The Nuclear Transcription Factor SlNF-YC9 Regulates the Protrusion of Tomato Fruit Tip
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Bioinformatics Analysis, Subcellular Localization, and Expression Pattern of SlNF-YC9
2.2. The Knockout of SlNF-YC9 Alters Fruit Morphology in Tomato
2.3. The Knockout of SlNF-YC9 Affects the Expression Levels of the FUL2 Gene in Tomato Fruits
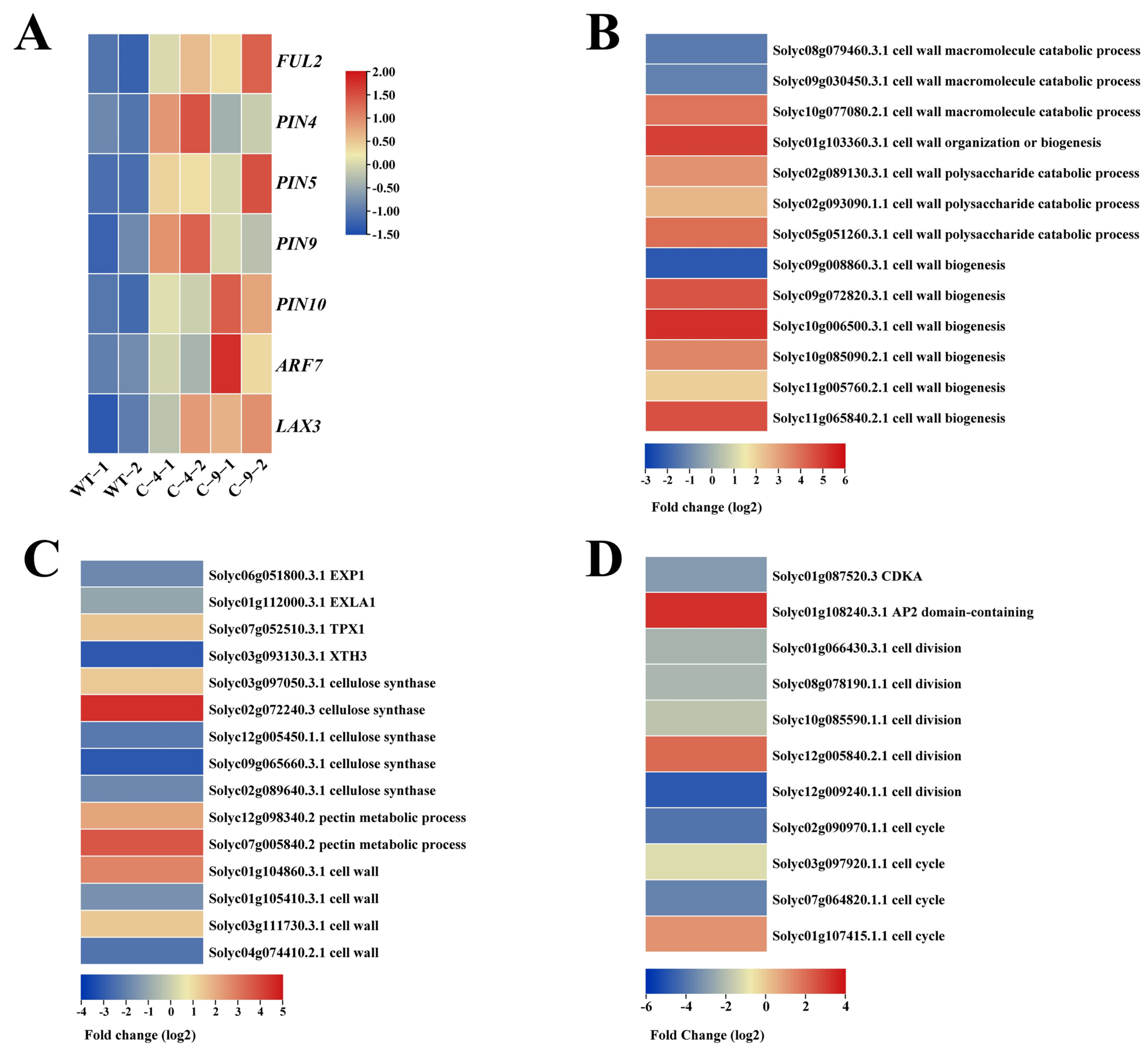
2.4. The Knockout of SlNF-YC9 Affects the IAA Content and Expression of Auxin-Related Genes in Tomato Fruits
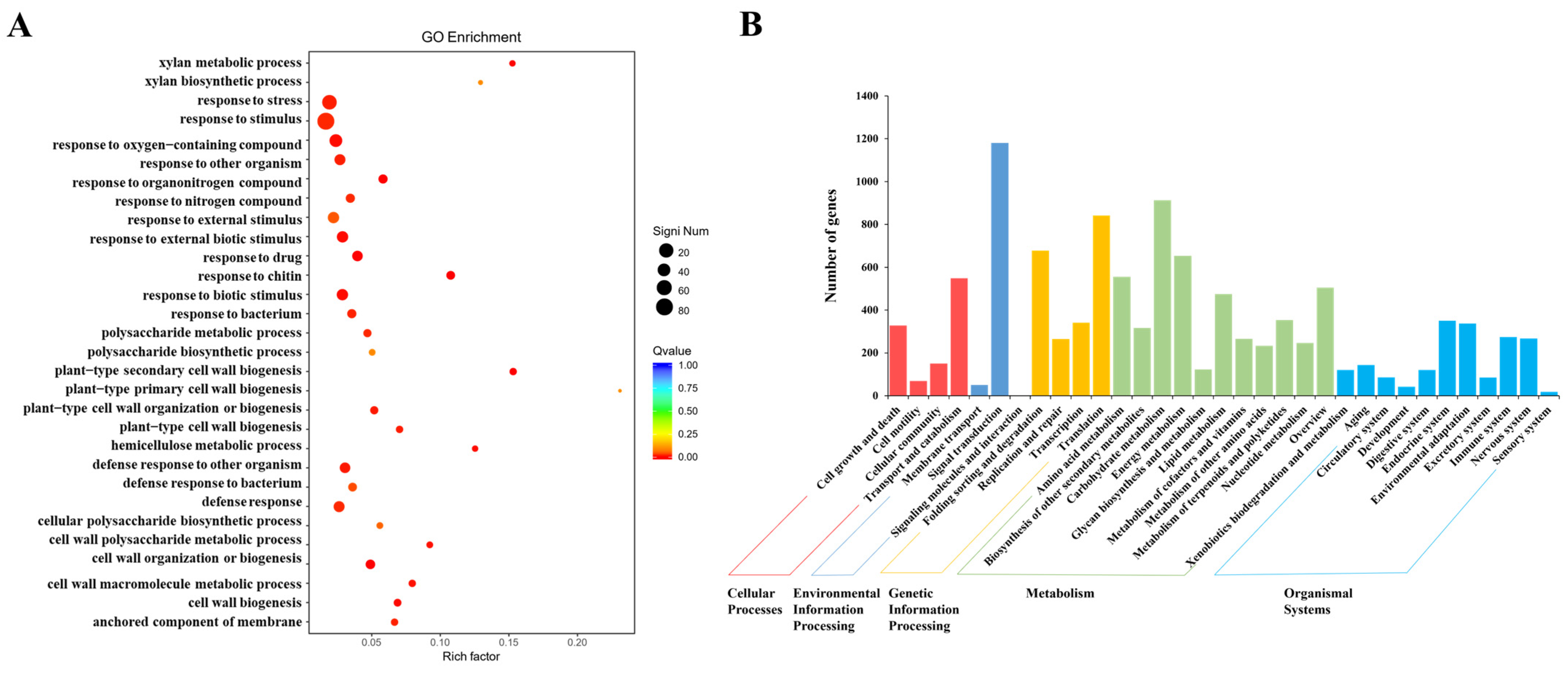
2.5. RNA Sequencing Analysis of CR-SlNF-YC9 Fruit Tips
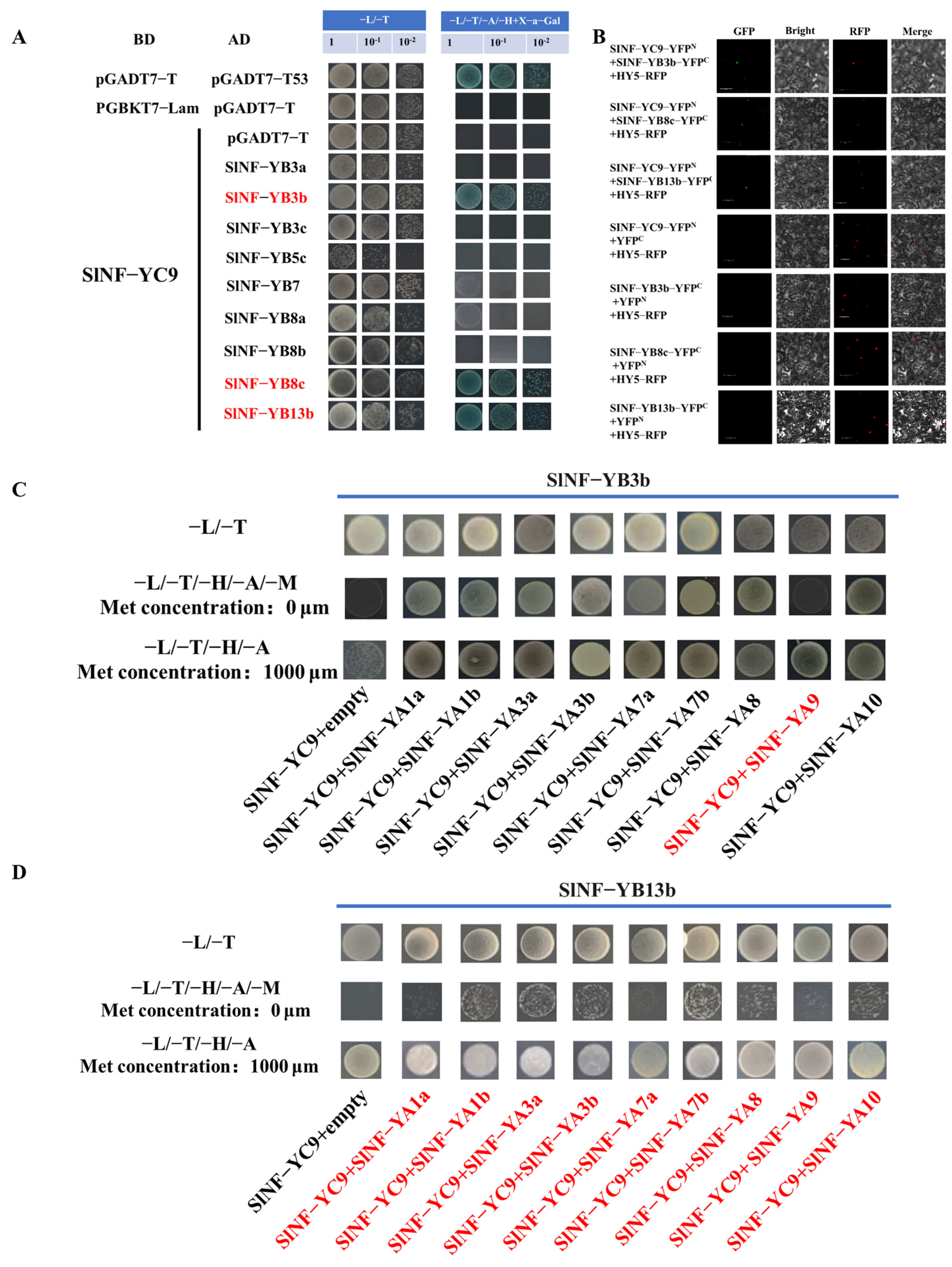
2.6. SlNF-YC9 Can Form Multiple Trimeric Complexes with SlNF-YBs and SlNF-YAs
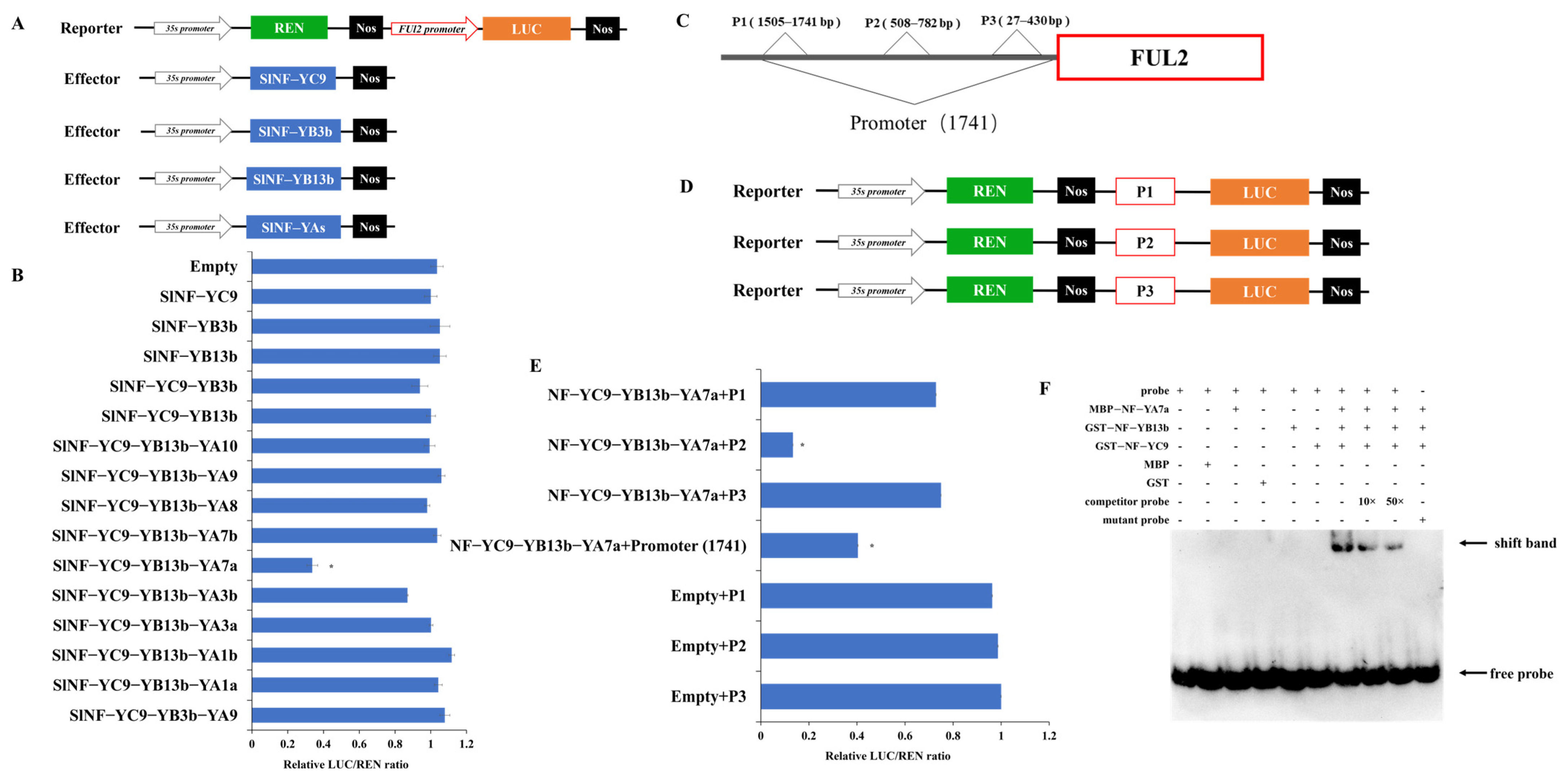
2.7. SlNF-YC9-YB13b-YA7a Trimeric Complex Represses the Promoter Activity of FUL2
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials and Growth Conditions
4.2. Bioinformatics Analysis
4.3. Subcellular Localization Assay
4.4. SlNF-YC9 Knockout Vector Construction and Plant Transformation
4.5. Measurement of Pectin and Cellulase Content
4.6. Fruit Tip Tissue Sections
4.7. qRT-PCR Analysis and RNA-Sequencing
4.8. RNA Sequencing
4.9. Yeast Two-Hybrid and BiFC Assays
4.10. Yeast Three-Hybrid
4.11. Transient Expression Assays
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schultink, A.; Qi, T.; Bally, J.; Staskawicz, B. Using forward genetics in Nicotiana benthamiana to uncover the immune signaling pathway mediating recognition of the Xanthomonas perforans effector XopJ4. New Phytol. 2019, 221, 1001–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klee, H.J.; Giovannoni, J.J. Genetics and control of tomato fruit ripening and quality attributes. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2011, 45, 41–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, G.R.; Munos, S.; Anderson, C.; Sim, S.C.; Michel, A.; Causse, M.; Gardener, B.B.; Francis, D.; van der Knaap, E. Distribution of SUN, OVATE, LC, and FAS in the tomato germplasm and the relationship to fruit shape diversity. Plant Physiol. 