Hydrogen Gas Attenuates Toxic Metabolites and Oxidative Stress-Mediated Signaling to Inhibit Neurodegeneration and Enhance Memory in Alzheimer’s Disease Models
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
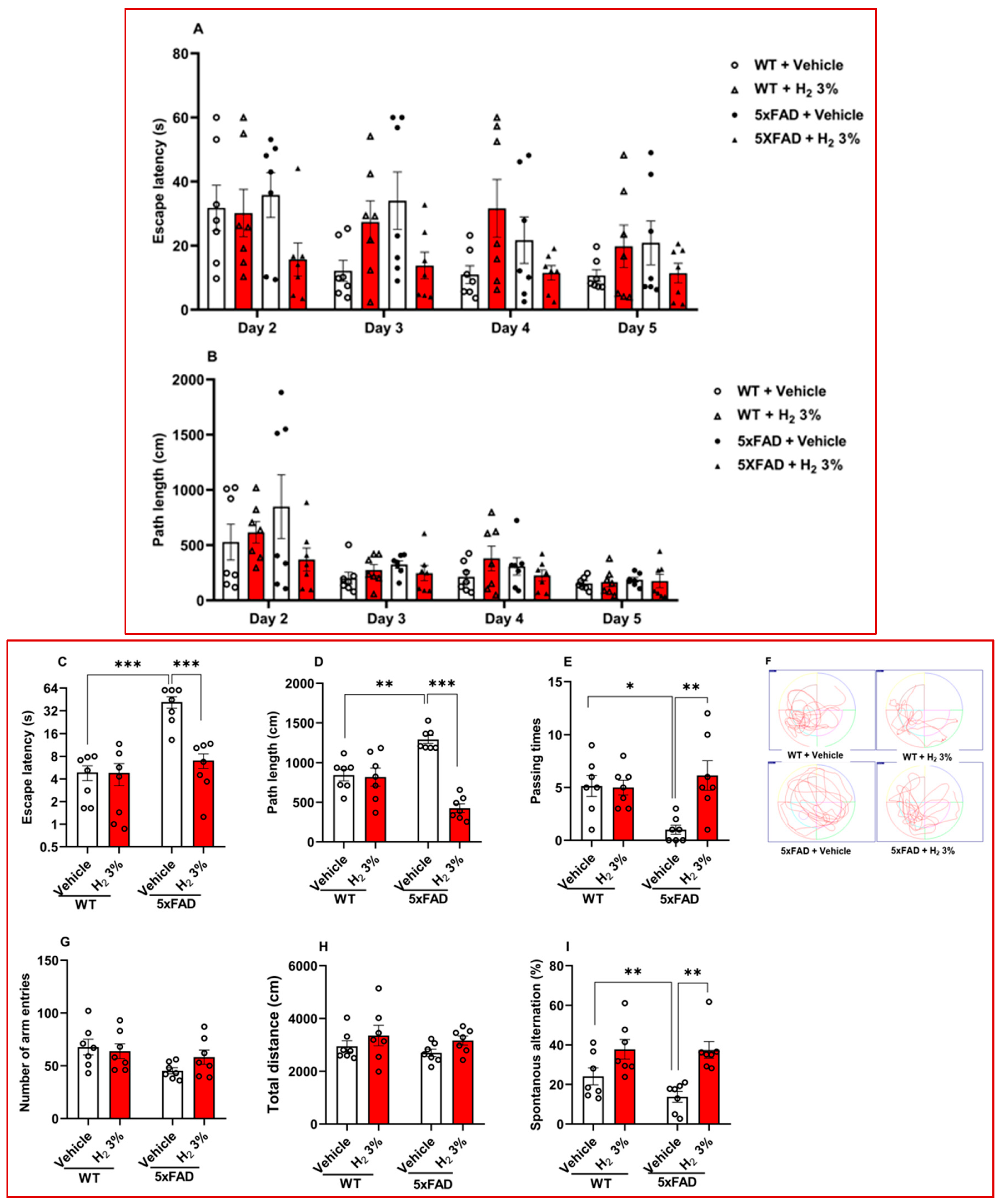
2.1. H2 Inhalation Attenuates Memory Impairment in 5xFAD Mice
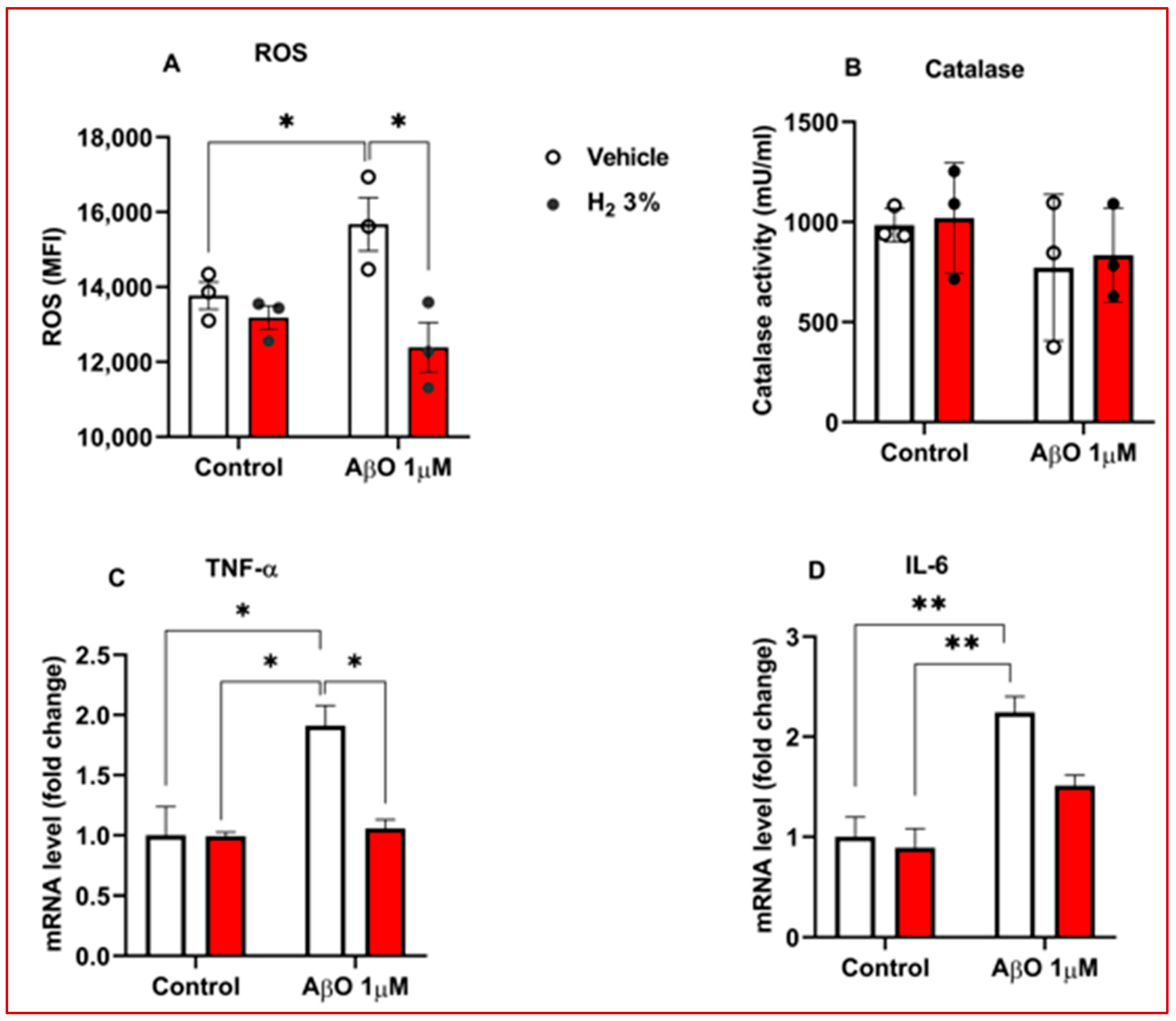
2.2. H2 Reduced OS and Decreased Neuroinflammation in AβO-Treated Astrocytes
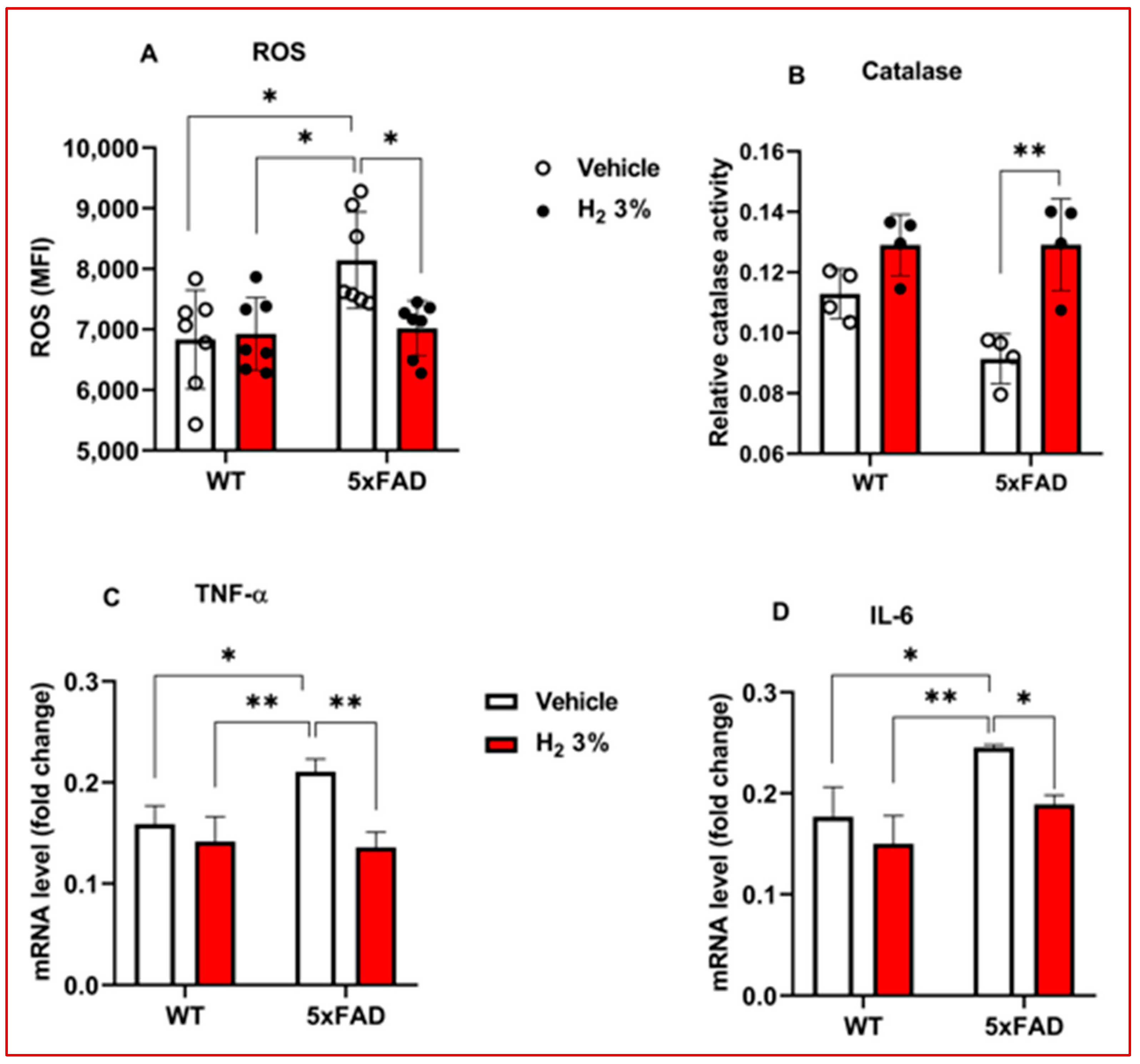
2.3. H2 Reduced OS and Neuroinflammation in 5xFAD Mice
2.4. H2 Improved Amyloid Pathology and Reduced Toxic Metabolite Accumulation in 5xFAD Mice and AβO-Induced Primary Astrocytes
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animal and Cell Culture Models
4.2. Behavior Test
4.3. Assessment of Toxic Metabolite Levels
4.3.1. ROS and Antioxidant Enzyme Assay
4.3.2. Ammonia Assay
4.3.3. IHC and ICC
4.4. RT-qPCR Analysis of Inflammatory Genes
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
List of Abbreviations
| Aβ | Amyloid-beta | |
| AβO | Amyloid-beta oligomer | |
| AD | Alzheimer’s disease | |
| ARG1 | Arginase 1 | |
| CA1 | Cornu Ammonis 1 | |
| CTX | Cortex | |
| DCF-DA | 2,7-dichlorofluorescein diacetate | |
| DG | Dentate gyrus | |
| 5xFAD | 5 Familial Alzheimer’s disease | |
| GABA | Aminobutyric acid | |
| GFAP | Glial fibrillary acidic protein | |
| H2 | Molecular hydrogen | |
| H2O2 | Hydrogen peroxide | |
| ICC | Immunocytochemistry | |
| IHC | Immunohistochemistry | |
| IL-6 | Interleukin 6 | |
| ODC1 | Ornithine decarboxylase 1 | |
| OS | Oxidative stress | |
| OTC | Ornithine transcarboxylase | |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species | |
| RT-qPCR | Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction | |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor-alpha | |
Appendix A
| Gene | Forward Primer Sequence | Reverse Primer Sequence |
|---|---|---|
| APP/PS1 | 5′-ACC CCC ATG TCA GAG TTC CT-3′ | 5′-CGG GCC TCT TCG CTA TTA C-3′ |
| TNF-α | 5′-TGTGCTCAGAGCTTTCAACAA -3′ | 5′-CTTGATGGTGGTGCATGAGA-3′ |
| IL-6 | 5′-GCTACCAAACTGGATATAATCAGGA-3′ | 5′-CCAGGTAGCTATGGTACTCCAGAA-3′ |
| Antibody | Host | Application | Source | Dilution |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anti-Aβ | Pig | IF | MILLIPORE, | 1:500 |
| Anti-GABA | Mouse | IF | MILLIPORE | 1:500 |
| Goat anti-rabbit IgG | Goat | IF | Invitrogen | 1:500 |
| Goat anti-mouse IgG | Goat | IF | Invitrogen | 1:500 |
| Goat anti-guinea pig IgG | Goat | IF | Invitrogen | 1:500 |
References
