An mRNA Vaccine Targeting the C-Terminal Region of P1 Protein Induces an Immune Response and Protects Against Mycoplasma pneumoniae
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
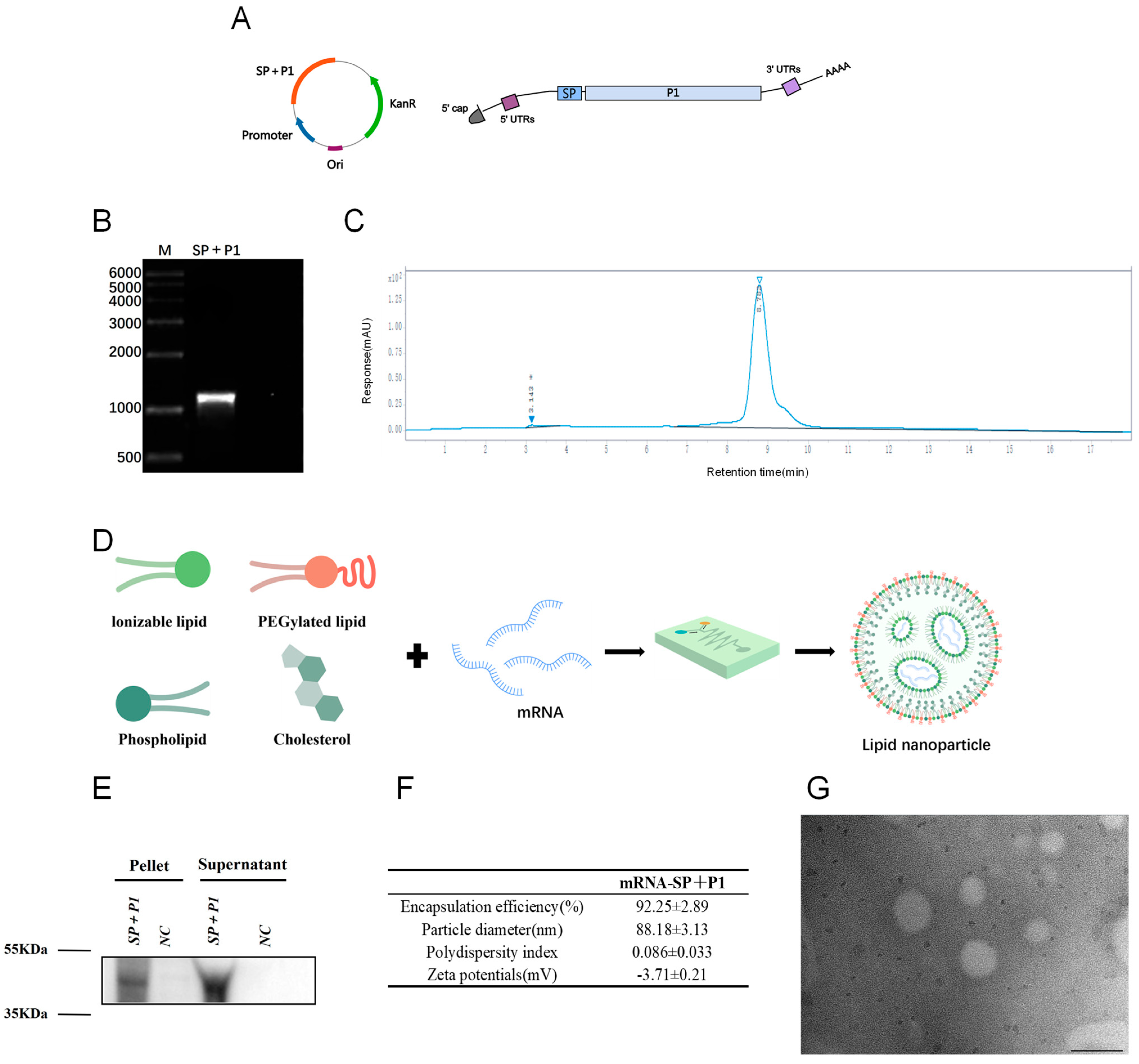
2.1. In Vitro Synthesis and Characterization of mRNA-SP+P1
2.2. The Prophylactic Administration of mRNA-SP+P1 Induces Potent Humoral Immunity and Effector Memory T Cell Responses in Mice
2.3. The Serum of Mice Immunized with mRNA-SP+P1 Can Attenuate the Adhesion Ability of ATCC M129 to KMB17 Cells
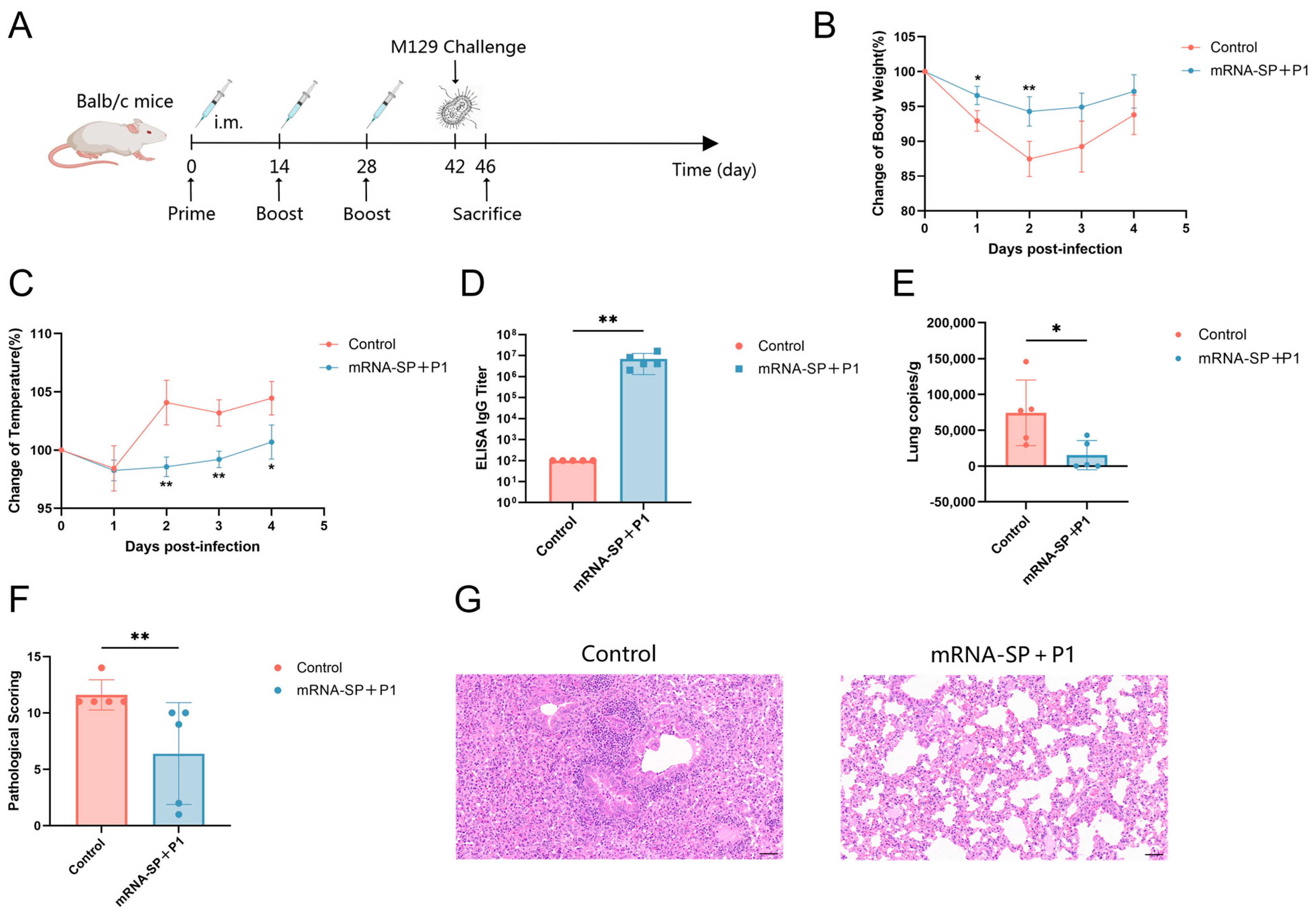
2.4. mRNA-SP+P1 Immunization Mitigates Infection Caused by ATCC M129 Challenge
2.5. mRNA-SP+P1 Immunization Mitigates Infection Caused by ATCC M129 Challenge on Day 62 After Booster Immunization
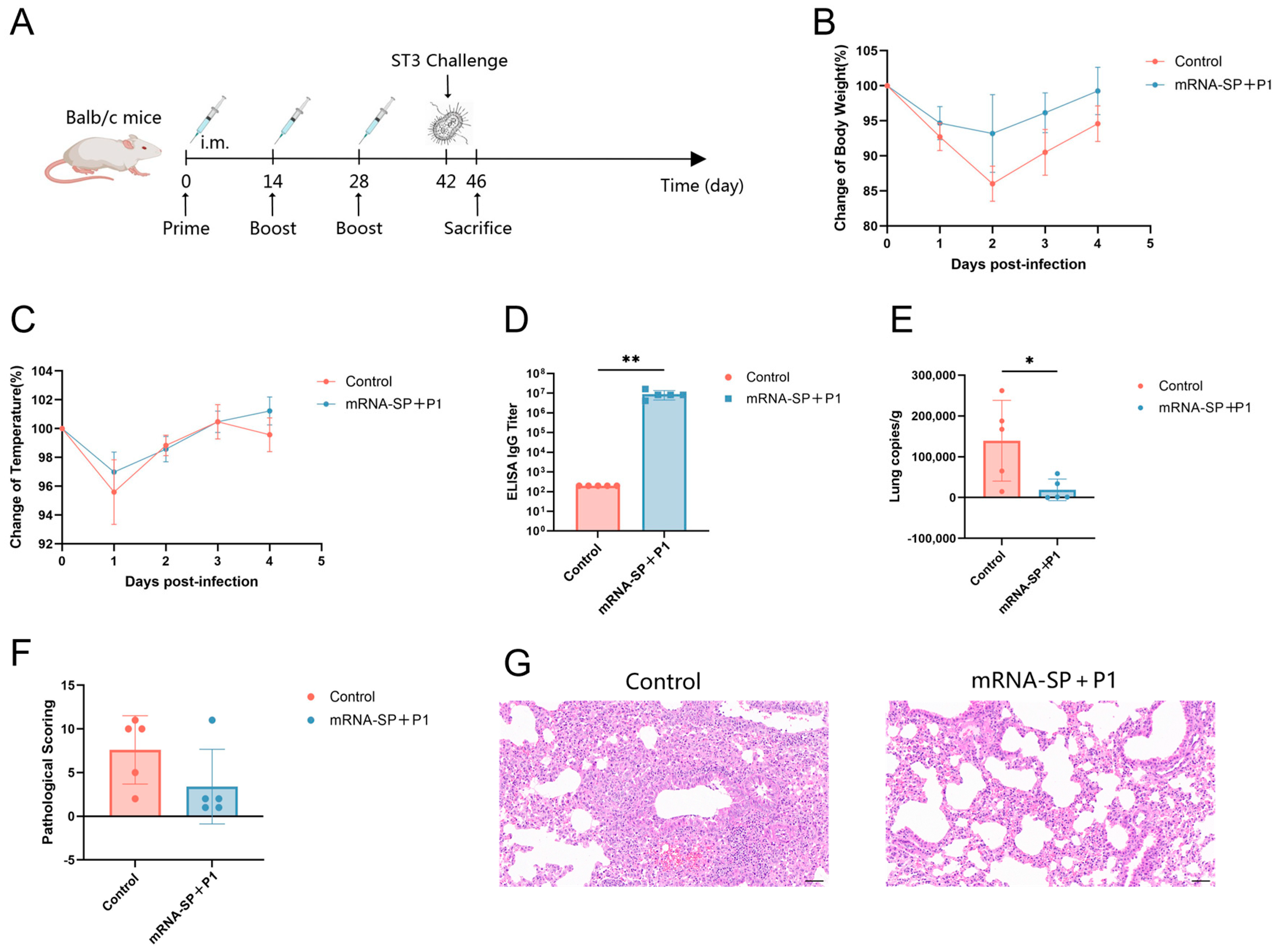
2.6. mRNA-SP+P1 Immunization Mitigates Infection Caused by the ST3-Resistant Strain of Mycoplasma pneumoniae
2.7. mRNA-SP+P1 Activates Immune System Responses
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Ethics Statement
4.2. Cells and Mycoplasma pneumoniae
4.3. Synthesis and Characterization of Mycoplasma pneumoniae mRNA
4.4. Formulation and Characterization of mRNA-LNPs
4.5. Mouse Vaccination
4.6. ELISA for Specific IgG Antibody Titers
4.7. Adhesion Inhibition
4.8. Flow Cytometry Assay
4.9. RNA Sequencing
4.10. Mouse Challenge
4.11. Histopathology
4.12. Quantification of Mycoplasma pneumoniae Load
4.13. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- Lee, E.; Kim, C.H.; Lee, Y.J.; Kim, H.B.; Kim, B.S.; Kim, H.Y.; Kim, Y.; Kim, S.; Park, C.; Seo, J.H.; et al. Annual and seasonal patterns in etiologies of pediatric community-acquired pneumonia due to respiratory viruses and Mycoplasma pneumoniae requiring hospitalization in South Korea. BMC Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Su, C.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, S.; Yan, X.; Zhang, J.; Tao, Z. Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of hospitalized pediatric patients with Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia before and after the COVID-19 pandemic in China: A retrospective multicenter study. BMC Infect. Dis. 2025, 25, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.; Williams, D.J.; Arnold, S.R.; Ampofo, K.; Bramley, A.M.; Reed, C.; Stockmann, C.; Anderson, E.J.; Grijalva, C.G.; Self, W.H.; et al. Community-acquired pneumonia requiring hospitalization among U.S. children. