The Relevance of G-Quadruplexes in Gene Promoters and the First Introns Associated with Transcriptional Regulation in Breast Cancer
Abstract
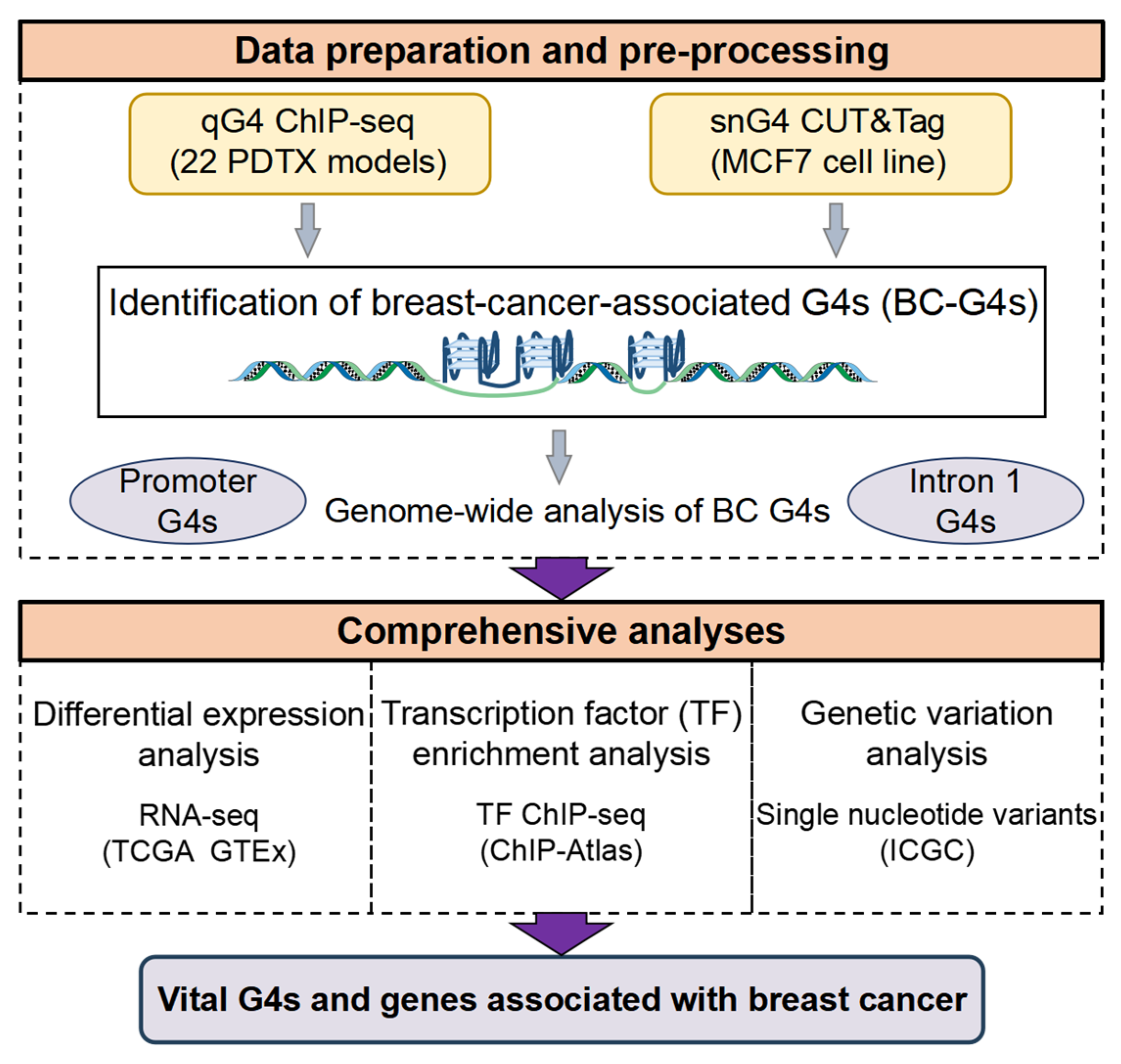
1. Introduction
2. Results
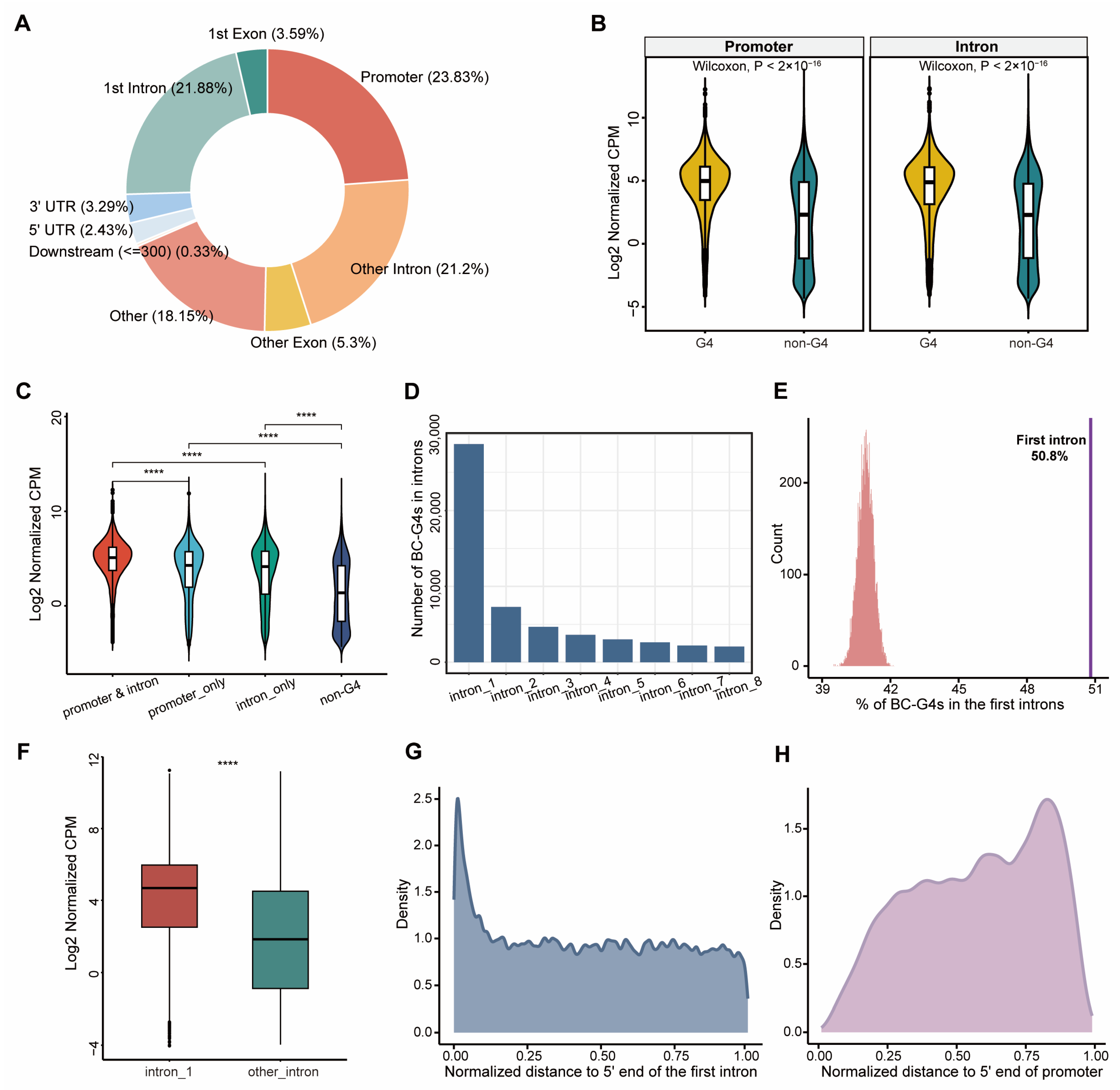
2.1. BC-G4s Are Enriched in Gene Promoters and the First Introns
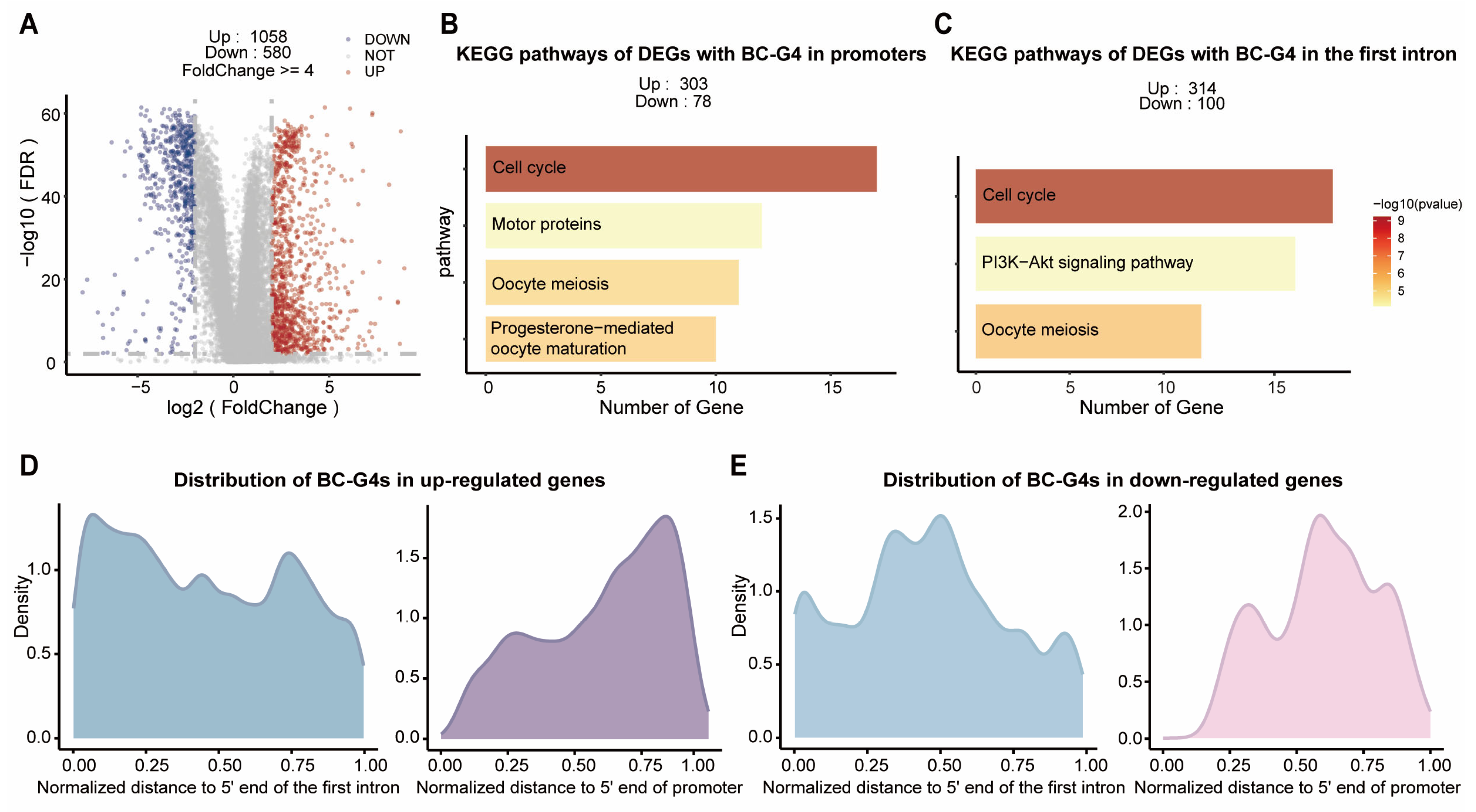
2.2. The Distribution of BC-G4s in Up-Regulated Genes Is Biased Toward the TSSs
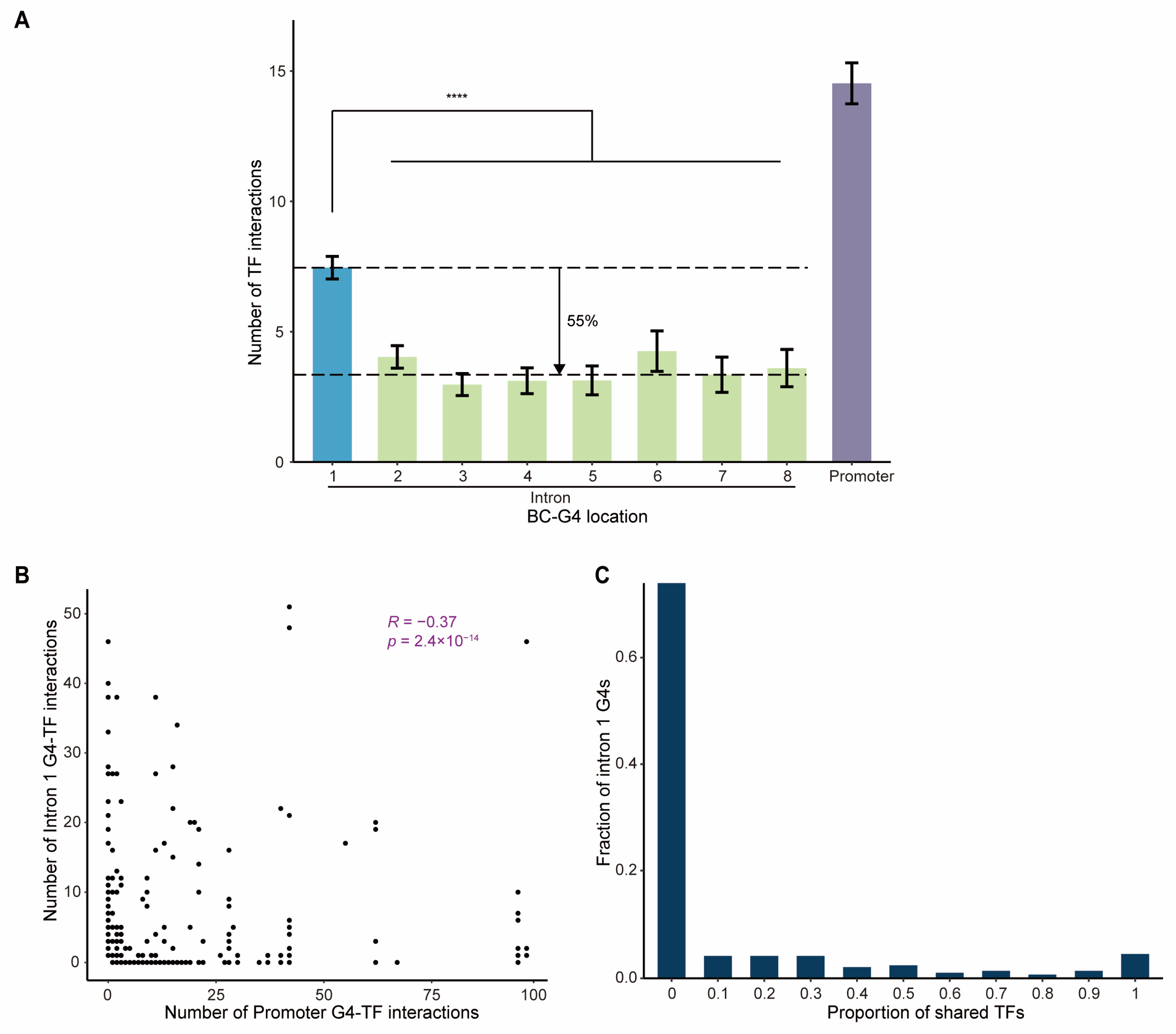
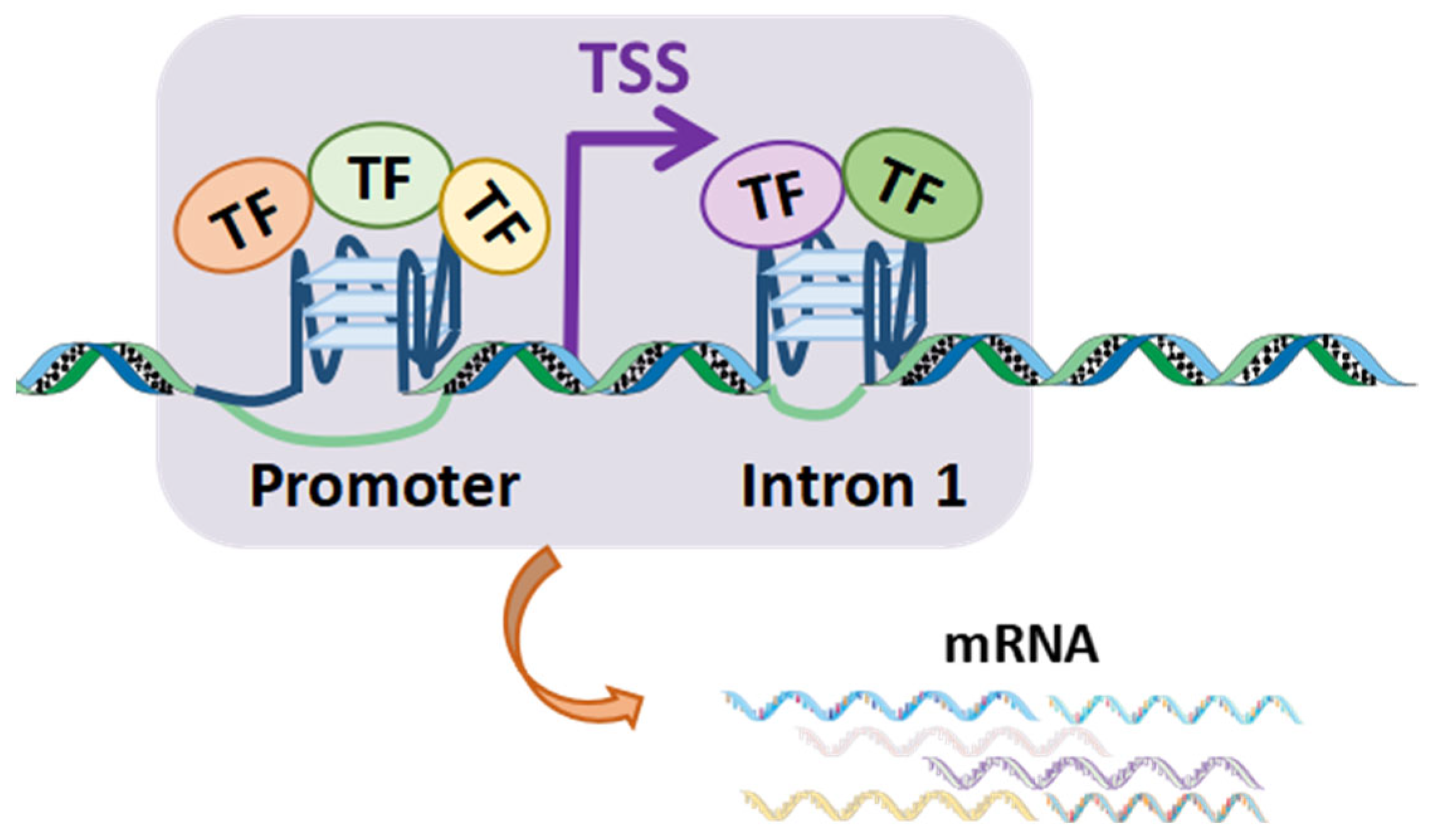
2.3. TF Binding to BC-G4s in the First Introns Compensates for G4–TF Interactions in the Cognate Promoters
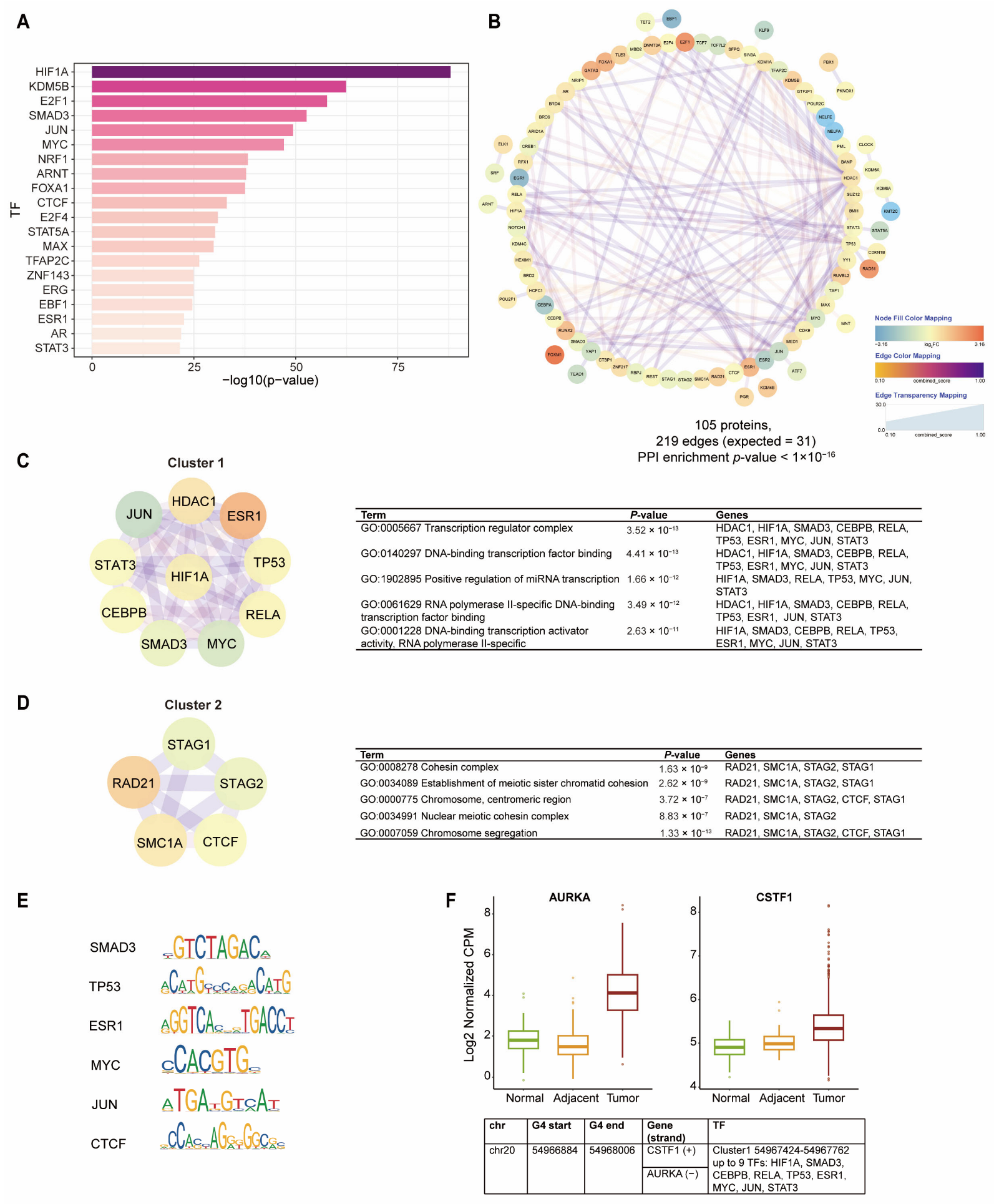
2.4. Promoter BC-G4s of DEGs Function as Hubs for TF Co-Binding
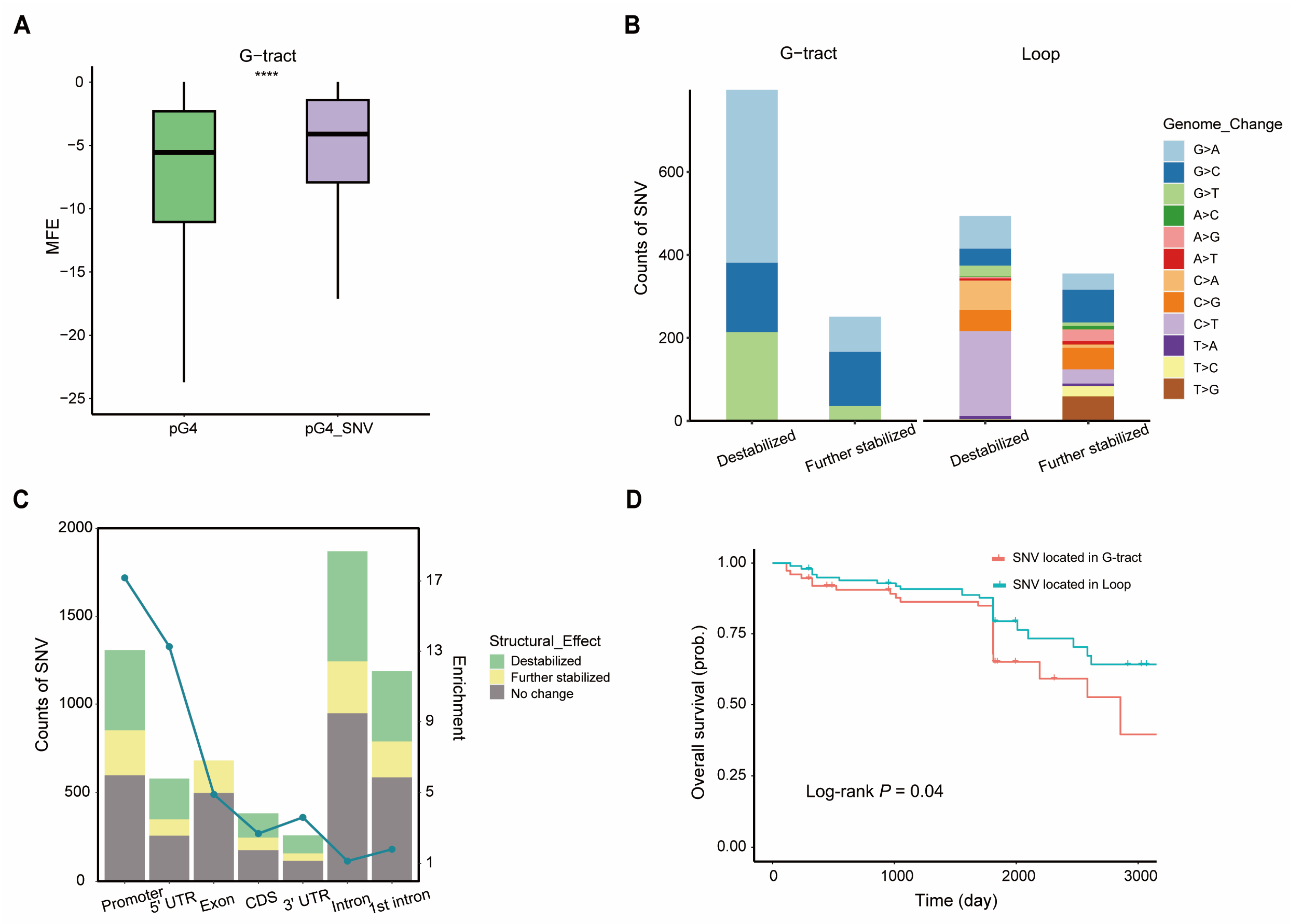
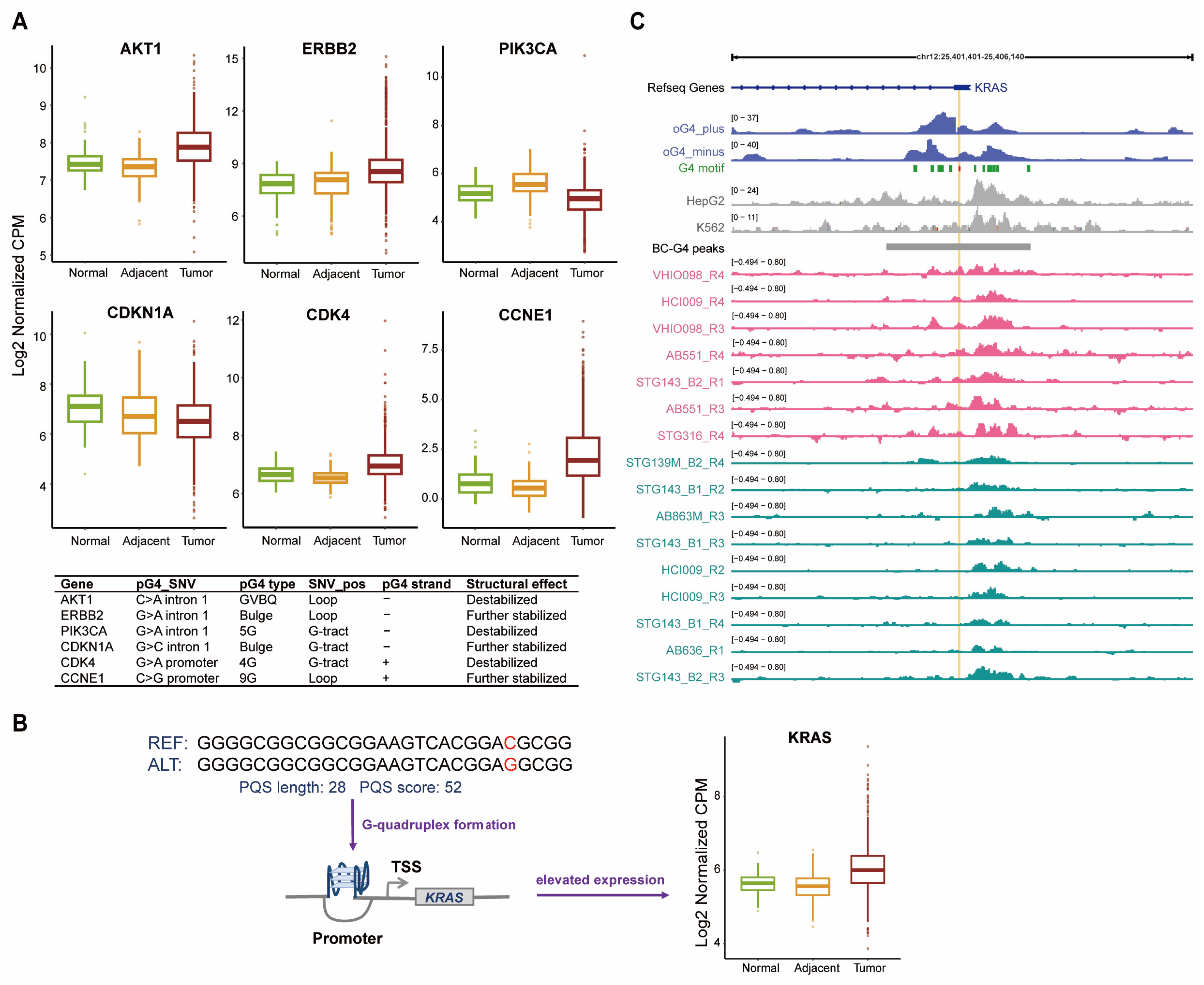
2.5. SNVs in BC-G4s Modulate G4 Structures and the Transcription of Breast Cancer-Associated Genes
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. G4 Dataset Acquisition
4.2. RNA-Seq Dataset Acquisition and Processing
4.3. Differential Expression Analysis
4.4. BC-G4 Overlapping Gene Promoter and Intron Expression Analysis
4.5. Transcription Factor Enrichment Analysis
4.6. ChIP Binding Site Analysis
4.7. Transcription Factor Network Analysis
4.8. SNV Dataset Acquisition
4.9. SNV Affecting BC-G4s
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| G4 | G-quadruplexes |
| TSS | transcription start site |
| TF | transcription factor |
| SNV | single nucleotide variant |
| PDTX | patient-derived tumor xenograft |
| DEG | differentially expressed gene |
| PPI | protein–protein interaction |
| MFE | minimum free energy |
References
- Varshney, D.; Spiegel, J.; Zyner, K.; Tannahill, D.; Balasubramanian, S. The regulation and functions of DNA and RNA G-quadruplexes. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 459–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhodes, D.; Lipps, H.J. G-quadruplexes and their regulatory roles in biology. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 8627–8637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maizels, N.; Gray, L.T. The G4 genome. PLoS Genet. 2013, 9, e1003468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todd, A.K.; Johnston, M.; Neidle, S. Highly prevalent putative quadruplex sequence motifs in human DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, 2901–2907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosiol, N.; Juranek, S.; Brossart, P.; Heine, A.; Paeschke, K. G-quadruplexes: A promising target for cancer therapy. Mol. Cancer 2021, 20, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgakopoulos-Soares, I.; Parada, G.E.; Wong, H.Y.; Medhi, R.; Furlan, G.; Munita, R.; Miska, E.A.; Kwok, C.K.; Hemberg, M. Alternative splicing modulation by G-quadruplexes. