Molecular Characterization of a Restriction Endonuclease PsaI from Pseudomonas anguilliseptica KM9 and Sequence Analysis of the PsaI R-M System
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Detection of Restriction Endonucleases Activity in Bacterial Isolates
2.2. Enzyme Purification
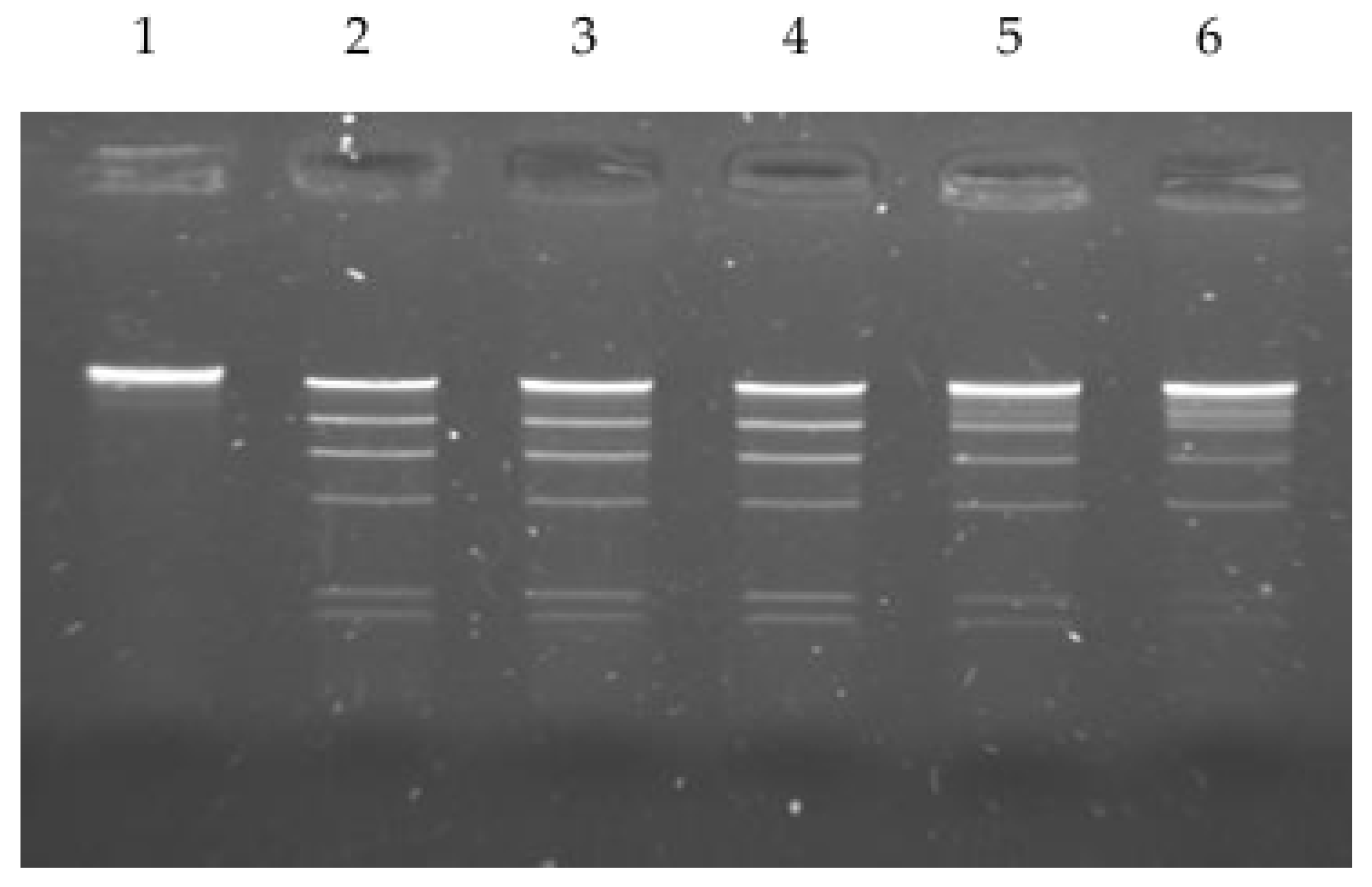
2.3. Optimal Conditions for Restriction Activity
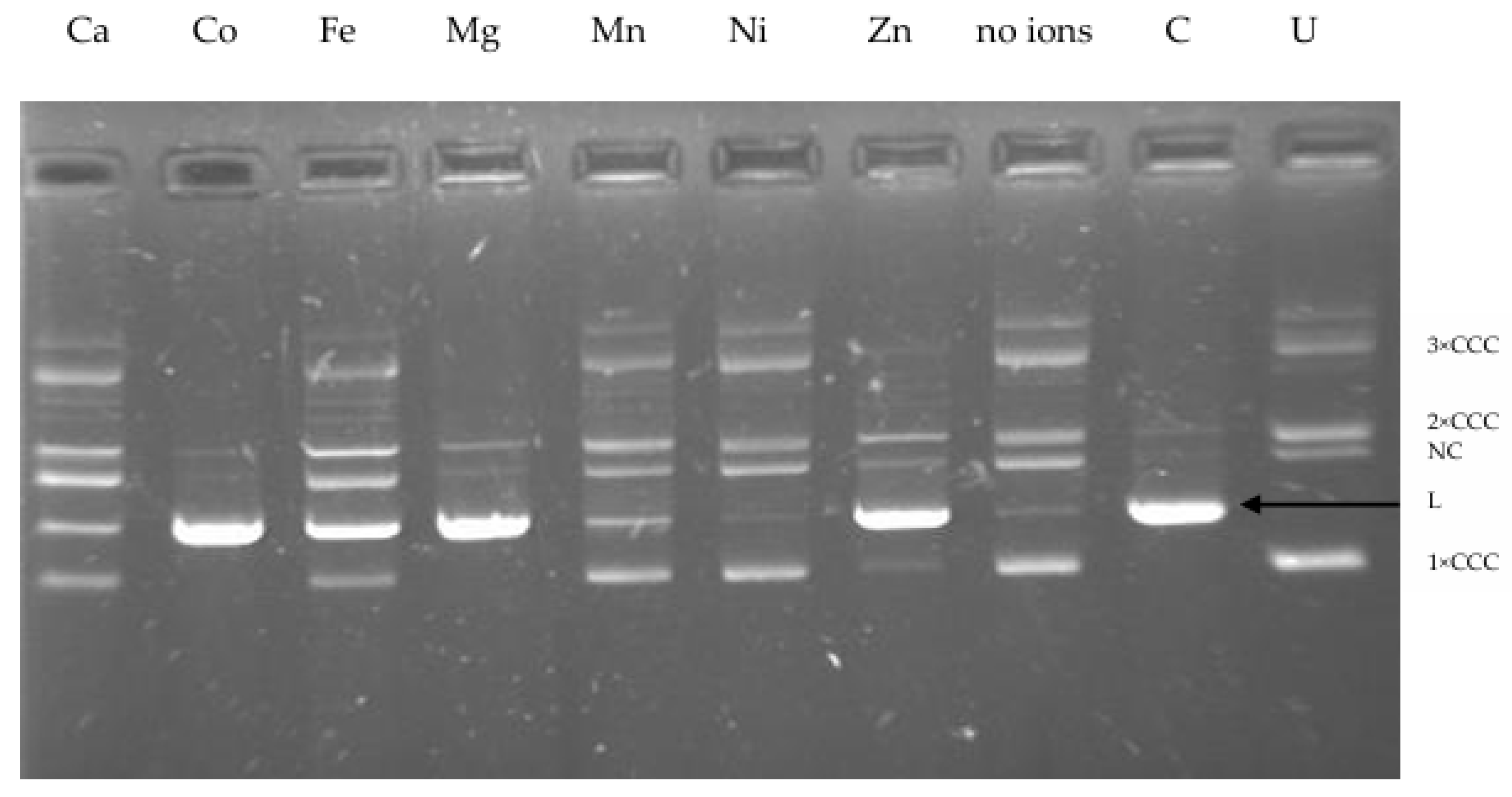
2.4. Effect of Divalent Metal Ions and Ionic Strength on R.PsaI Activity
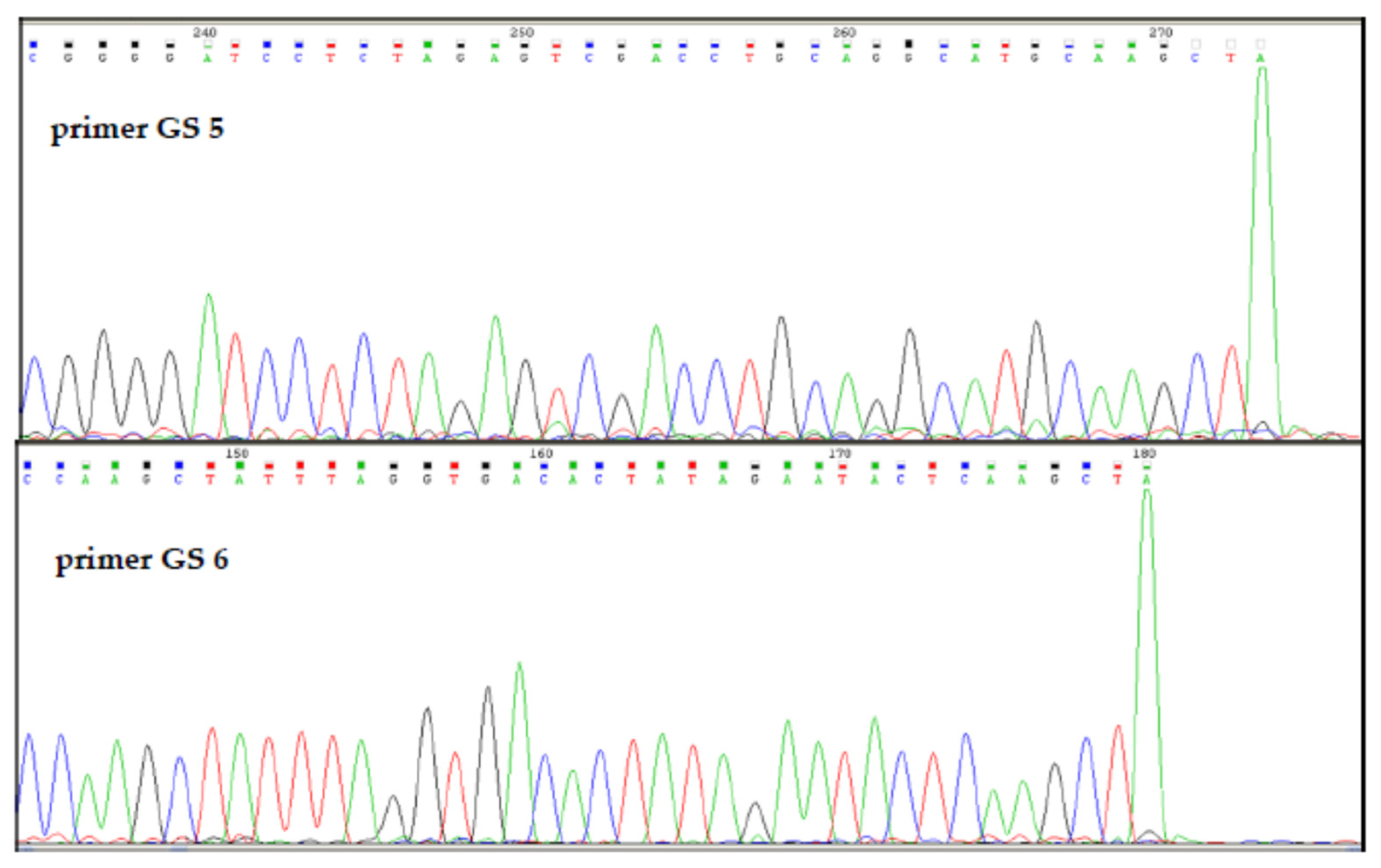
2.5. Determination of the R.PsaI Cleavage Site
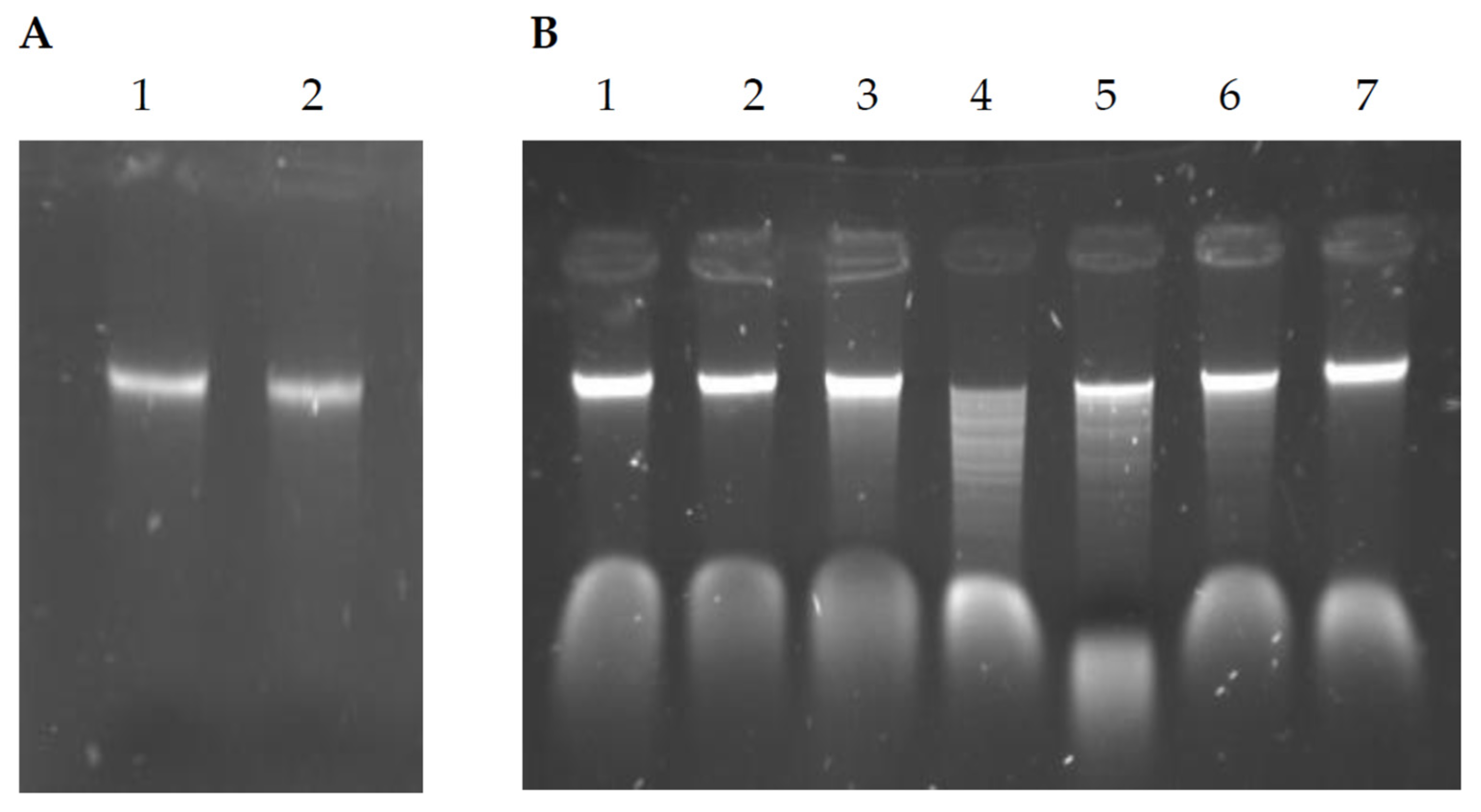
2.6. Genomic DNA Modification Status
2.7. PsaI R-M System Analysis
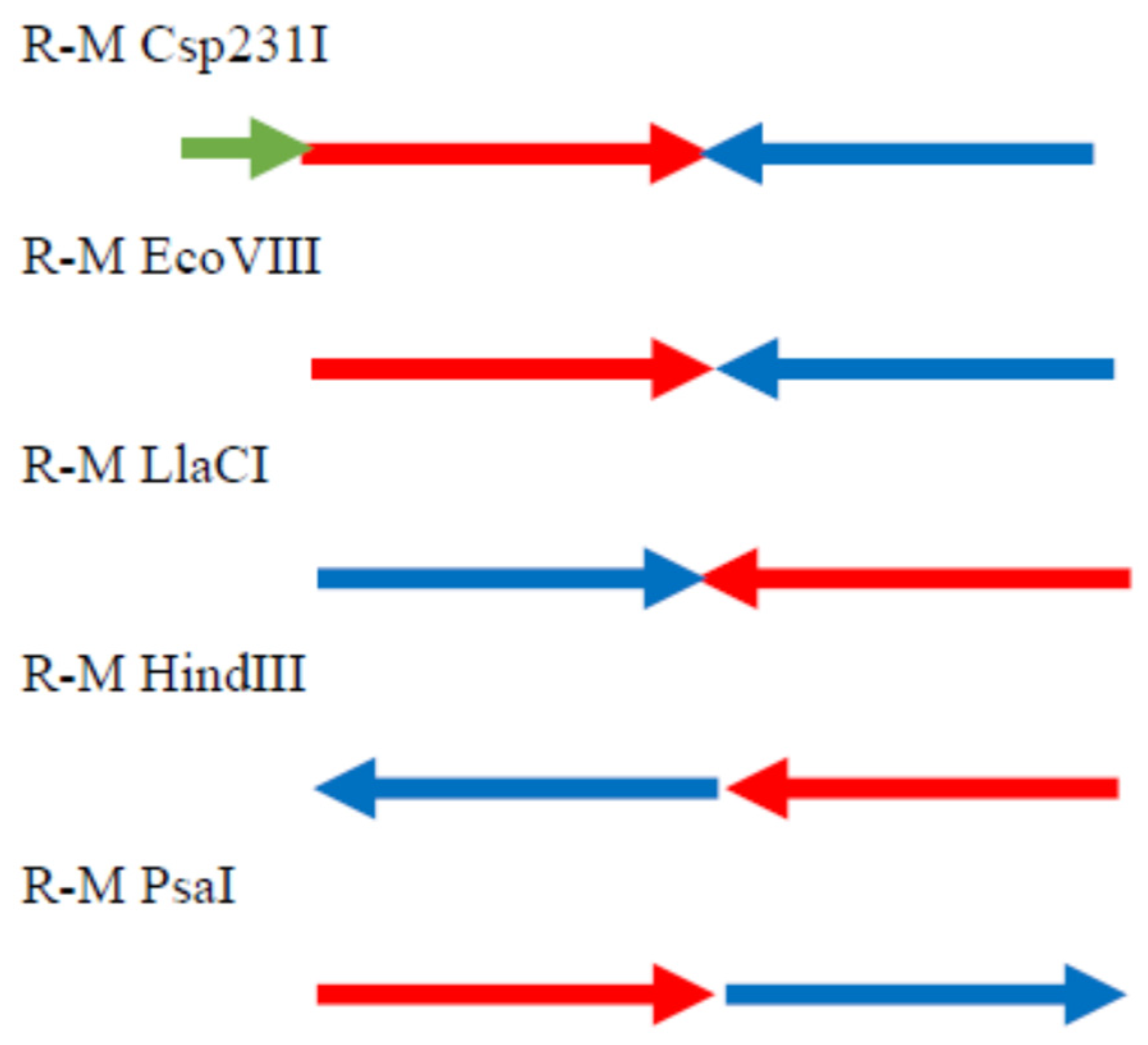
2.8. Analysis of the Regions Flanking the R-M System PsaI
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Site Description and Sampling Protocol
3.2. Growth Conditions
3.3. Restriction Endonuclease Activity Assay in Cell Lysate
3.4. Purification of the Native Restriction Endonuclease PsaI
3.5. Molecular Mass Determination
3.6. DNA Cleavage Activity Assays
3.7. Determination of the R.PsaI Recognition Sequence
3.8. Characterization of the R.PsaI Activity Optima
3.9. Determination of the DNA Modification Status of the P. anguilliseptica KM9 Strain
3.10. Determination of the Complete Nucleotide Sequence of the PsaI R-M System
