Adipo-Modulation by Turmeric Bioactive Phenolic Components: From Curcuma Plant to Effects
Abstract
1. Introduction
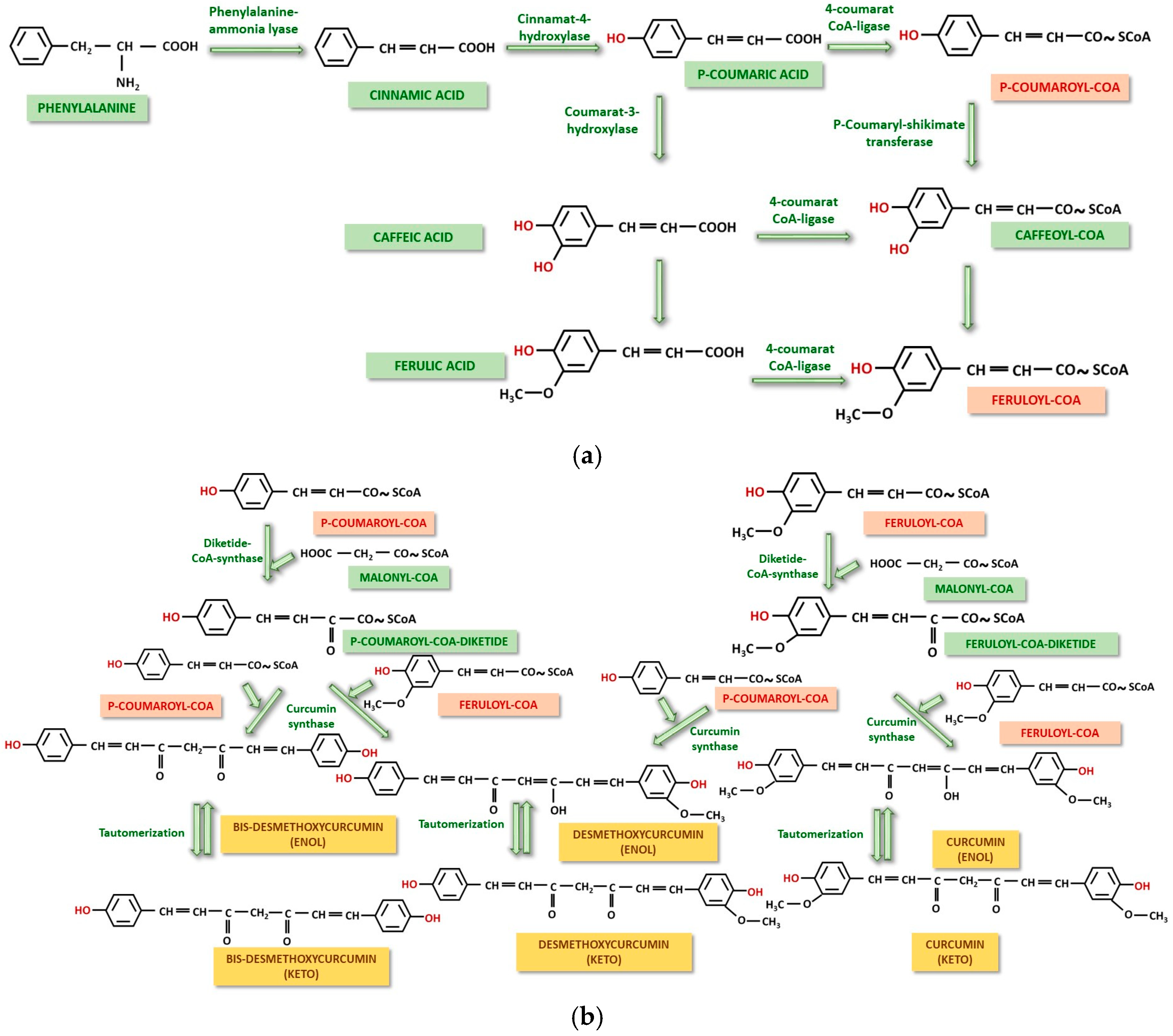
2. From Nature to the Appearance of Biologically Active Compounds: Biosynthesis of Curcumin and Other Related Phenols in Curcuma
3. From Exogenous Intake to Pharmacokinetics: Pharmacokinetics of Curcumin and Phenolic Derivatives in the Body
4. What Remains to Be Done from Pharmacokinetics to Pharmacodynamics: Studies That Explain the Adipo-Modulation Action of Curcumin and Phenolic Derivatives
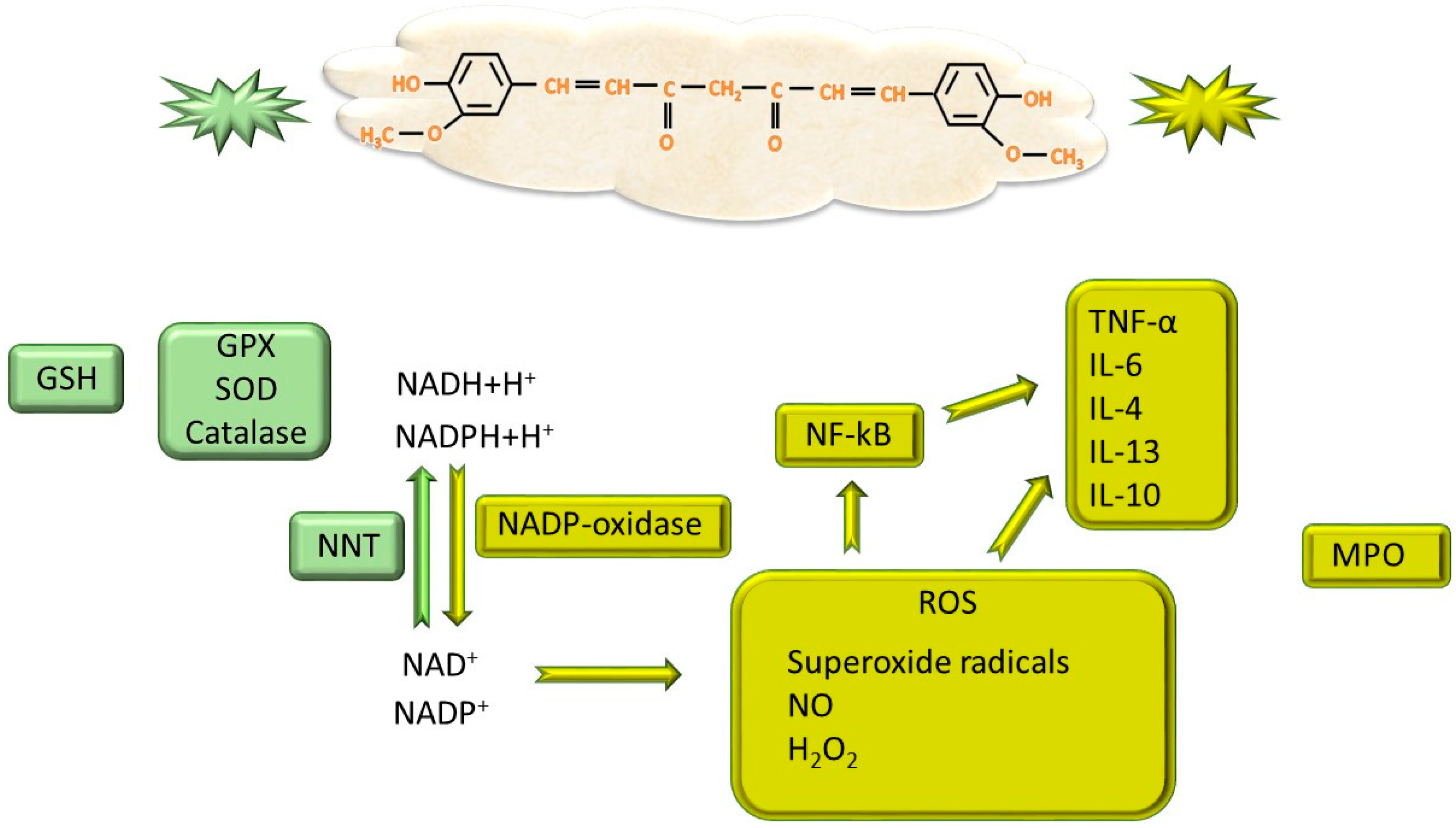
4.1. Modulation of Adipogenesis Through Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Capacity
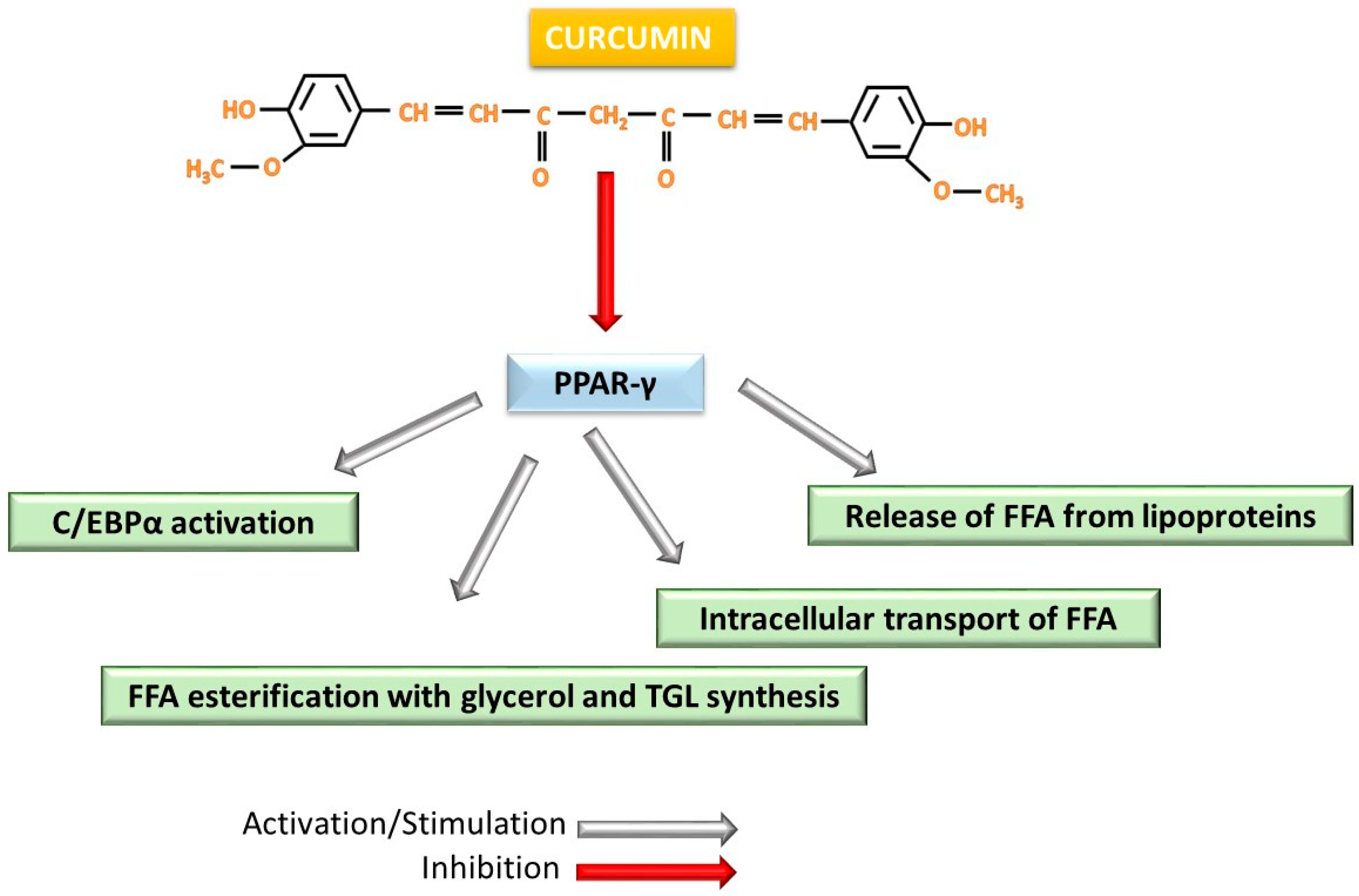
4.2. Effect on Lipid Metabolism
4.3. Interferences During Adipogenesis
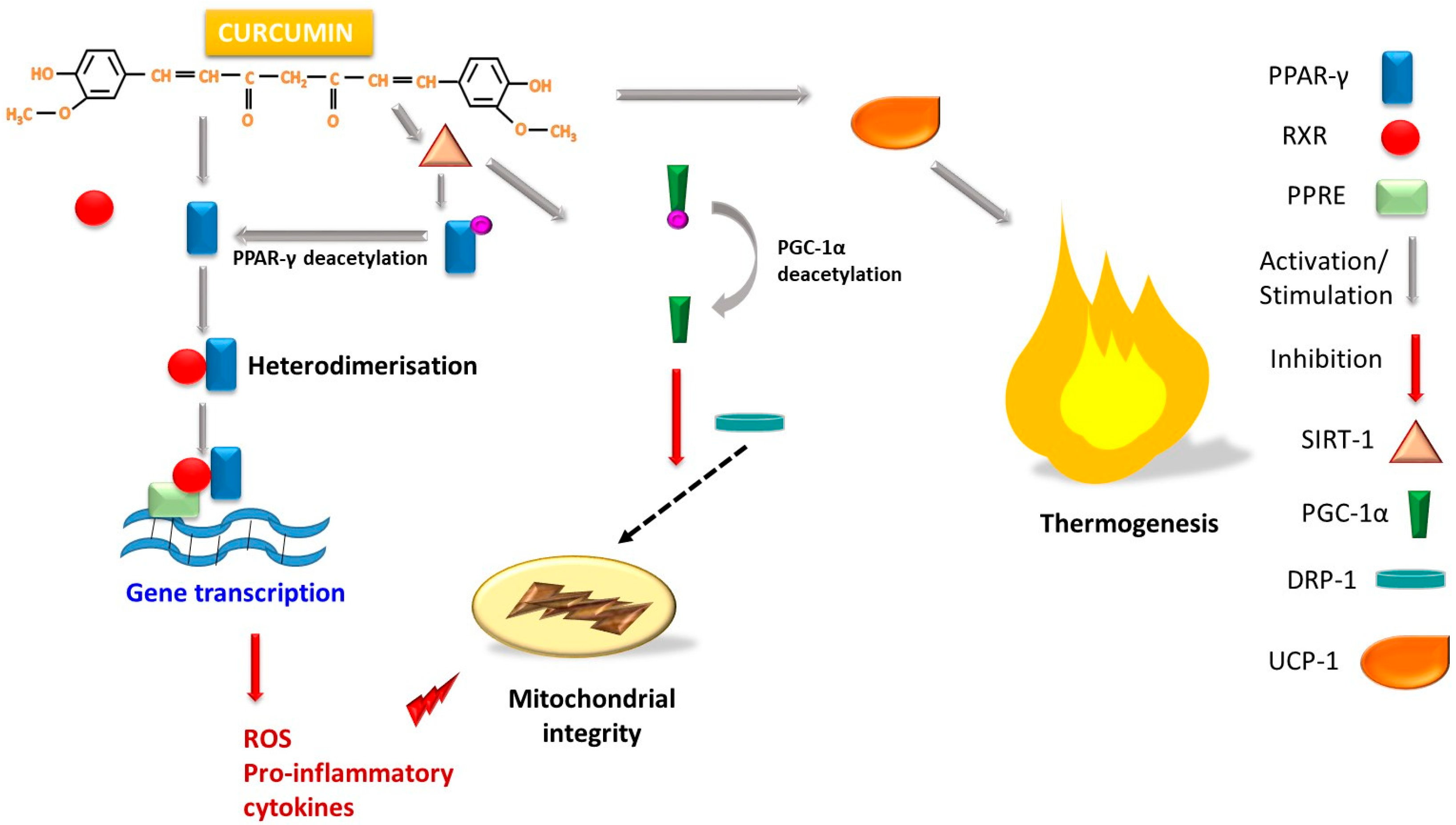
4.4. The Role of Curcumins in Increasing Energy Utilization and Stimulating Thermogenesis
5. Minor Amounts–Major Importance: The Role of Calebin A and Intermediates in the Global Effect of Turmeric
6. Discussions and Perspectives on the Real Weight Loss Effect
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| FDA | Food and Drug Administration |
| ROS | reactive oxygen species |
| IL | interleukin |
| TNF-α | tumor necrosis factor α |
| MCP-1 | monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| CoA | coenzyme A |
| NNT | nicotinamide nucleotide transhydrogenase |
| SOD | superoxide dismutase |
| GPX | gluthatione peroxidase |
| GSH | reduced glutathione |
| MPO | myeloperoxidase |
| PPAR | peroxisome-activating receptor |
| WAT | white adipose tissue |
| BAT | brown adipose tissue |
| BeAT | beige adipose tissue |
| UCP-1 | uncoupling protein-1 |
| NF-kB | nuclear factor-kB |
| TGF-β | transforming growth factor β |
| mTOR | mammalian target of rapamycin |
| TGL | triglyceride |
| FAS | fatty acid synthase |
| AMPK | 5′AMP-activated proteinkinase |
| SREBP | sterol regulating element binding proteins |
| ACC | acetyl-CoA carboxylase |
| C/EBP | CCAAT/enhancer-binding proteins |
| PGC-1α | peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor G coactivator 1-α |
| HFD | high fat diet |
| GM | gut microbiota |
| DRP-1 | dynamin-related protein 1 |
| SIRT-1 | sirtuin 1 |
| RXR | retinoid X receptor |
| PPRE | proliferation response element |
References
- Servida, S.; Piontini, A.; Gori, F.; Tomaino, L.; Moroncini, G.; De Gennaro Colonna, V.; La Vecchia, C.; Vigna, L. Curcumin and gut microbiota: A narrative overview with focus on glycemic control. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 7710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Liu, J.; He, L.; Liu, L.; Cheng, B.; Zhou, F.; Cao, D.; He, Y. A comprehensive review on the benefits and problems of curcumin with respect to human health. Molecules 2022, 27, 4400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharifi-Rad, J.; Rayess, Y.E.; Rizk, A.A.; Sadaka, C.; Zgheib, R.; Zam, W.; Sestito, S.; Rapposelli, S.; Neffe-Skocińska, K.; Zielińska, D.; et al. Turmeric and its major compound curcumin on health: Bioactive effects and safety profiles for food, pharmaceutical, biotechnological and medicinal applications. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 01021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panknin, T.M.; Howe, C.L.; Hauer, M.; Bucchireddigari, B.; Rossi, A.M.; Funk, J.L. Curcumin supplementation and human disease: A scoping review of clinical trials. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izadi, M.; Sadri, N.; Abdi, A.; Zadeh, M.M.R.; Jalaei, D.; Ghazimoradi, M.M.; Shouri, S.; Tahmasebi, S. Longevity and anti-aging effects of curcumin supplementation. GeroScience 2024, 46, 2933–2950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, L.; Gao, C.; Wang, H.; Ren, Y.; Li, J.; Li, M.; Du, X.; Li, W.; Zhang, J. Effects of dietary polyphenol curcumin supplementation on metabolic, inflammatory, and oxidative stress indices in patients with metabolic syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1216708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallya, P.; Lewis, S.A. Curcumin and its formulations for the treatment of polycystic ovary syndrome: Current insights and future prospects. J. Ovarian Res. 2025, 18, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alhar, M.S.O.; El-Sofany, W.I.; AlRashidi, A.A.; Hamden, K. Protective effects of isolated curcumin from curcuma longa on key enzymes involved in the insulin signaling pathway and digestive and metabolic enzymes associated with obesity, type 2 diabetes, and hypertension. J. Diab. Res. 2025, 2025, 8050374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uchio, R.; Kawasaki, K.; Okuda-Hanafusa, C.; Saji, R.; Muroyama, K.; Murosaki, S.; Yamamoto, Y.; Hirose, Y. Curcuma longa extract improves serum inflammatory markers and mental health in healthy participants who are overweight: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Nutr. J. 2021, 20, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calderón-Pérez, L.; Llauradó, E.; Companys, J.; Pla-Pagà, L.; Boqué, N.; Puiggrós, F.; Valls, R.M.; Pedret, A.; Llabrés, J.M.; Arola, L.; et al. Acute Effects of Turmeric Extracts on Knee Joint Pain: A Pilot, Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Med. Food 2021, 24, 436–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaikwawong, M.; Jansarikit, L.; Jirawatnotai, S.; Chuengsamarn, S. Curcumin extract improves beta cell functions in obese patients with type 2 diabetes: A randomized controlled trial. Nutr. J. 2024, 23, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, T.L.N.; Zenha, R.S.S.; Antunes, A.H.; Faria, F.R.; Rezende, K.R.; de Souza, E.L.; Mota, J.F. Evaluation of the Impact of Different Doses of Curcuma longa L. on Antioxidant Capacity: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Crossover Pilot Trial. BioMed Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 3532864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmadi, R.; Salari, S.; Sharifi, M.D.; Reihani, H.; Rostamiani, M.B.; Behmadi, M.; Taherzadeh, Z.; Eslami, S.; Rezayat, S.M.; Jaafari, M.R.; et al. Oral nano-curcumin formulation efficacy in the management of mild to moderate outpatient COVID-19: A randomized triple-blind placebo-controlled clinical trial. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 9, 4068–4075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heshmati, J.; Moini, A.; Sepidarkish, M.; Morvaridzadeh, M.; Salehi, M.; Palmowski, A.; Mojtahedi, M.F.; Shidfar, F. Effects of curcumin supplementation on blood glucose, insulin resistance and androgens in patients with polycystic ovary syndrome: A randomized double-blind placebo-controlled clinical trial. Phytomedicine 2021, 80, 153395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singhal, S.; Hasan, N.; Nirmal, K.; Chawla, R.; Chawla, S.; Kalra, B.S.; Dhal, A. Bioavailable turmeric extract for knee osteoarthritis: A randomized, non-inferiority trial versus paracetamol. Trials 2021, 22, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarhahzadeh, M.; Alavinejad, P.; Farsi, F.; Husain, D.; Rezazadeh, A. The effect of turmeric on lipid profile, malondialdehyde, liver echogenicity and enzymes among patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A randomized double blind clinical trial. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2021, 13, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halegoua-DeMarzio, D.; Navarro, V.; Ahmad, J.; Avula, B.; Barnhart, H.; Barritt, A.S.; Bonkovsky, H.L.; Fontana, R.J.; Ghabril, M.S.; Hoofnagle, J.H.; et al. Liver Injury Associated with Turmeric-A Growing Problem: Ten Cases from the Drug-Induced Liver Injury Network [DILIN]. Am. J. Med. 2023, 136, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajitkumar, A.; Mohan, G.; Ghose, M.; Yarrarapu, S.; Afiniwala, S. Drug-Induced Liver Injury Secondary to Turmeric Use. Eur. J. Case Rep. Intern. Med. 2023, 10, 003845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palaniappan, V.; Karthikeyan, K. Turmeric: The Yellow Allergen. Indian Dermatol. Online J. 2022, 14, 459–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopresti, A.L. Potential Role of Curcumin for the Treatment of Major Depressive Disorder. CNS Drugs 2022, 36, 123–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.-J.; Huang, S.-Y.; Zhou, D.-D.; Xiong, R.-G.; Zhao, C.-N.; Fang, A.-P.; Zhang, Y.-J.; Li, H.-B.; Zhu, H.-L. Effects and Mechanisms of Curcumin for the Prevention and Management of Cancers: An Updated Review. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Zhu, Q.; Chen, Y.; Ji, K.; Li, S.; Wu, Q.; Pan, Q.; Li, J. Review of the Protective Mechanism of Curcumin on Cardiovascular Disease. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2024, 18, 165–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stati, G.; Rossi, F.; Sancilio, S.; Basile, M.; Di Pietro, R. Curcuma longa Hepatotoxicity: A Baseless Accusation. Cases Assessed for Causality Using RUCAM Method. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 780330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, L.; Yu, G.; Hao, W.; Yang, K.; Chen, H. The efficacy and safety of Curcuma longa extract and curcumin supplements on osteoarthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Biosci. Rep. 2021, 41, BSR20210817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filardi, T.; Varì, R.; Ferretti, E.; Zicari, A.; Morano, S.; Santangelo, C. Curcumin: Could This Compound Be Useful in Pregnancy and Pregnancy-Related Complications? Nutrients 2020, 12, 3179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassanzadeh, K.; Buccarello, L.; Dragotto, J.; Mohammadi, A.; Corbo, M.; Feligioni, M. Obstacles against the marketing of curcumin as a drug. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pezzino, S.; Sofia, M.; Mazzone, C.; Litrico, G.; Greco, L.P.; Gallo, L.; La Greca, G.; Latteri, S. Innovative treatments for obesity and NAFLD: A bibliometric study on antioxidants, herbs, phytochemicals, and natural compounds. Heliyon 2024, 10, e35498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellulu, M.S.; Patimah, I.; Khaza’ai, H.; Rahmat, A.; Abed, Y. Obesity and inflammation: The linking mechanism and the complications. Arch. Med. Sci. AMS 2017, 13, 851–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Torres, I.; Castrejón-Téllez, V.; Soto, M.E.; Rubio-Ruiz, M.E.; Manzano-Pech, L.; Guarner-Lans, V. Oxidative Stress, Plant Natural Antioxidants, and Obesity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westbury, S.; Oyebode, O.; van Rens, T.; Barber, T.M. Obesity stigma: Causes, consequences, and potential solutions. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2023, 12, 10–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novelli, G.; Cassadonte, C.; Sbraccia, P.; Biancolella, M. Genetics: A starting point for the prevention and the treatment of obesity. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okunogbe, A.; Nugent, R.; Spencer, G.; Powis, J.; Ralston, J.; Wilding, J. Economic impacts of overweight and obesity: Current and future estimates for 161 countries. BMJ Glob. Health 2022, 7, e009773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anekwe, C.V.; Jarrell, A.R.; Townsend, M.J.; Gaudier, G.I.; Hiserodt, J.M.; Stanford, F.C. Socioeconomics of obesity. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2020, 9, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flangea, C.; Vlad, D.; Popescu, R.; Dumitrascu, V.; Rata, A.L.; Tryfon, M.E.; Balasoiu, B.; Vlad, C.S. Cannabis: Zone aspects of raw plant components in sport—A narrative review. Nutrients 2025, 17, 861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, J.L.; Prather, K.L.J.; Kluskens, L.D.; Rodrigues, L.R. Heterologous Production of Curcuminoids. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2015, 79, 39–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, T.T.P.; Huy, N.D.; Luong, N.N.; Nghi, N.V.; Tan, T.H.; Quan, L.V.; Loc, N.H. Identification and characterization of genes in the curcuminoid pathway of Curcuma zedoaria Roscoe. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2018, 19, 839–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayer, D.K.; Modha, K.; Parekh, V.; Patel, R.; Vadodariya, G.; Ramtekey, V.; Bhuriya, A. Associating gene expressions with curcuminoid biosynthesis in turmeric. J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. 2020, 18, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, J.L.; Gomes, D.; Rodrigues, L.R. A combinatorial approach to optimize the production of curcuminoids from tyrosine in Escherichia coli. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasan, A.A.; Tatarskiy, V.; Kalinina, E. Synthetic pathways and the therapeutic potential of quercetin and curcumin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majeed, M.; Nagabhushanam, K.; Devarajan, T.V.; Saklecha, S.; Reddy, S.V.K.; Mundkur, L. A minor metabolite from Curcuma longa effective against metabolic syndrome: Results from a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical study. Food Funct. 