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 835–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.S.; Wang, S.Y.; Hsieh, K.S.; Chiou, Y.H.; Huang, I.F.; Cheng, M.F.; Chiou, C.C. Necrotizing pneumonitis caused by Mycoplasma pneumoniae in pediatric patients: Report of five cases and review of literature. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2004, 23, 564–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, S.Y.; Jwa, H.J.; Yang, E.A.; Kil, H.R.; Lee, J.H. Effects of Methylprednisolone Pulse Therapy on Refractory Mycoplasma pneumoniae Pneumonia in Children. Allergy Asthma Immunol. Res. 2014, 6, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narita, M. Pathogenesis of extrapulmonary manifestations of Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection with special reference to pneumonia. J. Infect. Chemother. 2010, 16, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neimark, H.; Gesner, M. Is Mycoplasma pneumoniae adherence to erythrocytes a factor in extrapulmonary dissemination? PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1001219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yamazaki, T.; Kenri, T. Epidemiology of Mycoplasma pneumoniae Infections in Japan and Therapeutic Strategies for Macrolide-Resistant M. pneumoniae. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edens, C.; Clopper, B.R.; DeVies, J.; Benitez, A.; McKeever, E.R.; Johns, D.; Wolff, B.; Selvarangan, R.; Schuster, J.E.; Weinberg, G.A.; et al. Notes from the Field: Reemergence of Mycoplasma pneumoniae Infections in Children and Adolescents After the COVID-19 Pandemic, United States, 2018–2024. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2024, 73, 149–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuitunen, I.; Artama, M.; Haapanen, M.; Renko, M. Respiratory virus circulation in children after relaxation of COVID-19 restrictions in fall 2021-A nationwide register study in Finland. J. Med. Virol. 2022, 94, 4528–4532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordholm, A.C.; Søborg, B.; Jokelainen, P.; Lauenborg Møller, K.; Flink Sørensen, L.; Grove Krause, T.; Anker Uldum, S.; Emborg, H.D. Mycoplasma pneumoniae epidemic in Denmark, October to December, 2023. Euro Surveill. 2024, 29, 2300707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer Sauteur, P.M.; Beeton, M.L. Mycoplasma pneumoniae: Delayed re-emergence after COVID-19 pandemic restrictions. Lancet Microbe 2024, 5, e100–e101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer Sauteur, P.M.; Beeton, M.L.; Uldum, S.A.; Bossuyt, N.; Vermeulen, M.; Loens, K.; Pereyre, S.; Bébéar, C.; Keše, D.; Day, J.; et al. Mycoplasma pneumoniae detections before and during the COVID-19 pandemic: Results of a global survey, 2017 to 2021. Euro Surveill. 