- Goedert, M.; Spillantini, M.G. A Century of Alzheimer’s Disease. Science 2006, 314, 777–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohta, S.; Ohsawa, I. Dysfunction of Mitochondria and Oxidative Stress in the Pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s Disease: On Defects in the Cytochrome c Oxidase Complex and Aldehyde Detoxification. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2006, 9, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Xu, T.; Yan, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Melcher, K.; Xu, H.E. Amyloid Beta: Structure, Biology and Structure-Based Therapeutic Development. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2017, 38, 1205–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picca, A.; Calvani, R.; Coelho-Junior, H.J.; Landi, F.; Bernabei, R.; Marzetti, E. Mitochondrial Dysfunction, Oxidative Stress, and Neuroinflammation: Intertwined Roads to Neurodegeneration. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Jung, U.J.; Kim, S.R. Role of Oxidative Stress in Blood–Brain Barrier Disruption and Neurodegenerative Diseases. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montilla, P.; Feijóo, M.; Muñoz, M.C.; Muñoz-Castañeda, J.R.; Bujalance, I.; Túnez, I. Effect of Melatonin on the Oxidative Stress in N1E-115 Cells Is Not Mediated by Mt1 Receptors. J. Physiol. Biochem. 2003, 59, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takuma, K.; Yan, S.S.; Stern, D.M.; Yamada, K. Mitochondrial Dysfunction, Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress, and Apoptosis in Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2005, 97, 312–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peggion, C.; Calì, T.; Brini, M. Mitochondria Dysfunction and Neuroinflammation in Neurodegeneration: Who Comes First? Antioxidants 2024, 13, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beal, M.F. Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Bioenerg. 1998, 1366, 211–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trimmer, P.A.; Keeney, P.M.; Borland, M.K.; Simon, F.A.; Almeida, J.; Swerdlow, R.H.; Parks, J.P.; Parker, W.D.; Bennett, J.P. Mitochondrial Abnormalities in Cybrid Cell Models of Sporadic Alzheimer’s Disease Worsen with Passage in Culture. Neurobiol. Dis. 2004, 15, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheehan, J.P.; Swerdlow, R.H.; Miller, S.W.; Davis, R.E.; Parks, J.K.; Parker, W.D.; Tuttle, J.B. Calcium Homeostasis and Reactive Oxygen Species Production in Cells Transformed by Mitochondria from Individuals with Sporadic Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Neurosci. 