2011, 156, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munos, S.; Ranc, N.; Botton, E.; Berard, A.; Rolland, S.; Duffe, P.; Carretero, Y.; Le Paslier, M.C.; Delalande, C.; Bouzayen, M.; et al. Increase in tomato locule number is controlled by two single-nucleotide polymorphisms located near WUSCHEL. Plant Physiol. 2011, 156, 2244–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, B.; Barrero, L.S.; Tanksley, S.D. Regulatory change in YABBY-like transcription factor led to evolution of extreme fruit size during tomato domestication. Nat. Genet. 2008, 40, 800–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, H.; Jiang, N.; Schaffner, E.; Stockinger, E.J.; van der Knaap, E. A retrotransposon-mediated gene duplication underlies morphological variation of tomato fruit. Science 2008, 319, 1527–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Van Eck, J.; Cong, B.; Tanksley, S.D. A new class of regulatory genes underlying the cause of pear-shaped tomato fruit. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 13302–13306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Clevenger, J.P.; Illa-Berenguer, E.; Meulia, T.; van der Knaap, E.; Sun, L. A Comparison of sun, ovate, fs8.1 and Auxin Application on Tomato Fruit Shape and Gene Expression. Plant Cell Physiol. 2019, 60, 1067–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millar, A.H.; Whelan, J.; Soole, K.L.; Day, D.A. Organization and regulation of mitochondrial respiration in plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2011, 62, 79–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Lu, G.; Hou, Z.; Luo, Z.; Wang, T.; Li, H.; Zhang, J.; Ye, Z. Members of the tomato FRUITFULL MADS-box family regulate style abscission and fruit ripening. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 3005–3014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Shang, L.; Li, C.; Wang, W.; Wang, X.; Zhang, C.; Ai, G.; Ye, J.; Yang, C.; Li, H.; et al. Variation in the fruit development gene POINTED TIP regulates protuberance of tomato fruit tip. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 5940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Ji, Y.; Wang, K.; Li, J.; Zhu, G.; Ma, L.; Ostersetzer-Biran, O.; Zhu, B.; Fu, D.; Qu, G.; et al. RNA editing factor SlORRM2 regulates the formation of fruit pointed tips in tomato. Plant Physiol. 2024, 195, 2757–2771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gayathery, S.; Yuri, T.; Carlos, L.; Satomi, H.; Jacqueline, B.; José Ramón, B. Type B Heterotrimeric G Protein γ-Subunit Regulates Auxin and ABA Signaling in Tomato. Plant Physiol. 2015, 170, 1117–1134. [Google Scholar]
- Wenbin, K.; Juan, W.; Bin, L.; Ying, F.; Yu, Z.; Wenbo, Z.; Qian, L.; Ping, L. PYL9 is involved in the regulation of ABA signaling during tomato fruit ripening. J. Exp. Bot. 2019, 70, 6305–6319. [Google Scholar]
- Forsburg, S.L.; Guarente, L. Mutational analysis of upstream activation sequence 2 of the CYC1 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: A HAP2-HAP3-responsive site. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1988, 8, 647–654. [Google Scholar]
- Myers, Z.A.; Holt, B.R. NUCLEAR FACTOR-Y: Still complex after all these years? Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2018, 45, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Wu, D.; Kong, F.; Lin, K.; Zhang, H.; Li, G. The Arabidopsis thaliana Nuclear Factor Y Transcription Factors. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laloum, T.; De Mita, S.; Gamas, P.; Baudin, M.; Niebel, A. CCAAT-box binding transcription factors in plants: Y so many? Trends Plant Sci. 2013, 18, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantovani, R. The molecular biology of the CCAAT-binding factor NF-Y. Gene 1999, 239, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petroni, K.; Kumimoto, R.W.; Gnesutta, N.; Calvenzani, V.; Fornari, M.; Tonelli, C.; Holt, B.R.; Mantovani, R. The promiscuous life of plant NUCLEAR FACTOR Y transcription factors. Plant. Cell 2012, 24, 4777–4792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gusmaroli, G.; Tonelli, C.; Mantovani, R. Regulation of the CCAAT-Binding NF-Y subunits in Arabidopsis thaliana. Gene 2001, 264, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahle, J.; Baake, M.; Doenecke, D.; Albig, W. Subunits of the heterotrimeric transcription factor NF-Y are imported into the nucleus by distinct pathways involving importin beta and importin 13. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2005, 25, 5339–5354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romier, C.; Cocchiarella, F.; Mantovani, R.; Moras, D. The NF-YB/NF-YC structure gives insight into DNA binding and transcription regulation by CCAAT factor NF-Y. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 1336–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, K.; Ju, Z.; Cao, D.; Fu, D.; Zhu, H.; Zhu, B.; Luo, Y. Genome-wide analysis of tomato NF-Y factors and their role in fruit ripening. BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hackenberg, D.; Wu, Y.; Voigt, A.; Adams, R.; Schramm, P.; Grimm, B. Studies on differential nuclear translocation mechanism and assembly of the three subunits of the Arabidopsis thaliana transcription factor NF-Y. Mol. Plant 2012, 5, 876–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Kumimoto, R.W.; Siriwardana, C.L.; Risinger, J.R.; Holt, B.R. Identification and characterization of NF-Y transcription factor families in the monocot model plant Brachypodium distachyon. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e21805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirumurugan, T.; Ito, Y.; Kubo, T.; Serizawa, A.; Kurata, N. Identification, characterization and interaction of HAP family genes in rice. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2008, 279, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephenson, T.J.; McIntyre, C.L.; Collet, C.; Xue, G.P. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the NF-Y family of transcription factors in Triticum aestivum. Plant Mol. Biol. 2007, 65, 77–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, Z.A.; Kumimoto, R.W.; Siriwardana, C.L.; Gayler, K.K.; Risinger, J.R.; Pezzetta, D.; Holt, I.B. NUCLEAR FACTOR Y, Subunit C (NF-YC) Transcription Factors Are Positive Regulators of Photomorphogenesis in Arabidopsis thaliana. PLoS Genet. 