The Coiled Coil and C2 Domains Modulate BCR Localization and BCR-ABL1 Compartmentalization, Transforming Activity and TKI Responsiveness
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
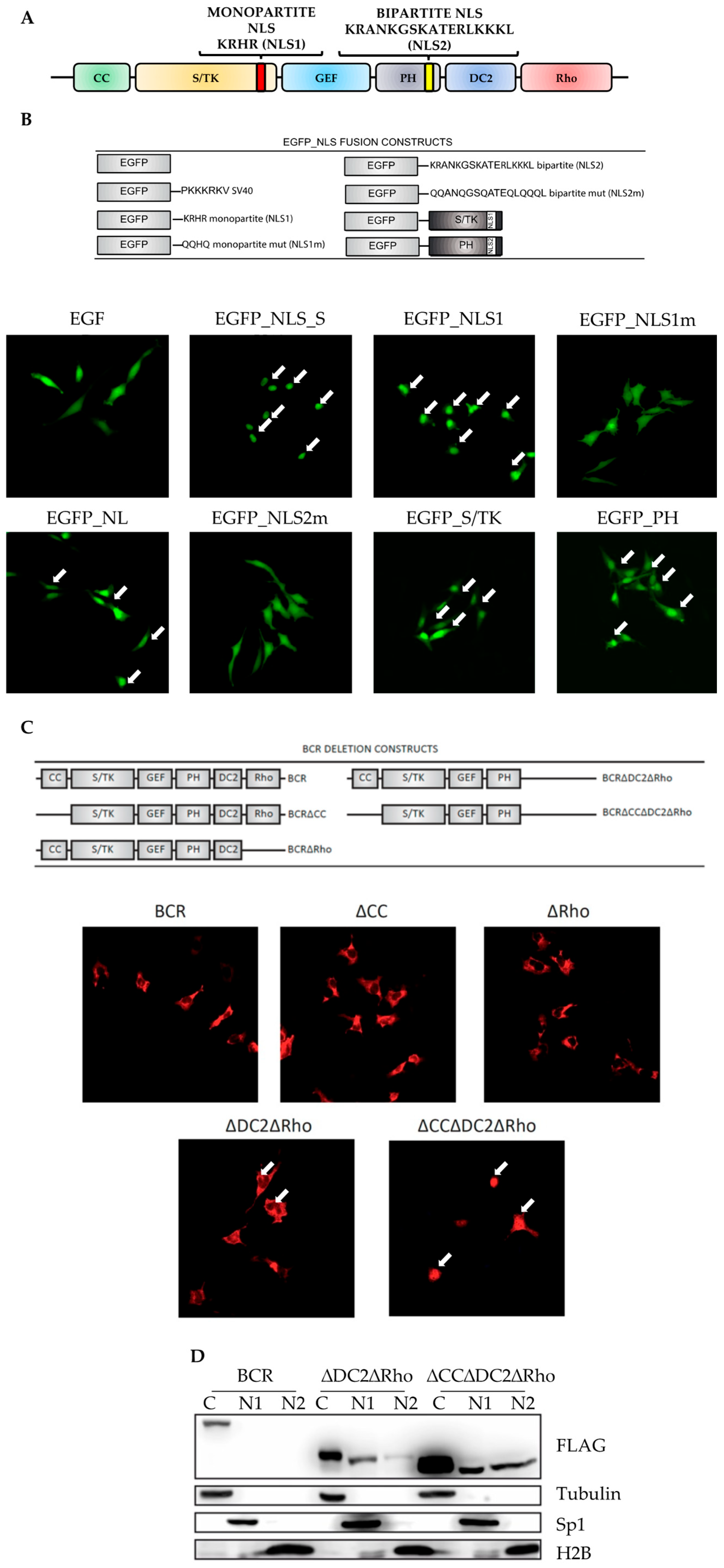
2.1. Cytoplasmic Localization of BCR Is Dependent on Functionally Inactivated Nuclear Localization Sequences
2.2. The CC and DC2 Contribute to BCR-ABL1 Cytoplasmic Retention
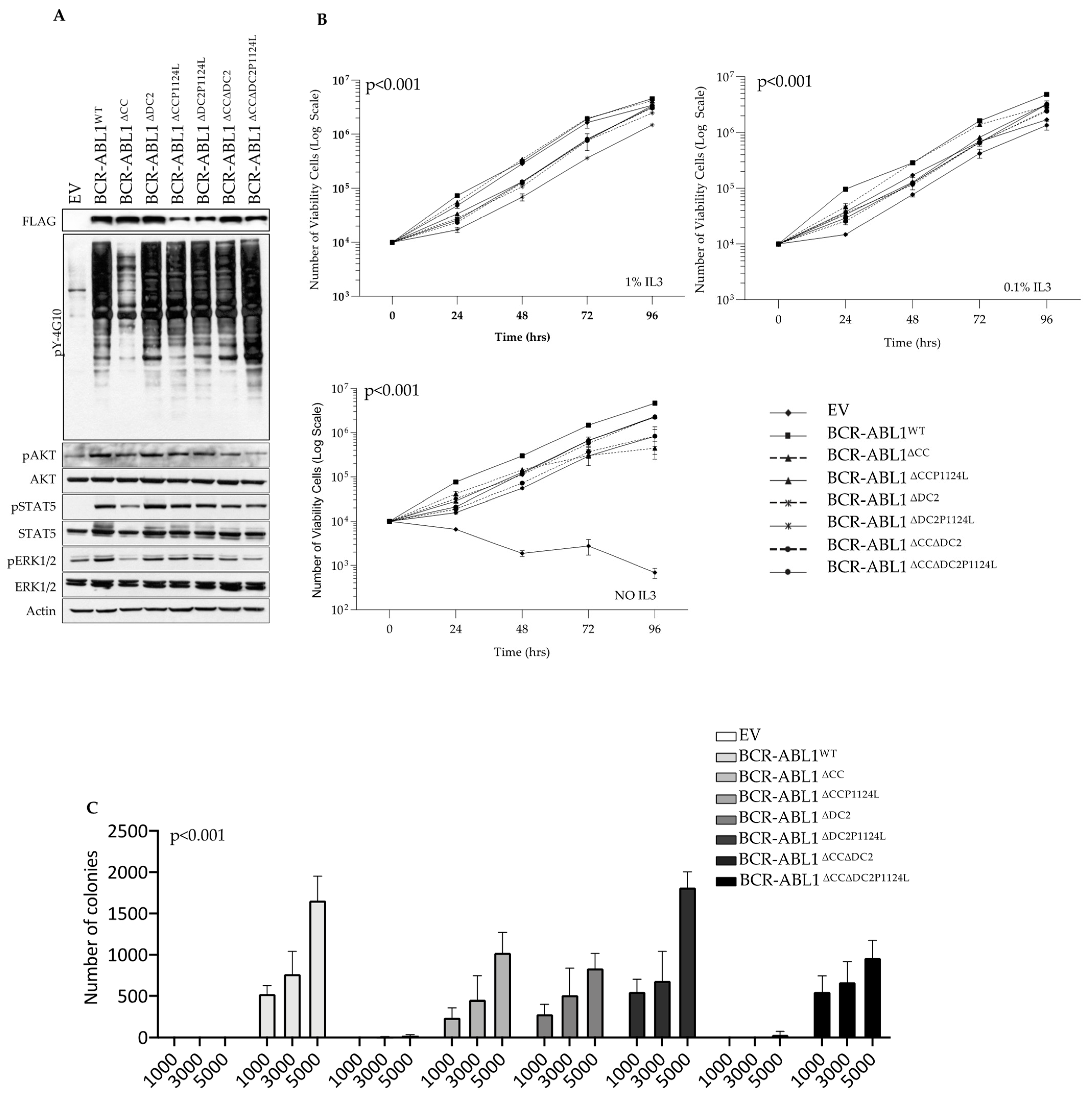
2.3. The DC2 Modulates BCR-ABL1 Tyrosine Kinase Activity and Transforming Potential
2.4. The DC2 Reduces TKI-Dependent Inhibition of BCR-ABL1 Catalytic and Clonogenic Activity
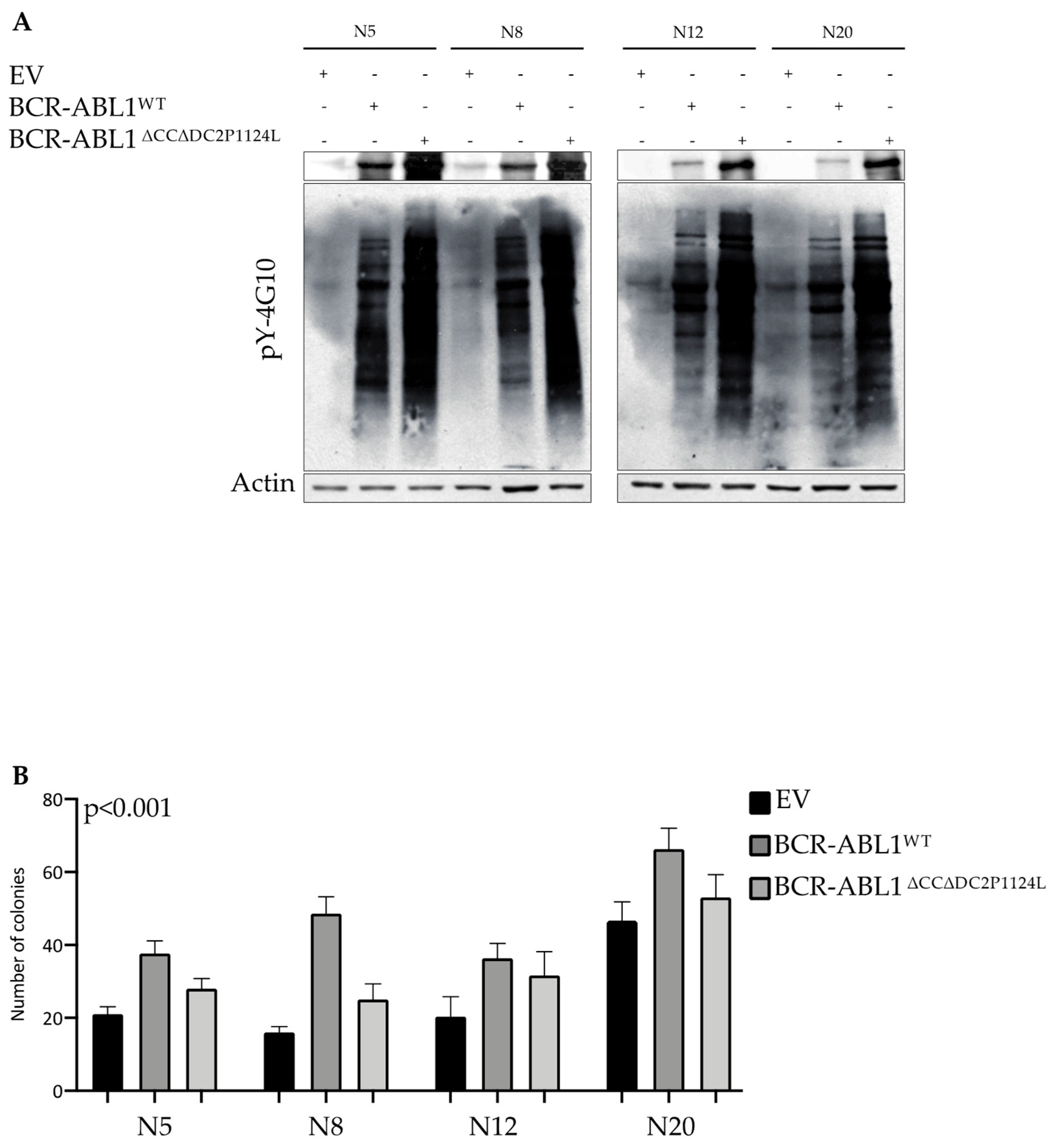
2.5. Deletion of the CC and DC2 Reduces BCR-ABL1 Transforming Potential in CD34+ Progenitors
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Lines and Drugs
4.2. CD34+ Progenitor Isolation, Culture, and Colony-Forming Unit Assays
4.3. Generation of Plasmids, Lentiviral Vectors and Mutagenesis Reactions
4.4. Cell Transfection
4.5. Lentivirus Production and Transduction
4.6. Immunofluorescence
4.7. Nuclear-Cytoplasmic Subcellular Fractionation and Immunoblot
4.8. Soft-Agar Colony-Forming Unit Assay
4.9. IL3-Independent Growth
4.10. MTS Assay
4.11. Bioinformatic Prediction of NLS Sequences
4.12. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cilloni, D.; Saglio, G. Molecular pathways: BCR-ABL. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 930–937. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ishii, Y.; Nhiayi, M.K.; Tse, E.; Cheng, J.; Massimino, M.; Durden, D.L.; Vigneri, P.; Wang, J.Y.J.; Villunger, A. Knockout Serum Replacement Promotes Cell Survival by Preventing BIM from Inducing Mitochondrial Cytochrome C Release. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0140585. [Google Scholar]
- Alves, R.; Goncalves, A.C.; Rutella, S.; Almeida, A.M.; De Las Rivas, J.; Trougakos, I.P.; Sarmento Ribeiro, A.B. Resistance to Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia—From Molecular Mechanisms to Clinical Relevance. Cancers 2021, 13, 4820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braun, T.P.; Eide, C.A.; Druker, B.J. Response and Resistance to BCR-ABL1-Targeted Therapies. Cancer Cell 2020, 37, 530–542. [Google Scholar]
