells for cell and gene therapy. Mol. Ther. 2004, 9, 747–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crespo-Diaz, R.; Behfar, A.; Butler, G.W.; Padley, D.J.; Sarr, M.G.; Bartunek, J.; Dietz, A.B.; Terzic, A. Platelet lysate consisting of a natural repair proteome supports human mesenchymal stem cell proliferation and chromosomal stability. Cell Transplant. 2011, 20, 797–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernardo, M.E.; Avanzini, M.A.; Perotti, C.; Cometa, A.; Moretta, A.; Lenta, E.; Del Fante, C.; Novara, F.; de Silvestri, A.; Amendola, G.; et al. Optimization of in vitro expansion of human multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells for cell-therapy approaches: Further insights in the search for a fetal calf serum substitute. J. Cell. Physiol. 2007, 211, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flemming, A.; Schallmoser, K.; Strunk, D.; Stolk, M.; Volk, H.-D.; Seifert, M. Immunomodulative efficacy of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells cultured in human platelet lysate. J. Clin. Immunol. 2011, 31, 1143–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witwer, K.W.; Van Balkom, B.W.M.; Bruno, S.; Choo, A.; Dominici, M.; Gimona, M.; Hill, A.F.; De Kleijn, D.; Koh, M.; Lai, R.C.; et al. Defining mesenchymal stromal cell (MSC)-derived small extracellular vesicles for therapeutic applications. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2019, 8, 1609206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welsh, J.A.; Goberdhan, D.C.I.; O’Driscoll, L.; Buzas, E.I.; Blenkiron, C.; Bussolati, B.; Cai, H.; Di Vizio, D.; Driedonks, T.A.P.; Erdbrügger, U.; et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles (MISEV2023): From basic to advanced approaches. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2024, 13, e12404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaka, R.; Parent, S.; Risha, Y.; Khan, S.; Courtman, D.; Stewart, D.J.; Davis, D.R. Extracellular vesicle microRNA and protein cargo profiling in three clinical-grade stem cell products reveals key functional pathways. Mol. Ther.—Nucleic Acids 2023, 32, 80–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, X.Y.; Yu, Y.; Lin, S.; Zhong, L.; Sun, J.; Zhang, G.; Zhu, Y. Comprehensive miRNA Analysis of Human Umbilical Cord-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal Cells and Extracellular Vesicles. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2018, 43, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Ochiya, T.; Xiao, Z.; Itaya, T. Distinct Mirna Expression Patterns of Extracellular Vesicles Derived From 4 Types of Mesenchymal Stem Cells. J. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2018, 8, 1000415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.S.; Lai, R.C.; Lee, M.M.; Choo, A.B.H.; Lee, C.N.; Lim, S.K. Mesenchymal stem cell secretes microparticles enriched in pre-microRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 38, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, S.W.; Wang, J.; Lee, C.J.; Liu, M.; Neelamegham, S.; Canty, J.M.; Nguyen, J. The microRNA regulatory landscape of MSC-derived exosomes: A systems view. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuta, T.; Miyaki, S.; Ishitobi, H.; Ogura, T.; Kato, Y.; Kamei, N.; Miyado, K.; Higashi, Y.; Ochi, M. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes Promote Fracture Healing in a Mouse Model. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2016, 5, 1620–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueroa, J.; Phillips, L.M.; Shahar, T.; Hossain, A.; Gumin, J.; Kim, H.; Bean, A.J.; Calin, G.A.; Fueyo, J.; Walters, E.T.; et al. Exosomes from Glioma-Associated Mesenchymal Stem Cells Increase the Tumorigenicity of Glioma Stem-like Cells via Transfer of miR-1587. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 5808–5819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubkova, E.; Evtushenko, E.; Beloglazova, I.; Osmak, G.; Koshkin, P.; Moschenko, A.; Menshikov, M.; Parfyonova, Y. Analysis of MicroRNA Profile Alterations in Extracellular Vesicles From Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Overexpressing Stem Cell Factor. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 754025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, C.C.; Lopes-Pacheco, M.; English, K.; Rolandsson Enes, S.; Krasnodembskaya, A.; Rocco, P.R.M. The MSC-EV-microRNAome: A Perspective on Therapeutic Mechanisms of Action in Sepsis and ARDS. Cells 2024, 13, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazari-Shafti, T.Z.; Neuber, S.; Duran, A.G.; Exarchos, V.; Beez, C.M.; Meyborg, H.; Krüger, K.; Wolint, P.; Buschmann, J.; Böni, R.; et al. MiRNA Profiles of Extracellular Vesicles Secreted by Mesenchymal Stromal Cells-Can They Predict Potential Off-Target Effects? Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanjurjo-Rodríguez, C.; Crossland, R.E.; Reis, M.; Pandit, H.; Wang, X.-n.; Jones, E. Characterization and miRNA Profiling of Extracellular Vesicles from Human Osteoarthritic Subchondral Bone Multipotential Stromal Cells (MSCs). Stem Cells Int. 2021, 2021, 7232773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, S.; Zhang, C.; Ma, Q.; Li, M.; Yu, X.; Zhang, H.; Lv, S.; Shi, Y.; He, X. Unveiling the multifaceted roles of microRNAs in extracellular vesicles derived from mesenchymal stem cells: Implications in tumor progression and therapeutic interventions. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1438177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Mijiti, W.; Jia, Q.; Yi, Z.; Ma, J.; Zhou, Z.; Xie, Z. Exploration of altered miRNA expression and function in MSC-derived extracellular vesicles in response to hydatid antigen stimulation. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1381012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.C.; Venø, M.T.; Chen, L.; Ditzel, N.; Le, D.Q.S.; Dillschneider, P.; Kassem, M.; Kjems, J. Global MicroRNA Profiling in Human Bone Marrow Skeletal-Stromal or Mesenchymal-Stem Cells Identified Candidates for Bone Regeneration. Mol. Ther. 2018, 26, 593–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, M.; Huang, L.; Yang, J.; Chiang, Z.; Chen, S.; Liu, J.; Guo, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, X.; Xu, X.; et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles for immunomodulation and regeneration: A next generation therapeutic tool? Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kageyama, Y.; Koide, Y.; Yoshida, A.; Uchijima, M.; Arai, T.; Miyamoto, S.; Ozeki, T.; Hiyoshi, M.; Kushida, K.; Inoue, T. Reduced susceptibility to collagen-induced arthritis in mice deficient in IFN-gamma receptor. J. Immunol. 1998, 161, 1542–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.C.; Kang, M.; Leung, K.; Lu, Y.; Shirazi, S.; Gajendrareddy, P.; Ravindran, S. Micro RNA based MSC EV engineering: Targeting the BMP2 cascade for bone repair. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2023, 11, 1127594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Choi, Y.; Lim, C.W.; Park, J.M.; Yu, S.H.; Kim, Y.; Han, H.J.; Kim, C.H.; Song, Y.S.; Kim, C.; et al. Potential Therapeutic Effect of Micrornas in Extracellular Vesicles from Mesenchymal Stem Cells against SARS-CoV-2. Cells 2021, 10, 2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crossland, R.E.; Albiero, A.; Sanjurjo-Rodríguez, C.; Reis, M.; Resteu, A.; Anderson, A.E.; Dickinson, A.M.; Pratt, A.G.; Birch, M.; McCaskie, A.W.; et al. MicroRNA profiling of low concentration extracellular vesicle RNA utilizing NanoString nCounter technology. J. Extracell. Biol. 2023, 2, e72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, J.; Kundal, K.; Rai, B.; Saxena, P.; Katiyar, S.; Tripathy, N.; Yadav, S.; Gupta, R.; Kumar, R.; Nityanand, S.; et al. Global microRNA profiling of bone marrow-MSC derived extracellular vesicles identifies miRNAs associated with hematopoietic dysfunction in aplastic anemia. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 19654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Omar, O.; Vazirisani, F.; Thomsen, P.; Ekström, K. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes have altered microRNA profiles and induce osteogenic differentiation depending on the stage of differentiation. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0193059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eirin, A.; Zhu, X.-Y.; Puranik, A.S.; Woollard, J.R.; Tang, H.; Dasari, S.; Lerman, A.; van Wijnen, A.J.; Lerman, L.O. Integrated transcriptomic and proteomic analysis of the molecular cargo of extracellular vesicles derived from porcine adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0174303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, M.; Mavin, E.; Nicholson, L.; Green, K.; Dickinson, A.M.; Wang, X.N. Mesenchymal Stromal Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Attenuate Dendritic Cell Maturation and Function. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Théry, C.; Amigorena, S.; Raposo, G.; Clayton, A. Isolation and characterization of exosomes from cell culture supernatants and biological fluids. Curr. Protoc. Cell Biol. 2006, 30, 3.22.1–3.22.29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlachos, I.S.; Zagganas, K.; Paraskevopoulou, M.D.; Georgakilas, G.; Karagkouni, D.; Vergoulis, T.; Dalamagas, T.; Hatzigeorgiou, A.G. DIANA-miRPath v3.0: Deciphering microRNA function with experimental support. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, W460–W466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crossland, R.E.; Norden, J.; Juric, M.K.; Green, K.; Pearce, K.F.; Lendrem, C.; Greinix, H.T.; Dickinson, A.M. Expression of Serum microRNAs is Altered During Acute Graft-versus-Host Disease. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sticht, C.; De La Torre, C.; Parveen, A.; Gretz, N. miRWalk: An online resource for prediction of microRNA binding sites. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0206239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, S.; Xu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Xue, C.; Yang, C.; Bi, H.; Qian, X.; Wu, M.; Ji, K.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Umbilical Cord-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomal MicroRNAs Suppress Myofibroblast Differentiation by Inhibiting the Transforming Growth Factor-β/SMAD2 Pathway During Wound Healing. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2016, 5, 1425–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, A.; Rampersaud, Y.R.; Sharma, A.; Lewis, S.J.; Wu, B.; Datta, P.; Sundararajan, K.; Endisha, H.; Rossomacha, E.; Rockel, J.S.; et al. Identification of microRNA-181a-5p and microRNA-4454 as mediators of facet cartilage degeneration. JCI Insight 2016, 1, e86820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Crossland, R.E.; Sanjurjo-Rodríguez, C.; Reis, M.; Dickinson, A.M.; Jones, E.; Wang, X.-N. Selective MicroRNA Packaging Reveals Distinct Core Signatures in Human Mesenchymal-Stromal-Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 7010. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26147010
Crossland RE, Sanjurjo-Rodríguez C, Reis M, Dickinson AM, Jones E, Wang X-N. Selective MicroRNA Packaging Reveals Distinct Core Signatures in Human Mesenchymal-Stromal-Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(14):7010. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26147010
Chicago/Turabian StyleCrossland, Rachel E., Clara Sanjurjo-Rodríguez, Monica Reis, Anne M. Dickinson, Elena Jones, and Xiao-Nong Wang. 2025. "Selective MicroRNA Packaging Reveals Distinct Core Signatures in Human Mesenchymal-Stromal-Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 14: 7010. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26147010
APA StyleCrossland, R. E., Sanjurjo-Rodríguez, C., Reis, M., Dickinson, A. M., Jones, E., & Wang, X.-N. (2025). Selective MicroRNA Packaging Reveals Distinct Core Signatures in Human Mesenchymal-Stromal-Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(14), 7010. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26147010







