Kaempferol Alleviates Carbon Tetrachloride-Induced Liver Fibrosis in Mice by Regulating Intestinal Short-Chain Fatty Acids
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
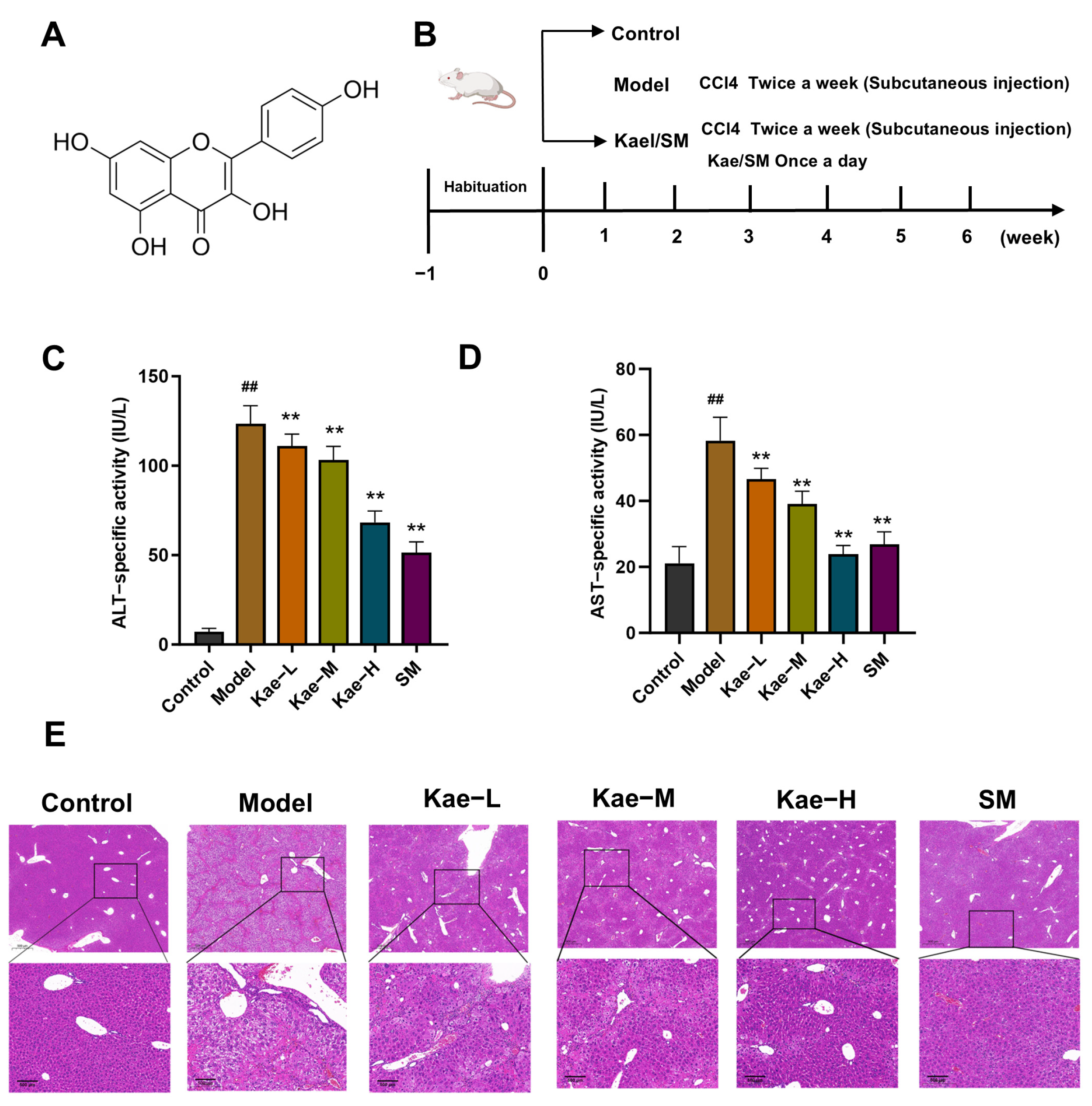
2.1. Kae Inhibits CCl4-Induced Mice Hepatic Injury and Fibrosis
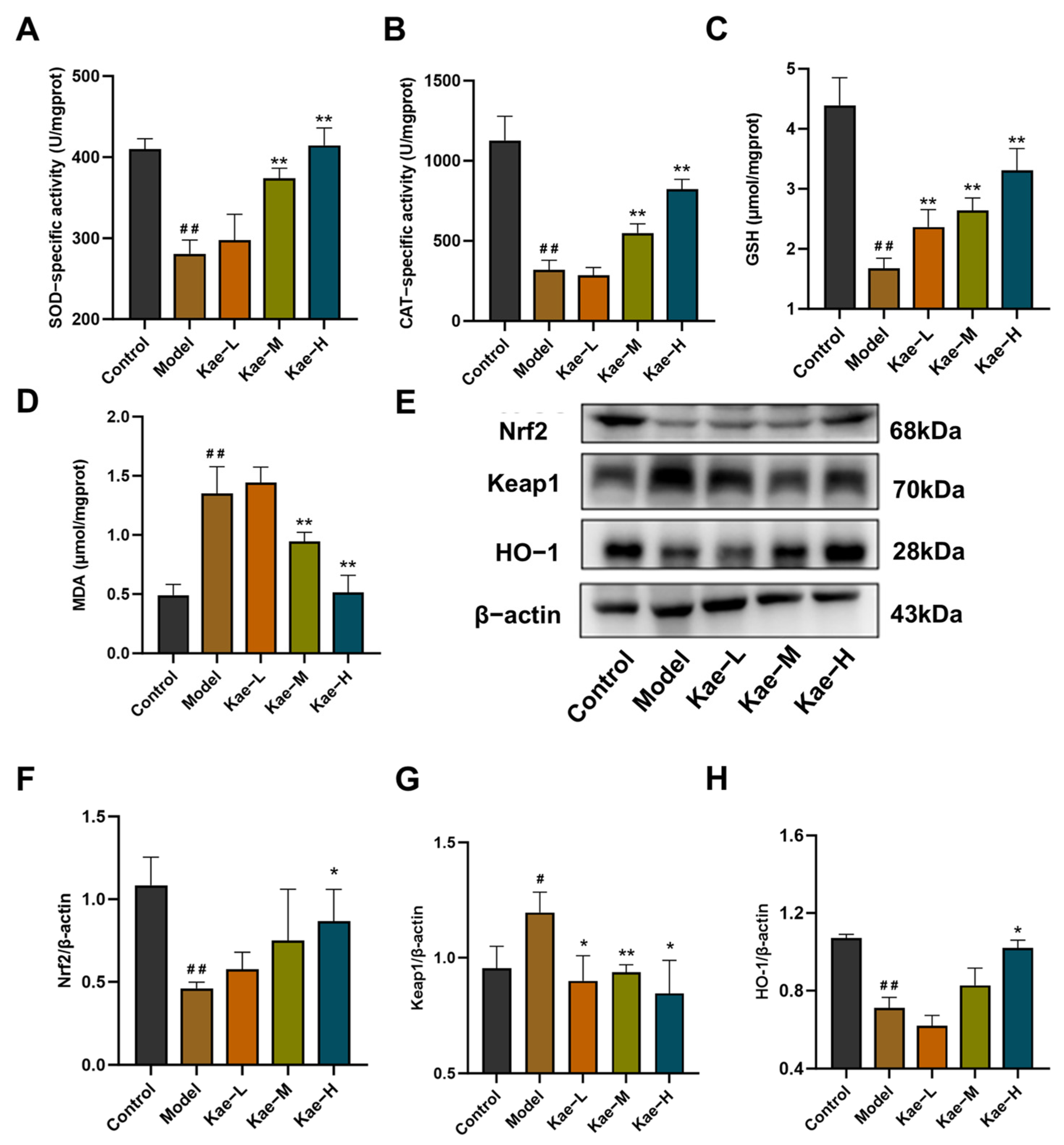
2.2. Kae Attenuates Oxidative Stress in Liver Tissues of CCl4-Treated Mice
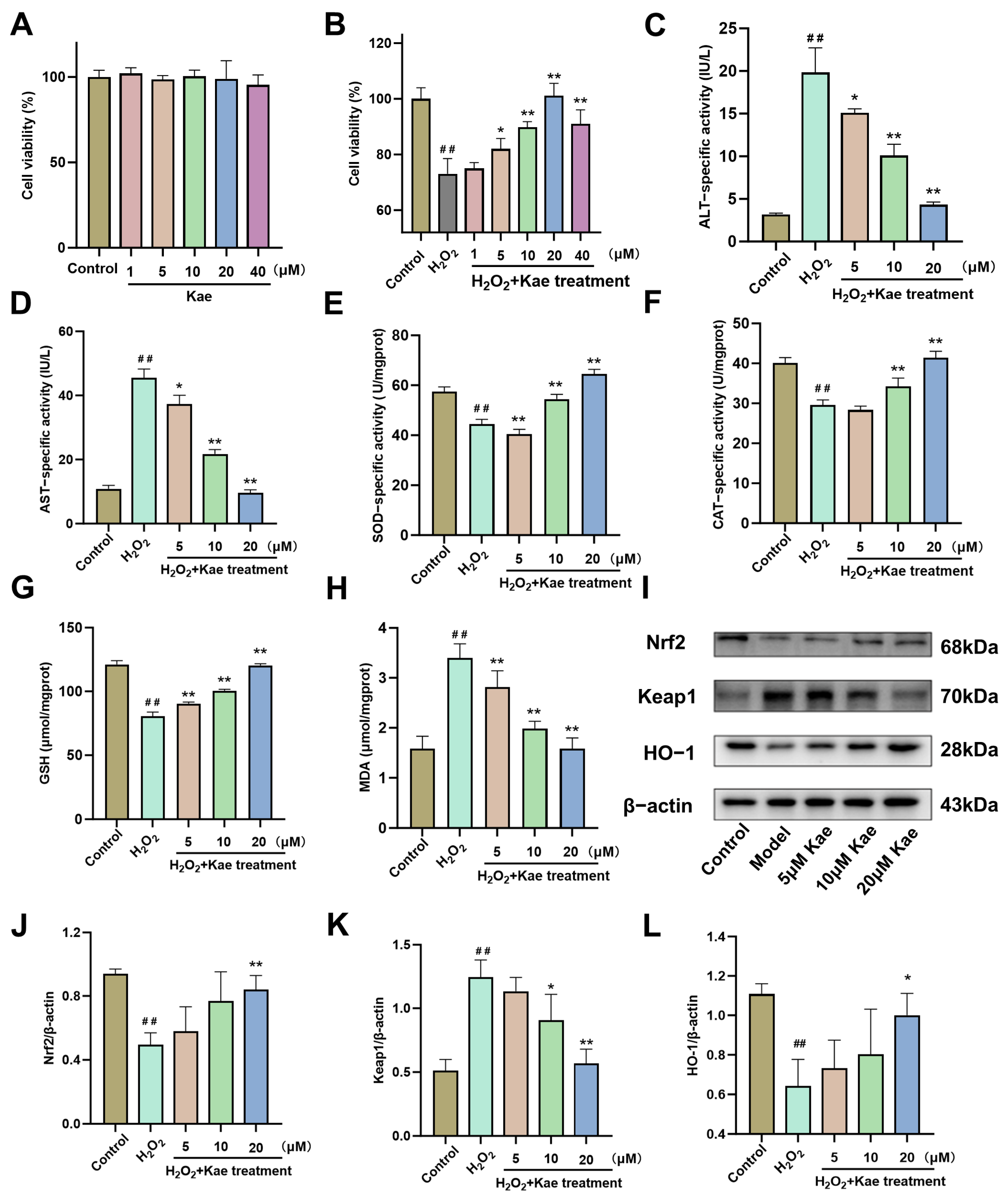
2.3. Kae Alleviates Hydrogen Peroxide-Induced Oxidative Damage in AML12 Cells
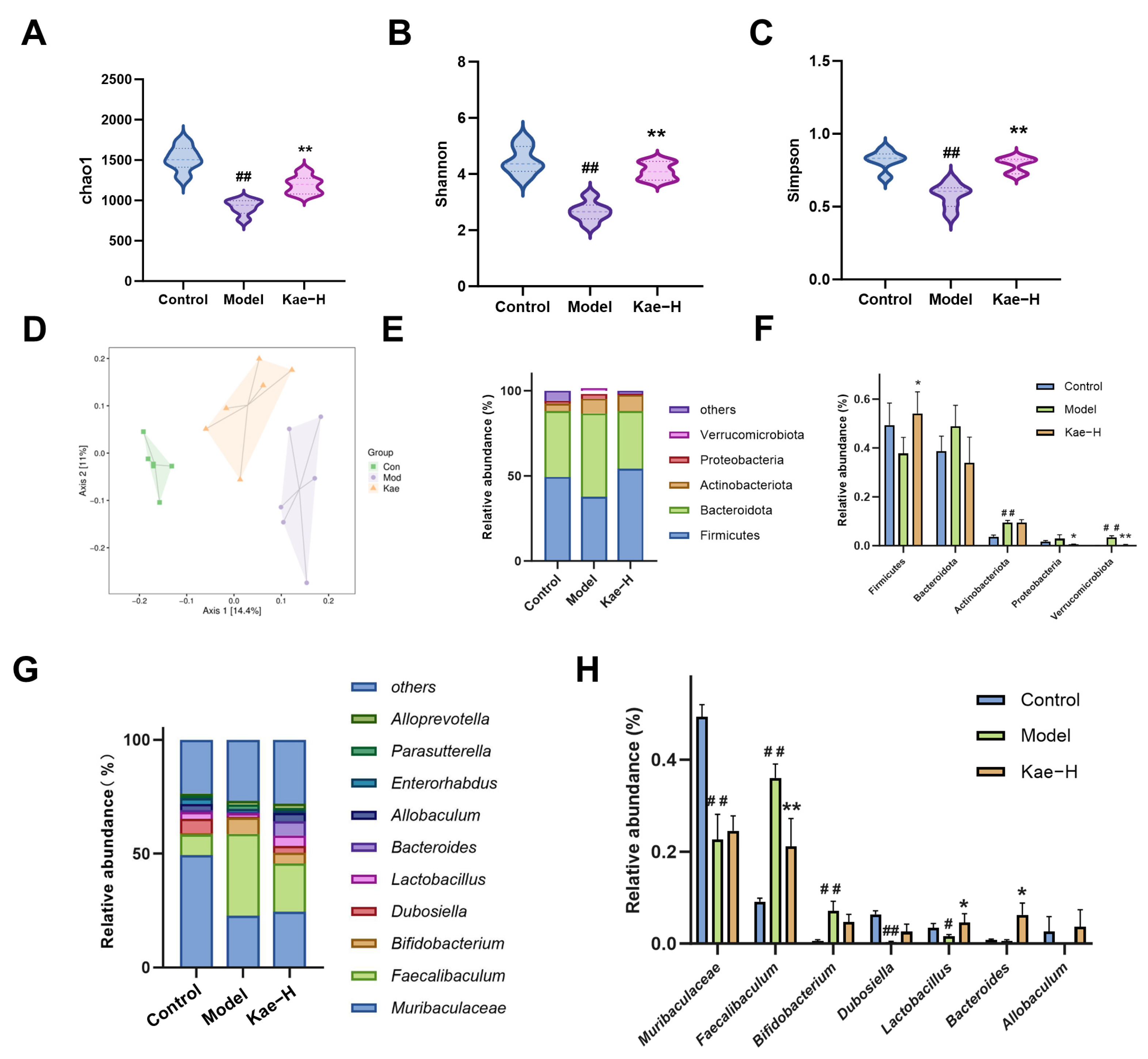
2.4. Kae Restores Gut Microbiota Disorder in Liver Fibrosis Mice
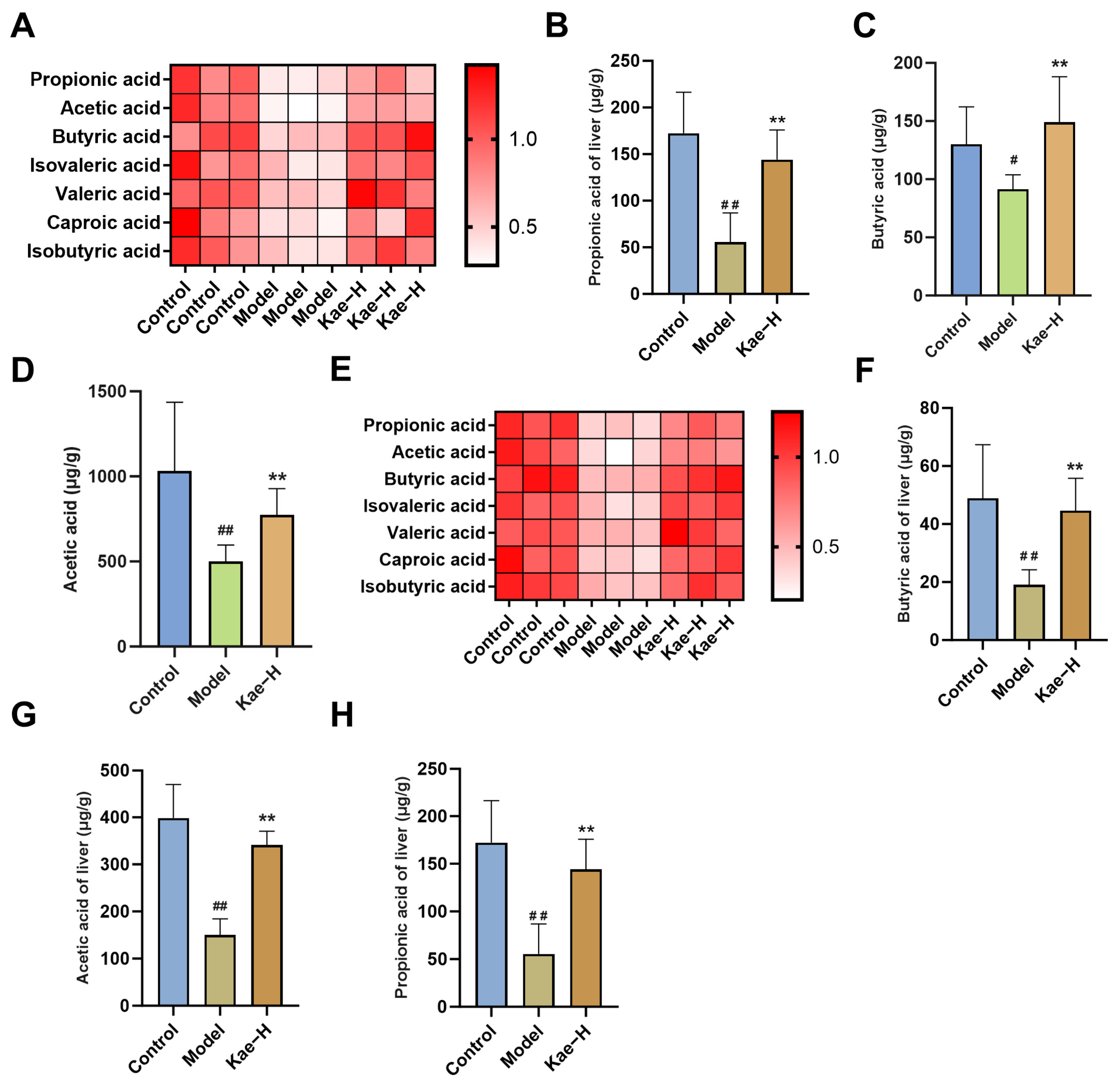
2.5. Kae Regulates SCFAs in Both Intestinal Contents and Liver Tissues
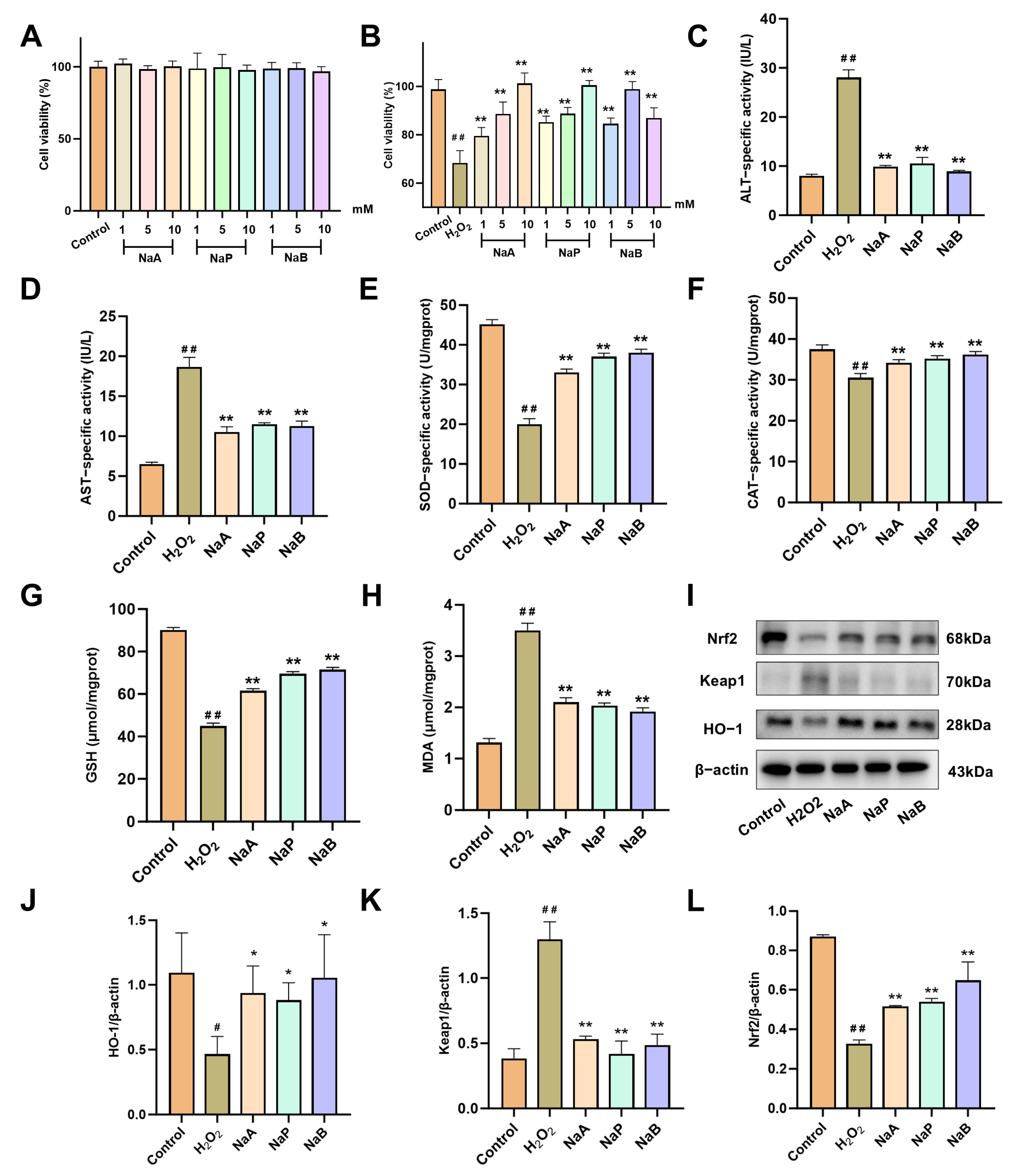
2.6. SCFAs Attenuate H2O2-Induced Oxidative Damage in AML12 Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents
4.2. Animals
4.3. Experimental Design
4.4. Histological Analysis
4.5. 16S rRNA Sequencing
4.6. Detection of SCFA Levels in Intestinal Contents and Liver Tissues
4.7. Cell Culture
4.8. CCK-8 Assay
4.9. Western Blot Analysis
4.10. Biochemical Kits
4.11. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Caligiuri, A.; Gentilini, A.; Pastore, M.; Gitto, S.; Marra, F. Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Liver Fibrosis Regression. Cells 2021, 10, 2759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, L.; Liu, Z.; Ci, L.; Shuai, C.; Lv, X.; Li, J. Research Progress on the Anti-Hepatic Fibrosis Action and Mechanism of Natural Products. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019, 75, 105765. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Friedman, S.L.; Pinzani, M. Hepatic Fibrosis 2022: Unmet Needs and a Blueprint for the Future. Hepatology 2022, 75, 473–488. [Google Scholar]