2016, 12, e1006333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siriwardana, C.L.; Kumimoto, R.W.; Jones, D.S.; Holt, B.R. Gene Family Analysis of the Arabidopsis NF-YA Transcription Factors Reveals Opposing Abscisic Acid Responses During Seed Germination. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 2014, 32, 971–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Zhou, J.; Liu, C.; Liu, L.; Shen, L.; Yu, H. Nuclear factor Y-mediated H3K27me3 demethylation of the SOC1 locus orchestrates flowering responses of Arabidopsis. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumimoto, R.W.; Zhang, Y.; Siefers, N.; Holt, B.R. NF-YC3, NF-YC4 and NF-YC9 are required for CONSTANS-mediated, photoperiod-dependent flowering in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. 2010, 63, 379–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, A.; Kagaya, Y.; Toyoshima, R.; Kagaya, M.; Takeda, S.; Hattori, T. Arabidopsis NF-YB subunits LEC1 and LEC1-LIKE activate transcription by interacting with seed-specific ABRE-binding factors. Plant J. 2009, 58, 843–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumimoto, R.W.; Adam, L.; Hymus, G.J.; Repetti, P.P.; Reuber, T.L.; Marion, C.M.; Hempel, F.D.; Ratcliffe, O.J. The Nuclear Factor Y subunits NF-YB2 and NF-YB3 play additive roles in the promotion of flowering by inductive long-day photoperiods in Arabidopsis. Planta 2008, 228, 709–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Naim, O.; Eshed, R.; Parnis, A.; Teper-Bamnolker, P.; Shalit, A.; Coupland, G.; Samach, A.; Lifschitz, E. The CCAAT binding factor can mediate interactions between CONSTANS-like proteins and DNA. Plant J. 2006, 46, 462–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwong, R.W.; Bui, A.Q.; Lee, H.; Kwong, L.W.; Fischer, R.L.; Goldberg, R.B.; Harada, J.J. LEAFY COTYLEDON1-LIKE defines a class of regulators essential for embryo development. Plant Cell 2003, 15, 