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, J.; He, X.; Wang, Y. G-quadruplex DNA contributes to RNA polymerase II-mediated 3D chromatin architecture. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, 8434–8446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenzatti, A.; Piga, E.J.; Gismondi, M.; Binolfi, A.; Margarit, E.; Calcaterra, N.B.; Armas, P. Genetic variations in G-quadruplex forming sequences affect the transcription of human disease-related genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, 12124–12139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Shu, H.; Wang, Y.; Tao, T.; Tu, J.; Wang, C.; Mergny, J.L.; Sun, X. G-Quadruplex Structures Are Key Modulators of Somatic Structural Variants in Cancers. Cancer Res. 2023, 83, 1234–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armas, P.; David, A.; Calcaterra, N.B. Transcriptional control by G-quadruplexes: In vivo roles and perspectives for specific intervention. Transcription 2017, 8, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armas, P.; Calcaterra, N.B. G-quadruplex in animal development: Contribution to gene expression and genomic heterogeneity. Mech. Dev. 2018, 154, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, J.; Raguseo, F.; Nuccio, S.P.; Liano, D.; Di Antonio, M. DNA G-quadruplex structures: More than simple roadblocks to transcription? Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, 8419–8431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halder, K.; Halder, R.; Chowdhury, S. Genome-wide analysis predicts DNA structural motifs as nucleosome exclusion signals. Mol. Biosyst. 2009, 5, 1703–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huppert, J.L.; Balasubramanian, S. G-quadruplexes in promoters throughout the human genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, 406–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.Z.; Varshney, D.; Simeone, A.; Zhang, X.Y.; Adhikari, S.; Tannahill, D.; Balasubramanian, S. Promoter G-quadruplex folding precedes transcription and is controlled by chromatin. Genome Biol. 2021, 22, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansel-Hertsch, R.; Beraldi, D.; Lensing, S.V.; Marsico, G.; Zyner, K.; Parry, A.; Di Antonio, M.; Pike, J.; Kimura, H.; Narita, M.; et al. G-quadruplex structures mark human regulatory chromatin. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 1267–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spiegel, J.; Cuesta, S.M.; Adhikari, S.; Hansel-Hertsch, R.; Tannahill, D.; Balasubramanian, S. G-quadruplexes are transcription factor binding hubs in human chromatin. Genome Biol. 2021, 22, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cogoi, S.; Paramasivam, M.; Membrino, A.; Yokoyama, K.K.; Xodo, L.E. The Promoter Responds to Myc-associated Zinc Finger and Poly(ADP-ribose) Polymerase 1 Proteins, Which Recognize a Critical Quadruplex-forming-element. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 22003–22016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raiber, E.A.; Kranaster, R.; Lam, E.; Nikan, M.; Balasubramanian, S. A non-canonical DNA structure is a binding motif for the transcription factor SP1. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 1499–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jo, S.S.; Choi, S.S. Analysis of the Functional Relevance of Epigenetic Chromatin Marks in the First Intron Associated with Specific Gene Expression Patterns. Genome Biol. Evol. 2019, 11, 786–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.G.; Hannenhalli, S.; Choi, S.S. Conservation in first introns is positively associated with the number of exons within genes and the presence of regulatory epigenetic signals. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuxman Bass, J.I.; Tamburino, A.M.; Mori, A.; Beittel, N.; Weirauch, M.T.; Reece-Hoyes, J.S.; Walhout, A.J. Transcription factor binding to Caenorhabditis elegans first introns reveals lack of redundancy with gene promoters. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, W.Y.; Huang, H.; Ming, W.L.; Zhang, R.X.; Gu, Y.; Bai, Y.F.; Liu, X.A.; Liu, H.D.; Liu, Y.; Gu, W.J.; et al. Delineating highly transcribed noncoding elements landscape in breast cancer. Comput. Struct. Biotec. 2023, 21, 4432–4445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eddy, J.; Maizels, N. Conserved elements with potential to form polymorphic G-quadruplex structures in the first intron of human genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, 1321–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lappalainen, T.; MacArthur, D.G. From variant to function in human disease genetics. Science 2021, 373, 1464–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurano, M.T.; Humbert, R.; Rynes, E.; Thurman, R.E.; Haugen, E.; Wang, H.; Reynolds, A.P.; Sandstrom, R.; Qu, H.; Brody, J.; et al. Systematic localization of common disease-associated variation in regulatory DNA. Science 2012, 337, 1190–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, J.Y.; Wen, C.J.; Tang, M.L.; Duan, R.F.; Chen, J.N.; Zhang, J.Y.; Zheng, K.W.; He, Y.D.; Hao, Y.H.; Yu, Q.; et al. G-quadruplex structural variations in human genome associated with single-nucleotide variations and their impact on gene activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2013230118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neupane, A.; Chariker, J.H.; Rouchka, E.C. Analysis of Nucleotide Variations in Human G-Quadruplex Forming Regions Associated with Disease States. Genes 2023, 14, 2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansel-Hertsch, R.; Simeone, A.; Shea, A.; Hui, W.W.I.; Zyner, K.G.; Marsico, G.; Rueda, O.M.; Bruna, A.; Martin, A.; Zhang, X.; et al. Landscape of G-quadruplex DNA structural regions in breast cancer. Nat. Genet. 