- Roehlen, N.; Crouchet, E.; Baumert, T.F. Liver Fibrosis: Mechanistic Concepts and Therapeutic Perspectives. Cells 2020, 9, 875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Dong, Y.; He, C.; Zhao, M.; He, Q. The Gut Microbiota and Oxidative Stress in Autism Spectrum Disorders (Asd). Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 8396708. [Google Scholar]
- Mignini, I.; Galasso, L.; Piccirilli, G.; Calvez, V.; Termite, F.; Esposto, G.; Borriello, R.; Miele, L.; Ainora, M.E.; Gasbarrini, A.; et al. Interplay of Oxidative Stress, Gut Microbiota, and Nicotine in Metabolic-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (Masld). Antioxidants 2024, 13, 1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, N.; Xu, Y.; Tan, H.Y.; Li, S.; Feng, Y. Molecular Mechanisms Involved in Oxidative Stress-Associated Liver Injury Induced by Chinese Herbal Medicine: An Experimental Evidence-Based Literature Review and Network Pharmacology Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2745. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, P.; Wang, Y.; Yang, G.; Zhang, Q.; Meng, L.; Xin, Y.; Jiang, X. The Role of Short-Chain Fatty Acids in Intestinal Barrier Function, Inflammation, Oxidative Stress, and Colonic Carcinogenesis. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 165, 105420. [Google Scholar]
- Pohl, K.; Moodley, P.; Dhanda, A. The Effect of Increasing Intestinal Short-Chain Fatty Acid Concentration on Gut Permeability and Liver Injury in the Context of Liver Disease: A Systematic Review. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 37, 1498–1506. [Google Scholar]
