Circulating microRNAs as Potential Diagnostic Tools for Asthma and for Indicating Severe Asthma Risk
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Demographics
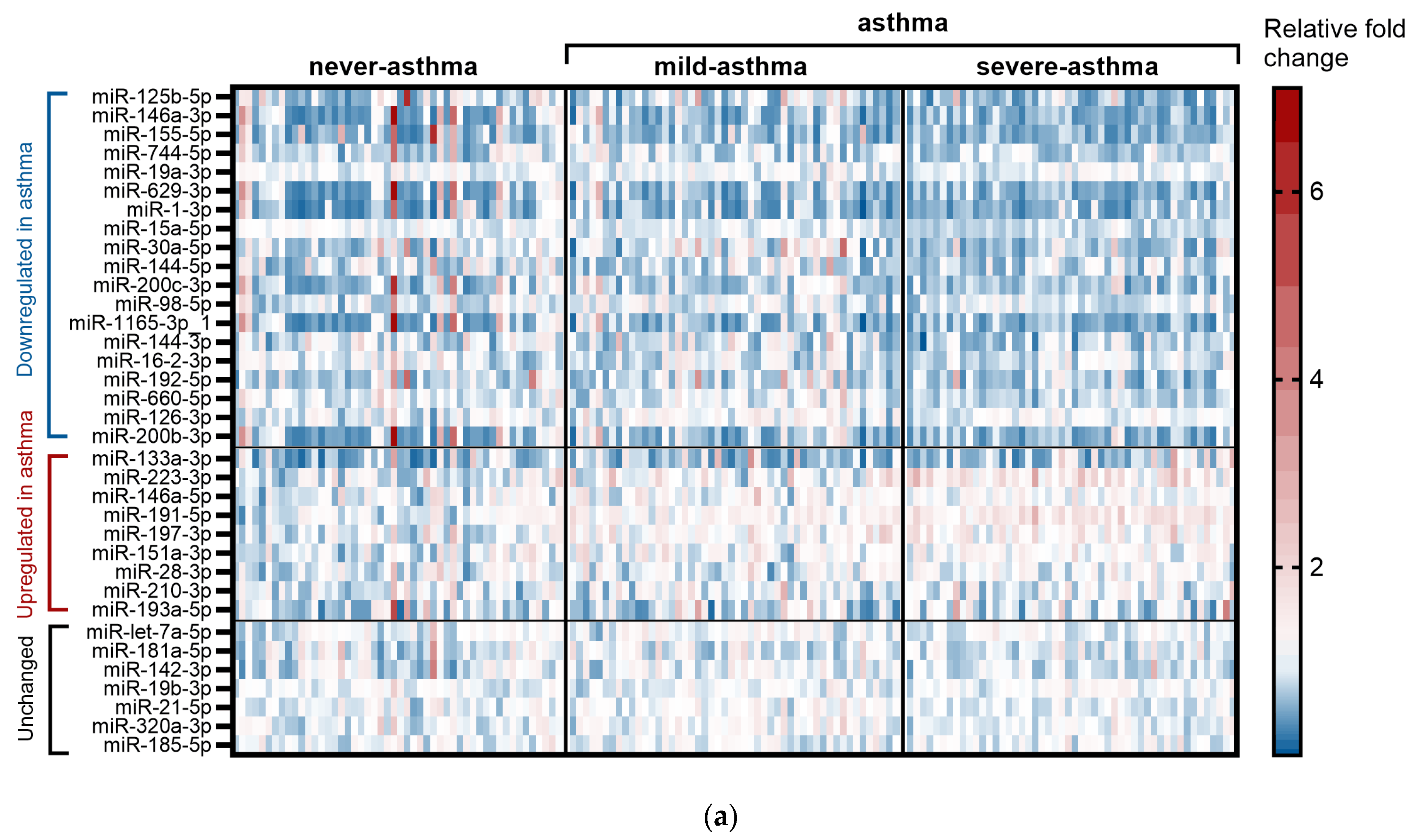
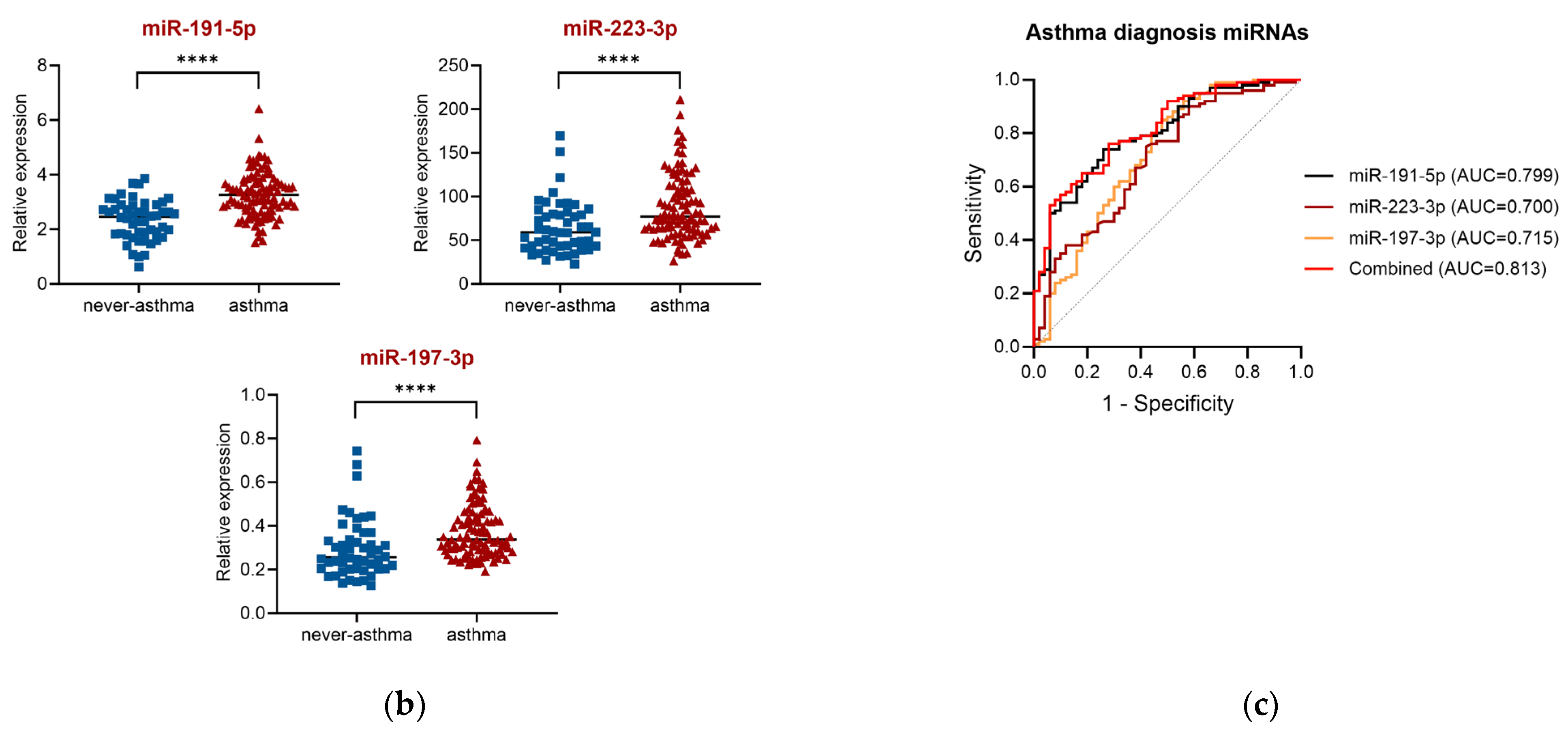
2.2. miRNA for Asthma Diagnosis (GeneGlobe Data and Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) Curve Analysis)
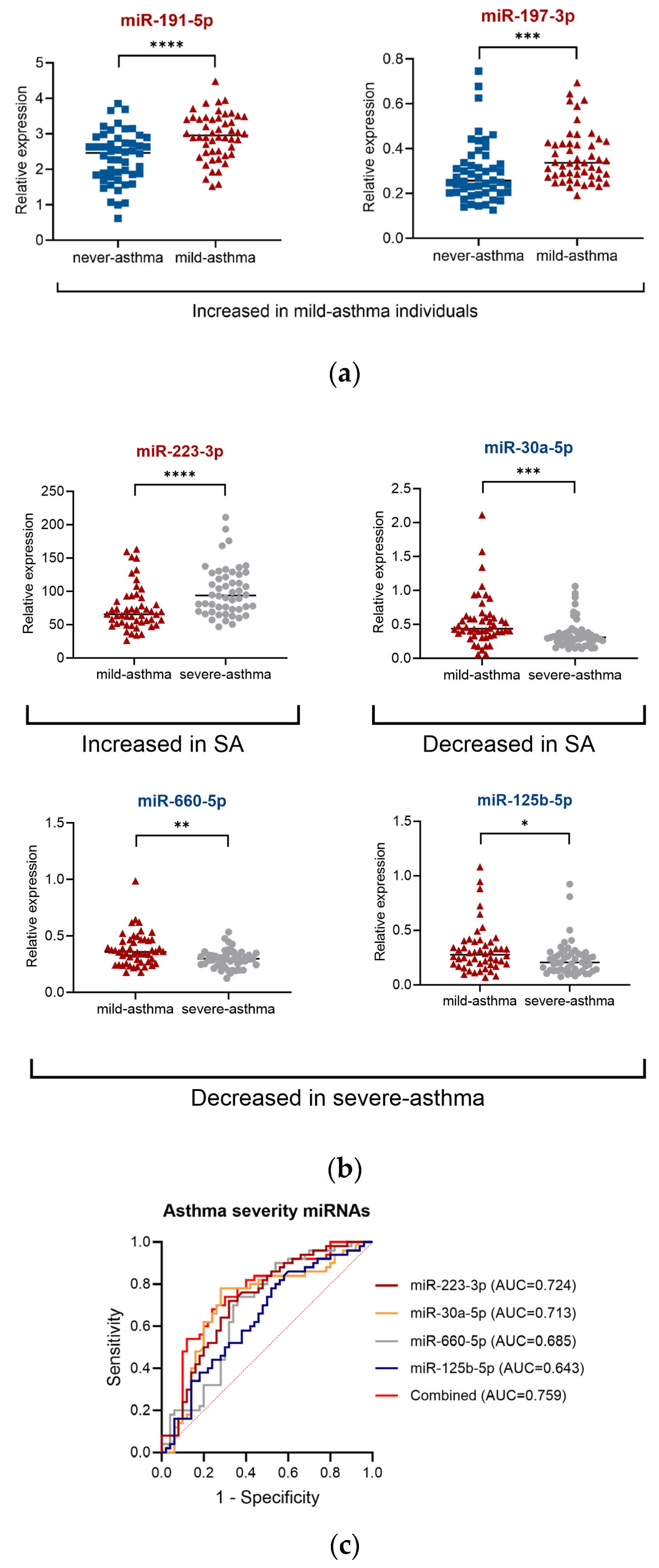
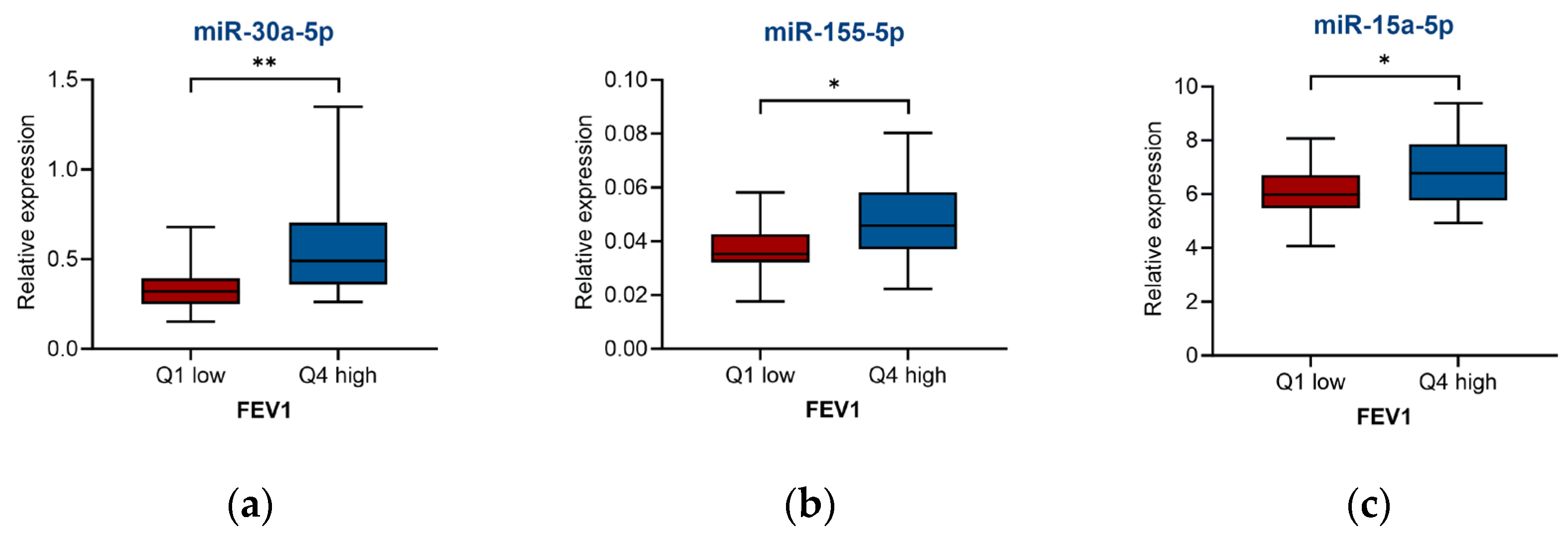
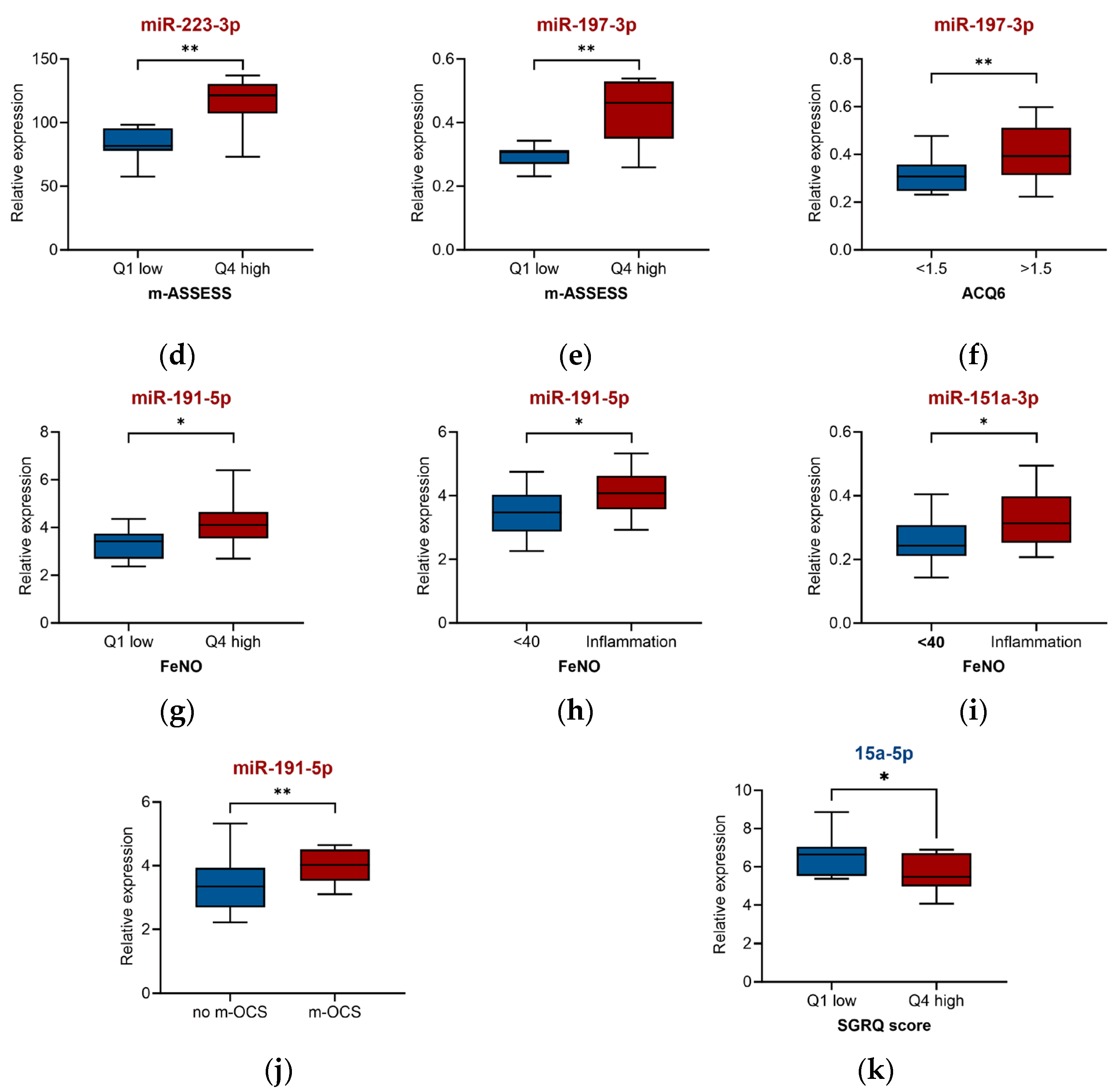
2.3. miRNA for Asthma Severity and Associated Clinical Parameters
2.4. Targets and Biological Pathways of miRNAs Differentially Expressed in the Sera of Severe-Asthma Patients