2020, 52, 878–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hui, W.W.I.; Simeone, A.; Zyner, K.G.; Tannahill, D.; Balasubramanian, S. Single-cell mapping of DNA G-quadruplex structures in human cancer cells. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 23641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradnam, K.R.; Korf, I. Longer First Introns Are a General Property of Eukaryotic Gene Structure. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e3093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.; Jackson, L.K.; Johnson, W.E.; Li, D.Y.; Bild, A.H.; Piccolo, S.R. Alternative preprocessing of RNA-Sequencing data in The Cancer Genome Atlas leads to improved analysis results. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 3666–3672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aran, D.; Camarda, R.; Odegaard, J.; Paik, H.; Oskotsky, B.; Krings, G.; Goga, A.; Sirota, M.; Butte, A.J. Comprehensive analysis of normal adjacent to tumor transcriptomes. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Risso, D.; Ngai, J.; Speed, T.P.; Dudoit, S. Normalization of RNA-seq data using factor analysis of control genes or samples. Nat. Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 896–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Pugh, B.F. What do Transcription Factors Interact With? J. Mol. Biol. 2021, 433, 166883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haberle, V.; Stark, A. Eukaryotic core promoters and the functional basis of transcription initiation. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 19, 621–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambert, S.A.; Jolma, A.; Campitelli, L.F.; Das, P.K.; Yin, Y.; Albu, M.; Chen, X.; Taipale, J.; Hughes, T.R.; Weirauch, M.T. The Human Transcription Factors. Cell 2018, 172, 650–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.B.; Vartak, S.V.; Conte, A.; Wang, X.; Garcia, D.A.; Stevens, E.; Jung, S.K.; Kieffer-Kwon, K.R.; Vian, L.; Stodola, T.; et al. “Stripe” transcription factors provide accessibility to co-binding partners in mammalian genomes. Mol. Cell 2022, 82, 3398–3411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morafraile, E.C.; Pérez-Peña, J.; Fuentes-Antrás, J.; Manzano, A.; Pérez-Segura, P.; Pandiella, A.; Galán-Moya, E.M.; Ocaña, A. Genomic Correlates of DNA Damage in Breast Cancer Subtypes. Cancers 2021, 13, 2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Gorin, A.; Majumdar, A.; Kettani, A.; Chernichenko, N.; Skripkin, E.; Patel, D.J. Dimeric DNA