Anti-Obesity and Metabolic Effects of Forskolin in Obese C57BL/6J Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
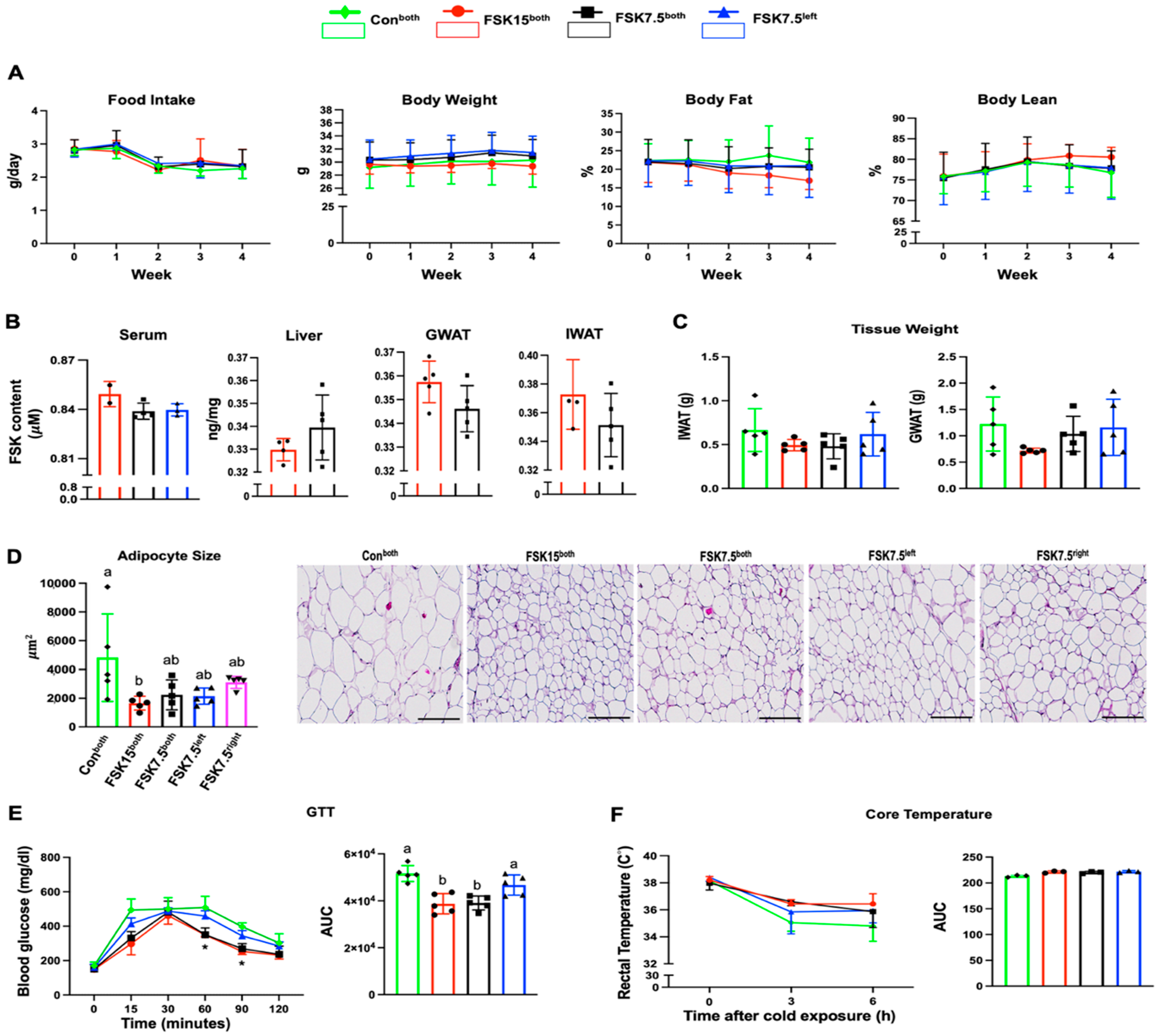
2.1. The Effects of FSK on Body Weight and Body Fat in HFD-Induced Obese Mice
2.2. The Effects of FSK on IWAT and GWAT Weights
2.3. The Effects of FSK on Adipocyte Size in IWAT
2.4. The Effects of FSK on Blood Glucose Levels and GTT-AUC
2.5. The Effects of FSK on Body Core Temperature
2.6. The Effects of FSK on Energy Metabolism
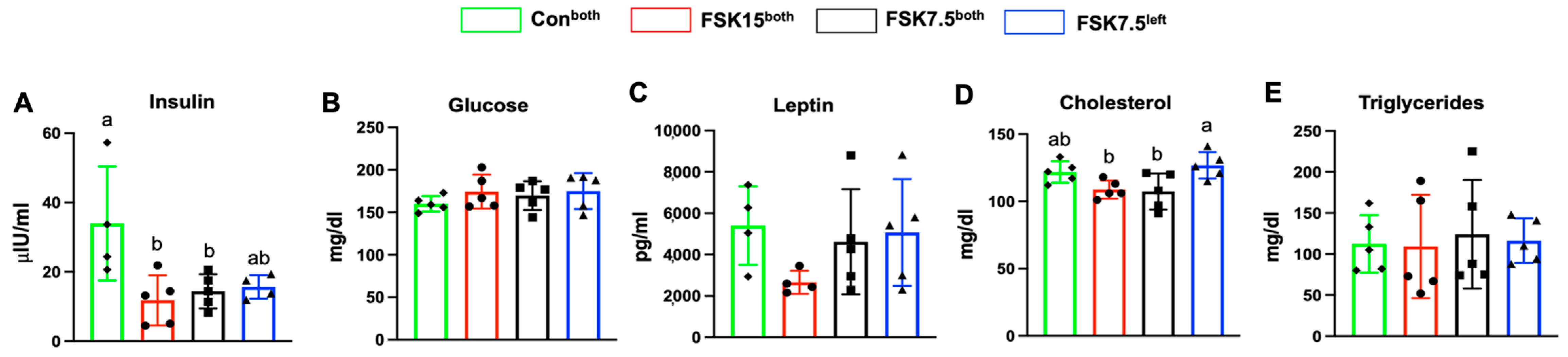
2.7. The Effects of FSK on Serum Insulin and Total Cholesterol Levels
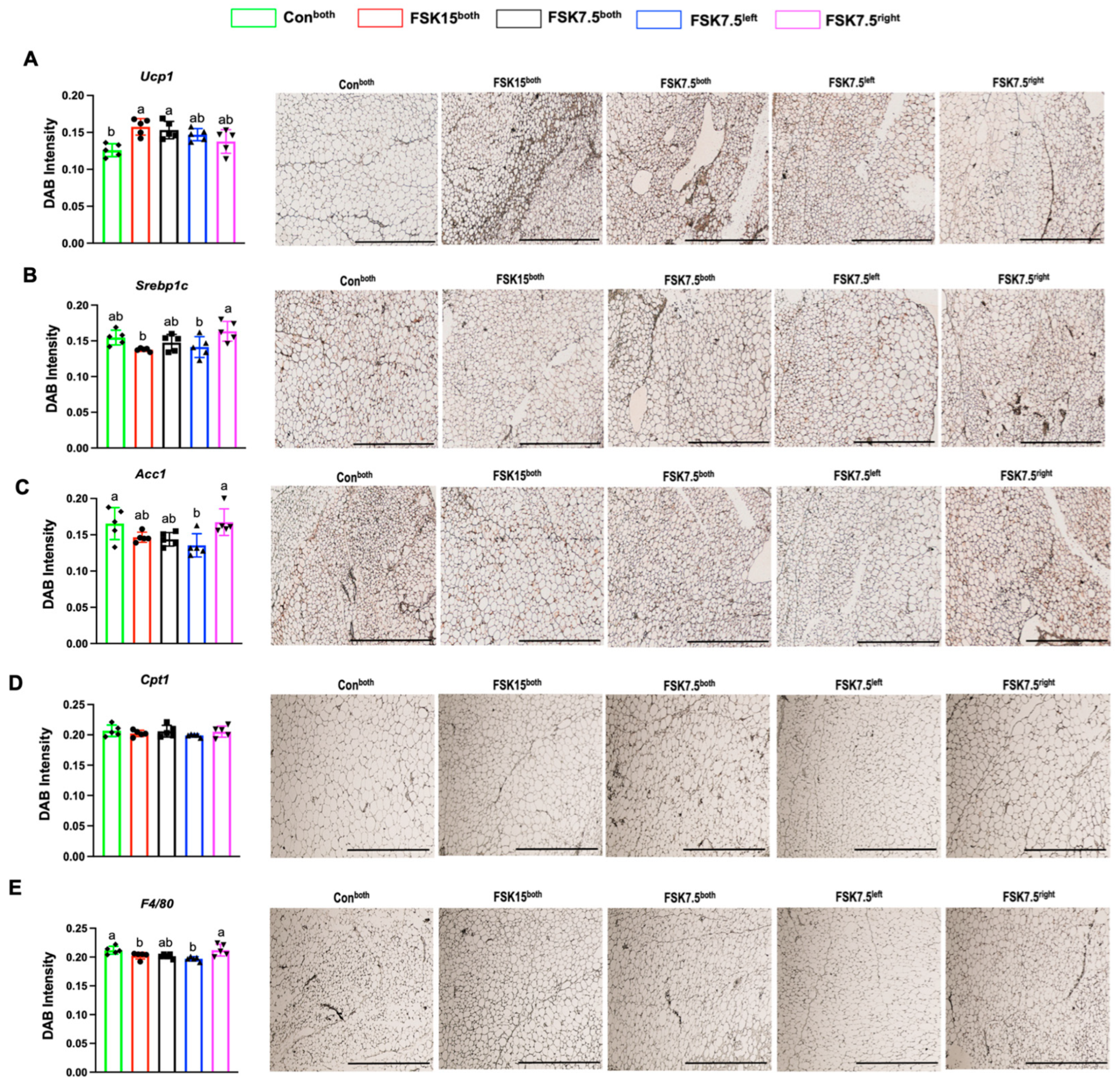
2.8. The Effects of FSK on the Expression of Browning Markers in IWAT
2.9. The Effects of FSK on the Expression of Glut4 Adipogenic Markers in IWAT
2.10. The Effects of FSK on the Expression of Inflammatory Markers in IWAT
2.11. The Effects of FSK on the Expression of Ac1 in IWAT
2.12. The Effects of FSK on the Expression of Glut2 and Adipogenic Markers in the Liver
2.13. The Effects of FSK on the Expression of Inflammatory Markers in the Liver
2.14. The Effects of FSK and Tween80 on Renal, Liver, or Electrolyte Safety Parameters
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Animals
4.3. Body Composition
4.4. GTT
4.5. Energy Expenditure
4.6. Cold-Tolerance Test
4.7. Quantification PCR
4.8. Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) Staining
4.9. Adipocyte Size
4.10. Immunohistochemistry
4.11. Serum Glucose, Insulin, Leptin, and Lipid Profile Analysis
4.12. LC-MS/MS Measurement of FSK
4.12.1. Serum Preparation
4.12.2. Tissue Preparation
4.12.3. Targeted LC-MS/MS
4.13. Safety Evaluation
4.14. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Abbreviation | Full Name |
| DAB | 3,3′-Diaminobenzidine |
| HMG-CoA reductase | 3-hydroxy-3-methyl-glutaryl-coenzyme A reductase |
| Acc1 | Acetyl-CoA Carboxylase 1 |
| AC | Adenylate cyclase |
| ATGL | Adipose triglyceride lipase |
| ALP | Alkaline phosphatase |
| ALT | Alanine transaminase |
| AST | Aspartate transaminase |
| BW | Body weight |
| Cpt1 | Carnitine palmitoyl transferase I |
| Cidea | Cell death-inducing DFFA-like effector a |
| CFE | Coleus forskohlii root extract |
| CREB | cAMP-responsive transcription factors |
| CPK | Creatine phosphokinase |
| cAMP | Cyclic adenosine monophosphate |
| F4/80 | EGF-like module-containing mucin-like hormone receptor-like 1 |
