Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Regulates Hepatitis B Virus cccDNA Levels
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
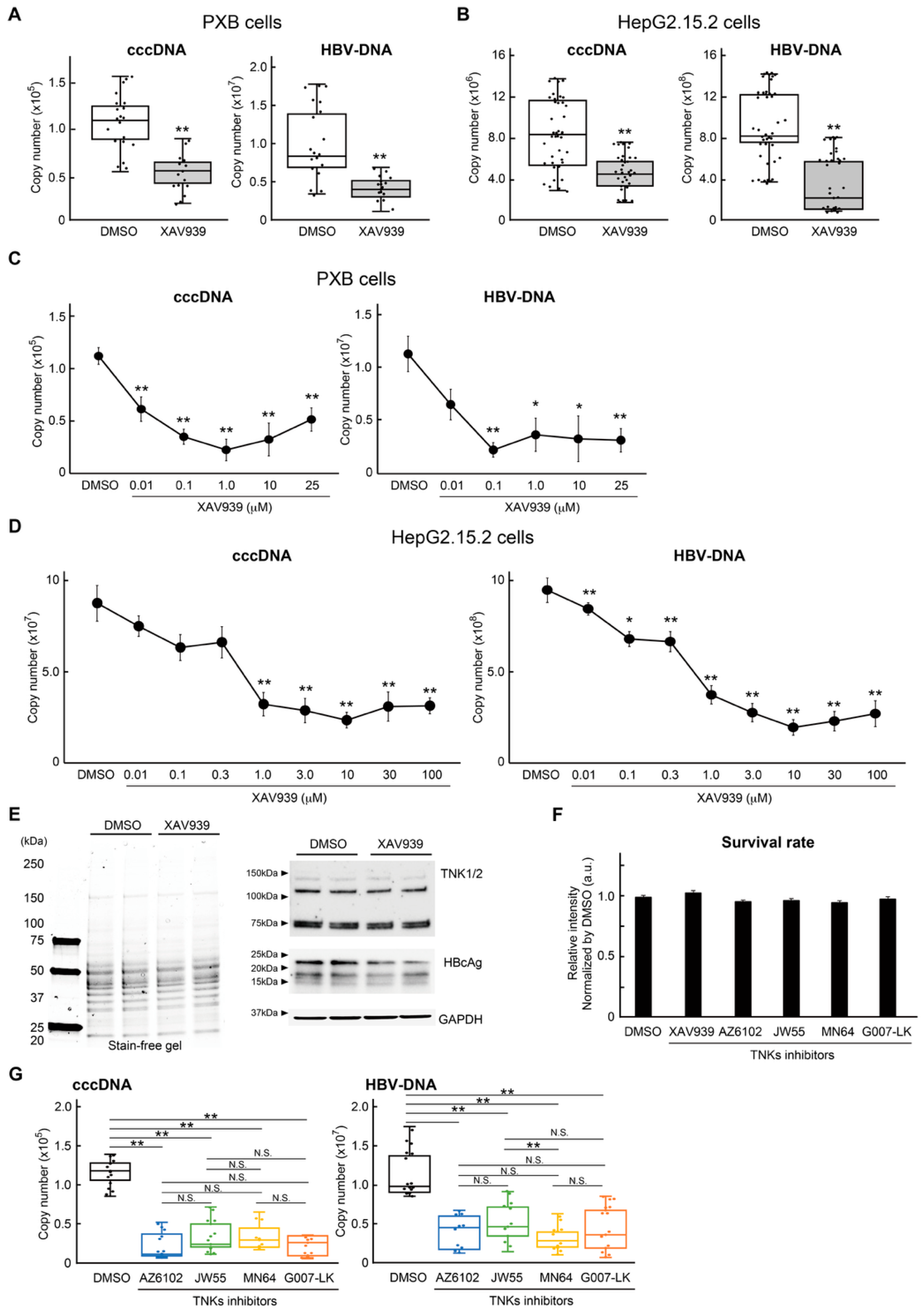
2.1. Inhibition of TNKS Eliminated HBV cccDNA
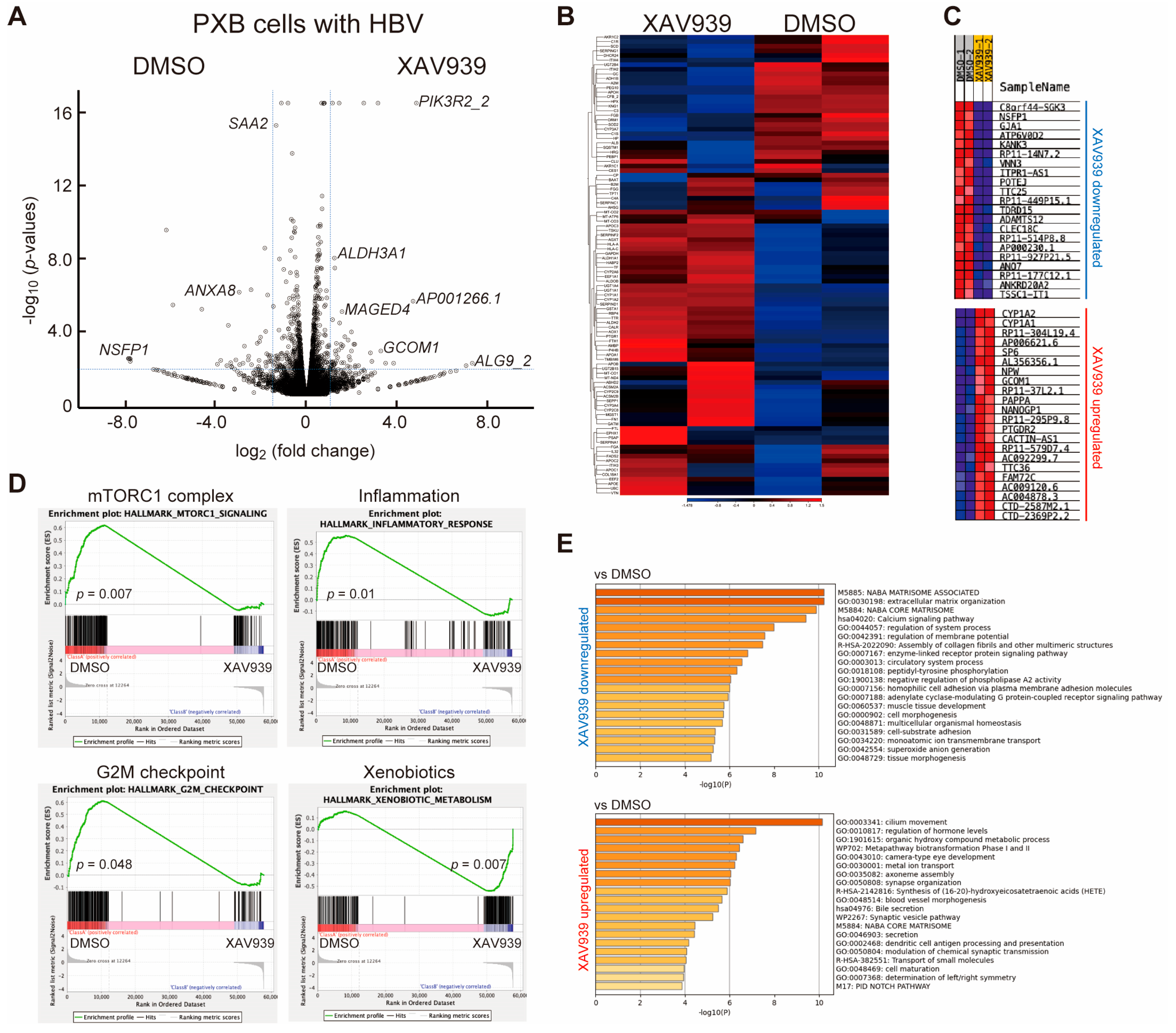
2.2. Identification of Differentially Expressed Genes (DEGs) Associated with TNKS Inhibition
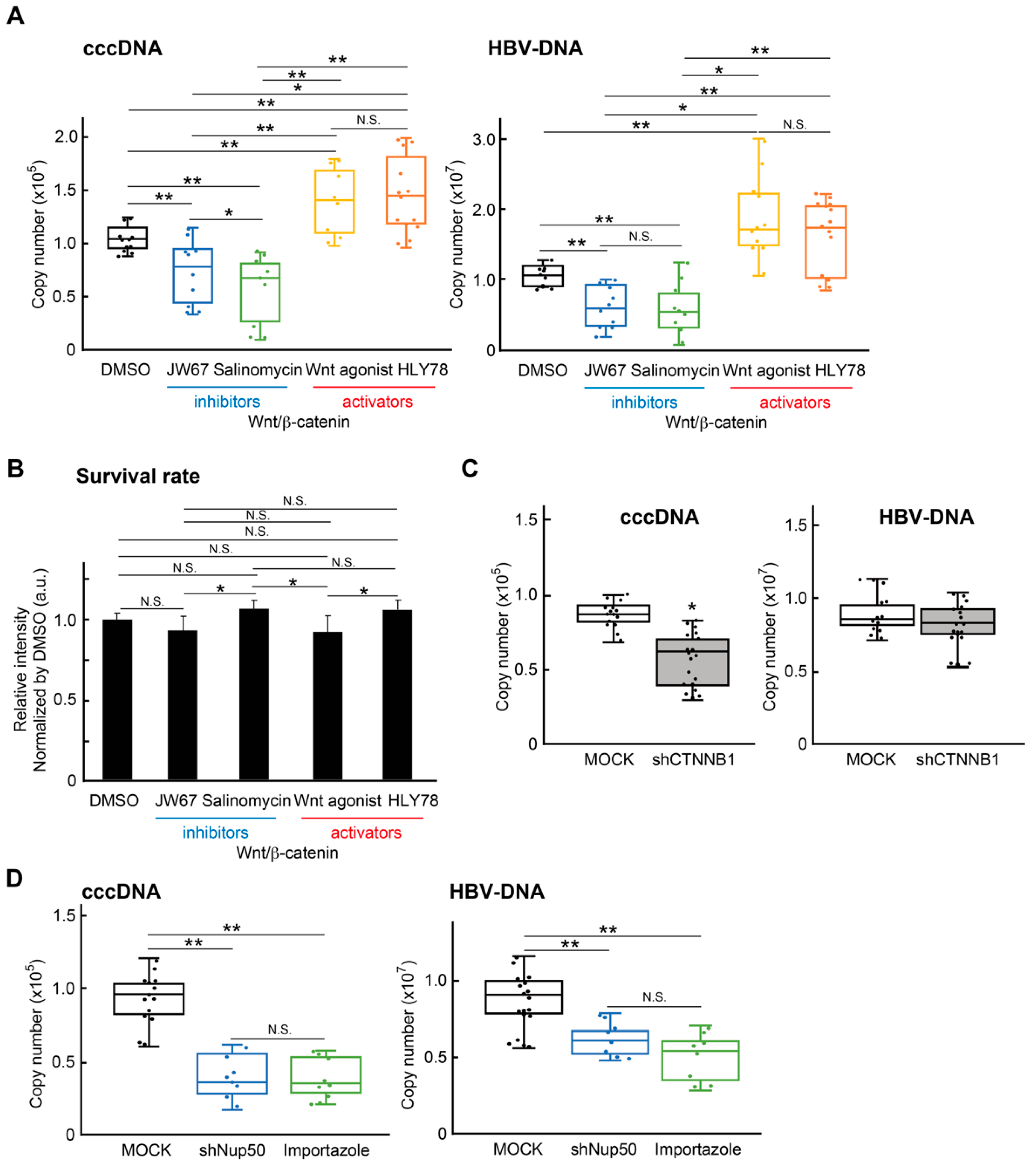
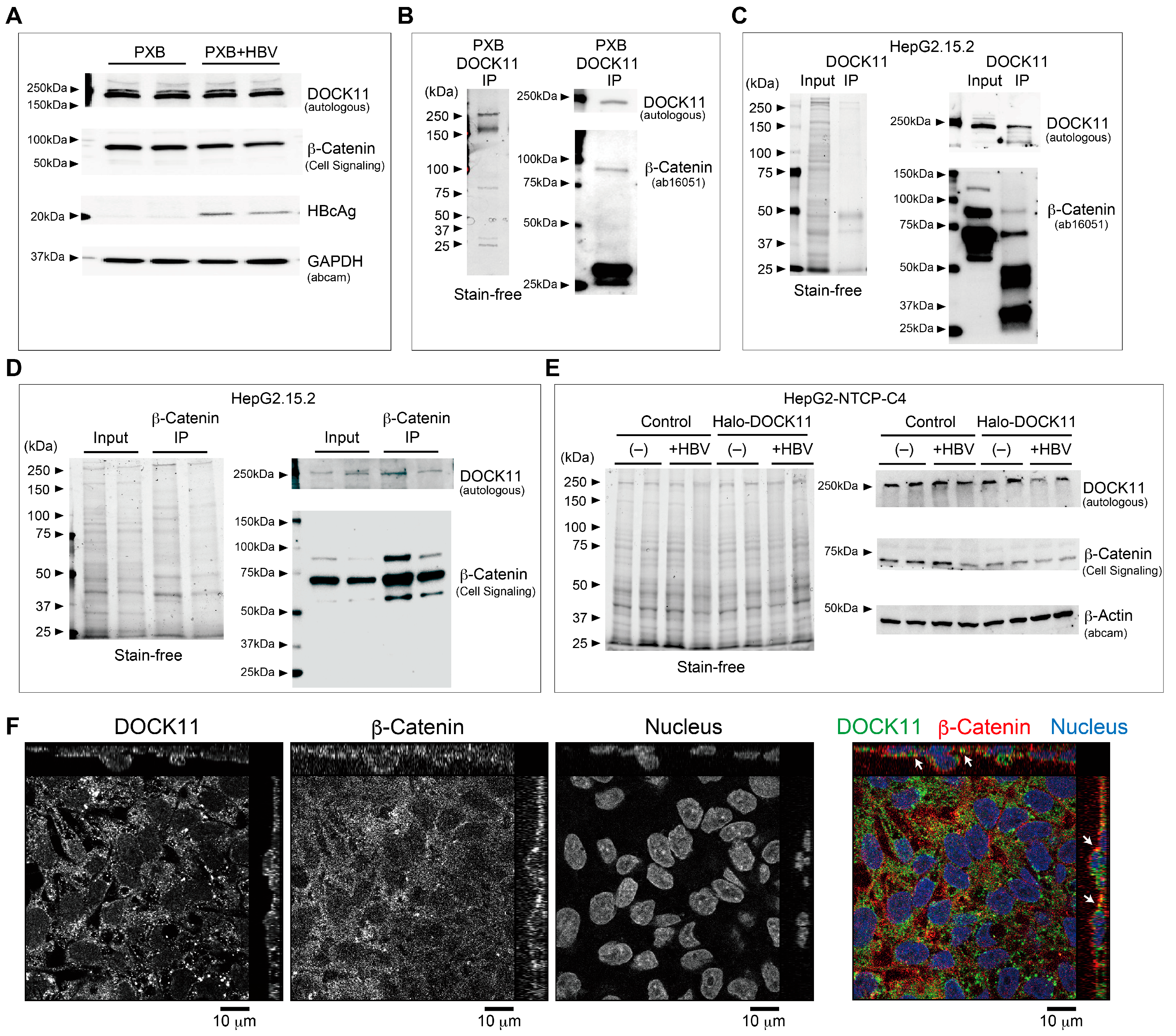
2.3. Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Regulates cccDNA and HBV-DNA Levels
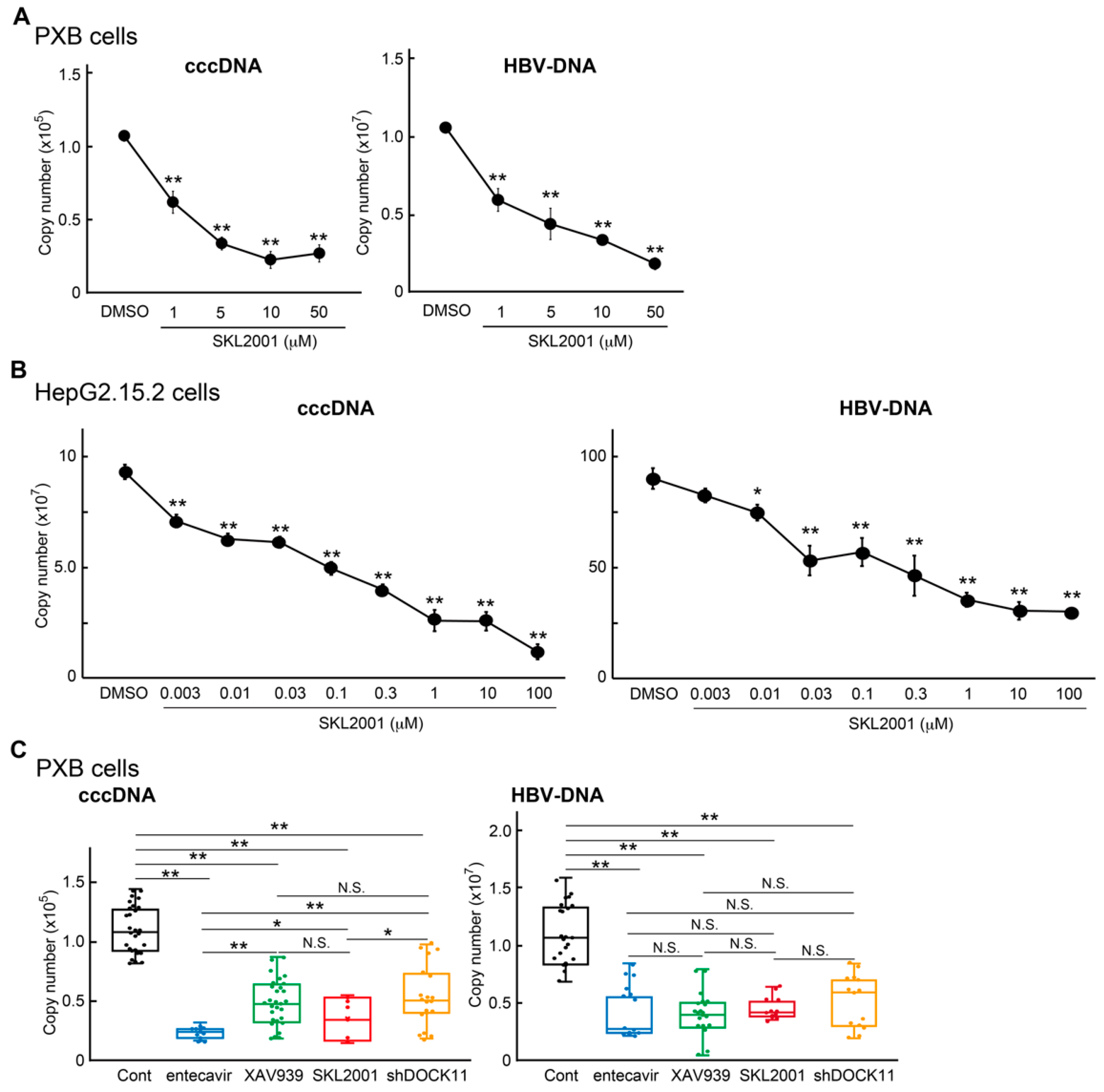
2.4. Wnt/β-Catenin Agonist SKL2001 Strongly Suppressed cccDNA and HBV-DNA Levels
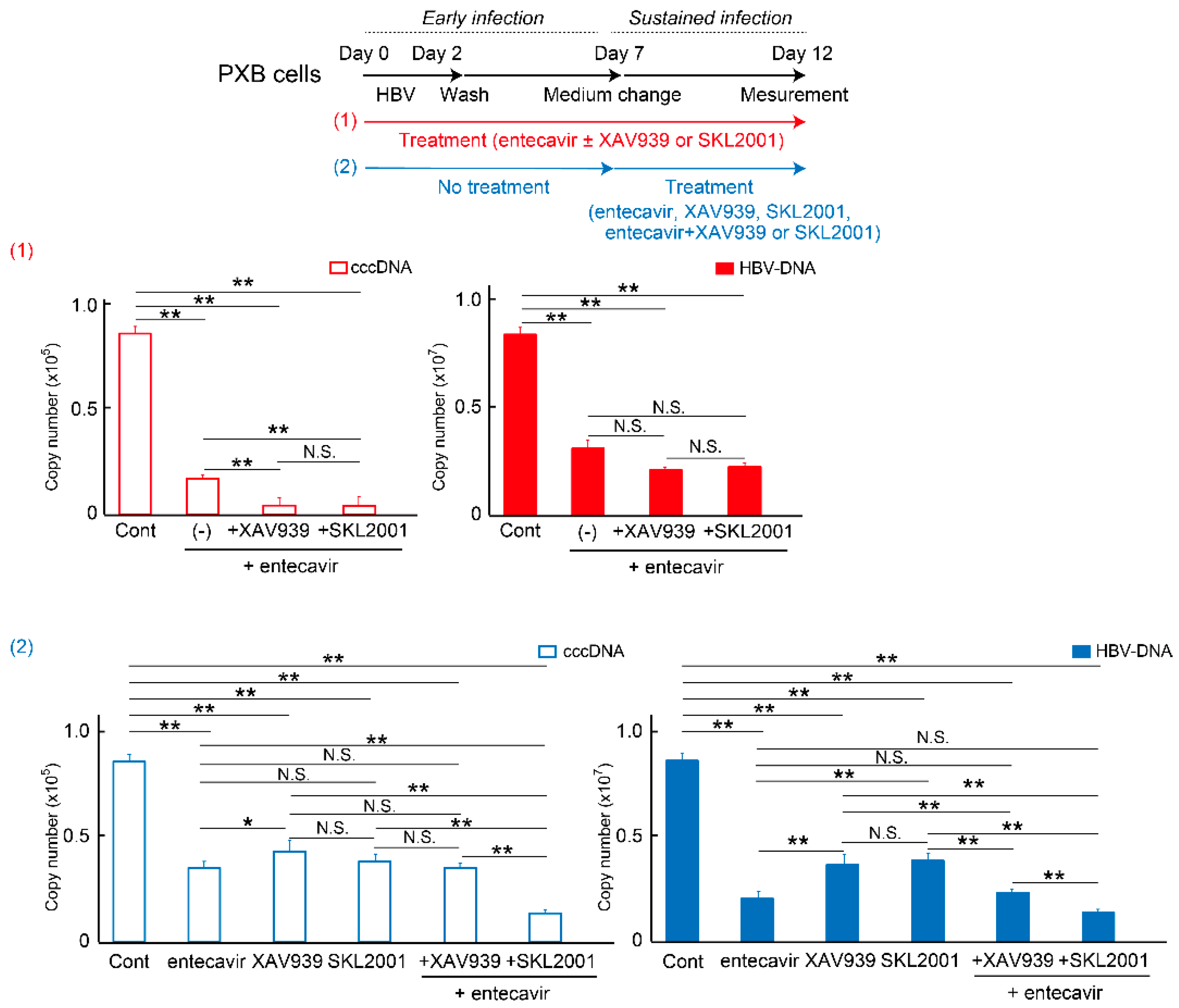
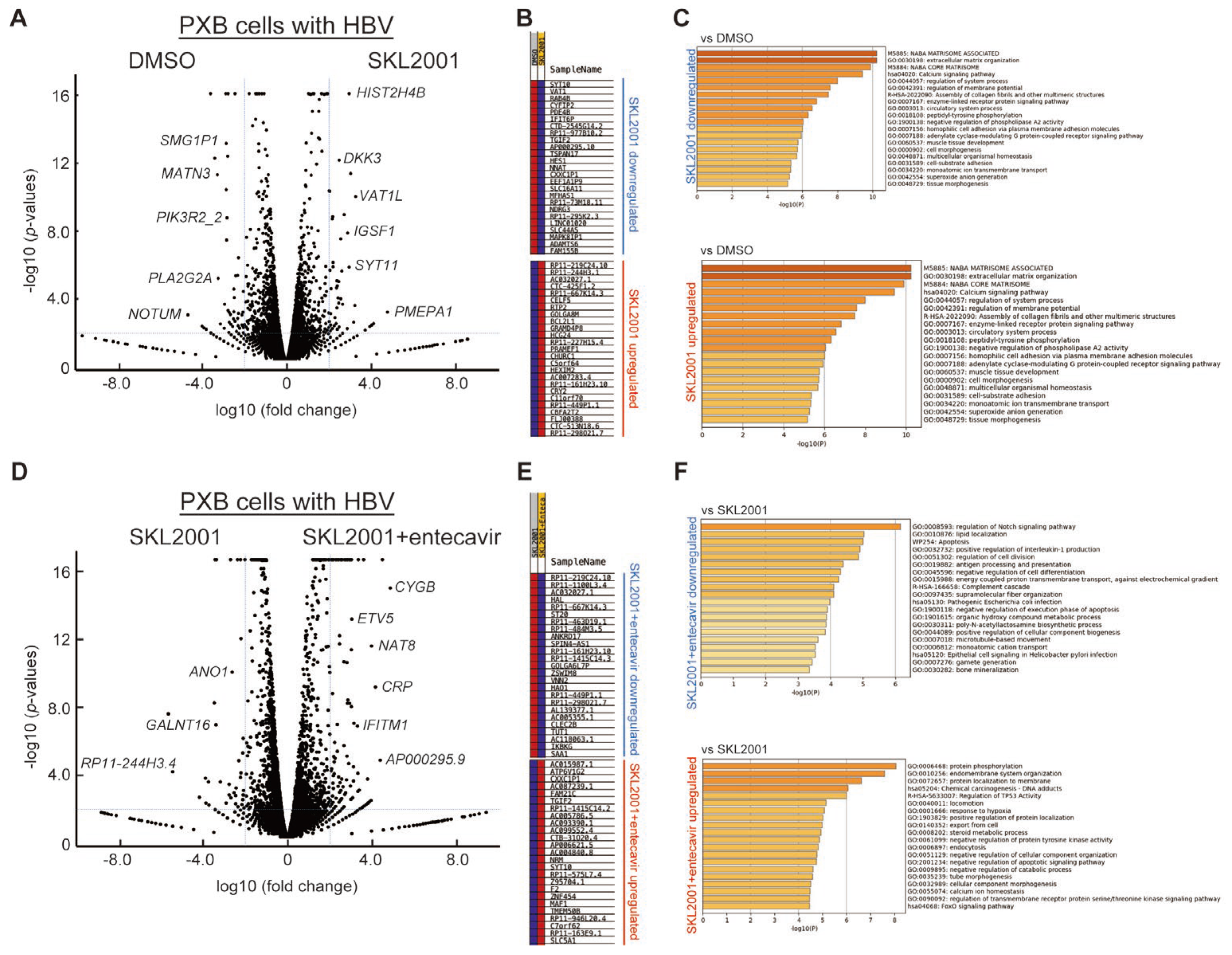
2.5. DEGs of Co-Treatment Effect of Wnt/β-Catenin Agonist SKL2001 and Entecavir
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture
4.2. Quantification of cccDNA and HBV-DNA
4.3. Western Blotting
4.4. Cell Proliferation Assay
4.5. RNA Sequencing (RNA-seq)
4.6. Short-Hairpin RNA (shRNA)
4.7. Immunoprecipitation (IP) Assay
4.8. Immunofluorescence Microscopy and Fluorescence Imaging
4.9. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Nassal, M. HBV cccDNA: Viral persistence reservoir and key obstacle for a cure of chronic hepatitis B. Gut 2015, 64, 1972–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.Y.; Zhang, B.H.; Theele, D.; Litwin, S.; Toll, E.; Summers, J. Single-cell analysis of covalently closed circular DNA copy numbers in a hepadnavirus-infected liver. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 12372–12377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doan, P.T.B.; Nio, K.; Shimakami, T.; Kuroki, K.; Li, Y.Y.; Sugimoto, S.; Takayama, H.; Okada, H.; Kaneko, S.; Honda, M.; et al. Super-Resolution Microscopy Analysis of Hepatitis B Viral cccDNA and Host Factors. Viruses 2023, 15, 1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.Y.; Kuroki, K.; Shimakami, T.; Murai, K.; Kawaguchi, K.; Shirasaki, T.; Nio, K.; Sugimoto, S.; Nishikawa, T.; Okada, H.; et al. Hepatitis B Virus Utilizes a Retrograde Trafficking Route via the Trans-Golgi Network to Avoid Lysosomal