Predicting the Damaging Potential of Uncharacterized KCNQ1 and KCNE1 Variants
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussions
2.1. Universal Residue Labels of Kv7.1 and Its Paralogues
2.2. Composing a Broad Dataset of Missense Variants for Channel hKv7.1 and Its Paralogues
2.3. Distribution of Missense Variants in Topological Regions of hKv7.1
2.4. Comparing Performance of Bioinformatics Tools
2.5. Paralogue Annotation of Kv7.1 Variants
2.6. AlphaMissense and Paralogue Annotations Consensually Predicted Damaging Potential for 79 VUSs
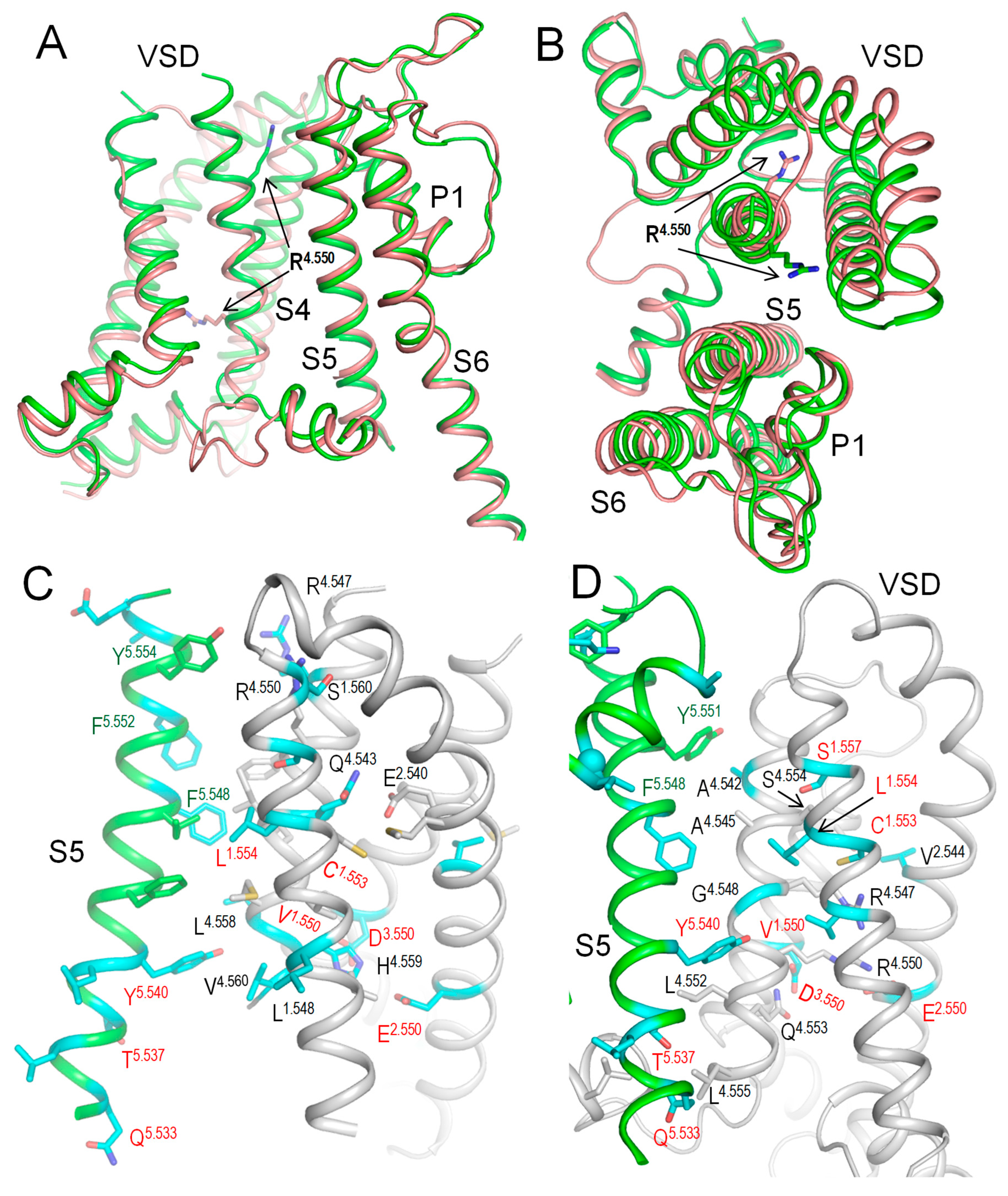
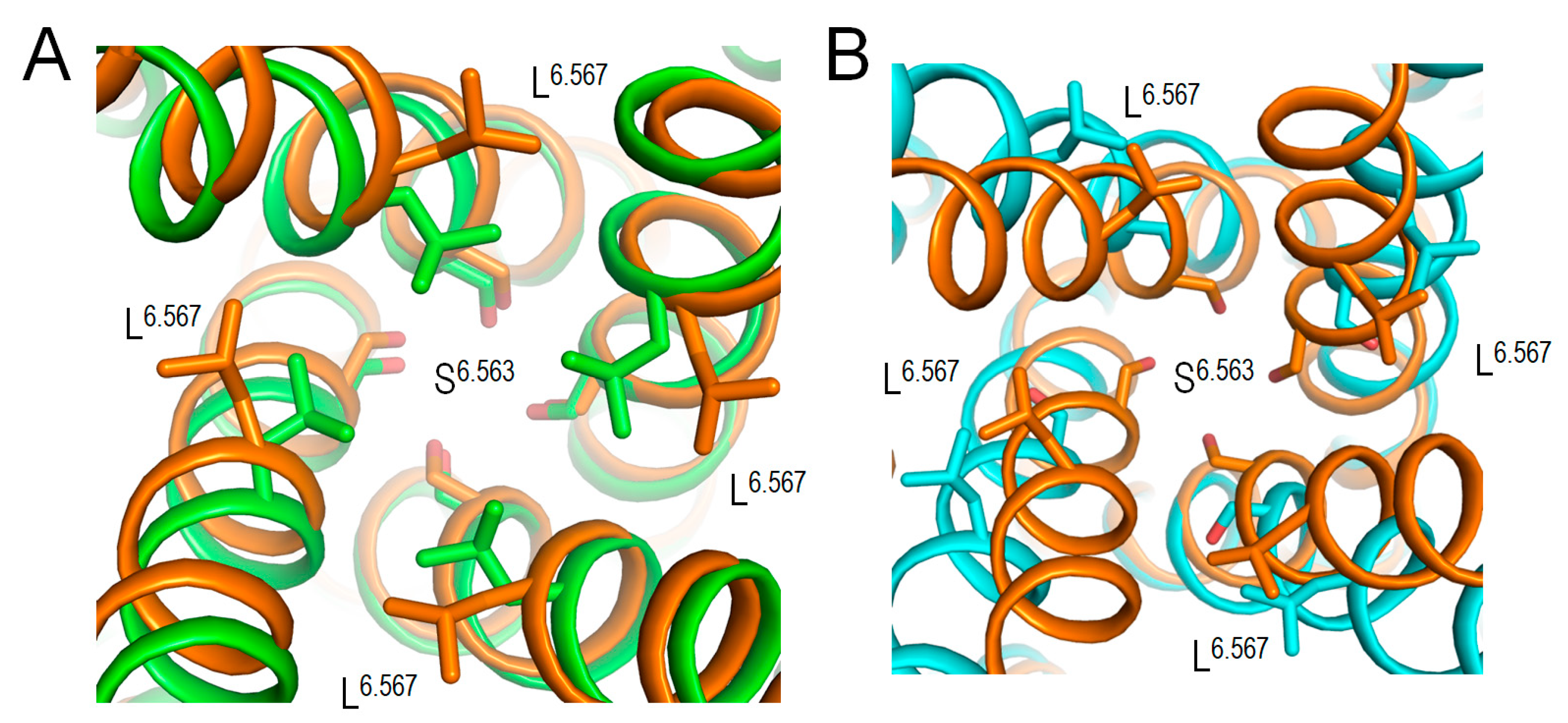
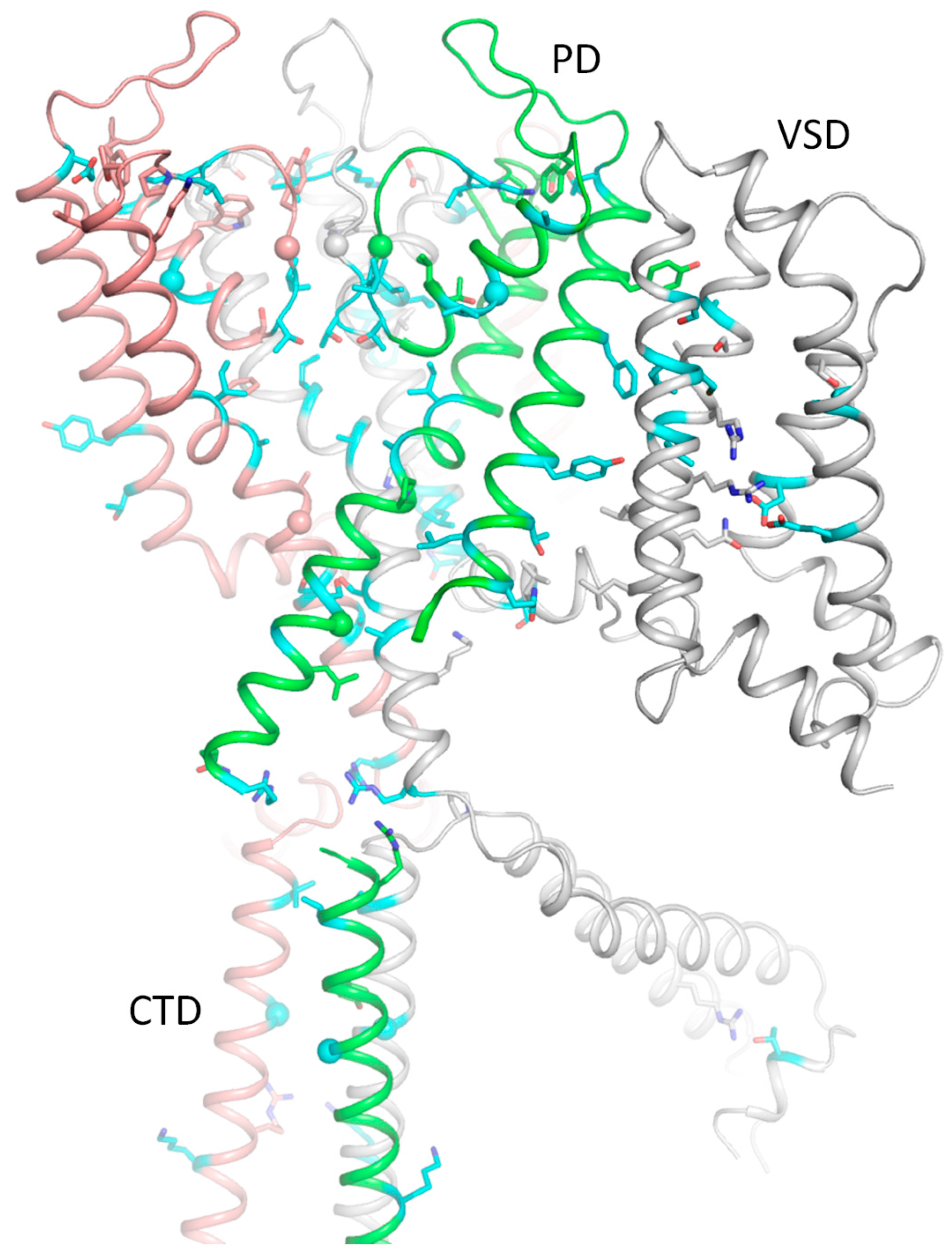
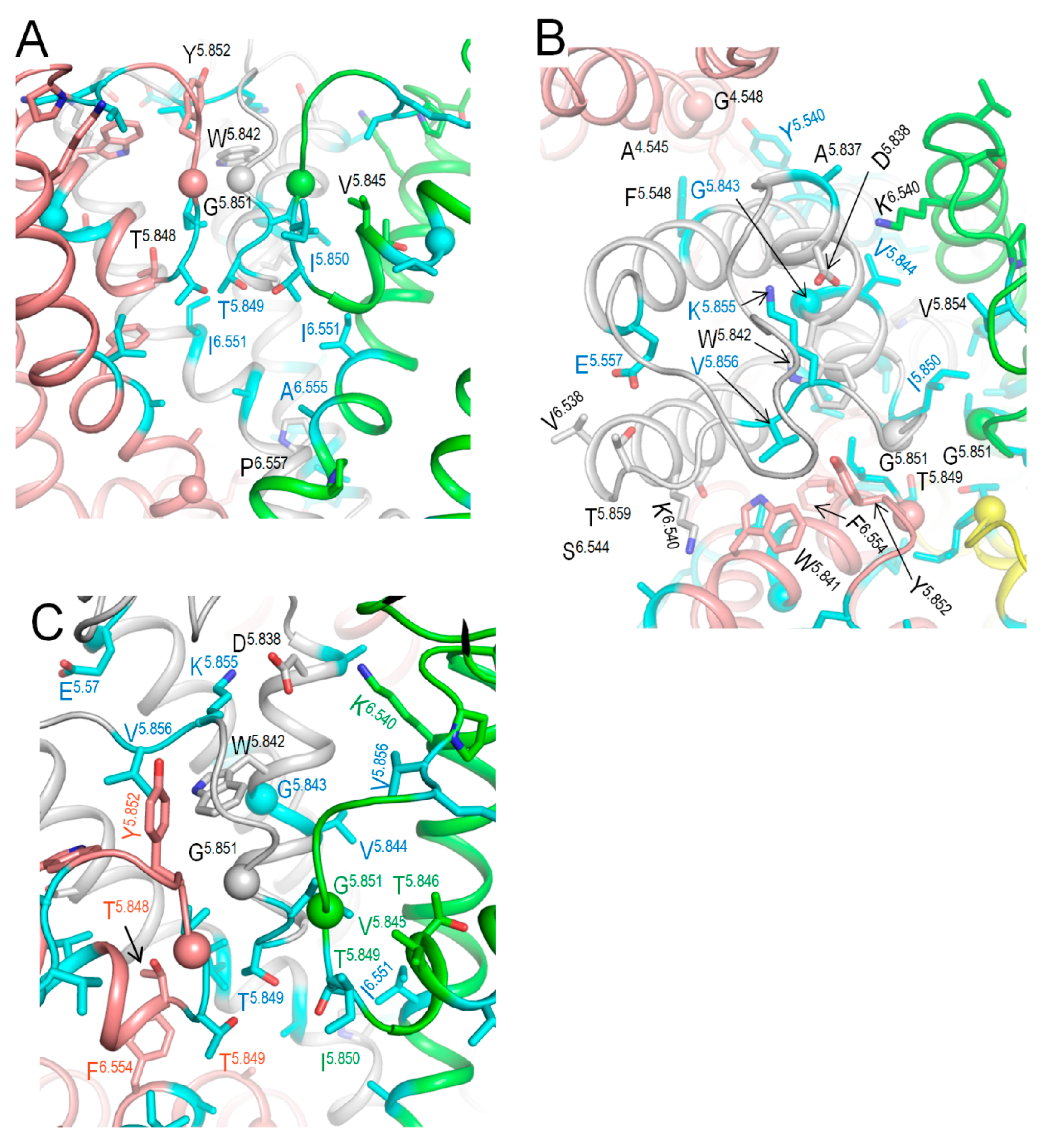
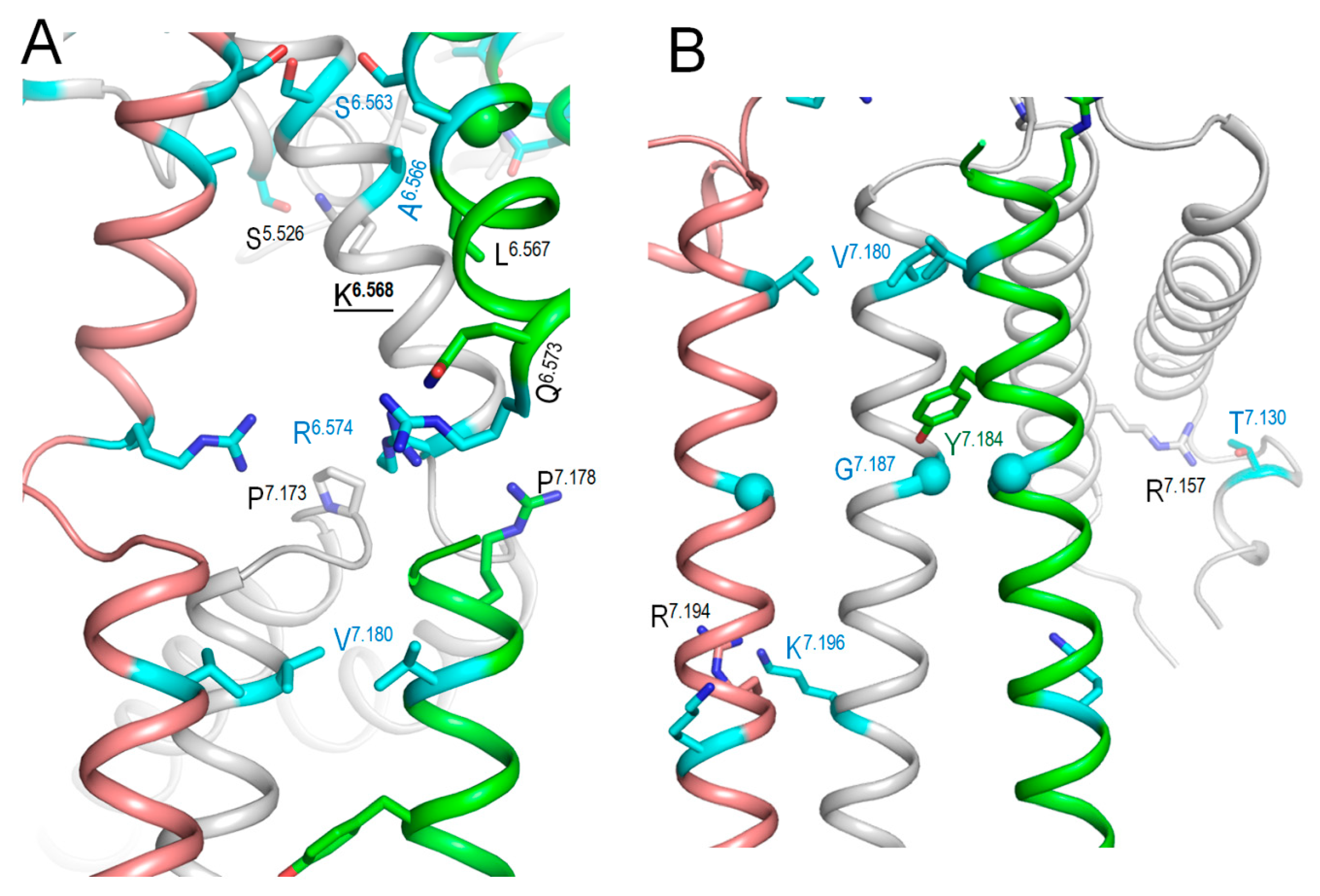
2.7. Intersegmental Contacts Involving WTRs with Likely Damaging VUSs
| LD VUS | P/LP | State b | LD VUS | P/LP | State | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| V133/1.550A | R231/4.550L | ↓ | L262/5.535V | P343/6.557A | ↓ | |||
| Q234/4.553P | ↑ | o | P343/6.557A/S | ↑ | ||||
| C136/1.553F | S225/4.544L/W | ↓ | T264/5.537S | L233/4.552M | ↓ | |||
| L156/2.536P | ↑ | o | L251/5.524Q/P | ↑ | ||||
| Q234/4.553P | ↑ | G269/5.542R/S/V/D | ↑ | |||||
| L137/1.554P | S225/4.544L/W | ↓ | Y267/5.540F | G229/4.548D | ↓ | |||
| G229/4.548D | ↓ | L233/4.552M | ↓ | |||||
| Q234/4.553P | ↑ | E284/5.557G | T322/5.859P/A/R | ↓ | ||||
| I235/4.554N | ↑ | P320/5.857S | ↓ | |||||
| I274/5.547D | ↑ | G325/6.539W | ||||||
