Magnetic Separation of Oil Spills from Water Using Cobalt Ferrite Nanoparticles with Fluorocarbon Functionalization
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
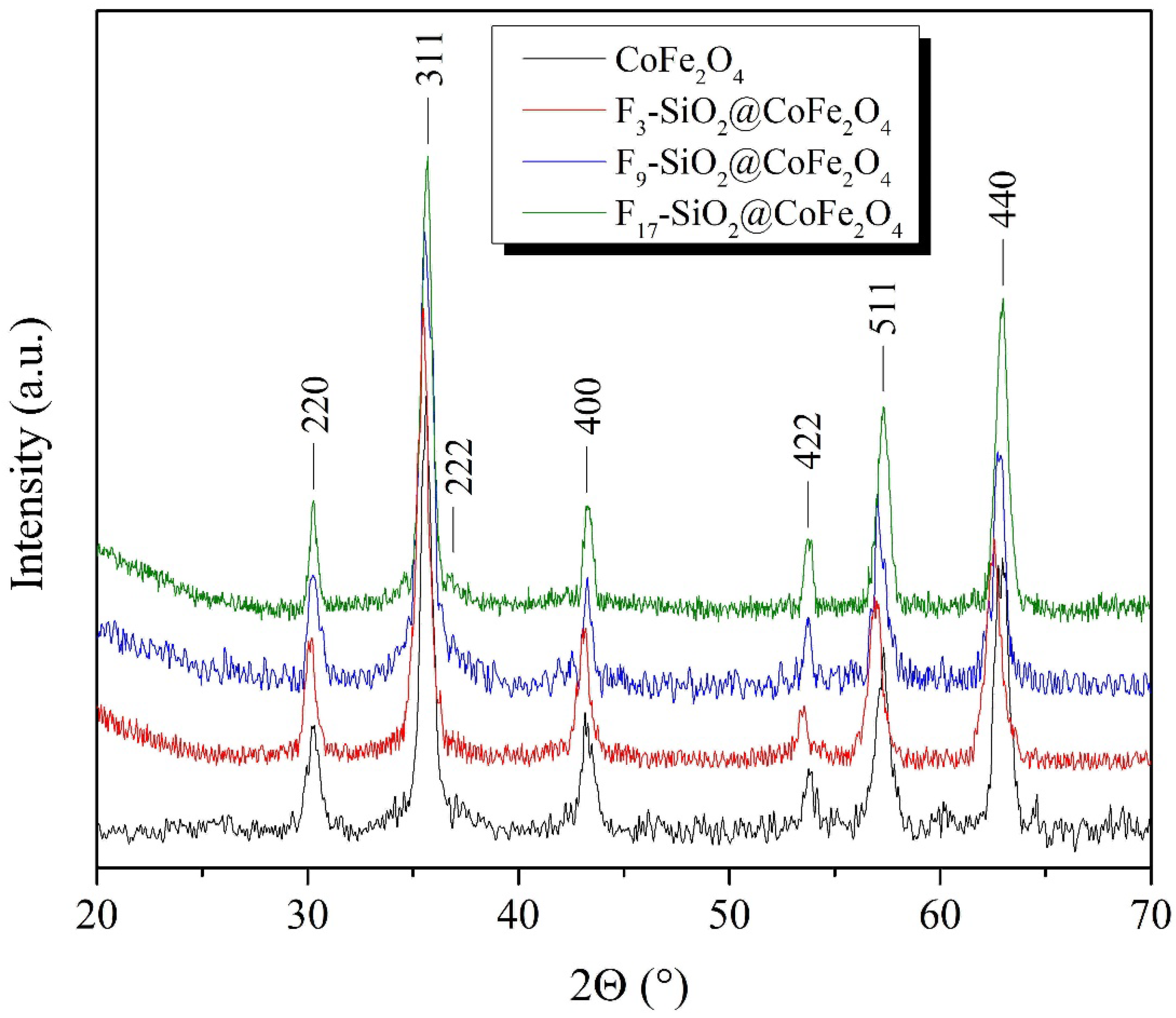
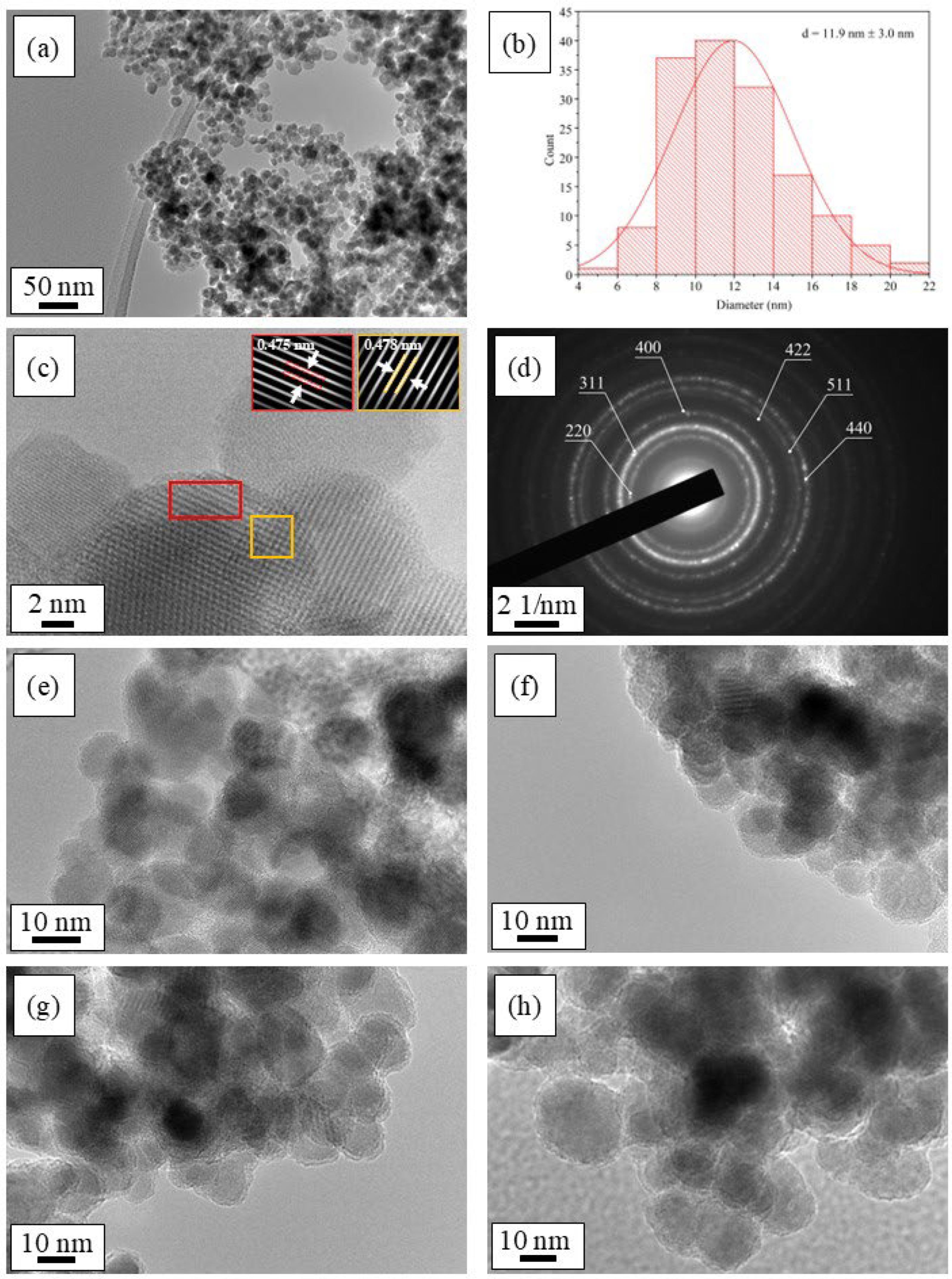
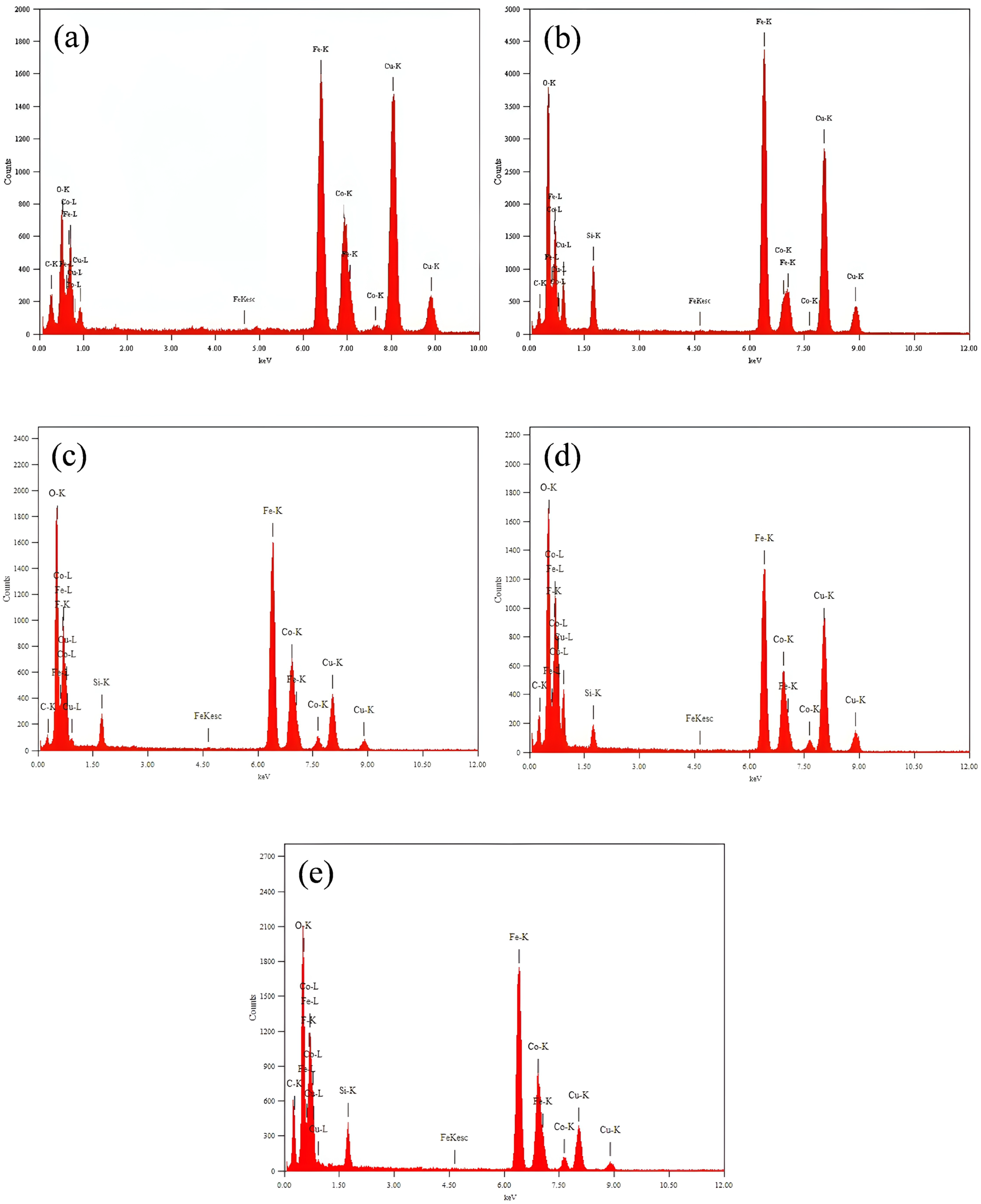
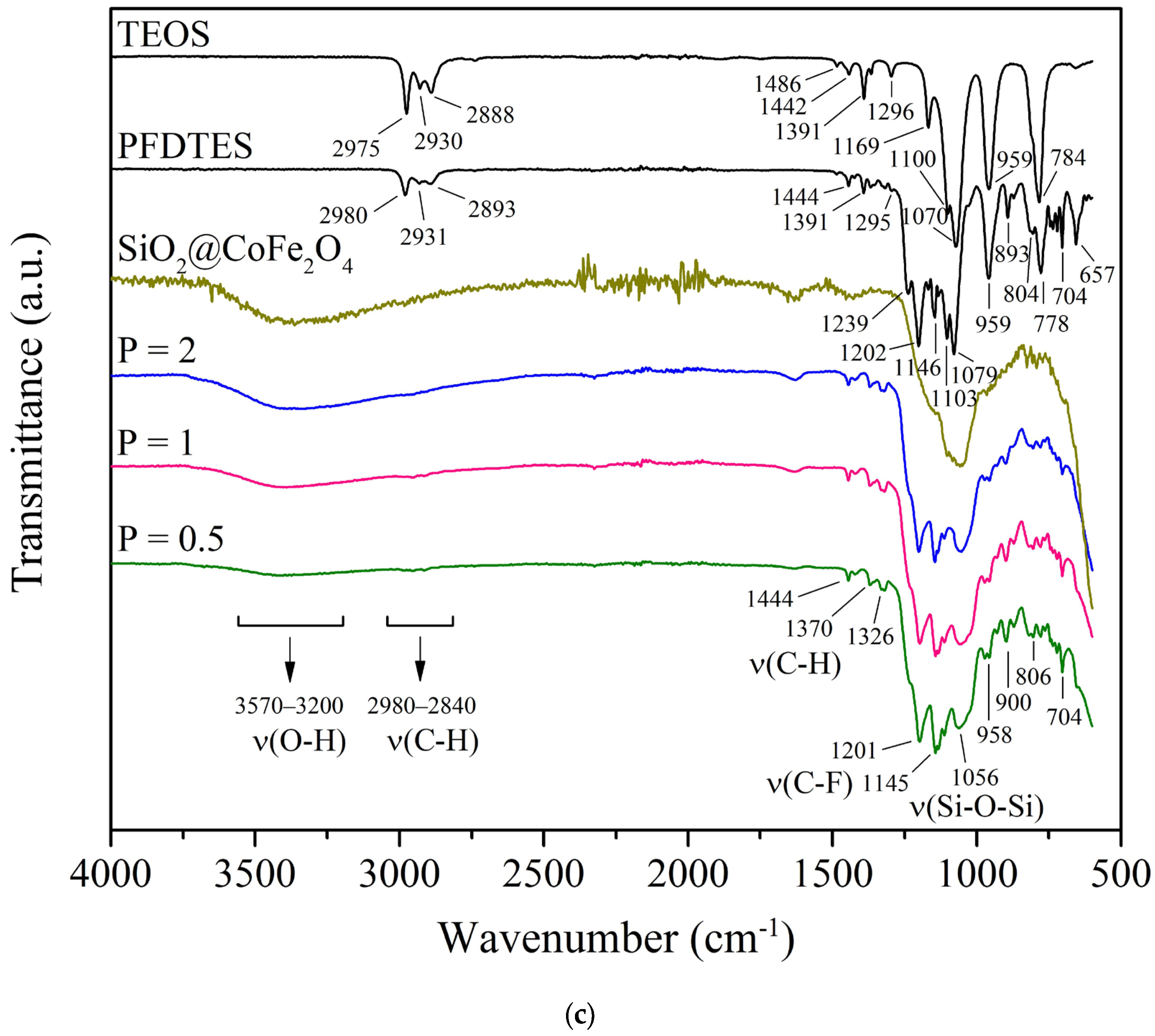
2.1. Synthesis and Characterization of Magnetic CoFe2O4 Nanoparticles
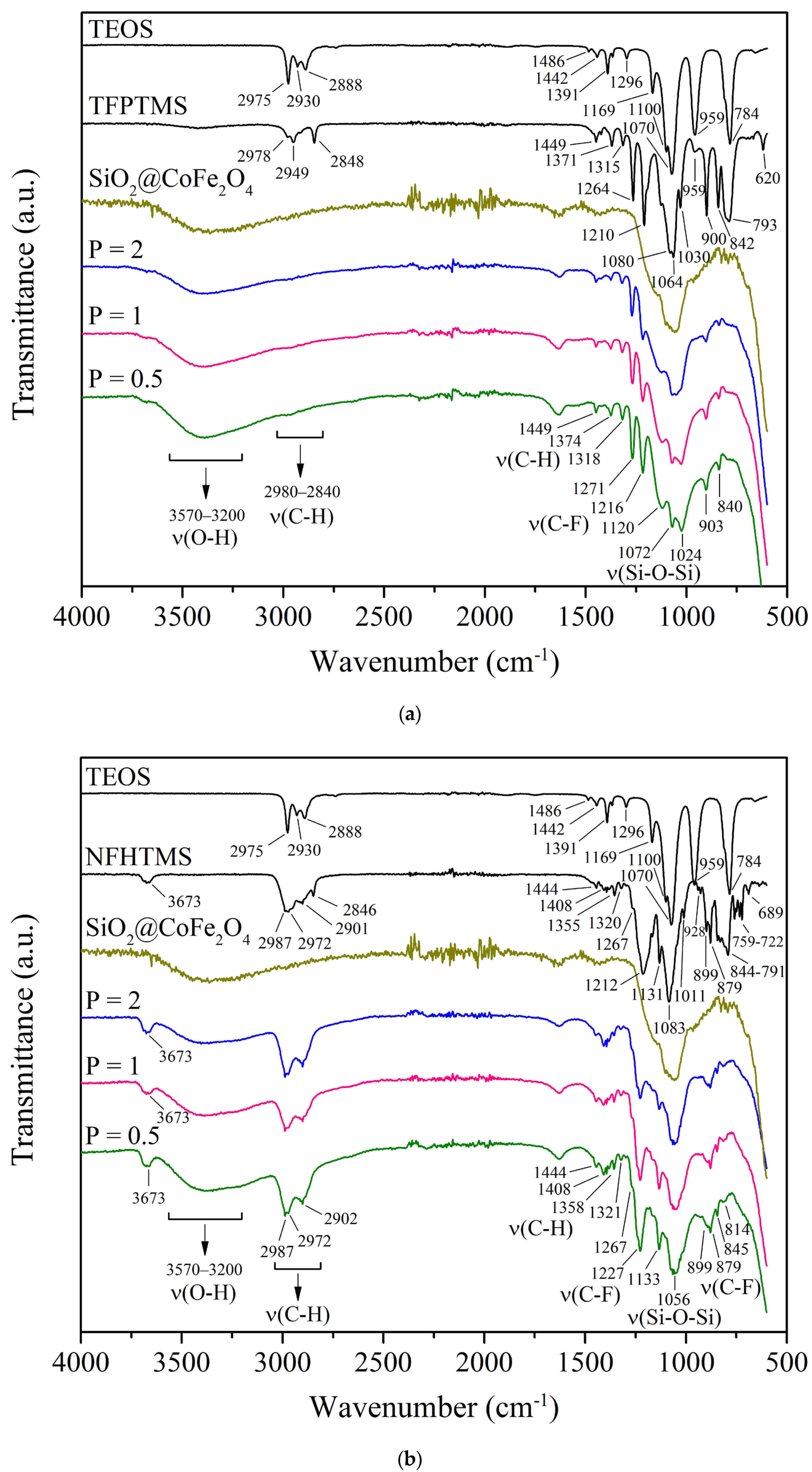
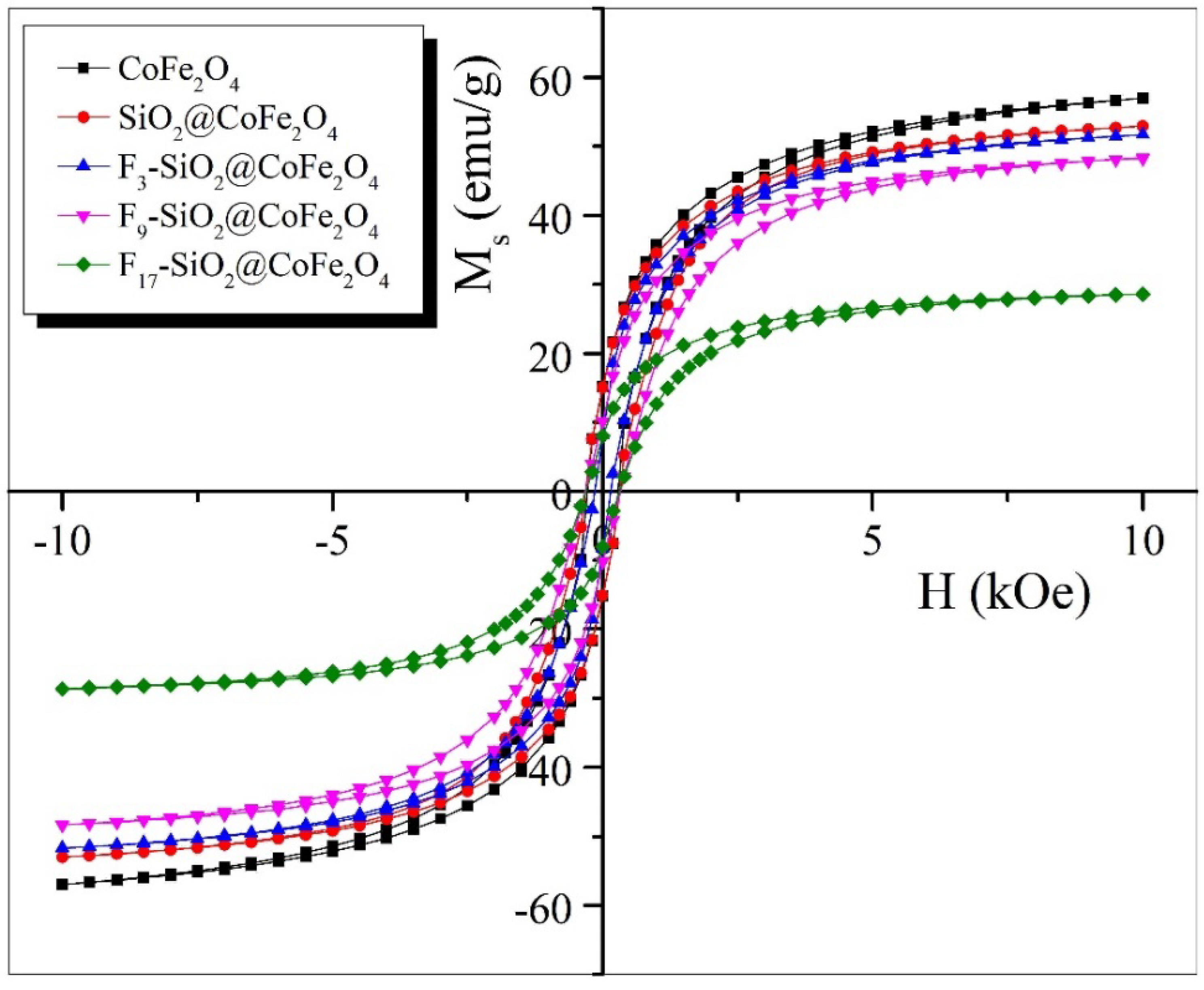
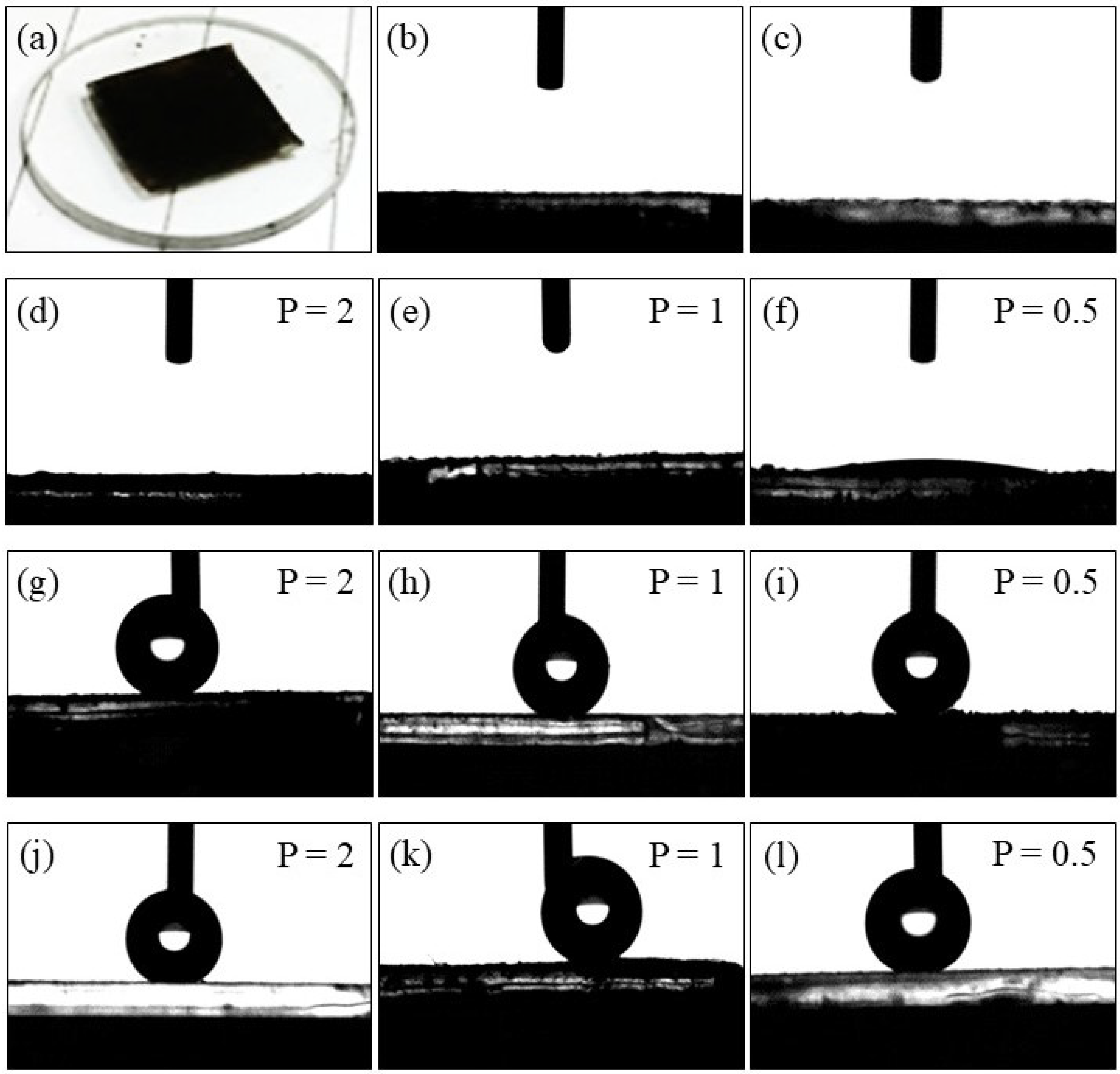
2.2. Surface Wettability and Hydrophobicity of Functionalized CoFe2O4 Nanoparticles
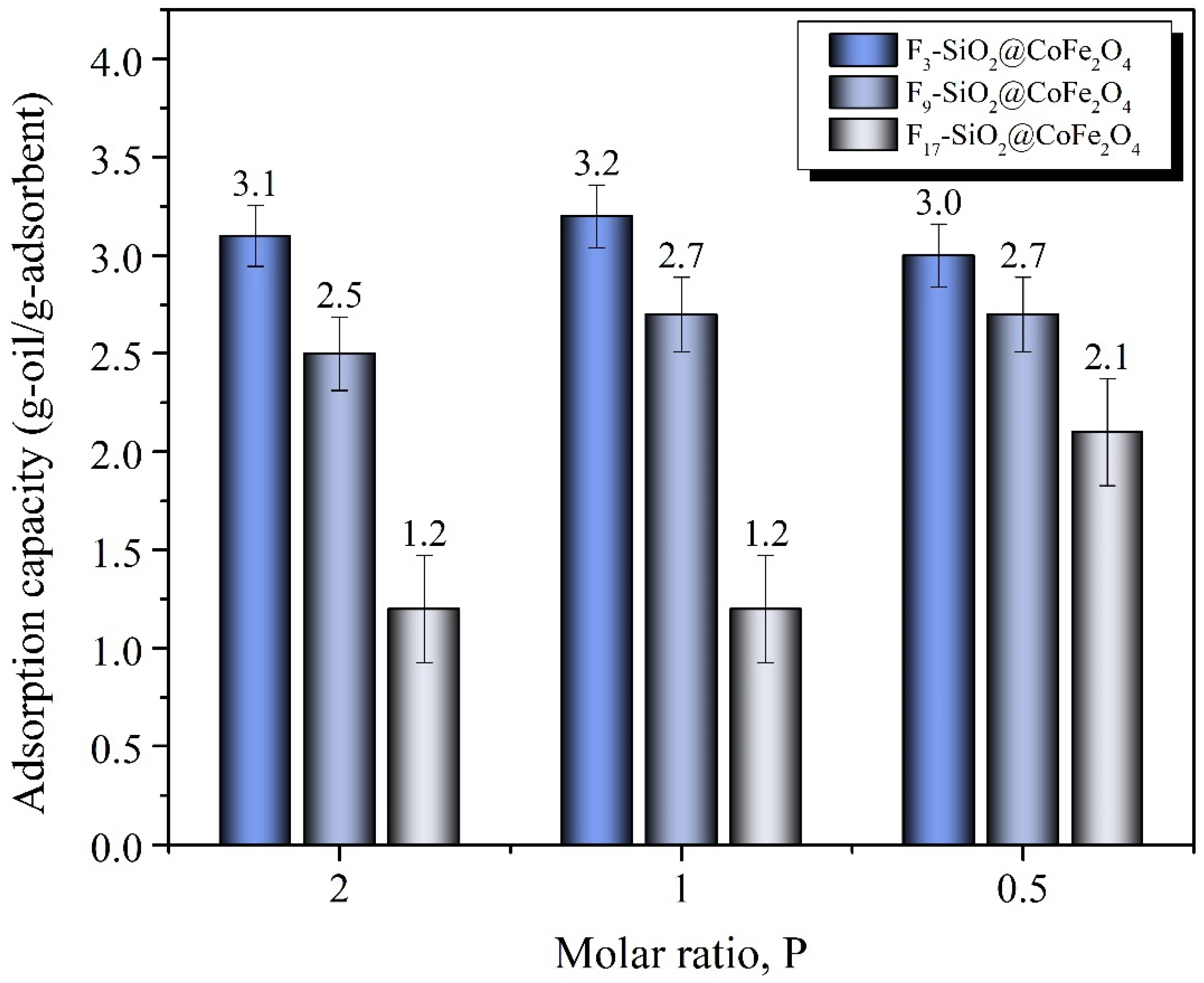
2.3. Evaluation of Oil Adsorption Capacity and Efficiency Using Functionalized CoFe2O4 Nanoparticles
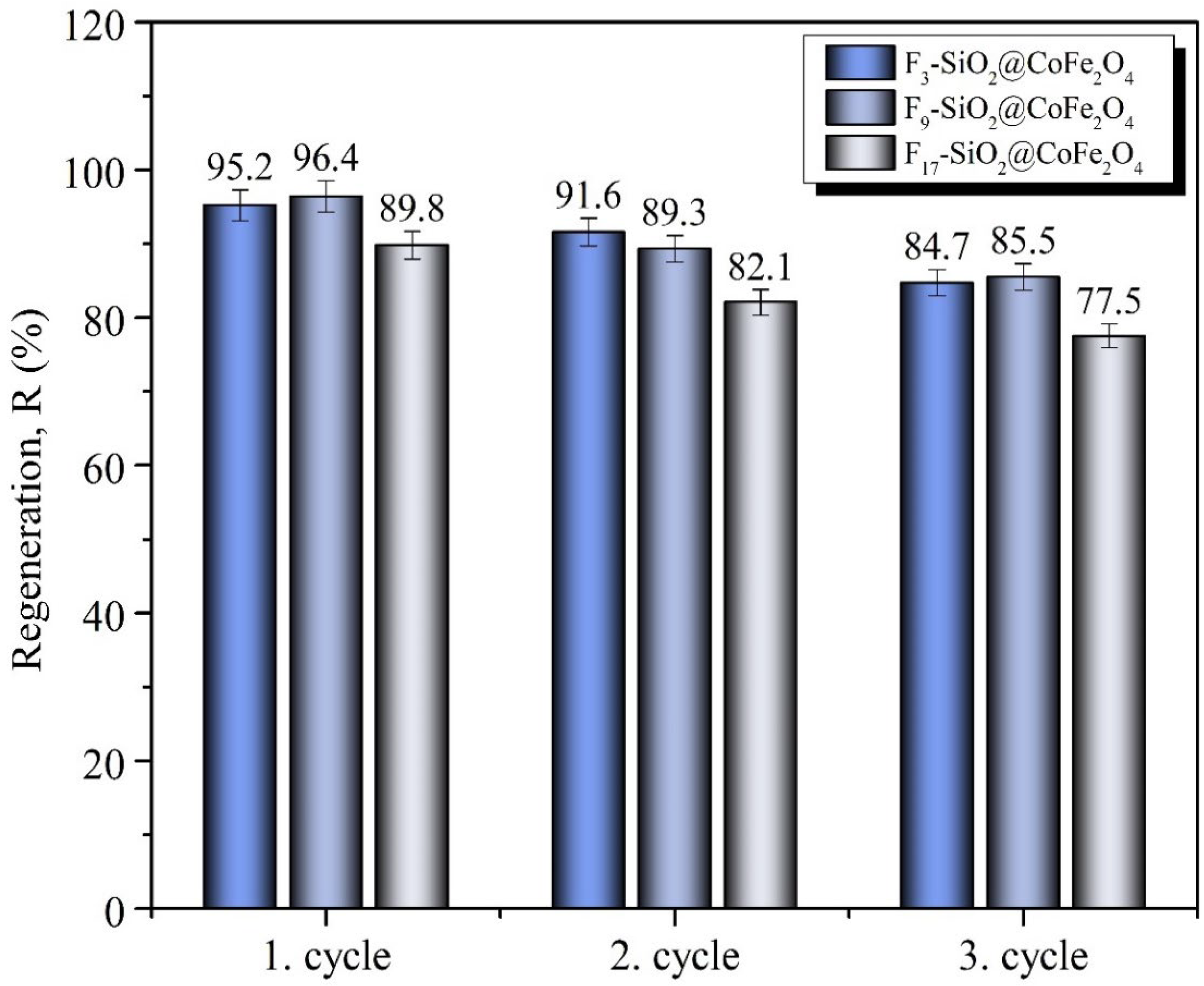
2.4. Oil Desorption and Regeneration of Adsorbents
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Synthesis of Magnetic Nanoparticles
3.1.1. Magnetic CoFe2O4 Nanoparticles
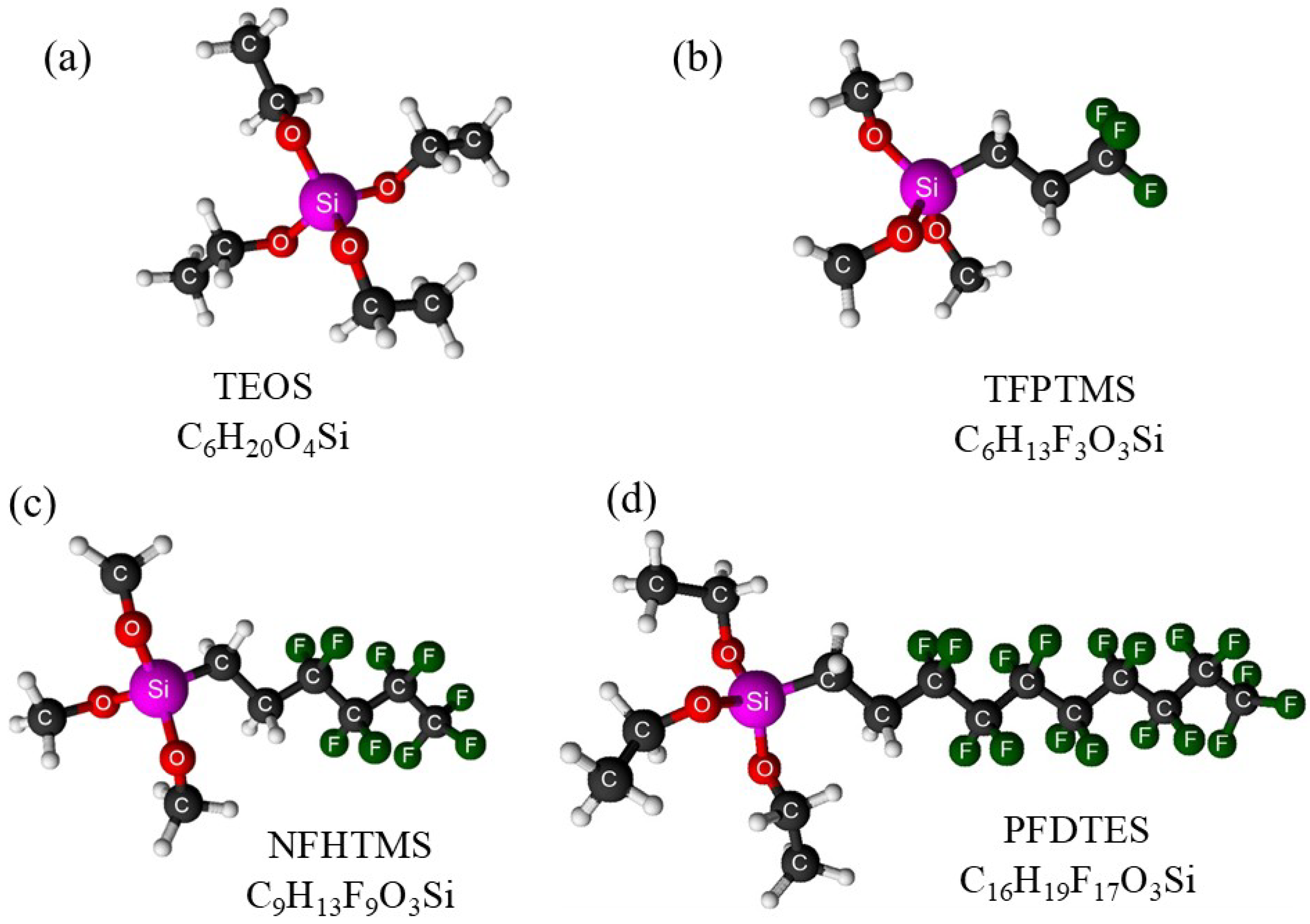
3.1.2. Magnetic Fluoroalkoxysilane-Coated CoFe2O4 Nanoparticles
3.2. Characterization of Nanoparticles
3.2.1. X-Ray Diffractometry (XRD)
3.2.2. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) with Energy Dispersive X-Ray Spectroscopy (EDXS)
3.2.3. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR)
3.2.4. Brunauer, Emmet, and Teller Method (BET)
3.2.5. Vibrating Sample Magnetometry (VSM)
3.2.6. Contact Angle (CA) Measurements
3.2.7. Surface Tension Measurements
3.3. Oil Adsorption and Desorption Tests
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rasouli, S.; Rezaei, N.; Hamedi, H.; Zendehboudi, S.; Duan, X. Superhydrophobic and Superoleophilic Membranes for Oil-Water Separation Application: A Comprehensive Review. Mater. Des. 2021, 204, 109599–109628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, H.; Bhardwaj, N.; Arya, S.K.; Khatri, M. Environmental Impacts of Oil Spills and Their Remediation by Magnetic Nanomaterials. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2020, 14, 100305–100328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuewen, D.; Adzigbli, L. Assessing the Impact of Oil Spills on Marine Organisms. J. Oceanogr. Mar. Res. 2018, 6, 472–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obi, E.O.; Kamgba, F.A.; Obi, D.A. Techniques of Oil Spill Response in the Sea. IOSR J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 6, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhas, R.; Al-Ibrahim, Y.; Al-Meraj, A.; Abdullah, H.; Alshatti, A. Application of Magnetic Separation for Oil Spill Remediation and Recovery in Kuwait Sea Water. Desalination Water Treat. 2021, 209, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Kumar, S.; Kishore, B.; Narayanan, T.N. Magnetic Scaffolds in Oil Spill Applications. Environ. Sci. 2020, 6, 436–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doshi, B.; Sillanpää, M.; Kalliola, S. A Review of Bio-Based Materials for Oil Spill Treatment. Water Res. 2018, 135, 262–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.; Zhao, H.-Y.; Zhu, H.-W.; Huang, J.; Shi, L.-A.; Yu, S.-H. Advanced Sorbents for Oil-Spill Cleanup: Recent Advances and Future Perspectives. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 10459–10490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Cao, E.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, A.; Hu, H. Perfluorosilane Treated Calotropis Gigantea Fiber: Instant Hydrophobic-Oleophilic Surface with Efficient Oil-Absorbing Performance. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 295, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvate, S.; Dixit, P.; Chattopadhyay, S. Superhydrophobic Surfaces: Insights from Theory and Experiment. J. Phys. Chem. B 2020, 124, 1323–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamopoulos, F.G.; Vouvoudi, E.C.; Achilias, D.S.; Karapanagiotis, I. Fluorosilane Water-Repellent Coating for the Protection of Marble, Wood and Other Materials. Heritage 2021, 4, 2668–2675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrozewicz, D.; Ciesielczyk, F.; Nowacka, M.; Karasiewicz, J.; Piasecki, A.; MacIejewski, H.; Jesionowski, T. Fluoroalkylsilane versus Alkylsilane as Hydrophobic Agents for Silica and Silicates. J. Nanomater. 