Degradation. Cell Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 15, 533–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ide, M.; Tabata, N.; Yonemura, Y.; Shirasaki, T.; Murai, K.; Wang, Y.; Ishida, A.; Okada, H.; Honda, M.; Kaneko, S.; et al. Guanine nucleotide exchange factor DOCK11-binding peptide fused with a single chain antibody inhibits hepatitis B virus infection and replication. J. Biol. Chem. 2022, 298, 102097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashimoto, S.; Shirasaki, T.; Yamashita, T.; Iwabuchi, S.; Suzuki, Y.; Takamura, Y.; Ukita, Y.; Deshimaru, S.; Okayama, T.; Ikeo, K.; et al. DOCK11 and DENND2A play pivotal roles in the maintenance of hepatitis B virus in host cells. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0246313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanagawa, H. Exploration of the origin and evolution of globular proteins by mRNA display. Biochemistry 2013, 52, 3841–3851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibson, B.A.; Kraus, W.L. New insights into the molecular and cellular functions of poly (ADP-ribose) and PARPs. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2012, 13, 411–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, S.; Mickanin, C.; Feng, Y.; Charlat, O.; Michaud, G.A.; Schirle, M.; Shi, X.; Hild, M.; Bauer, A.; et al. RNF146 is a poly (ADP-ribose)-directed E3 ligase that regulates axin degradation and Wnt signalling. Nat. Cell Biol. 2011, 13, 623–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, E.; Tacchelly-Benites, O.; Wang, Z.; Randall, M.P.; Tian, A.; Benchabane, H.; Freemantle, S.; Pikielny, C.; Tolwinski, N.S.; Lee, E.; et al. Wnt pathway activation by ADP-ribosylation. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimelman, D.; Xu, W. Beta-catenin destruction complex: Insights and questions from a structural perspective. Oncogene 2006, 25, 7482–7491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Rubin, J.S.; Kimmel, A.R. Rapid, Wnt-induced changes in GSK3 beta associations that regulate beta-catenin stabilization are mediated by Galpha proteins. Curr. Biol. 2005, 15, 