| R231/4.550S/C/L/H | o | G306/5.843E | L273/5.546I/V/P/R/F | ↓ | ||||
| Q234/4.553P | o | V307/5.844M/L/E | S330/\6.544Y | ↓ | ||||
| I235/4.554L/N | o | T312/5.849S | T312/5.849I/S | ↓ | ||||
| S140/1.557R | S225/4.544L/W | ↓ | I313/5.850F | G314/5.851R/D/S | ↓ | |||
| L156/2.536P | ↑ | T312/5.849S/I | ↓ | |||||
| R231/4.550S/C/L/H | ↑ | o | T309/5.846I | ↓ | ||||
| Q234/4.553P | ↑ | o | V319/5.856M | Y315/5.852S | ↓ | |||
| L156/2.536P | o | W304/5.841R/L/S | ↓ | |||||
| S143/1.560F | R231/4.550S/C/L/H | o | W304/5.841G | ↓ | ||||
| V164/2.544A | S209/3.557P | o | Y315/5.852D | ↓ | ||||
| E170/2.550G | R231/4.550S/H/C/L | ↓ | I337/6.551M | F340/6.554L | ↓ | |||
| D202/3.550V | Q234/4.553P | ↓ | F339/6.553V | L251/5.524Q | ↓ | |||
| R231/4.550S/C/L/H | ↓ | L251/5.524P | ↓ | |||||
| R234/4.562S/C/L/H/P | ↑ | A341/6.555T | A344/6.558E/V | ↓ | ||||
| R243/4.562S/C/L/H/P | o | S349/6.563A/L | G345/6.559R/V/E | ↓ | ||||
| Q260/A5.533H | L251/D5.524Q/P | ↓ | R360/6.574K/T | R539/7.178W/Q | ↓ | |||
| L262/5.535V | P343/6.557A/S | o | K557/7.196R | R555/7.194S/C | ↓ | |||
| LD VUS | Contact b | LD VUS | Contact b | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| V133/A1.550I/A | R228/A4.547W | VUS → LD | K318/A5.855N | D301/A5.838Y | VUS |
| G229/A4.548S/V | VUS | S349/A6.563A/L | S349/B,D6.563A/L | VUS → LD | |
| Y267/B5.540F | VUS → LD | A352/B,D6.566P/D | VUS → LD | ||
| C136/A1.553F | R228/A4.547W | VUS→ LD | A352/A6.566P/D | L353/B6.567P | VUS |
| L137/A1.554P | G229/A4.548S/V | VUS | S349/B6.563A/L | VUS → LD | |
