Transcriptomic Profiling of Paired Primary Tumors and CNS Metastases in Breast Cancer Reveals Immune Modulation Signatures
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Identification of Differentially Expressed Genes
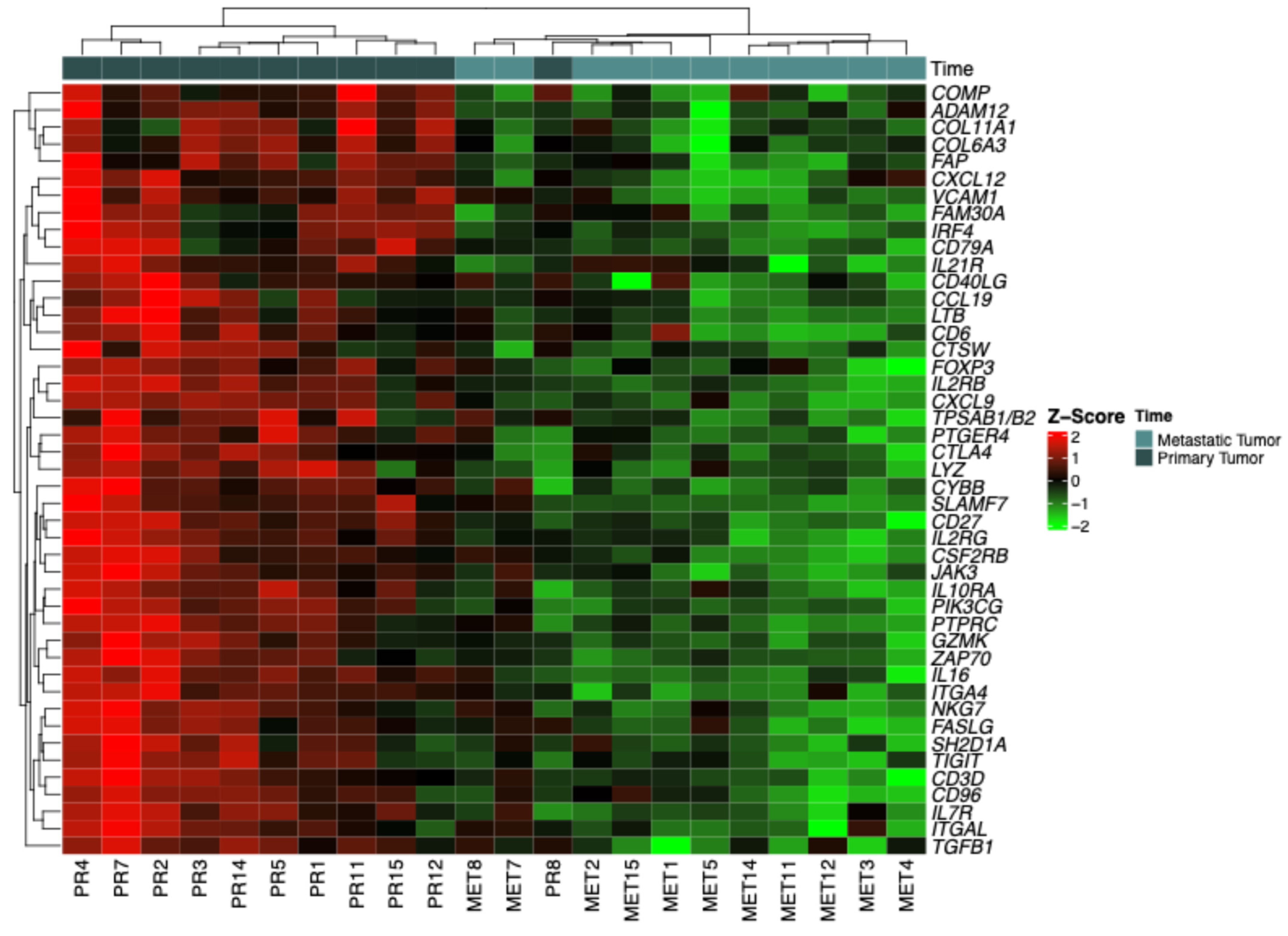
2.2. Categorization by Z-Scores
2.3. In Silico Analysis of Overall Survival and Recurrence-Free Survival
2.4. Overall Survival (OS)
2.5. Recurrence-Free Survival (RFS)
2.6. Gene Expression Comparison: Primary Tumor (T1) vs. Metastasis (T2)
2.7. Functional Enrichment Analysis of Immune-Related Genes
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sample Collection and RNA Extraction
4.2. Gene Expression Analysis Using NanoString Technology
4.3. Identification of Differentially Expressed Genes
4.4. Z-Score Categorization and Heatmap Visualization
4.5. Survival Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Instituto Nacional de Câncer (INCA). Estimativa 2023: Incidência de Câncer no Brasil; Instituto Nacional De Câncer: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2023; ISBN 9786588517093.