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Design
4.2. Study Population
4.3. Sample Collection and RNA Extraction
4.4. qRT-PCR and Data Analysis
4.5. Bioinformatics Analysis of Targets and Biological Pathways
4.6. Clinical Parameters
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACQ | Asthma control questionnaire |
| ACT | Asthma control test |
| ASSESS | Asthma severity scoring system |
| AUC | Area under the receiver operating characteristic |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| BTS | British Thoracic Society |
| CI | Confidence interval |
| COPD | Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease |
| FeNO | Fractional exhaled nitric oxide |
| FEV1 | Forced expiratory volume in 1 second |
| FOXA | Forkhead box |
| GINA | Global Initiative for Management of Asthma |
| IFN | Interferon |
| IOWBC | Isle of Wight Whole Population Birth Cohort |
| m-ASSESS | Modified asthma severity scoring system |
| miRNA | Micro RNA |
| mRNA | Messenger RNA |
| m-OCS | Being on maintenance (daily) oral corticosteroid |
| OCS | Oral corticosteroid |
| RNAs | Ribonucleic acids |
| ROC | Receiver operating characteristic |
| SGRQ | St. George Respiratory Questionnaire |
| WATCH | Wessex AsThma CoHort of difficult asthma |
References
- Global Asthma Network. The Global Asthma Report 2018; Global Asthma Network: Auckland, New Zealand, 2018. Available online: http://globalasthmareport.org/2018/resources/Global_Asthma_Report_2018.pdf (accessed on 12 January 2024).
- Asthma UK. Living in Limbo: The Scale of Unmet Need in Difficult and Severe Asthma; Asthma UK: London, UK, 2019; pp. 1–20. Available online: https://www.asthmaandlung.org.uk/sites/default/files/2023-03/living-in-limbo---the-scale-of-unmet-need-in-difficult-and-severe-asthma.pdf (accessed on 12 January 2024).
- Aaron, S.D.; Boulet, L.P.; Reddel, H.K.; Gershon, A.S. Underdiagnosis and overdiagnosis of asthma. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 198, 1012–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, K.F.; Wenzel, S.E.; Brozek, J.L.; Bush, A.; Castro, M.; Sterk, P.J.; Adcock, I.M.; Bateman, E.D.; Bel, E.H.; Bleecker, E.R.; et al. International ERS/ATS guidelines on definition, evaluation and treatment of severe asthma. Eur. Respir. J. 2014, 43, 343–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- BTS/SIGN Guideline for the Management of Asthma. Available online: https://www.brit-thoracic.org.uk/quality-improvement/guidelines/asthma/ (accessed on 10 July 2025).
- Global Initiative for Asthma. Global Strategy for Asthma Management and Prevention. Available online: https://ginasthma.org/ (accessed on 12 January 2024).
