Lower Initial Insulin-like Growth Factor-Binding Protein-3 Concentrations May Reflect Immune Suppression and Predict Increased Risk of Sepsis-Related Mortality
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Assess the prognostic performance of CRP, lactate, PCT, IL-6, MR-proADM, and IGFBP-3 levels in predicting 1-year mortality.
- Identify the independent predictors of 1-year mortality.
- Describe the characteristics of septic patient phenotypes, classified based on the levels of biomarkers shown to be independent predictors of 1-year mortality.
- Derive two multivariable models based on the independent predictors of 1-year mortality: one without biomarkers (Model 1) and one with biomarkers (Model 2).
- Compare the prognostic performance of Model 1 and Model 2 over time.
2. Results
2.1. Prognostic Performance of the SOFA Score and Serum Biomarkers in Predicting 1-Year Mortality
2.2. Independent Predictors of 1-Year Mortality
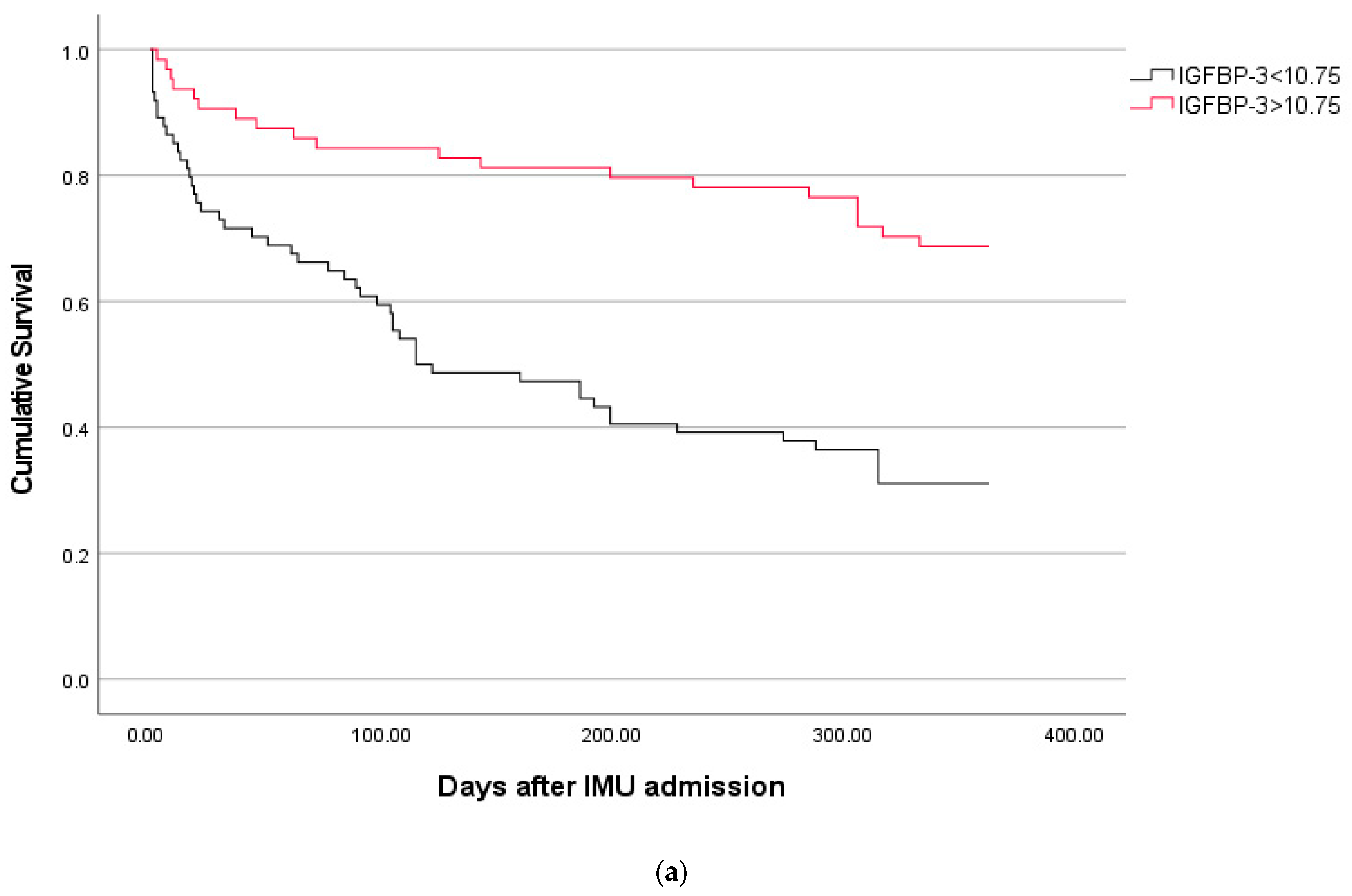
2.3. Phenotypes of Septic Patients According to the Best Prognostic Cut-Off of IGFBP-3 for Predicting 30-Day Mortality
2.4. Comparison of Prognostic Performance Between Model 1 and Model 2
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Serum Biomarkers
4.2. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Rudd, K.E.; Johnson, S.C.; Agesa, K.M.; Shackelford, K.A.; Tsoi, D.; Kievlan, D.R.; Colombara, D.V.; Ikuta, K.S.; Kissoon, N.; Reinhart, K.K.; et al. Global, regional, and national sepsis incidence and mortality, 1990–2017: Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study. Lancet 2020, 395, 200–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, L.; Rhodes, A.; Alhazzani, W.; Antonelli, M.; Coopersmith, C.M.; French, C.; Machado, F.R.; Mcintyre, L.; Ostermann, M.; Prescott, H.C.; et al. Surviving Sepsis Campaign: International Guidelines for Management of Sepsis and Septic Shock 2021. Crit. Care Med. 2021, 49, e1063–e1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierrakos, C.; Velissaris, D.; Bisdorff, M.; Marshall, J.C.; Vincent, J.-L. Biomarkers of sepsis: Time for a reappraisal. Crit. Care 2020, 24, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierrakos, C.; Vincent, J.-L. Sepsis biomarkers: A review. Crit. Care 2010, 14, R15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barichello, T.; Generoso, J.S.; Singer, M.; Dal-Pizzol, F. Biomarkers for sepsis: More than just fever and leukocytosis-a narrative review. Crit. Care 2022, 26, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Póvoa, P.; Coelho, L.; Dal-Pizzol, F.; Ferrer, R.; Huttner, A.; Morris, A.C.; Nobre, V.; Ramirez, P.; Rouze, A.; Salluh, J.; et al. How to use biomarkers of infection or sepsis at the bedside: Guide to clinicians. Intensive Care Med. 2023, 49, 142–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gritte, R.B.; Souza-Siqueira, T.; Curi, R.; Machado, M.C.C.; Soriano, F.G. Why Septic Patients Remain Sick After Hospital Discharge? Front. Immunol. 2021, 11, 605666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Slikke, E.C.; Beumeler, L.F.E.; Holmqvist, M.; Linder, A.; Mankowski, R.T.; Bouma, H.R. Understanding Post-Sepsis Syndrome: How Can Clinicians Help? Infect. Drug Resist. 2023, 16, 6493–6511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giamarellos-Bourboulis, E.J.; Aschenbrenner, A.C.; Bauer, M.; Bock, C.; Calandra, T.; Gat-Viks, I.; Kyriazopoulou, E.; Lupse, M.; Monneret, G.; Pickkers, P.; et al. The pathophysiology of sepsis and precision-medicine-based immunotherapy. Nat. Immunol. 