| R228/A4.547W | VUS → LD | G350/B6.564R | VUS | ||
| D202/A3.550V | Q234/A4.553L/R | VUS → LD | R360/A6.574K/T | P535/A7.174T | VUS |
| S253/A5.526A | K354/A6.568R | VUS → LD | T391/A7.030P | R518/A7.157Q/P | VUS |
| Y267/A5.540F | G229/D4.548S/V | VUS | V541/A7.180I | V541/B,D7.180I | VUS → LD |
| E284/A5.557G | V324/6.538L/I/F | VUS | Y545/B7.184F | VUS | |
| A300/A5.837S/G | K326/B6.540E | VUS | G548/A7.187D | Y545/B7.184F | VUS |
| T312/A5.849S | I313/5.850F | VUS → LD | |||
| I337/A6.551M | VUS → LD | ||||
| LD VUS | Contact | LD VUS | Contact | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| V164/A2.544A | S209/A3.557P | NP | I313/A5.850F | G314/B5.851C/A | NP |
| A223/A4.542T | Y278/B5.551H | NP | T309/B5.846S/R | NP | |
| Q260/A5.533H | L236/D4.555R/P | CIP | V308/B5.845D | NP | |
| T264/A5.537S | L236/D4.555R/P | CIP | K318/A5.855N | D301/A5.838V | CIP |
| L233/D4.552P | CIP | I337/A6.551M | T311/D5.848A | NP | |
| Y267/A5.540F | L233/4.552P | CIP | T311/D5.848I | CIP | |
| F275/A5.548L | A226/D4.545V | CIP | A341/A6.555T | A344/D6.558T/G | CIP |
| E284/A5.557G | T322/5.859K | CIP | S349/A6.563A/L | S349/B,D6.563P | CIP |
| F296/5.611S | CIP | A352/A6.566P/D | S349/B6.563P | CIP | |
| T312/A5.849S | I337/A6.551F | CIP | G350/B6.564V | CIP | |
| T391/A7.030P | R518/A7.157G | CIP | |||
| LD VUS | Contact | |
|---|---|---|
| C136/A1.553F | M159/2539L | VUS |
| S140/A1.557R | Q260/A5.533H | LD VUS |
| V164/A2.544A | M210/3558T/I | VUS |
| E170/A2.550G | H240/4.559Q | LD VUS |
