Comparative Transcriptome Analysis in Tomato Fruit Reveals Genes, Pathways, and Processes Affected by the LEC1-LIKE4 Transcription Factor
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
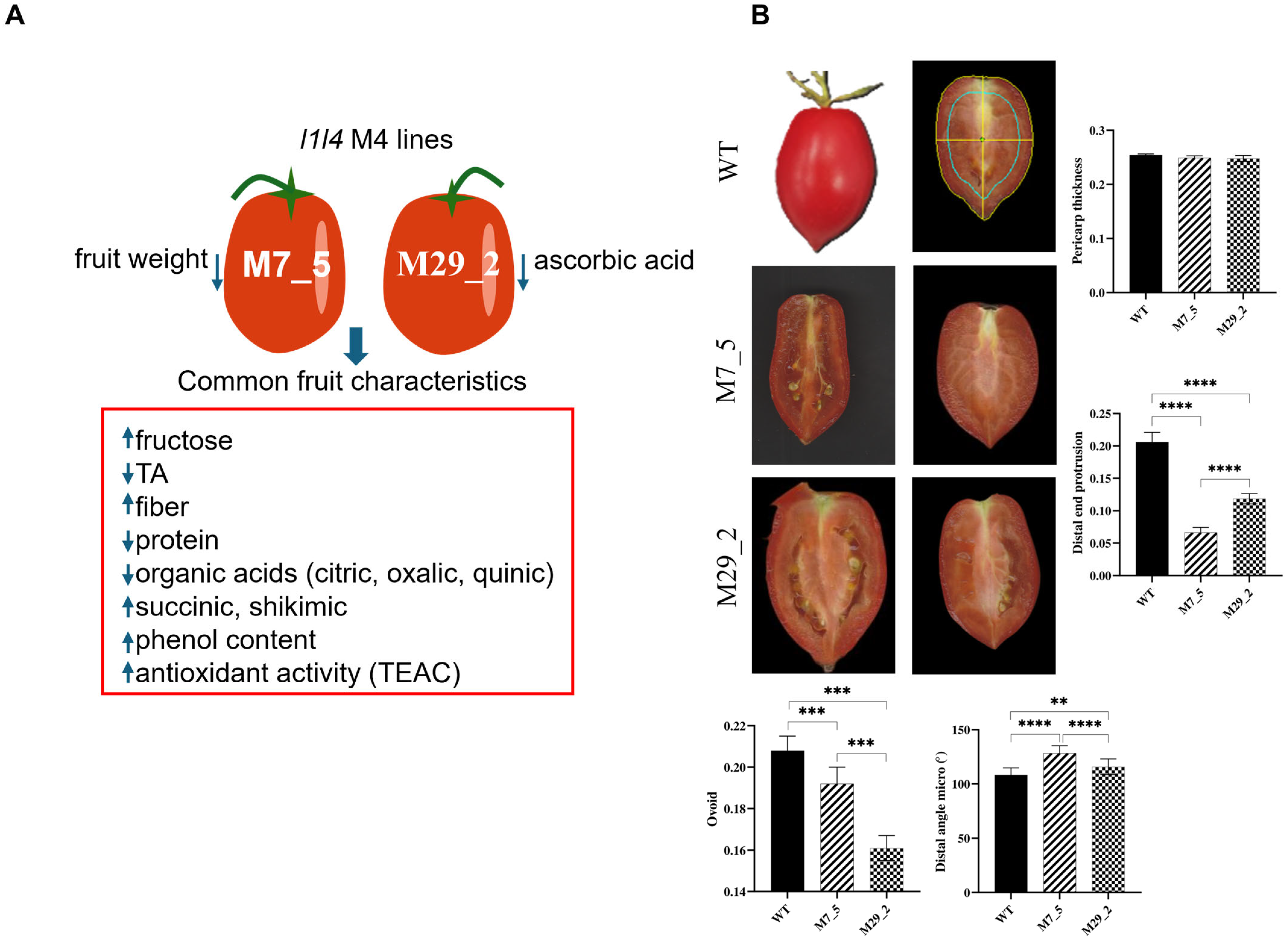
2.1. Fruit Morphometric Traits
2.2. Differentially Expressed Genes Among Samples and Groups
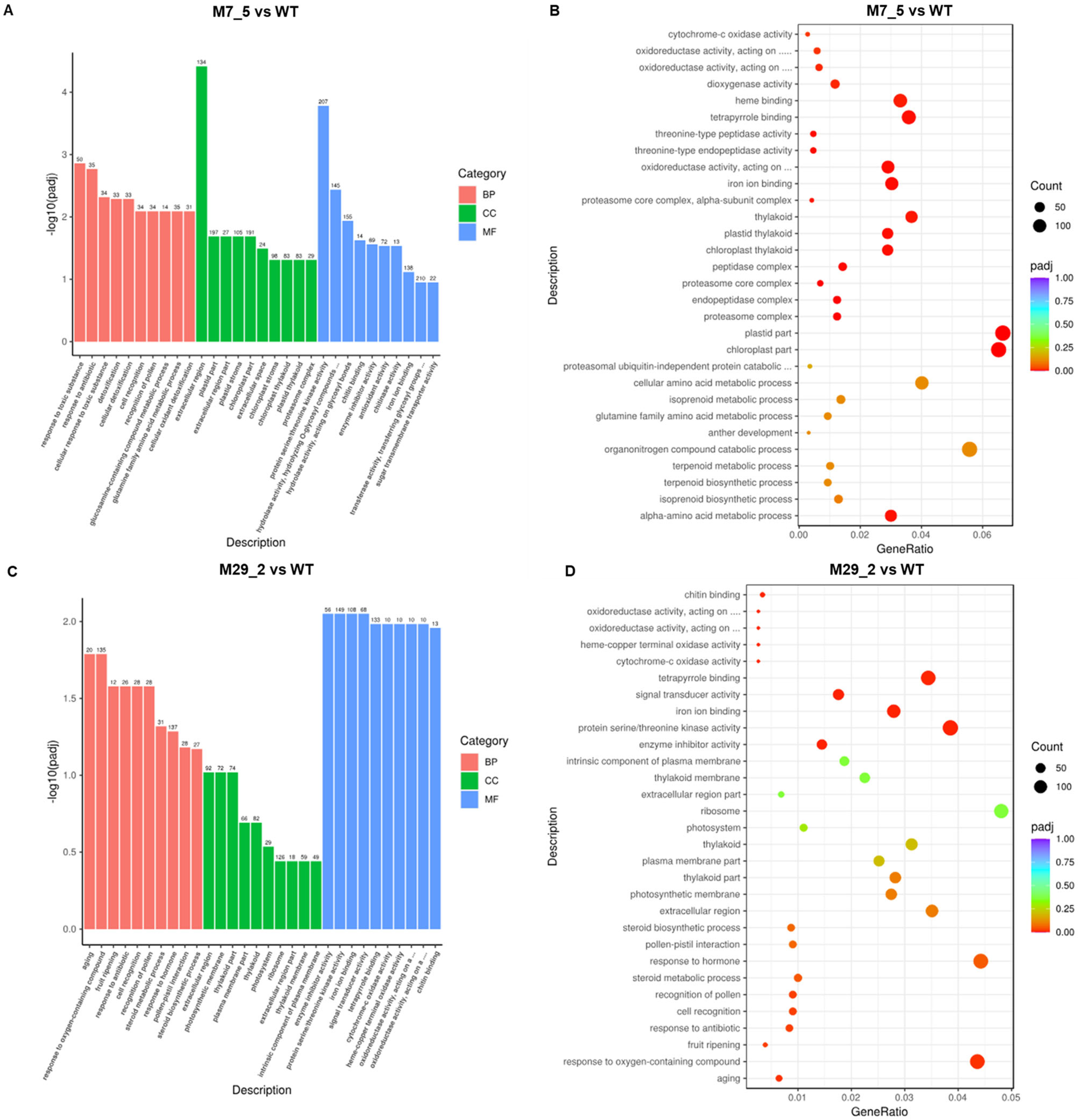
2.3. GO Term Analysis
2.4. KEGG Enrichment Analysis
2.5. Analysis of Histone-Related Genes
2.6. Analysis of TFs
2.7. Identification of Fruit Metabolism and Quality Genes
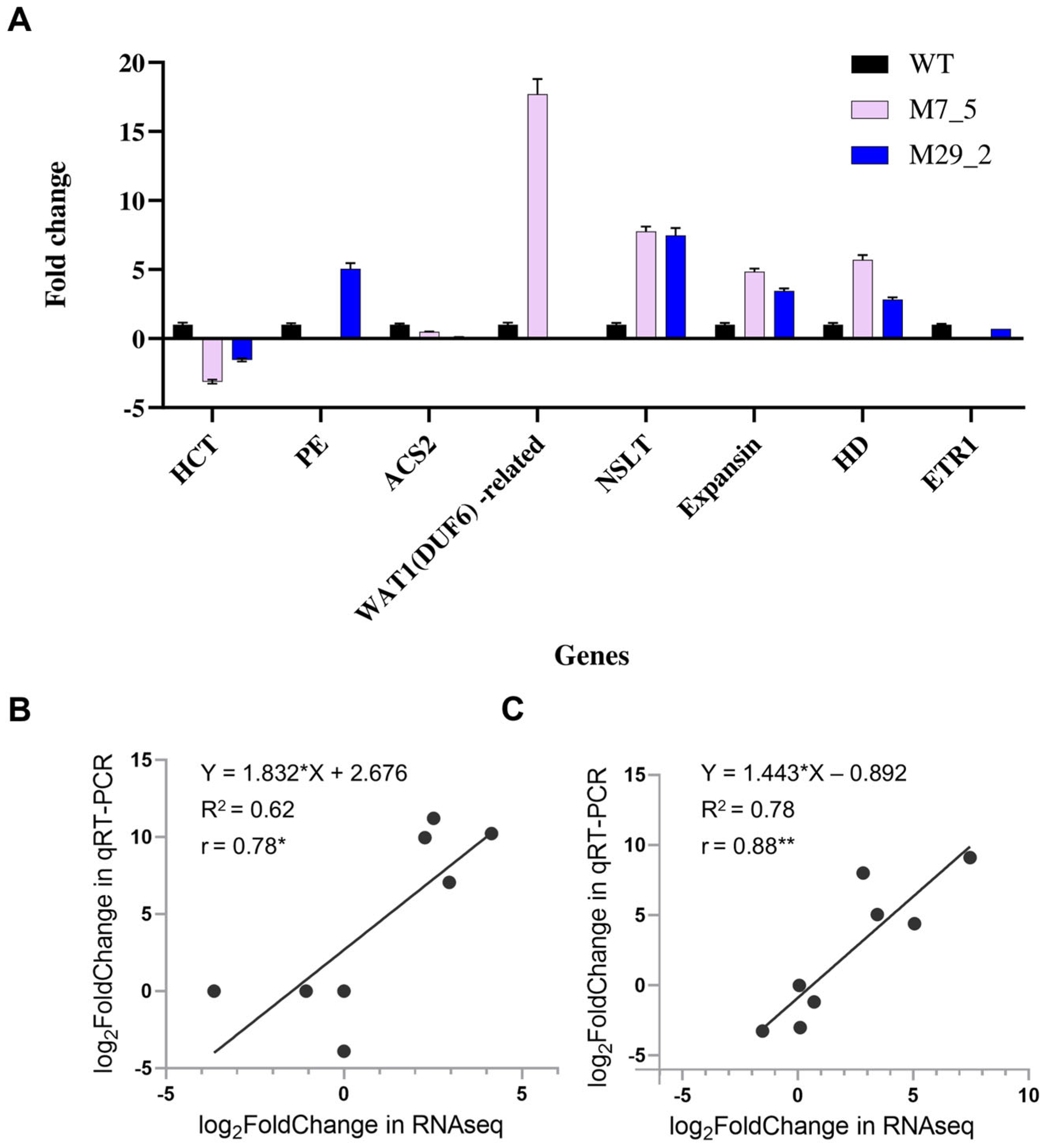
2.8. Validation of DEGs Genes with qRT-PCR Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Material
4.2. Digital Fruit Phenotyping
4.3. RNA Extraction
4.4. Preparation of cDNA Libraries for Sequencing
4.5. Bioinformatics Analysis
4.6. Real-Time Quantitative PCR (qRT-PCR) Analysis
4.7. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACS | 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate synthase |
| ADH | alcohol dehydrogenase |
| BD | binding domain |
| BP | biological processes |
| CC | cellular components |
| CESA | cellulose synthase |
| CS | citrate synthase |
| DEG | differential gene expression |
| EF1-α | Elongation factor 1-α |
| ERFs | Ethylene Response Factors |
| FDR | False Discovery Rate |
| HD | histidine decarboxylase |
| HDACs | histone deacetylases |
| HKMT | Histone methyltransferase |
| FPKM | Fragments Per Kilobase of transcript sequence per Millions base pairs sequenced |
| FRK | fructokinase |
| GGP | GDP-L-galactose phosphorylase |
| GMP | GDP-mannose pyrophosphorylase |
| GPP | L-galactose-1-phosphate phosphatase |
| GO | Gene Ontology |
| KEGG | Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes |
| KO | KEGG Orthology |
| LEA | late embryogenesis abundant protein |
| L1L4 | LEAFY-COTYLEDON1-LIKE4 |
| MDH | malate dehydrogenase |
| MF | molecular functions |
| NF-Y | nuclear factor Y |
| NSLT | non-specific lipid transfer |
| padj | adjusted p-value |
| PCA | principal component analysis |
| PG | polygalacturonase |
| PME | pectin methylesterase |
| PSY | phytoene synthase |
| qRT-PCR | real-time quantitative PCR |