- Anderson, W.F.; Rosenberg, P.S.; Prat, A.; Perou, C.M.; Sherman, M.E. How Many Etiological Subtypes of Breast Cancer: Two, Three, Four, or More? J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2014, 106, dju165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perou, C.M.; Sørlie, T.; Eisen, M.B.; van de Rijn, M.; Jeffrey, S.S.; Rees, C.A.; Pollack, J.R.; Ross, D.T.; Johnsen, H.; Akslen, L.A.; et al. Molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature 2000, 406, 747–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Januškevičienė, I.; Petrikaitė, V. Heterogeneity of breast cancer: The importance of interaction between different tumor cell populations. Life Sci. 2019, 239, 117009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesh, K.; Massagué, J. Targeting metastatic cancer. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerstberger, S.; Jiang, Q.; Ganesh, K. Metastasis. Cell 2023, 186, 1564–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castaneda, M.; den Hollander, P.; Kuburich, N.A.; Rosen, J.M.; Mani, S.A. Mechanisms of cancer metastasis. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2022, 87, 17–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, N.U.; Bellon, J.R.; Winer, E.P. CNS Metastases in Breast Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2004, 22, 3608–3617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukada, Y.; Fouad, A.; Pickren, J.W.; Lane, W.W. Central nervous system metastasis from breast carcinoma. Autopsy study. Cancer 1983, 52, 2349–2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altundag, K.; Bondy, M.L.; Mirza, N.Q.; Kau, S.-W.; Broglio, K.; Hortobagyi, G.N.; Rivera, E. Clinicopathologic characteristics and prognostic factors in 420 metastatic breast cancer patients with central nervous system metastasis. Cancer 2007, 110, 2640–2647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witzel, I.; Oliveira-Ferrer, L.; Pantel, K.; Müller, V.; Wikman, H. Breast cancer brain metastases: Biology and new clinical perspectives. Breast Cancer Res. 2016, 18, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graesslin, O.; Abdulkarim, B.S.; Coutant, C.; Huguet, F.; Gabos, Z.; Hsu, L.; Marpeau, O.; Uzan, S.; Pusztai, L.; Strom, E.A.; et al. Nomogram to Predict Subsequent Brain Metastasis in Patients with Metastatic Breast Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 2032–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quigley, M.R.; Fukui, O.; Chew, B.; Bhatia, S.; Karlovits, S. The shifting landscape of metastatic breast cancer to the CNS. Neurosurg. Rev. 2013, 36, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niikura, N.; Hayashi, N.; Masuda, N.; Takashima, S.; Nakamura, R.; Watanabe, K.; Kanbayashi, C.; Ishida, M.; Hozumi, Y.; Tsuneizumi, M.; et al. Treatment outcomes and prognostic factors for patients with brain metastases from breast cancer of each subtype: A multicenter retrospective analysis. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2014, 147, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amir, E.; Clemons, M. Should a biopsy be recommended to confirm metastatic disease in women with breast cancer? Lancet Oncol. 2009, 10, 933–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karagöz Özen, D.S.; Ozturk, M.A.; Aydin, Ö.; Turna, Z.H.; Ilvan, S.; Özgüroglu, M. Receptor expression discrepancy between primary and metastatic breast cancer lesions. Oncol. Res. Treat. 