quadruplex containing major groove-aligned A•T•A•T and G•C•G•C tetrads stabilized by inter-subunit Watson-Crick A•T and G•C pairs. J. Mol. Biol. 2001, 312, 1073–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guiblet, W.M.; DeGiorgio, M.; Cheng, X.; Chiaromonte, F.; Eckert, K.A.; Huang, Y.F.; Makova, K.D. Selection and thermostability suggest G-quadruplexes are novel functional elements of the human genome. Genome Res. 2021, 31, 1136–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Robinson, P.N.; Wang, K. Phenolyzer: Phenotype-based prioritization of candidate genes for human diseases. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 841–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chambers, V.S.; Marsico, G.; Boutell, J.M.; Di Antonio, M.; Smith, G.P.; Balasubramanian, S. High-throughput sequencing of DNA G-quadruplex structures in the human genome. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 877–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyu, J.; Shao, R.; Kwong Yung, P.Y.; Elsasser, S.J. Genome-wide mapping of G-quadruplex structures with CUT&Tag. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, K.W.; Zhang, J.Y.; He, Y.D.; Gong, J.Y.; Wen, C.J.; Chen, J.N.; Hao, Y.H.; Zhao, Y.; Tan, Z. Detection of genomic G-quadruplexes in living cells using a small artificial protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, 11706–11720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuentes-Antras, J.; Bedard, P.L.; Cescon, D.W. Seize the engine: Emerging cell cycle targets in breast cancer. Clin. Transl. Med. 2024, 14, e1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spring, L.M.; Wander, S.A.; Andre, F.; Moy, B.; Turner, N.C.; Bardia, A. Cyclin-dependent kinase 4 and 6 inhibitors for hormone receptor-positive breast cancer: Past, present, and future. Lancet 2020, 395, 817–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinberg, R.A. The retinoblastoma protein and cell cycle control. Cell 1995, 81, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.Y.; Knudsen, E.S.; Welch, P.J. The retinoblastoma tumor suppressor protein. Adv. Cancer Res. 1994, 64, 25–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickler, M.N.; Tolaney, S.M.; Rugo, H.S.; Cortés, J.; Diéras, V.; Patt, D.; Wildiers, H.; Hudis, C.A.; O’Shaughnessy, J.; Zamora, E.; et al. MONARCH 1, A Phase II Study of Abemaciclib, a CDK4 and CDK6 Inhibitor, as a Single Agent, in Patients with Refractory HR+/HER2-Metastatic Breast Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 5218–5224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finn, R.S.; Martin, M.; Rugo, H.S.; Jones, S.; Im, S.