| SD | standard deviation |
| TCA | tricarboxylic acid |
| TF | transcription factor |
| WT | wild-type |
| ZFN | zinc-finger nuclease |
References
- Giovannoni, J.J. Genetic regulation of fruit development and ripening. Plant Cell 2004, 16 (Suppl. S1), S170–S180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, K.; Ju, Z.; Cao, D.; Fu, D.; Zhu, H.; Zhu, B.; Luo, Y. Genome-Wide Analysis of Tomato NF-Y Factors and Their Role in Fruit Ripening. BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mantovani, R. The Molecular Biology of the CCAAT-Binding Factor NF-Y. Gene 1999, 239, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myers, Z.A.; Holt, B.F. NUCLEAR FACTOR-Y: Still Complex after All These Years? Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2018, 45, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, G.; Li, C.; Zhang, C.; Cui, L.; Ai, G.; Wang, X.; Zheng, F.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, J.; et al. NF-Y plays essential roles in flavonoid biosynthesis by modulating histone modifications in tomato. New Phytol. 2020, 229, 3237–3252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrou, N.; Tsigarida, N.; Hilioti, Z. Genome Editing of the NF-YA8 Gene Modifies Tomato Plant Architecture and Fruit Traits. Plants 2025, in press. [CrossRef]
- Hilioti, Z.; Ganopoulos, I.; Ajith, S.; Bossis, I.; Tsaftaris, A. A novel arrangement of zinc finger nuclease system for in vivo targeted genome engineering: The tomato LEC1-LIKE4 gene case. Plant Cell Rep. 2016, 35, 2241–2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilioti, Z.; Ganopoulos, I.; Bossis, I.; Tsaftaris, A. LEC1-LIKE paralog transcription factor: How to survive extinction and fit in NF-Y protein complex. Gene 2014, 543, 220–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gago, C.; Drosou, V.; Paschalidis, K.; Guerreiro, A.; Miguel, G.; Antunes, D.; Hilioti, Z. Targeted Gene Disruption Coupled with Metabolic Screen Approach to Uncover the LEAFY COTYLEDON1-LIKE4 (L1L4) Function in Tomato Fruit Metabolism. Plant Cell Rep. 2017, 36, 1065–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, G.R.; Muños, S.; Anderson, C.; Sim, S.