- Massimino, M.; Stella, S.; Tirro, E.; Pennisi, M.S.; Vitale, S.R.; Puma, A.; Romano, C.; Di Gregorio, S.; Tomarchio, C.; Di Raimondo, F.; et al. ABL1-Directed Inhibitors for CML: Efficacy, Resistance and Future Perspectives. Anticancer Res. 2020, 40, 2457–2465. [Google Scholar]
- Holyoake, T.L.; Helgason, G.V. Do we need more drugs for chronic myeloid leukemia? Immunol. Rev. 2015, 263, 106–123. [Google Scholar]
- Massimino, M.; Tirro, E.; Stella, S.; Pennisi, M.S.; Vitale, S.R.; Puma, A.; Romano, C.; Di Gregorio, S.; Romeo, M.A.; Di Raimondo, F.; et al. Targeting BCL-2 as a Therapeutic Strategy for Primary (p210)BCR-ABL1-positive B-ALL Cells. In Vivo 2020, 34, 511–516. [Google Scholar]
- Massimino, M.; Vigneri, P.; Stella, S.; Tirro, E.; Pennisi, M.S.; Parrinello, L.N.; Vetro, C.; Manzella, L.; Stagno, F.; Di Raimondo, F. Combined Inhibition of Bcl2 and Bcr-Abl1 Exercises Anti-Leukemia Activity but Does Not Eradicate the Primitive Leukemic Cells. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 5606. [Google Scholar]
- Westerweel, P.E.; Te Boekhorst, P.A.W.; Levin, M.D.; Cornelissen, J.J. New Approaches and Treatment Combinations for the Management of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 665. [Google Scholar]
- Vigneri, P.; Wang, J.Y.J. Induction of apoptosis in chronic myelogenous leukemia cells through nuclear entrapment of BCR-ABL tyrosine kinase. Nat. Med. 2001, 7, 228–234. [Google Scholar]
- Allan, E.K.; Hamilton, A.; Hatziieremia, S.; Zhou, P.; Jørgensen, H.G.; Vigneri, P.; Holyoake, T.L. Nuclear entrapment of BCR-ABL by combining imatinib mesylate with leptomycin B does not eliminate CD34+ chronic myeloid leukaemia cells. Leukemia 2009, 23, 1006–1008. [Google Scholar]
- Dierov, J.; Dierova, R.; Carroll, M. BCR/ABL translocates to the nucleus and disrupts an ATR-dependent intra-S phase checkpoint. Cancer Cell 2004, 5, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Preyer, M.; Vigneri, P.; Wang, J.Y.J.; Wu, G.S. Interplay between kinase domain autophosphorylation and F-actin binding domain in regulating imatinib sensitivity and nuclear import of BCR-ABL. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17020. [Google Scholar]