-A.; Gelmon, K.; Harbeck, N.; Lipatov, O.N.; Walshe, J.M.; Moulder, S.; et al. Palbociclib and Letrozole in Advanced Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1925–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hortobagyi, G.N.; Stemmer, S.M.; Burris, H.A.; Yap, Y.-S.; Sonke, G.S.; Paluch-Shimon, S.; Campone, M.; Blackwell, K.L.; André, F.; Winer, E.P.; et al. Ribociclib as First-Line Therapy for HR-Positive, Advanced Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1738–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Im, S.-A.; Lu, Y.-S.; Bardia, A.; Harbeck, N.; Colleoni, M.; Franke, F.; Chow, L.; Sohn, J.; Lee, K.-S.; Campos-Gomez, S.; et al. Overall Survival with Ribociclib plus Endocrine Therapy in Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, N.C.; Ro, J.; André, F.; Loi, S.; Verma, S.; Iwata, H.; Harbeck, N.; Loibl, S.; Huang Bartlett, C.; Zhang, K.; et al. Palbociclib in Hormone-Receptor-Positive Advanced Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, N.C.; Slamon, D.J.; Ro, J.; Bondarenko, I.; Im, S.-A.; Masuda, N.; Colleoni, M.; DeMichele, A.; Loi, S.; Verma, S.; et al. Overall Survival with Palbociclib and Fulvestrant in Advanced Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 1926–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wander, S.A.; Cohen, O.; Johnson, G.N.; Kim, D.; Luo, F.; Mao, P.; Nayar, U.; Helvie, K.; Marini, L.; Freeman, S.; et al. Whole exome sequencing (WES) in hormone-receptor positive (HR+) metastatic breast cancer (MBC) to identify mediators of resistance to cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibitors (CDK4/6i). J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 12016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Teng, X.; Zhang, Q.; Hou, H.; Li, J. Advances and challenges in identifying and characterizing G-quadruplex-protein interactions. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2023, 48, 894–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, H.; Zhang, R.; Xiao, K.; Yang, J.; Sun, X. G-Quadruplex-Binding Proteins: Promising Targets for Drug Design. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pramanik, S.; Chen, Y.; Song, H.; Khutsishvili, I.; Marky, L.A.; Ray, S.; Natarajan, A.; Singh, P.K.; Bhakat, K.K. The human AP-endonuclease 1 (APE1) is a DNA G-quadruplex structure binding protein and regulates KRAS expression in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, 3394–3412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cogoi, S.; Xodo, L.E. G-quadruplex formation within the promoter of the KRAS proto-oncogene and its effect on transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, 2536–2549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.-B.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Xiao, C.; Wang, Y.; Gu, W.; Li, Y.; Xia, Y.-Z.; Yan, T.; Yang, M.