Characterization of DNA Methylation Episignatures for Radon-Induced Lung Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
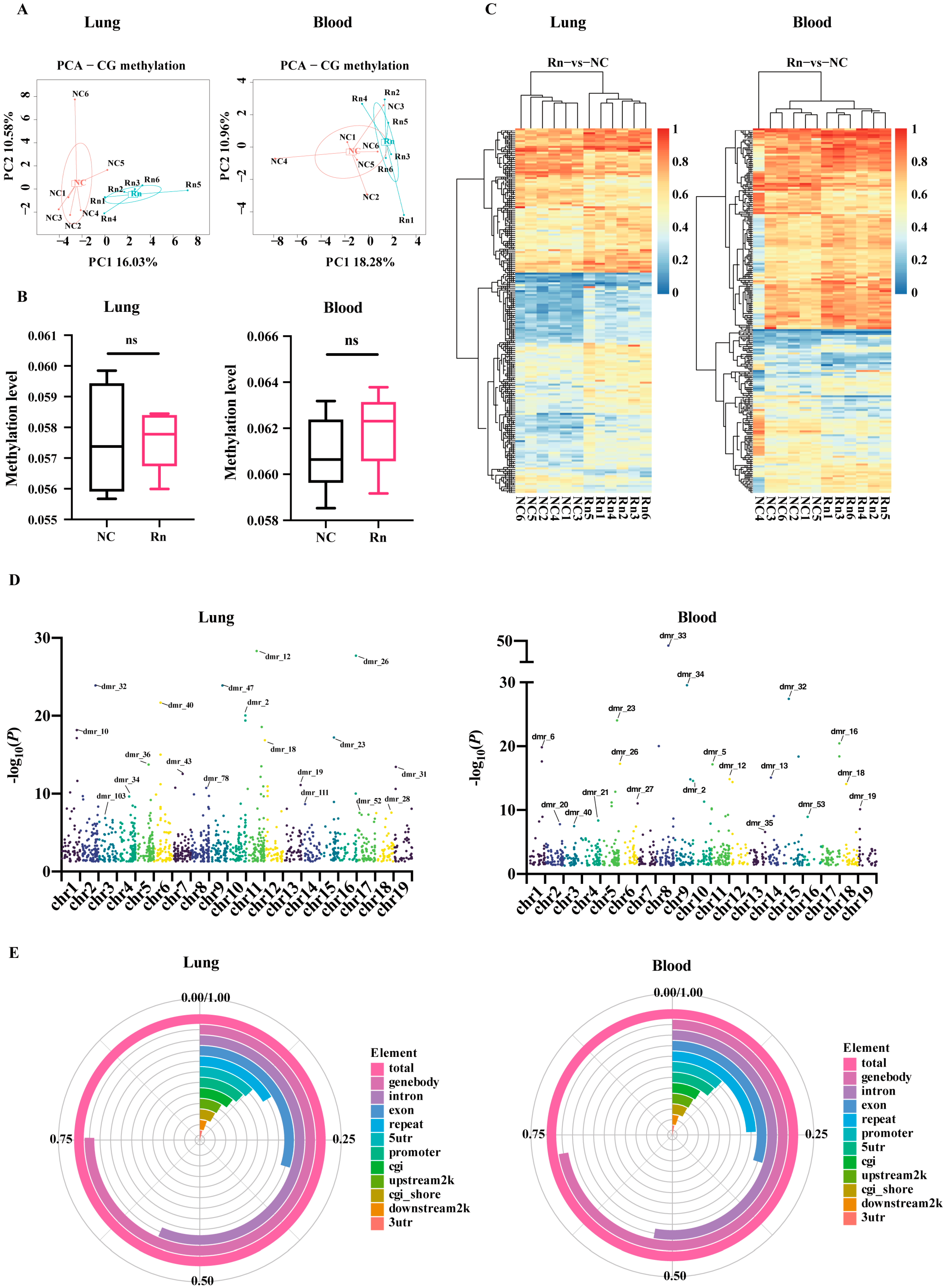
2.1. Blood and Lung-Derived DMRs of Mice Exposed to Radon
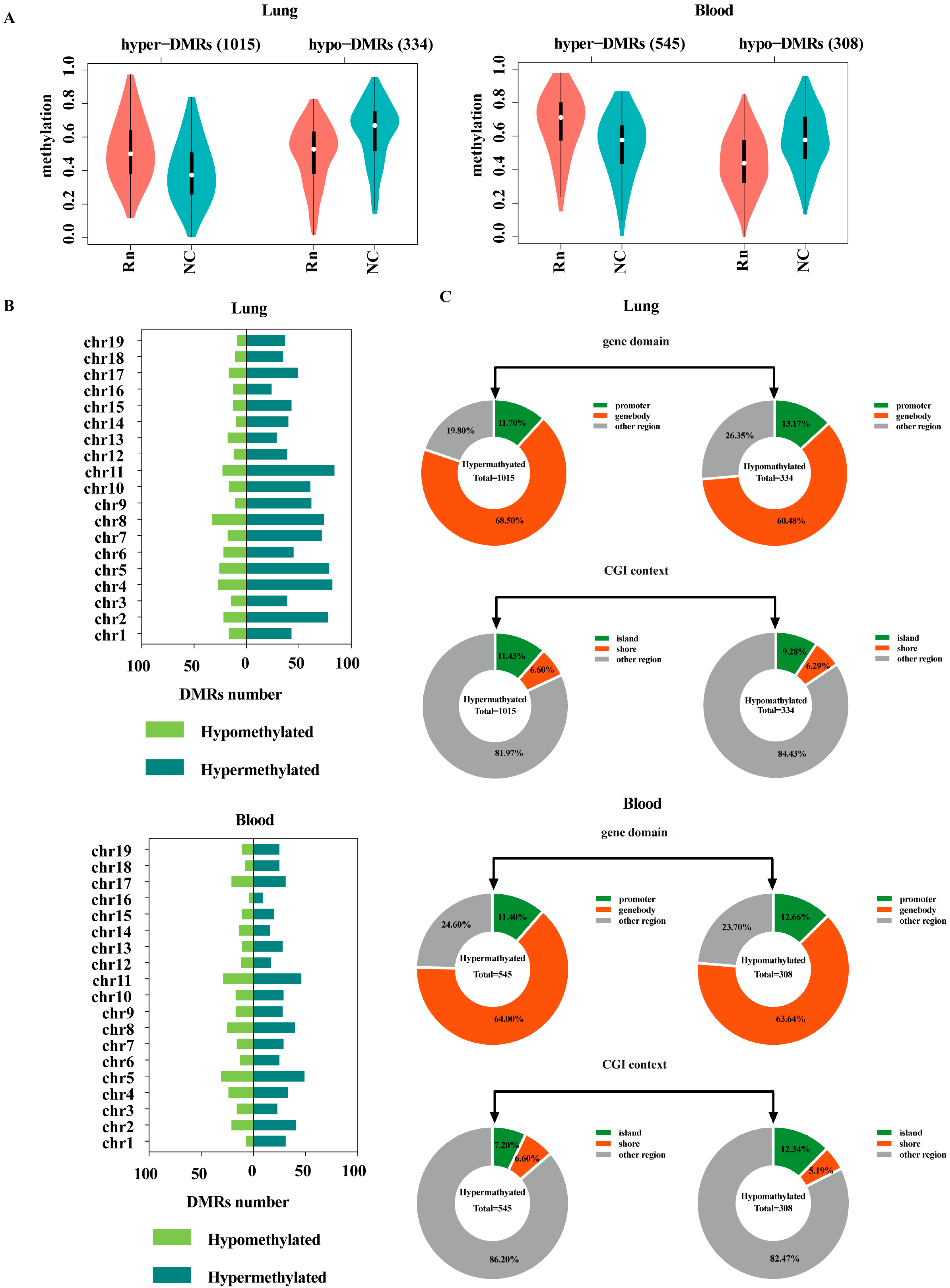
2.2. Regional Analysis of Hypomethylated and Hypermethylated DMRs
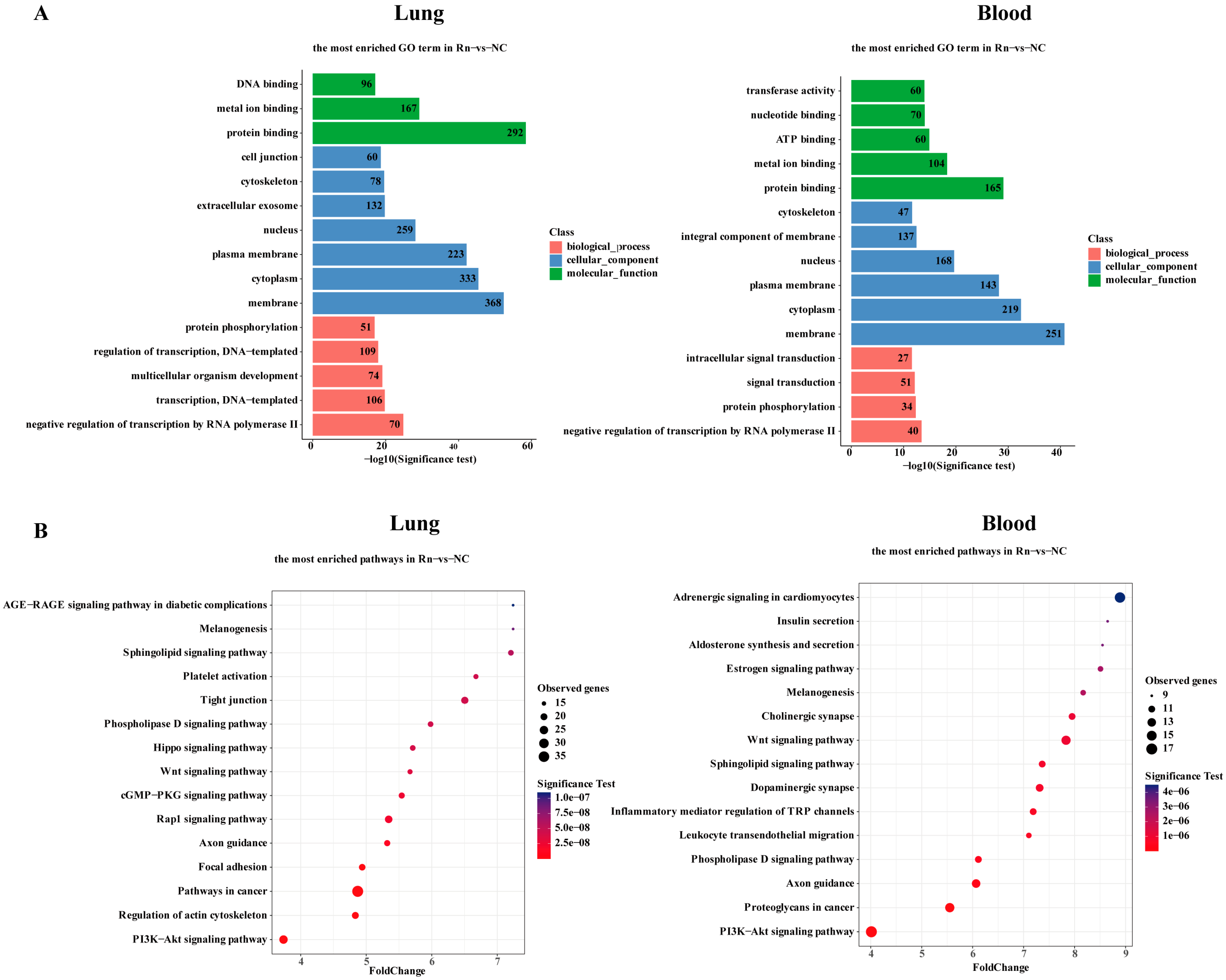
2.3. Functional Enrichment Analysis Associated with DMR-Mapped Genes
2.4. DNA Methylation Changes and Association Analysis in Cancer-Associated Genes
2.5. Validation of DNA Methylation in Cancer-Related Genes by MassArray
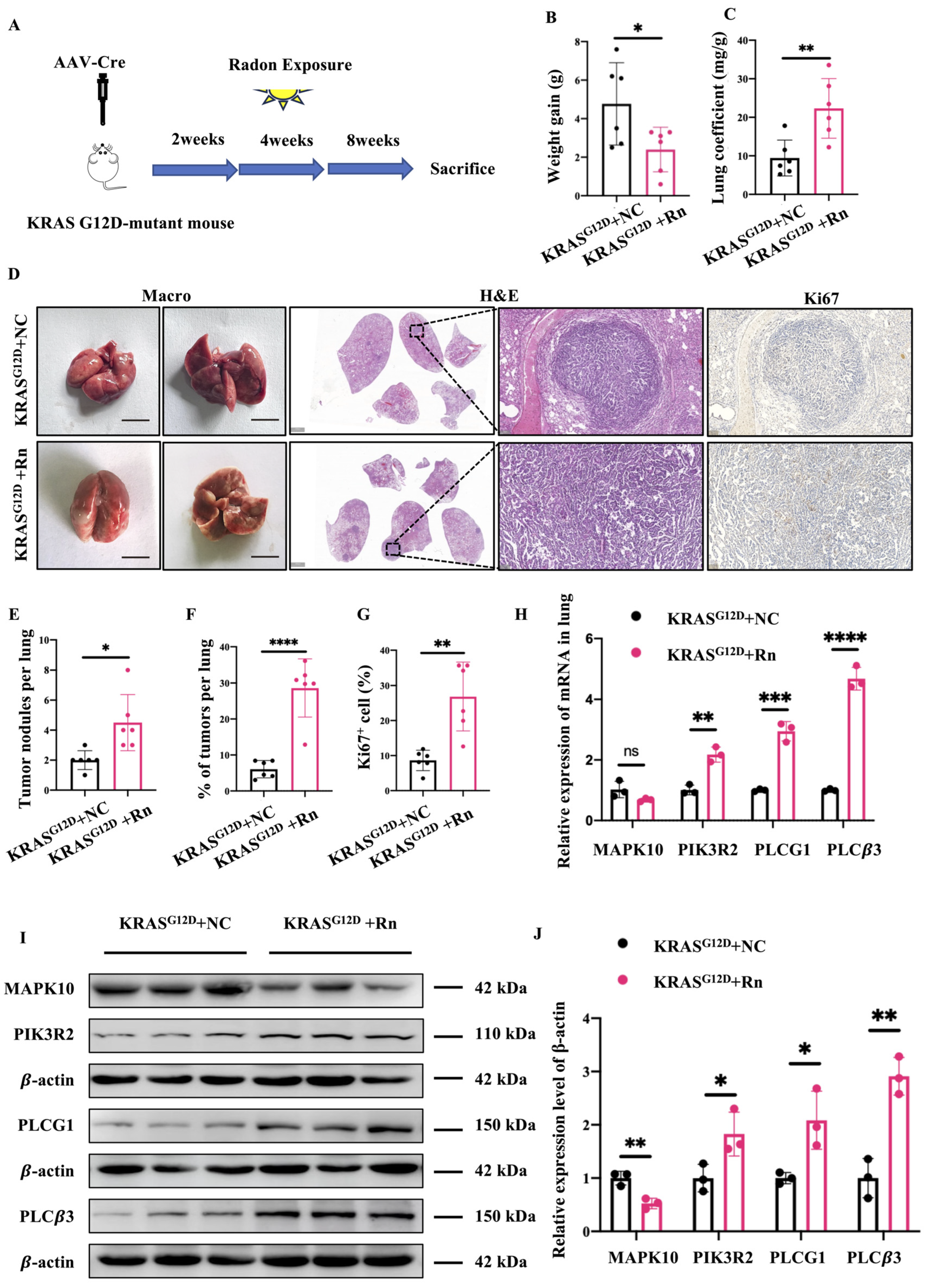
2.6. Carcinogenic Effects of Radon and Cancer-Related Gene Expression in GEMM
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Mouse Models
4.2. Radon Exposure
4.3. Tissue Collection
4.4. Reduced Representation Bisulfite Sequencing (RRBS)
4.5. Bioinformation Analysis
4.6. MassArray Methylation Analysis
4.7. Histology and Tumor Burden Analyses
4.8. Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
4.9. Real-Time Quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR)
4.10. Western Blots
4.11. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Rn | Radon |
| IARC | Agency for Research on Cancer |
| NSCLC | Non-small cell lung cancer |
| SCLC | Small cell lung cancer |
| DNAm | DNA methylation |
| TSGs | Tumor suppressor genes |
| ctDNA | Circulating tumor DNA |
| DMRs | Differentially methylated regions |
| PCA | principal component analysis |
| Hyper-DMR | Hypermethylated DMR |
| Hypo-DMR | Hypomethylated DMR |
| GO | Gene ontology |
| BP | Biological process |
| CC | Cellular component |
| MF | Molecular function |
| KEGG | Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes |
| cfDNA | Circulating cell-free DNA |
| PI3K | Phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase |
| TCGA | The Cancer Genome Atlas |
| WLM | Working Level Months |
References
- IARC Working Group on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. Man-Made Mineral Fibres and Radon; International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC): Lyon, France, 1988; Volume 43, p. 173. [Google Scholar]
- Eaton, R.S. Radon Reduction: Radon and Its Decay Products in Indoor Air. William, W. Nazaroff and Anthony, V. Nero, Jr., Eds. Wiley-Interscience, New York, 1988. Xxvi 518 pp., Illus. $75. Environmental Science and Technology. Science 1988, 241, 990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanchao, S.; Qingzhao, Z.; Hongxing, C.; Changsong, H.; Pinhua, Z.; Yunyun, W. Radon Concentration Measurement and Dose Estimation in Non-Uranium Mines in China (2019–2021). Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2023, 199, 491–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Wu, Y.; Piao, C.; Song, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Lyu, Y.; Sun, Q.; Liu, J. Alteration of Genome-Wide DNA Methylation in Non-Uranium Miners Induced by High Level Radon Exposure. Mutat. Res. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2023, 891, 503683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Wu, Y.; Piao, C.; Song, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Lyu, Y.; Sun, Q.; Liu, J. DNA Methylome Profiling in Occupational Radon Exposure Miners Using an Illumina Infinium Methylation EPIC BeadChip. Toxicol. Res. 2023, 12, 