Use of Radiomics in Characterizing Tumor Hypoxia
Abstract
1. Introduction
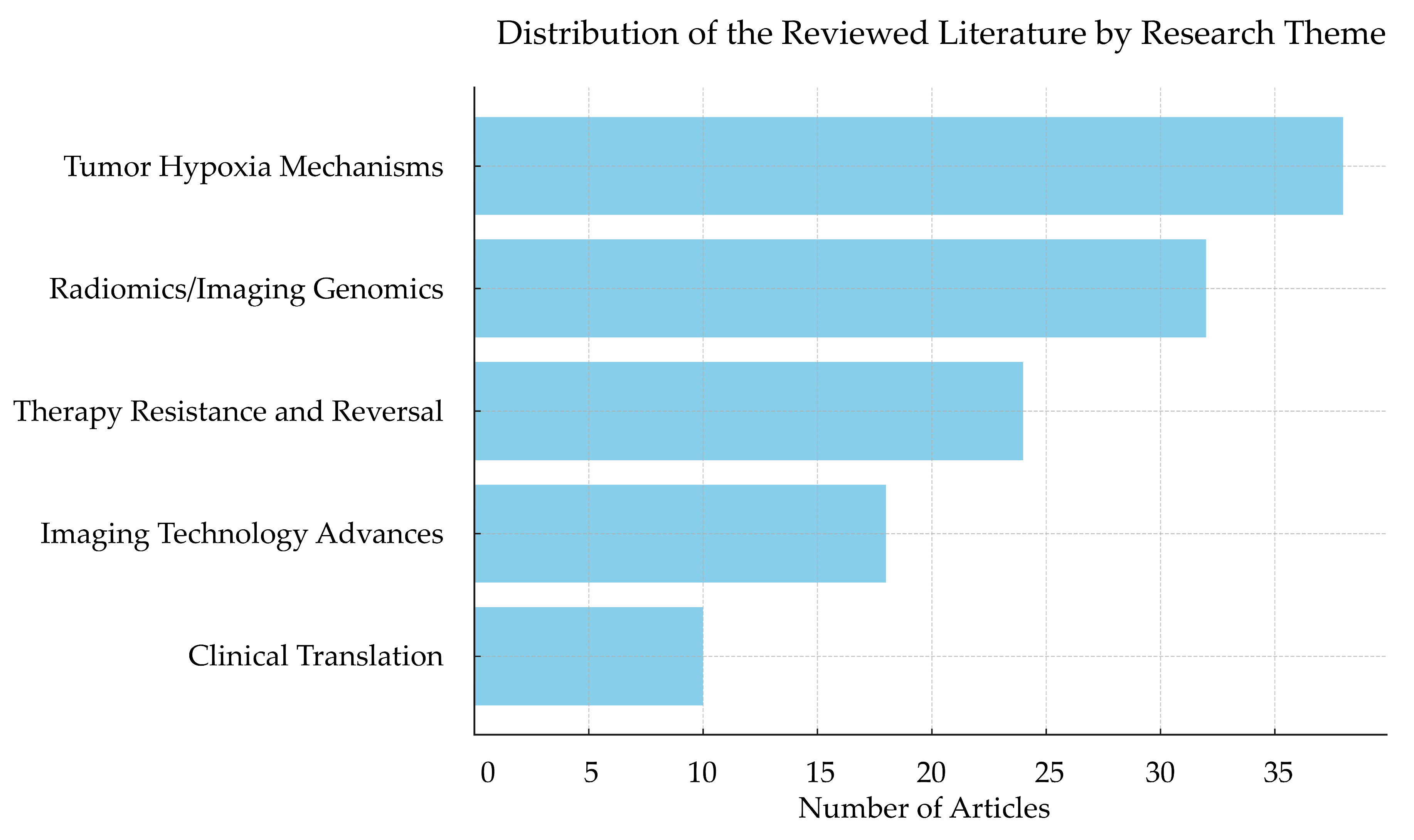
2. Review Methodology
3. Tumor Hypoxia: Mechanisms and Clinical Implications
3.1. Definition and Pathophysiology of Tumor Hypoxia
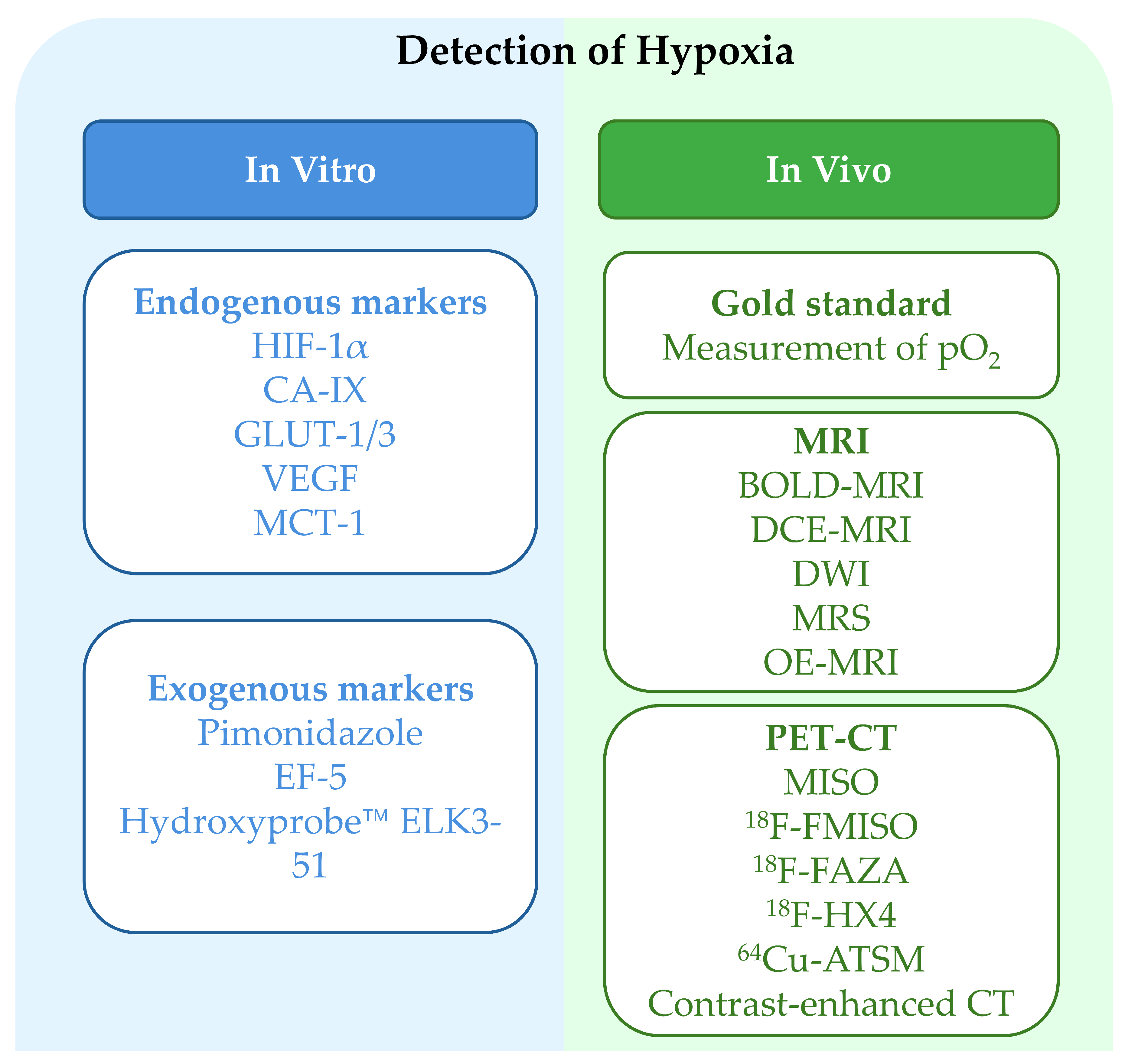
3.2. Methods for Assessing Tumor Hypoxia
3.3. Clinical Impact of Hypoxia on Cancer Therapy
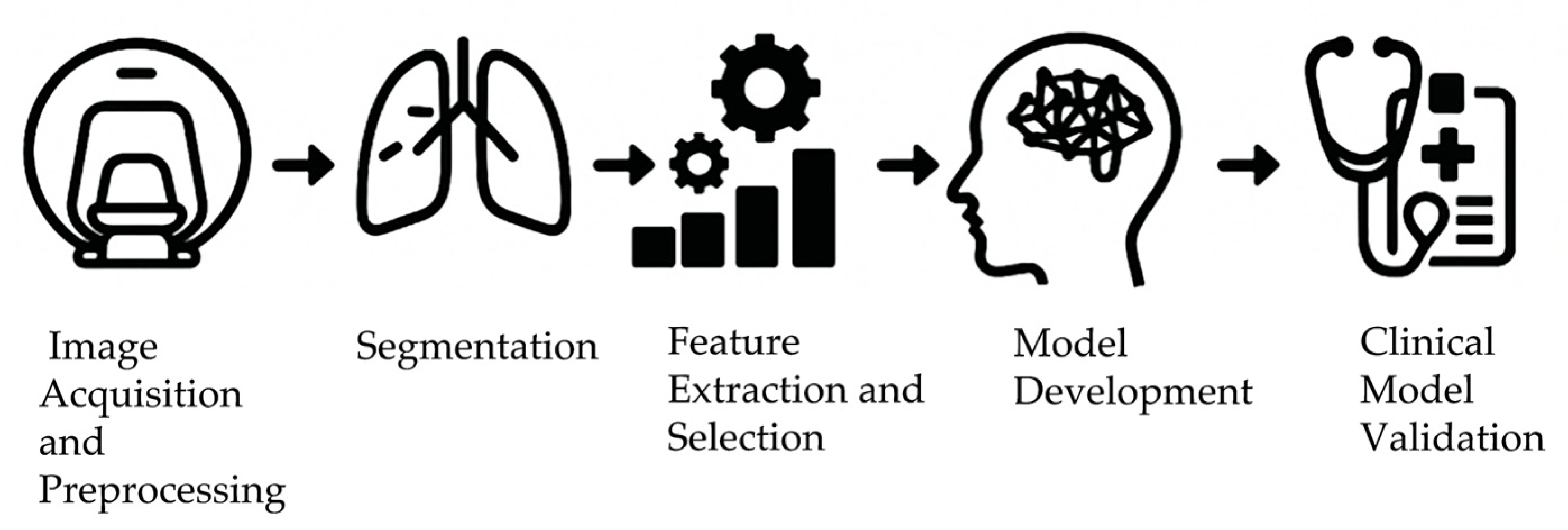
4. Radiomics in Tumor Hypoxia Characterization
4.1. Extraction of Radiomics-Based Hypoxia Imaging Features
4.2. Application of Radiomics in Tumor Hypoxia Characterization
4.3. Application of Radiogenomics in Tumor Hypoxia
5. Clinical Applications of Radiomics in Tumor Hypoxia
5.1. Clinical Translation and Therapeutic Optimization
5.2. Radiomics-Based Monitoring of Hypoxia Treatment Response
5.3. Integrating Radiomics and Clinical Data for Personalized Treatment
6. Challenges and Future Perspectives
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Simoes-Sousa, S.; Littler, S.; Thompson, S.L.; Minshall, P.; Whalley, H.; Bakker, B.; Belkot, K.; Moralli, D.; Bronder, D.; Tighe, A.; et al. The p38alpha Stress Kinase Suppresses Aneuploidy Tolerance by Inhibiting Hif-1alpha. Cell Rep. 2018, 25, 749–760 e746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feldman, L. Hypoxia within the glioblastoma tumor microenvironment: A master saboteur of novel treatments. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1384249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, M.H.; Wong, C.C. Hypoxia, Metabolic Reprogramming, and Drug Resistance in Liver Cancer. Cells 2021, 10, 1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Wu, M.; Zhao, J.; Li, Y. Advances in hypoxia microenvironment and chemotherapy-resistant of lung cancer. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi 2014, 17, 265–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, K.; Zhan, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Qiu, Y.; Wang, H.; Fan, G.; Wang, J.; Li, W.; Cao, Y.; Shen, X.; et al. Hypoxia Induces Drug Resistance in Colorectal Cancer through the HIF-1alpha/miR-338-5p/IL-6 Feedback Loop. Mol. Ther. 2019, 27, 1810–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rockwell, S.; Dobrucki, I.T.; Kim, E.Y.; Marrison, S.T.; Vu, V.T. Hypoxia and radiation therapy: Past history, ongoing research, and future promise. Curr. Mol. Med. 2009, 9, 442–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, L.; Blackwell, K. Hypoxia and anemia: Factors in decreased sensitivity to radiation therapy and chemotherapy? Oncologist 2004, 9 (Suppl. S5), 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, M.; Das, P.K. Hypoxia: Intriguing Feature in Cancer Cell Biology. ChemMedChem 2024, 19, e202300551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Lv, X.; Yan, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Ma, R.; He, M.; Wei, M. Hypoxia-mediated cancer stem cell resistance and targeted therapy. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 130, 110623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigos, K.J.; Quiles, C.G.; Lunj, S.; Smith, D.J.; Krause, M.; Troost, E.G.; West, C.M.; Hoskin, P.; Choudhury, A. Tumour response to hypoxia: Understanding the hypoxic tumour microenvironment to improve treatment outcome in solid tumours. Front. Oncol. 2024, 14, 1331355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, W.; Thulasi Seetha, S.; Refaee, T.A.G.; Lieverse, R.I.Y.; Granzier, R.W.Y.; Ibrahim, A.; Keek, S.A.; Sanduleanu, S.; Primakov, S.P.; Beuque, M.P.L.; et al. Radiomics: From qualitative to quantitative imaging. Br. J. Radiol. 2020, 93, 20190948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, S.; Dong, D.; Wei, J.; Fang, C.; Zhou, X.; Sun, K.; Li, L.; Li, B.; Wang, M.; et al. The Applications of Radiomics in Precision Diagnosis and Treatment of Oncology: Opportunities and Challenges. Theranostics 2019, 9, 1303–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Zhou, B. A review of radiomics and genomics applications in cancers: The way towards precision medicine. Radiat. Oncol. 2022, 17, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.P.; Zhang, X.Y.; Cheng, Y.T.; Li, B.; Teng, X.Z.; Zhang, J.; Lam, S.; Zhou, T.; Ma, Z.R.; Sheng, J.B.; et al. Artificial intelligence-driven radiomics study in cancer: The role of feature engineering and modeling. Mil. Med. Res. 2023, 10, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avanzo, M.; Wei, L.; Stancanello, J.; Vallieres, M.; Rao, A.; Morin, O.; Mattonen, S.A.; El Naqa, I. Machine and deep learning methods for radiomics. Med. Phys. 2020, 47, e185–e202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parekh, V.S.; Jacobs, M.A. Deep learning and radiomics in precision medicine. Expert. Rev. Precis. Med. Drug Dev. 2019, 4, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisson, C.S.; Lisson, C.G.; Mezger, M.F.; Wolf, D.; Schmidt, S.A.; Thaiss, W.M.; Tausch, E.; Beer, A.J.; Stilgenbauer, S.; Beer, M.; et al. Deep Neural Networks and Machine Learning Radiomics Modelling for Prediction of Relapse in Mantle Cell Lymphoma. Cancers 2022, 14, 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.E.; Kickingereder, P.; Kim, H.S. Radiomics and Deep Learning from Research to Clinical Workflow: Neuro-Oncologic Imaging. Korean J. Radiol. 