- Fitzpatrick, A.M.; Szefler, S.J.; Mauger, D.T.; Phillips, B.R.; Denlinger, L.C.; Moore, W.C.; Sorkness, R.L.; Wenzel, S.E.; Gergen, P.J.; Bleecker, E.R.; et al. Development and initial validation of the Asthma Severity Scoring System (ASSESS). J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020, 145, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 2004, 116, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortez, M.A.; Bueso-Ramos, C.; Ferdin, J.; Lopez-Berestein, G.; Sood, A.K.; Calin, G.A. MicroRNAs in body fluids-the mix of hormones and biomarkers. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 8, 467–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, M.; Schaefer, A.; Steiner, I.; Kempkensteffen, C.; Stephan, C.; Erbersdobler, A.; Jung, K. Robust microRNA stability in degraded RNA preparations from human tissue and cell samples. Clin. Chem. 2010, 56, 998–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witwer, K.W. Circulating microRNA biomarker studies: Pitfalls and potential solutions. Clin. Chem. 2015, 61, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinkerton, M.; Chinchilli, V.; Banta, E.; Craig, T.; August, A.; Bascom, R.; Cantorna, M.; Harvill, E.; Ishmael, F.T. Differential expression of microRNAs in exhaled breath condensates of patients with asthma, patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and healthy adults. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 132, 217–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panganiban, R.P.; Wang, Y.; Howrylak, J.; Chinchilli, V.M.; Craig, T.J.; August, A.; Ishmael, F.T. Circulating microRNAs as biomarkers in patients with allergic rhinitis and asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 137, 1423–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milger, K.; Götschke, J.; Krause, L.; Nathan, P.; Alessandrini, F.; Tufman, A.; Fischer, R.; Bartel, S.; Theis, F.J.; Behr, J.; et al. Identification of a plasma miRNA biomarker signature for allergic asthma: A translational approach. Allergy 2017, 72, 1962–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Yi, M.; Tan, Y.; Yi, Z.; Zhang, Y. A comprehensive analysis of microRNAs as diagnostic biomarkers for asthma. Ther. Adv. Respir. Dis. 2020, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roffel, M.P.; Boudewijn, I.M.; van Nijnatten, J.L.L.; Faiz, A.; Vermeulen, C.J.; van Oosterhout, A.J.; Affleck, K.; Timens, W.; Bracke, K.R.; Maes, T.; et al. Identification of asthma-associated microRNAs in bronchial biopsies. Eur. Respir. J. 2022, 59, 2101294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyyaly, M.A.; Vorobeva, E.V.; Kothalawala, D.M.; Fong, W.C.G.; He, P.; Sones, C.L.; Al-Zahrani, M.; Sanchez-Elsner, T.; Arshad, S.H.; Kurukulaaratchy, R.J. MicroRNAs-a promising tool for asthma diagnosis and severity assessment: A systematic review. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez-Mera, S.; Martelo-Vidal, L.; Miguéns-Suárez, P.; Saavedra-Nieves, P.; Arias, P.; González-Fernández, C.; Mosteiro-Añón, M.; Corbacho-Abelaira, M.D.; Blanco-Aparicio, M.; Méndez-Brea, P.; et al. Serum exosome inflamma-miRs are surrogate biomarkers for asthma phenotype and severity. Allergy 2023, 78, 141–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigo-Muñoz, J.M.; Cañas, J.A.; Sastre, B.; Rego, N.; Greif, G.; Rial, M.; Mínguez, P.; Mahíllo-Fernández, I.; Fernández-Nieto, M.; Mora, I.; et al. Asthma diagnosis using integrated analysis of eosinophil microRNAs. Allergy 2019, 74, 507–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyyaly, M.A.; Sanchez-Elsner, T.; He, P.; Sones, C.L.; Arshad, S.H.; Kurukulaaratchy, R.J. Circulating miRNAs-a potential tool to identify severe asthma risk? Clin. Transl. Allergy 2021, 11, e12040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.P.; Lee, C.Y.; Tsai, M.H.; Chiu, Y.C.; Hsiao, C.K.; Lai, L.C.; Chuang, E.Y. miRSystem: An integrated system for characterizing enriched functions and pathways of microRNA targets. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e42390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solberg, O.D.; Ostrin, E.J.; Love, M.I.; Peng, J.C.; Bhakta, N.R.; Hou, L.; Nguyen, C.; Solon, M.; Nguyen, C.; Barczak, A.J.; et al. Airway epithelial miRNA expression is altered in asthma. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 186, 965–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C.; Ma, Y.; He, S.; Kang, Y.; Yang, J. Increased miR-223-3p in leukocytes positively correlated with IL-17A in plasma of asthmatic patients. Iran. J. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2020, 19, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maes, T.; Cobos, F.A.; Schleich, F.; Sorbello, V.; Henket, M.; De Preter, K.; Bracke, K.R.; Conickx, G.; Mesnil, C.; Vandesompele, J.; et al. Asthma inflammatory phenotypes show differential microRNA expression in sputum. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 137, 1433–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, P.; Wang, X.P.; Luoreng, Z.M.; Yang, J.; Jia, L.; Ma, Y.; Wei, D.W. miR-223: An effective regulator of immune cell differentiation and inflammation. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 17, 2308–2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Nunez, R.T.; Bondanese, V.P.; Louafi, F.; Francisco-Garcia, A.S.; Rupani, H.; Bedke, N.; Holgate, S.; Howarth, P.H.; Davies, D.E.; Sanchez-Elsner, T.; et al. A microRNA network dysregulated in asthma controls IL-6 production in bronchial epithelial cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e111659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suojalehto, H.; Lindström, I.; Majuri, M.-L.; Mitts, C.; Karjalainen, J.; Wolff, H.; Alenius, H. Altered microRNA expression of nasal mucosa in long-term asthma and allergic rhinitis. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2014, 163, 168–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ElKashef, S.M.M.E.; Ahmad, S.E.-A.; Soliman, Y.M.A.; Mostafa, M.S. Role of microRNA-21 and microRNA-155 as biomarkers for bronchial asthma. Innate. Immun. 2021, 27, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Do, D.C.; Ke, X.; Zhang, S.; Lambert, K.; Kumar, S.; Hu, C.; Zhou, Y.; Ishmael, F.T.; et al. miR-155 modulates cockroach allergen- and oxidative stress-induced cyclooxygenase-2 in asthma. J. Immunol. 2018, 201, 916–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karam, R.A.; Abd Elrahman, D.M. Differential expression of miR-155 and Let-7a in the plasma of childhood asthma: Potential biomarkers for diagnosis and severity. Clin. Biochem. 2019, 68, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Yang, H.; Ma, X.; Wu, G. Strand-specific miR-28-3p and miR-28-5p have differential effects on nasopharyngeal cancer cells proliferation, apoptosis, migration and invasion. Cancer Cell Int. 2019, 19, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Li, J.; Gao, P.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, J. miR-155: A novel target in allergic asthma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahmer, T.; Krauss-Etschmann, S.; Buschmann, D.; Behrends, J.; Watz, H.; Kirsten, A.-M.; Pedersen, F.; Waschki, B.; Fuchs, O.; Pfaffl, M.; et al. MiR-122-5p and miR-191-5p are increased in plasma small extracellular vesicles in asthma. Eur. Resp. J. 2019, 54, PA5203. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, D.; Pan, Y.; Liu, X.; Qiao, X.; Cui, W.; Dong, L. Integrative analysis reveals a miRNA-mRNA regulatory network and potential causative agents in the asthmatic airway epithelium. J. Asthma Allergy 2021, 14, 1307–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, J.; Faiz, A.; Timens, W.; Berge, M.v.D.; Terpstra, M.M.; Kok, K.; Berg, A.v.D.; Kluiver, J.; Brandsma, C.A. Marked TGF-β-regulated miRNA expression changes in both COPD and control lung fbroblasts. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 18214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, B.; Huang, M.; Wang, X. miR-30a-3p participates in the development of asthma by targeting CCR3. Open Med. 2020, 15, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.B.; Chen, Y.L.; Pang, F. MicroRNA-30a targets ATG5 and attenuates airway fibrosis in asthma by suppressing autophagy. Inflammation 2020, 43, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Chen, X.; Wu, Q.; Song, J.; Wang, L.; Li, G. MiR-125b inhibits goblet cell differentiation in allergic airway inflammation by targeting SPDEF. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 782, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.; Li, J.; Fan, W.; Xie, J.; Huang, Q.; Zhang, H.; Liao, F.; Peng, H. Expression levels of microRNA-125b in serum exosomes of patients with asthma of different severity and its diagnostic significance. Curr. Drug Metab. 