943–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krewski, D.; Lubin, J.H.; Zielinski, J.M.; Alavanja, M.; Catalan, V.S.; Field, R.W.; Klotz, J.B.; Létourneau, E.G.; Lynch, C.F.; Lyon, J.I.; et al. Residential Radon and Risk of Lung Cancer: A Combined Analysis of 7 North American Case-Control Studies. Epidemiology 2005, 16, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lubin, J.H.; Wang, Z.Y.; Boice, J.D.; Xu, Z.Y.; Blot, W.J.; De Wang, L.; Kleinerman, R.A. Risk of Lung Cancer and Residential Radon in China: Pooled Results of Two Studies. Int. J. Cancer 2004, 109, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darby, S.; Hill, D.; Auvinen, A.; Barros-Dios, J.M.; Baysson, H.; Bochicchio, F.; Deo, H.; Falk, R.; Forastiere, F.; Hakama, M.; et al. Radon in Homes and Risk of Lung Cancer: Collaborative Analysis of Individual Data from 13 European Case-Control Studies. BMJ 2005, 330, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Wagle, N.S.; Jemal, A. Cancer Statistics, 2023. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2023, 73, 17–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melloni, B.B.M. Lung Cancer in Never-Smokers: Radon Exposure and Environmental Tobacco Smoke. Eur. Respir. J. 2014, 44, 850–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicholson, A.G.; Tsao, M.S.; Beasley, M.B.; Borczuk, A.C.; Brambilla, E.; Cooper, W.A.; Dacic, S.; Jain, D.; Kerr, K.M.; Lantuejoul, S.; et al. The 2021 WHO Classification of Lung Tumors: Impact of Advances Since 2015. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2022, 17, 362–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bach, P.B.; Mirkin, J.N.; Oliver, T.K.; Azzoli, C.G.; Berry, D.A.; Brawley, O.W.; Byers, T.; Colditz, G.A.; Gould, M.K.; Jett, J.R.; et al. Benefits and Harms of CT Screening