2013, 2013, 631938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueira, R.B. Hybrid Sol-Gel Coatings for Corrosion Mitigation: A Critical Review. Polymers 2020, 12, 689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, X.; Bai, H.; Cao, M. Advances in Bioinspired Superhydrophobic Surfaces Made from Silicones: Fabrication and Application. Polymers 2023, 15, 543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Lan, P.; Zhao, K.; Yu, L.; Zhou, L.; Wang, Y.; Deng, C. Biomimetic Modification of Sponges with Alkyl-Silica Hybrid Nanowires for Efficient Oil-Water Separation Applications. Surf. Interfaces 2025, 69, 106766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Zhao, Q.; Zhu, D.; Gao, S.; Fang, W.; Jin, J. Multifunctional Polydopamine-Modified CuO Nanowire-Haired Membranes for Efficient Oil/Water Separation and Dye Removal. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2024, 63, 9955–9963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.; Guo, H.; Zhou, J.; Li, Y.; He, X.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Y. Polyacrylonitrile Nanofibers Coated with Covalent Organic Frameworks for Oil/Water Separation. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2022, 5, 3925–3936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Long, B.; Gao, S.; Luo, J.; Wang, L.; Huang, X.; Wang, D.; Xue, H.; Gao, J. Carbon Nanofiber Based Superhydrophobic Foam Composite for High Performance Oil/Water Separation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 402, 123838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vojdani Saghir, S.; Goharshadi, E.K. Multifunctional MnO2 Nanorods-Modified Wood Sponge for Water Remediation: Applications for Heavy Metal Sorption and Oil/Water Separation. Wood Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 2097–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.W.; Jiang, L.W.; Yang, Y.M.; Lin, Z.K.; Xie, Z.W.; Bei, S.X.; He, F.A. Preparation of Superhydrophobic MnO2 Nanorod-Fe3O4 Nanoparticle Functionalized Melamine Sponges for Oil-Water Separation. New J. Chem. 2025, 48, 10907–10921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ieamviteevanich, P.; Palaporn, D.; Chanlek, N.; Poo-Arporn, Y.; Mongkolthanaruk, W.; Eichhorn, S.J.; Pinitsoontorn, S. Carbon Nanofiber Aerogel/Magnetic Core-Shell Nanoparticle Composites as Recyclable Oil Sorbents. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2020, 3, 3939–3950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihsanullah, I.; Bilal, M.; Sajid, M. Emerging Magnetic MXenes in Water Treatment, Desalination, and Resource Recovery: Advances, Challenges, and Prospects. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 372, 133426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Gao, B.; Zhao, P.; Fu, H.; Kamali, A.R. Magnetic Luffa/Graphene/CuFe2O4 Sponge for Efficient Oil/Water Separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 337, 126347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, P.; Wang, M.; Di, J.; Xiong, J.; Zhao, S.; Li, Z. Reusable Graphitic Carbon Nitride Nanosheet-Based Aerogels as Sorbents for Oils and Organic Solvents. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2020, 3, 8176–8181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Xu, M.; Zhao, Z.; Pan, J.; Zhao, S.; Xue, J.; Ye, Z. Preparation of 3D Superhydrophobic Porous G-C3N4 Nanosheets@carbonized Kapok Fiber Composites for Oil/Water Separation and Treating Organic Pollutants. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 648, 129298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, H.; Zhang, Q.; Cheng, F.; Feng, Z.; Hua, Y.; Zuo, S.; Cui, A.; Yao, C. Magnetically Separable Mesoporous Fe3O4@g-C3N4as a Multifunctional Material for Metallic Ion Adsorption, Oil Removal from the Aqueous Phase, Photocatalysis, and Efficient Synergistic Photoactivated Fenton Reaction. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2022, 61, 8895–8907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihsanullah, I.; Bilal, M.; Sajid, M.; Mohammad, A.W.; Atieh, M.A.; Ghaffour, N. Emerging MXenes: Revolutionizing Oily Wastewater Treatment—A Comprehensive and Critical Review. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 329, 125181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Ma, S.; Li, J.; Yuan, M.; Gao, J.; Xue, J.; Wang, M. Multifunctional 3D Polydimethylsiloxane Modified MoS2@biomass-Derived Carbon Composite for Oil/Water Separation and Organic Dye Adsorption/Photocatalysis. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 637, 128281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatima, J.; Shah, A.N.; Tahir, M.B.; Mehmood, T.; Shah, A.A.; Tanveer, M.; Nazir, R.; Jan, B.L.; Alansi, S. Tunable 2D Nanomaterials; Their Key Roles and Mechanisms in Water Purification and Monitoring. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 766743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natalya, S.A.C.; Kadja, G.T.M.; Azhari, N.J.; Khalil, M.; Fajar, A.T.N. Two-Dimensional (2D) Nanomaterials for Enhanced Oil Recovery (EOR): A Review. FlatChem 2022, 34, 100383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talukdar, M.; Behera, S.K.; Bhattacharya, K.; Deb, P. Surface Modified Mesoporous G-C 3 N 4 @FeNi 3 as Prompt and Proficient Magnetic Adsorbent for Crude Oil Recovery. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 473, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.; Li, K.; Chen, X.; Dan, R.; Yu, Y. Magnetic and Hydrophobic Composite Polyurethane Sponge for Oil-Water Separation. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, T.; Zhang, X.; Ma, R.; Qi, D.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, D.; Huang, J.; Zhao, H. Quaternary Ammonium Siloxane-Decorated Magnetic Nanoparticles for Emulsified Oil-Water Separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 309, 123097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehmood, A.; Saleem Ahmed Khan, F.; Mujawar Mubarak, N.; Ali Mazari, S.; Sattar Jatoi, A.; Khalid, M.; Hua Tan, Y.; Rao Karri, R.; Walvekar, R.; Chan Abdullah, E.; et al. Carbon and Polymer-Based Magnetic Nanocomposites for Oil-Spill Remediation-a Comprehensive Review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 54477–54496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmobarak, W.F.; Almomani, F. Application of Fe3O4 Magnetite Nanoparticles Grafted in Silica (SiO2) for Oil Recovery from Oil in Water Emulsions. Chemosphere 2021, 265, 129054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guselnikova, O.; Barras, A.; Addad, A.; Sviridova, E.; Szunerits, S.; Postnikov, P.; Boukherroub, R. Magnetic Polyurethane Sponge for Efficient Oil Adsorption and Separation of Oil from Oil-in-Water Emulsions. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 240, 116627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Wei, Y.; Wang, Q.; Di, J.; Miao, S.; Yu, J. Superhydrophobic Magnetic Core-Shell Mesoporous Organosilica Nanoparticles with Dendritic Architecture for Oil-Water Separation. Mater. Chem. Front. 2020, 4, 2184–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Halouane, F.; Mathias, D.; Barras, A.; Wang, Z.; Lv, A.; Lu, S.; Xu, W.; Meziane, D.; Tiercelin, N.; et al. Preparation of Magnetic, Superhydrophobic/Superoleophilic Polyurethane Sponge: Separation of Oil/Water Mixture and Demulsification. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 384, 123339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Li, Y.; Sun, S.; Kalulu, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Wang, X.; Du, Q.; Jiang, Y. Novel Magnetic and Flame-Retardant Superhydrophobic Sponge for Solar-Assisted High-Viscosity Oil/Water Separation. Prog. Org. Coat. 2020, 139, 105369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Fang, J.; Cheng, T.; Ding, J.; Qu, L.; Dai, L.; Wang, X.; Lin, T. One-Step Coating of Fluoro-Containing Silica Nanoparticles for Universal Generation of Surface Superhydrophobicity. Chem. Commun. 2008, 877–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saengkaew, J.; Le, D.; Samart, C.; Sawada, H.; Nishida, M.; Chanlek, N.; Kongparakul, S.; Kiatkamjornwong, S. Superhydrophobic Coating from Fluoroalkylsilane Modified Natural Rubber Encapsulated SiO2 Composites for Self-Driven Oil/Water Separation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 462, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodič, P.; Kapun, B.; Panjan, M.; Milošev, I. Easy and Fast Fabrication of Self-Cleaning and Anti-Icing Perfluoroalkyl Silane Film on Aluminium. Coatings 2020, 10, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Xue, Y.; Ding, J.; Feng, L.; Wang, X.; Lin, T. Durable, Self-Healing Superhydrophobic and Superoleophobic Surfaces from Fluorinated-Decyl Polyhedral Oligomeric Silsesquioxane and Hydrolyzed Fluorinated Alkyl Silane. Angew. Chem.—Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 11433–11436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Wang, H.; Niu, H.; Gestos, A.; Lin, T. Robust, Self-Healing Superamphiphobic Fabrics Prepared by Two-Step Coating of Fluoro-Containing Polymer, Fluoroalkyl Silane, and Modified Silica Nanoparticles. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2013, 23, 1664–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Jones, A.K.; Sikka, V.K.; Wu, J.; Gao, D. Anti-Icing Superhydrophobic Coatings. Langmuir 2009, 25, 12444–12448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Wang, H.; Niu, H.; Gestos, A.; Wang, X.; Lin, T. Fluoroalkyl Silane Modified Silicone Rubber/Nanoparticle Composite: A Super Durable, Robust Superhydrophobic Fabric Coating. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 2409–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Shao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, B. Preparation of a Superhydrophobic Coating Based on Polysiloxane Modified SiO2 and Study on Its Anti-Icing Performance. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2022, 437, 128359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Wang, L.; Qian, H.; Li, X. Superhydrophobic Surfaces for Corrosion Protection: A Review of Recent Progresses and Future Directions. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 2016, 13, 11–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Startek, K.; Szczurek, A.; Tran, T.N.L.; Krzak, J.; Bachmatiuk, A.; Lukowiak, A. Structural and Functional Properties of Fluorinated Silica Hybrid Barrier Layers on Flexible Polymeric Foil. Coatings 2021, 11, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacono, S.T.; Jennings, A.R. Recent Studies on Fluorinated Silica Nanometer-Sized Particles. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brassard, J.D.; Sarkar, D.K.; Perron, J. Fluorine Based Superhydrophobic Coatings. Appl. Sci. 2012, 2, 453–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Lin, D.; Li, H.; Lai, X.; Zeng, X. Facile Fabrication of Superhydrophobic, Flame-Retardant and Conductive Polyurethane Sponge via Dip-Coating. Mater. Lett. 2021, 287, 129307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, C.; Ai, K.; Li, X.; Lu, L. A Superhydrophobic Sponge with Excellent Absorbency and Flame Retardancy. Angew. Chem.—Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 5556–5560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farahat, M.; Sobhy, A.; Sanad, M.M.S. Superhydrophobic Magnetic Sorbent via Surface Modification of Banded Iron Formation for Oily Water Treatment. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 11016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadela, A.; Lakić, M.; Potočnik, M.; Košak, A.; Gutmaher, A.; Lobnik, A. Novel Reusable Functionalized Magnetic Cobalt Ferrite Nanoparticles as Oil Adsorbents. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2020, 38, 168–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmobarak, W.F.; Almomani, F. Application of Magnetic Nanoparticles for the Removal of Oil from Oil-in-Water Emulsion: Regeneration/Reuse of Spent Particles. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2021, 203, 108591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darwish, M.S.A.; Kim, H.; Lee, H.; Ryu, C.; Lee, J.Y.; Yoon, J. Synthesis of Magnetic Ferrite Nanoparticles with High Hyperthermia Performance via a Controlled Co-Precipitation Method. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, D.H.K.; Yun, Y.S. Spinel Ferrite Magnetic Adsorbents: Alternative Future Materials for Water Purification? Coord. Chem. Rev. 2016, 315, 90–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maaz, K.; Mumtaz, A.; Hasanain, S.K.; Ceylan, A. Synthesis and Magnetic Properties of Cobalt Ferrite (CoFe2O4) Nanoparticles Prepared by Wet Chemical Route. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2007, 308, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odio, O.F.; Reguera, E. Nanostructured Spinel Ferrites: Synthesis, Functionalization, Nanomagnetism and Environmental Applications. In Magnetic Spinels—Synthesis, Properties and Applications; InTech: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Abakumov, M.A.; Semkina, A.S.; Skorikov, A.S.; Vishnevskiy, D.A.; Ivanova, A.V.; Mironova, E.; Davydova, G.A.; Majouga, A.G.; Chekhonin, V.P. Toxicity of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles: Size and Coating Effects. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2018, 32, e22225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, P.S.; Parker, C.P.; Larsen, S.C. One-Pot Synthesis of Iron Oxide Mesoporous Silica Core/Shell Nanocomposites. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2015, 204, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolyar, S.V.; Krasitskaya, V.V.; Frank, L.A.; Yaroslavtsev, R.N.; Chekanova, L.A.; Gerasimova, Y.V.; Volochaev, M.N.; Bairmani, M.S.; Velikanov, D.A. Polysaccharide-Coated Iron Oxide Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Properties, Surface Modification. Mater. Lett. 2021, 284, 128920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Li, Y.; Song, T.; Bao, M.; Li, Y.; Lu, J.; Li, Y. An Environmentally Benign Approach to Prepare Superhydrophobic Magnetic Melamine Sponge for Effective Oil/Water Separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 236, 116308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Lei, J.; Li, L.; Zhang, R.; Mi, N.; Chen, H.; Huang, D.; Li, N. A Facile Method to Fabricate the Superhydrophobic Magnetic Sponge for Oil-Water Separation. Mater. Lett. 2017, 195, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmi Fard, N.; Fazaeli, R. Fabrication of Superhydrophobic CoFe2O4/Polyaniline/Covalent Organic Frameworks/Cotton Fabric Membrane and Evaluation of Its Efficiency in Separation of Olive Oil from Water. J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 2022, 69, 2014–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.P.; Huang, X.H.; Chen, J.N.; Dong, M.; Nie, C.Z.; Qin, L. Modified Superhydrophobic Magnetic Fe3O4 Nanoparticles for Removal of Microplastics in Liquid Foods. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 476, 146562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Joshi, M.; Nigam, S.; Avasthi, D.K.; Adelung, R.; Srivastava, S.K.; Mishra, Y.K. Efficient Oil Removal from Wastewater Based on Polymer Coated Superhydrophobic Tetrapodal Magnetic Nanocomposite Adsorbent. Appl. Mater. Today 2019, 17, 130–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, A.L. The Scherrer Formula for X-Ray Particle Size Determination. Phys. Rev. 1939, 56, 978–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzwarth, U.; Gibson, N. The Scherrer Equation versus the “Debye-Scherrer Equation”. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2011, 6, 534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hankare, P.P.; Sanadi, K.R.; Pandav, R.S.; Patil, N.M.; Garadkar, K.M.; Mulla, I.S. Structural, Electrical and Magnetic Properties of Cadmium Substituted Copper Ferrite by Sol-Gel Method. J. Alloys Compd. 2012, 540, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellamy, L.J. The Infra-Red Spectra of Complex Molecules, 3rd ed.; Bellamy, L.J., Ed.; Chapman and Hall: London, UK, 1975; ISBN 978-94-011-6019-3. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, X.; Chorover, J. Adsorption of Perfluorooctanoic Acid and Perfluorooctanesulfonic Acid to Iron Oxide Surfaces as Studied by Flow-through ATR-FTIR Spectroscopy. Environ. Chem. 2012, 9, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jitianu, A.; Amatucci, G.; Klein, L.C. Organic-Inorganic Sol-Gel Thick Films for Humidity Barriers. J. Mater. Res. 2008, 23, 2084–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Chen, H.; Jiang, F. Adsorption of Perflourooctane Sulfonate (PFOS) and Perfluorooctanoate (PFOA) on Polyaniline Nanotubes. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2015, 479, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.J.; Hwangbo, M.; Chen, Z.; Liu, Y.; Kameoka, J.; Chu, K.H. Reusable Functionalized Hydrogel Sorbents for Removing Long- and Short-Chain Perfluoroalkyl Acids (PFAAs) and GenX from Aqueous Solution. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 17447–17455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, E.Y.; Frischknecht, A.L.; Winey, K.I.; Riggleman, R.A. Effect of Surface Properties and Polymer Chain Length on Polymer Adsorption in Solution. J. Chem. Phys. 2021, 155, 034701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Kim, K.; Wang, W.; Chen, B.; Mattoussi, H.; Hallinan, D.T. Scaling Laws for Polymer Chains Grafted onto Nanoparticles. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2018, 219, 1700417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.; Zhao, N.; Hou, Z. The Effect of Hydrodynamic Interactions on Nanoparticle Diffusion in Polymer Solutions: A Multiparticle Collision Dynamics Study. Soft Matter 2017, 13, 8625–8635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeppson, P.; Sailer, R.; Jarabek, E.; Sandstrom, J.; Anderson, B.; Bremer, M.; Grier, D.G.; Schulz, D.L.; Caruso, A.N.; Payne, S.A.; et al. Cobalt Ferrite Nanoparticles: Achieving the Superparamagnetic Limit by Chemical Reduction. J. Appl. Phys. 2006, 100, 114324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saddeler, S.; Bendt, G.; Salamon, S.; Haase, F.T.; Landers, J.; Timoshenko, J.; Rettenmaier, C.; Jeon, H.S.; Bergmann, A.; Wende, H.; et al. Influence of the Cobalt Content in Cobalt Iron Oxides on the Electrocatalytic OER Activity. J. Mater. Chem. A Mater. 