5–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotan, T.; Ohto, M.; Yee, K.M.; West, M.A.; Lo, R.; Kwong, R.W.; Yamagishi, K.; Fischer, R.L.; Goldberg, R.B.; Harada, J.J. Arabidopsis LEAFY COTYLEDON1 is sufficient to induce embryo development in vegetative cells. Cell 1998, 93, 1195–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baudin, M.; Laloum, T.; Lepage, A.; Ripodas, C.; Ariel, F.; Frances, L.; Crespi, M.; Gamas, P.; Blanco, F.A.; Zanetti, M.E.; et al. A Phylogenetically Conserved Group of Nuclear Factor-Y Transcription Factors Interact to Control Nodulation in Legumes. Plant Physiol. 2015, 169, 2761–2773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Liu, G.; Li, B.; Xie, Y.; Wei, Y.; Shang, S.; Tian, L.; Shi, H. Functional analysis of the heterotrimeric NF-Y transcription factor complex in cassava disease resistance. Ann. Bot. 2020, 124, 1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.M.; Tanaka, T.; Nakamura, H.; Ichikawa, H.; Kobayashi, K.; Yaeno, T.; Yamaoka, N.; Shimomoto, K.; Takayama, K.; Nishina, H.; et al. Overexpression of a rice heme activator protein gene (OsHAP2E) confers resistance to pathogens, salinity and drought, and increases photosynthesis and tiller number. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2015, 13, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Lian, H.; Liu, X.; Zhou, S.; Liu, S. The garlic NF-YC gene, AsNF-YC8, positively regulates non-ionic hyperosmotic stress tolerance in tobacco. Protoplasma 2017, 254, 1353–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Zhao, Y.; Zhuo, C.; Lu, S.; Guo, Z. Overexpression of a NF-YC transcription factor from bermudagrass confers tolerance to drought and salinity in transgenic rice. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2015, 13, 482–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephenson, T.J.; McIntyre, C.L.; Collet, C.; Xue, G.P. TaNF-YC11, one of the light-upregulated NF-YC members in Triticum aestivum, is co-regulated with photosynthesis-related genes. Funct. Integr. Genom. 