for Lung Cancer: A Systematic Review. JAMA 2012, 307, 2418–2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, B.; Zhang, H.; Wei, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, F.; Wang, X.; Li, L. Does Adenomatous Polyposis Coli Gene Promoter 1A Methylation Increase Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Risk? A Meta-Analysis. Thorac. Cancer 2017, 8, 410–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belinsky, S.A.; Nikula, K.J.; Palmisano, W.A.; Michels, R.; Saccomanno, G.; Gabrielson, E.; Baylin, S.B.; Herman, J.G. Aberrant Methylation of P16(INK4a) Is an Early Event in Lung Cancer and a Potential Biomarker for Early Diagnosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 11891–11896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.-H.; Kim, J.S.; Ji, Y.-I.; Shim, Y.M.; Kim, H.; Han, J.; Park, J. Hypermethylation of RASSF1A Promoter Is Associated with the Age at Starting Smoking and a Poor Prognosis in Primary Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer1. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 3743–3746. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.J.; Tan, X.H.; Guo, B.P.; Ke, Q.; Sun, J.; Cen, H. Associations Between RASSF1A Promoter Methylation and NSCLC: A Meta-Analysis of Published Data. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2013, 14, 3719–3724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, H.; Dai, Q.; Wang, S.; Wei, Y.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Huang, Y. A Panel of SHOX2 and PTGER4 DNA Methylation Biomarkers to Enhance Diagnostic Efficiency for Lung Cancer in Chinese Patients. 2024. Available online: https://ssrn.com/abstract=5058449 (accessed on 1 January 2024).