3.11. Bioinformatic Tools
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Loenen, W.A.; Dryden, D.T.; Raleigh, E.A.; Wilson, G.G.; Murray, N.E. Highlights of the DNA cutters: A short history of the restriction enzymes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 3–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pingoud, V.; Wende, W.; Friedhoff, P.; Reuter, M.; Alves, J.; Jeltsch, A.; Mones, L.; Fuxreiter, M.; Pingoud, A. On the divalent metal ion dependence of DNA cleavage by restriction endonucleases of the EcoRI family. J. Mol. Biol. 2009, 393, 140–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pingoud, A.; Wilson, G.G.; Wende, W. Type II restriction endonucleases—A historical perspective and more. Nucleic Acid Res. 2014, 42, 7489–7527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, R.J.; Vincze, T.; Posfai, J.; Macelis, D. REBASE—A database for DNA restriction and modification: Enzymes, genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, D298–D299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Withey, S.; Cartmell, E.; Avery, L.M.; Stephenson, T. Bacteriophages-potential for application in wastewater treatment processes. Sci. Total Environ. 2005, 339, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Shen, Z.; Fang, W.; Gao, G. Composition of bacterial communities in municipal wastewater treatment plant. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 689, 1181–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silby, M.W.; Winstanley, C.; Godfrey, S.A.; Levy, S.B.; Jackson, R.W. Pseudomonas genomes: Diverse and adaptable. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2011, 35, 652–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belavin, P.A.; Dedkov, V.S.; Degtyarev, S.K.H. A method for detecting restriction endonucleases in bacterial colonies. Appl. Biochem. Microbiol. 1988, 24, 121–124. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, R.J.; Belfort, M.; Bestor, T.; Bhagwat, A.S.; Bickle, T.A.; Bitinaite, J.; Blumenthal, R.M.; Degtyarev, S.K.H.; Dryden, D.T.; Dybvig, K.; et al. A nomenclature for restriction enzymes, DNA methyltransferases, homing endonucleases and their genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 1805–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlowski, J.; Bujnicki, J.M. Structural and evolutionary classification of Type II restriction enzymes based on theoretical and experimental analyses. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, 3552–3569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowan, J.A. Role of metal ions in promoting DNA binding and cleavage by restriction endonucleases. In Restriction Endonucleases; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004; Volume 14, pp. 339–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasu, K.; Nagaraja, V. Diverse functions of restriction-modification systems in addition to cellular defense. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2013, 77, 53–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malone, T.; Blumenthal, R.M.; Cheng, X. Structure-guided analysis reveals nine sequence motifs conserved among DNA amino-methyltransferases, and suggests a catalytic mechanism for these enzymes. J. Mol. Biol. 1995, 253, 618–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bujnicki, J.M. Sequence permutations in the molecular evolution of DNA methyltransferases. BMC Evol. Biol. 2002, 2, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Pathirana, S.N.J.; Elvitigala, D.A.S.; Nanayakkara, C.M.; Suravajhala, P.; Rajapakse, S.; Hettiarachchi, G.H.C.M.; Chandrasekharan, N.V. Identification and in-silico analysis of a novel restriction enzyme coding gene from Pseudomonas anguilliseptica. Gene Rep. 2022, 26, 101487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nwankwo, D.O.; Moran, L.S.; Slatko, B.E.; Waite-Rees, B.P.A.; Dorner, L.F.; Benner, J.S.; Wilson, G.G. Cloning, analysis and expression of the HindIII R-M-encoding genes. Gene 1994, 150, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franck, C.J.; Berthe, C.M.; Bernadet, J.-F. Identification of Pseudomonas anguilliseptica isolated from several fish species in France. Dis. Aquat. Org. 1995, 121, 51–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen, A.; Josephsen, J. Characterization of LlaCI, a new restriction-modification system from Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris W15. Biol. Chem. 1998, 379, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mruk, I.; Kaczorowski, T. Genetic organization and molecular analysis of the EcoVIII restriction-modification system of Escherichia coli E1585-68 and its comparison with isospecific homolog. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 2638–2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mruk, I.; Kaczorowski, T. A rapid and efficient method for cloning genes of type II restriction-modification systems by use of a killer plasmid. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 4286–4293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, P.H.; Touchon, M.; Rocha, E.P. The interplay of restriction-modification systems with mobile genetic elements and their prokaryotic hosts. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 10618–10631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuta, Y.; Abe, K.; Kobayashi, I. Genome comparison and context analysis reveals putative mobile forms of restriction-modification systems and related rearrangements. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, 2428–2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincze, T.; Posfai, J.; Roberts, R.J. NEBcutter: A program to cleave DNA with restriction enzymes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 3688–3691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gingeras, T.R.; Milazzo, J.P.; Roberts, R.J. A computer assisted method for the determination of restriction enzyme recognition sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978, 5, 4105–4127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochman, H.; Gerber, A.S.; Hartl, D.L. Genetic applications of an inverse polymerase chain reaction. Genetics 1988, 120, 621–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larkin, M.A.; Blackshields, G.; Brown, N.; Chenna, R.; McGettigan, P.A.; McWilliam, H.; Valentin, F.; Wallace, I.M.; Wilm, A.; Lopez, R.J.; et al. Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 2947–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| R.PsaI Purification Step | Total Protein (mg) | Total Activity (U × 103) | Specific Activity (U mg−1) | Yield (%) | Purification (Fold) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell free extract | 652 | 10,000 | 15.54 × 103 | 1 | 100 |
| Phosphocellulose | 48 | 2920 | 60.83 × 103 | 4 | 29 |
| Hydroxylapatite | 13.5 | 1280 | 94.81 × 103 | 6 | 12.8 |
| CM Sephadex | 1.35 | 450 | 333.3 × 103 | 22 | 4.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Furmanek-Blaszk, B.; Mruk, I.; Sektas, M. Molecular Characterization of a Restriction Endonuclease PsaI from Pseudomonas anguilliseptica KM9 and Sequence Analysis of the PsaI R-M System. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6548. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146548
Furmanek-Blaszk B, Mruk I, Sektas M. Molecular Characterization of a Restriction Endonuclease PsaI from Pseudomonas anguilliseptica KM9 and Sequence Analysis of the PsaI R-M System. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(14):6548. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146548
Chicago/Turabian StyleFurmanek-Blaszk, Beata, Iwona Mruk, and Marian Sektas. 2025. "Molecular Characterization of a Restriction Endonuclease PsaI from Pseudomonas anguilliseptica KM9 and Sequence Analysis of the PsaI R-M System" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 14: 6548. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146548
APA StyleFurmanek-Blaszk, B., Mruk, I., & Sektas, M. (2025). Molecular Characterization of a Restriction Endonuclease PsaI from Pseudomonas anguilliseptica KM9 and Sequence Analysis of the PsaI R-M System. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(14), 6548. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146548




