Pyridostigmine Treatment Significantly Alleviates Isoprenaline-Induced Chronic Heart Failure in Rats
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Effects of Pyridostigmine Treatment on Body Weight (BW), Heart Weight (HW), and Heart-to-Body Weight (HWBW) Ratio
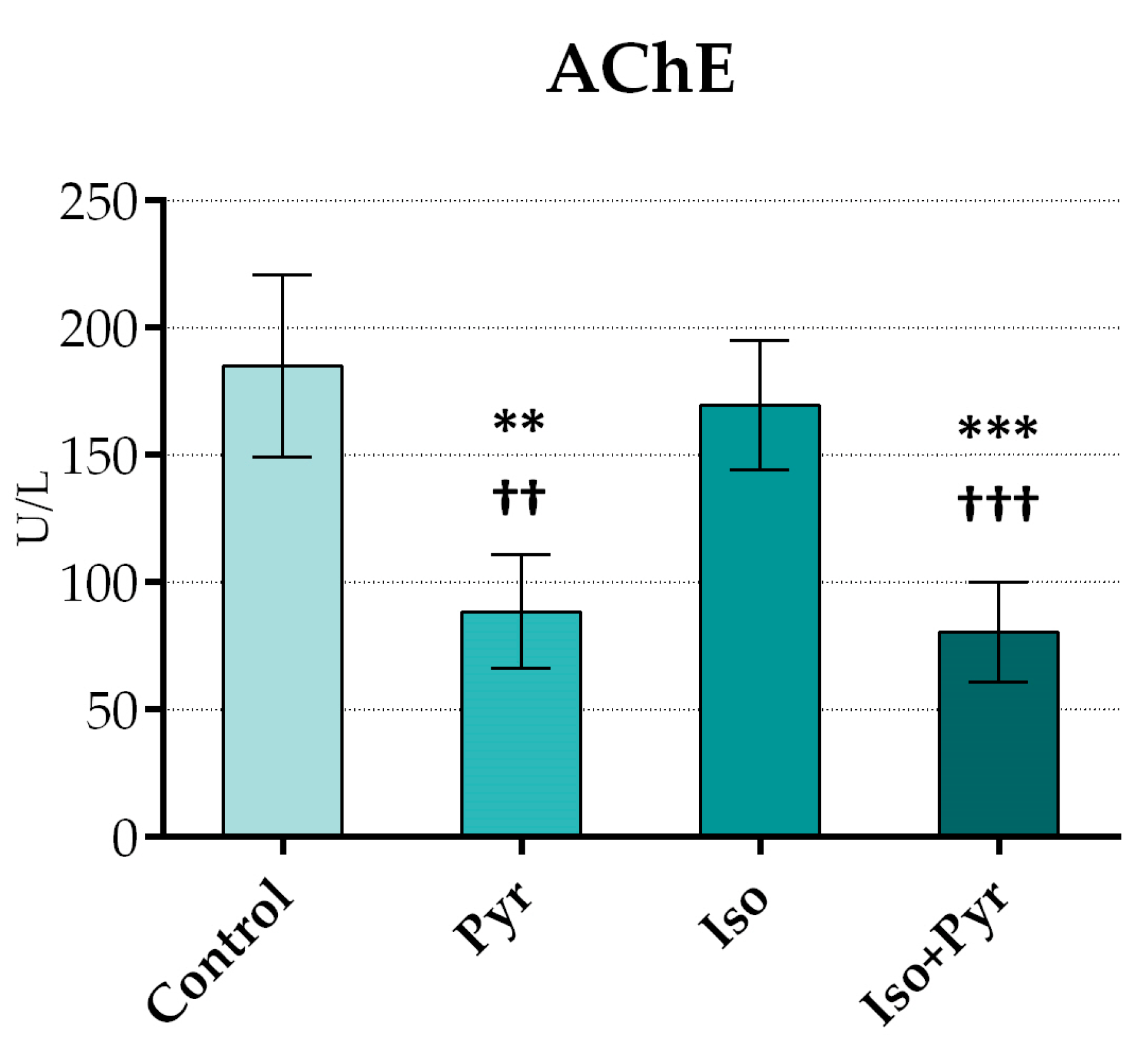
2.2. Effects of Pyridostigmine Treatment on Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) Activity
2.3. Effects of Pyridostigmine Treatment on Electrocardiogram (ECG) Recordings
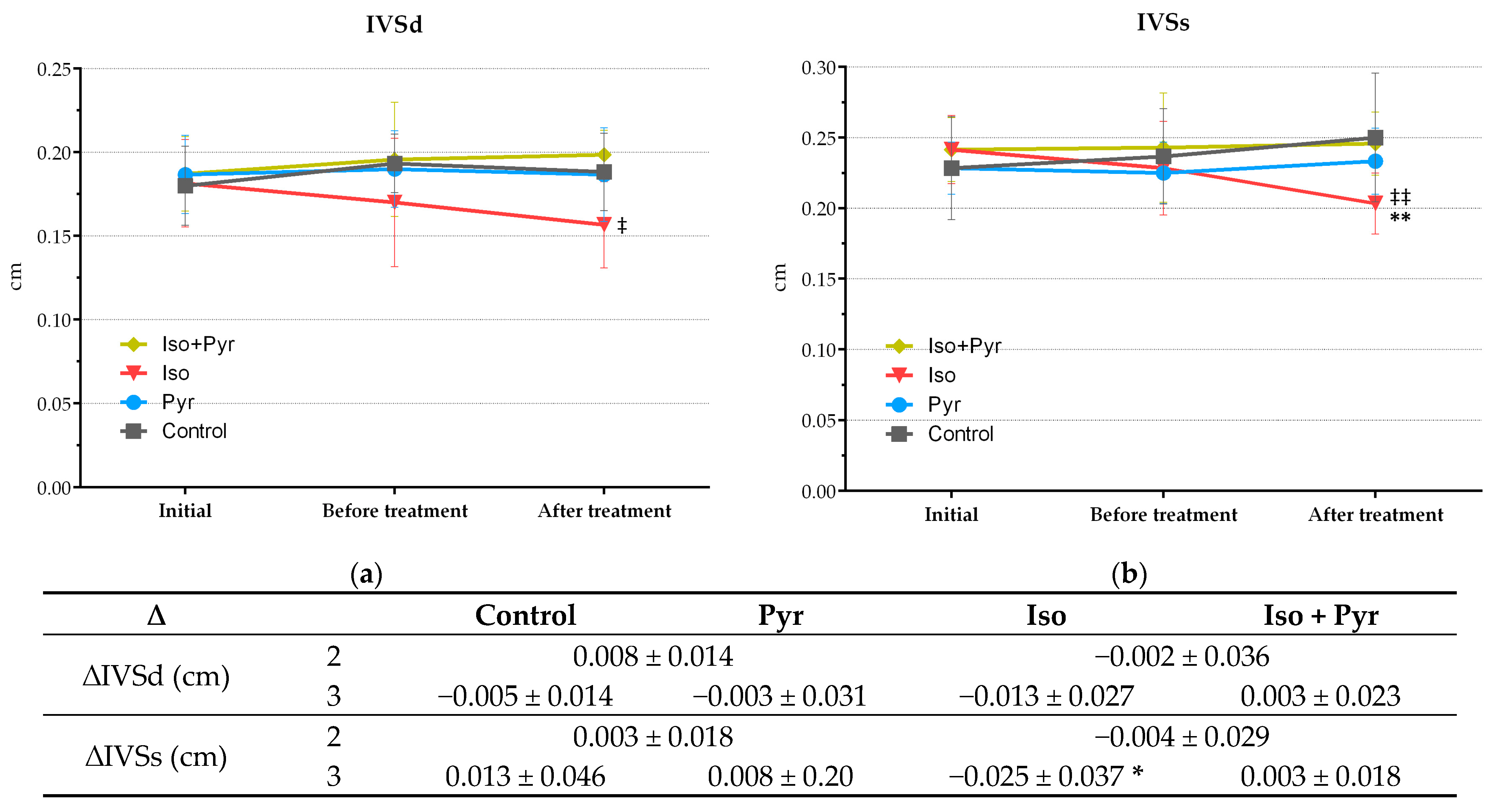
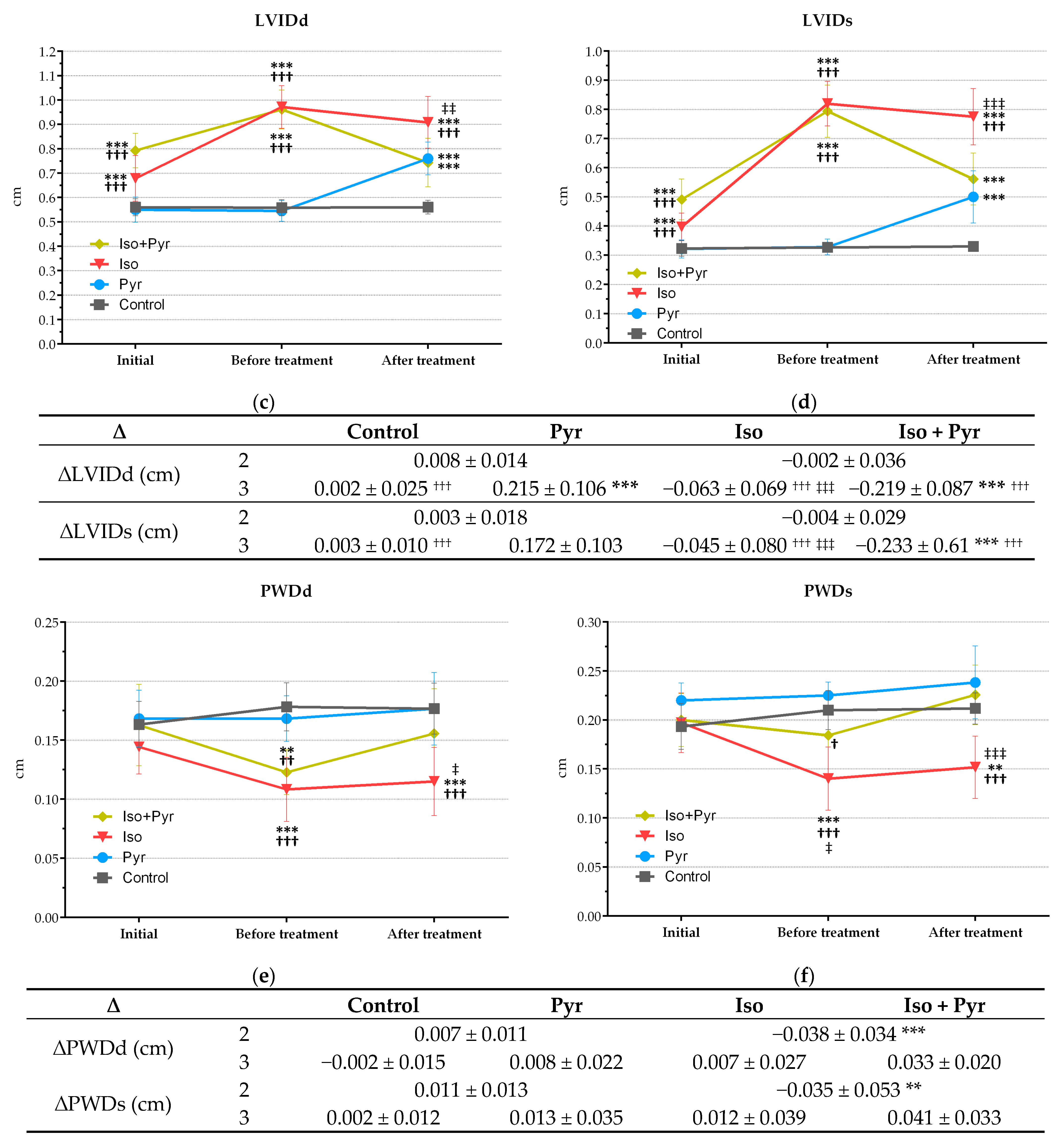
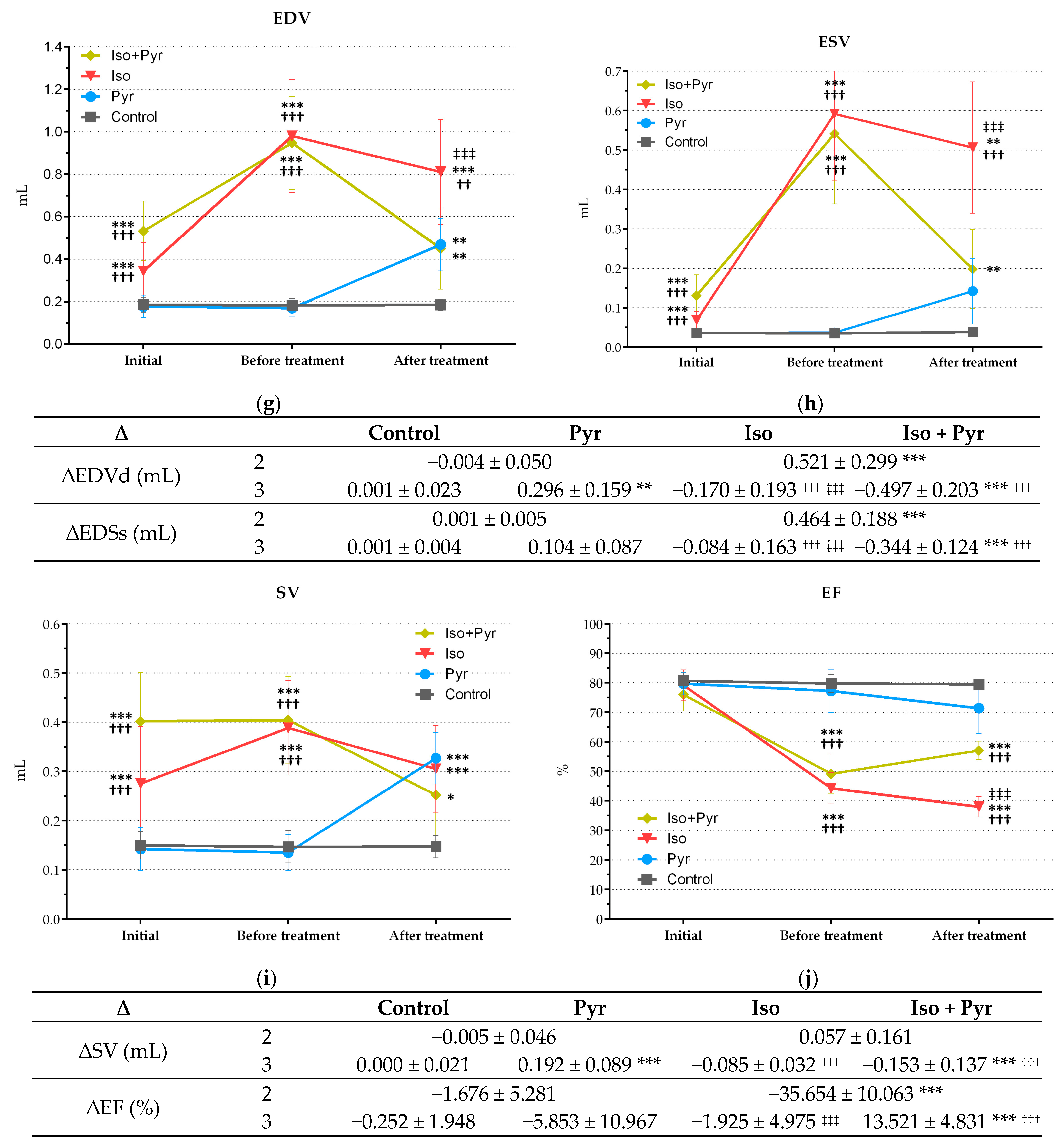
2.4. Effects of Pyridostigmine Treatment on Echocardiogram (ECHO) Parameters
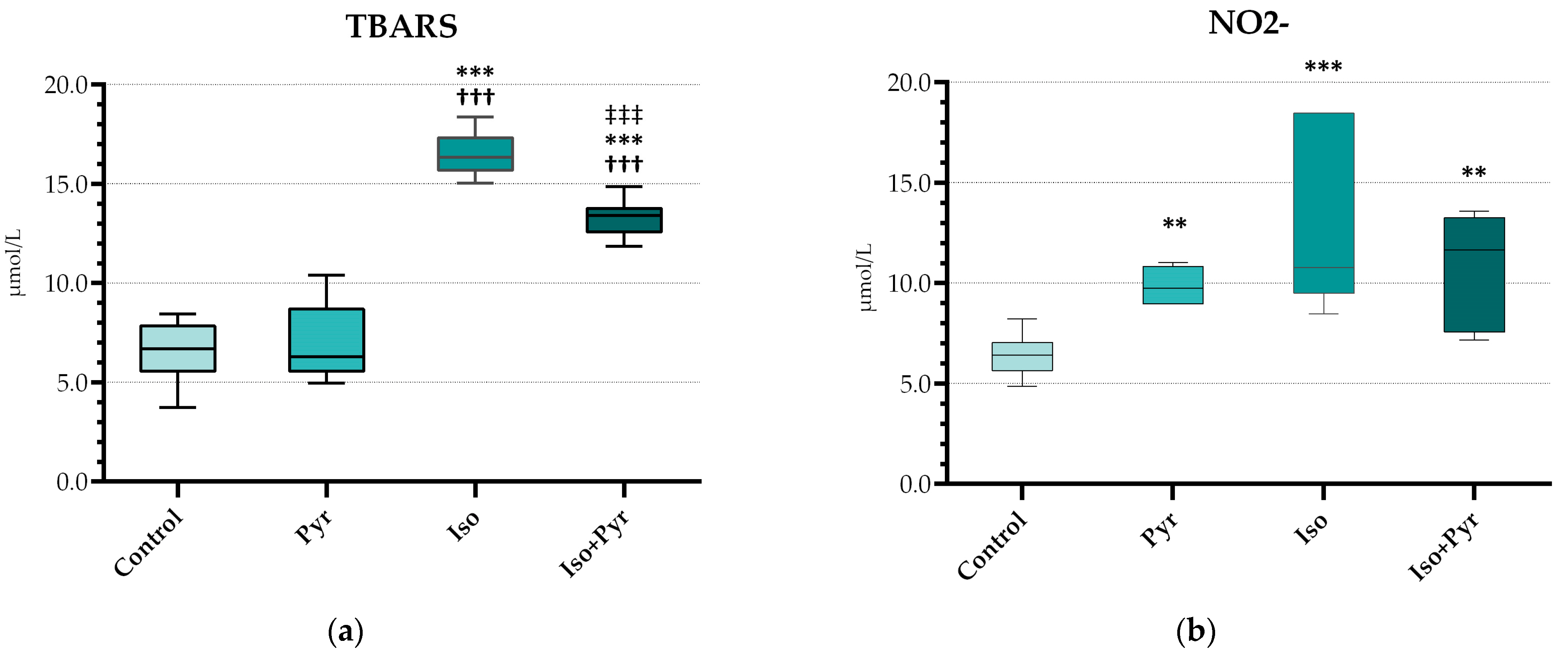
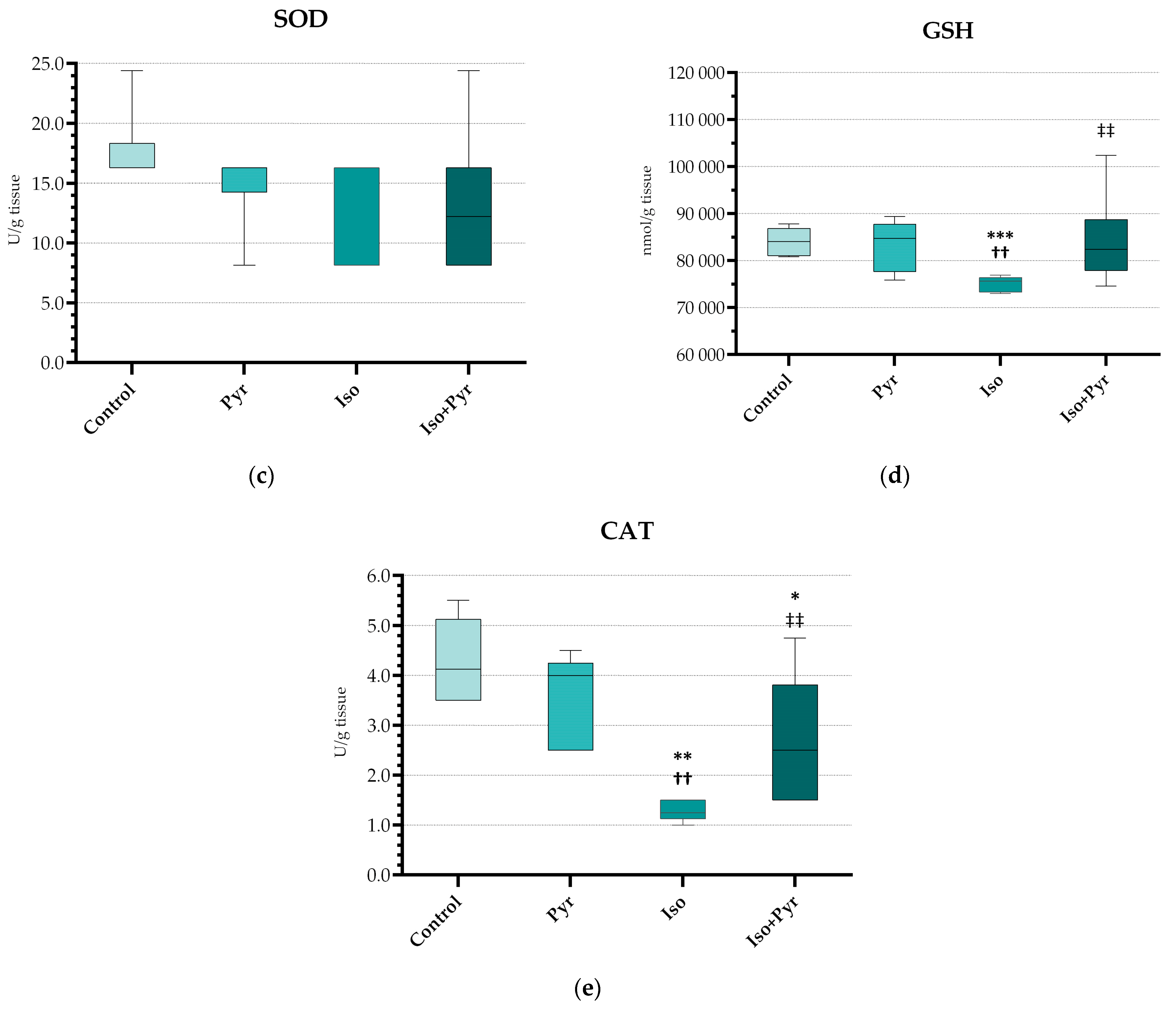
2.5. Effects of Pyridostigmine Treatment on Prooxidative and Antioxidative Markers in Myocardial Tissue Samples
2.6. Effects of Pyridostigmine Treatment on NTproBNP, MMP-2, and MMP-9 in Serum Samples
2.7. Effects of Pyridostigmine Treatment on Histological Structure of Cardiac Muscle, H&E Stain, Masson’s Trichrome Stain, and Tissue Damage Score
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
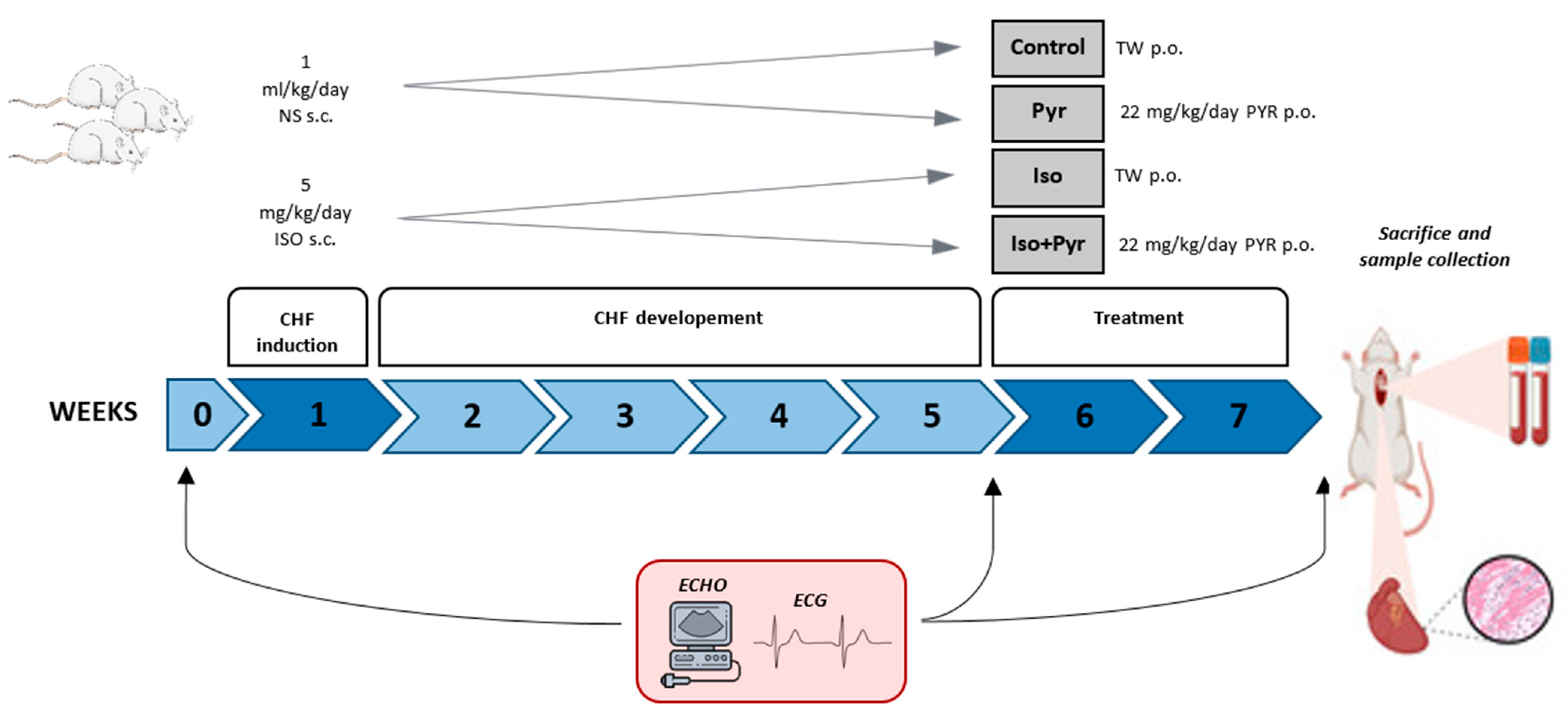
4.1. Experimental Animals and Experimental Protocol
4.2. ECG Recording and Echocardiogram (ECHO)
4.3. Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) Activity Measurement
4.4. NTproBNP, MMP-2, and MMP-9
4.5. Hearth Tissue Homogenisation
4.6. Prooxidative and Antioxidative Markers
4.7. Histopathological Analysis
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ANS | Autonomic nervous system |
| SNS | Sympathetic nervous system |
| PNS | Parasympathetic nervous system |
| CHF | Chronic heart failure |
| RAAS | Renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system |
| ACh | Acetylcholine |
| AChE | Acetylcholinesterase |
| AMI | Acute myocardial infarction |
| LV | Left ventricle |
| BW | Body weight |
| HW | Heart weight |
| HW/BW | Heart-to-body weight ratio |
| ECG | Electrocardiogram |
| ECHO | Echocardiogram |
| LVIDd | Left ventricle internal diameter end diastole |
| LVIDs | Left ventricle internal diameter end systole |
| EDV | End-diastolic volume |
| ESV | End-systolic volume |
| EF | Ejection fraction |
| IVSd | Intraventricular septum thickness end diastole |
| IVSs | Intraventricular septum thickness end systole |
| PWDd | Posterior wall diameter end diastole |
| PWDs | Posterior wall diameter end systole |
| SV | Stroke volume |
| ISO | Isoprenaline |
| TBARS | Thiobarbituric acid reactive substances |
| NO2− | Nitrite |
| CAT | Catalase |
| GSH | Reduced glutathione |
| SOD | Superoxide dismutase |
| NTproBNP | N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide |
| MMP-2 | Matrix metalloproteinase 2 |
| MMP-9 | Matrix metalloproteinase 9 |