-H.; et al. Structural insight into the bulge-containing KRAS oncogene promoter G-quadruplex bound to berberine and coptisine. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 6016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cogoi, S.; Paramasivam, M.; Spolaore, B.; Xodo, L.E. Structural polymorphism within a regulatory element of the human KRAS promoter: Formation of G4-DNA recognized by nuclear proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, 3765–3780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.; Zhang, Y.; Qian, L.; Wang, P. Emerging strategies to target RAS signaling in human cancer therapy. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 14, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Li, M.; Wu, T.; Zhan, L.; Li, L.; Chen, M.; Xie, W.; Xie, Z.; Hu, E.; Xu, S.; et al. Exploring Epigenomic Datasets by ChIPseeker. Curr. Protoc. 2022, 2, e585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eisenberg, E.; Levanon, E.Y. Human housekeeping genes, revisited. Trends Genet. 2013, 29, 569–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Lindsay, H.; Robinson, M.D. Robustly detecting differential expression in RNA sequencing data using observation weights. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, e91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Ge, X.; Peng, F.; Li, W.; Li, J.J. Exaggerated false positives by popular differential expression methods when analyzing human population samples. Genome Biol. 2022, 23, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oki, S.; Ohta, T.; Shioi, G.; Hatanaka, H.; Ogasawara, O.; Okuda, Y.; Kawaji, H.; Nakaki, R.; Sese, J.; Meno, C. ChIP-Atlas: A data-mining suite powered by full integration of public ChIP-seq data. EMBO Rep. 2018, 19, e46255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Z.; Ohta, T.; Miura, F.; Oki, S. ChIP-Atlas 2021 update: A data-mining suite for exploring epigenomic landscapes by fully integrating ChIP-seq, ATAC-seq and Bisulfite-seq data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, W175–W182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Franceschini, A.; Wyder, S.; Forslund, K.; Heller, D.; Huerta-Cepas, J.; Simonovic, M.; Roth, A.; Santos, A.; Tsafou, K.P.; et al. STRING v10: Protein-protein interaction networks, integrated over the tree of life. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, D447–D452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rauluseviciute, I.; Riudavets-Puig, R.; Blanc-Mathieu, R.; Castro-Mondragon, J.A.; Ferenc, K.; Kumar, V.; Lemma, R.B.; Lucas, J.; Chéneby, J.; Baranasic, D.; et al. JASPAR 2024: 20th anniversary of the open-access database of transcription factor binding profiles. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 52, D174–D182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Bajari, R.; Andric, D.; Gerthoffert, F.; Lepsa, A.; Nahal-Bose, H.; Stein, L.D.; Ferretti, V. The International Cancer Genome Consortium Data Portal. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 367–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruber, A.R.; Lorenz, R.; Bernhart, S.H.; Neubock, R.; Hofacker, I.L. The Vienna RNA websuite. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, W70–W74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hon, J.; Martinek, T.; Zendulka, J.; Lexa, M. pqsfinder: An exhaustive and imperfection-tolerant search tool for potential quadruplex-forming sequences in R. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 3373–3379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Class Labeled by # of Proteins | # of Sites | Overlaps in G4R | Overlaps in Control | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cluster 1 | ||||
| ≥2 | 56,089 | 267/424 | 6/424 | 2.00578 × 10−97 |
| ≥3 | 27,651 | 217/424 | 3/424 | 1.801687 × 10−76 |
| ≥4 | 16,064 | 172/424 | 3/424 | 2.081164 × 10−56 |
| ≥5 | 9648 | 116/424 | 3/424 | 1.390859 × 10−34 |
| ≥6 | 3483 | 44/424 | 0/424 | 3.505748 × 10−14 |
| ≥7 | 739 | 15/424 | 0/424 | 5.381052 × 10−5 |
| ≥8 | 127 | 5/424 | 0/424 | 0.06176341 |
| Cluster 2 | ||||
| ≥2 | 47,269 | 164/424 | 10/424 | 1.053576 × 10−44 |
| ≥3 | 32,097 | 74/424 | 5/424 | 3.748428 × 10−18 |
| ≥4 | 23,600 | 42/424 | 3/424 | 3.429332 × 10−10 |
| ≥5 | 18,483 | 36/424 | 1/424 | 2.652893 × 10−10 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shu, H.; Xiao, K.; Zhu, W.; Zhang, R.; Tao, T.; Sun, X. The Relevance of G-Quadruplexes in Gene Promoters and the First Introns Associated with Transcriptional Regulation in Breast Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6874. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146874
Shu H, Xiao K, Zhu W, Zhang R, Tao T, Sun X. The Relevance of G-Quadruplexes in Gene Promoters and the First Introns Associated with Transcriptional Regulation in Breast Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(14):6874. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146874
Chicago/Turabian StyleShu, Huiling, Ke Xiao, Wenyong Zhu, Rongxin Zhang, Tiantong Tao, and Xiao Sun. 2025. "The Relevance of G-Quadruplexes in Gene Promoters and the First Introns Associated with Transcriptional Regulation in Breast Cancer" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 14: 6874. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146874
APA StyleShu, H., Xiao, K., Zhu, W., Zhang, R., Tao, T., & Sun, X. (2025). The Relevance of G-Quadruplexes in Gene Promoters and the First Introns Associated with Transcriptional Regulation in Breast Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(14), 6874. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146874






