Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Mitigates Silver Nanoparticle (AgNP)-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis via iNOS/CD68/CASP3/TWIST1 Regulation: An Experimental Study and Bioinformatics Analysis †
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Background
1.2. Problem Statement/Hypothesis
1.3. Aim
2. Results
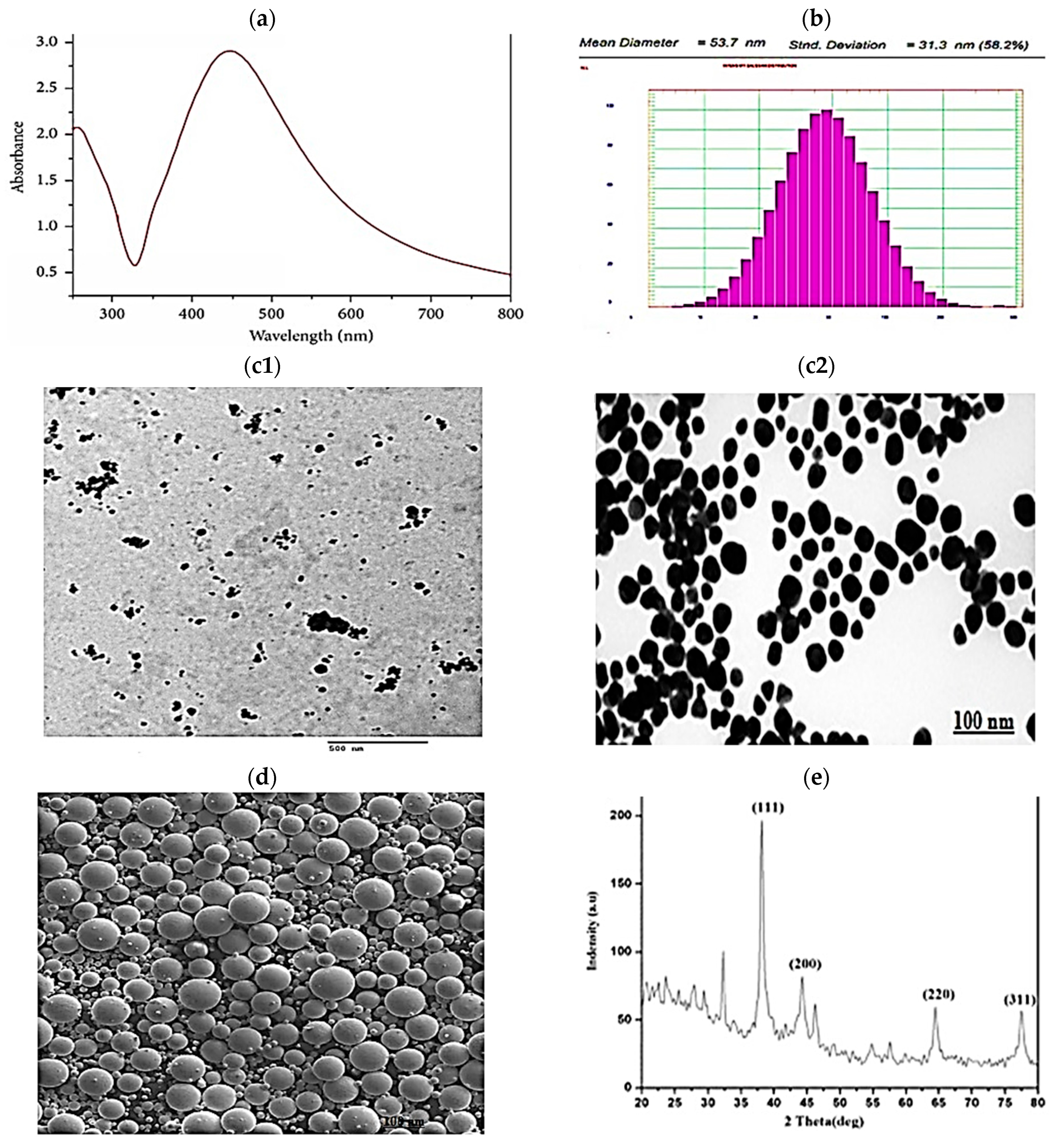
2.1. AgNP Characterization Results
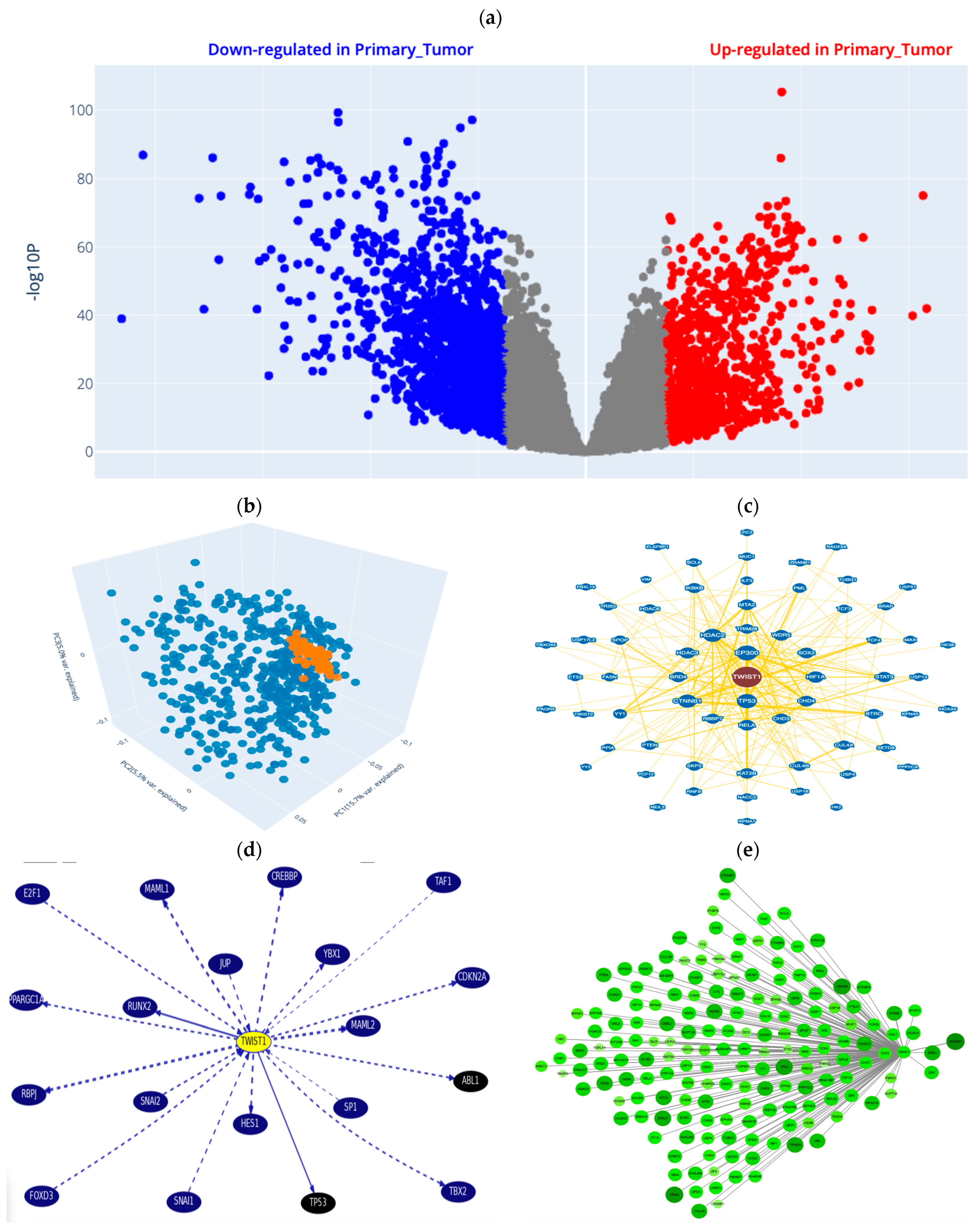
2.2. Bioinformatics/In Silico Analysis (Figure 2)
2.2.1. DEGs from Online Datasets in Lung Cancer
2.2.2. Data Sourcing
2.2.3. Data Processing Results
Gene–Gene and Protein–Protein Interactions (PPIs)
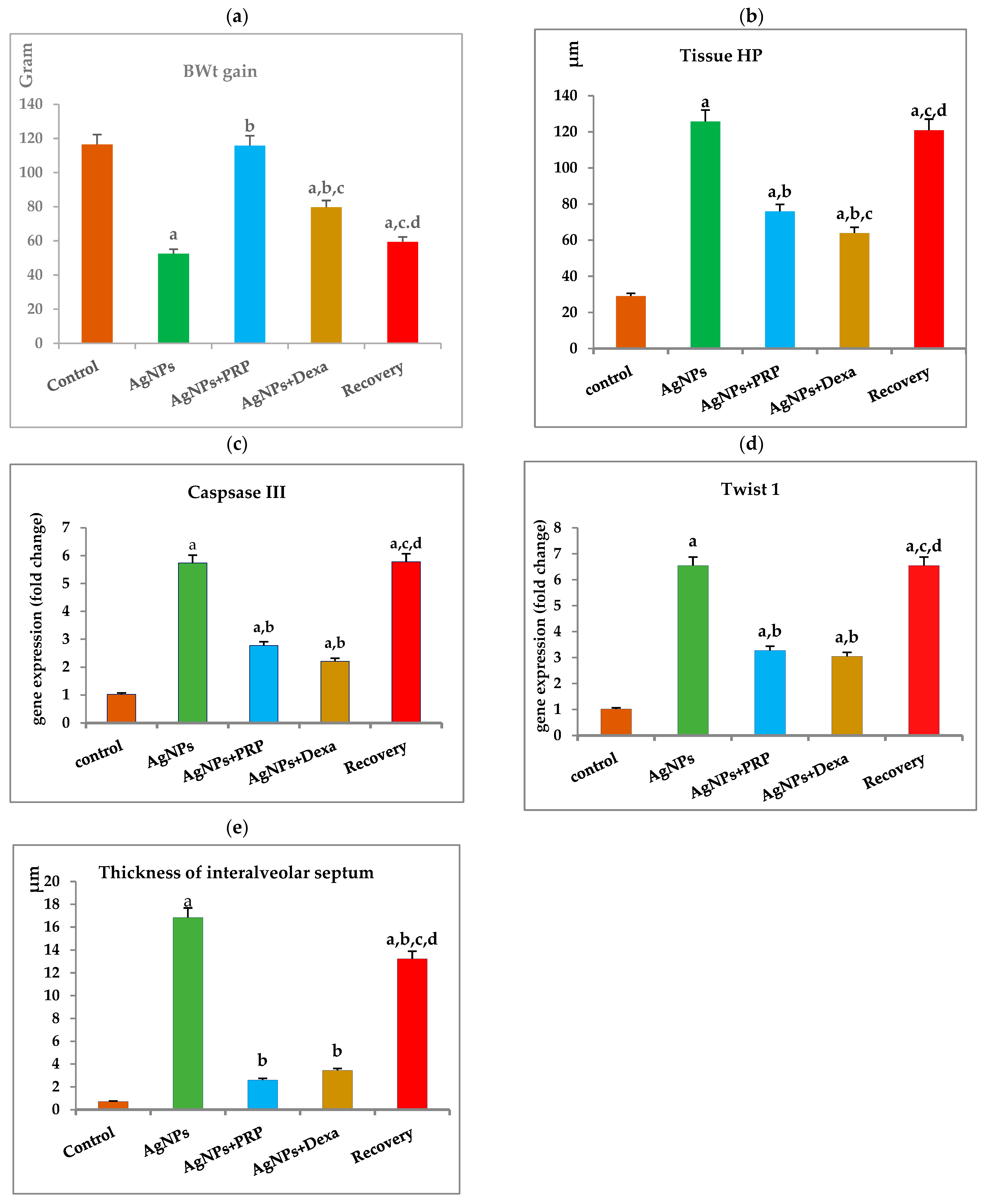
2.3. Changes in Body Weight (BWt) in the Different Groups
2.4. Levels of the Lung Tissue Fibrosis Marker Hydroxyproline (HP) in the Different Groups
2.5. PRP Alleviates the Expression of the Apoptotic Marker CASP3 and the Fibrosis Indicator TWIST1
2.6. Histological Studies Results
2.6.1. Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) Staining
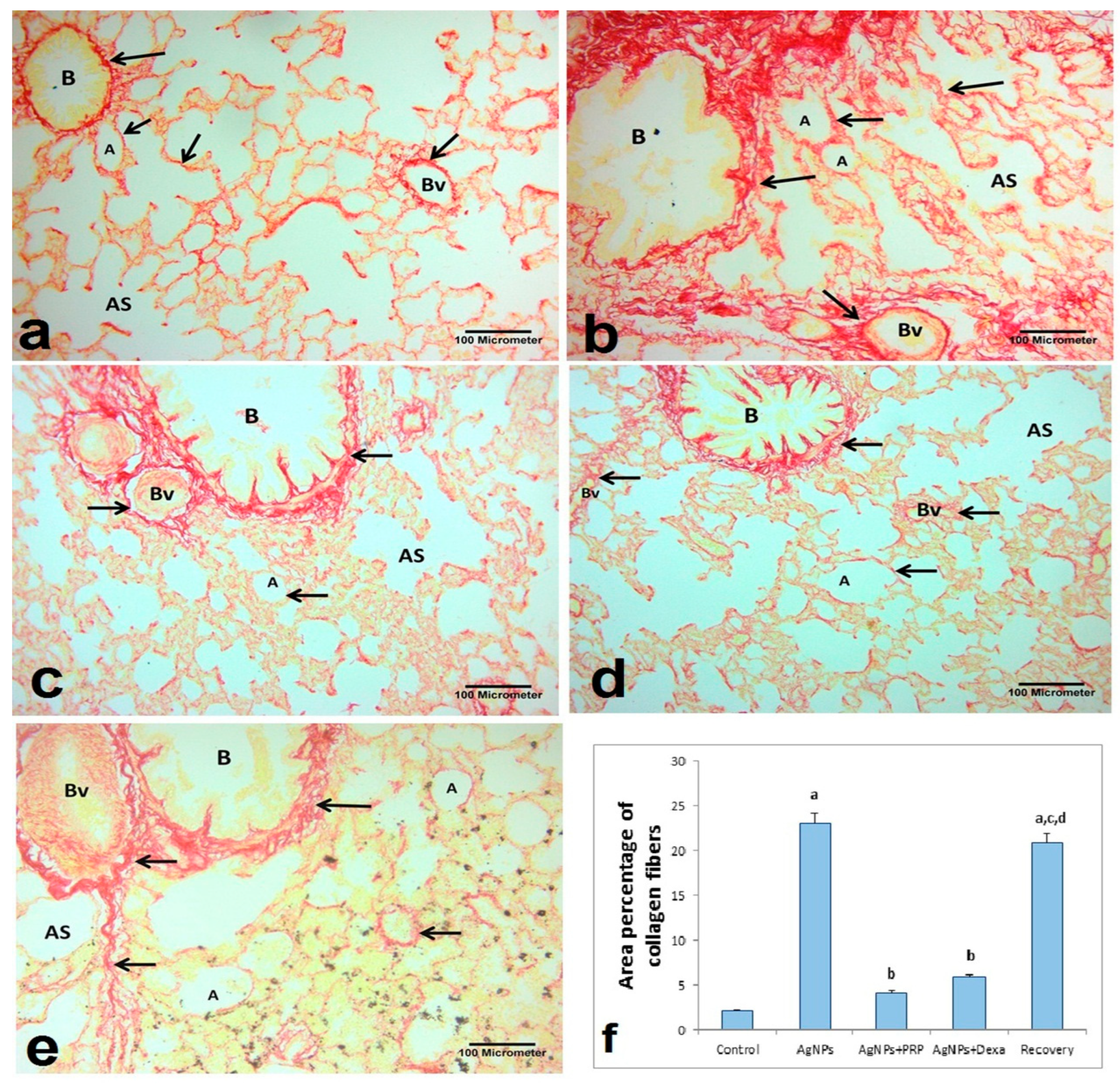
2.6.2. Sirius Red Stain
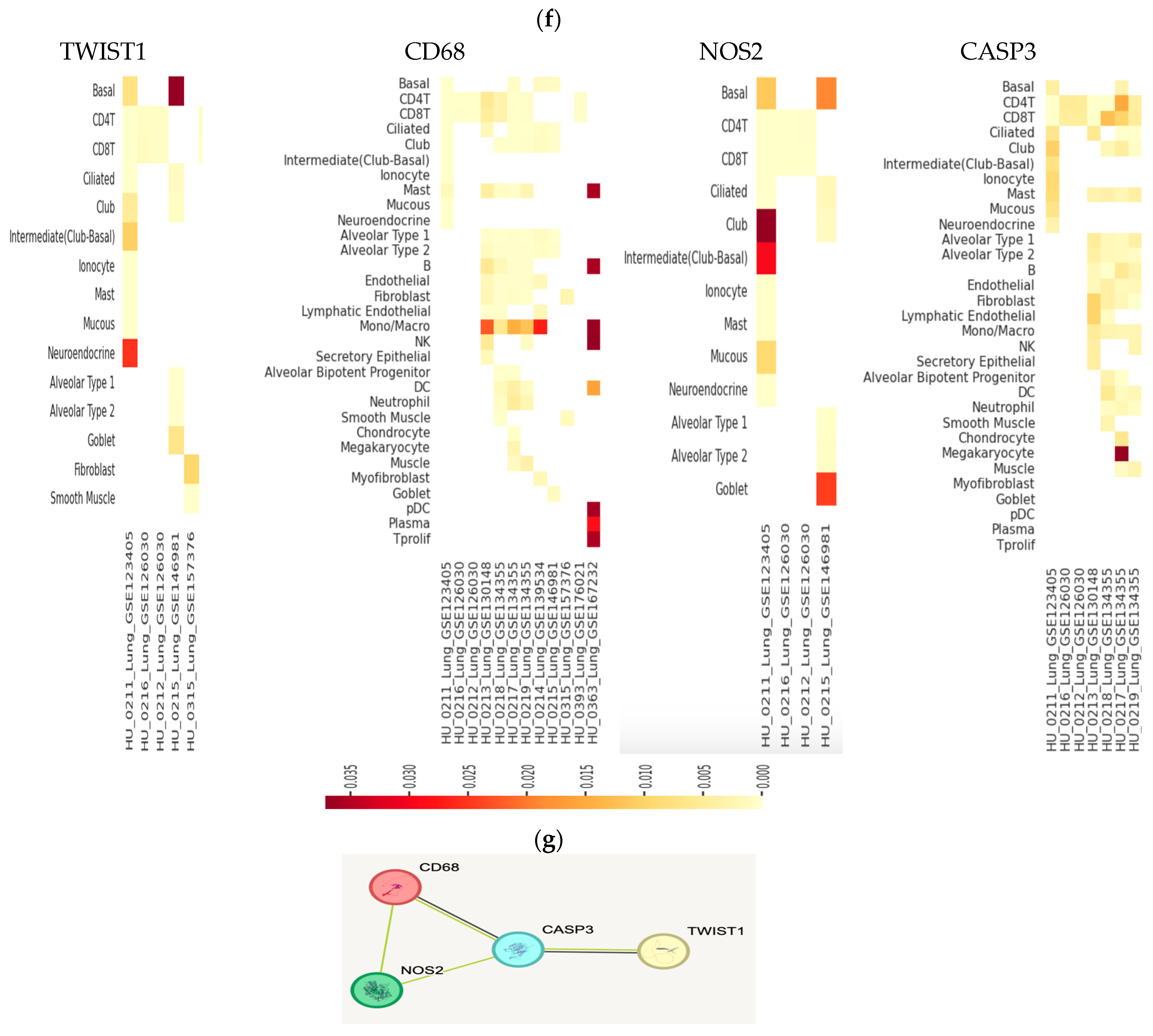
2.7. Immunohistochemistry Results
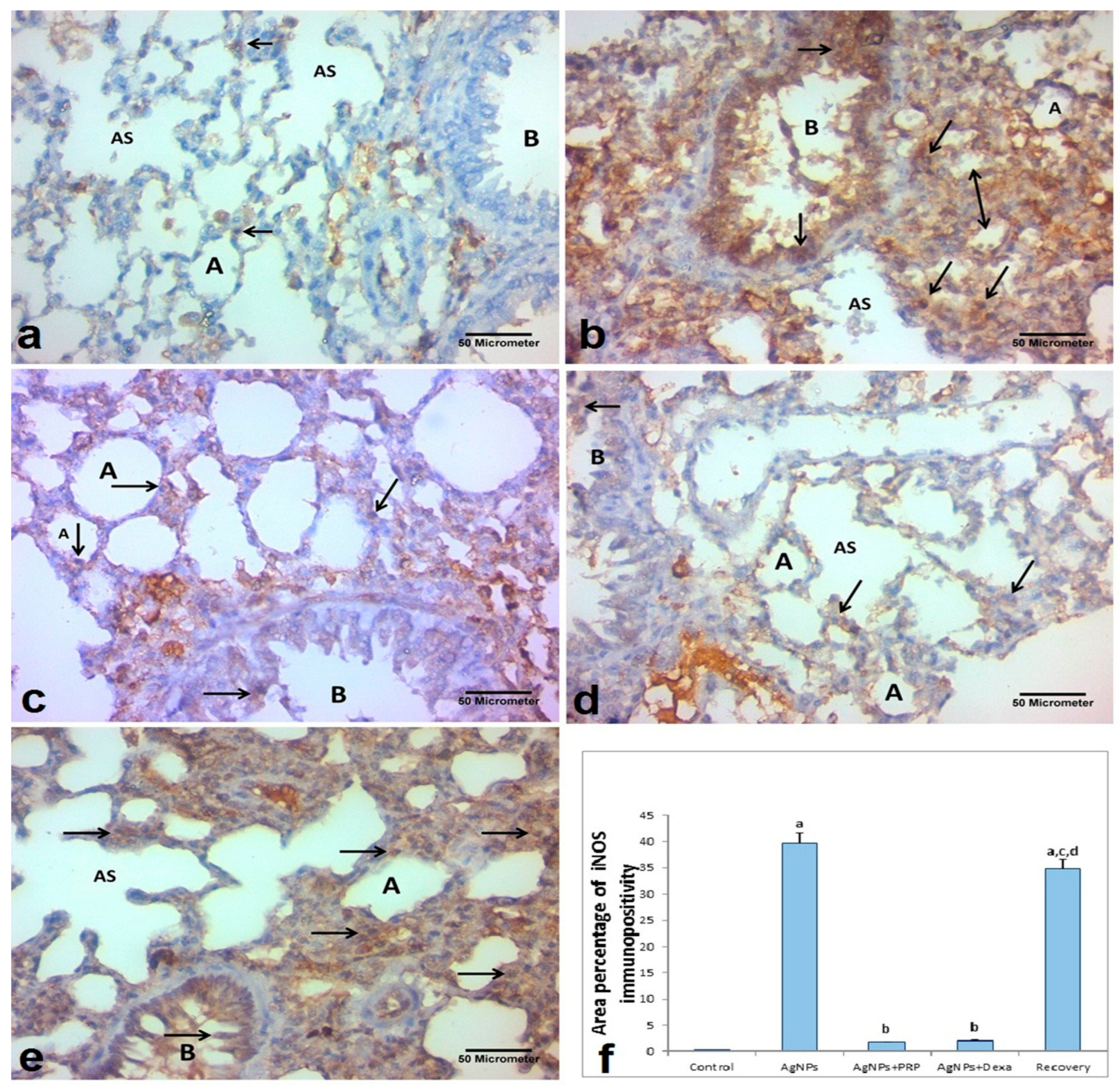
2.7.1. iNOS
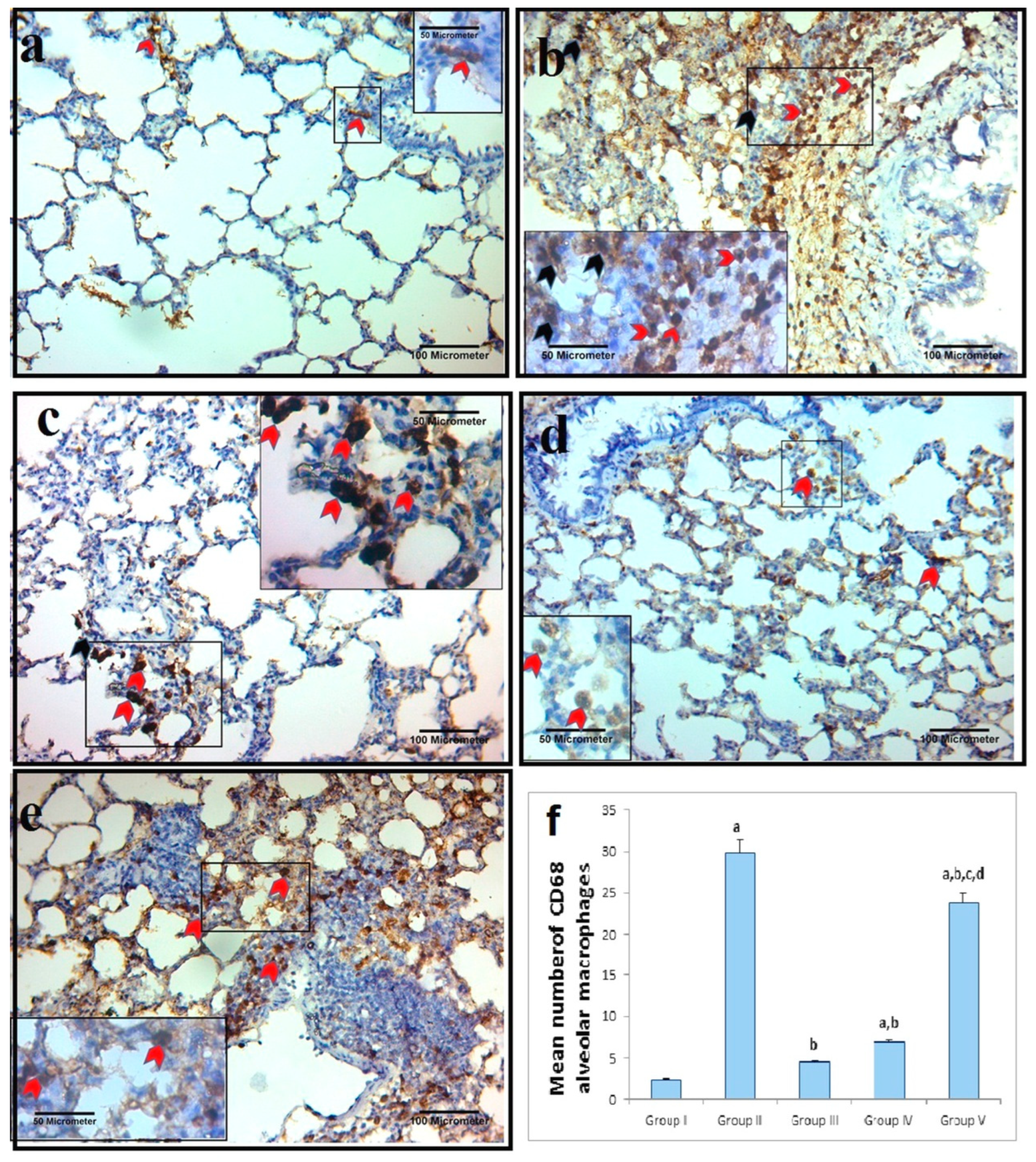
2.7.2. Alveolar Macrophage IHC Response to Cluster of Differentiation 68 (CD68)
2.7.3. Morphometric Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Drugs, Chemicals, Reagents, Antibodies, and Kits
4.2. AgNP Biosynthesis
4.3. The AgNP Suspension Was Purified via Centrifugation [63,64]
4.4. AgNP Characterization
4.5. Bioinformatics/In Silico Analysis
4.5.1. DGE of the Different Genes from Online Datasets in Lung Cancer
4.5.2. Data Sourcing
4.5.3. Data Processing
4.6. PRP Preparation
4.7. Experimental Design
4.7.1. Sample Size and Study Power
4.7.2. Experimental Protocol (Figure 8)

4.8. Body Weight
4.9. Biochemical Assays
4.9.1. Detection of HP Levels per Lung
4.9.2. Detection of the Gene Expression of CASP3 and TWIST1 in Lung Tissue via Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT–PCR)
4.10. Histological Analysis
4.11. Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
4.11.1. iNOS and CD68
4.11.2. Morphometric Studies
- The interalveolar septa thickness in H&E-stained sections at 400× magnification;
- Sirius Red-stained sections at ×200 magnification; the mean percentage area of red-stained collagen fibers/μm2 in the lung interstitium and around the pulmonary blood vessels [77];
- At 400× magnification, the mean percentage of positive iNOS immunoreactivity in the sections stained with anti-iNOS antibodies was evaluated [73];
4.12. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AgNPs | Silver nanoparticles |
| ANOVA | One-way analysis of variance |
| BWt | Body weight |
| CaCl2 | Calcium chloride |
| CD68 | Cluster of differentiation 68 |
| DAB | Diaminobenzidine |
| DLS | Dynamic light scattering |
| Fcc | Face-centered cubic |
| H&E | Hematoxylin and eosin |
| HP | Hydroxyproline (HP) |
| IHC | Immunohistochemical |
| iNOS | Inducible nitric oxide synthetase |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline |
| PF | Pulmonary fibrosis |
| PPP | Platelet-poor plasma |
| qRT–PCR | Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscope |
| TEM | Transmission electron microscopy |
| XRD | X-ray diffraction |
References
- Yoo, H.; Chung, M.P. Clinical implications of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and lung cancer. Precis. Future Med. 2025, 9, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaee, R.; Hosseinzadeh, H. Pulmonary Fibrosis. In Comprehensive Pharmacology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 803–811. [Google Scholar]
