Identification of a PAK6-Mediated MDM2/p21 Axis That Modulates Survival and Cell Cycle Control of Drug-Resistant Stem/Progenitor Cells in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
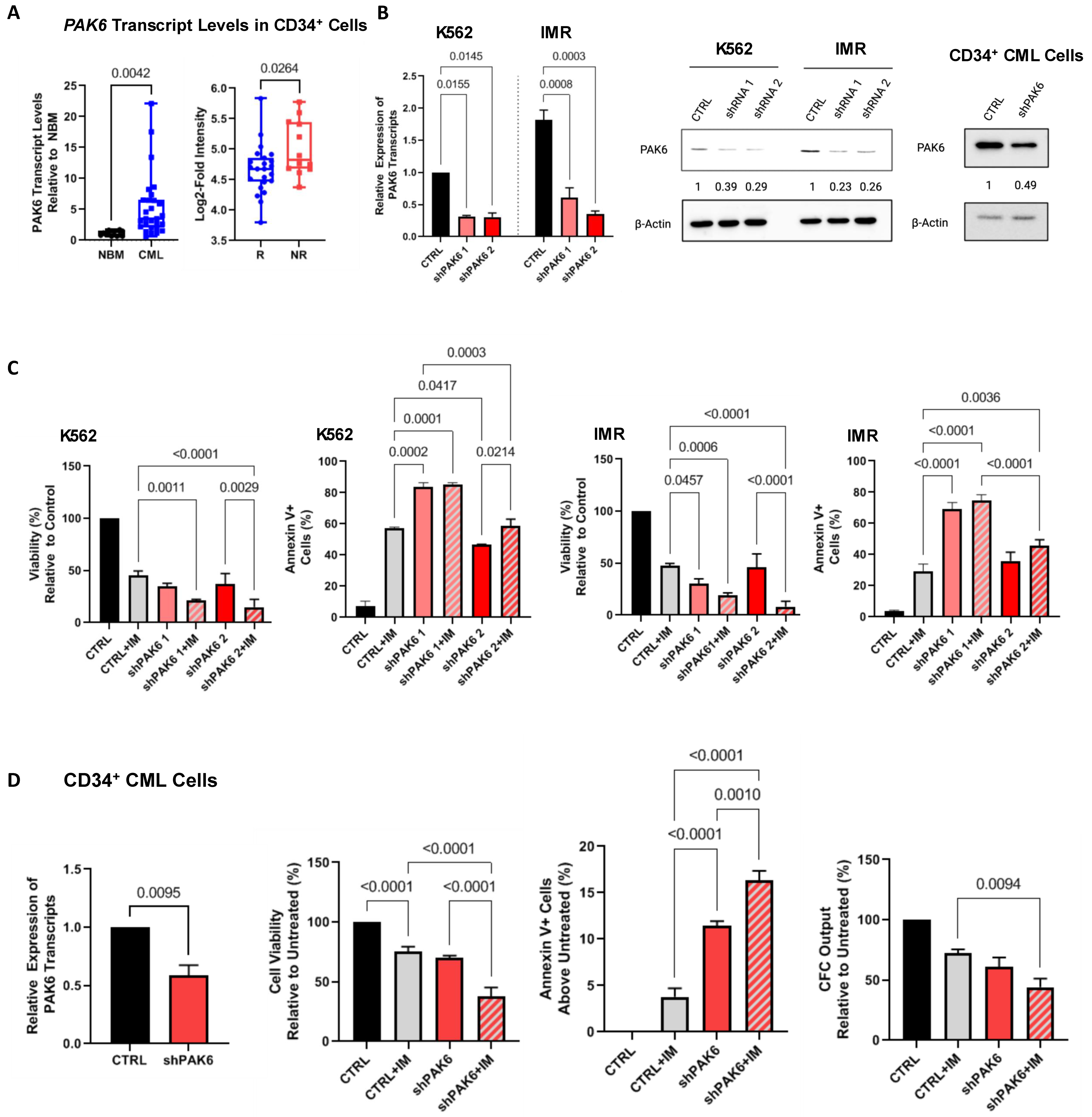
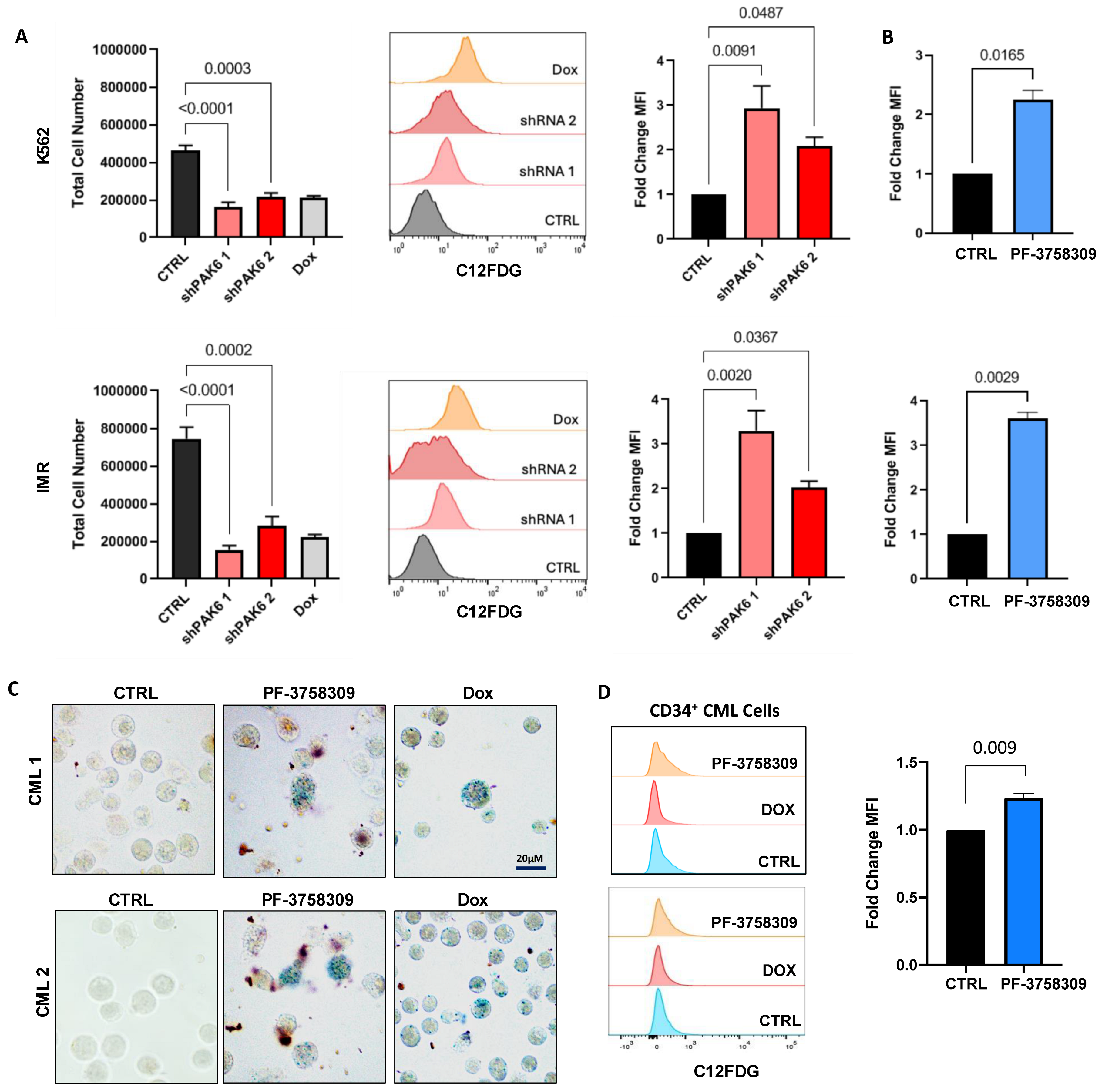
2.1. Lentiviral-Mediated PAK6 Knockdown Sensitizes TKI-Resistant CML Cells to IM
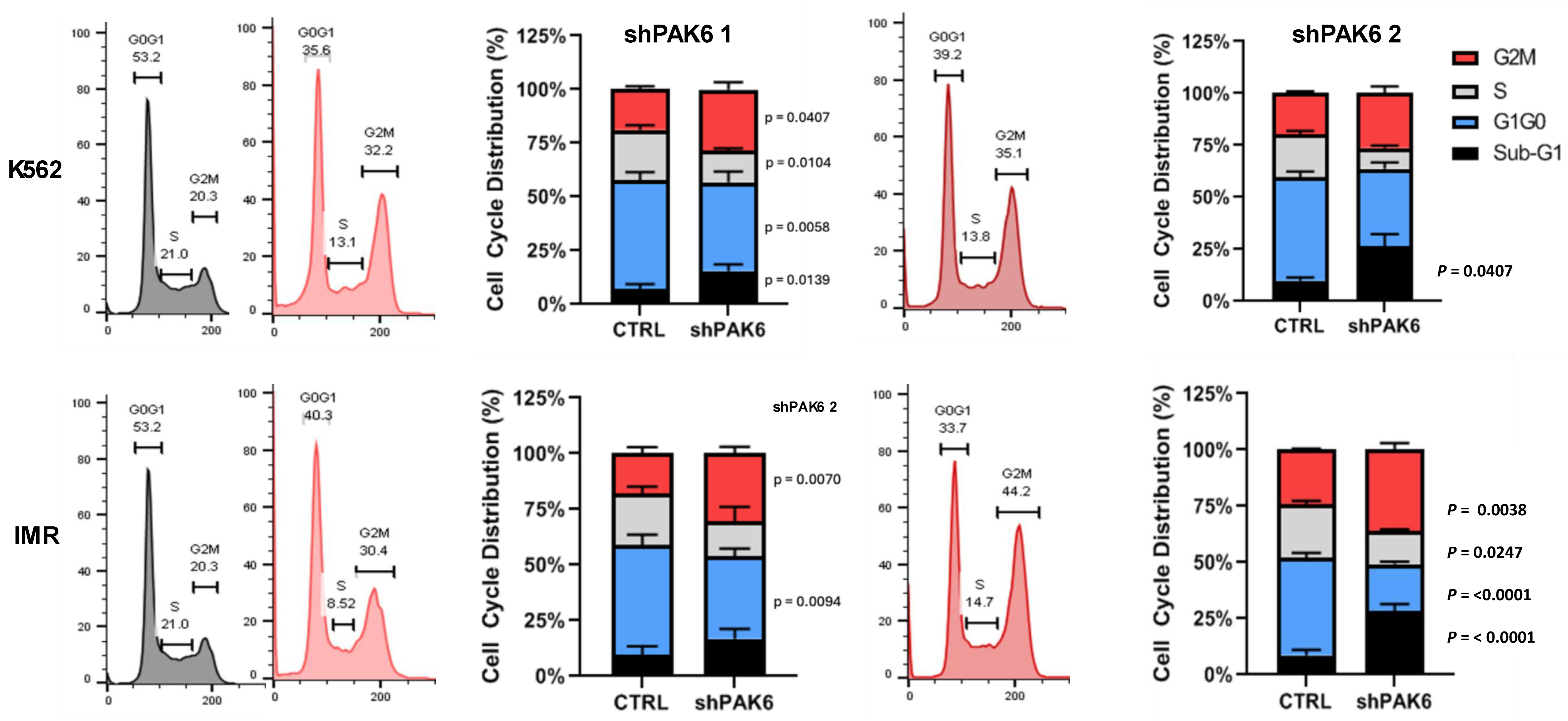
2.2. Lentiviral-Mediated PAK6 Knockdown Induces G2/M Cell Cycle Arrest in IM-Resistant Cells
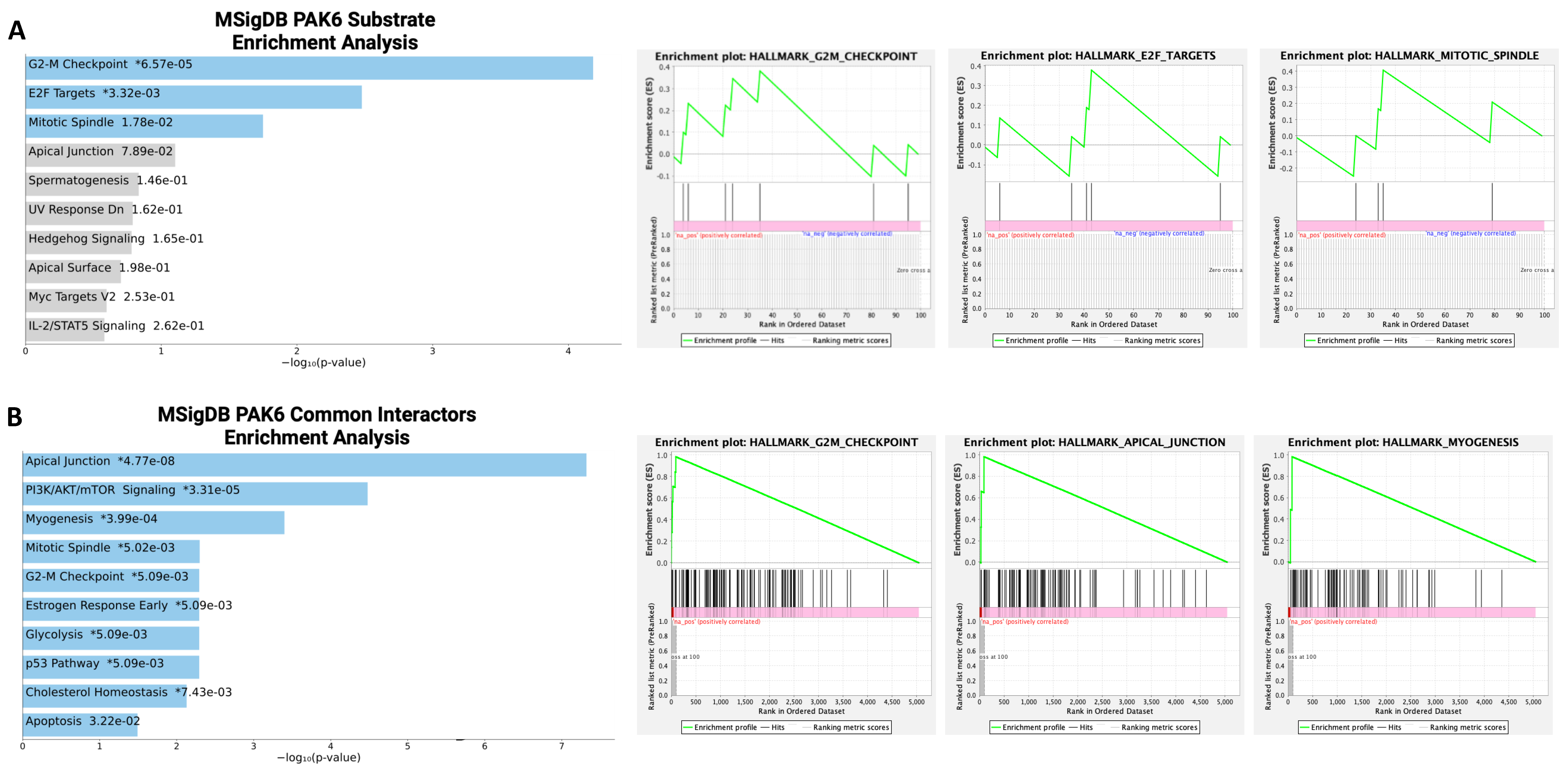
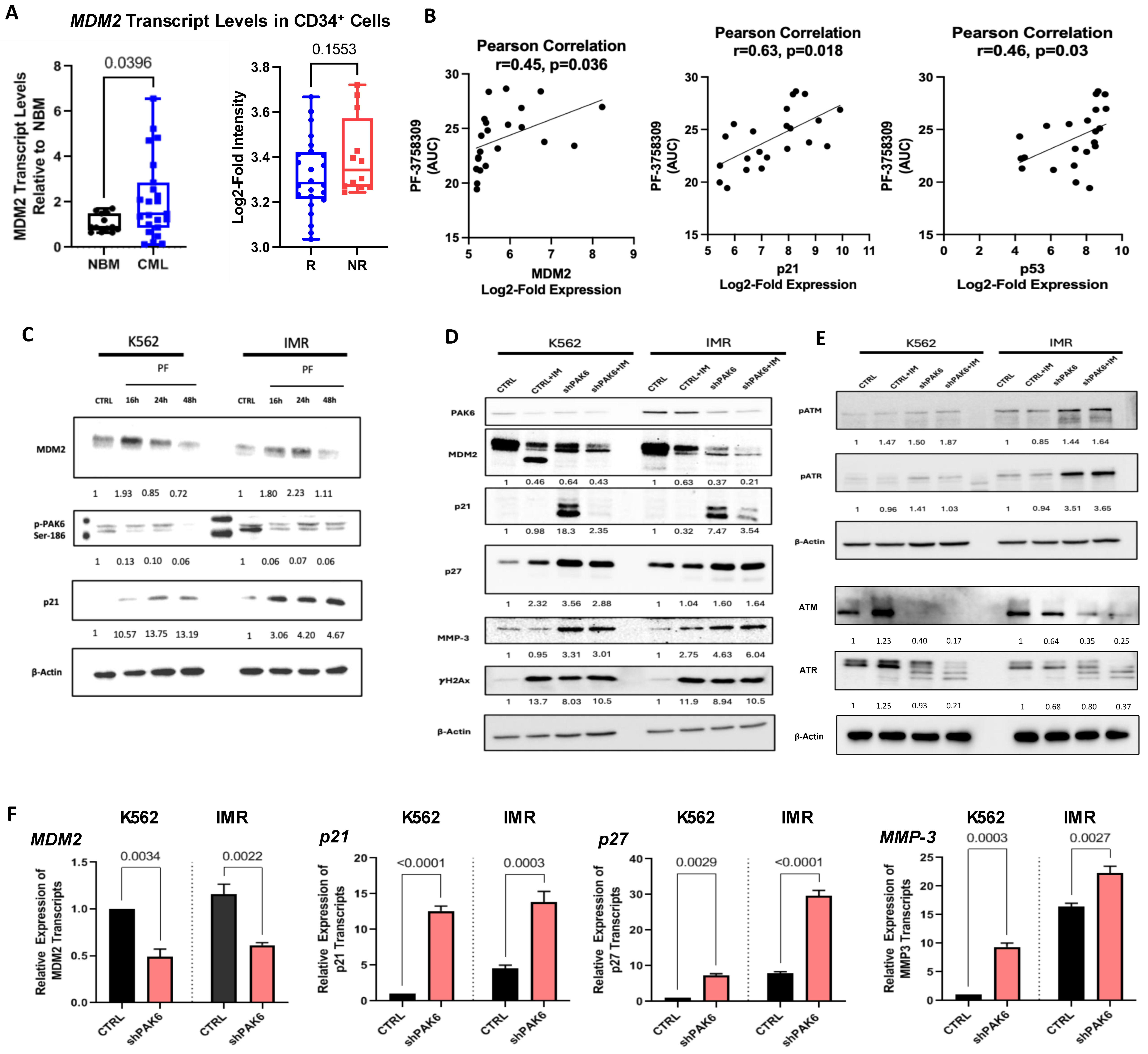
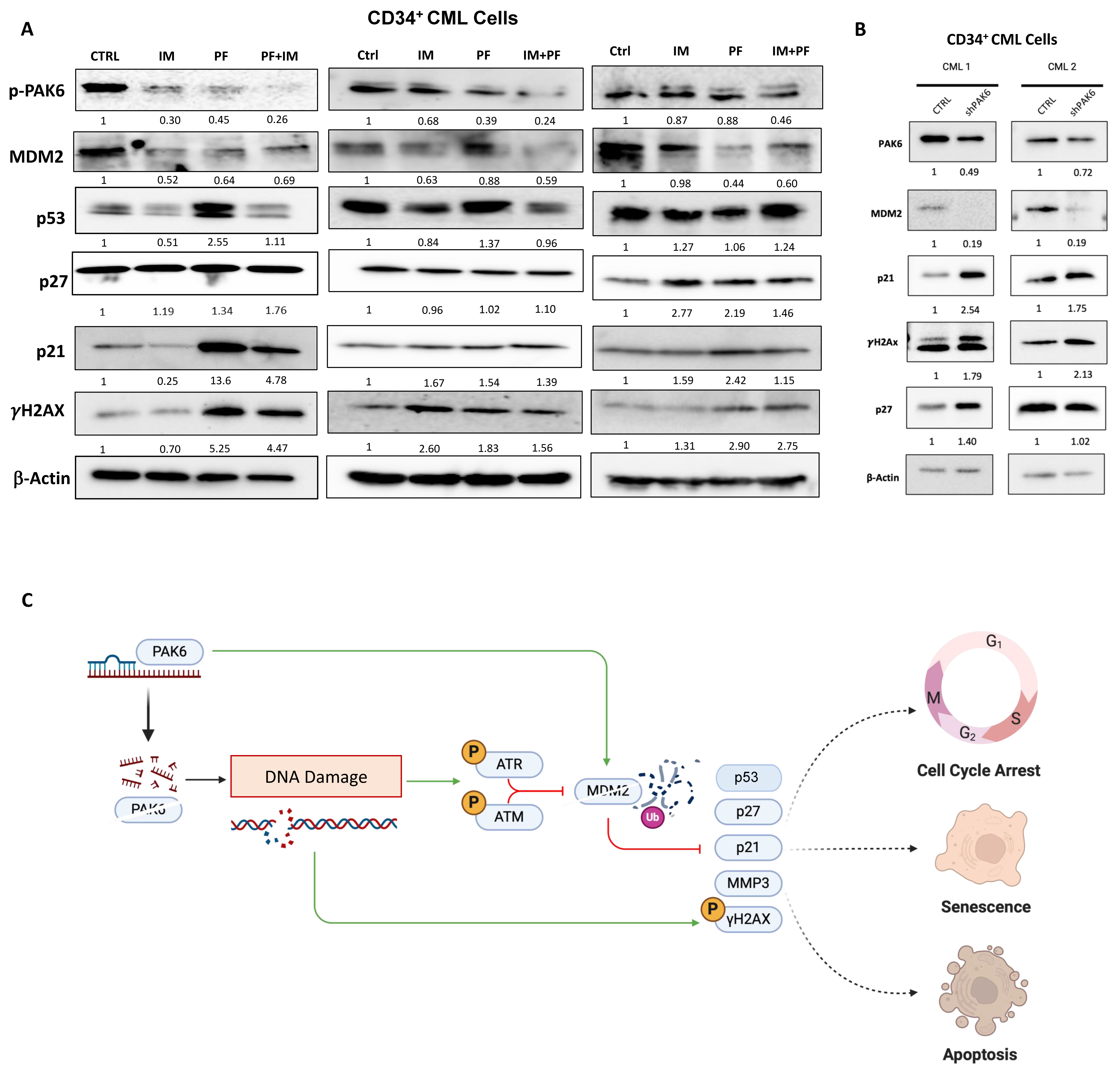
2.3. Identification of an MDM2-P21 Axis Mediated by PAK6 in IM-Resistant Cells
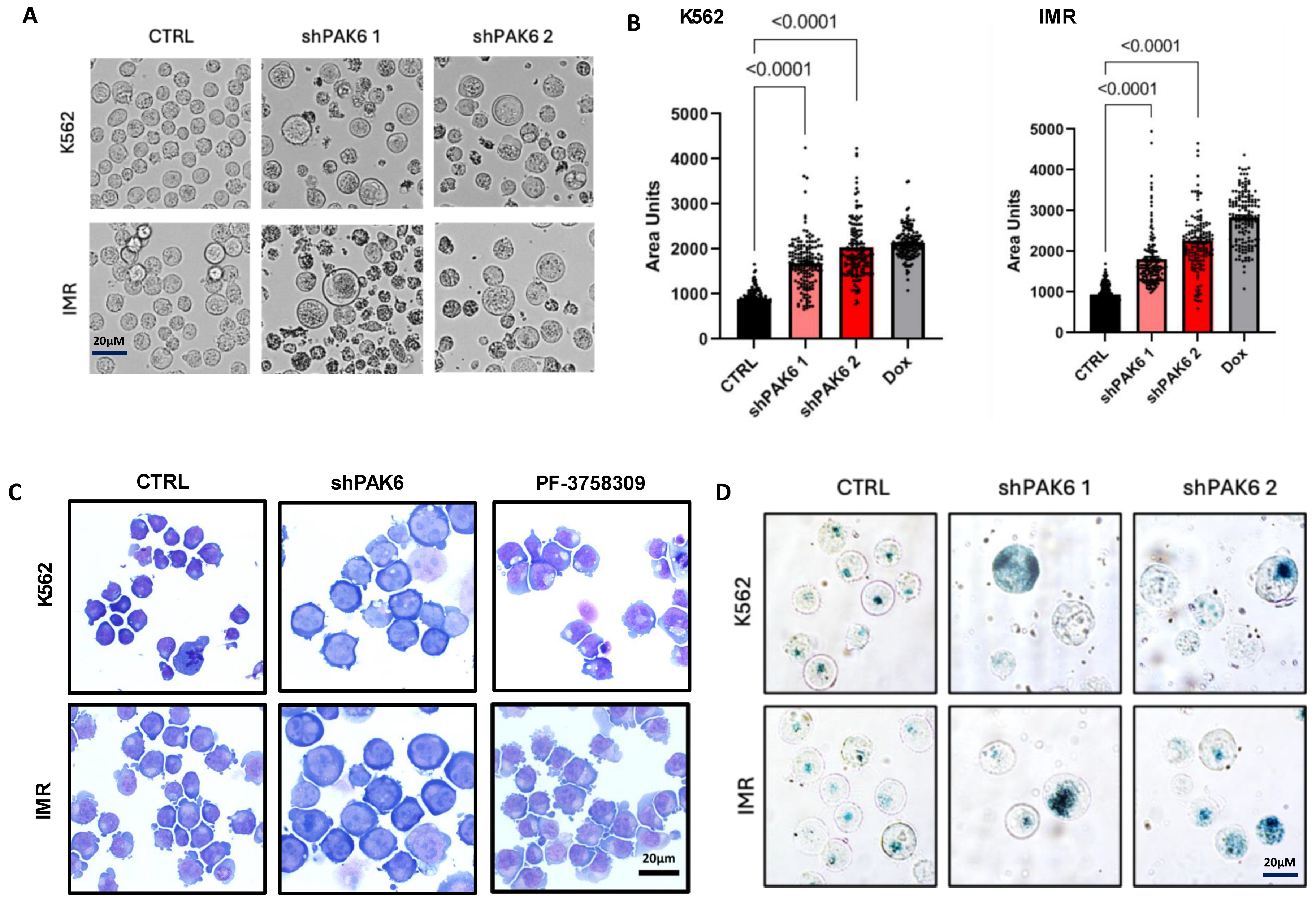
2.4. Pharmacological and Genetic PAK6 Suppression Induces Senescence in IM-Resistant Cells
2.5. Suppression of PAK6 Induces Activation of Senescence-Associated Protein Markers in IM-Resistant Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Lines
4.2. Primary Patient Samples
4.3. Small-Molecule Inhibitors
4.4. Lentiviral Transfection of PAK6 shRNA Constructs
4.5. Lentiviral-Mediated PAK6 Knockdown in CML Cells
4.6. Trypan Blue Viability Assay
4.7. PI-Annexin V Apoptosis Assay
4.8. CFC Assay
4.9. Cell Cycle Assay
4.10. Senescence-Associated β-Galactosidase Staining
4.11. Wright-Giemsa Staining
4.12. RNA Extraction
4.13. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
4.14. Cell Lysis and Protein Quantification
4.15. Western Blot Analysis
4.16. Bioinformatic Analysis
4.17. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sawyers, C.L. Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 340, 1330–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, S.M.; Jørgensen, H.G.; Allan, E.; Pearson, C.; Alcorn, M.J.; Richmond, L.; Holyoake, T.L. Primitive, Quiescent, Philadelphia-Positive Stem Cells from Patients with Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Are Insensitive to STI571 In Vitro. Blood 2002, 99, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houshmand, M.; Simonetti, G.; Circosta, P.; Gaidano, V.; Cignetti, A.; Martinelli, G.; Saglio, G.; Gale, R.P. Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Stem Cells. Leukemia 2019, 33, 1543–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holyoake, T.; Jiang, X.; Eaves, C.; Eaves, A. Isolation of a Highly Quiescent Subpopulation of Primitive Leukemic Cells in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. Blood 1999, 94, 2056–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.L.; Zhao, Y.; Ringrose, A.; DeGeer, D.; Kennah, E.; Lin, A.E.-J.; Sheng, G.; Li, X.-J.; Turhan, A.; Jiang, X. AHI-1 Interacts with BCR-ABL and Modulates BCR-ABL Transforming Activity and Imatinib Response of CML Stem/Progenitor Cells. J. Exp. Med. 2008, 205, 2657–2671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothe, K.; Babaian, A.; Nakamichi, N.; Chen, M.; Chafe, S.C.; Watanabe, A.; Forrest, D.L.; Mager, D.L.; Eaves, C.J.; Dedhar, S.; et al. Integrin-Linked Kinase Mediates Therapeutic Resistance of Quiescent CML Stem Cells to Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors. Cell Stem Cell 2020, 27, 110–124.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loscocco, F.; Visani, G.; Galimberti, S.; Curti, A.; Isidori, A. BCR-ABL Independent Mechanisms of Resistance in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, T.P.; Eide, C.A.; Druker, B.J. Response and Resistance to BCR-ABL1-Targeted Therapies. Cancer Cell 2020, 37, 530–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, R.; Grasedieck, S.; Wu, A.; Lin, H.; Su, J.; Rothe, K.; Nakamoto, H.; Forrest, D.L.; Eaves, C.J.; Jiang, X. Identification of Key microRNAs as Predictive Biomarkers of Nilotinib Response in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: A Sub-Analysis of the ENESTxtnd Clinical Trial. Leukemia 2022, 36, 2443–2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, A.; Yen, R.; Grasedieck, S.; Lin, H.; Nakamoto, H.; Forrest, D.L.; Eaves, C.J.; Jiang, X. Identification of Multivariable microRNA and Clinical Biomarker Panels to Predict Imatinib Response in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia at Diagnosis. Leukemia 2023, 37, 2426–2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, A.; Jiang, X. P21-Activated Kinases as Promising Therapeutic Targets in Hematological Malignancies. Leukemia 2022, 36, 315–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.; Rothe, K.; Chen, M.; Wu, A.; Babaian, A.; Yen, R.; Zeng, J.; Ruschmann, J.; Petriv, O.I.; O’Neill, K.; et al. The miR-185/PAK6 Axis Predicts Therapy Response and Regulates Survival of Drug-Resistant Leukemic Stem Cells in CML. Blood 2020, 136, 596–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, R.; Sanawar, R.; Li, X.; Li, F. Structure, Biochemistry, and Biology of PAK Kinases. Gene 2017, 605, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Gururaj, A.E.; Barnes, C.J. P21-Activated Kinases in Cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2006, 6, 459–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eswaran, J.; Soundararajan, M.; Kumar, R.; Knapp, S. UnPAKing the Class Differences among P21-Activated Kinases. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2008, 33, 394–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Han, Z.; Sun, Z.; Feng, H.; Zhao, L.; Yuan, Q.; Chen, C.; Yu, S.; Hu, Y.; Yu, J.; et al. PAK6 Promotes Homologous-Recombination to Enhance Chemoresistance to Oxaliplatin through ATR/CHK1 Signaling in Gastric Cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quan, L.; Cheng, Z.; Dai, Y.; Jiao, Y.; Shi, J.; Fu, L. Prognostic Significance of PAK Family Kinases in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Cancer Gene Ther. 2020, 27, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edlinger, L.; Berger-Becvar, A.; Menzl, I.; Hoermann, G.; Greiner, G.; Grundschober, E.; Bago-Horvath, Z.; Al-Zoughbi, W.; Hoefler, G.; Brostjan, C.; et al. Expansion of BCR/ABL1+ Cells Requires PAK2 but Not PAK1. Br. J. Haematol. 2017, 179, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Liu, K.; Dong, Z. The Role of P21-Activated Kinases in Cancer and Beyond: Where Are We Heading? Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 641381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McWeeney, S.K.; Pemberton, L.C.; Loriaux, M.M.; Vartanian, K.; Willis, S.G.; Yochum, G.; Wilmot, B.; Turpaz, Y.; Pillai, R.; Druker, B.J.; et al. A Gene Expression Signature of CD34+ Cells to Predict Major Cytogenetic Response in Chronic-Phase Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Patients Treated with Imatinib. Blood 2010, 115, 315–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamant, I.; Clarke, J.B.; Evangelista, E.; Lingam, N.; Ma’ayan, A. Harmonizome 3.0: Integrated Knowledge about Genes and Proteins from Diverse Multi-Omics Resources. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025, 53, D1016–D1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hornbeck, P.V.; Zhang, B.; Murray, B.; Kornhauser, J.M.; Latham, V.; Skrzypek, E. PhosphoSitePlus, 2014: Mutations, PTMs and Recalibrations. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, D512–D520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luna, A.; Elloumi, F.; Varma, S.; Wang, Y.; Rajapakse, V.N.; Aladjem, M.I.; Robert, J.; Sander, C.; Pommier, Y.; Reinhold, W.C. CellMiner Cross-Database (CellMinerCDB) Version 1.2: Exploration of Patient-Derived Cancer Cell Line Pharmacogenomics. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D1083–D1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, B.W.; Guo, C.; Piraino, J.; Westwick, J.K.; Zhang, C.; Lamerdin, J.; Dagostino, E.; Knighton, D.; Loi, C.-M.; Zager, M.; et al. Small-Molecule P21-Activated Kinase Inhibitor PF-3758309 Is a Potent Inhibitor of Oncogenic Signaling and Tumor Growth. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 9446–9451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouillard, A.D.; Gundersen, G.W.; Fernandez, N.F.; Wang, Z.; Monteiro, C.D.; McDermott, M.G.; Ma’ayan, A. The Harmonizome: A Collection of Processed Datasets Gathered to Serve and Mine Knowledge about Genes and Proteins. Database 2016, 2016, baw100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuleshov, M.V.; Jones, M.R.; Rouillard, A.D.; Fernandez, N.F.; Duan, Q.; Wang, Z.; Koplev, S.; Jenkins, S.L.; Jagodnik, K.M.; Lachmann, A.; et