| V129/1546I/G/A | VUS | |
| D202/A3.550V | H240/4.559Q | LD VUS |
| L239/4.558V | Y267/A5.540F | LD VUS |
| F275/A5.548S/L | LD VUS | |
| H240/4.559Q/R | E170/A2.550G | LD VUS |
| D202/A3.550H | LD VUS | |
| V241/4.560I | Y267/5.540F | VUS |
| Y267/A5.540F | V241/4.560I | LD VUS |
| L239/4.558V | LD VUS | |
| F275/A5.548L | L239/4.558V | LD VUS |
2.8. Predicting Damaging Potential for KCNE1 VUSs with High ClinPred Score and ClinVar-Reported Variants in Sequentially Matching Positions of Paralogues
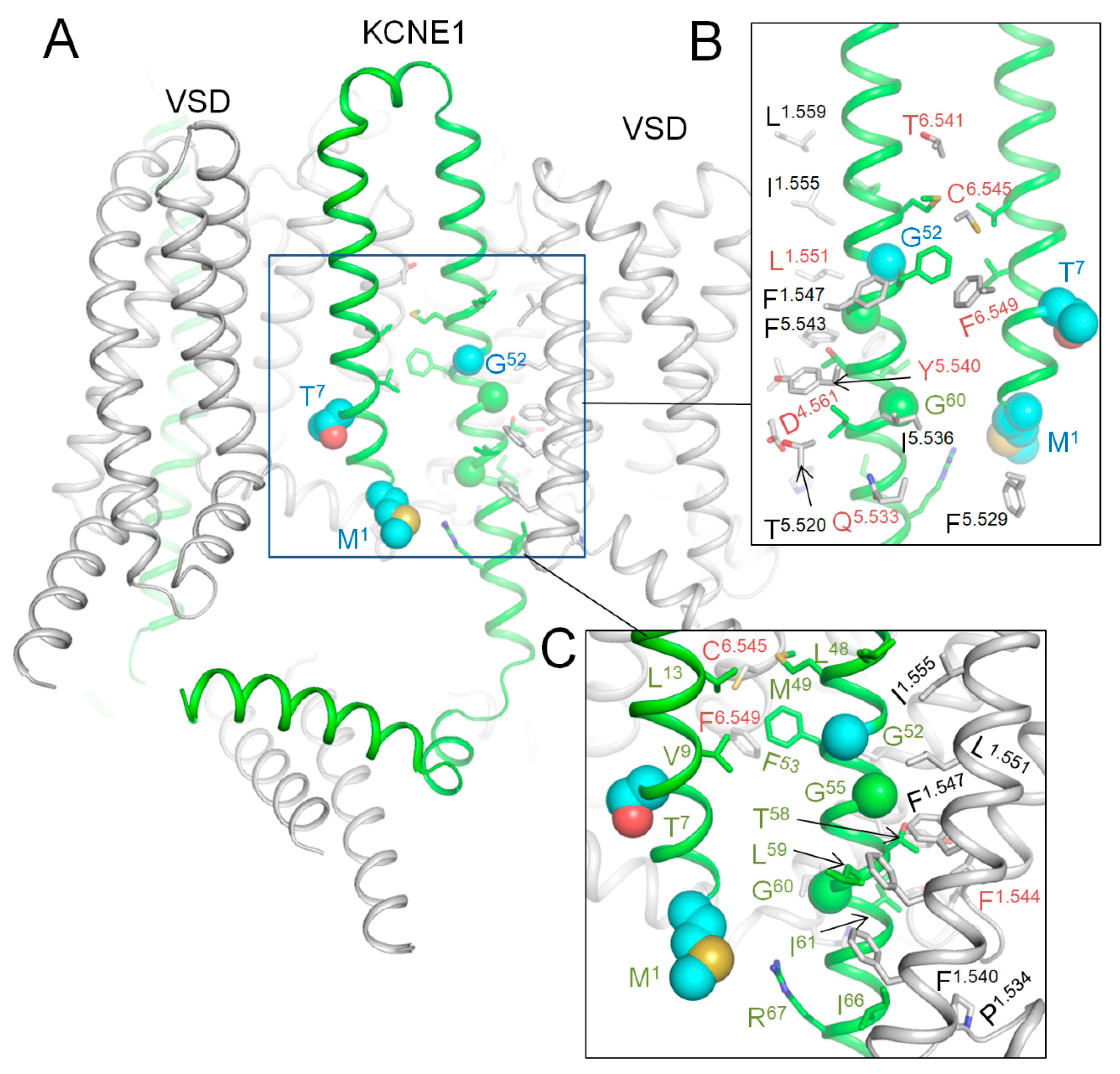
2.9. AlphaFold 3 (AF3) Model of Kv7.1 with KCNE1
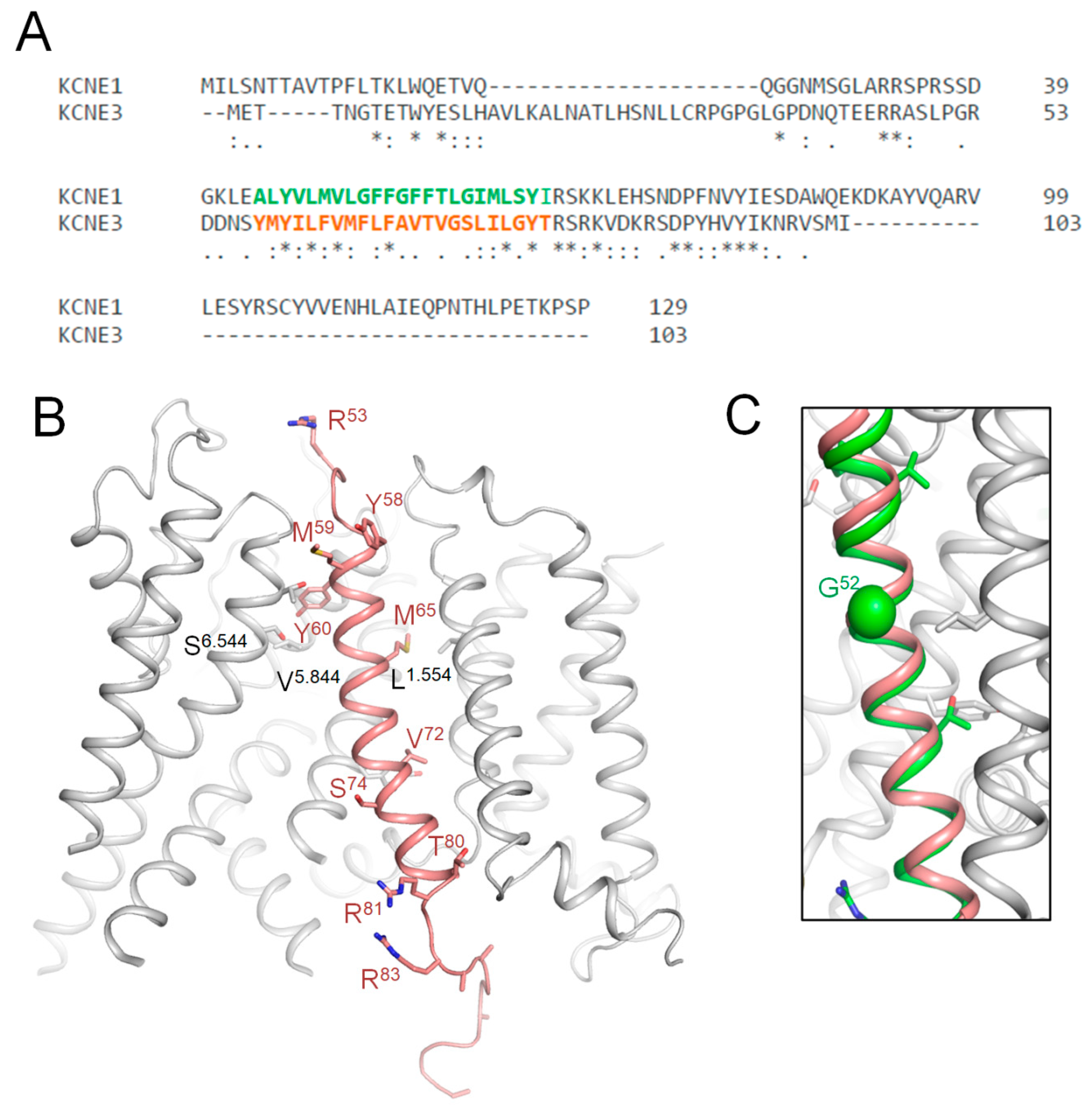
2.10. CryoEM Structure of KCNE3-Bound Kv7.1
3. Methods and Materials
3.1. Sequence Data of Human Channels and Collection of Variants
3.2. Topology of the Kv7.1 Channel
3.3. Multiple Sequence Alignment and Paralogue Annotation
3.4. Sequence-Based Prediction of Likely Damaging Variants
- TP (true-positive) is the number of disease-causing variants correctly predicted to be pathogenic;
- FN (false-negative) is the number of disease-causing variants incorrectly predicted as tolerated;
- TN (true-negative) is the number of neutral variants correctly predicted as tolerated;
- FP (false-positive) is the number of neutral variants incorrectly predicted as pathogenic;
- MCC is a correlation coefficient between the observed and predicted binary classification, ranging from −1 (total disagreement between prediction and observation) to 1 (perfect prediction).