2010, 10, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyoshi, K.; Ito, Y.; Serizawa, A.; Kurata, N. OsHAP3 genes regulate chloroplast biogenesis in rice. Plant J. 2003, 36, 532–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Li, G.; Li, C.; Zhang, C.; Cui, L.; Ai, G.; Wang, X.; Zheng, F.; Zhang, D.; Larkin, R.M.; et al. NF-Y plays essential roles in flavonoid biosynthesis by modulating histone modifications in tomato. New Phytol. 2021, 229, 3237–3252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Zhou, L.; Li, Y.; Hou, X. Temporal-Specific Interaction of NF-YC and CURLY LEAF during the Floral Transition Regulates Flowering. Plant Physiol. 2018, 177, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Xu, J.; Guo, H.; Jiang, L.; Chen, S.; Yu, C.; Zhou, Z.; Hu, P.; Zhai, H.; Wan, J. DTH8 suppresses flowering in rice, influencing plant height and yield potential simultaneously. Plant Physiol. 2010, 153, 1747–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardini, M.; Gnesutta, N.; Donati, G.; Gatta, R.; Forni, C.; Fossati, A.; Vonrhein, C.; Moras, D.; Romier, C.; Bolognesi, M.; et al. Sequence-specific transcription factor NF-Y displays histone-like DNA binding and H2B-like ubiquitination. Cell 2013, 152, 132–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha, S.; Kim, I.S.; Sohn, K.Y.; de Crombrugghe, B.; Maity, S.N. Three classes of mutations in the A subunit of the CCAAT-binding factor CBF delineate functional domains involved in the three-step assembly of the CBF-DNA complex. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1996, 16, 328–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chaves-Sanjuan, A.; Gnesutta, N.; Gobbini, A.; Martignago, D.; Bernardini, A.; Fornara, F.; Mantovani, R.; Nardini, M. Structural determinants for NF-Y subunit organization and NF-Y/DNA association in plants. Plant J. 2021, 105, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maity, S.N.; Vuorio, T.; de Crombrugghe, B. The B subunit of a rat heteromeric CCAAT-binding transcription factor shows a striking sequence identity with the yeast Hap2 transcription factor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 