-C.; Michel, A.; Causse, M.; Gardener, B.B.M.; Francis, D.; van der Knaap, E. Distribution ofSUN, OVATE, LC, and FASin the Tomato Germplasm and the Relationship to Fruit Shape Diversity. Plant Physiol. 2011, 156, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillaspy, G.; Ben-David, H.; Gruissem, W. Fruits: A Developmental Perspective. Plant Cell 1993, 5, 1439–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, S.; Fei, Z.; Chen, Y.-R.; Zheng, Y.; Huang, M.; Vrebalov, J.; McQuinn, R.; Gapper, N.; Liu, B.; Xiang, J.; et al. Single-Base Resolution Methylomes of Tomato Fruit Development Reveal Epigenome Modifications Associated with Ripening. Nat. Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 154–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Tang, K.; Tang, D.; Datsenka, T.; Cheng, J.; Zhang, Y.; Handa, A.K.; Zhu, J.-K. Critical Roles of DNA Demethylation in the Activation of Ripening-Induced Genes and Inhibition of Ripening-Repressed Genes in Tomato Fruit. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E4511–E4519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Liu, X.; Liu, X.; Li, Y.; Wu, K.; Hou, X. Arabidopsis NF-YCs Mediate the Light-Controlled Hypocotyl Elongation via Modulating Histone Acetylation. Mol. Plant 2017, 10, 260–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rea, S.; Eisenhaber, F.; O’Carroll, D.; Strahl, B.D.; Sun, Z.-W.; Schmid, M.; Opravil, S.; Mechtler, K.; Ponting, C.P.; Allis, C.D.; et al. Regulation of Chromatin Structure by Site-Specific Histone H3 Methyltransferases. Nature 2000, 406, 593–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karlić, R.; Chung, H.-R.; Lasserre, J.; Vlahoviček, K.; Vingron, M. Histone Modification Levels Are Predictive for Gene Expression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 2926–2931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, P.; Yu, S.; Zhu, N.; Chen, Y.