1989–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarnow, G.; McLachlan, A. Selective effect of beta-catenin on nuclear receptor-dependent hepatitis B virus transcription and replication. Virology 2022, 571, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarnow, G.; McLachlan, A. Beta-catenin Signaling Regulates the In Vivo Distribution of Hepatitis B Virus Biosynthesis Across the Liver Lobule. J. Virol. 2021, 95, e0078021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, R.; Wang, T.Z.; Kong, D.; Zhang, L.; Meng, H.X.; Jiang, Y.; Wu, Y.Q.; Yu, Z.X.; Jin, X.M. Hepatoma cell line HepG2.2.15 demonstrates distinct biological features compared with parental HepG2. World J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 17, 1152–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamasaki, C.; Tateno, C.; Aratani, A.; Ohnishi, C.; Katayama, S.; Kohashi, T.; Hino, H.; Marusawa, H.; Asahara, T.; Yoshizato, K. Growth and differentiation of colony-forming human hepatocytes in vitro. J. Hepatol. 2006, 44, 749–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Wang, Y.; Neri, S.; Zhen, Y.; Fong, L.W.R.; Qiao, Y.; Li, X.; Chen, Z.; Stephan, C.; Deng, W.; et al. Tankyrase disrupts metabolic homeostasis and promotes tumorigenesis by inhibiting LKB1-AMPK signalling. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narwal, M.; Koivunen, J.; Haikarainen, T.; Obaji, E.; Legala, O.E.; Venkannagari, H.; Joensuu, P.; Pihlajaniemi, T.; Lehtio, L. Discovery of tankyrase inhibiting flavones with increased potency and isoenzyme selectivity. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 7880–7889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norum, J.H.; Skarpen, E.; Brech, A.; Kuiper, R.; Waaler, J.; Krauss, S.; Sorlie, T. The tankyrase inhibitor G007-LK inhibits small intestine LGR5+ stem cell proliferation without altering tissue morphology. Biol. Res. 2018, 51, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorsell, A.G.; Ekblad, T.; Karlberg, T.; Low, M.; Pinto, A.F.; Tresaugues, L.; Moche, M.; Cohen, M.S.; Schuler, H. Structural Basis for Potency and Promiscuity in Poly (ADP-Ribose) Polymerase (PARP) and Tankyrase Inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 1262–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waaler, J.; Machon, O.; Tumova, L.; Dinh, H.; Korinek, V.; Wilson, S.R.; Paulsen, J.E.; Pedersen, N.M.; Eide, T.J.; Machonova, O.; et al. A novel tankyrase inhibitor decreases canonical Wnt signaling in colon carcinoma cells and reduces tumor growth in conditional APC mutant mice. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 2822–2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Dhfyan, A.; Alhoshani, A.; Korashy, H.M. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor/cytochrome P450 1A1 pathway mediates breast cancer stem cells expansion through PTEN inhibition and beta-catenin and Akt activation. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhou, B.; Pache, L.; Chang, M.; Khodabakhshi, A.H.; Tanaseichuk, O.; Benner, C.; Chanda, S.K. Metascape provides a biologist-oriented resource for the analysis of systems-level datasets. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.M.; Mishina, Y.M.; Liu, S.; Cheung, A.; Stegmeier, F.; Michaud, G.A.; Charlat, O.; Wiellette, E.; Zhang, Y.; Wiessner, S.; et al. Tankyrase inhibition stabilizes axin and antagonizes Wnt signalling. Nature 2009, 461, 614–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waaler, J.; Machon, O.; von Kries, J.P.; Wilson, S.R.; Lundenes, E.; Wedlich, D.; Gradl, D.; Paulsen, J.E.; Machonova, O.; Dembinski, J.L.; et al. Novel synthetic antagonists of canonical Wnt signaling inhibit colorectal cancer cell growth. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, D.; Choi, M.Y.; Yu, J.; Castro, J.E.; Kipps, T.J.; Carson, D.A. Salinomycin inhibits Wnt signaling and selectively induces apoptosis in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 13253–13257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Wu, X.; Mitchell, B.; Kintner, C.; Ding, S.; Schultz, P.G. A small-molecule agonist of the Wnt signaling pathway. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 1987–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Yin, J.; Chen, D.; Nie, F.; Song, X.; Fei, C.; Miao, H.; Jing, C.; Ma, W.; Wang, L.; et al. Small-molecule modulation of Wnt signaling via modulating the Axin-LRP5/6 interaction. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2013, 9, 579–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fagotto, F.; Gluck, U.; Gumbiner, B.M. Nuclear localization signal-independent and importin/karyopherin-independent nuclear import of beta-catenin. Curr. Biol. 1998, 8, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuura, Y.; Stewart, M. Nup50/Npap60 function in nuclear protein import complex disassembly and importin recycling. EMBO J. 2005, 24, 3681–3689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Wang, J.C.; Pierson, E.E.; Keifer, D.Z.; Delaleau, M.; Gallucci, L.; Cazenave, C.; Kann, M.; Jarrold, M.F.; Zlotnick, A. Importin Beta Can Bind Hepatitis B Virus Core Protein and Empty Core-Like Particles and Induce Structural Changes. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1005802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soderholm, J.F.; Bird, S.L.; Kalab, P.; Sampathkumar, Y.; Hasegawa, K.; Uehara-Bingen, M.; Weis, K.; Heald, R. Importazole, a small molecule inhibitor of the transport receptor importin-beta. ACS Chem. Biol. 2011, 6, 700–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gwak, J.; Hwang, S.G.; Park, H.S.; Choi, S.R.; Park, S.H.; Kim, H.; Ha, N.C.; Bae, S.J.; Han, J.K.; Kim, D.E.; et al. Small molecule-based disruption of the Axin/beta-catenin protein complex regulates mesenchymal stem cell differentiation. Cell Res. 2012, 22, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, S.; Chen, H.; Liu, M.; Gan, L.; Li, C.; Zhang, W.; Lv, L.; Mei, Z. Aquaporin 9 inhibits growth and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. Aging 2020, 12, 1527–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohashi, W.; Yamamine, N.; Imura, J.; Hattori, Y. SKL2001 suppresses colon cancer spheroid growth through regulation of the E-cadherin/beta-catenin complex. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 493, 1342–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhijun, Z.; Jingkang, H. MicroRNA-520e suppresses non-small-cell lung cancer cell growth by targeting Zbtb7a-mediated Wnt signaling pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 486, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Kawaguchi, K.; Honda, M.; Sakai, Y.; Yamashita, T.; Mizukoshi, E.; Kaneko, S. Distinct notch signaling expression patterns between nucleoside and nucleotide analogues treatment for hepatitis B virus infection. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 501, 682–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Zhou, H.; Xia, X.; Sun, Q.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, B. Activated Notch signaling is required for hepatitis B virus X protein to promote proliferation and survival of human hepatic cells. Cancer Lett. 2010, 298, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pei, J.; Tang, Z.; Zang, G.; Yu, Y. Blockage of Notch1 signaling modulates the T-helper (Th) 1/Th2 cell balance in chronic hepatitis B patients. Hepatol. Res. 2010, 40, 799–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Xiong, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, G.; Xu, H. Hepatitis B virus X protein activates Notch signaling by its effects on Notch1 and Notch4 in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Int. J. Oncol. 2016, 48, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Kawaguchi, K.; Honda, M.; Hashimoto, S.; Shirasaki, T.; Okada, H.; Orita, N.; Shimakami, T.; Yamashita, T.; Sakai, Y.; et al. Notch signaling facilitates hepatitis B virus covalently closed circular DNA transcription via cAMP response element-binding protein with E3 ubiquitin ligase-modulation. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cha, M.Y.; Kim, C.M.; Park, Y.M.; Ryu, W.S. Hepatitis B virus X protein is essential for the activation of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in hepatoma cells. Hepatology 2004, 39, 1683–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Olshausen, G.; Quasdorff, M.; Bester, R.; Arzberger, S.; Ko, C.; van de Klundert, M.; Zhang, K.; Odenthal, M.; Ringelhan, M.; Niessen, C.M.; et al. Hepatitis B virus promotes beta-catenin-signalling and disassembly of adherens junctions in a Src kinase dependent fashion. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 33947–33960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Nadda, N.; Quadri, A.; Kumar, R.; Paul, S.; Tanwar, P.; Gamanagatti, S.; Dash, N.R.; Saraya, A.; Shalimar; et al. Assessments of TP53 and CTNNB1 gene hotspot mutations in circulating tumour DNA of hepatitis B virus-induced hepatocellular carcinoma. Front. Genet. 2023, 14, 1235260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, S.; Tang, S. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in the development of liver cancers. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 132, 110851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rana, M.A.; Ijaz, B.; Daud, M.; Tariq, S.; Nadeem, T.; Husnain, T. Interplay of Wnt beta-catenin pathway and miRNAs in HBV pathogenesis leading to HCC. Clin. Res. Hepatol. Gastroenterol. 2019, 43, 373–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Evert, M.; Calvisi, D.F.; Chen, X. Beta-catenin signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Clin. Investig. 2022, 132, e154515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Tang, J.; Cai, X.; Huang, Y.; Gao, Q.; Liang, L.; Tian, L.; Yang, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Hu, Y.; et al. HBx mutations promote hepatoma cell migration through the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Cancer Sci. 2016, 107, 1380–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.D.; Wang, Y.; Ye, L.H. Hepatitis B virus X protein accelerates the development of hepatoma. Cancer Biol. Med. 2014, 11, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Geng, M.; Xin, X.; Bi, L.Q.; Zhou, L.T.; Liu, X.H. Molecular mechanism of hepatitis B virus X protein function in hepatocarcinogenesis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 10732–10738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Tschudy-Seney, B.; Ma, X.; Zern, M.A.; Liu, P.; Duan, Y. Salvianolic Acid B Enhances Hepatic Differentiation of Human Embryonic Stem Cells Through Upregulation of WNT Pathway and Inhibition of Notch Pathway. Stem Cells Dev. 2018, 27, 252–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.T.; Han, T.; Li, Y.; Yang, B.; Wang, Y.J.; Wang, F.M.; Jing, X.; Du, Z. Enhanced