| Fabp1 | Fatty Acid-Binding Protein 1 |
| FSK | Forskolin |
| FSK15both | FSK 15 mg/kg Body Weight/injection into both inguinal WAT depots |
| FSK7.5both | FSK 7.5 mg/kg Body Weight/injection into both inguinal WAT depots |
| FSK7.5left | FSK 7.5 mg/kg Body Weight/injection into the left inguinal WAT depot |
| GTT | Glucose tolerance test |
| Glut2 | Glucose transporter 2 |
| Glut4 | Glucose transporter 4 |
| G6P | Glucose 6 phosphatase |
| GWAT | Gonadal WAT |
| H&E | Hematoxylin and eosin |
| HFD | High-fat diet |
| HSL | Hormone-sensitive lipase |
| Il6 | Interleukin-6 |
| Mcp1 | Monocyte chemoattractant protein |
| MAPK | P38 mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| Pgc1α | Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ co-activator1α |
| PEPCK | Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase |
| PKA | Protein kinase A |
| QC | Quality control |
| RER | Respiratory exchange ratio |
| Serbp1c | Sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1c |
| Scd1 | Stearoyl-CoA desaturase 1 |
| Tmem26 | Transmembrane protein 26 |
| Tnfα | Tumor necrosis factor α |
| Conboth | Tween 80 Control into both IWAT depots |
| Ucp1 | Uncoupling protein 1 |
| WAT | White adipose tissue |
References
- Dickschat, J.S. 1.16—Biosynthesis of Diterpenoid Natural Products. In Comprehensive Natural Products III; Liu, H.-W., Begley, T.P., Eds.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2020; pp. 506–552. [Google Scholar]
- Pateraki, I.; Andersen-Ranberg, J.; Jensen, N.B.; Wubshet, S.G.; Heskes, A.M.; Forman, V.; Hallström, B.; Hamberger, B.; Motawia, M.S.; Olsen, C.E.; et al. Total biosynthesis of the cyclic AMP booster forskolin from Coleus forskohlii. Elife 2017, 6, 23001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ríos-Silva, M.; Trujillo, X.; Trujillo-Hernández, B.; Sánchez-Pastor, E.; Urzúa, Z.; Mancilla, E.; Huerta, M. Effect of chronic administration of forskolin on glycemia and oxidative stress in rats with and without experimental diabetes. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2014, 11, 448–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.Y.; Peng, S.Y.; Cheng, Y.H.; Lee, I.T.; Yu, Y.H. Effect of Forskolin on Body Weight, Glucose Metabolism and Adipocyte Size of Diet-Induced Obesity in Mice. Animals 2021, 11, 645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitehead, A.; Krause, F.N.; Moran, A.; MacCannell, A.D.V.; Scragg, J.L.; McNally, B.D.; Boateng, E.; Murfitt, S.A.; Virtue, S.; Wright, J.; et al. Brown and beige adipose tissue regulate systemic metabolism through a metabolite interorgan signaling axis. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapio, L.; Gallo, M.; Illiano, M.; Chiosi, E.; Naviglio, D.; Spina, A.; Naviglio, S. The Natural cAMP Elevating Compound Forskolin in Cancer Therapy: Is It Time? J. Cell Physiol. 2017, 232, 922–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majeed, M.; Majeed, S.; Nagabhushanam, K.; Gnanamani, M.; Mundkur, L. Lesser Investigated Natural Ingredients for the Management of Obesity. Nutrients 2021, 13, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- London, E.; Bloyd, M.; Stratakis, C.A. PKA functions in metabolism and resistance to obesity: Lessons from mouse and human studies. J. Endocrinol. 2020, 246, R51–R64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godard, M.P.; Johnson, B.A.; Richmond, S.R. Body composition and hormonal adaptations associated with forskolin consumption in overweight and obese men. Obes. Res. 2005, 13, 1335–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loftus, H.L.; Astell, K.J.; Mathai, M.L.; Su, X.Q. Coleus forskohlii Extract Supplementation in Conjunction with a Hypocaloric Diet Reduces the Risk Factors of Metabolic Syndrome in Overweight and Obese Subjects: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2015, 7, 9508–9522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alasbahi, R.H.; Melzig, M.F. Plectranthus barbatus: A review of phytochemistry, ethnobotanical uses and pharmacology—Part 2. Planta Med. 2010, 76, 753–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alasbahi, R.H.; Melzig, M.F. Plectranthus barbatus: A review of phytochemistry, ethnobotanical uses and pharmacology—Part 1. Planta Med. 2010, 76, 653–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Virgona, N.; Taki, Y.; Yamada, S.; Umegaki, K. Dietary Coleus forskohlii extract generates dose-related hepatotoxicity in mice. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2013, 33, 924–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sacks, H.; Symonds, M.E. Anatomical locations of human brown adipose tissue: Functional relevance and implications in obesity and type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 2013, 62, 1783–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zu, Y.; Zhao, L.; Hao, L.; Mechref, Y.; Zabet-Moghaddam, M.; Keyel, P.A.; Abbasi, M.; Wu, D.; Dawson, J.A.; Zhang, R.; et al. Browning white adipose tissue using adipose stromal cell-targeted resveratrol-loaded nanoparticles for combating obesity. J. Control. Release 2021, 333, 339–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badmaev, V.; Majeed, M.; Conte, A.; Parker, J. Diterpene Forskolin (Coleus forskohlii, Benth.): A possible new compound for reduction of body weight by increasing lean body mass. NutraCos Nutraceuticals 2002, 1, 6–7. [Google Scholar]
- Bagchi, D.; Preuss, H.G. (Eds.) Coleus Forskohlii Extract in the Management of Obesity. In OBESITY: Epidemiology Pathophysiology, and Prevention; CRC Press, Tylor and Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Umegaki, K.; Yamazaki, Y.; Yokotani, K.; Chiba, T.; Sato, Y.; Shimura, F. Induction of fatty liver by Coleus forskohlii extract through enhancement of de novo triglyceride synthesis in mice. Toxicol. Rep. 2014, 1, 787–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reverte-Salisa, L.; Sanyal, A.; Pfeifer, A. Role of cAMP and cGMP Signaling in Brown Fat. In Brown Adipose Tissue; Pfeifer, A., Klingenspor, M., Herzig, S., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 161–182. [Google Scholar]
- Pinto, C.; Papa, D.; Hübner, M.; Mou, T.C.; Lushington, G.H.; Seifert, R. Activation and inhibition of adenylyl cyclase isoforms by forskolin analogs. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2008, 325, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, D.O.; Ahmed, B.; Naseer, K. Relationships between cyclic AMP levels and lipolysis in fat cells after isoproterenol and forskolin stimulation. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1986, 238, 659–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickson, L.M.; Gandhi, S.; Layden, B.T.; Cohen, R.N.; Wicksteed, B. Protein kinase A induces UCP1 expression in specific adipose depots to increase energy expenditure and improve metabolic health. Am. J. Physiol.-Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2016, 311, R79–R88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Tang, L.; Hipple, T.; Mowry, C.D.; Brinker, C.J.; Brey, E.; Noureddine, A.; Porras, M.A.G. Local Administration of Lipid-Silica Nanohybrid-Carried Forskolin Modulates Thermogenesis in Human Adipocytes and Impedes Weight Gain in Mice. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2025, 35, 2404179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahlang, B.; McClain, C.; Barve, S.; Gobejishvili, L. Role of cAMP and phosphodiesterase signaling in liver health and disease. Cell. Signal. 2018, 49, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, X.; Yi, L.; Yang, L.; Wang, W.E.; Zeng, C.; Mi, M.; Chen, X. Hepatic PKA inhibition accelerates the lipid accumulation in liver. Nutr. Metab. 2019, 16, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, I.; Moreno, F.J.; Fain, J.N. Forskolin Inhibition of Glucose Metabolism in Rat Adipocytes Independent of Adenosine 3′,5′-Monophosphate Accumulation and Lipolysis. Endocrinology 1984, 115, 1066–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, Z.P.; Xiong, B.; Zhang, Y.L.; Shi, L.; Shi, K. Forskolin attenuates retinal inflammation in diabetic mice. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 17, 2321–2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamoorthy, K.; Senguttuvan, J. Evaluation of Anti-inflammatory and Antioxidant Properties of Crude Extract and Forskolin from Solena amplexicaulis Leaf. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 78, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiadak, J.D.; Arsenijevic, T.; Verstrepen, K.; Gregoire, F.; Bolaky, N.; Delforge, V.; Flamand, V.; Perret, J.; Delporte, C. Forskolin Inhibits Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Modulation of MCP-1 and GPR120 in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes through an Inhibition of NFκB. Mediators Inflamm. 2016, 2016, 1431789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Shi, R.; Wang, Y.; Wu, W.; Sun, S.; Dai, Z.; Chen, C.; Weng, Z.; Li, X.; Liu, Q.; et al. Isoforskolin and forskolin attenuate lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation through TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB cascades in human mononuclear leukocytes. Phytother. Res. 2019, 33, 602–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Liu, A.; Shen, L.; Xu, C.; Zhu, Z.; Yang, J.; Han, X.; Bao, F.; Yang, W. Isoforskolin downregulates proinflammatory responses induced by Borrelia burgdorferi basic membrane protein A. Exp. Ther. Med. 2017, 14, 5974–5980. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Wen, J.G.; Feng, J.J.; Wang, Y.H.; Li, T.F.; Nurmi, K.; Eklund, K.K.; Xing, D. Forskolin attenuates the NLRP3 inflammasome activation and IL-1β secretion in human macrophages. Pediatr. Res. 2019, 86, 692–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.; Zhou, T.; Shu, J.Y.; Mao, J.-H. Quantifying chromogen intensity in immunohistochemistry via reciprocal intensity. Cancer InCytes 2013, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eghlimi, R.; Shi, X.; Hrovat, J.; Xi, B.; Gu, H. Triple Negative Breast Cancer Detection Using LC-MS/MS Lipidomic Profiling. J. Proteome Res. 2020, 19, 2367–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jasbi, P.; Shi, X.; Chu, P.; Elliott, N.; Hudson, H.; Jones, D.; Serrano, G.; Chow, B.; Beach, T.G.; Liu, L.; et al. Metabolic Profiling of Neocortical Tissue Discriminates Alzheimer’s Disease from Mild Cognitive Impairment, High Pathology Controls, and Normal Controls. J. Proteome Res. 2021, 20, 4303–4317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Y.; Chi, J.; LoMonaco, K.; Boon, A.; Gu, H. Recent review on selected xenobiotics and their impacts on gut microbiome and metabolome. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2023, 166, 117155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abbasi, M.; Zhou, F.; Ly, N.K.; Taylor, A.; Hu, Q.; Chi, J.; Gu, H.; Wang, S. Anti-Obesity and Metabolic Effects of Forskolin in Obese C57BL/6J Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6607. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146607
Abbasi M, Zhou F, Ly NK, Taylor A, Hu Q, Chi J, Gu H, Wang S. Anti-Obesity and Metabolic Effects of Forskolin in Obese C57BL/6J Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(14):6607. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146607
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbbasi, Mehrnaz, Fang Zhou, Ngoc Kim Ly, Austin Taylor, Qiaobin Hu, Jinhua Chi, Haiwei Gu, and Shu Wang. 2025. "Anti-Obesity and Metabolic Effects of Forskolin in Obese C57BL/6J Mice" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 14: 6607. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146607
APA StyleAbbasi, M., Zhou, F., Ly, N. K., Taylor, A., Hu, Q., Chi, J., Gu, H., & Wang, S. (2025). Anti-Obesity and Metabolic Effects of Forskolin in Obese C57BL/6J Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(14), 6607. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146607