-R.; Zhou, B.; Pan, Y.; Tzeng, D.; Fabi, J.P.; Argyris, J.; Garcia-Mas, J.; et al. Genome Encode Analyses Reveal the Basis of Convergent Evolution of Fleshy Fruit Ripening. Nat. Plants 2018, 4, 784–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eulgem, T.; Rushton, P.J.; Robatzek, S.; Somssich, I.E. The WRKY superfamily of plant transcription factors. Trends Plant Sci. 2000, 5, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; Tian, Y.; Jia, N.; Chen, S.; Shi, N.; Huang, X.; Zhou, C.; Yu, Y.; et al. Regulation of Ethylene-Responsive SlWRKYs Involved in Color Change during Tomato Fruit Ripening. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allan, A.C.; Hellens, R.P.; Laing, W.A. MYB Transcription Factors That Colour Our Fruit. Trends Plant Sci. 2008, 13, 99–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feller, A.; Machemer, K.; Braun, E.L.; Grotewold, E. Evolutionary and Comparative Analysis of MYB and BHLH Plant Transcription Factors. Plant J. 2011, 66, 94–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loreti, E.; Betti, F.; Ladera-Carmona, M.J.; Fontana, F.; Novi, G.; Valeri, M.C.; Perata, P. ARGONAUTE1 and ARGONAUTE4 Regulate Gene Expression and Hypoxia Tolerance. Plant Physiol. 2019, 182, 287–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brummell, D.A. Cell Wall Metabolism during Maturation, Ripening and Senescence of Peach Fruit. J. Exp. Bot. 2004, 55, 2029–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadfield, K.A.; Bennett, A.B. Polygalacturonases: Many Genes in Search of a Function. Plant Physiol. 1998, 117, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosgrove, D.J. Loosening of Plant Cell Walls by Expansins. Nature 2000, 407, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osorio, S.; Alba, R.; Damasceno, C.M.B.; Lopez-Casado, G.; Lohse, M.; Zanor, M.I.; Tohge, T.; Usadel, B.; Rose, J.K.C.; Fei, Z.; et al. Systems Biology of Tomato Fruit Development: Combined Transcript, Protein, and Metabolite Analysis of Tomato Transcription Factor (Nor, Rin) and Ethylene Receptor (Nr) Mutants Reveals Novel Regulatory Interactions. Plant Physiol. 2011, 157, 405–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smirnoff, N.; Wheeler, G.L. Ascorbic Acid in Plants: Biosynthesis and Function. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2000, 19, 267–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foyer, C.H.; Noctor, G. Ascorbate and Glutathione: The Heart of the Redox Hub. Plant Physiol. 