2014, 37, 622–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Poznak, C.; Somerfield, M.R.; Bast, R.C.; Cristofanilli, M.; Goetz, M.P.; Gonzalez-Angulo, A.M.; Hicks, D.G.; Hill, E.G.; Liu, M.C.; Lucas, W.; et al. Use of Biomarkers to Guide Decisions on Systemic Therapy for Women With Metastatic Breast Cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology Clinical Practice Guideline. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 2695–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regitnig, P.; Schippinger, W.; Lindbauer, M.; Samonigg, H.; Lax, S.F. Change of HER-2/neu status in a subset of distant metastases from breast carcinomas. J. Pathol. 2004, 203, 918–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, R.; Osako, T.; Okumura, Y.; Tashima, R.; Toyozumi, Y.; Arima, N. Changes in the ER, PgR, HER2, p53 and Ki-67 biological markers between primary and recurrent breast cancer: Discordance rates and prognosis. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2011, 9, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishizuka, I.; Ishikawa, T.; Hamaguchi, Y.; Kamiyama, M.; Ichikawa, Y.; Kadota, K.; Miki, R.; Tomaru, Y.; Mizuno, Y.; Tominaga, N.; et al. Analysis of gene expression involved in brain metastasis from breast cancer using cDNA microarray. Breast Cancer 2002, 9, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, L.; Simpson, P.T.; Smart, C.E.; Cocciardi, S.; Waddell, N.; Lane, A.; Morrison, B.J.; Vargas, A.C.; Healey, S.; Beesley, J.; et al. HER3 and downstream pathways are involved in colonization of brain metastases from breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2010, 12, R46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, A.H.; McGrane, J.; Mathew, J.; Palmer, J.; Hilton, D.A.; Purvis, G.; Jenkins, R. Changing molecular profile of brain metastases compared with matched breast primary cancers and impact on clinical outcomes. Br. J. Cancer 2016, 114, 793–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.S.; Ahn, J.-H.; Kim, M.K.; Sym, S.J.; Gong, G.; Ahn, S.D.; Kim, S.-B.; Kim, W.K. Brain metastases in breast cancer: Prognostic factors and management. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2008, 111, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyeong, S.; Cha, Y.J.; Ahn, S.G.; Suh, S.H.; Son, E.J.; Ahn, S.J. Subtypes of breast cancer show different spatial distributions of brain metastases. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0188542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neman, J.; Choy, C.; Kowolik, C.M.; Anderson, A.; Duenas, V.J.; Waliany, S.; Chen, B.T.; Chen, M.Y.; Jandial, R. Co-evolution of breast-to-brain metastasis and neural progenitor cells. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2013, 30, 753–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Momeny, M.; Saunus, J.M.; Marturana, F.; McCart Reed, A.E.; Black, D.; Sala, G.; Iacobelli, S.; Holland, J.D.; Yu, D.; Da Silva, L.; et al. Heregulin-HER3-HER2 signaling promotes matrix metalloproteinase-dependent blood-brain-barrier transendothelial migration of human breast cancer cell lines. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 3932–3946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neman, J.; Termini, J.; Wilczynski, S.; Vaidehi, N.; Choy, C.; Kowolik, C.M.; Li, H.; Hambrecht, A.C.; Roberts, E.; Jandial, R. Human breast cancer metastases to the brain display GABAergic properties in the neural niche. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 984–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, L.; Yang, H.; Li, C.; Fang, C. Identification of potential genes related to breast cancer brain metastasis in breast cancer patients. Biosci. Rep. 2021, 41, BSR20211615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gril, B.; Palmieri, D.; Qian, Y.; Anwar, T.; Liewehr, D.J.; Steinberg, S.M.; Andreu, Z.; Masana, D.; Fernández, P.; Steeg, P.S.; et al. Pazopanib inhibits the activation of PDGFRβ-expressing astrocytes in the brain metastatic microenvironment of breast cancer cells. Am. J. Pathol. 2013, 182, 2368–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, W.C.; Bader, J.S.; Braun, T.P.; Califano, A.; Clemons, P.A.; Druker, B.J.; Ewald, A.J.; Fu, H.; Jagu, S.; Kemp, C.J.; et al. An expanded universe of cancer targets. Cell 2021, 184, 1142–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakravarty, D.; Solit, D.B. Clinical cancer genomic profiling. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2021, 22, 483–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, J.J.; Jones, M.G.; Okimoto, R.A.; Nanjo, S.; Chan, M.M.; Yosef, N.; Bivona, T.G.; Weissman, J.S. Single-cell lineages reveal the rates, routes, and drivers of metastasis in cancer xenografts. Science 2021, 371, eabc1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ionkina, A.A.; Balderrama-Gutierrez, G.; Ibanez, K.J.; Phan, S.H.D.; Cortez, A.N.; Mortazavi, A.; Prescher, J.A. Transcriptome analysis of heterogeneity in mouse model of metastatic breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2021, 23, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedrosa, R.M.S.M.; Kros, J.M.; Schrijver, B.; Berrevoets, C.; Marques, R.B.; van Eijck, C.C.H.J.; Debets, R.; Leenen, P.M.; Dik, W.A.; Mustafa, D.M. T lymphocyte-derived IFN-γ facilitates breast cancer cells to pass the blood-brain barrier: An in vitro study corroborating translational data. Heliyon 2024, 10, e36598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, J.; Zhu, L.; Li, J.; Wu, K.; Zhang, M.; Ma, S.; Chen, X.; Xia, B. Comprehensive analysis to identify IL7R as a immunotherapy biomarker from pan-cancer analysis to in vitro validation. Discov. Oncol. 2024, 15, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Liang, M.; Lin, Y.; Lv, J.; Chen, M.; Zhou, P.; Fu, F.; Wang, C. Transcriptional Expressions of CXCL9/10/12/13 as Prognosis Factors in Breast Cancer. J. Oncol. 2020, 2020, 4270957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Zhang, H.; Liu, J.; Hou, C.; Zhang, H.; Yang, Z. IL-7R Expression Correlates with Prognosis in Breast Cancer. Comb. Chem. High Throughput Screen. 2024, 28, 973–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khojasteh-Leylakoohi, F.; Mohit, R.; Khalili-Tanha, N.; Asadnia, A.; Naderi, H.; Pourali, G.; Yousefli, Z.; Khalili-Tanha, G.; Khazaei, M.; Maftooh, M.; et al. Down regulation of Cathepsin W is associated with poor prognosis in pancreatic cancer. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 16678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, S.; Huang, Z.; Wei, C.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, H.; Chen, S.; Huang, Z. CD79A work as a potential target for the prognosis of patients with OSCC: Analysis of immune cell infiltration in oral squamous cell carcinoma based on the CIBERSORTx deconvolution algorithm. BMC Oral Health 2023, 23, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fidler, I.J. The role of the organ microenvironment in brain metastasis. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2011, 21, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Niu, W.; Ge, X.; Huang, F.; Pang, J.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Gao, W.; Fan, F.; et al. Experimental Study of Almonertinib Crossing the Blood-Brain Barrier in EGFR-Mutant NSCLC Brain Metastasis and Spinal Cord Metastasis Models. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 750031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Ou, Q.; Li, D.; Qin, T.; Bao, H.; Hou, X.; Wang, K.; Wang, F.; Deng, Q.; Liang, J.; et al. Genes associated with increased brain metastasis risk in non-small cell lung cancer: Comprehensive genomic profiling of 61 resected brain metastases versus primary non-small cell lung cancer (Guangdong Association Study of Thoracic Oncology 1036). Cancer 2019, 125, 3535–3544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padzińska-Pruszyńska, I.B.; Akbar, M.W.; Isbilen, M.; Górka, E.; Kucukkaraduman, B.; Canlı, S.D.; Dedeoğlu, E.; Azizolli, S.; Cela, I.; Akcay, A.G.; et al. Breast Cancer Plasticity after Chemotherapy Highlights the Need for Re-Evaluation of Subtyping in Residual Cancer and Metastatic Tissues. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 6054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Genes | Log Fold-Change | p-Value | Protein Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| CXCL9 | −4.26 | 0.000001 | Chemotactic for T-cells |
| IRF4 | −2.33 | 0.000002 | Interferon regulation |
| IL2RB | −2.10 | 0.000003 | T-cell-mediated immune response |
| IL16 | −1.78 | 0.000005 | Modulator of T-cell activation |
| IL2RG | −1.63 | 0.000006 | Signaling component of interleukin receptors |
| CD27 | −2.18 | 0.000006 | Maintenance of T-cell immunity |
| ITGA4 | −1.41 | 0.000009 | Cell surface adhesion and signaling |
| CXCL12 | −1.66 | 0.000141 | Signaling receptor and chemokine activity |
| COMP | −2.61 | 0.000153 | Extracellular matrix protein |
| COL6A3 | −2.32 | 0.000167 | Binding to extracellular matrix |
| CD79A | −2.40 | 0.000376 | B-cell antigen component |
| VCAM1 | −1.59 | 0.000391 | Leukocyte–endothelial cell adhesion |
| SLAMF7 | −1.54 | 0.000491 | Protein binding activity |
| GZMK | −1.58 | 0.000553 | Serine proteases |
| LTB | −1.99 | 0.000568 | Inflammatory response system |
| JAK3 | −1.54 | 0.000621 | Cytokine receptor-mediated |
| ADAM12 | −1.55 | 0.000646 | Cell–matrix interactions |
| FASLG | −1.45 | 0.000670 | Induction of apoptosis |
| CTSW | −1.52 | 0.000736 | Regulation of T-cell cytolytic activity |
| CSF2RB | −1.37 | 0.000839 | Interleukin-3 receptor activity |
| FAM30A | −1.58 | 0.000894 | LncRNA class |
| CD3D | −1.72 | 0.000904 | T-cell development and signal transduction |
| ZAP70 | −1.44 | 0.000112 | T-cell development and lymphocyte activation |
| PIK3CG | −1.20 | 0.000117 | Cell growth, survival, proliferation, and motility |
| FAP | −1.17 | 0.000161 | Epithelial–mesenchymal interactions |
| TPSAB1/B2 | −2.44 | 0.000170 | Tryptases |
| IL7R | −1.68 | 0.000189 | Lymphocyte development |
| COL11A1 | −2,00 | 0.000253 | Extracellular matrix structural constituent |
| CTLA4 | −1.39 | 0.000337 | Inhibitory signal to T-cells |
| LYZ | −2.03 | 0.000357 | Antitumor immune activity |
| PTPRC | −1.40 | 0.000365 | Cell growth, differentiation, and mitosis |
| CD6 | −1.20 | 0.000388 | Binding site for adhesion molecules |
| NKG7 | −1.84 | 0.000417 | Regulates cytotoxic granule exocytosis |
| PTGER4 | −1.04 | 0.000435 | Activates T-cell factor signaling |
| CCL19 | −1.96 | 0.000465 | Immunoregulatory and inflammatory processes |
| TIGIT | −1.45 | 0.000497 | Signaling receptor binding |
| CD96 | −1.10 | 0.000519 | Adhesive interactions of activated T- and NK cells |
| CYBB | −1.43 | 0.000712 | Microbicidal oxidase system of phagocytes |
| FOXP3 | −0.99 | 0.000725 | DNA-binding transcription factor activity |