al. Enrichr: A Comprehensive Gene Set Enrichment Analysis Web Server 2016 Update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W90–W97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Bailey, A.; Kuleshov, M.V.; Clarke, D.J.B.; Evangelista, J.E.; Jenkins, S.L.; Lachmann, A.; Wojciechowicz, M.L.; Kropiwnicki, E.; Jagodnik, K.M.; et al. Gene Set Knowledge Discovery with Enrichr. Curr. Protoc. 2021, 1, e90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubbutat, M.H.; Jones, S.N.; Vousden, K.H. Regulation of P53 Stability by Mdm2. Nature 1997, 387, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momand, J.; Zambetti, G.P.; Olson, D.C.; George, D.; Levine, A.J. The Mdm-2 Oncogene Product Forms a Complex with the P53 Protein and Inhibits P53-Mediated Transactivation. Cell 1992, 69, 1237–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Li, Y.; Gu, H.; Zhu, G.; Li, J.; Cao, L.; Li, F. P21-Activated Kinase 6 (PAK6) Inhibits Prostate Cancer Growth via Phosphorylation of Androgen Receptor and Tumorigenic E3 Ligase Murine Double Minute-2 (Mdm2). J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 3359–3369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, B.Z.; Mak, P.Y.; Mak, D.H.; Ruvolo, V.R.; Schober, W.; McQueen, T.; Cortes, J.; Kantarjian, H.M.; Champlin, R.E.; Konopleva, M.; et al. Synergistic Effects of P53 Activation via MDM2 Inhibition in Combination with Inhibition of Bcl-2 or Bcr-Abl in CD34+ Proliferating and Quiescent Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Blast Crisis Cells. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 30487–30499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajapakse, V.N.; Luna, A.; Yamade, M.; Loman, L.; Varma, S.; Sunshine, M.; Iorio, F.; Sousa, F.G.; Elloumi, F.; Aladjem, M.I.; et al. CellMinerCDB for Integrative Cross-Database Genomics and Pharmacogenomics Analyses of Cancer Cell Lines. iScience 2018, 10, 