1997, 17, 4612–4622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rather, M.A.; Khan, A.; Alshahrani, S.; Rashid, H.; Qadri, M.; Rashid, S.; Alsaffar, R.M.; Kamal, M.A.; Rehman, M.U. Inflammation and Alzheimer’s Disease: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Implications by Natural Products. Mediat. Inflamm. 2021, 2021, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chun, H.; Lee, C.J. Reactive Astrocytes in Alzheimer’s Disease: A Double-Edged Sword. Neurosci. Res. 2018, 126, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chun, H.; Im, H.; Kang, Y.J.; Kim, Y.; Shin, J.H.; Won, W.; Lim, J.; Ju, Y.; Park, Y.M.; Kim, S.; et al. Severe Reactive Astrocytes Precipitate Pathological Hallmarks of Alzheimer’s Disease via H2O2− Production. Nat. Neurosci. 2020, 23, 1555–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escartin, C.; Galea, E.; Lakatos, A.; O’Callaghan, J.P.; Petzold, G.C.; Serrano-Pozo, A.; Steinhäuser, C.; Volterra, A.; Carmignoto, G.; Agarwal, A.; et al. Reactive Astrocyte Nomenclature, Definitions, and Future Directions. Nat. Neurosci. 2021, 24, 312–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wunderlichová, L.; Buňková, L.; Koutný, M.; Jančová, P.; Buňka, F. Formation, Degradation, and Detoxification of Putrescine by Foodborne Bacteria: A Review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2014, 13, 1012–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-M.A.; Stanford, A.D.; Mao, X.; Abi-Dargham, A.; Shungu, D.C.; Lisanby, S.H.; Schroeder, C.E.; Kegeles, L.S. GABA Level, Gamma Oscillation, and Working Memory Performance in Schizophrenia. Neuroimage Clin. 2014, 4, 531–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju, Y.H.; Bhalla, M.; Hyeon, S.J.; Oh, J.E.; Yoo, S.; Chae, U.; Kwon, J.; Koh, W.; Lim, J.; Park, Y.M.; et al. Astrocytic Urea Cycle Detoxifies Aβ-Derived Ammonia While Impairing Memory in Alzheimer’s Disease. Cell Metab. 2022, 34, 1104–1120.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansmannel, F.; Sillaire, A.; Kamboh, M.I.; Lendon, C.; Pasquier, F.; Hannequin, D.; Laumet, G.; Mounier, A.; Ayral, A.-M.; DeKosky, S.T.; et al. Is the Urea Cycle Involved in Alzheimer’s Disease? J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2010, 21, 1013–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alzheimer’s Association. Treatment for Alzheimer’s. Available online: https://www.alz.org/alzheimers-dementia/treatments (accessed on 5 February 2025).