- Periferakis, A.; Periferakis, K.; Badarau, I.A.; Petran, E.M.; Popa, D.C.; Caruntu, A.; Costache, R.S.; Scheau, C.; Caruntu, C.; Costache, D.O. Kaempferol: Antimicrobial Properties, Sources, Clinical, and Traditional Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15054. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, Y.X.; Yu, Y.J.; Dai, S.; Zhang, C.Y.; Xue, X.Y.; Zhou, M.L.; Yao, C.H.; Li, Y.X. Kaempferol Efficacy in Metabolic Diseases: Molecular Mechanisms of Action in Diabetes Mellitus, Obesity, Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease, Steatohepatitis, and Atherosclerosis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 175, 116694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, T.; Huang, S.; Huang, Q.; Ming, Z.; Wang, M.; Li, R.; Zhao, Y. Kaempferol Attenuates Liver Fibrosis by Inhibiting Activin Receptor-Like Kinase 5. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 6403–6410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Weng, Q.; Gong, S.; Zhang, W.; Wang, J.; Huang, Y.; Li, Y.; Guo, J.; Lan, T. Kaempferol Prevents Acetaminophen-Induced Liver Injury by Suppressing Hepatocyte Ferroptosis Via Nrf2 Pathway Activation. Food Funct. 2023, 14, 1884–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Shao, M.; Zhang, C.; Xiang, H.; Wang, J.; Wu, T.; Ji, G. Kaempferol Attenuates Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis by Regulating Serum and Liver Bile Acid Metabolism. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 946360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, R.; Cao, C.; Hu, X.; Du, K.; Zhang, J.; Li, M.; Li, B.; Lin, H.; Zhang, A.; Li, Y.; et al. Kaempferol Attenuates Carbon Tetrachloride (CCl(4))-Induced Hepatic Fibrosis by Promoting Asic1a Degradation and Suppression of the Asic1a-Mediated Ers. Phytomedicine 2023, 121, 155125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkandahri, M.Y.; Pamungkas, B.T.; Oktoba, Z.; Shafirany, M.Z.; Sulastri, L.; Arfania, M.; Anggraeny, E.N.; Pratiwi, A.; Astuti, F.D.; Indriyani; et al. Hepatoprotective Effect of Kaempferol: A Review of the Dietary Sources, Bioavailability, Mechanisms of Action, and Safety. Adv. Pharmacol. Pharm. Sci. 2023, 2023, 1387665. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, Y.; Li, X.; Xu, F.; Zhao, S.; Wu, X.; Wang, Y.; Xie, J. Kaempferol Alleviates Murine Experimental Colitis by Restoring Gut Microbiota and Inhibiting the Lps-Tlr4-Nf-Κb Axis. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 679897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Shi, Z.; Wang, C.; Chen, F. Kaempferol Remodels Liver Monocyte Populations and Treats Hepatic Fibrosis in Mice by Modulating Intestinal Flora and Metabolic Reprogramming. Inflammation 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Yang, X. Intestinal Flora Plays a Role in the Progression of Hepatitis-Cirrhosis-Liver Cancer. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1140126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartsch, L.M.; Damasio, M.P.S.; Subudhi, S.; Drescher, H.K. Tissue-Resident Memory T Cells in the Liver-Unique Characteristics of Local Specialists. Cells 2020, 9, 2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Wang, B. The Gut-Liver Axis in Health and Disease: The Role of Gut Microbiota-Derived Signals in Liver Injury and Regeneration. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 775526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shandilya, S.; Kumar, S.; Jha, N.K.; Kesari, K.K.; Ruokolainen, J. Interplay of Gut Microbiota and Oxidative Stress: Perspective on Neurodegeneration and Neuroprotection. J. Adv. Res. 2022, 38, 223–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Lu, T.; Song, P.; Dong, Y.; Dai, C.; Zhang, W.; Jia, X.; Guo, Z.