| CD40LG | −1.11 | 0.000758 | Regulates B-cell function |
| TGFB1 | −0.82 | 0.000778 | Regulates gene expression |
| IL21R | −1.20 | 0.000835 | Proliferation and differentiation of immune cells |
| ITGAL | −1.29 | 0.000900 | Leukocyte intercellular adhesion |
| IL10RA | −1.09 | 0.000990 | Related to interferon receptors |
| SH2D1A | −1.29 | 0.016551 | Stimulation of T- and B-cells |
| Gene Set | Ratio of Proteins | Proteins in Pathway | Genes From Network | p-Value | FDR | Involved Genes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primary immunodeficiency (KEGG) | 0.0032 | 38 | 2 | 5.95 × 10−5 | 0.00143 | CD79A, IL7R |
| Cytokine–cytokine receptor interaction (KEGG) | 0.0245 | 295 | 2 | 3.48 × 10−3 | 0.034 | CXCL9, IL7R |
| ctcf: first multivalent nuclear factor (BioCarta) | 0.0018 | 22 | 1 | 7.29 × 10−3 | 0.034 | CD79A |
| Interleukin-7 signaling (Reactome) | 0.0018 | 22 | 1 | 7.29 × 10−3 | 0.034 | IL7R |
| BCR signaling pathway (BioCarta) | 0.0022 | 26 | 1 | 8.61 × 10−3 | 0.034 | CD79A |
| CXCR3-mediated signaling events (NCI) | 0.0029 | 35 | 1 | 0.012 | 0.034 | CXCL9 |
| IL-23-mediated signaling events (NCI) | 0.0031 | 37 | 1 | 0.012 | 0.034 | CXCL9 |
| B-cell activation (PID) | 0.0039 | 47 | 1 | 0.016 | 0.034 | CD79A |
| BCR signaling pathway (NCI) | 0.0054 | 65 | 1 | 0.021 | 0.034 | CD79A |
| B-cell receptor signaling pathway (KEGG) | 0.0068 | 82 | 1 | 0.027 | 0.034 | CD79A |
| Hematopoietic cell lineage (KEGG) | 0.0082 | 99 | 1 | 0.032 | 0.034 | IL7R |
| Viral protein interaction with cytokine and cytokine receptor (KEGG) | 0.0083 | 100 | 1 | 0.033 | 0.034 | CXCL9 |
| Toll-like receptor signaling pathway (KEGG) | 0.0086 | 104 | 1 | 0.034 | 0.034 | CXCL9 |
| Clathrin-mediated endocytosis (Reactome) | 0.0103 | 124 | 1 | 0.041 | 0.041 | IL7R |
| Lysosome (KEGG) | 0.0106 | 128 | 1 | 0.042 | 0.042 | CTSW |
| FoxO signaling pathway (KEGG) | 0.0109 | 131 | 1 | 0.043 | 0.043 | IL7R |
| Apoptosis (KEGG) | 0.0113 | 136 | 1 | 0.044 | 0.044 | CTSW |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Freitas, A.J.A.d.; Varuzza, M.B.; Calfa, S.; Causin, R.L.; Silva, V.D.d.; Souza, C.d.P.; Marques, M.M.C. Transcriptomic Profiling of Paired Primary Tumors and CNS Metastases in Breast Cancer Reveals Immune Modulation Signatures. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6944. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146944
Freitas AJAd, Varuzza MB, Calfa S, Causin RL, Silva VDd, Souza CdP, Marques MMC. Transcriptomic Profiling of Paired Primary Tumors and CNS Metastases in Breast Cancer Reveals Immune Modulation Signatures. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(14):6944. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146944
Chicago/Turabian StyleFreitas, Ana Julia Aguiar de, Muriele Bertagna Varuzza, Stéphanie Calfa, Rhafaela Lima Causin, Vinicius Duval da Silva, Cristiano de Pádua Souza, and Márcia Maria Chiquitelli Marques. 2025. "Transcriptomic Profiling of Paired Primary Tumors and CNS Metastases in Breast Cancer Reveals Immune Modulation Signatures" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 14: 6944. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146944
APA StyleFreitas, A. J. A. d., Varuzza, M. B., Calfa, S., Causin, R. L., Silva, V. D. d., Souza, C. d. P., & Marques, M. M. C. (2025). Transcriptomic Profiling of Paired Primary Tumors and CNS Metastases in Breast Cancer Reveals Immune Modulation Signatures. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(14), 6944. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146944