2024, 25, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papastathi, C.; Mavrommatis, A.; Mentzelopoulos, S.; Konstandelou, E.; Alevizaki, M.; Zakynthinos, S. Insulin-like Growth Factor I and its binding protein 3 in sepsis. Growth Horm. IGF Res. 2013, 23, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuetz, P.; Müller, B.; Nusbaumer, C.; Wieland, M.; Christ-Crain, M. Circulating levels of GH predict mortality and complement prognostic scores in critically ill medical patients. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2009, 160, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jogie-Brahim, S.; Feldman, D.; Oh, Y. Unraveling insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 actions in human disease. Endocr. Rev. 2009, 30, 417–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrivastav, S.V.; Bhardwaj, A.; Pathak, K.A.; Shrivastav, A. Insulin-like Growth Factor Binding Protein-3 (IGFBP-3): Unraveling the Role in Mediating IGF-Independent Effects Within the Cell. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baxter, R.C. Signaling Pathways of the Insulin-like Growth Factor Binding Proteins. Endocr. Rev. 2023, 44, 753–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahn, M.S.; Lange, M.P.; Jacobs, L.A. Insulinlike growth factor 1 production is inhibited in human sepsis. Arch. Surg. 1988, 123, 1409–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priego, T.; de Cáceres, I.I.; Martín, A.; Villanúa, M.; López-Calderón, A. Endotoxin decreases serum IGFBP-3 and liver IGFBP-3 mRNA: Comparison between Lewis and Wistar rats. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2003, 199, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priego, T.; de Cáceres, I.I.; Martín, A.I.; Villanúa, M.Á.; López-Calderón, A. NO plays a role in LPS-induced decreases in circulating IGF-I and IGFBP-3 and their gene expression in the liver. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2004, 286, E50–E56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Zhang, W.; Sun, R.; Liu, J.; Hong, J.; Li, Q.; Hu, B.; Gong, F. IGF-1 may predict the severity and outcome of patients with sepsis and be associated with microRNA-1 level changes. Exp. Ther. Med. 2017, 14, 797–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmins, A.C.; Cotterill, A.M.; Hughes, S.C.; Holly, J.M.; Ross, R.J.; Blum, W.; Hinds, C.J. Critical illness is associated with low circulating concentrations of insulin-like growth factors-I and -II, alterations in insulin-like growth factor binding proteins, and induction of an insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3 protease. Crit. Care Med. 1996, 24, 1460–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Park, B.H.; Song, J.H.; Kim, S.Y.; Chung, K.S.; Kim, E.Y.; Jung, J.Y.; Kim, Y.S.; Kim, S.K.; Chang, J.; et al. Changes in Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 Level in Patients with Sepsis and Septic Shock. Korean J. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 31, 324–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, M.S.; Kluge, S.; Holzmann, M.; Moritz, E.; Robbe, L.; Bauer, A.; Zahrte, C.; Priefler, M.; Schwedhelm, E.; Böger, R.H.; et al. Markers of nitric oxide are associated with sepsis severity: An observational study. Crit. Care 2017, 21, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín, S.; Pérez, A.; Aldecoa, C. Sepsis and Immunosenescence in the Elderly Patient: A Review. Front. Med. 2017, 4, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auernhammer, C.; Fottner, C.; Engelhardt, D.; Bidlingmaier, M.; Strasburger, C.; Weber, M. Differential regulation of insulin-like growth factor-(IGF) I and IGF-binding protein (IGFBP) secretion by human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Horm. Res. 2002, 57, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weischendorff, S.; Sengeløv, H.; Juul, A.; Nielsen, C.H.; Ryder, L.P.; Kielsen, K.; Müller, K. Insulin-like growth factor-1 and insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3: Impact on early haematopoietic reconstitution following allogeneic haematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Eur. J. Haematol. 