- Taagepera, S.; McDonald, D.; Loeb, J.E.; Whitaker, L.L.; McElroy, A.K.; Wang, J.Y.; Hope, T.J. Nuclear-cytoplasmic shuttling of C-ABL tyrosine kinase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 7457–7462. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bai, R.Y.; Jahn, T.; Schrem, S.; Munzert, G.; Weidner, K.M.; Wang, J.Y.; Duyster, J. The SH2-containing adapter protein GRB10 interacts with BCR-ABL. Oncogene 1998, 17, 941–948. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, S.; Li, L.; Singh, H.; Bhatia, R. BCR-tyrosine 177 plays an essential role in Ras and Akt activation and in human hematopoietic progenitor transformation in chronic myelogenous leukemia. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 7045–7053. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.; Wertheim, J.A.; Xu, L.; Miller, J.P.; Karnell, F.G.; Choi, J.K.; Ren, R.; Pear, W.S. The coiled-coil domain and Tyr177 of bcr are required to induce a murine chronic myelogenous leukemia-like disease by bcr/abl. Blood 2002, 99, 2957–2968. [Google Scholar]
- Takeda, N.; Shibuya, M.; Maru, Y. The BCR-ABL oncoprotein potentially interacts with the xeroderma pigmentosum group B protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 203–207. [Google Scholar]
- Laurent, E.; Talpaz, M.; Kantarjian, H.; Kurzrock, R. The BCR gene and philadelphia chromosome-positive leukemogenesis. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 2343–2355. [Google Scholar]
- Lifshitz, B.; Fainstein, E.; Marcelle, C.; Shtivelman, E.; Amson, R.; Gale, R.P.; Canaani, E. bcr genes and transcripts. Oncogene 1988, 2, 113–117. [Google Scholar]
- Wetzler, M.; Talpaz, M.; Yee, G.; Stass, S.A.; Van Etten, R.A.; Andreeff, M.; Goodacre, A.M.; Kleine, H.D.; Mahadevia, R.K.; Kurzrock, R. Cell cycle-related shifts in subcellular localization of BCR: Association with mitotic chromosomes and with heterochromatin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 3488–3492. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Laurent, E.; Talpaz, M.; Wetzler, M.; Kurzrock, R. Cytoplasmic and nuclear localization of the 130 and 160 kDa Bcr proteins. Leukemia 2000, 14, 1892–1897. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, S.T.; Jackson, P.K.; Van Etten, R.A. The cytostatic function of c-Abl is controlled by multiple nuclear localization signals and requires the p53 and Rb tumor suppressor gene products. EMBO J. 1996, 15, 1583–1595. [Google Scholar]