247–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, P.K.; Eldridge, A.G.; Freed, E.; Furstenthal, L.; Hsu, J.Y.; Kaiser, B.K.; Reimann, J.D. The Lore of the RINGs: Substrate Recognition and Catalysis by Ubiquitin Ligases. Trends Cell Biol. 2000, 10, 429–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Law, J.C.; Ritke, M.K.; Yalowich, J.C.; Leder, G.H.; Ferrell, R.E. Mutational Inactivation of the P53 Gene in the Human Erythroid Leukemic K562 Cell Line. Leuk. Res. 1993, 17, 1045–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, H.; Li, M.; Agrawal, S.; Chen, X.; Zhang, R. MDM2 Is a Negative Regulator of p21WAF1/CIP1, Independent of P53. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 16000–16006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Childs, B.G.; Baker, D.J.; Kirkland, J.L.; Campisi, J.; van Deursen, J.M. Senescence and Apoptosis: Dueling or Complementary Cell Fates? EMBO Rep. 2014, 15, 1139–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payne, S.R.; Zhang, S.; Tsuchiya, K.; Moser, R.; Gurley, K.E.; Longton, G.; deBoer, J.; Kemp, C.J. P27kip1 Deficiency Impairs G2/M Arrest in Response to DNA Damage, Leading to an Increase in Genetic Instability. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 28, 258–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaltiel, I.A.; Krenning, L.; Bruinsma, W.; Medema, R.H. The Same, Only Different—DNA Damage Checkpoints and Their Reversal throughout the Cell Cycle. J. Cell Sci. 2015, 128, 607–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gire, V.; Dulic, V. Senescence from G2 Arrest, Revisited. Cell Cycle 2015, 14, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lossaint, G.; Horvat, A.; Gire, V.; Bačević, K.; Mrouj, K.; Charrier-Savournin, F.; Georget, V.; Fisher, D.; Dulić, V. Reciprocal Regulation of P21 and Chk1 Controls the Cyclin D1-RB Pathway to Mediate Senescence Onset after G2 Arrest. J. Cell Sci. 2022, 135, jcs259114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ando, T.; Kawabe, T.; Ohara, H.; Ducommun, B.; Itoh, M.; Okamoto, T. Involvement of the Interaction between P21 and Proliferating Cell Nuclear Antigen for the Maintenance of G2/M Arrest after DNA Damage. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 42971–42977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shreeya, T.; Ansari, M.S.; Kumar, P.; Saifi, M.; Shati, A.A.; Alfaifi, M.Y.; Elbehairi, S.E.I. Senescence: A DNA Damage Response and Its Role in Aging and Neurodegenerative Diseases. Front. Aging 2024, 4, 1292053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drullion, C.; Trégoat, C.; Lagarde, V.; Tan, S.; Gioia, R.; Priault, M.; Djavaheri-Mergny, M.; Brisson, A.; Auberger, P.; Mahon, F.-X.; et al. Apoptosis and Autophagy Have Opposite Roles on Imatinib-Induced K562 Leukemia Cell Senescence. Cell Death Dis. 2012, 3, e373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlowska, E.; Szczepanska, J.; Szatkowska, M.; Blasiak, J. An Interplay between Senescence, Apoptosis and Autophagy in Glioblastoma Multiforme—Role in Pathogenesis and Therapeutic Perspective. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Tchkonia, T.; Pirtskhalava, T.; Gower, A.C.; Ding, H.; Giorgadze, N.; Palmer, A.K.; Ikeno, Y.; Hubbard, G.B.; Lenburg, M.; et al. The Achilles’ Heel of Senescent Cells: From Transcriptome to Senolytic Drugs. Aging Cell 2015, 14, 644–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochhaus, A.; Baccarani, M.; Silver, R.T.; Schiffer, C.; Apperley, J.F.; Cervantes, F.; Clark, R.E.; Cortes, J.E.; Deininger, M.W.; Guilhot, F.; et al. European LeukemiaNet 2020 Recommendations for Treating Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. Leukemia 2020, 34, 966–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forrest, D.L.; Jiang, X.; Eaves, C.J.; Smith, C.L. An Approach to the Management of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia in British Columbia. Curr. Oncol. 