2021, 9, 25381–25390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozaffari, M.; Hadadian, Y.; Aftabi, A.; Oveisy Moakhar, M. The Effect of Cobalt Substitution on Magnetic Hardening of Magnetite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2014, 354, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Q.; Lam, M.; Swanson, S.; Yu, R.H.R.; Milliron, D.J.; Topuria, T.; Jubert, P.O.; Nelson, A. Monodisperse Cobalt Ferrite Nanomagnets with Uniform Silica Coatings. Langmuir 2010, 26, 17546–17551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faaliyan, K.; Abdoos, H.; Borhani, E.; Afghahi, S.S.S. Magnetite-Silica Nanoparticles with Core-Shell Structure: Single-Step Synthesis, Characterization and Magnetic Behavior. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2018, 88, 609–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spoială, A.; Ilie, C.I.; Crăciun, L.N.; Ficai, D.; Ficai, A.; Andronescu, E. Magnetite-silica Core/Shell Nanostructures: From Surface Functionalization towards Biomedical Applications—A Review. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 11075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knežević, N.Ž.; Ruiz-Hernández, E.; Hennink, W.E.; Vallet-Regí, M. Magnetic Mesoporous Silica-Based Core/Shell Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 9584–9593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkowitz, A.E.; Schuele, W.J. Magnetic Properties of Some Ferrite Micropowders. J. Appl. Phys. 1959, 30, S134–S135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunlop, D.J. Superparamagnetic and Single-Domain Threshold Sizes in Magnetite. J. Geophys. Res. 1973, 78, 1780–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorai, A.; Souici, A.; Dragoe, D.; Rivière, E.; Ouhenia, S.; Belloni, J.; Mostafavi, M. Superparamagnetic Cobalt Ferrite Nanoparticles Synthesized by Gamma Irradiation. New J. Chem. 2022, 47, 2626–2634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girardet, T.; Venturini, P.; Martinez, H.; Dupin, J.C.; Cleymand, F.; Fleutot, S. Spinel Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles: Properties, Synthesis and Washing Methods. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 8127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinnasamy, C.N.; Jeyadevan, B.; Shinoda, K.; Tohji, K.; Djayaprawira, D.J.; Takahashi, M.; Justin Joseyphus, R.; Narayanasamy, A. Unusually High Coercivity and Critical Single-Domain Size of Nearly Monodispersed CoFe2O4 Nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2003, 83, 2862–2864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigorova, M.; Blythe, H.J.; Blaskov, V.; Rusanov, V.; Petkov, V.; Masheva, V.; Nihtianova, D.; Martinez, L.M.; Mun Oz, J.S.; Mikhov, M. Magnetic Properties and Mossbauer Spectra of Nanosized Powders. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1998, 183, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arkles, B.; Pan, Y.; Kim, Y.M. The Role of Polarity in the Structure of Silanes Employed in Surface Modification. In Silanes and Other Coupling Agents; Mittal, K.L., Ed.; CRC Press: London, UK, 2009; Volume 5, pp. 51–64. [Google Scholar]
- Arkles, B. Tailoring Surfaces with Silanes. Chemtech 1977, 7, 766–779. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, J.; Fu, K.; Liu, Y.; Xu, S.; Sun, Z.; Cao, M.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhou, Y. Fluorine-Functionalized Mesoporous Alumina Materials with Superhydrophobic Surfaces. Surf. Interfaces 2023, 40, 103046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brzoska, J.B.; Ben Azouz, I.; Rondelez, F. Silanization of Solid Substrates: A Step toward Reproducibility. Langmuir 1994, 10, 4367–4373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshino, N.; Hamano, K.; Omiya, Y.; Yukishige Kondo, J.; Ito, A.; Abe, M. Synthesis of Hybrid Anionic Surfactants Containing Fluorocarbon and Hydrocarbon Chains. Langmuir 1996, 11, 466–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zisman, W.A. Relation of the Equilibrium Contact Angle to Liquid and Solid Constitution. Adv. Chem. 1964, 17, 41. [Google Scholar]
- Mittal, K.L. Advances in Contact Angle, Wettability and Adhesion; Mittal, K.L., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2019; Volume 4, ISBN 978-1-119-59254-9. [Google Scholar]