- Hamdy, N.M.; Basalious, E.B.; El-Sisi, M.G.; Nossier, E.S.; Abadi, A.H. Advancements in current one-size-fits-all therapies compared to future treatment innovations for better improved chemotherapeutic outcomes: A step-toward personalized medicine. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2024, 40, 1943–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Mesallamy, H.O.; Diab, M.R.; Hamdy, N.M.; Dardir, S.M. Cell-based regenerative strategies for treatment of diabetic skin wounds, a comparative study between human umbilical cord blood-mononuclear cells and calves’ blood haemodialysate. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e89853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez, M.; Beitia, M.; Pompei, O.; Jorquera, C.; Sánchez, P.; Knörr, J.; Soldado, F.; López, L.; Oraa, J.; Bilbao, A.M.; et al. Isolation, Activation, and Mechanism of Action of Platelet-Rich Plasma and Its Applications for Joint Repair. In Regenerative Medicine; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Fice, M.P.; Miller, J.C.; Christian, R.; Hannon, C.P.; Smyth, N.; Murawski, C.D.; Cole, B.J.; Kennedy, J.G. The Role of Platelet-Rich Plasma in Cartilage Pathology: An Updated Systematic Review of the Basic Science Evidence. Arthrosc. J. Arthrosc. Relat. Surg. 2019, 35, 961–976.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berndt, S.; Turzi, A.; Modarressi, A. Production of Autologous Platelet-Rich Plasma for Boosting In Vitro Human Fibroblast Expansion. J. Vis. Exp. JoVE 2021, 168, e60816. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Teichtahl, A.J.; Pelletier, J.P.; Abram, F.; Wluka, A.E.; Hussain, S.M.; Martel-Pelletier, J.; Cicuttini, F.M. Knee effusion volume assessed by magnetic resonance imaging and progression of knee osteoarthritis: Data from the Osteoarthritis Initiative. Rheumatology 2019, 58, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anitua, E.; de la Fuente, M.; Sánchez-Ávila, R.M.; de la Sen-Corcuera, B.; Merayo-Lloves, J.; Muruzábal, F. Beneficial Effects of Plasma Rich in Growth Factors (PRGF) Versus Autologous Serum and Topical Insulin in Ocular Surface Cells. Curr. Eye Res. 2023, 48, 456–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beitia, M.; Delgado, D.; Mercader, J.; Sánchez, P.; López de Dicastillo, L.; Sánchez, M. Action of Platelet-Rich Plasma on In Vitro Cellular Bioactivity: More than Platelets. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, J.; Tomás-Hernández, S.; García, T.; Mulero, M.; Gómez, M.; Domingo, J.L.; Sánchez, D.J. Oral exposure to silver nanoparticles increases oxidative stress markers in the livers of male rats and deregulates the insulin signaling pathway and p53 and cleaved caspase 3 protein expression. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 115, 398–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noga, M.; Milan, J.; Frydrych, A.; Jurowski, K. Toxicological Aspects, Safety Assessment, and Green Toxicology of Silver Nanoparticles (AgNPs)-Critical Review: State of the Art. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehzad, A.; Qureshi, M.; Jabeen, S.; Ahmad, R.; Alabdalall, A.H.; Aljafary, M.A.; Al-Suhaimi, E. Synthesis, characterization and antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles using Rhazya stricta. PeerJ 2018, 6, e6086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemmar, A.; Al-Salam, S.; Beegam, S.; Zaaba, N.E.; Elzaki, O.; Yasin, J.; Ali, B.H. Assessment of the Hepatotoxicity of Intratracheally Instilled Silver Nanoparticles in Hypertensive Mice. Hamdan Med. J. 2023, 16, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Lu, J.; Liu, N.; Lu, W.; Li, Y.; Shang, C.; Li, X.; Hu, L.; Jiang, G. Antiviral Properties of Silver Nanoparticles against SARS-CoV-2: Effects of Surface Coating and Particle Size. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altwaijry, N.; El-Masry, T.A.; Alotaibi, B.; Tousson, E.; Saleh, A. Therapeutic effects of rocket seeds (Eruca sativa L.) against testicular toxicity and oxidative stress caused by silver nanoparticles injection in rats. Environ. Toxicol. 2020, 35, 952–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamdy, N.M.; Boseila, A.A.; Ramadan, A.; Basalious, E.B. Iron Oxide Nanoparticles-Plant Insignia Synthesis with Favorable Biomedical Activities and Less Toxicity, in the “Era of the-Green”: A Systematic Review. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamdy, N.M.; Eskander, G.; Basalious, E.B. Insights on the Dynamic Innovative Tumor Targeted-Nanoparticles-Based Drug Delivery Systems Activation Techniques. Int. J. Nanomed. 2022, 17, 6131–6155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Vega, J.G.; García-Ramos, J.C.; Chavez-Santoscoy, R.A.; Castillo-Quiñones, J.E.; Arellano-Garcia, M.E.; Toledano-Magaña, Y. Lung Models to Evaluate Silver Nanoparticles’ Toxicity and Their Impact on Human Health. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, A.J.; Cemlyn-Jones, J.; Robalo Cordeiro, C. Nanoparticles, nanotechnology and pulmonary nanotoxicology. Rev. Port. De Pneumol. 2013, 19, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqahtani, S.; Xia, L.; Shannahan, J.H. Enhanced silver nanoparticle-induced pulmonary inflammation in a metabolic syndrome mouse model and resolvin D1 treatment. Part. Fiber Toxicol. 2022, 19, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Gong, L.; Zhang, L.; Wang, H.; Qi, X.; Wu, X.; Xiao, Y.; Cai, Y.; Liu, L.; Li, X.; et al. Short courses of low dose dexamethasone delay bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis in rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2006, 536, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano-Mollar, A.; Closa, D.; Prats, N.; Blesa, S.; Martinez-Losa, M.; Cortijo, J.; Estrela, J.M.; Morcillo, E.J.; Bulbena, O. In vivo antioxidant treatment protects against bleomycin-induced lung damage in rats. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2003, 138, 1037–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Chen, H.; Yu, P.; Ge, C.; Fang, M.; Zhao, X.; Geng, Q.; Wang, H. Inducible factors and interaction of pulmonary fibrosis induced by prenatal dexamethasone exposure in offspring rats. Toxicol. Lett. 2022, 359, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendee, K.; Hunyenyiwa, T.; Matus, K.; Toledo, M.; Mammoto, A.; Mammoto, T. Twist1 signaling in age-dependent decline in angiogenesis and lung regeneration. Aging 2021, 13, 7781–7799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, A.V.; Norinder, U.; Liiv, E.; Platzack, B.; Öberg, M.; Törnqvist, E. Associations between clinical signs and pathological findings in toxicity testing. Altex 2021, 38, 198–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Naggar, S.; Ayyad Ek Khandil, R.; Salem, M. Phoenix dactylifera seed extract ameliorates the biochemical toxicity induced by silver nanoparticles in mice. Egypt J. Cancer Biomed. Res. 2021, 5, 73–84. [Google Scholar]