2023, 14, 4722–4733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majeed, A.; Majeed, M.; Thajuddin, N.; Arumugam, S.; Ali, F.; Beede, K.; Adams, S.J.; Gnanamani, M. Bioconversion of curcumin into calebin-A by the endophytic fungus Ovatospora brasiliensis EPE-10 MTCC 25236 associated with Curcuma caesia. AMB Expr. 2019, 9, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mueller, A.-L.; Brockmueller, A.; Kunnumakkara, A.B.; Shakibaei, M. Calebin A, a compound of turmeric, down-regulates inflammation in tenocytes by NF-κB/Scleraxis Signaling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brockmueller, A.; Buhrmann, C.; Shayan, P.; Shakibaei, M. Calebin A modulates inflammatory and autophagy signals for the prevention and treatment of osteoarthritis. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1363947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nan, A.; Dumitrascu, V.; Flangea, C.; Dumitrescu, G.; Puscasiu, D.; Vlad, T.; Popescu, R.; Vlad, C. From chemical composition to antiproliferative effects through in vitro studies: Honey, an ancient and modern hot topic remedy. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olas, B. Honey and its phenolic compounds as an effective natural medicine for cardiovascular diseases in humans? Nutrients 2020, 12, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayoub, W.S.; Zahoor, R.I.; Dar, A.H.; Farooq, S.; Mir, T.A.; Ganaie, T.A.; Srivastava, S.; Pandey, V.K.; Altaf, A. Exploiting the polyphenolic potential of honey in the prevention of chronic diseases. Food Chem. Adv. 2023, 3, 100373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chumroenphat, T.; Somboonwatthanakul, I.; Saensouk, S.; Siriamornpun, S. Changes in curcuminoids and chemical components of turmeric (Curcuma longa L.) under freeze-drying and low-temperature drying methods. Food Chem. 2021, 339, 128121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salem, M.A.; El-Shiekh, R.A.; Fernie, A.R.; Alseekh, S.; Zayed, A. Metabolomics-based profiling for quality assessment and revealing the impact of drying of Turmeric (Curcuma longa L.). Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 10288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komonsing, N.; Reyer, S.; Khuwijitjaru, P.; Mahayothee, B.; Müller, J. Drying behavior and curcuminoids changes in turmeric slices during drying under simulated solar radiation as influenced by different transparent cover materials. Foods 2022, 11, 696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dei Cas, M.; Ghidoni, R. Dietary Curcumin: Correlation between bioavailability and health potential. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hegde, M.; Girisa, S.; BharathwajChetty, B.; Vishwa, R.; Kunnumakkara, A.B. Curcumin formulations for better bioavailability: What we learned from clinical trials thus far? ACS Omega 2023, 8, 10713–10746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertoncini-Silva, C.; Vlad, A.; Ricciarelli, R.; Giacomo Fassini, P.; Suen, V.M.M.; Zingg, J.-M. Enhancing the bioavailability and bioactivity of curcumin for disease prevention and treatment. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bučević Popović, V.; Karahmet Farhat, E.; Banjari, I.; Jeličić Kadić, A.; Puljak, L. Bioavailability of oral curcumin in systematic reviews: A methodological study. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabanelli, R.; Brogi, S.; Calderone, V. Improving curcumin bioavailability: Current strategies and future perspectives. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohn, S.I.; Priya, A.; Balasubramaniam, B.; Muthuramalingam, P.; Sivasankar, C.; Selvaraj, A.; Valliammai, A.; Jothi, R.; Pandian, S. Biomedical Applications and Bioavailability of Curcumin-An Updated Overview. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laurindo, L.F.; de Carvalho, G.M.; de Oliveira Zanuso, B.; Figueira, M.E.; Direito, R.; de Alvares Goulart, R.; Buglio, D.S.; Barbalho, S.M. Curcumin-based nanomedicines in the treatment of inflammatory and immunomodulated diseases: An evidence-based comprehensive review. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Xu, F.; Dai, Y.; Zhang, J.; Shi, Y.; Lai, D.; Sriboonvorakul, N.; Hu, J. A review of cyclodextrin encapsulation and intelligent response for the release of curcumin. Polymers 2022, 14, 5421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasprzak-Drozd, K.; Oniszczuk, T.; Gancarz, M.; Kondracka, A.; Rusinek, R.; Oniszczuk, A. Curcumin and weight loss: Does it work? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varì, R.; Scazzocchio, B.; Silenzi, A.; Giovannini, C.; Masella, R. Obesity-associated inflammation: Does curcumin exert a beneficial role? Nutrients 2021, 13, 1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masenga, S.K.; Kabwe, L.S.; Chakulya, M.; Kirabo, A. Mechanisms of oxidative stress in metabolic syndrome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corkey, B.E. Reactive oxygen species: Role in obesity and mitochondrial energy efficiency. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2023, 378, 20220210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, B.; Sultana, R.; Greene, M.W. Adipose tissue and insulin resistance in obese. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 137, 111315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heindel, J.J.; Lustig, R.H.; Howard, S.; Corkey, B.E. Obesogens: A unifying theory for the global rise in obesity. Int. J. Obes. 2024, 48, 449–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, M.; Ding, F.; Li, L.; Dai, C.; Sun, X.; Xu, J.; Chen, F.; Li, M.; Li, X. Exploring the role of curcumin in mitigating oxidative stress to alleviate lipid metabolism disorders. Front. Pharmacol. 2025, 16, 1517174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, M.H.; Awadalla, E.A.; Abd El-Kader, A.E.M.; Seifeldin, E.A.; Mahmoud, M.A.; Muddathir, A.R.M.; Abdelsadik, A. Antitoxic effects of curcumin against obesity-induced multi-organs’ biochemical and histopathological abnormalities in an animal model. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2022, 2022, 9707278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, D.; Pan, Y.; Yu, N.; Bai, Y.; Ma, R.; Mo, F.; Zuo, J.; Chen, B.; Jia, Q.; Zhang, D.; et al. Curcumin improves adipocytes browning and mitochondrial function in 3T3-L1 cells and obese rodent model. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2021, 8, 200974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, T. Mechanisms underlying the metabolic beneficial effect of curcumin intervention: Beyond anti-inflammation and anti-oxidative stress. Obes. Med. 2019, 13, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.W.; Choi, J.H.; Mukherjee, R.; Hwang, K.C.; Yun, J.W. Proteomic identification of fat-browning markers in cultured white adipocytes treated with curcumin. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2016, 415, 51–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.B.; Lee, J.; Lee, J.Y. Targeting mitochondrial dysfunction for the prevention and treatment of metabolic disease by bioactive food components. J. Lipid Atheroscler. 2024, 13, 306–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacob, A.; Wu, R.; Zhou, M.; Wang, P. Mechanism of the Anti-inflammatory Effect of Curcumin: PPAR-gamma Activation. PPAR Res. 2007, 2007, 89369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.; Mao, S.; Chen, S.; Zhang, W.; Liu, C. PPARs-Orchestrated Metabolic Homeostasis in the Adipose Tissue. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Zhang, R.; Yu, L.; Zahr, T.; Li, X.; Kim, T.-W.; Qiang, L. PPARγ Acetylation in Adipocytes Exacerbates BAT Whitening and Worsens Age-Associated Metabolic Dysfunction. Cells 2023, 12, 1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Wang, D.; Zhao, W.; Xu, L. Deciphering the Roles of PPARγ in Adipocytes via Dynamic Change of Transcription Complex. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasetyawan, S.; Safitri, A.; Atho’illah, M.F.; Rahayu, S. Computational evaluation of bioactive compounds in Curcuma zanthorrhiza targeting SIRT1 and NFκB. BioTechnologia 2023, 104, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, D.; Liao, H.; Hao, S.; Liu, R.; Huang, H.; Duan, C. Curcumin simultaneously improves mitochondrial dynamics and myocardial cell bioenergy after sepsis via the SIRT1-DRP1/PGC-1α pathway. Heliyon 2024, 10, e28501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cox, F.F.; Misiou, A.; Vierkant, A.; Ale-Agha, N.; Grandoch, M.; Haendeler, J.; Altschmied, J. Protective effects of curcumin in cardiovascular diseases—Impact on oxidative stress and mitochondria. Cells 2022, 11, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zia, A.; Farkhondeh, T.; Pourbagher-Shahri, A.M.; Samarghandian, S. The role of curcumin in aging and senescence: Molecular mechanisms. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 134, 111119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Y.; Liu, C.; Feng, J.; Li, J.F.; Fan, Z.C. Curcumin affects ox-LDL-induced IL-6, TNF-α, MCP-1 secretion and cholesterol efflux in THP-1 cells by suppressing the TLR4/NF-κB/miR33a signaling pathway. Exp. Therap. Med. 2020, 20, 1856–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, T.; Scoggin, S.; Gong, X.; Zabet-Moghaddam, M.; Kalupahana, N.S.; Moustaid-Moussa, N. Anti-Inflammatory mechanisms of curcumin and its metabolites in white adipose tissue and cultured adipocytes. Nutrients 2024, 16, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadeghi, M.; Dehnavi, S.; Asadirad, A.; Xu, S.; Majeed, M.; Jamialahmadi, T.; Johnston, T.P.; Sahebkar, A. Curcumin and chemokines: Mechanism of action and therapeutic potential in inflammatory diseases. Inflammopharmacology 2023, 31, 1069–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayub, H.; Islam, M.; Saeed, M.; Ahmad, H.; Al-Asmari, F.; Ramadan, M.F.; Alissa, M.; Arif, M.A.; Rana, M.U.J.; Subtain, M.; et al. On the health effects of curcumin and its derivatives. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 12, 8623–8650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scarano, F.; Gliozzi, M.; Zito, M.C.; Guarnieri, L.; Carresi, C.; Macrì, R.; Nucera, S.; Scicchitano, M.; Bosco, F.; Ruga, S.; et al. Potential of nutraceutical supplementation in the modulation of white and brown fat tissues in obesity-associated disorders: Role of inflammatory signalling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, Y.; Alam, W.; Ullah, H.; Dacrema, M.; Daglia, M.; Khan, H.; Arciola, C.R. Antimicrobial Potential of Curcumin: Therapeutic Potential and Challenges to Clinical Applications. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imaizumi, U.; Inaba, K.; Kurahashi, A.; Kuroda, H.; Sanuki, T.; Yoshida, A.; Yoshino, F.; Hamada, N. Effectiveness of curcumin-based antimicrobial photodynamic therapy against Staphylococcus aureus. J. Oral Sci. 2023, 65, 270–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamczak, A.; Ożarowski, M.; Karpiński, T.M. Curcumin, a Natural Antimicrobial Agent with Strain-Specific Activity. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubizna, M.; Dawiec, G.; Wiench, R. Efficacy of Curcumin-Mediated Antimicrobial Photodynamic Therapy on Candida spp.—A Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 8136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shabbir, U.; Rubab, M.; Daliri, E.B.-M.; Chelliah, R.; Javed, A.; Oh, D.-H. Curcumin, Quercetin, Catechins and Metabolic Diseases: The Role of Gut Microbiota. Nutrients 2021, 13, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; He, L. The Modulatory Effects of Curcumin on the Gut Microbiota: A Potential Strategy for Disease Treatment and Health Promotion. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamichhane, G.; Olawale, F.; Liu, J.; Lee, D.-Y.; Lee, S.-J.; Chaffin, N.; Alake, S.; Lucas, E.A.; Zhang, G.; Egan, J.M.; et al. Curcumin Mitigates Gut Dysbiosis and Enhances Gut Barrier Function to Alleviate Metabolic Dysfunction in Obese, Aged Mice. Biology 2024, 13, 955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neyrinck, A.M.; Sánchez, C.R.; Rodriguez, J.; Cani, P.D.; Bindels, L.B.; Delzenne, N.M. Prebiotic Effect of Berberine and Curcumin Is Associated with the Improvement of Obesity in Mice. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, S.; Meng, M.; Luo, P.; Liu, J.; Wang, J.; Chen, Y. Tetrahydrocurcumin Alleviates Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatohepatitis in Mice by Regulating Serum Lipids, Bile Acids, and Gut Microbiota. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Wang, K.; Liao, X.; Hu, H.; Chen, L.; Meng, L.; Gao, W.; Li, Q. Carnitine palmitoyltransferase system: A new target for anti-inflammatory and anticancer therapy? Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 760581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, S.; Liu, M.; Han, Y.; Li, S.; Zhu, X.; Li, D.; Shi, Y.; Liu, B. Effects of saponins on lipid metabolism: The gut–liver axis plays a key role. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Bounkari, O.; Zan, C.; Yang, B.; Ebert, S.; Wagner, J.; Bugar, E.; Kramer, N.; Bourilhon, P.; Kontos, C.; Zarwel, M.; et al. An atypical atherogenic chemokine that promotes advanced atherosclerosis and hepatic lipogenesis. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, D.; Guo, M.; Yuan, X.; Wang, X. Unlocking the lipid code: SREBPs as key drivers in gastrointestinal tumour metabolism. Lipids Health Dis. 2025, 24, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sangouni, A.A.; Taghdir, M.; Mirahmadi, J.; Sepandi, M.; Parastouei, K. Effects of curcumin and/or coenzyme Q10 supplementation on metabolic control in subjects with metabolic syndrome: A randomized clinical trial. Nutr. J. 2022, 21, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehman, A.; Mehta, K.J. Betaine in ameliorating alcohol-induced hepatic steatosis. Eur. J. Nutr. 2022, 61, 1167–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceja-Galicia, Z.A.; García-Arroyo, F.E.; Aparicio-Trejo, O.E.; El-Hafidi, M.; Gonzaga-Sánchez, G.; León-Contreras, J.C.; Hernández-Pando, R.; Guevara-Cruz, M.; Tovar, A.R.; Rojas-Morales, P.; et al. Therapeutic effect of curcumin on 5/6Nx hypertriglyceridemia: Association with the improvement of renal mitochondrial β-oxidation and lipid metabolism in kidney and liver. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Y.; Luo, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, K.; Peng, J.; Fan, G. Therapeutic Effect of Curcumin on Metabolic Diseases: Evidence from Clinical Studies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boretti, A. Curcumin-based fixed dose combination products for cholesterol management: A narrative review. ACS Pharmacol. Transl. Sci. 2024, 7, 300–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaikwawong, M.; Jansarikit, L.; Jirawatnotai, S.; Chuengsamarn, S. The effect of curcumin on reducing atherogenic risks in obese patients with type 2 diabetes: A randomized controlled trial. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, C.; Zhou, L.; Wen, W.; Xiao, N. Curcumin promotes cholesterol efflux by regulating ABCA1 expression through miR-125a-5p/SIRT6 axis in THP-1 macrophage to prevent atherosclerosis. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2021, 46, 209–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, K.; Chen, J.; Zhang, T.; Yuan, X.; Ge, A.; Wang, S.; Xu, H.; Zeng, L.; Ge, J. Efficacy and safety of dietary polyphenol supplementation in the treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 949746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, L.; Sharma, S.; Xu, S.; Tewari, D.; Fang, J. Curcumin as a natural remedy for atherosclerosis: A pharmacological review. Molecules 2021, 26, 4036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baratzadeh, F.; Butler, A.E.; Kesharwani, P.; Moallem, S.A.; Sahebkar, A. Effects of curcumin on low-density lipoprotein oxidation: From experimental studies to clinical practice. EXCLI J. 2022, 21, 840–851. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Reyes-Farias, M.; Fos-Domenech, J.; Serra, D.; Herrero, L.; Sánchez-Infantes, D. White adipose tissue dysfunction in obesity and aging. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2021, 192, 114723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Q.; An, Y.A.; Scherer, P.E. Mitochondrial regulation and white adipose tissue homeostasis. Trends Cell Biol. 2022, 32, 351–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, W.-J.; Zhu, J.-Y.; Chen, M.; Guo, L. Exercise-mediated browning of white adipose tissue: Its significance, mechanism and effectiveness. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, J.; Quan, Y.; Zhu, S.; Lin, J.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, J.; Liang, Z.; Liao, Y.; Jiang, W.; He, Y.; et al. The browning and mobilization of subcutaneous white adipose tissue supports efficient skin repair. Cell Metab. 2024, 36, 1287–1301.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, L.; Wang, J.; Dai, H.; Duan, Y.; An, Y.; Shi, L.; Lv, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, C.; Ma, Q.; et al. Brown and beige adipose tissue: A novel therapeutic strategy for obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Adipocyte 2021, 10, 48–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alalaiwe, A.; Fang, J.-Y.; Lee, H.-J.; Chiu, C.-H.; Hsu, C.-Y. The demethoxy derivatives of curcumin exhibit greater differentiation suppression in 3t3-l1 adipocytes than curcumin: A mechanistic study of adipogenesis and molecular docking. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moetlediwa, M.T.; Ramashia, R.; Pheiffer, C.; Titinchi, S.J.J.; Mazibuko-Mbeje, S.E.; Jack, B.U. Therapeutic effects of curcumin derivatives against obesity and associated metabolic complications: A review of in vitro and in vivo studies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, J.L.; Usategui-Martín, R.; Hernández-Cosido, L.; Bernardo, E.; Manzanedo-Bueno, L.; Hernández-García, I.; Mateos-Díaz, A.-M.; Rozo, O.; Matesanz, N.; Salete-Granado, D.; et al. PPAR-γ Gene Expression in Human Adipose Tissue Is Associated with Weight Loss After Sleeve Gastrectomy. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2022, 26, 286–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soares, R.M.V.; da Silva, M.A.; Campos, J.T.A.M.; Lima, J.G. Familial partial lipodystrophy resulting from loss-of-function PPARγ pathogenic variants: Phenotypic, clinical, and genetic features. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1394102. [Google Scholar]
- Enayati, A.; Ghojoghnejad, M.; Roufogalis, B.D.; Maollem, S.A.; Sahebkar, A. Impact of phytochemicals on PPAR Receptors: Implications for Disease Treatments. PPAR Res. 2022, 2022, 4714914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corrales, P.; Vidal-Puig, A.; Medina-Gómez, G. PPARs and Metabolic Disorders Associated with Challenged Adipose Tissue Plasticity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.-Y.; Chen, C.-W.; Chen, L.-K.; Chou, H.-Y.; Chang, C.-L.; Juan, C.-C. Curcumin attenuates adipogenesis by inducing preadipocyte apoptosis and inhibiting adipocyte differentiation. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.J.; Jin, B.Y.; Park, M.R.; Kim, N.H.; Seo, K.S.; Jeong, Y.T.; Wada, T.; Lee, J.S.; Choi, S.H.; Kim, D.H. Inhibition of adipose tissue angiogenesis prevents rebound weight gain after caloric restriction in mice fed a high-fat diet. Life Sci. 2023, 332, 122101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pélissier, L.; Bagot, S.; Miles-Chan, J.L.; Pereira, B.; Boirie, Y.; Duclos, M.; Dulloo, A.; Isacco, L.; Thivel, D. Is dieting a risk for higher weight gain in normal-weight individual? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Br. J. Nutr. 2023, 130, 1190–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Suyama, S.; Lee, S.A.; Ueta, Y.; Seino, Y.; Sharp, G.W.G.; Yada, T. Fasting inhibits excitatory synaptic input on paraventricular oxytocin neurons via neuropeptide Y and Y1 receptor, inducing rebound hyperphagia, and weight gain. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 994827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanasie, G.; Bojin, F.; Tatu, R.F.; Sisu, A.M.; Cristea, M.; Puscasiu, D.A.; Nemes, E.A.; Tatu, C.S. In vitro effects of biomaterials on mesenchymal stem cells viability and proliferation. Mater. Plast. 2017, 54, 523–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurmuz, M.; Bojin, F.; Ionac, M.; Tatu, F.; Puscasiu, D.; Tatu, C. Plastic adherence method for isolation of stem cells derived from infrapatellar fat pad. Mater. Plast. 2016, 53, 553–556. [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda, K.; Yamada, T. UCP1 dependent and independent thermogenesis in brown and beige adipocytes. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Nguyen, T.T.; Van Vu, V.; Van Pham, P. Brown adipocyte and browning thermogenesis: Metabolic crosstalk beyond mitochondrial limits and physiological impacts. Adipocyte 2023, 12, 2237164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Liu, W.; Qi, Z. Adipose tissue browning and thermogenesis under physiologically energetic challenges: A remodelled thermogenic system. J. Physiol. 2024, 602, 23–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakers, A.; De Siqueira, M.K.; Seale, P.; Villanueva, C.J. Adipose-tissue plasticity in health and disease. Cell 2022, 185, 419–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, Y.H.; Chou, W.L.; Ko, M.C.; Liao, J.C.; Huang, T.H. Curcumin mitigates obesity-driven dysbiosis and liver steatosis while promoting browning and thermogenesis in white adipose tissue of high-fat diet-fed mice. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2025, 143, 109920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, L.; Su, Z.; Wang, S. The anti-obesity effects of polyphenols: A comprehensive review of molecular mechanisms and signal pathways in regulating adipocytes. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1393575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Du, S.; Yan, Q.; Min, C.; Zhou, N.; Zhou, W.; Li, X. Dietary curcumin supplementation promotes browning and energy expenditure in postnatal overfed rats. Nutr. Metab. 2021, 18, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brockmueller, A.; Mueller, A.L.; Kunnumakkara, A.B.; Aggarwal, B.B.; Shakibaei, M. Multifunctionality of Calebin A in inflammation, chronic diseases and cancer. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 962066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chalichem, N.S.S.; Jupudi, S.; Yasam, V.R.; Basavan, D. Dipeptidyl peptidase-IV inhibitory action of Calebin A: An in silico and in vitro analysis. J. Ayurveda Integr. Med. 2021, 12, 663–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, P.S.; Lu, Y.Y.; Nagabhushanam, K.; Ho, C.T.; Mei, H.C.; Pan, M.H. Calebin-A prevents HFD-induced obesity in mice by promoting thermogenesis and modulating gut microbiota. J. Tradit. Complement. Med. 2022, 13, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buhrmann, C.; Shayan, P.; Banik, K.; Kunnumakkara, A.B.; Kubatka, P.; Koklesova, L.; Shakibaei, M. Targeting NF-κB signaling by Calebin A, a compound of turmeric, in multicellular tumor microenvironment: Potential role of apoptosis induction in CRC cells. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de, P. Oliveira, A.L.; Martinez, S.E.; Nagabushnam, K.; Majeed, M.; Alrushaid, S.; Sayre, C.L.; Davies, N.M. Calebin A: Analytical Development for Pharmacokinetics Study, Elucidation of Pharmacological Activities and Content Analysis of Natural Health Products. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 18, 494–514. [Google Scholar]
- Sabir, S.M.; Zeb, A.; Mahmood, M.; Abbas, S.R.; Ahmad, Z.; Iqbal, N. Phytochemical analysis and biological activities of ethanolic extract of Curcuma longa rhizome. Braz. J. Biol. 2021, 81, 737–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, G.H.; Lee, H.D.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, S.; Lee, S. Profiling of the leaves and stems of Curcuma longa using LC-ESI-MS and HPLC analysis. J. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2023, 66, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, D.S.; Cho, S.Y.; Yoon, H.J.; Kim, S.R.; Jung, U.J. Protective effects of p-coumaric acid against high-fat diet-induced metabolic dysregulation in mice. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 142, 111969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, M.A.; Subhan, N.; Hossain, H.; Hossain, M.; Reza, H.M.; Rahman, M.M.; Ullah, M.O. Hydroxycinnamic acid derivatives: A potential class of natural compounds for the management of lipid metabolism and obesity. Nutr. Metab. 2016, 13, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.; Nam, S.H.; Yoon, H.G.; Kim, S.; You, Y.; Choi, K.C.; Lee, Y.H.; Lee, J.; Park, J.; Jun, W. Fermented Curcuma longa L. prevents alcoholic fatty liver disease in mice by regulating CYP2E1, SREBP-1c, and PPAR-α. J. Med. Food 2022, 25, 456–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muhammad Abdul Kadar, N.N.; Ahmad, F.; Teoh, S.L.; Yahaya, M.F. Caffeic Acid on metabolic syndrome: A review. Molecules 2021, 26, 5490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, L.; Hu, P.; Feng, L.-P.; Huang, L.-L.; Wang, Y.; Yan, X.; Xiong, J.; Xia, H.-L. Protective effects of ferulic acid on metabolic syndrome: A comprehensive review. Molecules 2023, 28, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Z.; Li, M.; Yang, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, F.; El-Omar, E.; Han, L.; Bian, J.; Gong, L.; et al. Ferulic acid attenuates high-fat diet-induced hypercholesterolemia by activating classic bile acid synthesis pathway. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 976638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, J.; Park, E. Ferulic acid maintains the self-renewal capacity of embryo stem cells and adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells in high fat diet-induced obese mice. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2020, 77, 108327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salazar-López, N.J.; Astiazarán-García, H.; González-Aguilar, G.A.; Loarca-Piña, G.; Ezquerra-Brauer, J.-M.; Domínguez Avila, J.A.; Robles-Sánchez, M. Ferulic Acid on glucose dysregulation, dyslipidemia, and inflammation in diet-induced obese rats: An integrated study. Nutrients 2017, 9, 675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dosoky, N.S.; Setzer, W.N. Chemical Composition and Biological Activities of Essential Oils of Curcuma Species. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotha, R.R.; Luthria, D.L. Curcumin: Biological, Pharmaceutical, Nutraceutical, and Analytical Aspects. Molecules 2019, 24, 2930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dosoky, N.S.; Satyal, P.; Setzer, W.N. Variations in the Volatile Compositions of Curcuma Species. Foods 2019, 8, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poudel, D.K.; Ojha, P.K.; Rokaya, A.; Satyal, R.; Satyal, P.; Setzer, W.N. Analysis of Volatile Constituents in Curcuma Species, viz. C. aeruginosa, C. zedoaria, and C. longa, from Nepal. Plants 2022, 11, 1932. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, W.; Chen, X.; Xiao, C.; Lin, D.; Li, Y.; Luo, S.; Zeng, Z.; Sun, B.; Lei, S. Ar-turmerone inhibits the proliferation and mobility of glioma by downregulating cathepsin B. Aging 2023, 15, 9377–9390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hori, Y.; Tsutsumi, R.; Nasu, K.; Boateng, A.; Ashikari, Y.; Sugiura, M.; Nakajima, M.; Kurauchi, Y.; Hisatsune, A.; Katsuki, H.; et al. Aromatic-Turmerone Analogs Protect Dopaminergic Neurons in Midbrain Slice Cultures through Their Neuroprotective Activities. Cells 2021, 10, 1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duangyod, T.; Rujanapan, N.; Champakam, S.; Charoensup, R. Anti-inflammatory activity and chemical constituents of red limestone. J. Adv. Pharm. Technol. Res. 2021, 12, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gadnayak, A.; Dehury, B.; Nayak, A.; Jena, S.; Sahoo, A.; Panda, P.C.; Ray, A.; Nayak, S. Mechanistic insights into 5-lipoxygenase inhibition by active principles derived from essential oils of Curcuma species: Molecular docking, ADMET analysis and molecular dynamic simulation study. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0271956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Shen, Y.; Thakur, K.; Han, J.; Zhang, J.-G.; Hu, F.; Wei, Z.-J. Antibacterial Activity and Mechanism of Ginger Essential Oil against Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. Molecules 2020, 25, 3955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zohmachhuana, A.; Malsawmdawngliana; Lalnunmawia, F.; Mathipi, V.; Lalrinzuali, K.; Kumar, N.S. Curcuma aeruginosa Roxb. exhibits cytotoxicity in A-549 and HeLa cells by inducing apoptosis through caspase-dependent pathways. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 150, 113039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, X.; Luo, R.; Li, J.; He, A.; Wang, X.; Wan, H.; Cai, Y.; Dong, W.; Lin, J. Zingiberene targets the miR-16/cyclin-B1 axis to regulate the growth, migration and invasion of human liver cancer cells. J. BUON 2020, 25, 1904–1910. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.-J.; Tsai, T.-H.; Liao, H.-R.; Chen, L.-C.; Kuo, Y.-H.; Sung, P.-J.; Chen, C.-L.; Wei, C.-S. New Sesquiterpenoids and Anti-Platelet Aggregation Constituents from the Rhizomes of Curcuma zedoaria. Molecules 2016, 21, 1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.; Xu, J.; Shao, M.; Zou, J. Germacrone Induces Apoptosis as Well as Protective Autophagy in Human Prostate Cancer Cells. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 4009–4016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Hao, J.; Guo, K.; Liu, W.; Yao, F.; Wu, Q.; Liu, C.; Wang, Q.; Yang, X. Germacrone Inhibits Cell Proliferation and Induces Apoptosis in Human Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cells. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 7643248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhyani, P.; Sati, P.; Sharma, E.; Attri, D.C.; Bahukhandi, A.; Tynybekov, B.; Szopa, A.; Sharifi-Rad, J.; Calina, D.; Suleria, H.A.R.; et al. Sesquiterpenoid lactones as potential anti-cancer agents: An update on molecular mechanisms and recent studies. Cancer Cell Int. 2022, 22, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Septembre-Malaterre, A.; Bedoui, Y.; Giry, C.; Gasque, P.; Guiraud, P.; Sélambarom, J. Quercetin can reduce viral RNA level of O’nyong-nyong virus and resulting innate immune cytokine responses in cultured human synovial fibroblasts. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 6369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Q.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, P. Mechanisms of main components in Curcuma longa L. on hepatic fibrosis based on network pharmacology and molecular docking: A review. Medicine 2023, 102, e34353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamil, Q.U.A.; Iqbal, S.M.; Jaeger, W.; Studenik, C. Vasodilating, spasmolytic, inotropic and chronotropic activities of curcuminoids from Curcuma longa in isolated organ preparations of guinea pigs. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2018, 69, 441–449. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Sun, Y.; Li, G.; Cheng, C.; Sui, X.; Wu, Q. The Extraction, Determination, and Bioactivity of Curcumenol: A Comprehensive Review. Molecules 2024, 29, 656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Qi, Q.; Qiao, Y.; Huang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Gu, K.; Liu, H.; Gao, C.; Liu, S.; Wu, H. Curcumenol inhibits malignant progression and promotes ferroptosis via the SLC7A11/NF-κB/TGF-β pathway in triple-negative breast cancer. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2025, 56, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unhapipatpong, C.; Polruang, N.; Shantavasinkul, P.C.; Julanon, N.; Numthavaj, P.; Thakkinstian, A. The effect of curcumin supplementation on weight loss and anthropometric indices: An umbrella review and updated meta-analyses of randomized controlled trials. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2023, 117, 1005–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbari, M.; Lankarani, K.B.; Tabrizi, R.; Ghayour-Mobarhan, M.; Peymani, P.; Ferns, G.; Ghaderi, A.; Asemi, Z. The Effects of Curcumin on Weight Loss Among Patients With Metabolic Syndrome and Related Disorders: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsharif, F.J.; Almuhtadi, Y.A. The Effect of curcumin supplementation on anthropometric measures among overweight or obese adults. Nutrients 2021, 13, 680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.; Arif, M.; Laraib, H.; Naqvi, S.N.; Shah, O.A.; Farooq, U.; Sami-Ullah, M.; Khan, G.A. The effect of turmeric and black pepper powder incorporated in breakfast on postprandial glycemia, appetite, palatability, and gastrointestinal well-being in normal-weight adults. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 12, 2846–2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karandish, M.; Mozaffari-khosravi, H.; Mohammadi, S.M.; Cheraghian, B.; Azhdari, M. Curcumin and zinc co-supplementation along with a loss-weight diet can improve lipid profiles in subjects with prediabetes: A multi-arm, parallel-group, randomized, double-blind placebo-controlled phase 2 clinical trial. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2022, 14, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batsis, J.A.; Apolzan, J.W.; Bagley, P.J.; Blunt, H.B.; Divan, V.; Gill, S.; Golden, A.; Gundumraj, S.; Heymsfield, S.B.; Kahan, S.; et al. A Systematic Review of Dietary Supplements and Alternative Therapies for Weight Loss. Obesity 2021, 29, 1102–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexandru, I.; Nistor, D.; Motofelea, A.C.; Cadar, B.-A.; Crintea, A.; Tatu, C.; Pop, G.N.; Csep, A.N. Vitamins, Coenzyme Q10, and Antioxidant Strategies to Improve Oocyte Quality in Women with Gynecological Cancers: A Comprehensive Review. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munteanu, C.; Schwartz, B. Interactions between Dietary Antioxidants, Dietary Fiber and the Gut Microbiome: Their Putative Role in Inflammation and Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 8250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.-H. Role of Phytochemicals in Treatment of Aging and Cancer: Focus on Mechanism of FOXO3 Activation. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scafuri, L.; Buonerba, C.; Strianese, O.; de Azambuja, E.; Palleschi, M.; Riccio, V.; Marotta, V.; Scocca, C.; Riccio, G.; Errico, C.; et al. Impact of Dietary Supplements on Clinical Outcomes and Quality of Life in Patients with Breast Cancer: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2025, 17, 981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Population | Study Type | Intervention | Outcome | Duration | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Middle-aged and elderly overweight participants | Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled | Turmeric extract mixture (CLE) |
| 12 Weeks | [9] |
| Subjects with mild/moderate knee joint pain | Pilot, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial | B-Turmactive® (a new formulation of dry extracts of turmeric roots) and brewer’s yeast as a placebo |
| 1 week | [10] |
| Obese subjects with type-2 diabetes | Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial | Curcumin extract 1500 mg/day |
| 12 months | [11] |
| Healthy males 20–40 years old | Randomized, double-blind, crossover pilot trial | Curcuma longa powder; low dose (1.5 g), moderate dose (3 g), high dose (6 g), separated by 7-day washout |
| 3 weeks | [12] |
| Mild to moderate hospitalized COVID-19 patients | Triple-blind randomized, placebo-controlled | Oral nanocurcumin formulation (Sinacurmin® soft-gel 40 mg) | With the exception of a sore throat, symptoms were reduced considerably faster compared to the placebo treatment | 4 months | [13] |
| Female subjects with polycystic ovary syndrome | Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial | Curcumin 500 mg three times daily | Significantly decreased fasting plasma glucose and insulin, reducing sex hormone levels and hirsutism score | 12 weeks | [14] |
| Patients with knee osteoarthritis (OA) | Randomized, non-inferiority, controlled clinical trial | Bioavailable turmeric extract (BCM-95®) 500 mg capsules versus paracetamol 650 mg tablets | The results obtained considering bioavailable turmeric extract were comparable to those observed with paracetamol, improving physical function and pain relief in patients with knee OA | 6 weeks | [15] |
| Patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease | Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial | Turmeric 2 g/day |
| 8 weeks | [16] |
| Component | Structure | Main Activity |
|---|---|---|
| Turmerones: Aromatic (Ar)-turmerone |  | |
| α-turmerone | 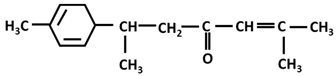 |
|
| β-turmerone | 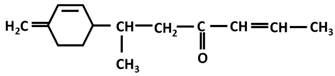 |
|
| Sesquiterpenes: α-curcumene | 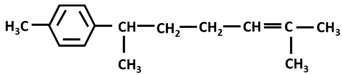 |
|
| Curcumanolide | 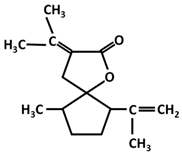 |
|
| Zingiberene |  |
|
| Germacrane: Germacrone | 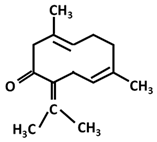 |
|
| Germacrene | 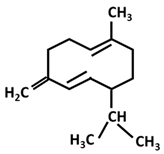 | |
| Phenols/polyphenols: Quercetin | 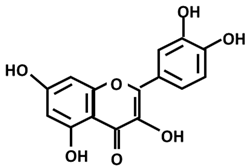 | |
| Vanillin |  |
|
| Guaiane: Curcumenol | 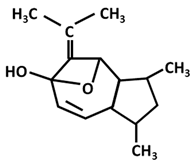 |
|
| Procurcumenol | 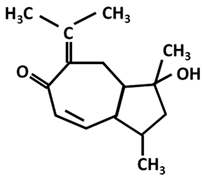 |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marina, C.D.; Puscasiu, D.; Flangea, C.; Vlad, T.; Cimporescu, A.; Popescu, R.; Moatar, A.E.; Vlad, D.C. Adipo-Modulation by Turmeric Bioactive Phenolic Components: From Curcuma Plant to Effects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6880. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146880
Marina CD, Puscasiu D, Flangea C, Vlad T, Cimporescu A, Popescu R, Moatar AE, Vlad DC. Adipo-Modulation by Turmeric Bioactive Phenolic Components: From Curcuma Plant to Effects. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(14):6880. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146880
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarina, Cristina Doriana, Daniela Puscasiu, Corina Flangea, Tania Vlad, Adinela Cimporescu, Roxana Popescu, Aurica Elisabeta Moatar, and Daliborca Cristina Vlad. 2025. "Adipo-Modulation by Turmeric Bioactive Phenolic Components: From Curcuma Plant to Effects" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 14: 6880. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146880
APA StyleMarina, C. D., Puscasiu, D., Flangea, C., Vlad, T., Cimporescu, A., Popescu, R., Moatar, A. E., & Vlad, D. C. (2025). Adipo-Modulation by Turmeric Bioactive Phenolic Components: From Curcuma Plant to Effects. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(14), 6880. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146880