| H&E | Haematoxylin and eosin |
| HRV | Heart rate variability |
| VLF | Very low frequency |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| RNS | Reactive nitrogen species |
| CAP | Cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway |
| α7nAChR | α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor |
| mAChR | Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor |
| M3AchR | M3 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor |
References
- Bencze, M.; Boroš, A.; Behuliak, M.; Vavřínová, A.; Vaněčková, I.; Zicha, J. Changes in Cardiovascular Autonomic Control Induced by Chronic Inhibition of Acetylcholinesterase During Pyridostigmine or Donepezil Treatment of Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2024, 971, 176526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Zheng, C.; Kawada, T.; Uemura, K.; Yokota, S.; Matsushita, H.; Saku, K. Donepezil Attenuates Progression of Cardiovascular Remodeling and Improves Prognosis in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats with Chronic Myocardial Infarction. Hypertens. Res. 2024, 47, 1298–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zheng, C.; Kawada, T.; Inagaki, M.; Uemura, K.; Sugimachi, M. Adding the Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitor, Donepezil, to Losartan Treatment Markedly Improves Long-Term Survival in Rats with Chronic Heart Failure. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2014, 16, 1056–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Zheng, C.; Kawada, T.; Inagaki, M.; Uemura, K.; Shishido, T.; Sugimachi, M. Donepezil Markedly Improves Long-Term Survival in Rats with Chronic Heart Failure After Extensive Myocardial Infarction. Circ. J. 2013, 77, 2519–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khuanjing, T.; Palee, S.; Chattipakorn, S.C.; Chattipakorn, N. The Effects of Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors on the Heart in Acute Myocardial Infarction and Heart Failure: From Cells to Patient Reports. Acta Physiol. 2020, 228, e13396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zheng, C.; Inagaki, M.; Kawada, T.; Sunagawa, K.; Sugimachi, M. Chronic Vagal Stimulation Decreased Vasopressin Secretion and Sodium Ingestion in Heart Failure Rats after Myocardial Infarction. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology 27th Annual Conference, Shanghai, China, 1–4 September 2005 17–18 January 2006; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2005; pp. 3962–3965. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Zheng, C.; Sato, T.; Kawada, T.; Sugimachi, M.; Sunagawa, K. Vagal Nerve Stimulation Markedly Improves Long-Term Survival After Chronic Heart Failure in Rats. Circulation 2004, 109, 120–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lataro, R.M.; Silva, C.A.A.; Fazan, R.; Rossi, M.A.; Prado, C.M.; Godinho, R.O.; Salgado, H.C. Increase in Parasympathetic Tone by Pyridostigmine Prevents Ventricular Dysfunction During the Onset of Heart Failure. Am. J. Physiol.-Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2013, 305, R908–R916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezerra, O.C.; França, C.M.; Rocha, J.A.; Neves, G.A.; Souza, P.R.M.; Teixeira Gomes, M.; Malfitano, C.; Loleiro, T.C.A.; Dourado, P.M.; Llesuy, S.; et al. Cholinergic Stimulation Improves Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Experimental Myocardial Infarction. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabino, J.P.J.; Da Silva, C.A.A.; De Melo, R.F.; Fazan, R.; Salgado, H.C. The Treatment with Pyridostigmine Improves the Cardiocirculatory Function in Rats with Chronic Heart Failure. Auton. Neurosci. 2013, 173, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, B.; Lira, F.S.; Consolim-Colombo, F.M.; Rocha, J.A.; Caperuto, E.C.; De Angelis, K.; Irigoyen, M.-C. Role of Exercise Training on Autonomic Changes and Inflammatory Profile Induced by Myocardial Infarction. Mediat. Inflamm. 2014, 2014, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos-Almeida, F.M.; Girão, H.; Da Silva, C.A.A.; Salgado, H.C.; Fazan, R. Cholinergic Stimulation with Pyridostigmine Protects Myocardial Infarcted Rats Against Ischemic-Induced Arrhythmias and Preserves Connexin43 Protein. Am. J. Physiol.-Heart Circ. Physiol. 2015, 308, H101–H107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soares, P.P.D.S.; Da Nóbrega, A.C.L.; Ushizima, M.R.; Irigoyen, M.C.C. Cholinergic Stimulation with Pyridostigmine Increases Heart Rate Variability and Baroreflex Sensitivity in Rats. Auton. Neurosci. 2004, 113, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.-J.; Huang, N.; Lu, Y.; Zhao, M.; Yu, X.-J.; Yang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zang, W.-J. Improving Vagal Activity Ameliorates Cardiac Fibrosis Induced by Angiotensin II: In Vivo and In Vitro. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, X.; Gao, C. Huperzine A Ameliorates Damage Induced by Acute Myocardial Infarction in Rats through Antioxidant, Anti-Apoptotic and Anti-Inflammatory Mechanisms. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2014, 33, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, J.A.; Ribeiro, S.P.; França, C.M.; Coelho, O.; Alves, G.; Lacchini, S.; Kallás, E.G.; Irigoyen, M.C.; Consolim-Colombo, F.M. Increase in Cholinergic Modulation with Pyridostigmine Induces Anti-Inflammatory Cell Recruitment Soon After Acute Myocardial Infarction in Rats. Am. J. Physiol.-Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2016, 310, R697–R706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arikawa, M.; Kakinuma, Y.; Handa, T.; Yamasaki, F.; Sato, T. Donepezil, Anti-Alzheimer’s Disease Drug, Prevents Cardiac Rupture During Acute Phase of Myocardial Infarction in Mice. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Liu, J.-J.; Bi, X.-Y.; Yu, X.-J.; Kong, S.-S.; Qin, F.-F.; Zhou, J.; Zang, W.-J. Pyridostigmine Ameliorates Cardiac Remodeling Induced by Myocardial Infarction via Inhibition of the Transforming Growth Factor-Β1/TGF-Β1–Activated Kinase Pathway. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2014, 63, 412–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feriani, D.J.; Coelho-Júnior, H.J.; De Oliveira, J.C.M.F.; Delbin, M.A.; Mostarda, C.T.; Dourado, P.M.M.; Caperuto, É.C.; Irigoyen, M.C.C.; Rodrigues, B. Pyridostigmine Improves the Effects of Resistance Exercise Training after Myocardial Infarction in Rats. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feriani, D.J.; Souza, G.I.H.; Carrozzi, N.M.; Mostarda, C.; Dourado, P.M.M.; Consolim-Colombo, F.M.; De Angelis, K.; Moreno, H.; Irigoyen, M.C.; Rodrigues, B. Impact of Exercise Training Associated to Pyridostigmine Treatment on Autonomic Function and Inflammatory Profile After Myocardial Infarction in Rats. Int. J. Cardiol. 2017, 227, 757–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha-Resende, C.; Roy, A.; Resende, R.; Ladeira, M.S.; Lara, A.; De Morais Gomes, E.R.; Prado, V.F.; Gros, R.; Guatimosim, C.; Prado, M.A.M.; et al. Non-Neuronal Cholinergic Machinery Present in Cardiomyocytes Offsets Hypertrophic Signals. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2012, 53, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakinuma, Y.; Akiyama, T.; Sato, T. Cholinoceptive and Cholinergic Properties of Cardiomyocytes Involving an Amplification Mechanism for Vagal Efferent Effects in Sparsely Innervated Ventricular Myocardium. FEBS J. 2009, 276, 5111–5125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lechat, P.; Hulot, J.-S.; Escolano, S.; Mallet, A.; Leizorovicz, A.; Werhlen-Grandjean, M.; Pochmalicki, G.; Dargie, H. Heart Rate and Cardiac Rhythm Relationships with Bisoprolol Benefit in Chronic Heart Failure in CIBIS II Trial. Circulation 2001, 103, 1428–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dewland, T.A.; Androne, A.S.; Lee, F.A.; Lampert, R.J.; Katz, S.D. Effect of Acetylcholinesterase Inhibition with Pyridostigmine on Cardiac Parasympathetic Function in Sedentary Adults and Trained Athletes. Am. J. Physiol.-Heart Circ. Physiol. 2007, 293, H86–H92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pontes, P.V.D.; Bastos, B.G.; Romêo Filho, L.J.; Mesquita, E.T.; Nóbrega, A.C.L.D. Cholinergic Stimulation with Pyridostigmine, Hemodynamic and Echocardiographic Analysis in Healthy Subjects. Arq. Bras. Cardiol. 1999, 72, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nóbrega, A.C.; Carvalho, A.C.; Bastos, B.G. Resting and Reflex Heart Rate Responses during Cholinergic Stimulation with Pyridostigmine in Humans. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 1996, 29, 1461–1465. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Roman-Pepine, D.; Serban, A.M.; Capras, R.-D.; Cismaru, C.M.; Filip, A.G. A Comprehensive Review: Unraveling the Role of Inflammation in the Etiology of Heart Failure. Heart Fail. Rev. 2025. online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heller, M.; Edelstein, P.; Mayer, M. Membrane-Bound Enzymes. III. Protease Activity in Leucocytes in Relation to Erythrocyte Membranes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1975, 413, 472–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, M.J.; Liu, Z. Crosstalk of Reactive Oxygen Species and NF-κB Signaling. Cell Res. 2011, 21, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aimo, A.; Castiglione, V.; Borrelli, C.; Saccaro, L.F.; Franzini, M.; Masi, S.; Emdin, M.; Giannoni, A. Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in the Evolution of Heart Failure: From Pathophysiology to Therapeutic Strategies. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2020, 27, 494–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Yu, B.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, S.; Guan, Z. Mesenchymal Stem Cell Transplantation Attenuates Cardiac Fibrosis Associated with Isoproterenol-Induced Global Heart Failure. Transpl. Int. 2008, 21, 1181–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanhoutte, D.; Schellings, M.; Pinto, Y.; Heymans, S. Relevance of Matrix Metalloproteinases and Their Inhibitors After Myocardial Infarction: A Temporal and Spatial Window. Cardiovasc. Res. 2006, 69, 604–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavlov, V.A.; Chavan, S.S.; Tracey, K.J. Molecular and Functional Neuroscience in Immunity. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 36, 783–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olofsson, P.S.; Rosas-Ballina, M.; Levine, Y.A.; Tracey, K.J. Rethinking Inflammation: Neural Circuits in the Regulation of Immunity. Immunol. Rev. 2012, 248, 188–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bandoni, R.L.; Bricher Choque, P.N.; Dellê, H.; De Moraes, T.L.; Porter, M.H.M.; Da Silva, B.D.; Neves, G.A.; Irigoyen, M.-C.; De Angelis, K.; Pavlov, V.A.; et al. Cholinergic Stimulation with Pyridostigmine Modulates a Heart-Spleen Axis after Acute Myocardial Infarction in Spontaneous Hypertensive Rats. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 9563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ding, S.; Wang, Y. Targeting the Cholinergic Anti-Inflammatory Pathway: An Innovative Strategy for Treating Diseases. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2025, 52, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liao, H.; Ochani, M.; Justiniani, M.; Lin, X.; Yang, L.; Al-Abed, Y.; Wang, H.; Metz, C.; Miller, E.J.; et al. Cholinergic Agonists Inhibit HMGB1 Release and Improve Survival in Experimental Sepsis. Nat. Med. 2004, 10, 1216–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prathumsap, N.; Ongnok, B.; Khuanjing, T.; Arinno, A.; Maneechote, C.; Apaijai, N.; Chunchai, T.; Arunsak, B.; Shinlapawittayatorn, K.; Chattipakorn, S.C.; et al. Acetylcholine Receptor Agonists Provide Cardioprotection in Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity via Modulating Muscarinic M2 and A7 Nicotinic Receptor Expression. Transl. Res. 2022, 243, 33–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Liu, H.; Sun, P.; Wang, X.; Wang, C.; Wang, L.; Wang, T. Chronic Vagus Nerve Stimulation Attenuates Vascular Endothelial Impairments and Reduces the Inflammatory Profile via Inhibition of the NF-κB Signaling Pathway in Ovariectomized Rats. Exp. Gerontol. 2016, 74, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, R.; Wu, Q.; Guo, L.; Ye, D.; Cao, Q.; Zhang, M.; Xian, Y.; Chen, M.; Yan, K.; Zheng, J. Pyridostigmine Attenuated High-fat-diet Induced Liver Injury by the Reduction of Mitochondrial Damage and Oxidative Stress via α7nAChR and M3AChR. J. Biochem. Amp; Mol. Tox 2024, 38, e23671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muric, M.; Srejovic, I.; Novakovic, J.; Zivkovic, V.; Jovic, J.J.; Sretenovic, J.; Nikolic, M.; Lazarevic, N.; Andjic, M.; Kocovic, A.; et al. The Combined Empagliflozin and Sacubitril/Valsartan Therapy Attenuates Isoproterenol-Induced Heart Failure in Rats: Functional, Molecular, and Structural Insights. Cardiovasc. Drugs Ther. 2025. online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flori, L.; Lazzarini, G.; Spezzini, J.; Pirone, A.; Calderone, V.; Testai, L.; Miragliotta, V. The Isoproterenol-Induced Myocardial Fibrosis: A Biochemical and Histological Investigation. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 174, 116534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redfors, B.; Shao, Y.; Omerovic, E. Influence of Anesthetic Agent, Depth of Anesthesia and Body Temperature on Cardiovascular Functional Parameters in the Rat. Lab. Anim. 2014, 48, 6–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajic, Z.; Sobot, T.; Smitran, A.; Uletilovic, S.; Mandić-Kovačević, N.; Cvjetkovic, T.; Malicevic, U.; Stanetic, B.; Đukanović, Đ.; Maticic, M.; et al. Liraglutide Treatment Restores Cardiac Function After Isoprenaline-Induced Myocardial Injury and Prevents Heart Failure in Rats. Life 2025, 15, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, L.; Fenning, A.; Chan, V.; Loch, D.; Wilson, K.; Anderson, B.; Burstow, D. Echocardiographic Assessment of Cardiac Structure and Function in Rats. Heart Lung Circ. 2002, 11, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hubesch, G.; Hanthazi, A.; Acheampong, A.; Chomette, L.; Lasolle, H.; Hupkens, E.; Jespers, P.; Vegh, G.; Wembonyama, C.W.M.; Verhoeven, C.; et al. A Preclinical Rat Model of Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction with Multiple Comorbidities. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 8, 809885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dohi, K. Echocardiographic Assessment of Cardiac Structure and Function in Chronic Renal Disease. J. Echocardiogr. 2019, 17, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, L.C.; Wagner, D.A.; Glogowski, J.; Skipper, P.L.; Wishnok, J.S.; Tannenbaum, S.R. Analysis of Nitrate, Nitrite, and [15N]Nitrate in Biological Fluids. Anal. Biochem. 1982, 126, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandić-Kovačević, N.; Kukrić, Z.; Latinović, S.; Cvjetković, T.; Šobot, T.; Bajić, Z.; Maličević, U.; Marinković, S.; Đukanović, Đ.; Uletilović, S.; et al. Antioxidative Potential of Pomegranate Peel Extract: In Vitro and in Vivo Studies. Scr. Medica 2023, 54, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohkawa, H.; Ohishi, N.; Yagi, K. Assay for Lipid Peroxides in Animal Tissues by Thiobarbituric Acid Reaction. Anal. Biochem. 1979, 95, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinković, S.T.; Đukanović, Đ.; Duran, M.; Bajic, Z.; Sobot, T.; Uletilović, S.; Mandić-Kovacević, N.; Cvjetković, T.; Maksimović, Ž.M.; Maličević, U.; et al. Pomegranate Peel Extract Attenuates Isoprenaline-Induced Takotsubo-like Myocardial Injury in Rats. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beutler, E.; Duron, O.; Kelly, B.M. Improved Method for the Determination of Blood Glutathione. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 1963, 61, 882–888. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vasiljević, J.D.; Otašević, P.; Popović, Z.B.; Nešković, A.N.; Vidaković, R.; Popović, Z.V.; Radovančević, B.; Frazier, O.H.; Gradinac, S. Semiquantitative Histomorphometric Analysis of Myocardium Following Partial Left Ventriculectomy: 1-year Follow-Up. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2005, 7, 763–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| HW (mg) | BW (g) | HW/BW Ratio (mg/g) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 1340.00 ± 330.00 | 409.67 ± 38.05 | 3.26 ± 0.75 |
| Pyr | 1400.00 ± 310.00 | 390.00 ± 20.14 | 3.58 ± 0.81 |
| Iso | 1270.00 ± 260.00 | 409.71 ± 65.86 | 3.10 ± 0.49 |
| Iso + Pyr | 1340.00 ± 60.00 | 396.50 ± 25.73 | 3.40 ± 0.22 |
| Control | Pyr | Iso | Iso + Pyr | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR (bpm) | 1 | 244.09 ± 28.88 | 258.27 ± 23.73 | 261.85 ± 16.99 | 268.18 ± 18.37 |
| 2 | 246.44 ± 20.99 | 259.50 ± 27.32 | 244.13 ± 29.39 | 257.12 ± 17.24 | |