- Tiwari, D.K.; Jin, T.; Behari, J. Dose-dependent in vivo toxicity assessment of silver nanoparticle in Wistar rats. Toxicol. Mech. Methods 2011, 21, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, N.; Yao, X.; Zhou, Q.; Faiola, F.; Jiang, G. Vitamin E attenuates silver nanoparticle-induced effects on BWtand neurotoxicity in rats. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 458, 405–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Xia, D.L.; Wang, Y.F.; Bao, N.; He, H.; Li, X.D.; Chen, Y.-P.; Gu, H.-Y. Influence of reducing agents on biosafety and biocompatibility of gold nanoparticles. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2014, 174, 2458–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; He, S.; Xu, Y.; Qi, G.; Ma, H.; Bang, J.J.; Li, P.A. Ameliorative Effect of Sodium Selenite on Silver Nanoparticles-Induced Myocardiocyte Structural Alterations in Rats. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 8281–8292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeyemi, O.S.; Adewumi, I. Biochemical Evaluation of Silver Nanoparticles in Wistar Rats. Int. Sch. Res. Not. 2014, 2014, 196091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Wang, L.; Guan, J.; Tang, C.; He, N.; Zhang, W.; Fu, S. Wound healing effects of a Curcuma zedoaria polysaccharide with platelet-rich plasma exosomes assembled on chitosan/silk hydrogel sponge in a diabetic rat model. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 117, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, S.; Yin, J.; Liu, J. Platelet-rich plasma has beneficial effects in mice with osteonecrosis of the femoral head by promoting angiogenesis. Exp. Ther. Med. 2018, 15, 1781–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, F.; Kakudo, N.; Morimoto, N.; Taketani, S.; Hara, T.; Ogawa, T.; Kusumoto, K. Platelet-rich plasma enhances the proliferation of human adipose stem cells through multiple signaling pathways. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018, 9, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roskoski, R., Jr. Cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase inhibitors as anticancer drugs. Pharmacol Res. 2019, 139, 471–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukaya, Y.; Kuroda, M.; Aoyagi, Y.; Asada, S.; Kubota, Y.; Okamoto, Y.; Nakayama, T.; Saito, Y.; Satoh, K.; Bujo, H. Platelet-rich plasma inhibits the apoptosis of highly adipogenic homogeneous preadipocytes in an in vitro culture system. Exp. Mol. Med. 2012, 44, 330–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Fu, Z.; Guan, R.; Zhao, J.; Yang, P.; Li, Y.; Yin, H.; Lai, Y.; Gong, G.; Zhao, S.; et al. Intracellular hydroxyproline imprinting following resolution of bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Eur. Respir. J. 2022, 59, 2100864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, N.; Helmi, N.; Assaf, N. Renoprotective Effect of Platelet-Rich Plasma on Cisplatin-Induced Nephrotoxicity in Rats. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018, 9658230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, N.A.; Hamza, A.; Alnahdi, H.; Ayaz, N. Biochemical and Molecular Mechanisms of Platelet-Rich Plasma in Ameliorating Liver Fibrosis Induced by Dimethylnitrosurea. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 47, 2331–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, L.P.; Stitik, T.P.; Foye, P.M.; Georgy, J.S.; Patibanda, V.; Chen, B. Use of Platelet-Rich Plasma in Intra-Articular Knee Injections for Osteoarthritis: A Systematic Review. PM R J. Inj. Funct. Rehabil. 2015, 7, 637–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everts, P.; Onishi, K.; Jayaram, P.; Lana, J.F.; Mautner, K. Platelet-Rich Plasma: New Performance Understandings and Therapeutic Considerations in 2020. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andia, I.; Maffulli, N. A Contemporary View of Platelet-Rich Plasma Therapies: Moving Toward Refined Clinical Protocols and Precise Indications. Regen. Med. 2018, 13, 717–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beitia, M.; Delgado, D.; Sánchez, P.; Vallejo de la Cueva, A.; Cugat, J.R.; Sánchez, M. Platelet Lysate Nebulization Protocol for the Treatment of COVID-19 and Its Sequels: Proof of Concept and Scientific Rationale. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, N.; Liu, Q.; Liu, J.; He, B.; Cui, L.; Li, Z.; Yun, Z.; Qu, G.; Liu, S.; Zhou, Q.; et al. Silver nanoparticle exposure attenuates the viability of rat cerebellum granule cells through apoptosis coupled to oxidative stress. Small 2013, 9, 1831–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.Y.; Li, N.J.; Cheng, F.Y.; Hsueh, J.F.; Huang, C.C.; Lu, F.-I.; Fu, T.-F.; Yan, S.-J.; Lee, Y.-H.; Wang, Y.-J. The Effect of the Chorion on Size-Dependent Acute Toxicity and Underlying Mechanisms of Amine-Modified Silver Nanoparticles in Zebrafish Embryos. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, B.H.; Chen, Z.Y.; Wang, Y.J.; Yan, S.J. Silver nanoparticles have lethal and sublethal adverse effects on development and longevity by inducing ROS-mediated stress responses. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karina, K.; Christoffel, L.M.; Novariani, R.; Rosadi, I.; Rosliana, I.; Rosidah, S.; Sobariah, S.; Fatkhurohman, N.; Puspitaningrum, N.; Hertati, Y.; et al. The Effect of Intravenous Autologous Activated Platelet-Rich Plasma Therapy on “Profibrotic Cytokine” IL-1β Levels in Severe and Critical COVID-19 Patients: A Preliminary Study. Scientifica 2021, 2021, 9427978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekerci, C.A.; Tanidir, Y.; Sener, T.E.; Sener, G.; Cevik, O.; Yarat, A.; Alev-Tuzuner, B.; Cetinel, S.; Kervancioglu, E.; Sahan, A.; et al. Effects of platelet-rich plasma against experimental ischemia/reperfusion injury in rat testis. J. Pediatr. Urol. 2017, 13, 317.e1–317.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.L.; Shih, Y.S.; Chen, Z.Y.; Cheng, F.Y.; Lu, J.Y.; Wu, Y.-H.; Wang, Y.-J. Toxic Effects and Mechanisms of Silver and Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles on Zebrafish Embryos in Aquatic Ecosystems. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousef, M.I.; Abuzreda, A.A.; Kamel, M.A. Cardiotoxicity and lung toxicity in male rats induced by long-term exposure to iron oxide and silver nanoparticles. Exp. Ther. Med. 2019, 18, 4329–4339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HDehkordi, M.; Tashakor, A.; O’Connell, E.; Fearnhead, H.O. Apoptosome-dependent myotube formation involves activation of CASP3 in differentiating myoblasts. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Li, J.; Ma, L.; Shang, H.; Zou, Z. SAR-guided development of indole-matrine hybrids as potential anticancer agents via mitochondrial stress/cytochrome c/caspase 3 signaling pathway. Bioorganic Chem. 2023, 134, 106341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Xiong, P.; Cheng, Y.; Chen, Y.; Peng, S.; Zhu, Z.Q. Enzymatic oxydate-triggered AgNPs etching: A novel signal-on photoelectrochemical immunosensing platform based on Ag@AgCl nanocubes loaded RGO plasmonic heterostructure. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 130, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Yu, Y.; Li, Y.; Yu, Y.; Duan, J.; Zou, Y.; Li, Q.; Sun, Z. Oxidative Damage and Energy Metabolism Disorder Contribute to the Hemolytic Effect of Amorphous Silica Nanoparticles. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunyenyiwa, T.; Hendee, K.; Matus, K.; Kyi, P.; Mammoto, T.; Mammoto, A. Obesity Inhibits Angiogenesis Through TWIST1-SLIT2 Signaling. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 693410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamad, N.; Malik, S.; Suchal, K.; Vasisht, S.; Tomar, A.; Arava, S.; Arya, D.S.; Bhatia, J. Metformin alleviates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in rats: Pharmacological effects and molecular mechanisms. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 97, 1544–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.C.; Zou, Z.J.; Zhou, M.G.; Chen, L.; Zhou, L.; Zheng, Y.-K.; He, Z.-J. Effects of simvastatin on the expression of inducible NOS in acute lung injury in septic rats. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 15106–15111. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Jin, X.; Yu, D.; Liu, G. Suppression of NLRP3 and NF-κB signaling pathways by α-Cyperone by activating SIRT1 contributes to attenuation of LPS-induced acute lung injury in mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019, 76, 105886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, D.S.; Silva, R.M.; Lee, D.; Edwards, P.C.; Sharmah, A.; Guo, T.; Pinkerton, K.E.; Van Winkle, L.S. Persistence of silver nanoparticles in the rat lung: Influence of dose, size, and chemical composition. Nanotoxicology 2015, 9, 591–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everts, P.A.; Sadeghi, P.; Smith, D.R. Basic Science of Autologous Orthobiologics: Part 1. Platelet-Rich Plasma. Phys. Med. Rehabil. Clin. N. Am. 2023, 34, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoeib, H.M.; Keshk, W.A.; Foda, A.M.; Abo El Noeman, S. A study on the regenerative effect of platelet-rich plasma on experimentally induced hepatic damage in albino rats. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2018, 96, 630–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fareid, M.A.; El-Sherbiny, G.M.; Askar, A.A.; Abdelaziz, A.M.; Hegazy, A.M.; Ab Aziz, R.; Hamada, F.A. Impeding Biofilm-Forming Mediated Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus and Virulence Genes Using a Biosynthesized Silver Nanoparticles–Antibiotic Combination. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashem, A.H.; Abdelaziz, A.M.; Askar, A.A.; Fouda, H.M.; Khalil, A.; Abd-Elsalam, K.A.; Khaleil, M.M. Bacillus megaterium-Mediated Synthesis of Selenium Nanoparticles and Their Antifungal Activity against Rhizoctonia solani in Faba Bean Plants. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.A.; Selim, M.S.; El-Safty, S.A.; Hashem, A.I.; Selim, M.M.; Shenashen, M.A. Antimicrobial and immunomodulatory potential of nanoscale hierarchical one-dimensional zinc oxide and silicon carbide materials. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2021, 263, 124376. [Google Scholar]
- Pazzini, J.; Nardi, A.; Huppes, R.; Gering, A.; Ferreira, M.; Silveira, C.P.; Luzzi, M.C.; Santos, R. Method to obtain platelet-rich plasma from rabbits (Oryctolagus cuniculus). Pesqui. Veterinária Bras. 2016, 36, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemnejad, S.; Allameh, A.; Gharehbaghian, A.; Soleimani, M.; Amirizadeh, N.; Jazayeri, M. Efficient replacing of fetal bovine serum with human platelet releasate during propagation and differentiation of human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells to functional hepatocytes-like cells. Vox Sang. 2008, 95, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousef, J.; Hendi, H.; Hakami, S.F. Toxicity of silver nanoparticles after Injected intraperitoneally in rats. J. Am Sci. 2012, 8, 589–593. [Google Scholar]