2022, 108, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, S.E.; Woodside, K.J.; Ramirez, R.J.; Kobayashi, M.; Suzuki, F.; Herndon, D.N. Insulin-like growth factor-I/insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 alters lymphocyte responsiveness following severe burn. J. Surg. Res. 2004, 117, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kooijman, R.; Coppens, A.; Hooghe-Peters, E. Igf-I inhibits spontaneous apoptosis in human granulocytes. Endocrinology 2002, 143, 1206–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kushimoto, S.; Gando, S.; Saitoh, D.; Mayumi, T.; Ogura, H.; Fujishima, S.; Araki, T.; Ikeda, H.; Kotani, J.; Miki, Y.; et al. JAAM Sepsis Registry Study Group. The impact of body temperature abnormalities on the disease severity and outcome in patients with severe sepsis: An analysis from a multicenter, prospective survey of severe sepsis. Crit. Care 2013, 17, R271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piton, G.; Capellier, G. Biomarkers of gut barrier failure in the ICU. Curr. Opin. Crit. Care 2016, 22, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirman, I.; Whelan, R.L.; Jain, S.; Seidelin, J.B.; Nielsen, O.H.; Nielsen, S.E. Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3 in inflammatory bowel disease. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2005, 50, 780–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eivindson, M.; Grønbæk, H.; Flyvbjerg, A.; Frystyk, J.; Zimmermann-Nielsen, E.; Dahlerup, J.F. The insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-system in active ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease: Relations to disease activity and corticosteroid treatment. Growth Horm. IGF Res. 2007, 17, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunninghake, G.W.; Doerschug, K.C.; Nymon, A.B.; Schmidt, G.A.; Meyerholz, D.K.; Ashare, A. Insulin-like growth factor-1 levels contribute to the development of bacterial translocation in sepsis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2010, 182, 517–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Yuan, X.; Zhou, G.; Feng, A. Activation of IGF-1/IGFBP-3 signaling by berberine improves intestinal mucosal barrier of rats with acute endotoxemia. Fitoterapia 2018, 124, 200–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeschke, M.G.; Bolder, U.; Chung, D.H.; Przkora, R.; Mueller, U.; Thompson, J.C.; Wolf, S.E.; Herndon, D.N. Gut mucosal homeostasis and cellular mediators after severe thermal trauma and the effect of insulin-like growth factor-I in combination with insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3. Endocrinology 2007, 148, 354–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varkila, M.R.J.; Verboom, D.M.; Derde, L.P.G.; van der Poll, T.; Bonten, M.J.M.; Cremer, O.L.; MARS Consortium. Gut barrier dysfunction and the risk of ICU-acquired bacteremia- a case-control study. Ann. Intensive Care 2024, 14, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Priego, T.; Granado, M.; Martín, A.I.; López-Calderón, A.; Villanúa, M.A. Dexamethasone administration attenuates the inhibitory effect of lipopolysaccharide on IGF-I and IGF-binding protein-3 in adult rats. J. Endocrinol. 