- Mittal, J.; Hummer, G. Static and Dynamic Correlations in Water at Hydrophobic Interfaces. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 105, 20130–20135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seisenbaeva, G.A.; Ali, L.M.A.; Vardanyan, A.; Gary-Bobo, M.; Budnyak, T.M.; Kessler, V.G.; Durand, J.O. Mesoporous Silica Adsorbents Modified with Amino Polycarboxylate Ligands—Functional Characteristics, Health and Environmental Effects. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 406, 124698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grainger, D.W.; Stewart, C.W. Fluorinated Coatings and Films: Motivation and Significance. In Fluorinated Surfaces, Coatings, and Films; Castner, D.G., Grainger, D.W., Eds.; ACS Symposium Series; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2001; Volume 787, pp. 1–14. ISBN 9780841236233. [Google Scholar]
- Cassie, A.B.D.; Baxter, S. Wettability of Porous Surfaces. Trans. Faraday Soc. 1944, 40, 546–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenzel, R.N. Resistance of Solid Surfaces to Wetting by Water. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1936, 28, 988–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Tao, F.; Pan, Q. Fast and Selective Removal of Oils from Water Surface via Highly Hydrophobic Core-Shell Fe2O3@C Nanoparticles under Magnetic Field. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2010, 2, 3141–3146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Jiang, W.; Wang, F.; Shen, P.; Ma, P.; Gu, J.; Mao, J.; Li, F. Synthesis of Highly Hydrophobic Floating Magnetic Polymer Nanocomposites for the Removal of Oils from Water Surface. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 286, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Y.; Li, M.; Qu, H.; Xing, Z.; Wei, C.; Zhan, J. Facile and Tunable Synthesis of Carbon-γ-Fe2O3 Submicron Spheres through an Aerosol-Assisted Technology and Their Application in Oil Spill Recovery. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 103910–103918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haynes, W.M.; Lide, D.R.; Bruno, T.J. CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 97th ed.; Haynes, W.M., Lide, D.R., Bruno, T.J., Eds.; CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017; ISBN 978-1-4987-5429-3. [Google Scholar]
- Schwerdtfeger, P.; Nagle, J.K. 2018 Table of Static Dipole Polarizabilities of the Neutral Elements in the Periodic Table. Mol. Phys. 2019, 117, 1200–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruths, M. Surface Forces, Surface Tension, and Adhesion. In Encyclopedia of Tribology; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2013; pp. 3435–3443. [Google Scholar]
- Pauling, L. The nature of the chemical bond. iv. the energy of single bonds and the relative electronegativity of atoms. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1932, 54, 3570–3582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandler, D. Interfaces and the Driving Force of Hydrophobic Assembly. Nature 2005, 437, 640–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lum, K.; Chandler, D.; Weeks, J.D. Hydrophobicity at Small and Large Length Scales. J. Phys. Chem. B 1999, 103, 4570–4577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q. The Hydrophobic Effects: Our Current Understanding. Molecules 2022, 27, 7009–7036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Vegt, N.F.A.; Nayar, D. The Hydrophobic Effect and the Role of Cosolvents. J. Phys. Chem. B 2017, 121, 9986–9998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshino, N. Studies on Synthesis, Physical Properties. J. Oleo Sci. 2007, 12, 513–518. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Najar, J.A.; Al-Humairi, S.T.; Lutfee, T.; Balakrishnan, D.; Veza, I.; Soudagar, M.E.M.; Fattah, I.M.R. Cost-Effective Natural Adsorbents for Remediation of Oil-Contaminated Water. Water 2023, 15, 1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omorogie, M.O.; Babalola, J.O.; Unuabonah, E.I. Regeneration Strategies for Spent Solid Matrices Used in Adsorption of Organic Pollutants from Surface Water: A Critical Review. Desalination Water Treat. 2016, 57, 518–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkika, D.A.; Tolkou, A.K.; Katsoyiannis, I.A.; Kyzas, G.Z. The Adsorption-Desorption-Regeneration Pathway to a Circular Economy: The Role of Waste-Derived Adsorbents on Chromium Removal. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 368, 132996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kow, S.H.; Fahmi, M.R.; Abidin, C.Z.A.; Ong, S.A.; Ibrahim, N. Regeneration of Spent Activated Carbon from Industrial Application by NaOH Solution and Hot Water. Desalination Water Treat. 