- Erkinjuntti, T.; Kurz, A.; Gauthier, S.; Bullock, R.; Lilienfeld, S.; Damaraju, C.V. Efficacy of Galantamine in Probable Vascular Dementia and Alzheimer’s Disease Combined with Cerebrovascular Disease: A Randomised Trial. Lancet 2002, 359, 1283–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sims, J.R.; Zimmer, J.A.; Evans, C.D.; Lu, M.; Ardayfio, P.; Sparks, J.; Wessels, A.M.; Shcherbinin, S.; Wang, H.; Monkul Nery, E.S.; et al. Donanemab in Early Symptomatic Alzheimer Disease. JAMA 2023, 330, 512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Dyck, C.H.; Swanson, C.J.; Aisen, P.; Bateman, R.J.; Chen, C.; Gee, M.; Kanekiyo, M.; Li, D.; Reyderman, L.; Cohen, S.; et al. Lecanemab in Early Alzheimer’s Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LeBaron, T.W.; Kura, B.; Kalocayova, B.; Tribulova, N.; Slezak, J. A New Approach for the Prevention and Treatment of Cardiovascular Disorders. Molecular Hydrogen Significantly Reduces the Effects of Oxidative Stress. Molecules 2019, 24, 2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamimura, N.; Nishimaki, K.; Ohsawa, I.; Ohta, S. Molecular Hydrogen Improves Obesity and Diabetes by Inducing Hepatic FGF21 and Stimulating Energy Metabolism in Db/Db Mice. Obesity 2011, 19, 1396–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dole, M.; Wilson, F.R.; Fife, W.P. Hyperbaric Hydrogen Therapy: A Possible Treatment for Cancer. Science 1975, 190, 152–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohsawa, I.; Ishikawa, M.; Takahashi, K.; Watanabe, M.; Nishimaki, K.; Yamagata, K.; Katsura, K.; Katayama, Y.; Asoh, S.; Ohta, S. Hydrogen Acts as a Therapeutic Antioxidant by Selectively Reducing Cytotoxic Oxygen Radicals. Nat. Med. 2007, 13, 688–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.H.; Cha, M.; Lee, B.H. Neuroprotective Effect of Antioxidants in the Brain. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, E.-S.; Bajgai, J.; You, I.-S.; Rahman, M.H.; Fadriquela, A.; Sharma, S.; Kwon, H.-U.; Lee, S.-Y.; Kim, C.-S.; Lee, K.-J. Therapeutic Effects of Hydrogen Gas Inhalation on Trimethyltin-Induced Neurotoxicity and Cognitive Impairment in the C57BL/6 Mice Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 13313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohta, S. Molecular Hydrogen as a Preventive and Therapeutic Medical Gas: Initiation, Development and Potential of Hydrogen Medicine. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 144, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sim, M.; Kim, C.-S.; Shon, W.-J.; Lee, Y.-K.; Choi, E.Y.; Shin, D.