2022, 27, 2100746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereyre, S.; Goret, J.; Bébéar, C. Mycoplasma pneumoniae: Current Knowledge on Macrolide Resistance and Treatment. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gayam, V.; Konala, V.M.; Naramala, S.; Garlapati, P.R.; Merghani, M.A.; Regmi, N.; Balla, M.; Adapa, S. Presenting characteristics, comorbidities, and outcomes of patients coinfected with COVID-19 and Mycoplasma pneumoniae in the USA. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 2181–2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Jung, S.; Kim, M.; Park, S.; Yang, H.J.; Lee, E. Global Trends in the Proportion of Macrolide-Resistant Mycoplasma pneumoniae Infections: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Netw. Open 2022, 5, e2220949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanata, M.M.; Wang, H.; Everhart, K.; Moore-Clingenpeel, M.; Ramilo, O.; Leber, A. Macrolide-Resistant Mycoplasma pneumoniae Infections in Children, Ohio, USA. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2021, 27, 1588–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.J.; Chung, E.H.; Lee, E.; Kim, C.H.; Lee, Y.J.; Kim, H.B.; Kim, B.S.; Kim, H.Y.; Cho, Y.; Seo, J.H.; et al. Clinical Characteristics of Macrolide-Refractory Mycoplasma pneumoniae Pneumonia in Korean Children: A Multicenter Retrospective Study. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beeton, M.L.; Zhang, X.S.; Uldum, S.A.; Bébéar, C.; Dumke, R.; Gullsby, K.; Ieven, M.; Loens, K.; Nir-Paz, R.; Pereyre, S.; et al. Mycoplasma pneumoniae infections, 11 countries in Europe and Israel, 2011 to 2016. Euro Surveill. 2020, 25, 1900112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Lee, S.; Selvarangan, R.; Qin, X.; Tang, Y.W.; Stiles, J.; Hong, T.; Todd, K.; Ratliff, A.E.; Crabb, D.M.; et al. Macrolide-Resistant Mycoplasma pneumoniae, United States. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2015, 21, 1470–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Park, G.W.; Kim, S.; Moon, H.J.; Won, S.; Chung, W.; Yang, H.J. Fluoroquinolone and no risk of Achilles-tendinopathy in childhood pneumonia under eight years of age-a nationwide retrospective cohort. J. Thorac. Dis. 2021, 13, 3399–3408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.Y.; Feng, Z.Q.; Wang, Z.P.; Wang, X.Q.; Luo, C.; Liu, Q.Z. Efficacy of azithromycin combined with intravenous immunoglobulin in the treatment of refractory Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia in children: A meta-analysis. BMC Pediatr. 