- Stewart, M. Molecular mechanism of the nuclear protein import cycle. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 8, 195–208. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rajakyla, E.K.; Vartiainen, M.K. Rho, nuclear actin, and actin-binding proteins in the regulation of transcription and gene expression. Small GTPases 2014, 5, e27539. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sit, S.T.; Manser, E. Rho GTPases and their role in organizing the actin cytoskeleton. J. Cell Sci. 2011, 124 Pt 5, 679–683. [Google Scholar]
- Spiering, D.; Hodgson, L. Dynamics of the Rho-family small GTPases in actin regulation and motility. Cell Adhes. Migr. 2011, 5, 170–180. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, K.M.; Yacobi, R.; Van Etten, R.A. Autoinhibition of Bcr-Abl through its SH3 domain. Mol. Cell 2003, 12, 27–37. [Google Scholar]
- Chari, A.; Vogl, D.T.; Gavriatopoulou, M.; Nooka, A.K.; Yee, A.J.; Huff, C.A.; Moreau, P.; Dingli, D.; Cole, C.; Lonial, S.; et al. Oral Selinexor-Dexamethasone for Triple-Class Refractory Multiple Myeloma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 727–738. [Google Scholar]
- Bradeen, H.A.; Eide, C.A.; O’Hare, T.; Johnson, K.J.; Willis, S.G.; Lee, F.Y.; Druker, B.J.; Deininger, M.W. Comparison of imatinib mesylate, dasatinib (BMS-354825), and nilotinib (AMN107) in an N-ethyl-N-nitrosourea (ENU)-based mutagenesis screen: High efficacy of drug combinations. Blood 2006, 108, 2332–2338. [Google Scholar]
- O’Hare, T.; Shakespeare, W.C.; Zhu, X.; Eide, C.A.; Rivera, V.M.; Wang, F.; Adrian, L.T.; Zhou, T.; Huang, W.S.; Xu, Q.; et al. AP24534, a pan-BCR-ABL inhibitor for chronic myeloid leukemia, potently inhibits the T315I mutant and overcomes mutation-based resistance. Cancer Cell 2009, 16, 401–412. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yasu, T.; Momo, K.; Kobayashi, S.; Kuroda, S.; Tojo, A. Simple Determination of Plasma Ponatinib Concentration Using HPLC. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2018, 41, 254–258. [Google Scholar]