-M. Hydrogen-Rich Water Reduces Inflammatory Responses and Prevents Apoptosis of Peripheral Blood Cells in Healthy Adults: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Controlled Trial. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 12130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, X.; Shen, F.; Dong, W.-L.; Yang, Y.; Chen, G. The Role of Hydrogen in Alzheimer’s Disease. Med. Gas. Res. 2018, 8, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonelli, C.; Chio, I.I.C.; Tuveson, D.A. Transcriptional Regulation by Nrf2. Antioxid. Redox Signal 2018, 29, 1727–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Lin, J.; Jiang, S.; Li, W. The Nrf2 Antioxidant Defense System in Intervertebral Disc Degeneration: Molecular Insights. Exp. Mol. Med. 2022, 54, 1067–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.; Wu, Q.; Lu, F.; Lei, J.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, N.; Yu, Y.; Ning, Z.; She, T.; et al. Nrf2 Signaling Pathway: Current Status and Potential Therapeutic Targetable Role in Human Cancers. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1184079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohta, S. Recent Progress Toward Hydrogen Medicine: Potential of Molecular Hydrogen for Preventive and Therapeutic Applications. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2011, 17, 2241–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakagawa, K.; Kodama, K.; Nagata, W.; Takahashi, S.; Satoh, Y.; Ishizuka, T. Molecular Hydrogen Inhibits Neuroinflammation and Ameliorates Depressive-like Behaviors and Short-Term Cognitive Impairment in Senescence-Accelerated Mouse Prone 8 Mice. Behav. Brain Res. 2025, 478, 115330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ono, H.; Nishijima, Y.; Sakamoto, M.; Kitamura, S.; Naitoh, Y.; Suzuki, K.; Fujii, N.; Kikura, R.; Ohta, S. Long-Term Inhalation of Hydrogen Gas for Patients with Advanced Alzheimer’s Disease: A Case Report Showing Improvement in Fecal Incontinence. Med. Res. Arch. 2022, 10, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-T.; Shi, Q.-Q.; Zhang, L.; Yue, C.-P.; He, Z.-J.; Li, X.-X.; He, Q.-J.; Liu, Q.; Du, X.-B. Hydrogen-Rich Water Ameliorates Neuropathological Impairments in a Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease through Reducing Neuroinflammation and Modulating Intestinal Microbiota. Neural Regen. Res. 2022, 17, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhalla, M.; Lee, C.J. Long-Term Inhibition of ODC1 in APP/PS1 Mice Rescues Amyloid Pathology and Switches Astrocytes from a Reactive to Active State. Mol. Brain 2024, 17, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.C. A Novel Suicide Inhibitor Strategy for Antiparasitic Drug Development. J. Cell Biochem. 