2024, 24, 678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.B.; Friedewald, W.T.; Chanock, R.M. Inactivated Mycoplasma pneumoniae vaccine. Evaluation in volunteers. JAMA 1967, 199, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wenzel, R.P.; Craven, R.B.; Davies, J.A.; Hendley, J.O.; Hamory, B.H.; Gwaltney, J.M., Jr. Protective efficacy of an inactivated Mycoplasma pneumoniae vaccine. J. Infect. Dis. 1977, 136 (Suppl. 1), S204–S207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mara, A.B.; Gavitt, T.D.; Tulman, E.R.; Geary, S.J.; Szczepanek, S.M. Lipid moieties of Mycoplasma pneumoniae lipoproteins are the causative factor of vaccine-enhanced disease. npj Vaccines 2020, 5, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghmorad, D.; Eslami, M.; Orooji, N.; Halabitska, I.; Kamyshna, I.; Kamyshnyi, O.; Oksenych, V. mRNA vaccine platforms: Linking infectious disease prevention and cancer immunotherapy. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2025, 13, 1547025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, S.; Kwon, M.; Im, S.; Lee, K.; Lee, H. mRNA vaccines: The most recent clinical applications of synthetic mRNA. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2022, 45, 245–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.W.; Lagniton, P.N.P.; Liu, Y.; Xu, R.H. mRNA vaccines for COVID-19: What, why and how. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 17, 1446–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polack, F.P.; Thomas, S.J.; Kitchin, N.; Absalon, J.; Gurtman, A.; Lockhart, S.; Perez, J.L.; Pérez Marc, G.; Moreira, E.D.; Zerbini, C.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA Covid-19 Vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2603–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenri, T.; Kawakita, Y.; Kudo, H.; Matsumoto, U.; Mori, S.; Furukawa, Y.; Tahara, Y.O.; Shibayama, K.; Hayashi, Y.; Arai, M.; et al. Production and characterization of recombinant P1 adhesin essential for adhesion, gliding, and antigenic variation in the human pathogenic bacterium, Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 508, 1050–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vizarraga, D.; Kawamoto, A.; Matsumoto, U.; Illanes, R.; Pérez-Luque, R.; Martín, J.; Mazzolini, R.; Bierge, P.; Pich, O.Q.; Espasa, M.; et al. Immunodominant proteins P1 and P40/P90 from human pathogen Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muroyama, Y.; Wherry, E.J. Memory T-Cell Heterogeneity and Terminology. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2021, 13, a037929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Su, Y.; Jiao, A.; Wang, X.; Zhang, B. T cells in health and disease. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swain, S.L.; McKinstry, K.K.; Strutt, T.M. Expanding roles for CD44 T cells in immunity to viruses. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 12, 136–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, W.C.; Hsieh, Y.C.; Chen, Y.C.; Kuo, C.Y.; Chen, C.J.; Huang, Y.C.; Chiu, C.H.; Lin, T.Y.; Huang, K.A. A potent antibody-secreting B cell response to Mycoplasma pneumoniae in children with pneumonia. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2022, 55, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, X.; Fu, Y.; Yu, Y.; Zhou, H. Whole-genome sequencing unveils the outbreak of Mycoplasma pneumoniae in mainland China. Lancet Microbe 2024, 5, 100870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.K.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, H.; Ahn, Y.M.; Eun, B.W.; Cho, E.Y.; Cho, H.J.; Yun, K.W.; Lee, H.J.; Choi, E.H. Clonal Expansion of Macrolide-Resistant Sequence Type 3 Mycoplasma pneumoniae, South Korea. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2018, 24, 1465–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morozumi, M.; Tajima, T.; Sakuma, M.; Shouji, M.; Meguro, H.; Saito, K.; Iwata, S.; Ubukata, K. Sequence Type Changes Associated with Decreasing Macrolide-Resistant Mycoplasma pneumoniae, Japan. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 2210–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global spatiotemporal dynamics of Mycoplasma pneumoniae re-emergence after COVID-19 pandemic restrictions: An epidemiological and transmission modelling study. Lancet Microbe 2025, 6, 101019. [CrossRef]