- Balgkouranidou, I.; Chimonidou, M.; Milaki, G.; Tsaroucha, E.; Kakolyris, S.; Georgoulias, V.; Lianidou, E. SOX17 Promoter Methylation in Plasma Circulating Tumor DNA of Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2016, 54, 1385–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wrangle, J.; Machida, E.O.; Danilova, L.; Hulbert, A.; Franco, N.; Zhang, W.; Glöckner, S.C.; Tessema, M.; Van Neste, L.; Easwaran, H.; et al. Functional Identification of Cancer-Specific Methylation of CDO1, HOXA9, and TAC1 for the Diagnosis of Lung Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 1856–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Field, R.W.; Steck, D.J.; Smith, B.J.; Brus, C.P.; Fisher, E.F.; Neuberger, J.S.; Lynch, C.F. The Iowa Radon Lung Cancer Study--Phase I: Residential Radon Gas Exposure and Lung Cancer. Sci. Total Environ. 2001, 272, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, D.; Ei, S. Radiation-Induced Transgenerational Effects in Animals. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2022, 98, 1047–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Shi, W.; Wang, J.; Guan, C.; Dong, Q.; Sheng, J.; Zou, X.; Xu, Z.; Ge, Y.; Yang, C.; et al. Research Progress and Applications of Epigenetic Biomarkers in Cancer. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1308309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, M. Environmental Epigenetics: Unraveling the Impact of Exposures on Gene Regulation. Ann. Clin. Lab. Res. 2023, 11, 488. [Google Scholar]
- Vivanco, I.; Sawyers, C.L. The Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase–AKT Pathway in Human Cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2, 489–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bugter, J.M.; Fenderico, N.; Maurice, M.M. Publisher Correction: Mutations and Mechanisms of WNT Pathway Tumour Suppressors in Cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2021, 21, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathew, B.; Jacobson, J.R.; Berdyshev, E.; Huang, Y.; Sun, X.; Zhao, Y.; Gerhold, L.M.; Siegler, J.; Evenoski, C.; Wang, T.; et al. Role of Sphingolipids in Murine Radiation-Induced Lung Injury: Protection by Sphingosine 1-Phosphate Analogs. FASEB J. 2011, 25, 3388–3400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Epshtein, Y.; Wang, H.; Jacobson, J.R.; Malik, A. Role of Trpm2 in Sphingolipid-Mediated Radiation-Induced Lung Injury. J. Investig. Med. 2016, 64, 972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, J.R. Sphingolipids as a Novel Therapeutic Target in Radiation-Induced Lung Injury. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2021, 79, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Natarajan, V.; Dudek, S.M.; Jacobson, J.R.; Moreno-Vinasco, L.; Huang, L.S.; Abassi, T.; Mathew, B.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, L.; Bittman, R.; et al. Sphingosine-1-Phosphate, FTY720, and Sphingosine-1-Phosphate Receptors in the Pathobiology of Acute Lung Injury. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2013, 49, 6–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almasi, S.; Long, C.Y.; Sterea, A.; Clements, D.R.; Gujar, S.; El Hiani, Y. TRPM2 Silencing Causes G2/M Arrest and Apoptosis in Lung Cancer Cells via Increasing Intracellular ROS and RNS Levels and Activating the JNK Pathway. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 52, 742–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proskocil, B.J.; Fryer, A.D. Beta2-Agonist and Anticholinergic Drugs in the Treatment of Lung Disease. Proc. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2005, 2, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gill, S.; Wight, T.N.; Frevert, C.W. Proteoglycans: Key Regulators of Pulmonary Inflammation and the Innate Immune Response to Lung Infection. Anat. Rec. 2010, 293, 968–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karsdal, M.A.; Nielsen, M.J.; Sand, J.M.; Henriksen, K.; Genovese, F.; Bay-Jensen, A.-C.; Smith, V.; Adamkewicz, J.I.; Christiansen, C.; Leeming, D.J. Extracellular Matrix Remodeling: The Common Denominator in Connective Tissue Diseases. Possibilities for Evaluation and Current Understanding of the Matrix as More than a Passive Architecture, but a Key Player in Tissue Failure. Assay Drug Dev. Technol. 2013, 11, 70–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Handbook on Indoor Radon; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009.