1991, 45, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McWilliams, M.L. Characterization of the Ototoxicity of Difluoromethylornithine and Its Enantiomers. Toxicol. Sci. 2000, 56, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saulnier Sholler, G.L.; Gerner, E.W.; Bergendahl, G.; MacArthur, R.B.; VanderWerff, A.; Ashikaga, T.; Bond, J.P.; Ferguson, W.; Roberts, W.; Wada, R.K.; et al. A Phase I Trial of DFMO Targeting Polyamine Addiction in Patients with Relapsed/Refractory Neuroblastoma. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0127246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koh, W.; Lee, C.J. Diagnostic and Therapeutic Potential of Tonic Gamma-aminobutyric Acid from Reactive Astrocytes in Brain Diseases. Clin. Transl. Med. 2024, 14, e1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.H.; Bajgai, J.; Sharma, S.; Jeong, E.-S.; Goh, S.H.; Jang, Y.-G.; Kim, C.-S.; Lee, K.-J. Effects of Hydrogen Gas Inhalation on Community-Dwelling Adults of Various Ages: A Single-Arm, Open-Label, Prospective Clinical Trial. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de la Torre, J.C. Is Alzheimer’s Disease a Neurodegenerative or a Vascular Disorder? Data, Dogma, and Dialectics. Lancet Neurol. 2004, 3, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pappolla, M.A.; Omar, R.A.; Kim, K.S.; Robakis, N.K. Immunohistochemical Evidence of Oxidative [Corrected] Stress in Alzheimer’s Disease. Am. J. Pathol. 1992, 140, 621–628. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- De Strooper, B.; Annaert, W. Novel Research Horizons for Presenilins and γ-Secretases in Cell Biology and Disease. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2010, 26, 235–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selkoe, D.J. Alzheimer’s Disease: Genes, Proteins, and Therapy. Physiol. Rev. 2001, 81, 741–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, D.H.; Han, K.-S.; Shim, J.W.; Yoon, B.-E.; Kim, E.; Bae, J.Y.; Oh, S.-J.; Hwang, E.M.; Marmorstein, A.D.; Bae, Y.C.; et al. TREK-1 and Best1 Channels Mediate Fast and Slow Glutamate Release in Astrocytes upon GPCR Activation. Cell 2012, 151, 25–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, R.G.M. Spatial Localization Does Not Require the Presence of Local Cues. Learn. Motiv. 1981, 12, 239–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraeuter, A.-K.; Guest, P.C.; Sarnyai, Z. The Y-Maze for Assessment of Spatial Working and Reference Memory in Mice. In Pre-Clinical Models: Techniques and Protocols; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 105–111. [Google Scholar]