2008, 15, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baccarani, M.; Deininger, M.W.; Rosti, G.; Hochhaus, A.; Soverini, S.; Apperley, J.F.; Cervantes, F.; Clark, R.E.; Cortes, J.E.; Guilhot, F.; et al. European LeukemiaNet Recommendations for the Management of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: 2013. Blood 2013, 122, 872–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debacq-Chainiaux, F.; Erusalimsky, J.D.; Campisi, J.; Toussaint, O. Protocols to Detect Senescence-Associated Beta-Galactosidase (SA-Βgal) Activity, a Biomarker of Senescent Cells in Culture and In Vivo. Nat. Protoc. 2009, 4, 1798–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.L.; Yaron, T.M.; Huntsman, E.M.; Kerelsky, A.; Song, J.; Regev, A.; Lin, T.-Y.; Liberatore, K.; Cizin, D.M.; Cohen, B.M.; et al. An Atlas of Substrate Specificities for the Human Serine/Threonine Kinome. Nature 2023, 613, 759–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, A.; Chen, M.; Phoa, A.; Yang, Z.; Forrest, D.L.; Jiang, X. Identification of a PAK6-Mediated MDM2/p21 Axis That Modulates Survival and Cell Cycle Control of Drug-Resistant Stem/Progenitor Cells in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6533. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136533
Wu A, Chen M, Phoa A, Yang Z, Forrest DL, Jiang X. Identification of a PAK6-Mediated MDM2/p21 Axis That Modulates Survival and Cell Cycle Control of Drug-Resistant Stem/Progenitor Cells in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(13):6533. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136533
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Andrew, Min Chen, Athena Phoa, Zesong Yang, Donna L. Forrest, and Xiaoyan Jiang. 2025. "Identification of a PAK6-Mediated MDM2/p21 Axis That Modulates Survival and Cell Cycle Control of Drug-Resistant Stem/Progenitor Cells in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 13: 6533. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136533
APA StyleWu, A., Chen, M., Phoa, A., Yang, Z., Forrest, D. L., & Jiang, X. (2025). Identification of a PAK6-Mediated MDM2/p21 Axis That Modulates Survival and Cell Cycle Control of Drug-Resistant Stem/Progenitor Cells in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(13), 6533. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136533