2011, 155, 2–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, J.; Tan, H.; Zheng, Q.; Fu, F.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yang, X.; Wang, T.; Chong, K.; Wang, X.-J.; et al. LEAFY COTYLEDON1 Is a Key Regulator of Fatty Acid Biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2008, 148, 1042–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manan, S.; Alabbosh, K.F.; Al-Andal, A.; Ahmad, W.; Khan, K.A.; Zhao, J. Soybean LEAFY COTYLEDON 1: A Key Target for Genetic Enhancement of Oil Biosynthesis. Agronomy 2023, 13, 2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of Relative Gene Expression Data Using Real-Time Quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Koidou, V.; Valasiadis, D.; Petrou, N.; Emmanouilidou, C.; Hilioti, Z. Comparative Transcriptome Analysis in Tomato Fruit Reveals Genes, Pathways, and Processes Affected by the LEC1-LIKE4 Transcription Factor. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6728. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146728
Koidou V, Valasiadis D, Petrou N, Emmanouilidou C, Hilioti Z. Comparative Transcriptome Analysis in Tomato Fruit Reveals Genes, Pathways, and Processes Affected by the LEC1-LIKE4 Transcription Factor. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(14):6728. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146728
Chicago/Turabian StyleKoidou, Venetia, Dimitrios Valasiadis, Nestor Petrou, Christina Emmanouilidou, and Zoe Hilioti. 2025. "Comparative Transcriptome Analysis in Tomato Fruit Reveals Genes, Pathways, and Processes Affected by the LEC1-LIKE4 Transcription Factor" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 14: 6728. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146728
APA StyleKoidou, V., Valasiadis, D., Petrou, N., Emmanouilidou, C., & Hilioti, Z. (2025). Comparative Transcriptome Analysis in Tomato Fruit Reveals Genes, Pathways, and Processes Affected by the LEC1-LIKE4 Transcription Factor. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(14), 6728. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146728