2020, 21, 1126–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh, B.N.; Groendahl, A.R.; Tomic, O.; Liland, K.H.; Knudtsen, I.S.; Hoebers, F.; van Elmpt, W.; Malinen, E.; Dale, E.; Futsaether, C.M. Head and neck cancer treatment outcome prediction: A comparison between machine learning with conventional radiomics features and deep learning radiomics. Front. Med. 2023, 10, 1217037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muz, B.; de la Puente, P.; Azab, F.; Azab, A.K. The role of hypoxia in cancer progression, angiogenesis, metastasis, and resistance to therapy. Hypoxia 2015, 3, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, T.; Hallis, S.P.; Kwak, M.K. Hypoxia, oxidative stress, and the interplay of HIFs and NRF2 signaling in cancer. Exp. Mol. Med. 2024, 56, 501–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, M.; Yang, L.; Peng, X.; Wei, S.; Fan, Q.; Yang, S.; Li, X.; Li, B.; Jin, H.; Wu, B.; et al. Autonomous glucose metabolic reprogramming of tumour cells under hypoxia: Opportunities for targeted therapy. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 39, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.; Liu, X.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Q. Tumor hypoxia: From basic knowledge to therapeutic implications. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2023, 88, 172–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.C.S.; Pyo, A.H.A.; Koritzinsky, M. Longitudinal dynamics of the tumor hypoxia response: From enzyme activity to biological phenotype. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eadj6409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, J.S.; Manda, G. Metabolic Pathways of the Warburg Effect in Health and Disease: Perspectives of Choice, Chain or Chance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Lazaro, M. The warburg effect: Why and how do cancer cells activate glycolysis in the presence of oxygen? Anticancer. Agents Med. Chem. 2008, 8, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, S.; Zhao, Y.; Lee, W.C.; Ong, L.T.; Lee, P.L.; Jiang, Z.; Oguz, G.; Niu, Z.; Liu, M.; Goh, J.Y.; et al. Hypoxia induces HIF1alpha-dependent epigenetic vulnerability in triple negative breast cancer to confer immune effector dysfunction and resistance to anti-PD-1 immunotherapy. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 4118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplan, A.R.; Glazer, P.M. Impact of hypoxia on DNA repair and genome integrity. Mutagenesis 2020, 35, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Han, F.; Du, Y.; Shi, H.; Zhou, W. Hypoxic microenvironment in cancer: Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic interventions. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lin, A.; Yang, H.; Liu, Z.; Cheng, Q.; Zhang, J.; Luo, P. THER: Integrative Web Tool for Tumor Hypoxia Exploration and Research. bioRxiv 2023, e70053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuijper, A.; van der Groep, P.; van der Wall, E.; van Diest, P.J. Expression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha and its downstream targets in fibroepithelial tumors of the breast. Breast Cancer Res. 2005, 7, R808–R818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.H.; Griffiths, J.R. How and Why Are Cancers Acidic? Carbonic Anhydrase IX and the Homeostatic Control of Tumour Extracellular pH. Cancers 2020, 12, 1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanetti, J.S.; Soave, D.F.; Oliveira-Costa, J.P.; da Silveira, G.G.; Ramalho, L.N.; Garcia, S.B.; Zucoloto, S.; Ribeiro-Silva, A. The role of tumor hypoxia in MUC1-positive breast carcinomas. Virchows Arch. 2011, 459, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguilera, K.Y.; Brekken, R.A. Hypoxia Studies with Pimonidazole in vivo. Bio-Protocol 2014, 4, e1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Siemann, D.W.; Koch, C.J.; Lord, E.M. Direct relationship between radiobiological hypoxia in tumors and monoclonal antibody detection of EF5 cellular adducts. Int. J. Cancer 1996, 67, 372–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godet, I.; Doctorman, S.; Wu, F.; Gilkes, D.M. Detection of Hypoxia in Cancer Models: Significance, Challenges, and Advances. Cells 2022, 11, 686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, A.D.; Li, Z.; Thomas, Z.; Stevens, C.W. Assessment of tissue oxygen tension: Comparison of dynamic fluorescence quenching and polarographic electrode technique. Crit. Care 2002, 6, 76–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, J.C.; Lebedev, A.; Aten, E.; Madsen, K.; Marciano, L.; Kolb, H.C. The clinical importance of assessing tumor hypoxia: Relationship of tumor hypoxia to prognosis and therapeutic opportunities. Antioxid. Redox Signal 2014, 21, 1516–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou Khouzam, R.; Janji, B.; Thiery, J.; Zaarour, R.F.; Chamseddine, A.N.; Mayr, H.; Savagner, P.; Kieda, C.; Gad, S.; Buart, S.; et al. Hypoxia as a potential inducer of immune tolerance, tumor plasticity and a driver of tumor mutational burden: Impact on cancer immunotherapy. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2023, 97, 104–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Wang, Y. Hypoxia Mediates Tumor Malignancy and Therapy Resistance. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019, 1136, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rickard, A.G.; Palmer, G.M.; Dewhirst, M.W. Clinical and Pre-clinical Methods for Quantifying Tumor Hypoxia. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019, 1136, 19–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsien, C.; Cao, Y.; Chenevert, T. Clinical applications for diffusion magnetic resonance imaging in radiotherapy. Semin. Radiat. Oncol. 2014, 24, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glunde, K.; Jiang, L.; Moestue, S.A.; Gribbestad, I.S. MRS and MRSI guidance in molecular medicine: Targeting and monitoring of choline and glucose metabolism in cancer. NMR Biomed. 2011, 24, 673–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubec, M.J.; Price, J.; Berks, M.; Gaffney, J.; Little, R.A.; Porta, N.; Sridharan, N.; Datta, A.; McHugh, D.J.; Hague, C.J.; et al. Oxygen-Enhanced MRI Detects Incidence, Onset, and Heterogeneity of Radiation-Induced Hypoxia Modification in HPV-Associated Oropharyngeal Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2024, 30, 5620–5629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleming, I.N.; Manavaki, R.; Blower, P.J.; West, C.; Williams, K.J.; Harris, A.L.; Domarkas, J.; Lord, S.; Baldry, C.; Gilbert, F.J. Imaging tumour hypoxia with positron emission tomography. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 112, 238–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gouel, P.; Decazes, P.; Vera, P.; Gardin, I.; Thureau, S.; Bohn, P. Advances in PET and MRI imaging of tumor hypoxia. Front. Med. 2023, 10, 1055062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapman, J.D. Hypoxic sensitizers--implications for radiation therapy. N. Engl. J. Med. 1979, 301, 1429–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, X.; Cheng, S.P.; Huang, J.B. Predicting angiogenesis in adrenal pheochromocytoma: The role of modified parameters from contrast-enhanced CT. Discov. Oncol. 2024, 15, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellano, A.; Bailo, M.; Cicone, F.; Carideo, L.; Quartuccio, N.; Mortini, P.; Falini, A.; Cascini, G.L.; Minniti, G. Advanced Imaging Techniques for Radiotherapy Planning of Gliomas. Cancers 2021, 13, 1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrias, G.; Lai, E.; Ziranu, P.; Mariani, S.; Donisi, C.; Liscia, N.; Saba, G.; Pretta, A.; Persano, M.; Fanni, D.; et al. Prediction of Response to Anti-Angiogenic Treatment for Advanced Colorectal Cancer Patients: From Biological Factors to Functional Imaging. Cancers 2024, 16, 1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciepla, J.; Smolarczyk, R. Tumor hypoxia unveiled: Insights into microenvironment, detection tools and emerging therapies. Clin. Exp. Med. 2024, 24, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouleftour, W.; Rowinski, E.; Louati, S.; Sotton, S.; Wozny, A.S.; Moreno-Acosta, P.; Mery, B.; Rodriguez-Lafrasse, C.; Magne, N. A Review of the Role of Hypoxia in Radioresistance in Cancer Therapy. Med. Sci. Monit. 2021, 27, e934116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Jiang, H.; Van De Gucht, M.; De Ridder, M. Hypoxic Radioresistance: Can ROS Be the Key to Overcome It? Cancers 2019, 11, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorensen, B.S.; Horsman, M.R. Tumor Hypoxia: Impact on Radiation Therapy and Molecular Pathways. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanley, R.; Pagliari, F.; Garcia-Calderon, D.; Fernandes Guerreiro, J.; Genard, G.; Jansen, J.; Nistico, C.; Marafioti, M.G.; Tirinato, L.; Seco, J. Radio-resistance of hypoxic tumors: Exploring the effects of oxygen and X-ray radiation on non-small lung cancer cell lines. Radiat. Oncol. 2023, 18, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Lei, Y.; Wang, Y.; Lai, J.; Wang, J.; Xia, F. Mechanism of multidrug resistance to chemotherapy mediated by P-glycoprotein (Review). Int. J. Oncol. 2023, 63, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bui, B.P.; Nguyen, P.L.; Lee, K.; Cho, J. Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1: A Novel Therapeutic Target for the Management of Cancer, Drug Resistance, and Cancer-Related Pain. Cancers 2022, 14, 6054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Jiang, L.; Zhong, T. The role of HIF-1alpha in chemo-/radioresistant tumors. Onco Targets Ther. 2018, 11, 3003–3011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scanlon, S.E.; Glazer, P.M. Multifaceted control of DNA repair pathways by the hypoxic tumor microenvironment. DNA Repair 2015, 32, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozward, A.G.; Warricker, F.; Oo, Y.H.; Khakoo, S.I. Natural Killer Cells and Regulatory T Cells Cross Talk in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Exploring Therapeutic Options for the Next Decade. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 643310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zheng, Z.; Liu, S.; Meng, L.; Xin, Y.; Jiang, X. Targeting hypoxia in the tumor microenvironment: A potential strategy to improve cancer immunotherapy. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 40, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, C.; Liu, T.; Dai, X.; Bazhin, A.V. Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells in Tumors: From Mechanisms to Antigen Specificity and Microenvironmental Regulation. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sethumadhavan, S.; Silva, M.; Philbrook, P.; Nguyen, T.; Hatfield, S.M.; Ohta, A.; Sitkovsky, M.V. Hypoxia and hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) downregulate antigen-presenting MHC class I molecules limiting tumor cell recognition by T cells. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0187314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, M.; Ji, C.; Liu, X.; Gu, B.; Dong, T. Macrophage polarization in the tumor microenvironment: Emerging roles and therapeutic potentials. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 177, 116930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillies, R.J.; Kinahan, P.E.; Hricak, H. Radiomics: Images Are More than Pictures, They Are Data. Radiology 2016, 278, 563–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beig, N.; Patel, J.; Prasanna, P.; Hill, V.; Gupta, A.; Correa, R.; Bera, K.; Singh, S.; Partovi, S.; Varadan, V.; et al. Radiogenomic analysis of hypoxia pathway is predictive of overall survival in Glioblastoma. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Cen, H.S.; Dhananjay, A.; Pawan, S.J.; Lei, X.; Gill, I.S.; D’Souza, A.; Duddalwar, V.A. Radiogenomic correlation of hypoxia-related biomarkers in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2025, 151, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muller, J.; Leger, S.; Zwanenburg, A.; Suckert, T.; Luhr, A.; Beyreuther, E.; von Neubeck, C.; Krause, M.; Lock, S.; Dietrich, A.; et al. Radiomics-based tumor phenotype determination based on medical imaging and tumor microenvironment in a preclinical setting. Radiother. Oncol. 2022, 169, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D.; Grandgenett, P.M.; Zhang, Q.; Baine, M.; Shi, Y.; Du, Q.; Liang, X.; Wong, J.; Iqbal, S.; Preuss, K.; et al. radioGWAS links radiome to genome to discover driver genes with somatic mutations for heterogeneous tumor image phenotype in pancreatic cancer. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 12316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Baz, A.; Beache, G.M.; Gimel’farb, G.; Suzuki, K.; Okada, K.; Elnakib, A.; Soliman, A.; Abdollahi, B. Computer-aided diagnosis systems for lung cancer: Challenges and methodologies. Int. J. Biomed. Imaging 2013, 2013, 942353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, F.J.; Grigsby, P.W. The effect of small tumor volumes on studies of intratumoral heterogeneity of tracer uptake. J. Nucl. Med. 2014, 55, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, S.; Hong, S.; Oh, E.; Lee, W.J.; Jeong, W.K.; Kim, K. Development of a flexible feature selection framework in radiomics-based prediction modeling: Assessment with four real-world datasets. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 29297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majumder, S.; Katz, S.; Kontos, D.; Roshkovan, L. State of the art: Radiomics and radiomics-related artificial intelligence on the road to clinical translation. BJR Open 2024, 6, tzad004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, K.; Vendt, B.; Smith, K.; Freymann, J.; Kirby, J.; Koppel, P.; Moore, S.; Phillips, S.; Maffitt, D.; Pringle, M.; et al. The Cancer Imaging Archive (TCIA): Maintaining and operating a public information repository. J. Digit. Imaging 2013, 26, 1045–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aerts, H.J.; Velazquez, E.R.; Leijenaar, R.T.; Parmar, C.; Grossmann, P.; Carvalho, S.; Bussink, J.; Monshouwer, R.; Haibe-Kains, B.; Rietveld, D.; et al. Decoding tumour phenotype by noninvasive imaging using a quantitative radiomics approach. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chau, M.; Vu, H.; Debnath, T.; Rahman, M.G. A scoping review of automatic and semi-automatic MRI segmentation in human brain imaging. Radiography 2025, 31, 102878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedorov, A.; Beichel, R.; Kalpathy-Cramer, J.; Finet, J.; Fillion-Robin, J.C.; Pujol, S.; Bauer, C.; Jennings, D.; Fennessy, F.; Sonka, M.; et al. 3D Slicer as an image computing platform for the Quantitative Imaging Network. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2012, 30, 1323–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yushkevich, P.A.; Yang, G.; Gerig, G. ITK-SNAP: An interactive tool for semi-automatic segmentation of multi-modality biomedical images. In Proceedings of the 2016 38th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Orlando, FL, USA, 16–20 August 2016; Volume 2016, pp. 3342–3345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention—MICCAI 2015, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- van Griethuysen, J.J.M.; Fedorov, A.; Parmar, C.; Hosny, A.; Aucoin, N.; Narayan, V.; Beets-Tan, R.G.H.; Fillion-Robin, J.C.; Pieper, S.; Aerts, H. Computational Radiomics System to Decode the Radiographic Phenotype. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, e104–e107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Traverso, A.; van Soest, J.; Dekker, A.; Wee, L. Technical Note: Ontology-guided radiomics analysis workflow (O-RAW). Med. Phys. 2019, 46, 5677–5684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakas, S.; Akbari, H.; Sotiras, A.; Bilello, M.; Rozycki, M.; Kirby, J.S.; Freymann, J.B.; Farahani, K.; Davatzikos, C. Advancing The Cancer Genome Atlas glioma MRI collections with expert segmentation labels and radiomic features. Sci. Data 2017, 4, 170117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsilla, J.; Weiss, J.; Ye, X.Y.; Welch, M.; Milosevic, M.; Lyng, H.; Hompland, T.; Bruheim, K.; Tadic, T.; Haibe-Kains, B.; et al. A T2-weighted MRI-based radiomic signature for disease-free survival in locally advanced cervical cancer following chemoradiation: An international, multicentre study. Radiother. Oncol. 2024, 199, 110463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Manzalawy, Y.; Hsieh, T.Y.; Shivakumar, M.; Kim, D.; Honavar, V. Min-redundancy and max-relevance multi-view feature selection for predicting ovarian cancer survival using multi-omics data. BMC Med. Genomics 2018, 11, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.; Li, L.; Jiang, H.; Yin, J.; Lu, B.; Han, W.; Li, J.; Zhang, J. Cervical spine osteoradionecrosis or bone metastasis after radiotherapy for nasopharyngeal carcinoma? The MRI-based radiomics for characterization. BMC Med. Imaging 2020, 20, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Tan, L.; Wang, L.; Zou, D.; Liu, J.; Lu, X.; Fu, D.; Wang, G.; Wang, L.; Wang, Z. The Expression Pattern of Hypoxia-Related Genes Predicts the Prognosis and Mediates Drug Resistance in Colorectal Cancer. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 814621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, C.; Jia, H.; Jiang, N.; Zhao, J.; Nan, X. Establishment of Chemotherapy Prediction Model Based on Hypoxia-Related Genes for Oral Cancer. J. Cancer 2024, 15, 5191–5203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Chang, Z.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Feng, C.; Ping, Y.; Feng, X. Predictive Value of Machine Learning for Platinum Chemotherapy Responses in Ovarian Cancer: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Med. Internet Res. 2024, 26, e48527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.; Du, Y.; Ma, R.; Teng, N.; Ou, S.; Zhao, H.; Li, X. Construction of the XGBoost model for early lung cancer prediction based on metabolic indices. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2023, 23, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Fan, J.; Li, Y.; Fu, S.; Chen, Y.; Wu, J. Imaging of Tumor Hypoxia with Radionuclide-Labeled Tracers for PET. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 731503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, S.; Kadoya, N.; Sugai, Y.; Umeda, M.; Ishizawa, M.; Katsuta, Y.; Ito, K.; Takeda, K.; Jingu, K. A deep learning-based radiomics approach to predict head and neck tumor regression for adaptive radiotherapy. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 8899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manescu, P.; Geradts, J.; Fernández-Reyes, D. Deep learning-based detection of morphological features associated with hypoxia in H&E breast cancer whole slide images. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2311.12601. [Google Scholar]
- Pigat, L.; Geisler, B.P.; Sheikhalishahi, S.; Sander, J.; Kaspar, M.; Schmutz, M.; Rohr, S.O.; Wild, C.M.; Goss, S.; Zaghdoudi, S.; et al. Predicting Hypoxia Using Machine Learning: Systematic Review. JMIR Med. Inform. 2024, 12, e50642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Vries, B.M.; Zwezerijnen, G.J.C.; Burchell, G.L.; van Velden, F.H.P.; Menke-van der Houven van Oordt, C.W.; Boellaard, R. Explainable artificial intelligence (XAI) in radiology and nuclear medicine: A literature review. Front. Med. 2023, 10, 1180773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, T.; Wittenborn, T.; Horsman, M.R. Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging (DCE-MRI) in Preclinical Studies of Antivascular Treatments. Pharmaceutics 2012, 4, 563–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, P.V.; Li, L.P.; Hack, B.; Leloudas, N.; Sprague, S.M. Quantitative Blood Oxygenation Level Dependent Magnetic Resonance Imaging for Estimating Intra-renal Oxygen Availability Demonstrates Kidneys Are Hypoxemic in Human CKD. Kidney Int. Rep. 2023, 8, 1057–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, J.P.B.; Robinson, S.P.; Waterton, J.C. Imaging tumour hypoxia with oxygen-enhanced MRI and BOLD MRI. Br. J. Radiol. 