- You, H.; Yang, B.; Liu, H.; Wu, W.; Yu, F.; Lin, N.; Yang, W.; Hu, B.; Liu, Y.; Zou, H.; et al. Unravelling distinct patterns of metagenomic surveillance and respiratory microbiota between two P1 genotypes of Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2025, 14, 2449087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhry, R.; Nisar, N.; Hora, B.; Chirasani, S.R.; Malhotra, P. Expression and immunological characterization of the carboxy-terminal region of the P1 adhesin protein of Mycoplasma pneumoniae. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 321–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Winden, V.J.C.; Houben, E.N.G.; Braunstein, M. Protein Export into and across the Atypical Diderm Cell Envelope of Mycobacteria. Microbiol. Spectr. 2019, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berks, B.C. The twin-arginine protein translocation pathway. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2015, 84, 843–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ono, K. Signal Peptides and Their Fragments in Post-Translation: Novel Insights of Signal Peptides. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 13534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dallo, S.F.; Su, C.J.; Horton, J.R.; Baseman, J.B. Identification of P1 gene domain containing epitope(s) mediating Mycoplasma pneumoniae cytoadherence. J. Exp. Med. 1988, 167, 718–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerstenecker, B.; Jacobs, E. Topological mapping of the P1-adhesin of Mycoplasma pneumoniae with adherence-inhibiting monoclonal antibodies. J. Gen. Microbiol. 1990, 136, 471–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lugli, E.; Galletti, G.; Boi, S.K.; Youngblood, B.A. Stem, Effector, and Hybrid States of Memory CD8+ T Cells. Trends Immunol. 2020, 41, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumamoto, Y.; Mattei, L.M.; Sellers, S.; Payne, G.W.; Iwasaki, A. CD4+ T cells support cytotoxic T lymphocyte priming by controlling lymph node input. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 8749–8754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| CARD | ARO Name | Gene Family | Drug Class |
|---|---|---|---|
| ARO: 3000024 | patA | ATP-binding cassette (ABC) antibiotic efflux pump | fluoroquinolone antibiotic |
| ARO: 3000191 | tet(Q) | tetracycline resistant ribosomal protection protein | tetracycline antibiotic |
| ARO: 3000501 | rpoB2 | rifamycin resistant beta subunit of RNA polymerase (rpoB) | rifamycin antibiotic |
| ARO: 3000510 | Staphylococcus aureus mupB confening resistance to mupirocin | antibiotic resistant isoleucyl tRNA synthetase (ileS) | mupirocin-like antibiotic |
| ARO: 3000521 | Staphylococcus aureus mupA confenring resistance to mupirocin | antibiotic resistant isoleucyl tRNA synthetase (ileS) | mupirocin-like antibiotic |