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, J.; et al. Glycyrrhizic Acid Ameliorates Hepatic Fibrosis by Inhibiting Oxidative Stress Via Akr7a2. Phytomedicine 2024, 133, 155878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Tan, S.; Liu, H.; Jiang, J.; Wang, X.; Li, L.; Wu, B. Hepatocyte-Derived Masp1-Enriched Small Extracellular Vesicles Activate Hscs to Promote Liver Fibrosis. Hepatology 2023, 77, 1181–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Zhou, X.; Wang, L.; Fan, W.; Gao, S.; Zhang, D.; Ling, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, L.; Bai, F.; et al. Salvianolic Acid B Attenuates Liver Fibrosis by Targeting Ecm1 and Inhibiting Hepatocyte Ferroptosis. Redox Biol. 2024, 69, 103029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Y.; Zhao, C.; Tai, Y.; Li, B.; Lan, T.; Lai, E.; Dai, W.; Guo, Y.; Gan, C.; Kostallari, E.; et al. Sting Mediates Hepatocyte Pyroptosis in Liver Fibrosis by Epigenetically Activating the Nlrp3 Inflammasome. Redox Biol. 2023, 62, 102691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Y.; Wang, W.; Wang, L.; Ma, L.; Zhai, D.; Wang, F.; Shi, R.; Liu, C.; Xu, Q.; Chen, G.; et al. Obacunone Attenuates Liver Fibrosis with Enhancing Anti-Oxidant Effects of Gpx-4 and Inhibition of Emt. Molecules 2021, 26, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wang, S.; Zhang, L.; Ka, Y.; Zhou, M.; Wang, Y.; Tang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Wang, W.; Liu, W. Research Progress on Pharmacokinetics, Anti-Inflammatory and Immunomodulatory Effects of Kaempferol. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2025, 152, 114387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghemo, A.; Alekseeva, O.P.; Angelico, F.; Bakulin, I.G.; Bakulina, N.V.; Bordin, D.; Bueverov, A.O.; Drapkina, O.M.; Gillessen, A.; Kagarmanova, E.M.; et al. Role of Silymarin as Antioxidant in Clinical Management of Chronic Liver Diseases: A Narrative Review. Ann. Med. 2022, 54, 