2005, 185, 467–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashare, A.; Nymon, A.B.; Doerschug, K.C.; Morrison, J.M.; Monick, M.M.; Hunninghake, G.W. Insulin-like growth factor-1 improves survival in sepsis via enhanced hepatic bacterial clearance. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2008, 178, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, L.; Li, X.; Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Li, S.; Zhao, C. Recombinant human insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3 attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in mice. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2020, 13, 1924–1931. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Ye, G.; Lv, Y.; Guo, Y.; Pan, X.; Li, Y.; Shen, G.; He, Y.; Lei, P. IL-6 drives T cell death to participate in lymphopenia in COVID-19. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2022, 111, 109132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaarawy, M.; Fikry, M.A.; Massoud, B.A.; Lotfy, S. Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3: A novel biomarker for the assessment of the synthetic capacity of hepatocytes in liver cirrhosis. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1998, 83, 3316–3319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, C.H.; Frost, R.A. Role of growth hormone, insulin-like growth factor-I, and insulin-like growth factor binding proteins in the catabolic response to injury and infection. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2002, 5, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mearelli, F.; Fiotti, N.; Giansante, C.; Casarsa, C.; Orso, D.; De Helmersen, M.; Altamura, N.; Ruscio, M.; Castello, L.M.; Colonetti, E.; et al. Derivation and Validation of a Biomarker-Based Clinical Algorithm to Rule Out Sepsis from Noninfectious Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome at Emergency Department Admission: A Multicenter Prospective Study. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 46, 1421–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mearelli, F.; Nunnari, A.; Rombini, A.; Chitti, F.; Spagnol, F.; Casarsa, C.; Bolzan, G.; Martini, I.; Marinelli, A.; Rizzo, S.; et al. Inhibitory Immune Checkpoints Predict 7-Day, In-Hospital, and 1-Year Mortality of Internal Medicine Patients Admitted With Bacterial Sepsis. J. Infect. Dis. 2025, 231, 706–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mearelli, F.; Nunnari, A.; Chitti, F.; Rombini, A.; Macor, A.; Denora, D.; Messana, L.; Scardino, M.; Martini, I.; Bolzan, G.; et al. Low, Intermediate, and High Glutamine Levels Are Progressively Associated with Increased Lymphopenia, a Diminished Inflammatory Response, and Higher Mortality in Internal Medicine Patients with Sepsis. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 3313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Characteristics | n = 139 (100) |
|---|---|
| Female | 55 (40) |
| Median age | 79 (72–86) |
| Median Charlson Comorbidity Index | 3 (2–5) |
| Median SOFA score at IMU admission | 3 (2–5) |
| Biomarkers | |
| Median CRP (mg/L) | 128 (51–240) |
| Median PCT (ng/mL) | 1.8 (0.33–11.4) |
| Median MR-proADM (nmol/L) | 2.8 (1.71–4.37) |
| Median IL-6 (pg/mL) | 186.6 (43.8–605.2) |
| Median lactate (mg/dl) | 15 (11–23) |
| Median IGFBP-3 (pg/mL) | 42,150 (29,478–66,077) |
| Source of infection | |
| Multiple | 16 (12) |
| Respiratory | 36 (26) |
| Etiology of infection | |
| Monomicrobial | 110 (79) |
| -Gram + | 39 (35) |
| -Gram – | 68 (62) |
| -Non bacterial | 3 (3) |
| Polymicrobial | 29 (21) |
| Bloodstream infections | 77 (55) |
| Mortality | |