- Bromley-Brits, K.; Deng, Y.; Song, W. Morris Water Maze Test for Learning and Memory Deficits in Alzheimer’s Disease Model Mice. J. Vis. Exp. 2011, 53, 2920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mueller, S.; Riedel, H.-D.; Stremmel, W. Determination of Catalase Activity at Physiological Hydrogen Peroxide Concentrations. Anal. Biochem. 1997, 245, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwak, H.; Koh, W.; Kim, S.; Song, K.; Shin, J.-I.; Lee, J.M.; Lee, E.H.; Bae, J.Y.; Ha, G.E.; Oh, J.-E.; et al. Astrocytes Control Sensory Acuity via Tonic Inhibition in the Thalamus. Neuron 2020, 108, 691–706.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abdul-Nasir, S.; Chau, C.T.; Nguyen, T.T.; Bajgai, J.; Rahman, M.H.; Hwang-Un, K.; You, I.-S.; Kim, C.-S.; Seo, B.A.; Lee, K.-J. Hydrogen Gas Attenuates Toxic Metabolites and Oxidative Stress-Mediated Signaling to Inhibit Neurodegeneration and Enhance Memory in Alzheimer’s Disease Models. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6922. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146922
Abdul-Nasir S, Chau CT, Nguyen TT, Bajgai J, Rahman MH, Hwang-Un K, You I-S, Kim C-S, Seo BA, Lee K-J. Hydrogen Gas Attenuates Toxic Metabolites and Oxidative Stress-Mediated Signaling to Inhibit Neurodegeneration and Enhance Memory in Alzheimer’s Disease Models. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(14):6922. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146922
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbdul-Nasir, Sofian, Cat Tuong Chau, Tien Thuy Nguyen, Johny Bajgai, Md. Habibur Rahman, Kwon Hwang-Un, In-Soo You, Cheol-Su Kim, Bo Am Seo, and Kyu-Jae Lee. 2025. "Hydrogen Gas Attenuates Toxic Metabolites and Oxidative Stress-Mediated Signaling to Inhibit Neurodegeneration and Enhance Memory in Alzheimer’s Disease Models" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 14: 6922. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146922
APA StyleAbdul-Nasir, S., Chau, C. T., Nguyen, T. T., Bajgai, J., Rahman, M. H., Hwang-Un, K., You, I.-S., Kim, C.-S., Seo, B. A., & Lee, K.-J. (2025). Hydrogen Gas Attenuates Toxic Metabolites and Oxidative Stress-Mediated Signaling to Inhibit Neurodegeneration and Enhance Memory in Alzheimer’s Disease Models. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(14), 6922. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146922