specificity of real-time PCR for measurement of hepatitis B virus cccDNA using restriction endonuclease and plasmid-safe ATP-dependent DNase and selective primers. J. Virol. Methods 2010, 169, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mootha, V.K.; Lindgren, C.M.; Eriksson, K.F.; Subramanian, A.; Sihag, S.; Lehar, J.; Puigserver, P.; Carlsson, E.; Ridderstrale, M.; Laurila, E.; et al. PGC-1alpha-responsive genes involved in oxidative phosphorylation are coordinately downregulated in human diabetes. Nat. Genet. 2003, 34, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ishida, A.; Iwabuchi, S.; Li, Y.-Y.; Murai, K.; Shirasaki, T.; Kuroki, K.; Shimakami, T.; Nio, K.; Kawaguchi, K.; Imafuku, T.; et al. Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Regulates Hepatitis B Virus cccDNA Levels. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6942. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146942
Ishida A, Iwabuchi S, Li Y-Y, Murai K, Shirasaki T, Kuroki K, Shimakami T, Nio K, Kawaguchi K, Imafuku T, et al. Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Regulates Hepatitis B Virus cccDNA Levels. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(14):6942. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146942
Chicago/Turabian StyleIshida, Atsuya, Sadahiro Iwabuchi, Ying-Yi Li, Kazuhisa Murai, Takayoshi Shirasaki, Kazuyuki Kuroki, Tetsuro Shimakami, Koki Nio, Kazunori Kawaguchi, Tadashi Imafuku, and et al. 2025. "Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Regulates Hepatitis B Virus cccDNA Levels" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 14: 6942. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146942
APA StyleIshida, A., Iwabuchi, S., Li, Y.-Y., Murai, K., Shirasaki, T., Kuroki, K., Shimakami, T., Nio, K., Kawaguchi, K., Imafuku, T., Ito, S., Yamashita, T., Kaneko, S., Yanagawa, H., Matsushima, K., Honda, M., & Hashimoto, S. (2025). Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Regulates Hepatitis B Virus cccDNA Levels. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(14), 6942. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146942