3.5. Molecular Modeling
4. Conclusions
Study Limitations
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AF3 | AlphaFold3 |
| AUC | Area under the ROC curve |
| CIP | Conflicting Interpretation of Pathogenicity |
| LD | Likely damaging variant |
| LQTS | Long QT Syndrome |
| MC | Monte Carlo |
| NP | Germline classification of pathogenicity is Not Provided |
| P/LP | Pathogenic/Likely Pathogenic variant |
| PLIC | P-loop ion channel |
| TM | Transmembrane |
| ROC | Receiver Operating Characteristic |
| VSD | Voltage-sensing domain |
| VUS | Variant of unknown clinical significance |
| WTR | Wildtype residue |
References
- Wu, X.; Larsson, H.P. Insights into Cardiac IKs (KCNQ1/KCNE1) Channels Regulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kekenes-Huskey, P.M.; Burgess, D.E.; Sun, B.; Bartos, D.C.; Rozmus, E.R.; Anderson, C.L.; January, C.T.; Eckhardt, L.L.; Delisle, B.P. Mutation-Specific Differences in Kv7.1 (KCNQ1) and Kv11.1 (KCNH2) Channel Dysfunction and Long QT Syndrome Phenotypes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbott, J.W. Biology of the KCNQ1 Potassium Channel. New J. Sci. 2014, 2014, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jespersen, T.; Grunnet, M.; Olesen, S.P. The KCNQ1 potassium channel: From gene to physiological function. Physiology 2005, 20, 408–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanguinetti, M.C.; Seebohm, G. Physiological Functions, Biophysical Properties, and Regulation of KCNQ1 (K(V)7.1) Potassium Channels. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2021, 1349, 335–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; MacKinnon, R. Cryo-EM Structure of a KCNQ1/CaM Complex Reveals Insights into Congenital Long QT Syndrome. Cell 2017, 169, 1042–1050.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bains, S.; Giammarino, L.; Nimani, S.; Alerni, N.; Tester, D.J.; Kim, C.S.J.; Christoforou, N.; Louradour, J.; Horvath, A.; Beslac, O.; et al. KCNQ1 suppression-replacement gene therapy in transgenic rabbits with type 1 long QT syndrome. Eur. Heart J. 2024, 45, 3751–3763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothenberg, I.; Piccini, I.; Wrobel, E.; Stallmeyer, B.; Muller, J.; Greber, B.; Strutz-Seebohm, N.; Schulze-Bahr, E.; Schmitt, N.; Seebohm, G. Structural interplay of K(V)7.1 and KCNE1 is essential for normal repolarization and is compromised in short QT syndrome 2 (K(V)7.1-A287T). Hear. Case Rep. 2016, 2, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellocq, C.; van Ginneken, A.C.; Bezzina, C.R.; Alders, M.; Escande, D.; Mannens, M.M.; Baro, I.; Wilde, A.A. Mutation in the KCNQ1 gene leading to the short QT-interval syndrome. Circulation 2004, 109, 2394–2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.H.; Xu, S.J.; Bendahhou, S.; Wang, X.L.; Wang, Y.; Xu, W.Y.; Jin, H.W.; Sun, H.; Su, X.Y.; Zhuang, Q.N.; et al. KCNQ1 gain-of-function mutation in familial atrial fibrillation. Science 2003, 299, 251–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hateley, S.; Lopez-Izquierdo, A.; Jou, C.J.; Cho, S.; Schraiber, J.G.; Song, S.; Maguire, C.T.; Torres, N.; Riedel, M.; Bowles, N.E.; et al. The history and geographic distribution of a KCNQ1 atrial fibrillation risk allele. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campuzano, O.; Sarquella-Brugada, G.; Brugada, R.; Brugada, J. Genetics of channelopathies associated with sudden cardiac death. Glob. Cardiol. Sci. Pract. 2015, 2015, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albert, C.M.; MacRae, C.A.; Chasman, D.I.; VanDenburgh, M.; Buring, J.E.; Manson, J.E.; Cook, N.R.; Newton-Cheh, C. Common variants in cardiac ion channel genes are associated with sudden cardiac death. Circ. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. 2010, 3, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiper, A.K.; Wegner, S.; Kadala, A.; Rinne, S.; Schutte, S.; Winter, Z.; Bertoune, M.A.R.; Touska, F.; Matschke, V.; Wrobel, E.; et al. KCNQ1 is an essential mediator of the sex-dependent perception of moderate cold temperatures. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2024, 121, e2322475121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachyani, D.; Dvir, M.; Strulovich, R.; Tria, G.; Tobelaim, W.; Peretz, A.; Pongs, O.; Svergun, D.; Attali, B.; Hirsch, J.A. Structural basis of a Kv7.1 potassium channel gating module: Studies of the intracellular c-terminal domain in complex with calmodulin. Structure 2014, 22, 1582–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrobel, E.; Tapken, D.; Seebohm, G. The KCNE Tango—How KCNE1 Interacts with Kv7.1. Front. Pharmacol. 2012, 3, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banyasz, T.; Jian, Z.; Horvath, B.; Khabbaz, S.; Izu, L.T.; Chen-Izu, Y. Beta-adrenergic stimulation reverses the I Kr-I Ks dominant pattern during cardiac action potential. Pflug. Arch. 2014, 466, 2067–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burg, S.; Attali, B. Targeting of Potassium Channels in Cardiac Arrhythmias. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2021, 42, 491–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landrum, M.J.; Lee, J.M.; Benson, M.; Brown, G.R.; Chao, C.; Chitipiralla, S.; Gu, B.; Hart, J.; Hoffman, D.; Jang, W.; et al. ClinVar: Improving access to variant interpretations and supporting evidence. Nucleic Acids. Res. 2018, 46, D1062–D1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Kuenze, G.; Smith, J.A.; Taylor, K.C.; Duran, A.M.; Hadziselimovic, A.; Meiler, J.; Vanoye, C.G.; George, A.L., Jr.; Sanders, C.R. Mechanisms of KCNQ1 channel dysfunction in long QT syndrome involving voltage sensor domain mutations. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaar2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phul, S.; Kuenze, G.; Vanoye, C.G.; Sanders, C.R.; George, A.L., Jr.; Meiler, J. Predicting the functional impact of KCNQ1 variants with artificial neural networks. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2022, 18, e1010038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanoye, C.G.; Desai, R.R.; Fabre, K.L.; Gallagher, S.L.; Potet, F.; DeKeyser, J.M.; Macaya, D.; Meiler, J.; Sanders, C.R.; George, A.L., Jr. High-Throughput Functional Evaluation of KCNQ1 Decrypts Variants of Unknown Significance. Circ. Genom. Precis. Med. 2018, 11, e002345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brewer, K.R.; Vanoye, C.G.; Huang, H.; Clowes Moster, K.R.; Desai, R.R.; Hayes, J.B.; Burnette, D.T.; George, A.L.; Sanders, C.R. Integrative analysis of KCNQ1 variants reveals molecular mechanisms of type 1 long QT syndrome pathogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2025, 122, e2412971122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, S.; Aziz, N.; Bale, S.; Bick, D.; Das, S.; Gastier-Foster, J.; Grody, W.W.; Hegde, M.; Lyon, E.; Spector, E.; et al. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: A joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet. Med. 2015, 17, 405–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.; Wei, P.; Jian, X.; Gibbs, R.; Boerwinkle, E.; Wang, K.; Liu, X. Comparison and integration of deleteriousness prediction methods for nonsynonymous SNVs in whole exome sequencing studies. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2015, 24, 2125–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niroula, A.; Vihinen, M. Variation Interpretation Predictors: Principles, Types, Performance, and Choice. Hum. Mutat. 2016, 37, 579–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, R.; Oak, N.; Plon, S.E. Evaluation of in silico algorithms for use with ACMG/AMP clinical variant interpretation guidelines. Genome Biol. 2017, 18, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tordai, H.; Torres, O.; Csepi, M.; Padanyi, R.; Lukacs, G.L.; Hegedus, T. Analysis of AlphaMissense data in different protein groups and structural context. Sci. Data 2024, 11, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D.; Lassmann, T. A phenotype centric benchmark of variant prioritisation tools. NPJ Genom. Med. 2018, 3, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarnovskaya, S.I.; Korkosh, V.S.; Zhorov, B.S.; Frishman, D. Predicting novel disease mutations in the cardiac sodium channel. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 521, 603–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, R.; Peters, N.S.; Cook, S.A.; Ware, J.S. Paralogue annotation identifies novel pathogenic variants in patients with Brugada syndrome and catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia. J. Med. Genet. 2014, 51, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarnovskaya, S.I.; Kostareva, A.A.; Zhorov, B.S. L-Type Calcium Channel: Predicting Pathogenic/Likely Pathogenic Status for Variants of Uncertain Clinical Significance. Membranes 2021, 11, 599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarnovskaya, S.I.; Kostareva, A.A.; Zhorov, B.S. In silico analysis of TRPM4 variants of unknown clinical significance. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0295974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tikhonov, D.B.; Korkosh, V.S.; Zhorov, B.S. 3D-aligned tetrameric ion channels with universal residue labels for comparative structural analysis. Biophys. J. 2025, 124, 458–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gigolaev, A.M.; Iurevaa, D.A.; Lagosha, S.V.; Brazhe, A.R.; Zhorov, B.S.; Vassilevski, A.A. Golden Gate cloning enables efficient concatemer construction for biophysical analysis of heterozygous potassium channel variants from patients with epilepsy. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandala, V.S.; MacKinnon, R. The membrane electric field regulates the PIP(2)-binding site to gate the KCNQ1 channel. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2301985120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barro-Soria, R.; Perez, M.E.; Larsson, H.P. KCNE3 acts by promoting voltage sensor activation in KCNQ1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E7286–E7292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasuya, G.; Nakajo, K. Optimized tight binding between the S1 segment and KCNE3 is required for the constitutively open nature of the KCNQ1-KCNE3 channel complex. eLife 2022, 11, e81683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korkosh, V.S.; Zaytseva, A.K.; Kostareva, A.A.; Zhorov, B.S. Intersegment Contacts of Potentially Damaging Variants of Cardiac Sodium Channel. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 756415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; MacKinnon, R. Structural Basis of Human KCNQ1 Modulation and Gating. Cell 2020, 180, 340–347.E9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanoye, C.G.; Desai, R.R.; John, J.D.; Hoffman, S.C.; Fink, N.; Zhang, Y.; Venkatesh, O.G.; Roe, J.; Adusumilli, S.; Jairam, N.P.; et al. Functional profiling of KCNE1 variants informs population carrier frequency of Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome type 2. bioRxiv 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jumper, J.; Evans, R.; Pritzel, A.; Green, T.; Figurnov, M.; Ronneberger, O.; Tunyasuvunakool, K.; Bates, R.; Zidek, A.; Potapenko, A.; et al. Highly accurate protein structure prediction with AlphaFold. Nature 2021, 596, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, R.; O’Neill, M.; Pritzel, A.; Antropova, N.; Senior, A.; Green, T.; Green, T.; Bates, R.; Blackwell, S.; Yim, J.; et al. Protein complex prediction with AlphaFold-Multimer. bioRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, G.W. KCNE1 and KCNE3: The yin and yang of voltage-gated K(+) channel regulation. Gene 2016, 576, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundquist, A.L.; Manderfield, L.J.; Vanoye, C.G.; Rogers, C.S.; Donahue, B.S.; Chang, P.A.; Drinkwater, D.C.; Murray, K.T.; George, A.L., Jr. Expression of multiple KCNE genes in human heart may enable variable modulation of I(Ks). J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2005, 38, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- UniProt, C. UniProt: A hub for protein information. Nucleic Acids. Res. 2015, 43, D204–D212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyer, S.C.; Austine-Orimoloye, O.; Azov, A.G.; Barba, M.; Barnes, I.; Barrera-Enriquez, V.P.; Becker, A.; Bennett, R.; Beracochea, M.; Berry, A.; et al. Ensembl 2025. Nucleic Acids. Res. 2025, 53, D948–D957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutet, E.; Lieberherr, D.; Tognolli, M.; Schneider, M.; Bansal, P.; Bridge, A.J.; Poux, S.; Bougueleret, L.; Xenarios, I. UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot, the Manually Annotated Section of the UniProt KnowledgeBase: How to Use the Entry View. Methods Mol. Biol. 2016, 1374, 23–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landrum, M.J.; Lee, J.M.; Benson, M.; Brown, G.; Chao, C.; Chitipiralla, S.; Gu, B.; Hart, J.; Hoffman, D.; Hoover, J.; et al. ClinVar: Public archive of interpretations of clinically relevant variants. Nucleic Acids. Res. 2016, 44, D862–D868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karczewski, K.J.; Francioli, L.C.; Tiao, G.; Cummings, B.B.; Alföldi, J.; Wang, Q.; Collins, R.L.; Laricchia, K.M.; Ganna, A.; Birnbaum, D.P.; et al. The mutational constraint spectrum quantified from variation in 141,456 humans. Nature 2020, 581, 434–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaltman, J.R.; Evans, F.; Fu, Y.-P. Re-evaluating pathogenicity of variants associated with the long QT syndrome. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2018, 29, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, R.; Thomson, K.L.; Ware, J.S.; Funke, B.H.; Woodley, J.; McGuire, K.J.; Mazzarotto, F.; Blair, E.; Seller, A.; Taylor, J.C.; et al. Reassessment of Mendelian gene pathogenicity using 7,855 cardiomyopathy cases and 60,706 reference samples. Genet. Med. 2017, 19, 192–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haitin, Y.; Wiener, R.; Shaham, D.; Peretz, A.; Cohen, E.B.; Shamgar, L.; Pongs, O.; Hirsch, J.A.; Attali, B. Intracellular domains interactions and gated motions of I(KS) potassium channel subunits. EMBO J. 2009, 28, 1994–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sievers, F.; Wilm, A.; Dineen, D.; Gibson, T.J.; Karplus, K.; Li, W.; Lopez, R.; McWilliam, H.; Remmert, M.; Söding, J.; et al. Fast, scalable generation of high-quality protein multiple sequence alignments using Clustal Omega. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2011, 7, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livingstone, C.D.; Barton, G.J. Protein sequence alignments: A strategy for the hierarchical analysis of residue conservation. Comput. Appl. Biosci. CABIOS 1993, 9, 745–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zvelebil, M.J.; Barton, G.J.; Taylor, W.R.; Sternberg, M.J. Prediction of protein secondary structure and active sites using the alignment of homologous sequences. J. Mol. Biol. 1987, 195, 957–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golicz, A.; Troshin, P.V.; Madeira, F.; Martin, D.M.A.; Procter, J.B.; Barton, G.J. AACon: A Fast Amino Acid Conservation Calculation Service. 2018; submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Li, C.; Mou, C.; Dong, Y.; Tu, Y. dbNSFP v4: A comprehensive database of transcript-specific functional predictions and annotations for human nonsynonymous and splice-site SNVs. Genome Med. 2020, 12, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiner, S.J.; Kollman, P.A.; Nguyen, D.T.; Case, D.A. An all atom force field for simulations of proteins and nucleic acids. J. Comput. Chem. 1986, 7, 230–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garden, D.P.; Zhorov, B.S. Docking flexible ligands in proteins with a solvent exposure- and distance-dependent dielectric function. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 2010, 24, 91–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Scheraga, H.A. Monte Carlo-minimization approach to the multiple-minima problem in protein folding. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1987, 84, 6611–6615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhorov, B.S. Vector method for calculating derivatives of energy of atom-atom interactions of complex molecules according to generalized coordiantes. J. Struct. Chem. 1981, 22, 4–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, S.B.; Tao, X.; Campbell, E.B.; MacKinnon, R. Atomic structure of a voltage-dependent K+ channel in a lipid membrane-like environment. Nature 2007, 450, 376–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhorov, B.S. Possible Mechanism of Ion Selectivity in Eukaryotic Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels. J. Phys. Chem. B 2021, 125, 2074–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Gene a | UniProt ID b | P/LP c | VUS d | Common Neutral e |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KCNA1 | Q09470 | 38 | 245 | 14 |
| KCNA2 | P16389 | 44 | 207 | 10 |
| KCNA5 | P22460 | 4 | 276 | 56 |
| KCNB1 | Q14721 | 87 | 212 | 62 |
| KCNC1 | P48547 | 11 | 149 | 11 |
| KCNC2 | Q96PR1 | 12 | 44 | 37 |
| KCNC3 | Q14003 | 10 | 173 | 82 |
| KCND2 | Q9NZV8 | 7 | 176 | 22 |
| KCND3 | Q9UK17 | 21 | 207 | 17 |
| KCNQ1 | P51787 | 299 | 519 | 43 |
| KCNQ2 | O43526 | 394 | 474 | 57 |
| KCNQ3 | O43525 | 39 | 458 | 49 |
| KCNQ4 | P56696 | 28 | 153 | 63 |
| KCNQ5 | Q9NR82 | 20 | 228 | 65 |
| KCNV2 | Q8TDN2 | 45 | 361 | 103 |
| Tool | Deleterious Threshold a | Sensitivity b | Specificity c | MCC d | ACC e | AUC f |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AlphaMissense | >0.5 | 0.95 | 0.86 | 0.81 | 0.9 | 0.96 |
| ClinPred | >0.8 | 0.97 | 0.79 | 0.77 | 0.87 | 0.95 |
| DEOGEN2 | >0.5 | 0.96 | 0.67 | 0.65 | 0.81 | 0.95 |
| MetaRNN | >0.6 | 0.97 | 0.82 | 0.79 | 0.89 | 0.95 |
| VARITYR | >0.5 | 0.93 | 0.86 | 0.78 | 0.89 | 0.95 |
| REVEL | >0.45 | 0.99 | 0.56 | 0.59 | 0.76 | 0.94 |
| VARITYER | >0.5 | 0.9 | 0.85 | 0.75 | 0.87 | 0.93 |
| VEST4 | >0.5 | 0.97 | 0.73 | 0.72 | 0.85 | 0.93 |
| LISTS2 | >0.85 | 0.97 | 0.54 | 0.55 | 0.73 | 0.91 |
| PROVEAN | <−1.5 | 0.96 | 0.62 | 0.61 | 0.78 | 0.91 |
| SIFT4G | <0.05 | 0.9 | 0.75 | 0.65 | 0.82 | 0.9 |
| CADD | >3 | 0.93 | 0.68 | 0.63 | 0.8 | 0.89 |
| MetaLR | >0.4 | 0.99 | 0.15 | 0.25 | 0.54 | 0.88 |
| MPC | >2 | 0.57 | 0.92 | 0.51 | 0.74 | 0.88 |
| MutationAssessor | >1.7 | 0.89 | 0.68 | 0.58 | 0.78 | 0.88 |
| MVP | >0.75 | 0.99 | 0.43 | 0.49 | 0.68 | 0.88 |
| PPH_HVAR | >0.45 | 0.91 | 0.69 | 0.61 | 0.79 | 0.88 |
| SIFT | <0.0045 | 0.82 | 0.8 | 0.62 | 0.81 | 0.88 |
| MetaSVM | >0 | 0.99 | 0.28 | 0.37 | 0.61 | 0.86 |
| PPH_HDIV | >0.45 | 0.93 | 0.56 | 0.52 | 0.73 | 0.86 |
| MCap | >0.05 | 1 | 0.19 | 0.31 | 0.57 | 0.84 |
| PrimateAI | >0.6 | 0.98 | 0.46 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 0.84 |
| DANN | >0.5 | 1 | 0.04 | 0.14 | 0.52 | 0.76 |
| GenoCanyon | >0.7 | 0.89 | 0.35 | 0.29 | 0.62 | 0.68 |
| FATHMM | <−1 | 0.99 | 0.08 | 0.18 | 0.5 | 0.64 |
| ESM1b | <−3 | 0.69 | 0.35 | 0.05 | 0.51 | 0.52 |
| PLIC Label | hKv7.1 Variant | Paralogue | ClinPred | α Missense | Current Change b |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.532 | E115D | KCNQ2-E86K | 0.878 | 0.997 | |
| 1.545 | A128P | KCNQ2-Y98X | 0.185 | 0.861 | |
| 1.548 | L131P | KCNQ2-L101H | 0.995 | 0.958 | ↓↓ |
| 1.550 | V133A | KCNA1-I177N, KCNB1-I199F, KCNQ2-V103D | 0.984 | 0.964 | ↓ |
| 1.553 | C136F | KCNQ2-C106G | 1 | 0.954 | ↓↓ |
| 1.554 | L137P | KCNQ2-L107F | 0.986 | 0.999 | |
| 1.557 | S140R | KCNA1-F184C | 0.996 | 0.999 | ↓↓ |
| 1.560 | S143F | KCNB1-N209K | 0.997 | 0.953 | |
| 2.544 | V164A | KCNQ2-I134N | 0.998 | 0.797 | |
| 2.550 | E170G | KCNQ2-E140A | 1 | 0.987 | |
| 2.551 | Y171H | KCNV2-Y317X | 0.998 | 0.998 | |
| 2.556 | W176S | KCNQ2-W146X | 1 | 0.926 | |
| 2.609 | G189A | KCNQ2-G159E/R/V | 0.998 | 0.978 | ↓↓ |
| 3.549 | I201V | KCNA2-I258N | 0.944 | 0.507 | |
| 3.550 | D202V | KCNQ2-D172G | 1 | 0.998 | |
| 3.560 | V212A | KCNQ2-V182M | 0.994 | 0.958 | |
| 3.560 | V212F | KCNQ2-V182M | 0.997 | 0.917 | |
| 3.600 | G219E | KCNA1-E283K, KCNQ2-G189D | 0.989 | 0.817 | |
| 4.542 | A223T | KCNQ2-A193D/V | 0.994 | 0.772 | |
| 4.547 | R228W | KCNA2-R294H, KCNQ2-R198W | 1 | 0.966 | |
| 4.553 | Q234L | KCNA2-R300S, KCNB1-R303Q, KCNC3-R420H, KCNQ2-Q204H | 0.998 | 0.965 | |
| 4.553 | Q234R | KCNA2-R300S, KCNB1-R303Q, KCNC3-R420H, KCNQ2-Q204H | 0.97 | 0.992 | |
| 4.558 | L239V | KCNQ2-I209S/T | 0.829 | 0.86 | |
| 4.559 | H240R | KCNQ2-R210C/H/P | 0.331 | 0.949 | |
| 4.559 | H240Q | KCNQ2-R210C/H/P | 0.993 | 0.991 | |
| 5.518 | G245R | KCND3-S304F | 0.998 | 0.998 | ↓↓ |
| 5.523 | L250P | KCNA1-I314T, KCNB1-S319F/Y | 0.995 | 1 | |
| 5.525 | G252R | KCNB1-G321S | 1 | 0.996 | |
| 5.525 | G252S | KCNB1-G321S | 0.998 | 0.885 | |
| 5.526 | S253A | KCNQ2-S223F/P | 0.972 | 0.792 | |
| 5.530 | I257S | KCNQ2-A227V | 0.993 | 0.947 | |