| 30 days | 26 (19) |
| 1 year | 71 (51) |
| Predictor | B | p | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | AUROC (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 0.037 | 0.013 | 1.03 (1–1.06) | 0.59 (0.49–0.68) |
| SOFA score | 0.10 | 0.039 | 1.10 (1–1.21) | 0.66 (0.57–0.75) |
| Multiple source | 1.174 | <0.001 | 3.24 (1.74–5.98) | 0.58 (0.49–0.68) |
| IGFBP-3 ^ | −0.622 | 0.005 | 0.53 (0.34–0.83) | 0.70 (0.61–0.78) |
| Characteristics | IGFBP-3 < 10.64 * n = 67 | IGFBP-3 > 10.64 * n = 72 | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chronic liver disease | 13 (19) | 4 (6) | 0.018 |
| Median body temperature (°C) | 37 (36–38) | 38 (37–38.1) | 0.008 |
| Median SOFA score at IMU admission | 4 (3–6) | 3 (2–5) | 0.040 |
| Laboratory available at IMU admission | |||
| Median lymphocyte count (×109/L) | 0.86 (0.35–1.28) | 1.02 (0.68–1.7) | 0.007 |
| -Lymphocyte count <0.5 (×109/L) | 24 (36) | 5 (7) | <0.001 |
| Median serum levels of IL-6 (pg/mL) | 305 (76–1004) | 107 (37–341) | 0.004 |
| Etiology of infection | |||
| Polymicrobial sepsis | 20 (30) | 9 (13) | 0.013 |
| Outcome | |||
| 30-day mortality | 19 (28) | 7 (10) | 0.008 |
| 1-year mortality | 46 (69) | 25 (35) | <0.001 |
| Models | 30 Days AUROC (95% CI) | 60 Days AUROC (95% CI) | 90 Days AUROC (95% CI) | 180 Days AUROC (95% CI) | 365 Days AUROC (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model 1: clinical variables ^ | 0.72 (0.6–0.84) | 0.71 (0.57–0.85) | 0.69 (0.58–0.79) | 0.74 (0.65–0.82) | 0.70 (0.61–0.79) |
| Model 2: clinical variables ^ + IGFBP-3 | 0.82 (0.74–0.91) | 0.81 (0.72–0.90) | 0.82 (0.75–0.89) | 0.82 (0.75–0.89) | 0.78 (0.70–0.86) |
| p ° | 0.052 | 0.043 | 0.006 | 0.06 | 0.042 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mearelli, F.; Nunnari, A.; Chitti, F.; Rombini, A.; Macor, A.; Denora, D.; Messana, L.; Scardino, M.; Martini, I.; Bolzan, G.; et al. Lower Initial Insulin-like Growth Factor-Binding Protein-3 Concentrations May Reflect Immune Suppression and Predict Increased Risk of Sepsis-Related Mortality. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6549. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146549
Mearelli F, Nunnari A, Chitti F, Rombini A, Macor A, Denora D, Messana L, Scardino M, Martini I, Bolzan G, et al. Lower Initial Insulin-like Growth Factor-Binding Protein-3 Concentrations May Reflect Immune Suppression and Predict Increased Risk of Sepsis-Related Mortality. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(14):6549. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146549
Chicago/Turabian StyleMearelli, Filippo, Alessio Nunnari, Federica Chitti, Annalisa Rombini, Alessandra Macor, Donatella Denora, Luca Messana, Marianna Scardino, Ilaria Martini, Giulia Bolzan, and et al. 2025. "Lower Initial Insulin-like Growth Factor-Binding Protein-3 Concentrations May Reflect Immune Suppression and Predict Increased Risk of Sepsis-Related Mortality" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 14: 6549. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146549
APA StyleMearelli, F., Nunnari, A., Chitti, F., Rombini, A., Macor, A., Denora, D., Messana, L., Scardino, M., Martini, I., Bolzan, G., Spagnol, F., Casarsa, C., Fiotti, N., Zerbato, V., Di Bella, S., Tascini, C., Di Girolamo, F. G., Sturma, M., Costantino, V., & Biolo, G. (2025). Lower Initial Insulin-like Growth Factor-Binding Protein-3 Concentrations May Reflect Immune Suppression and Predict Increased Risk of Sepsis-Related Mortality. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(14), 6549. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146549