| 3 | 246.29 ± 20.99 | 224.67 ± 16.96 *† | 249.12 ± 23.24 | 231.34 ± 12.12 **† | |
| PQ/PR (ms) | 1 | 49.17 ± 8.01 | 46.67 ± 8.16 | 45.00 ± 5.35 | 44.38 ± 4.96 |
| 2 | 50.00 ± 7.07 | 47.50 ± 5.00 | 44.29 ± 5.35 | 49.17 ± 6.65 | |
| 3 | 50.00 ± 7.07 | 46.67 ± 5.77 | 48.57 ± 6.90 | 43.33 ± 5.16 | |
| QT/RT interval (ms) | 1 | 86.67 ± 5.16 | 94.17 ± 10.21 | 101.25 ± 9.91 | 93.75 ± 5.18 |
| 2 | 96.67 ± 10.33 | 103.33 ± 8.16 | 107.14 ± 9.51 | 104.29 ± 9.76 | |
| 3 | 96.67 ± 10.33 | 95.00 ± 10.49 | 102.86 ± 7.56 | 95.71 ± 7.87 | |
| QRS peak-to-peak voltage amplitude (mV) | 1 | 0.26 ± 0.04 | 0.25 ± 0.03 | 0.26 ± 0.05 | 0.26 ± 0.02 |
| 2 | 0.27 ± 0.07 | 0.28 ± 0.06 | 0.23 ± 0.06 | 0.20 ± 0.03 ‡‡ | |
| 3 | 0.27 ± 0.07 | 0.25 ± 0.07 | 0.24 ± 0.06 | 0.20 ± 0.03 ‡‡‡ |
| NTproBNP | MMP-2 | MMP-9 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 346.00 ± 44.66 | 134.70 ± 18.57 | 47951.42 ± 9486.37 |
| Pyr | 366.19 ± 26.26 | 212.96 ± 82.17 | 49905.53 ± 10813.50 |
| Iso | 517.72 ± 52.24 ** †† | 307.04 ± 54.50 ** | 59619.24 ± 4502.97 * |
| Iso + Pyr | 383.15 ± 50.36 ‡‡ | 203.09 ± 70.22 ‡ | 52025.53 ± 5861.58 ‡ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marinković, S.T.; Sobot, T.; Maksimović, Ž.M.; Ðukanović, Ð.; Uletilović, S.; Mandić-Kovačević, N.; Jovičić, S.; Matičić, M.; Gajić Bojić, M.; Stojmenovski, A.; et al. Pyridostigmine Treatment Significantly Alleviates Isoprenaline-Induced Chronic Heart Failure in Rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6892. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146892
Marinković ST, Sobot T, Maksimović ŽM, Ðukanović Ð, Uletilović S, Mandić-Kovačević N, Jovičić S, Matičić M, Gajić Bojić M, Stojmenovski A, et al. Pyridostigmine Treatment Significantly Alleviates Isoprenaline-Induced Chronic Heart Failure in Rats. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(14):6892. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146892
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarinković, Sonja T., Tanja Sobot, Žana M. Maksimović, Ðorđe Ðukanović, Snežana Uletilović, Nebojša Mandić-Kovačević, Sanja Jovičić, Milka Matičić, Milica Gajić Bojić, Aneta Stojmenovski, and et al. 2025. "Pyridostigmine Treatment Significantly Alleviates Isoprenaline-Induced Chronic Heart Failure in Rats" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 14: 6892. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146892
APA StyleMarinković, S. T., Sobot, T., Maksimović, Ž. M., Ðukanović, Ð., Uletilović, S., Mandić-Kovačević, N., Jovičić, S., Matičić, M., Gajić Bojić, M., Stojmenovski, A., Bojanić, A., Škrbić, R., & Stojiljković, M. P. (2025). Pyridostigmine Treatment Significantly Alleviates Isoprenaline-Induced Chronic Heart Failure in Rats. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(14), 6892. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146892