2016, 57, 29137–29142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allwin Mabes Raj, A.F.P.; Bauman, M.; Lakić, M.; Dimitrušev, N.; Lobnik, A.; Košak, A. Removal of Pb2+, CrT, and Hg2+ Ions from Aqueous Solutions Using Amino-Functionalized Magnetic Nanoparticles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 16186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allwin Mabes Raj, A.F.P.; Bauman, M.; Dimitrušev, N.; Ali, L.M.A.; Onofre, M.; Gary-Bobo, M.; Durand, J.O.; Lobnik, A.; Košak, A. Superparamagnetic Spinel-Ferrite Nano-Adsorbents Adapted for Hg2+, Dy3+, Tb3+ Removal/Recycling: Synthesis, Characterization, and Assessment of Toxicity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viltužnik, B.; Lobnik, A.; Košak, A. The Removal of Hg(II) Ions from Aqueous Solutions by Using Thiol-Functionalized Cobalt Ferrite Magnetic Nanoparticles. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2015, 74, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TotalEnergies Lubrifiants Safety Data Sheet QUARTZ INEO MC3 5W-30. Available online: https://totalenergies.co.uk/Material-safety-data-sheet (accessed on 11 November 2024).
- Schikorr, V.G. Uber Eisen(L1)-Hydroxyd Und Ein Lferromagnetisches Eisen(Ll1)-Hydroxyd. Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 1931, 35, 33–39. [Google Scholar]
| Molar Ratio (P) | Fluoroalkylsilane-Coated CoFe2O4 Nanoparticles | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F3-SiO2@CoFe2O4 | F9-SiO2@CoFe2O4 | F17-SiO2@CoFe2O4 | ||||
| SA (m2/g) | DBET (nm) | SA (m2/g) | DBET (nm) | SA (m2/g) | DBET (nm) | |
| 2.0 | 94.4 ± 0.5 | 11.86 ± 0.06 | 92.1 ± 0.5 | 12.15 ± 0.07 | 44.9 ± 0.2 | 24.93 ± 0.11 |
| 1.0 | 100.0 ± 0.4 | 11.19 ± 0.04 | 77.1 ± 0.4 | 14.52 ± 0.08 | 5.3 ± 0.1 | 211.20 ± 4.06 |
| 0.5 | 101.3 ± 0.4 | 11.05 ± 0.04 | 70.8 ± 0.3 | 15.81 ± 0.07 | 0.8 ± 0.1 | 1399.30 ± 199.90 |
| Sample | Specific Magnetization (Ms) [emu/g] | Retentivity (Mr) [emu/g] | Coercivity (Hc) [Oe] | Squareness Ratio (Mr/Ms) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CoFe2O4 | 56.9 | 15.2 | 269.7 | 0.27 |
| SiO2@CoFe2O4 | 52.9 | 15.0 | 318.3 | 0.28 |
| F3-SiO2@CoFe2O4 | 51.7 | 8.1 | 152.3 | 0.16 |
| F9-SiO2@CoFe2O4 | 50.3 | 10.1 | 331.2 | 0.20 |
| F17-SiO2@CoFe2O4 | 28.6 | 8.1 | 314.1 | 0.28 |
| Adsorbent Nanoparticles | Contact Angle, CA (Degree) | Critical Surface Tension γc (mN/m) * | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molar Ratio (P) | ||||
| 2 | 1 | 0.5 | ||
| F3-SiO2@CoFe2O4 | 0 | 0 | 11.5 | 33.5 |
| F9-SiO2@CoFe2O4 | 148.9 | 149.9 | 152.7 | 23 |
| F17-SiO2@CoFe2O4 | 151.3 | 153.1 | 159.2 | 12 |
| Adsorbent Nanoparticles | Average Oil Adsorption Capacity, Qads [g/g] | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Molar Ratio (P) | |||
| 2 | 1 | 0.5 | |
| F3-SiO2@CoFe2O4 | 3.12 ± 0.15 | 3.21 ± 0.16 | 3.01 ± 0.16 |
| F9-SiO2@CoFe2O4 | 2.51 ± 0.18 | 2.74 ± 0.19 | 2.78 ± 0.19 |
| F17-SiO2@CoFe2O4 | 1.22 ± 0.27 | 1.25 ± 0.27 | 2.11 ± 0.27 |
| Adsorbent Nanoparticles | Average Oil Desorption Efficiency, Re (%), with Standard Deviations (n = 3) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1st Cycle | 2nd Cycle | 3rd Cycle | |
| F3-SiO2@CoFe2O4 | 95.2 ± 2.1 | 91.6 ± 1.9 | 84.7 ± 1.8 |
| F9-SiO2@CoFe2O4 | 96.4 ± 2.1 | 89.3 ± 1.8 | 85.5 ± 1.8 |
| F17-SiO2@CoFe2O4 | 89.9 ± 1.9 | 82.1 ± 1.7 | 77.5 ± 1.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Košak, A.; Hadela, A.; Poberžnik, M.; Lobnik, A. Magnetic Separation of Oil Spills from Water Using Cobalt Ferrite Nanoparticles with Fluorocarbon Functionalization. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6562. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146562
Košak A, Hadela A, Poberžnik M, Lobnik A. Magnetic Separation of Oil Spills from Water Using Cobalt Ferrite Nanoparticles with Fluorocarbon Functionalization. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(14):6562. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146562
Chicago/Turabian StyleKošak, Aljoša, Ajra Hadela, Mojca Poberžnik, and Aleksandra Lobnik. 2025. "Magnetic Separation of Oil Spills from Water Using Cobalt Ferrite Nanoparticles with Fluorocarbon Functionalization" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 14: 6562. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146562
APA StyleKošak, A., Hadela, A., Poberžnik, M., & Lobnik, A. (2025). Magnetic Separation of Oil Spills from Water Using Cobalt Ferrite Nanoparticles with Fluorocarbon Functionalization. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(14), 6562. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146562