- Riudavets, M.; de Herreros, M.G.; Besse, B.; Mezquita, L. Radon and Lung Cancer: Current Trends and Future Perspectives. Cancers 2022, 14, 3142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martín-Gisbert, L.; Ruano-Raviña, A.; García, G.; Piñeiro-Lamas, M.; García-Talavera, M.; Teijeiro, A.; Candal-Pedreira, C. Duration versus Intensity of Exposure on the Risk of Lung Cancer Due to Radon Exposure in the General Population. Sci. Total Environ. 2025, 981, 179569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuan, C.-Y.; Whitmarsh, A.J.; Yang, D.D.; Liao, G.; Schloemer, A.J.; Dong, C.; Bao, J.; Banasiak, K.J.; Haddad, G.G.; Flavell, R.A.; et al. A Critical Role of Neural-Specific JNK3 for Ischemic Apoptosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 15184–15189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weston, C.R.; Wong, A.; Hall, J.P.; Goad, M.E.P.; Flavell, R.A.; Davis, R.J. JNK Initiates a Cytokine Cascade That Causes Pax2 Expression and Closure of the Optic Fissure. Genes Dev. 2003, 17, 1271–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oka, H.; Chatani, Y.; Hoshino, R.; Ogawa, O.; Kakehi, Y.; Terachi, T.; Okada, Y.; Kawaichi, M.; Kohno, M.; Yoshida, O. Constitutive Activation of Mitogen-Activated Protein (MAP) Kinases in Human Renal Cell Carcinoma. Cancer Res. 1995, 55, 4182–4187. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yoo, K.H.; Park, Y.-K.; Kim, H.-S.; Jung, W.-W.; Chang, S.-G. Identification of MAPK10 as a Novel Epigenetic Marker for Chromophobe Kidney Cancer. Pathol. Int. 2011, 61, 52–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, R.; Xiang, T.; Tang, J.; Peng, W.; Luo, J.; Li, L.; Qiu, Z.; Tan, Y.; Ye, L.; Zhang, M.; et al. 19q13 KRAB Zinc-Finger Protein ZNF471 Activates MAPK10/JNK3 Signaling but Is Frequently Silenced by Promoter CpG Methylation in Esophageal Cancer. Theranostics 2020, 10, 2243–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebelt, N.D.; Cantrell, M.A.; Berg, C.L.V.D. C-Jun N-Terminal Kinases Mediate a Wide Range of Targets in the Metastatic Cascade. Genes Cancer 2013, 4, 378–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Tan, B.; Huang, T.; Xiong, J.; Tan, X.; Ermolaeva, M.A.; Fu, L. MAPK10 Expression as a Prognostic Marker of the Immunosuppressive Tumor Microenvironment in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 687371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, L.; Chen, Y.; Liang, N.; Xie, J.; Deng, G.; Chen, F.; Wang, X.; Liu, F.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J. Targeting Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition in Radioresistance: Crosslinked Mechanisms and Strategies. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 775238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.; Li, X.; Cheng, T.; Wu, J. miR-21-5p/SMAD7 Axis Promotes the Progress of Lung Cancer. Thorac. Cancer 2021, 12, 2307–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Liu, L.; Li, X.; Xu, S. EphA10 Drives Tumor Progression and Immune Evasion by Regulating the MAPK/ERK Cascade in Lung Adenocarcinoma. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2022, 110, 109031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, A.S.; Prasad, A.; Pradeep, S.; Dharmashekar, C.; Achar, R.R.; Silina, E.; Stupin, V.; Amachawadi, R.G.; Prasad, S.K.; Pruthvish, R.; et al. Everything Old Is New Again: Drug Repurposing Approach for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Targeting MAPK Signaling Pathway. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 822865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Li, X.; Xu, G. Propofol Suppresses the Progression of Non-small Cell Lung Cancer via Downregulation of the miR-21-5p/MAPK10 Axis. Oncol. Rep. 2020, 44, 487–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ying, J.; Gao, Z. Frequent epigenetic silencing of proapoptotic gene MAPK10 by methylation in B cell lymphoma. J. Leuk. Lymphoma 2010, 19, 272–275. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Yu, J.; Pan, T.; Feng, H.; Li, J.; Yu, B.; Fan, Z.; Sang, Q.; Chen, M.; Zang, M.; et al. BPTF Drives Gastric Cancer Resistance to EGFR Inhibitor by Epigenetically Regulating the C-MYC/PLCG1/Perk Axis. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, 2303091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marvi, M.V.; Neri, I.; Evangelisti, C.; Ramazzotti, G.; Asioli, S.; Zoli, M.; Mazzatenta, D.; Neri, N.; Morandi, L.; Tonon, C.; et al. Phospholipases in Gliomas: Current Knowledge and Future Perspectives from Bench to Bedside. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marvi, M.V.; Mongiorgi, S.; Ramazzotti, G.; Follo, M.Y.; Billi, A.M.; Zoli, M.; Mazzatenta, D.; Morandi, L.; Asioli, S.; Papa, V.; et al. Role of PLCγ1 in the Modulation of Cell Migration and Cell Invasion in Glioblastoma. Adv. Biol. Regul. 2022, 83, 100838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, W.; Kim, L.C.; Han, W.; Hou, Y.; Edwards, D.N.; Wang, S.; Blackwell, T.S.; Cheng, F.; Brantley-Sieders, D.M.; Chen, J. Phosphorylation of PLCγ1 by EphA2 Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Promotes Tumor Growth in Lung Cancer. Mol. Cancer Res. 2020, 18, 1735–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.; Fu, H.; Chen, R.; Wang, Y.; Zhan, Y.; Song, G.; Hu, T.; Xia, C.; Tian, X.; Zhang, B. Phosphoinositide Specific Phospholipase Cγ1 Inhibition-Driven Autophagy Caused Cell Death in Human Lung Adenocarcinoma A549 Cells in Vivo and in Vitro. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 16, 1427–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saliakoura, M.; Rossi Sebastiano, M.; Pozzato, C.; Heidel, F.H.; Schnöder, T.M.; Savic Prince, S.; Bubendorf, L.; Pinton, P.; A Schmid, R.; Baumgartner, J.; et al. PLCγ1 Suppression Promotes the Adaptation of KRAS-Mutant Lung Adenocarcinomas to Hypoxia. Nat. Cell Biol. 2020, 22, 1382–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girardini, K.N.; Olthof, A.M.; Kanadia, R.N. Introns: The “Dark Matter” of the Eukaryotic Genome. Front. Genet. 2023, 14, 1150212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang, C.-Y.; Fan, S.; Zheng, H.; Guo, W.; Zheng, Z.; Sun, Y.; Zhong, C.; Zeng, J.; Li, S.; Zhang, M.; et al. Methylation of KRAS by SETD7 Promotes KRAS Degradation in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cell Rep. 2023, 42, 113003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinheiro, H.; Carvalho, J.; Oliveira, P.; Ferreira, D.; Pinto, M.T.; Osório, H.; Licastro, D.; Bordeira-Carriço, R.; Jordan, P.; Lazarevic, D.; et al. Transcription Initiation Arising from E-Cadherin/CDH1 Intron2: A Novel Protein Isoform That Increases Gastric Cancer Cell Invasion and Angiogenesis. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2012, 21, 4253–4269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terai, H.; Soejima, K.; Yasuda, H.; Sato, T.; Naoki, K.; Ikemura, S.; Arai, D.; Ohgino, K.; Ishioka, K.; Hamamoto, J.; et al. Long-term Exposure to Gefitinib Induces Acquired Resistance through DNA Methylation Changes in the EGFR-mutant PC9 Lung Cancer Cell Line. Int. J. Oncol. 2015, 46, 430–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Stålberg, P.; Wang, S.; Larsson, C.; Weber, G.; Öberg, K.; Gobl, A.; Skogseid, B. Suppression of the Neoplastic Phenotype by Transfection of Phospholipase C β 3 to Neuroendocrine Tumor Cells. FEBS Lett. 1999, 450, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Zhang, T.; Song, X.; Liao, X.; Wang, X.; Zhu, G.; Yang, C.; Xie, X. Distinct Prognostic Values of Phospholipase C Beta Family Members for Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma. BioMed Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 4256524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, L.; Qin, Y.-R.; Xie, D.; Hu, L.; Kwong, D.L.; Srivastava, G.; Tsao, S.W.; Guan, X.-Y. Characterization of a Novel Tumor-Suppressor Gene PLCδ1 at 3p22 in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 10720–10726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.; Yi, S.; Qiu, P. Comprehensive Analysis of TCGA Data Reveals Correlation between DNA Methylation and Alternative Splicing. BMC Genom. 2022, 23, 758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarris, E.G.; Saif, M.W.; Syrigos, K.N. The Biological Role of PI3K Pathway in Lung Cancer. Pharmaceuticals 2012, 5, 1236–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallejo-Díaz, J.; Olazabal-Morán, M.; Cariaga-Martínez, A.E.; Pajares, M.J.; Flores, J.M.; Pio, R.; Montuenga, L.M.; Carrera, A.C. Targeted Depletion of PIK3R2 Induces Regression of Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 85063–85078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Lau, A.Y.T.; Ng, A.S.N.; Aldehaiman, A.; Zhou, Y.; Ng, P.K.S.; Arold, S.T.; Cheung, L.W.T. Cancer-Associated Mutations in the P85α N-Terminal SH2 Domain Activate a Spectrum of Receptor Tyrosine Kinases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2101751118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, D.; Li, Z.; Li, X.; Jin, M.; Jia, N.; Cui, X.; Hu, G.; Tang, T.; Yu, Q. Pan-Cancer Analysis on the Role of PIK3R1 and PIK3R2 in Human Tumors. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 5924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrow, A.K.; Thornal, A.; Flynn, E.D.; Hoelzli, E.; Shan, M.; Garipler, G.; Kirchner, R.; Reddy, A.J.; Tabchouri, S.; Gupta, A.; et al. ML-Driven Design of 3′ UTRs for mRNA Stability. BioRxiv 2024, 2024–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasekhian, M.; Roohvand, F.; Habtemariam, S.; Marzbany, M.; Kazemimanesh, M. The Role of 3′UTR of RNA Viruses on mRNA Stability and Translation Enhancement. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2021, 21, 2389–2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.-J.; Zhao, Z.-F.; Kang, X.-J.; Wang, H.-J.; Zhao, J.; Pu, X.-M. MicroRNA-126-3p Suppresses Cell Proliferation by Targeting PIK3R2 in Kaposi’s Sarcoma Cells. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 36614–36621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szostak, E.; Gebauer, F. Translational Control by 3′-UTR-Binding Proteins. Brief. Funct. Genom. 2013, 12, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bird, A. DNA Methylation Patterns and Epigenetic Memory. Genes Dev. 2002, 16, 6–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belinsky, S.A.; Klinge, D.M.; Liechty, K.C.; March, T.H.; Kang, T.; Gilliland, F.D.; Sotnic, N.; Adamova, G.; Rusinova, G.; Telnov, V. Plutonium Targets the P16 Gene for Inactivation by Promoter Hypermethylation in Human Lung Adenocarcinoma. Carcinogenesis 2004, 25, 1063–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marsit, C.J.; Kim, D.