- Aloisi, A.; Di Gregorio, S.; Stagno, F.; Guglielmo, P.; Mannino, F.; Sormani, M.P.; Bruzzi, P.; Gambacorti-Passerini, C.; Saglio, G.; Venuta, S.; et al. BCR-ABL nuclear entrapment kills human CML cells: Ex vivo study on 35 patients with the combination of imatinib mesylate and leptomycin B. Blood 2006, 107, 1591–1598. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pennisi, M.S.; Stella, S.; Vitale, S.R.; Puma, A.; Di Gregorio, S.; Romano, C.; Tirro, E.; Massimino, M.; Antolino, A.; Siragusa, S.; et al. BCR-ABL1 Doubling-Times and Halving-Times May Predict CML Response to Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 764. [Google Scholar]
- Massimino, M.; Tirro, E.; Stella, S.; Manzella, L.; Pennisi, M.S.; Romano, C.; Vitale, S.R.; Puma, A.; Tomarchio, C.; Di Gregorio, S.; et al. Impact of the Breakpoint Region on the Leukemogenic Potential and the TKI Responsiveness of Atypical BCR-ABL1 Transcripts. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 669469. [Google Scholar]
- Conforti, F.; Wang, Y.; Rodriguez, J.A.; Alberobello, A.T.; Zhang, Y.W.; Giaccone, G. Molecular Pathways: Anticancer Activity by Inhibition of Nucleocytoplasmic Shuttling. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 4508–4513. [Google Scholar]
- Carra, G.; Cartella, A.; Maffeo, B.; Morotti, A. Strategies For Targeting Chronic Myeloid Leukaemia Stem Cells. Blood Lymphat. Cancer Targets Ther. 2019, 9, 45–52. [Google Scholar]
- Lange, A.; Mills, R.E.; Lange, C.J.; Stewart, M.; Devine, S.E.; Corbett, A.H. Classical nuclear localization signals: Definition, function, and interaction with importin alpha. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 5101–5105. [Google Scholar]
- Braselmann, S.; McCormick, F. Bcr and Raf form a complex in vivo via 14-3-3 proteins. EMBO J. 1995, 14, 4839–4848. [Google Scholar]
- Clokie, S.J.; Cheung, K.Y.; Mackie, S.; Marquez, R.; Peden, A.H.; Aitken, A. BCR kinase phosphorylates 14-3-3 Tau on residue 233. FEBS J. 2005, 272, 3767–3776. [Google Scholar]
- Lemmon, M.A.; Ferguson, K.M.; Abrams, C.S. Pleckstrin homology domains and the cytoskeleton. FEBS Lett. 2002, 513, 71–76. [Google Scholar]