2019, 92, 20180642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodalal, Z.; Bogveradze, N.; Ter Beek, L.C.; van den Berg, J.G.; Sanders, J.; Hofland, I.; Trebeschi, S.; Groot Lipman, K.B.W.; Storck, K.; Hong, E.K.; et al. Radiomic signatures from T2W and DWI MRI are predictive of tumour hypoxia in colorectal liver metastases. Insights Imaging 2023, 14, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sersa, I.; Bajd, F.; Savarin, M.; Jesenko, T.; Cemazar, M.; Sersa, G. Multiparametric High-Resolution MRI as a Tool for Mapping of Hypoxic Level in Tumors. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2018, 17, 1533033818797066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bekaert, L.; Valable, S.; Lechapt-Zalcman, E.; Ponte, K.; Collet, S.; Constans, J.M.; Levallet, G.; Bordji, K.; Petit, E.; Branger, P.; et al. [18F]-FMISO PET study of hypoxia in gliomas before surgery: Correlation with molecular markers of hypoxia and angiogenesis. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2017, 44, 1383–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorwarth, D.; Welz, S.; Monnich, D.; Pfannenberg, C.; Nikolaou, K.; Reimold, M.; La Fougere, C.; Reischl, G.; Mauz, P.S.; Paulsen, F.; et al. Prospective Evaluation of a Tumor Control Probability Model Based on Dynamic (18)F-FMISO PET for Head and Neck Cancer Radiotherapy. J. Nucl. Med. 2019, 60, 1698–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourigault, P.; Skwarski, M.; Macpherson, R.E.; Higgins, G.S.; McGowan, D.R. Timing of hypoxia PET/CT imaging after 18F-fluoromisonidazole injection in non-small cell lung cancer patients. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 21746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, R.C.; Kim, D.; Maxwell, A.W.P.; Camacho, J.C. Functional Imaging of Hypoxia: PET and MRI. Cancers 2023, 15, 3336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, Q.; Yeung, T.P.; Lee, T.Y.; Bauman, G.; Crukley, C.; Morrison, L.; Hoffman, L.; Yartsev, S. Evaluation of CT Perfusion Biomarkers of Tumor Hypoxia. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, S.; Xia, T.; Ge, Y.; Zhang, K.; Ji, X.; Luo, S.; Shen, Y. Computed Tomography Imaging-Based Radiogenomics Analysis Reveals Hypoxia Patterns and Immunological Characteristics in Ovarian Cancer. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 868067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Luo, Z.; Luo, C.; Wang, T. Application of a Comprehensive Model Based on CT Radiomics and Clinical Features for Postoperative Recurrence Risk Prediction in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer. Acad. Radiol. 2024, 31, 2579–2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, A.; Koh, T.S.; Prawira, A.; Ho, R.Z.W.; Le, T.B.U.; Vu, T.C.; Hartano, S.; Teo, X.Q.; Chen, W.C.; Lee, P.; et al. Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging as Imaging Biomarker for Vascular Normalization Effect of Infigratinib in High-FGFR-Expressing Hepatocellular Carcinoma Xenografts. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2021, 23, 70–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Figueiras, R.; Baleato-Gonzalez, S.; Luna, A.; Padhani, A.R.; Vilanova, J.C.; Carballo-Castro, A.M.; Oleaga-Zufiria, L.; Vallejo-Casas, J.A.; Marhuenda, A.; Gomez-Caamano, A. How Imaging Advances Are Defining the Future of Precision Radiation Therapy. Radiographics 2024, 44, e230152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, W.H.; Park, J.S.; Park, J.; Choi, S.H. Assessing the reproducibility of high temporal and spatial resolution dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging in patients with gliomas. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 23217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Agudo, E.; Mondejar, T.; Soto-Montenegro, M.L.; Megias, D.; Mouron, S.; Sanchez, J.; Hidalgo, M.; Lopez-Casas, P.P.; Mulero, F.; Desco, M.; et al. Monitoring vascular normalization induced by antiangiogenic treatment with (18)F-fluoromisonidazole-PET. Mol. Oncol. 2016, 10, 704–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirus, M.; Tokalov, S.V.; Abramyuk, A.; Heinold, J.; Prochnow, V.; Zophel, K.; Kotzerke, J.; Abolmaali, N. Noninvasive assessment and quantification of tumor vascularization using [18F]FDG-PET/CT and CE-CT in a tumor model with modifiable angiogenesis-an animal experimental prospective cohort study. EJNMMI Res. 2019, 9, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moses, W.W. Fundamental Limits of Spatial Resolution in PET. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A 2011, 648 (Suppl. S1), S236–S240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Figueiras, R.; Goh, V.J.; Padhani, A.R.; Baleato-Gonzalez, S.; Garrido, M.; Leon, L.; Gomez-Caamano, A. CT perfusion in oncologic imaging: A useful tool? AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2013, 200, 8–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, R.; Ellika, S.K.; Scarpace, L.; Schultz, L.R.; Rock, J.P.; Gutierrez, J.; Patel, S.C.; Ewing, J.; Mikkelsen, T. Quantitative estimation of permeability surface-area product in astroglial brain tumors using perfusion CT and correlation with histopathologic grade. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2008, 29, 694–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tachiiri, T.; Nishiofuku, H.; Maeda, S.; Sato, T.; Toyoda, S.; Matsumoto, T.; Chanoki, Y.; Minamiguchi, K.; Taiji, R.; Kunichika, H.; et al. Vascular Normalization Caused by Short-Term Lenvatinib Could Enhance Transarterial Chemoembolization in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Curr. Oncol. 2023, 30, 4779–4786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crispin-Ortuzar, M.; Apte, A.; Grkovski, M.; Oh, J.H.; Lee, N.Y.; Schoder, H.; Humm, J.L.; Deasy, J.O. Predicting hypoxia status using a combination of contrast-enhanced computed tomography and [(18)F]-Fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography radiomics features. Radiother. Oncol. 2018, 127, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tunali, I.; Tan, Y.; Gray, J.E.; Katsoulakis, E.; Eschrich, S.A.; Saller, J.; Aerts, H.; Boyle, T.; Qi, J.; Guvenis, A.; et al. Hypoxia-Related Radiomics and Immunotherapy Response: A Multicohort Study of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. JNCI Cancer Spectr. 2021, 5, pkab048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carles, M.; Fechter, T.; Grosu, A.L.; Sorensen, A.; Thomann, B.; Stoian, R.G.; Wiedenmann, N.; Ruhle, A.; Zamboglou, C.; Ruf, J.; et al. (18)F-FMISO-PET Hypoxia Monitoring for Head-and-Neck Cancer Patients: Radiomics Analyses Predict the Outcome of Chemo-Radiotherapy. Cancers 2021, 13, 3449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muzi, M.; Wolsztynski, E.; Fink, J.R.; O’Sullivan, J.N.; O’Sullivan, F.; Krohn, K.A.; Mankoff, D.A. Assessment of the Prognostic Value of Radiomic Features in (18)F-FMISO PET Imaging of Hypoxia in Postsurgery Brain Cancer Patients: Secondary Analysis of Imaging Data from a Single-Center Study and the Multicenter ACRIN 6684 Trial. Tomography 2020, 6, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogbonnaya, C.N.; Alsaedi, B.S.O.; Alhussaini, A.J.; Hislop, R.; Pratt, N.; Nabi, G. Radiogenomics Reveals Correlation between Quantitative Texture Radiomic Features of Biparametric MRI and Hypoxia-Related Gene Expression in Men with Localised Prostate Cancer. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shui, L.; Ren, H.; Yang, X.; Li, J.; Chen, Z.; Yi, C.; Zhu, H.; Shui, P. The Era of Radiogenomics in Precision Medicine: An Emerging Approach to Support Diagnosis, Treatment Decisions, and Prognostication in Oncology. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 570465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Manjila, S.; Sakla, N.; True, A.; Wardeh, A.H.; Beig, N.; Vaysberg, A.; Matthews, J.; Prasanna, P.; Spektor, V. Radiomics and radiogenomics in gliomas: A contemporary update. Br. J. Cancer 2021, 125, 641–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Jiang, Y.; Xiong, W.; Sun, Z.; Chen, C.; Yuan, Q.; Zhou, K.; Han, Z.; Feng, H.; Chen, H.; et al. Noninvasive imaging of the tumor immune microenvironment correlates with response to immunotherapy in gastric cancer. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 5095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.; Ackerstaff, E.; Carlin, S.; Lupu, M.E.; Wang, Y.; Rizwan, A.; O’Donoghue, J.; Ling, C.C.; Humm, J.L.; Zanzonico, P.B.; et al. Noninvasive multimodality imaging of the tumor microenvironment: Registered dynamic magnetic resonance imaging and positron emission tomography studies of a preclinical tumor model of tumor hypoxia. Neoplasia 2009, 11, 247–259, 242p following 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gertsenshteyn, I.; Epel, B.; Giurcanu, M.; Barth, E.; Lukens, J.; Hall, K.; Martinez, J.F.; Grana, M.; Maggio, M.; Miller, R.C.; et al. Absolute oxygen-guided radiation therapy improves tumor control in three preclinical tumor models. Front. Med. 2023, 10, 1269689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meissner, A.K.; Gutsche, R.; Galldiks, N.; Kocher, M.; Junger, S.T.; Eich, M.L.; Nogova, L.; Araceli, T.; Schmidt, N.O.; Ruge, M.I.; et al. Radiomics for the non-invasive prediction of PD-L1 expression in patients with brain metastases secondary to non-small cell lung cancer. J. Neurooncol. 2023, 163, 597–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhao, L.; Li, X.F. Targeting Hypoxia: Hypoxia-Activated Prodrugs in Cancer Therapy. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 700407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonald, P.C.; Winum, J.Y.; Supuran, C.T.; Dedhar, S. Recent developments in targeting carbonic anhydrase IX for cancer therapeutics. Oncotarget 2012, 3, 84–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanduleanu, S.; Jochems, A.; Upadhaya, T.; Even, A.J.G.; Leijenaar, R.T.H.; Dankers, F.; Klaassen, R.; Woodruff, H.C.; Hatt, M.; Kaanders, H.; et al. Non-invasive imaging prediction of tumor hypoxia: A novel developed and externally validated CT and FDG-PET-based radiomic signatures. Radiother. Oncol. 2020, 153, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, A.J.; Floyd, J.; Fichtel, L.; Michalek, J.; Kanakia, K.P.; Huang, S.; Reardon, D.; Wen, P.Y.; Lee, E.Q. Phase 2 trial of hypoxia activated evofosfamide (TH302) for treatment of recurrent bevacizumab-refractory glioblastoma. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welz, S.; Paulsen, F.; Pfannenberg, C.; Reimold, M.; Reischl, G.; Nikolaou, K.; La Fougere, C.; Alber, M.; Belka, C.; Zips, D.; et al. Dose escalation to hypoxic subvolumes in head and neck cancer: A randomized phase II study using dynamic [(18)F]FMISO PET/CT. Radiother. Oncol. 2022, 171, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Xu, S.; Wang, G.; Shi, Y. Applications of CT-based radiomics for the prediction of immune checkpoint markers and immunotherapeutic outcomes in non-small cell lung cancer. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1434171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Guo, H.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wang, C.; Bu, J.; Sun, T.; Wei, J. Liquid biopsy in cancer current: Status, challenges and future prospects. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stejskal, P.; Goodarzi, H.; Srovnal, J.; Hajduch, M.; van‘t Veer, L.J.; Magbanua, M.J.M. Circulating tumor nucleic acids: Biology, release mechanisms, and clinical relevance. Mol. Cancer 2023, 22, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Mao, C.; Fu, T.; Ding, X.; Bertolaccini, L.; Liu, A.; Zhang, J.; Li, S. Development of an AI model for predicting hypoxia status and prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer using multi-modal data. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2024, 13, 3642–3656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Captier, N.; Lerousseau, M.; Orlhac, F.; Hovhannisyan-Baghdasarian, N.; Luporsi, M.; Woff, E.; Lagha, S.; Salamoun Feghali, P.; Lonjou, C.; Beaulaton, C.; et al. Integration of clinical, pathological, radiological, and transcriptomic data improves prediction for first-line immunotherapy outcome in metastatic non-small cell lung cancer. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limkin, E.J.; Sun, R.; Dercle, L.; Zacharaki, E.I.; Robert, C.; Reuze, S.; Schernberg, A.; Paragios, N.; Deutsch, E.; Ferte, C. Promises and challenges for the implementation of computational medical imaging (radiomics) in oncology. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, 1191–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Tool Name | Description | URL |
|---|---|---|
| pyradiomics | Feature extraction from medical images (2D/3D) | https://github.com/AIM-Harvard/pyradiomics (accessed on 8 July 2025) |
| Py-rex (Version 2.1) | Radiomic extension supporting DICOM/RTSTRUCT | https://github.com/zhenweishi/Py-rex (accessed on 8 July 2025) |
| Pyadiomics-based glioma grading | Glioma grading workflow based on PyRadiomics feature extraction | https://github.com/adhaka3/Pyadiomics-based-glioma-grading (accessed on 8 July 2025) |
| Modality | Advantages | Disadvantages | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| MRI | Functional sequences (DWI, BOLD) related to hypoxia, excellent soft tissue contrast | Susceptible to motion/artifacts, variable protocols, very long scan times | [98,107,108,109] |
| PET | Direct hypoxia imaging with specific tracers, limitless penetration depth | Expensive, lower spatial resolution, high ionizing radiation | [110,111,112] |
| CT | High spatial resolution, widely applied in clinical and preclinical settings | High ionizing radiation, suboptimal contrast between tissues, inability to provide functional data | [108,113,114,115] |
| Feature Names | Radiomic Type | References |
|---|---|---|
| Volume of Voxels with Hounsfield Unit (HU) > 70 within Low-Standardized Uptake Value (SUV) Subvolume, Long-Run High Gray-Level Emphasis Along Direction with Maximum Value within High-SUV Subvolume | Contrast-Enhanced CT | [116] |
| 90th Percentile of Standardized SUV Distribution, Skewness of SUV Distribution | 18F-FMISO PET | [116] |
| Gray-Level Co-Occurrence Matrix Inverse Difference (GLCM Inverse Difference) | CT | [117] |
| Low Gray-Level Zone Emphasis (LGZE), Classification Parameter (CP) | 18F-FMISO PET | [118] |
| Tumor-to-Blood Maximum Ratio (T/Bmax), Hypoxic Volume (HV), Peak of SUV (SUVpeak) | 18F-FMISO PET | [119] |
| b-value of 200 s/mm2 (b200), Apparent Diffusion Coefficient (ADC) | DWI MRI | [98] |
| Histogram-Based, Gray-Level Co-Occurrence Matrix (GLCM) | Biparametric MRI | [120] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, M.; Law, H.K.W.; Tam, S.Y. Use of Radiomics in Characterizing Tumor Hypoxia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6679. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146679
Huang M, Law HKW, Tam SY. Use of Radiomics in Characterizing Tumor Hypoxia. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(14):6679. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146679
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Mohan, Helen K. W. Law, and Shing Yau Tam. 2025. "Use of Radiomics in Characterizing Tumor Hypoxia" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 14: 6679. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146679
APA StyleHuang, M., Law, H. K. W., & Tam, S. Y. (2025). Use of Radiomics in Characterizing Tumor Hypoxia. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(14), 6679. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146679