1548–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhou, F.; Guo, J.; Wang, T.; Shi, Y.; Yang, Y.; Lu, J.; Pei, G. Administration of a Mixture of Triterpenoids from Yeyachun and Phenolic Acids from Danshen Ameliorates Carbon Tetrachloride-Induced Liver Fibrosis in Mice by the Regulation of Intestinal Flora. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 143, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Xiang, H.; Xiang, H.; Sun, Z.; Xu, J.; Ren, H.; Hu, P.; Peng, M. Gw9662 Ameliorates Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis by Inhibiting the Pparγ/Cd36 Pathway and Altering the Gut Microbiota. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2023, 960, 176113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Zhao, J.; Xie, F.; He, H.; Johnston, L.J.; Dai, X.; Wu, C.; Ma, X. Dietary Fiber-Derived Short-Chain Fatty Acids: A Potential Therapeutic Target to Alleviate Obesity-Related Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Obes. Rev. 2021, 22, e13316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, L.; Yang, X.; He, F.; Wang, T.; Bao, T.; Lu, H.; Wang, H.; Yang, S. Inulin Alleviates Inflammation of Alcoholic Liver Disease Via Scfas-Inducing Suppression of M1 and Facilitation of M2 Macrophages in Mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 78, 106062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Sheng, L.; Zhong, J.; Tao, X.; Zhu, W.; Ma, J.; Yan, J.; Zhao, A.; Zheng, X.; Wu, G.; et al. Desulfovibrio Vulgaris, a Potent Acetic Acid-Producing Bacterium, Attenuates Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Mice. Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1930874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koutoukidis, D.A.; Yen, S.; Castro, P.G.; Misheva, M.; Jebb, S.A.; Aveyard, P.; Tomlinson, J.W.; Mozes, F.E.; Cobbold, J.F.; Johnson, J.S.; et al. Changes in Intestinal Permeability and Gut Microbiota Following Diet-Induced Weight Loss in Patients with Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatohepatitis and Liver Fibrosis. Gut Microbes 2024, 16, 2392864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parada Venegas, D.; De la Fuente, M.K.; Landskron, G.; González, M.J.; Quera, R.; Dijkstra, G.; Harmsen, H.J.M.; Faber, K.N.; Hermoso, M.A. Short Chain Fatty Acids (Scfas)-Mediated Gut Epithelial and Immune Regulation and Its Relevance for Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 277. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.K.; Yang, J.Z.; Cheng, C.H.; Wan, J.Y.; Chen, Y.C.; Zhou, H.Q.; Zheng, D.K.; Lan, Z.X.; You, Q.H.; Wang, Q.; et al. Short-Chain Fatty Acids Mitigate Methamphetamine-Induced Hepatic Injuries in a Sigma-1 Receptor-Dependent Manner. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 280, 116538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Xu, B.; Wang, X.; Wan, W.H.; Lu, J.; Kong, D.; Jin, Y.; You, W.; Sun, H.; Mu, X.; et al. Gut Microbiota-Derived Short-Chain Fatty Acids Regulate Group 3 Innate Lymphoid Cells in Hcc. Hepatology 2023, 77, 48–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, X.; Zhang, C.; Yang, J.; Tian, Y.; You, L.; Yang, H.; Li, Y.; Liu, H.; Pan, D.; Liu, Z. Kaempferol Improves Exercise Performance by Regulating Glucose Uptake, Mitochondrial Biogenesis, and Protein Synthesis Via Pi3k/Akt and Mapk Signaling Pathways. Foods 2024, 13, 1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, A.B.; Mehta, K.J. Liver Biopsy for Assessment of Chronic Liver Diseases: A Synopsis. Clin. Exp. Med. 2023, 23, 273–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Lauber, C.L.; Walters, W.A.; Berg-Lyons, D.; Lozupone, C.A.; Turnbaugh, P.J.; Fierer, N.; Knight, R. Global Patterns of 16s Rrna Diversity at a Depth of Millions of Sequences Per Sample. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108 (Suppl. 1), 4516–4522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, X.; Guo, J.; You, Y.; Yin, M.; Ren, C.; Zhan, J.; Huang, W. A Fast and Accurate Way to Determine Short Chain Fatty Acids in Mouse Feces Based on Gc-Ms. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed Life Sci. 2018, 1099, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, S.; Tang, F.; Zhou, Z.; Li, L.; Tang, Y.; Fu, K.; Tan, Y.; Li, L. Kaempferol Alleviates Carbon Tetrachloride-Induced Liver Fibrosis in Mice by Regulating Intestinal Short-Chain Fatty Acids. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6666. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146666
Zhang S, Tang F, Zhou Z, Li L, Tang Y, Fu K, Tan Y, Li L. Kaempferol Alleviates Carbon Tetrachloride-Induced Liver Fibrosis in Mice by Regulating Intestinal Short-Chain Fatty Acids. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(14):6666. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146666
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Siqi, Fei Tang, Zhe Zhou, Linhui Li, Yang Tang, Kaiwen Fu, Yang Tan, and Ling Li. 2025. "Kaempferol Alleviates Carbon Tetrachloride-Induced Liver Fibrosis in Mice by Regulating Intestinal Short-Chain Fatty Acids" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 14: 6666. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146666
APA StyleZhang, S., Tang, F., Zhou, Z., Li, L., Tang, Y., Fu, K., Tan, Y., & Li, L. (2025). Kaempferol Alleviates Carbon Tetrachloride-Induced Liver Fibrosis in Mice by Regulating Intestinal Short-Chain Fatty Acids. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(14), 6666. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146666