- Korus, M.; Mahon, G.M.; Cheng, L.; Whitehead, I.P. p38 MAPK-mediated activation of NF-kappaB by the RhoGEF domain of Bcr. Oncogene 2002, 21, 4601–4612. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sahay, S.; Pannucci, N.L.; Mahon, G.M.; Rodriguez, P.L.; Megjugorac, N.J.; Kostenko, E.V.; Ozer, H.L.; Whitehead, I.P. The RhoGEF domain of p210 Bcr-Abl activates RhoA and is required for transformation. Oncogene 2008, 27, 2064–2071. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nagar, B.; Hantschel, O.; Seeliger, M.; Davies, J.M.; Weis, W.I.; Superti-Furga, G.; Kuriyan, J. Organization of the SH3-SH2 unit in active and inactive forms of the c-Abl tyrosine kinase. Mol. Cell 2006, 21, 787–798. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sherbenou, D.W.; Hantschel, O.; Kaupe, I.; Willis, S.; Bumm, T.; Turaga, L.P.; Lange, T.; Dao, K.H.; Press, R.D.; Druker, B.J.; et al. BCR-ABL SH3-SH2 domain mutations in chronic myeloid leukemia patients on imatinib. Blood 2010, 116, 3278–3285. [Google Scholar]
- Manley, P.W.; Drueckes, P.; Fendrich, G.; Furet, P.; Liebetanz, J.; Martiny-Baron, G.; Mestan, J.; Trappe, J.; Wartmann, M.; Fabbro, D. Extended kinase profile and properties of the protein kinase inhibitor nilotinib. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1804, 445–453. [Google Scholar]
- Wagner, M.-C.; Dziadosz, M.; Melo, J.V.; Heidel, F.; Fischer, T.; Lipka, D.B. Nilotinib shows prolonged intracellular accumulation upon pulse-exposure: A novel mechanism for induction of apoptosis in CML cells. Leukemia 2013, 27, 1567–1570. [Google Scholar]
- Dixon, A.S.; Kakar, M.; Schneider, K.M.; Constance, J.E.; Paullin, B.C.; Lim, C.S. Controlling subcellular localization to alter function: Sending oncogenic Bcr-Abl to the nucleus causes apoptosis. J. Control. Release 2009, 140, 245–249. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, Y.; Huang, Z.; Zhou, F.; Wang, T.; Mou, K.; Feng, W. Effect of HSP90AB1 and CC domain interaction on Bcr-Abl protein cytoplasm localization and function in chronic myeloid leukemia cells. Cell Commun. Signal. 2021, 19, 71. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.