-H.; Liu, M.; Hinds, P.W.; Wiencke, J.K.; Nelson, H.H.; Kelsey, K.T. Hypermethylation of RASSF1A and BLU Tumor Suppressor Genes in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Implications for Tobacco Smoking during Adolescence. Int. J. Cancer 2005, 114, 219–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pankova, D.; Jiang, Y.; Chatzifrangkeskou, M.; Vendrell, I.; Buzzelli, J.; Ryan, A.; Brown, C.; O’Neill, E. RASSF1A Controls Tissue Stiffness and Cancer Stem-like Cells in Lung Adenocarcinoma. EMBO J. 2019, 38, e100532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esteller, M. Cancer Epigenomics: DNA Methylomes and Histone-Modification Maps. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2007, 8, 286–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deverman, B.E.; Pravdo, P.L.; Simpson, B.P.; Kumar, S.R.; Chan, K.Y.; Banerjee, A.; Wu, W.-L.; Yang, B.; Huber, N.; Pasca, S.P.; et al. Cre-Dependent Selection Yields AAV Variants for Widespread Gene Transfer to the Adult Brain. Nat. Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 204–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
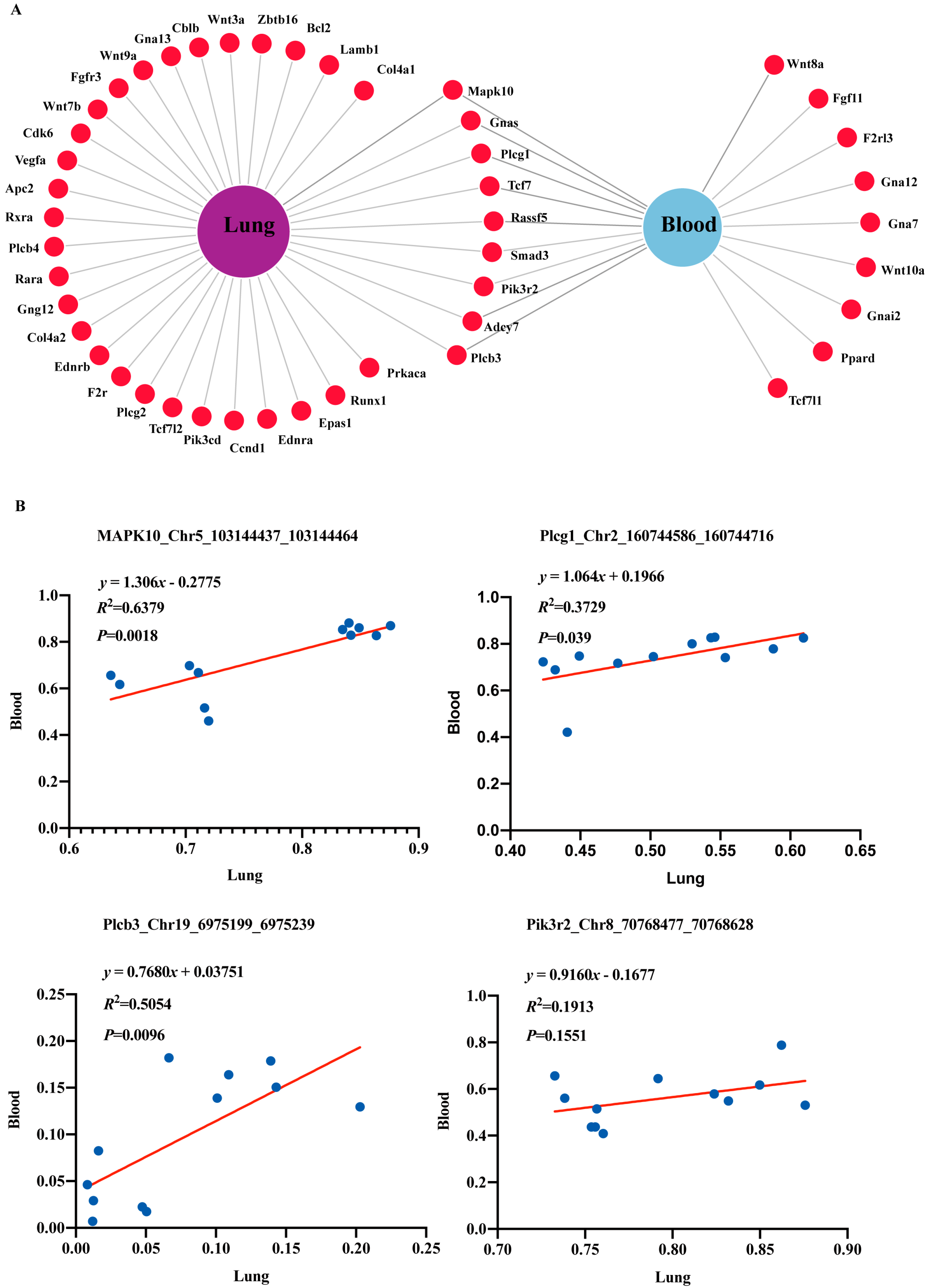

| Gene | Chr | Start | End | Adj.p | Genome Region | CpG Context | Methylation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tcf7 | chr11 | 52,282,391 | 52,282,403 | 3.03 × 10−4 | genebody; 5′-UTR | shore | Hyper |
| Smad3 | chr9 | 63,667,363 | 63,667,524 | 2.19 × 10−4 | genebody; exon; intron | other | Hyper |
| chr9 | 63,737,702 | 63,737,925 | 5.83 × 10−3 | genebody; intron | other | Hyper | |
| Mapk10 | chr5 | 103,144,437 | 103,144,464 | 1.60 × 10−3 | genebody; 5′-UTR | other | Hyper |
| Plcg1 | chr2 | 160,744,586 | 160,744,716 | 3.60 × 10−3 | genebody; intron | other | Hyper |
| Gnas | chr2 | 174,300,082 | 174,300,258 | 5.31 × 10−8 | genebody; 3′-UTR | Island; shore | Hyper |
| Plcb3 | chr19 | 6,975,199 | 6,975,239 | 2.38 × 10−11 | promoter; upstream 2k | shore | Hyper |
| Rassf5 | chr1 | 131,199,252 | 131,199,429 | 8.22 × 10−9 | genebody; intron | other | Hypo |
| Adcy7 | chr8 | 88,288,484 | 88,288,659 | 3.60 × 10−3 | genebody; 5′-UTR | other | Hypo |
| Pik3r2 | chr8 | 70,768,477 | 70,768,628 | 2.57 × 10−5 | genebody; 3′-UTR | Island; shore | Hypo |
| Gene | Chr | Start | End | Adj.p | Genome Region | CpG Context | Methylation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tcf7 | chr11 | 52,283,626 | 52,283,697 | 2.90 × 10−2 | promoter | other | Hyper |
| Mapk10 | chr5 | 103,144,437 | 103,144,464 | 2.56 × 10−4 | genebody; 5′-UTR | other | Hyper |
| Plcg1 | chr2 | 160,744,586 | 160,744,716 | 1.85 × 10−2 | genebody; intron | other | Hyper |
| Plcb3 | chr19 | 6,975,199 | 6,975,239 | 7.49 × 10−11 | Promoter | shore | Hyper |
| chr19 | 6,955,776 | 6,955,844 | 4.03 × 10−6 | genebody; exon | other | Hyper | |
| Rassf5 | chr1 | 131,187,911 | 131,188,029 | 1.95 × 10−3 | genebody; intron | other | Hyper |
| chr1 | 131,224,949 | 131,225,105 | 4.65 × 10−4 | genebody; intron | other | Hypo | |
| Adcy7 | chr8 | 88,291,538 | 88,291,629 | 1.16 × 10−2 | genebody; 5′-UTR | other | Hyper |
| Pik3r2 | chr8 | 70,768,476 | 70,768,628 | 2.16 × 10−2 | genebody; 3′-UTR | Island; shore | Hypo |
| Smad3 | chr9 | 63,740,160 | 63,740,360 | 1.54 × 10−2 | genebody; intron | other | Hypo |
| Experimental Group | Time Points | Sample Size | Purpose | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exposure Period | Observation Period | ||||
| Wild type | Control | 4 weeks | 8 weeks | 6 | RRBS and MassArray |
| Radon exposure | 4 weeks | 8 weeks | 6 | RRBS and MassArray | |
| GEMM | Control | 4 weeks | 8 weeks | 6 | Expression validation |
| Radon exposure | 4 weeks | 8 weeks | 6 | Expression validation | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, Z.; Chen, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, L.; Zhu, J.; Hou, Y.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, P.-K.; et al. Characterization of DNA Methylation Episignatures for Radon-Induced Lung Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6873. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146873
Yan Z, Chen H, Liu Y, Zhou L, Zhu J, Hou Y, Zhang X, Chen Z, Wang Y, Zhou P-K, et al. Characterization of DNA Methylation Episignatures for Radon-Induced Lung Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(14):6873. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146873
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Ziyan, Huixi Chen, Yuhao Liu, Lin Zhou, Jiaojiao Zhu, Yifan Hou, Xinyu Zhang, Zhongmin Chen, Yilong Wang, Ping-Kun Zhou, and et al. 2025. "Characterization of DNA Methylation Episignatures for Radon-Induced Lung Cancer" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 14: 6873. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146873
APA StyleYan, Z., Chen, H., Liu, Y., Zhou, L., Zhu, J., Hou, Y., Zhang, X., Chen, Z., Wang, Y., Zhou, P.-K., & Gu, Y. (2025). Characterization of DNA Methylation Episignatures for Radon-Induced Lung Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(14), 6873. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146873