| 5.533 | Q260H | KCNQ2-K230M | 0.991 | 0.99 | |
| 5.535 | L262V | KCNC3-F448L | 0.996 | 0.952 | |
| 5.536 | I263K | KCNB1-G332V | 0.997 | 0.997 | |
| 5.537 | T264S | KCNQ2-T234A/P | 0.992 | 0.895 | |
| 5.540 | Y267F | KCNQ2-Y237C | 0.996 | 0.644 | |
| 5.541 | I268V | KCNC2-F388S | 0.878 | 0.674 | |
| 5.548 | F275L | KCNQ2-L245P | 0.996 | 0.986 | |
| 5.552 | F279C | KCND3-V338E, KCNQ2-L249P | 0.999 | 0.788 | |
| 5.556 | A283T | KCNQ2-A253S/T | 0.996 | 0.504 | |
| 5.557 | E284G | KCNQ2-E254D | 1 | 0.972 | |
| 5.613 | S298R | KCNQ2-T263A/I | 0.997 | 0.977 | |
| 5.837 | A300G | KCNQ2-A265P/T/V | 0.986 | 0.747 | |
| 5.843 | G306E | KCNQ2-G271D/R/S/V, KCNQ3-G310D/V | 0.999 | 0.999 | |
| 5.844 | V307M | KCNB1-T372N/I | 0.991 | 0.79 | |
| 5.844 | V307L | KCNB1-T372N/I | 0.99 | 0.895 | |
| 5.844 | V307E | KCNB1-T372M/I | 0.993 | 0.989 | |
| 5.849 | T312S | KCNA2-T374A, KCNC2-T437A, KCNQ2-T277N/P/S | 0.995 | 0.966 | |
| 5.850 | I313F | KCNQ2-I278F/M/T, KCNQ3-I317M/T | 0.993 | 0.991 | |
| 5.855 | K318N | KCNQ2-K283E | 0.958 | 0.93 | |
| 5.856 | V319M | KCNQ2-Y284C/D | 0.995 | 0.616 | |
| 6.543 | A329V | KCND3-G384S, KCNQ2-A294G/S | 0.999 | 0.979 | |
| 6.543 | A329T | KCND3-G384S, KCNQ2-A294G/S | 0.987 | 0.935 | |
| 6.544 | S330Y | KCND3-S385P | 0.998 | 0.993 | |
| 6.545 | C331Y | KCNQ2-T296P | 0.998 | 0.976 | |
| 6.549 | F335C | KCNA1-A395S | 0.997 | 0.856 | |
| 6.551 | I337M | KCNA2-V399M | 0.962 | 0.775 | |
| 6.553 | F339V | KCNQ2-F304C, KCNQ2-F304S | 0.999 | 0.972 | |
| 6.555 | A341T | KCNA1-A401V, KCNB1-A406V, KCNQ2-A306P/T/V/E | 0.996 | 0.976 | |
| 6.563 | S349A | KCNB1-N414D | 0.995 | 0.92 | |
| 6.563 | S349L | KCNB1-N414D | 0.999 | 0.995 | |
| 6.566 | A352P | KCNB1-S417P, KCNQ2-A317T, KCNQ3-A356T | 0.999 | 0.997 | |
| 6.566 | A352D | KCNB1-S417P, KCNQ2-A317T, KCNQ3-A356T | 0.998 | 1 | |
| 6.569 | K354R | KCNQ2-K319E | 0.992 | 0.768 | |
| 6.571 | Q357R | KCNA1-R417X, KCNB1-E422A | 0.996 | 0.984 | |
| 6.571 | Q357E | KCNA1-R417X, KCNB1-E422A | 0.939 | 0.566 | |
| 6.574 | R360T | KCNQ2-R325G, KCNQ3-R364C/H | 0.999 | 0.999 | |
| 6.574 | R360K | KCNQ2-R325G, KCNQ3-R364C/H | 0.992 | 0.976 | |
| 7.013 | L374V | KCNQ2-L339Q, KCNQ2-L339R | 0.995 | 0.85 | |
| 7.030 | T391P | KCNQ2-T359K | 0.998 | 0.898 | |
| 7.165 | K526E | KCNQ2-K552N | 0.932 | 0.967 | |
| 7.165 | K526Q | KCNQ2-K552N | 0.838 | 0.717 | |
| 7.165 | K526N | KCNQ2-K552N | 0.984 | 0.995 | |
| 7.180 | V541I | KCNQ2-V567D | 0.903 | 0.814 | |
| 7.187 | G548D | KCNQ2-G574D/S | 0.999 | 0.999 | |
| 7.194 | R555L | KCNQ2-R581G | 0.998 | 0.994 | |
| 7.196 | K557R | KCNQ2-K583N | 0.982 | 0.63 | |
| 7.222 | R583S | KCNQ2-K606X | 0.885 | 0.902 | |
| 7.222 | R583G | KCNQ2-K606X | 0.79 | 0.606 | |
| 7.230 | R591P | KCNQ2-R622P | 0.997 | 0.997 |
| VUS | Cs | Functional Study a | ClinPred | Paralogue |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S28L | 0.6 | Smaller current | 0.818 | KCNE5-VUS:D44H |
| R32C | 0.8 | faster activation | 0.622 | KCNE3-VUS:R47G,KCNE3-VUS:R47Q, KCNE3-VUS:R47W |
| P35S | 0.4 | faster activation | 0.957 | KCNE2-VUS:V41A |
| L48I | 0.9 | ~ current | 0.963 | KCNE2-Disease:M54T, KCNE2-VUS:M54V |
| L48F | 0.9 | faster activation | 0.808 | KCNE2-Disease:M54T, KCNE2-VUS:M54V |
| L48P | 0.9 | 0.999 | KCNE2-Disease:M54T, KCNE2-VUS:M54V | |
| M49T | 0.7 | 0.958 | KCNE5-VUS:L65F | |
| F53L | 0.8 | ~ current | 0.756 | KCNE2-VUS:M59I, KCNE5-VUS:F69V |
| F53C | 0.8 | Small current | 0.996 | KCNE2-VUS:M59I,KCNE5-VUS:F69V |
| G55R | 0.8 | 0.994 | KCNE2-VUS:S61P | |
| T58P | 0.6 | Slower activation | 0.982 | NA-Disease:T58P,KCNE3-VUS:V72G |
| T58A | 0.6 | 0.987 | NA-Disease:T58P,KCNE3-VUS:V72G | |
| L59P | 0.7 | LoF | 0.978 | KCNE2-VUS:V65L,KCNE2-VUS:V65M, KCNE5-VUS:G75R |
| G60D | 0.8 | Small current | 0.994 | KCNE2-VUS:A66V,KCNE3-VUS:S74R, KCNE5-VUS:G76D |
| G60V | 0.8 | 0.995 | KCNE2-VUS:A66V,KCNE3-VUS:S74R, KCNE5-VUS:G76D | |
| I61F | 1 | 0.983 | KCNE2-VUS:I67M | |
| I66L | 0.7 | 0.905 | KCNE3-VUS:T80I | |
| R67G | 0.9 | Small current | 0.996 | KCNE3-VUS:R81C |
| R67S | 0.9 | Small current | 0.987 | KCNE3-VUS:R81C |
| R67L | 0.9 | Small current | 0.99 | KCNE3-VUS:R81C |
| R67H | 0.9 | Small current | 0.873 | KCNE3-VUS:R81C |
| K69E | 0.9 | 0.953 | KCNE3-VUS:R83C,KCNE3-VUS:R83P, KCNE5-VUS:R85H | |
| K70Q | 0.9 | 0.977 | KCNE3-VUS:K84E,KCNE5-VUS:K86E | |
| K70M | 0.9 | Small current | 0.994 | KCNE3-VUS:K84E,KCNE5-VUS:K86E |
| K70E | 0.9 | 0.983 | KCNE3-VUS:K84E,KCNE5-VUS:K86E | |
| L71V | 0.4 | 0.956 | KCNE2-Disease:R77W, KCNE3-VUS:V85A | |
| E72K | 0.4 | 0.984 | KCNE5-VUS:V88D,KCNE5-VUS:V88I | |
| H73R | 0.6 | 0.931 | KCNE2-VUS:H79R,KCNE5-VUS:E89K | |
| S74W | 0.4 | Small current | 0.998 | KCNE2-VUS:S80P,KCNE3-VUS:R88C, KCNE3-VUS:R88H |
| S74P | 0.4 | Smaller current | 0.629 | KCNE2-VUS:S80P,KCNE3-VUS:R88C, KCNE3-VUS:R88H |
| Y81C | 0.7 | Smaller current | 0.998 | KCNE2-VUS:Y87C |
| I82M | 0.4 | Smaller current | 0.885 | KCNE3-VUS:I96S |
| I82V | 0.4 | Smaller current | 0.978 | KCNE3-VUS:I96S |
| I82F | 0.4 | 0.993 | KCNE3-VUS:I96S |
| KCNE1 Variant | Classifi-cation | Current | Contact with | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Change a | KCNE1 | Kv7.1 | ||||
| M1L/I/R/T/K/V | P/VUS | R67G/S/L/H | VUS | F256/5.529 | ||
| L48I/F/P | LD VUS | ~ | I138/1.555 L142/1.559 | |||
| M49T/I | LD VUS | L13R/P/V/M | NP | C331/6.545Y T327/6.541D | LD VUS VUS | |
| G52R/V/E/A | P/NP | R ↓ | L134/1.551P | CIP | ||
| F53L/C | LD VUS | C ↓ L ~ | L13R/P/V/M V95I | NP VUS | F335/6.549C F270/5.543 | LD VUS |
| G55R | LD VUS | L134/1.551P F130/1.547 | CIP | |||
| T58P/A | LD VUS | P ↓ | F130/1.547 Y267/5.540F V241/4.560I | LD VUS LD VUS | ||
| L59P | LD VUS | F127/1.544L F123/1.540 | NP | |||
| G60D/V | LD VUS | D ↓ | I263/5.536V | VUS | ||
| I61F | LD VUS | Y267/5.540F D242/4.561Y/N/E Q260/5.533H I263/5.536V T247/5.520 | LD VUS P/LP LD VUS VUS | |||
| I66L | LD VUS | F123/1.540 P117/1.534T/S/L | LP | |||
| R67G/S/L/H | LD VUS | All ↓ | M1L/I/R/T/K/V | P/NP | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tarnovskaya, S.I.; Zhorov, B.S. Predicting the Damaging Potential of Uncharacterized KCNQ1 and KCNE1 Variants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6561. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146561
Tarnovskaya SI, Zhorov BS. Predicting the Damaging Potential of Uncharacterized KCNQ1 and KCNE1 Variants. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(14):6561. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146561
Chicago/Turabian StyleTarnovskaya, Svetlana I., and Boris S. Zhorov. 2025. "Predicting the Damaging Potential of Uncharacterized KCNQ1 and KCNE1 Variants" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 14: 6561. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146561
APA StyleTarnovskaya, S. I., & Zhorov, B. S. (2025). Predicting the Damaging Potential of Uncharacterized KCNQ1 and KCNE1 Variants. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(14), 6561. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146561