-H.; Hyun, J.-S.; Choi, J.; Choi, K.-E.; Jee, J.-G.; Park, S.J. Structural ensemble-based docking simulation and biophysical studies discovered new inhibitors of Hsp90 N-terminal domain. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 368. [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira, F.G.; Sant’anna, C.M.; Caffarena, E.R.; Dardenne, L.E.; Barreiro, E.J. Molecular docking study and development of an empirical binding free energy model for phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2006, 14, 6001–6011. [Google Scholar]
- Buffa, P.; Romano, C.; Pandini, A.; Massimino, M.; Tirro, E.; Di Raimondo, F.; Manzella, L.; Fraternali, F.; Vigneri, P.G. BCR-ABL residues interacting with ponatinib are critical to preserve the tumorigenic potential of the oncoprotein. FASEB J. 2014, 28, 1221–1236. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Huang, T.-T.; Wang, X.; Qiang, S.-J.; Zhao, Z.-N.; Wu, Z.-X.; Ashby, C.R.; Li, J.-Z.; Chen, Z.-S. The Discovery of Novel BCR-ABL Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors Using a Pharmacophore Modeling and Virtual Screening Approach. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 649434. [Google Scholar]
- Kalinichenko, E.; Faryna, A.; Kondrateva, V.; Vlasova, A.; Shevchenko, V.; Melnik, A.; Avdoshko, O.; Belko, A. Synthesis, Biological Activities and Docking Studies of Novel 4-(Arylaminomethyl)benzamide Derivatives as Potential Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors. Molecules 2019, 24, 3543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Réa, D.; Hughes, T.P. Development of asciminib, a novel allosteric inhibitor of BCR-ABL1. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2022, 171, 103580. [Google Scholar]
- Massimino, M.; Stella, S.; Tirro, E.; Pennisi, M.S.; Stagno, F.; Vitale, S.R.; Romano, C.; Tomarchio, C.; Parrinello, N.L.; Manzella, L.; et al. High BCR::ABL1 Expression Defines CD34+ Cells with Significant Alterations in Signal Transduction, Short-Proliferative Potential and Self-Renewal Ability. OncoTargets Ther. 2023, 16, 803–816. [Google Scholar]