- Hesami, Z.; Jamshidzadeh, A.; Ayatollahi, M.; Geramizadeh, B.; Farshad, O.; Vahdati, A. Effect of Platelet-Rich Plasma on CCl4-Induced Chronic Liver Injury in Male Rats. Int. J. Hepatol. 2014, 2014, 932930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minigalieva, I.A.; Katsnelson, B.A.; Panov, V.G.; Privalova, L.I.; Varaksin, A.N.; Gurvich, V.B.; Sutunkova, M.P.; Shur, V.Y.; Shishkina, E.V.; Valamina, I.E.; et al. In vivo toxicity of copper oxide, lead oxide and zinc oxide nanoparticles acting in different combinations and its attenuation with a complex of innocuous bioprotectors. Toxicology 2017, 380, 72–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kmiec, Z.J.A. Kiernan. Histological and Histochemical Methods: Theory and Practice. 5th edition, Scion Publishing, 2015, 571 pp. Folia Histochem. Et Cytobiol. 2016, 54, 58–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bancroft, J.D.; Gamble, M. Theory and Practice of Histological Techniques; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008; p. ix. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, R.-Q.; Guo, P.-F.; Ma, Z.; Chang, C.; Meng, Q.-N.; Gao, Y.; Khan, I.; Wang, X.; Cui, Z. Effects of simvastatin on iNOS and caspase-3 levels and oxidative stress following smoke inhalation injury. Mol. Med. Rep. 2020, 22, 3405–3417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrolyk, V.; Schneberger, D.; Le, K.; Wobeser, B.K.; Singh, B. Mouse model to study pulmonary intravascular macrophage recruitment and lung inflammation in acute necrotizing pancreatitis. Cell Tissue Res. 2019, 378, 97–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Vara, J.A.; Kiupel, M.; Baszler, T.; Bliven, L.; Brodersen, B.; Chelack, B.; Czub, S.; Del Piero, F.; Dial, S.; Ehrhart, E.J.; et al. Suggested guidelines for immunohistochemical techniques in veterinary diagnostic laboratories. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2008, 20, 393–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afsar, T.; Razak, S.; Khan, M.R.; Almajwal, A. Acacia hydaspica ethyl acetate extract protects against cisplatin-induced DNA damage, oxidative stress and testicular injuries in adult male rats. BMC Cancer 2017, 17, 883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, E.C. Quantitative analysis of histological staining and fluorescence using ImageJ. Anat. Rec. 2013, 296, 378–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nouno, T.; Okamoto, M.; Ohnishi, K.; Kaieda, S.; Tominaga, M.; Zaizen, Y.; Ichiki, M.; Momosaki, S.; Nakamura, M.; Fujimoto, K.; et al. Elevation of pulmonary CD163(+) and CD204(+) macrophages is associated with the clinical course of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis patients. J. Thorac. Dis. 2019, 11, 4005–4017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafa, A.M.; Hamdy, N.M.; El-Mesallamy, H.O.; Abdel-Rahman, S.Z. Glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1)-based therapy upregulates LXR-ABCA1/ABCG1 cascade in adipocytes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 468, 900–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafa, A.M.; Hamdy, N.M.; Abdel-Rahman, S.Z.; El-Mesallamy, H.O. Effect of vildagliptin and pravastatin combination on cholesterol efflux in adipocytes. IUBMB Life 2016, 68, 535–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, M.M.; Albanese, C.; Hamdy, N.M.; Sultan, A.S. Rise of the natural red pigment ‘prodigiosin’ as an immunomodulator in cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 2022, 22, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atta, H.; Alzahaby, N.; Hamdy, N.M.; Emam, S.H.; Sonousi, A.; Ziko, L. New trends in synthetic drugs and natural products targeting 20S proteasomes in cancers. Bioorganic Chem. 2023, 133, 106427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Mesallamy, H.O.; Hamdy, N.M.; Rashed, W.M.; Hamdy, N. High-dose methotrexate in Egyptian pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia: The impact of ABCG2 C421A genetic polymorphism on plasma levels, what is next? J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 140, 1359–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, Y.-F.; Huang, K.-C.; Chen, H.-Y.; Shieh, T.-M.; Huang, Y.-J. Hinokitiol Inhibits Breast Cancer Cells In Vitro Stemness-Progression and Self-Renewal with Apoptosis and Autophagy Modulation via the CD44/Nanog/SOX2/Oct4 Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 3904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Gene | Primer Sequence |
|---|---|
| CASP3 | Forward primer 5′-GTGGAACTGACGATGATATGGC-3′ Reverse primer 5′-CGCAAAGTGACTGGATGAACC-3′ |
| TWIST1 | Forward primer 5′-CCGGAGACCTAGATGTCATTGT-3′ Reverse primer 5′-CTGGGAATCTCTGTCCACCG-3′ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abdelmohsen, S.R.; Abdelgalil, R.M.; Elmaghraby, A.M.; Negm, A.M.; Hammad, R.; Efthimiadou, E.K.; Seriah, S.; El Magdoub, H.M.; Elariny, H.; Farrag, I.; et al. Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Mitigates Silver Nanoparticle (AgNP)-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis via iNOS/CD68/CASP3/TWIST1 Regulation: An Experimental Study and Bioinformatics Analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6782. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146782
Abdelmohsen SR, Abdelgalil RM, Elmaghraby AM, Negm AM, Hammad R, Efthimiadou EK, Seriah S, El Magdoub HM, Elariny H, Farrag I, et al. Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Mitigates Silver Nanoparticle (AgNP)-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis via iNOS/CD68/CASP3/TWIST1 Regulation: An Experimental Study and Bioinformatics Analysis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(14):6782. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146782
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbdelmohsen, Shaimaa R., Ranya M. Abdelgalil, Asmaa M. Elmaghraby, Amira M. Negm, Reham Hammad, Eleni K. Efthimiadou, Sara Seriah, Hekmat M. El Magdoub, Hemat Elariny, Islam Farrag, and et al. 2025. "Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Mitigates Silver Nanoparticle (AgNP)-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis via iNOS/CD68/CASP3/TWIST1 Regulation: An Experimental Study and Bioinformatics Analysis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 14: 6782. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146782
APA StyleAbdelmohsen, S. R., Abdelgalil, R. M., Elmaghraby, A. M., Negm, A. M., Hammad, R., Efthimiadou, E. K., Seriah, S., El Magdoub, H. M., Elariny, H., Farrag, I., El Shenawy, N., Abdelrahaman, D., Almalki, H., Askar, A. A., El-Mosely, M. M., Hakam, F. E. Z. A. E., & Hamdy, N. M. (2025). Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Mitigates Silver Nanoparticle (AgNP)-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis via iNOS/CD68/CASP3/TWIST1 Regulation: An Experimental Study and Bioinformatics Analysis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(14), 6782. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146782