| ARO: 3000535 | macB | ATP-binding cassette (ABC) antibiotic efflux pump | macrolide antibiotic |
| ARO: 3002882 | lmrD | ATP-binding cassette (ABC) antibiotic efflux pump | lincosamide antibiotic |
| ARO: 3003748 | oleC | ATP-binding cassette (ABC) antibiotic efflux pump | macrolide antibiotic |
| ARO: 3003948 | efrA | ATP-binding cassette (ABC) antibiotic efflux pump | Fluoroquinolone antibiotic; macrolide antibiotic; rifamycin antibiotic |
| ARO: 3003949 | efrB | ATP-binding cassette (ABC) antibiotic efflux pump | Fluoroquinolone antibiotic; macrolide antibiotic; rifamycin antibiotic |
| ARO: 3003950 | msbA | ATP-binding cassette (ABC) antibiotic efflux pump | nitroimidazole antibiotic |
| ARO: 3004480 | Bifidobacterium adolescentis rpoB mutants conferring resistance to rifampicin | rifamycin resistant beta subunit of RNA polymerase (rpoB) | rifamycin antibiotic |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, F.; Li, C.; Wu, Y.; Chuan, H.; Song, S.; Xie, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Chen, Q.; Tong, F.; Zhang, R.; et al. An mRNA Vaccine Targeting the C-Terminal Region of P1 Protein Induces an Immune Response and Protects Against Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6536. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136536
Zhang F, Li C, Wu Y, Chuan H, Song S, Xie Y, Zhu Q, Chen Q, Tong F, Zhang R, et al. An mRNA Vaccine Targeting the C-Terminal Region of P1 Protein Induces an Immune Response and Protects Against Mycoplasma pneumoniae. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(13):6536. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136536
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Fenglian, Chengwei Li, Yanan Wu, Hongyun Chuan, Shaohui Song, Yun Xie, Qi Zhu, Qianqian Chen, Fei Tong, Runfang Zhang, and et al. 2025. "An mRNA Vaccine Targeting the C-Terminal Region of P1 Protein Induces an Immune Response and Protects Against Mycoplasma pneumoniae" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 13: 6536. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136536
APA StyleZhang, F., Li, C., Wu, Y., Chuan, H., Song, S., Xie, Y., Zhu, Q., Chen, Q., Tong, F., Zhang, R., Yuan, G., Wu, X., Zhou, J., & Liao, G. (2025). An mRNA Vaccine Targeting the C-Terminal Region of P1 Protein Induces an Immune Response and Protects Against Mycoplasma pneumoniae. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(13), 6536. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136536