- Cokol, M.; Nair, R.; Rost, B. Finding nuclear localization signals. EMBO Rep. 2000, 1, 411–415. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Yang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Shen, H.-B. Discovering nuclear targeting signal sequence through protein language learning and multivariate analysis. Anal. Biochem. 2020, 591, 113565. [Google Scholar]
- Nakai, K.; Horton, P. PSORT: A program for detecting sorting signals in proteins and predicting their subcellular localization. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1999, 24, 34–36. [Google Scholar]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Massimino, M.; Stella, S.; Romano, C.; Buffa, P.; Tirrò, E.; Drago, M.; Manzella, L.; Tomarchio, C.; Vitale, S.R.; Di Raimondo, F.; et al. The Coiled Coil and C2 Domains Modulate BCR Localization and BCR-ABL1 Compartmentalization, Transforming Activity and TKI Responsiveness. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6591. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146591
Massimino M, Stella S, Romano C, Buffa P, Tirrò E, Drago M, Manzella L, Tomarchio C, Vitale SR, Di Raimondo F, et al. The Coiled Coil and C2 Domains Modulate BCR Localization and BCR-ABL1 Compartmentalization, Transforming Activity and TKI Responsiveness. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(14):6591. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146591
Chicago/Turabian StyleMassimino, Michele, Stefania Stella, Chiara Romano, Pietro Buffa, Elena Tirrò, Melissa Drago, Livia Manzella, Cristina Tomarchio, Silvia Rita Vitale, Francesco Di Raimondo, and et al. 2025. "The Coiled Coil and C2 Domains Modulate BCR Localization and BCR-ABL1 Compartmentalization, Transforming Activity and TKI Responsiveness" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 14: 6591. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146591
APA StyleMassimino, M., Stella, S., Romano, C., Buffa, P., Tirrò, E., Drago, M., Manzella, L., Tomarchio, C., Vitale, S. R., Di Raimondo, F., & Vigneri, P. (2025). The Coiled Coil and C2 Domains Modulate BCR Localization and BCR-ABL1 Compartmentalization, Transforming Activity and TKI Responsiveness. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(14), 6591. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146591