2019, 20, 781–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.-W.; Verhaeghe, C.; Nguyenvu, L.T.; Barbeau, R.; Eisley, C.J.; Nakagami, Y.; Huang, X.; Woodruff, P.G.; Fahy, J.V.; Erle, D.J. Distinct roles of FOXA2 and FOXA3 in allergic airway disease and asthma. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2009, 180, 603–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musiol, S.; Harris, C.P.; Karlina, R.; Gostner, J.M.; Rathkolb, B.; Schnautz, B.; Schneider, E.; Mair, L.; Vergara, E.E.; Flexeder, C.; et al. Dietary digestible carbohydrates are associated with higher prevalence of asthma in humans and with aggravated lung allergic inflammation in mice. Allergy 2023, 78, 1218–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durrani, S.R.; Montville, D.J.; Pratt, A.S.; Sahu, S.; DeVries, M.K.; Rajamanickam, V.; Gangnon, R.E.; Gill, M.A.; Gern, J.E.; Lemanske, R.F.; et al. Innate immune responses to rhinovirus are reduced by the high-affinity IgE receptor in allergic asthmatic children. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012, 130, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulos, N.G.; Stanciu, L.A.; Papi, A.; Holgate, S.T.; Johnston, S.L. Rhinovirus-induced alterations on peripheral blood mononuclear cell phenotype and costimulatory molecule expression in normal and atopic asthmatic subjects. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2002, 32, 537–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshad, S.H.; Holloway, J.W.; Karmaus, W.; Zhang, H.; Ewart, S.; Mansfield, L.; Matthews, S.; Hodgekiss, C.; Roberts, G.; Kurukulaaratchy, R. Cohort profile: The Isle of Wight whole population birth cohort (IOWBC). Int. J. Epidemiol. 2018, 47, 1043–1044i. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azim, A.; Mistry, H.; Freeman, A.; Barber, C.; Newell, C.; Gove, K.; Thirlwall, Y.; Harvey, M.; Bentley, K.; Knight, D.; et al. Protocol for the Wessex AsThma CoHort of difficult asthma (WATCH): A pragmatic real-life longitudinal study of difficult asthma in the clinic. BMC Pulm. Med. 2019, 19, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Group | Severe Asthma | Mild Asthma | Never Asthma | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median age (IQR) | 54.0 (40.0–88) | 26.0 (25.0–27.0) | 18.0 (17.0–18.0) | <0.001 |
| Male, N (%) | 15 (30.0) | 20 (40.0) | 23 (46.0) | <0.001 |
| Female, N (%) | 35 (70.0) | 30 (60.0) | 27 (54.0) | - |
| Median age at asthma diagnosis (IQR) | 28.0 (7.0–67) | 6 (0–25) | N.A. | <0.001 |
| Smoking (ever) N (%) | 24 (48) | 22 (44) | 23 (46) | 0.91 |
| Median BMI (IQR) | 28.9 (24.8–48.3) | 25.3 ((17.8–55.5) * | 25.1 (18–40.3) | <0.001 |
| Atopy (%) | 28 (56.0) | 35 (70.0) | 16 (32.0) | <0.001 |
| m-OCS N (%) | 14 (28) | N.A. | N.A. | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vorobeva, E.V.; Kyyaly, M.A.; Sones, C.L.; He, P.J.W.; Arshad, S.H.; Sanchez-Elsner, T.; Kurukulaaratchy, R.J. Circulating microRNAs as Potential Diagnostic Tools for Asthma and for Indicating Severe Asthma Risk. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6676. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146676
Vorobeva EV, Kyyaly MA, Sones CL, He PJW, Arshad SH, Sanchez-Elsner T, Kurukulaaratchy RJ. Circulating microRNAs as Potential Diagnostic Tools for Asthma and for Indicating Severe Asthma Risk. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(14):6676. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146676
Chicago/Turabian StyleVorobeva, Elena V., M. Aref Kyyaly, Collin L. Sones, Peijun J. W. He, S. Hasan Arshad, Tilman Sanchez-Elsner, and Ramesh J. Kurukulaaratchy. 2025. "Circulating microRNAs as Potential Diagnostic Tools for Asthma and for Indicating Severe Asthma Risk" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 14: 6676. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146676
APA StyleVorobeva, E. V., Kyyaly, M. A., Sones, C. L., He, P. J. W., Arshad, S. H., Sanchez-Elsner, T., & Kurukulaaratchy, R. J. (2025). Circulating microRNAs as Potential Diagnostic Tools for Asthma and for Indicating Severe Asthma Risk. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(14), 6676. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146676