5378–5382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olesen, J.T.; Guarente, L. The HAP2 subunit of yeast CCAAT transcriptional activator contains adjacent domains for subunit association and DNA recognition: Model for the HAP2/3/4 complex. Genes. Dev. 1990, 4, 1714–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, D.; Murray, J.A.; Smith, A.G. Multiple genes encoding the conserved CCAAT-box transcription factor complex are expressed in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 1998, 117, 1015–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gusmaroli, G.; Tonelli, C.; Mantovani, R. Regulation of novel members of the Arabidopsis thaliana CCAAT-binding nuclear factor Y subunits. Gene 2002, 283, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maity, S.N.; de Crombrugghe, B. Role of the CCAAT-binding protein CBF/NF-Y in transcription. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1998, 23, 174–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Hu, P.; Huang, M.; Tang, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, L.; Hou, X. The NF-YC-RGL2 module integrates GA and ABA signalling to regulate seed germination in Arabidopsis. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinozaki, Y.; Hao, S.; Kojima, M.; Sakakibara, H.; Ozeki-Iida, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Fei, Z.; Zhong, S.; Giovannoni, J.J.; Rose, J.K.; et al. Ethylene suppresses tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) fruit set through modification of gibberellin metabolism. Plant J. 2015, 83, 237–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, S.; Liu, Q.; Wu, K.; Zhang, J.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, C.; et al. The OsSPL16-GW7 regulatory module determines grain shape and simultaneously improves rice yield and grain quality. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 949–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Liberatore, K.L.; MacAlister, C.A.; Huang, Z.; Chu, Y.H.; Jiang, K.; Brooks, C.; Ogawa-Ohnishi, M.; Xiong, G.; Pauly, M.; et al. A cascade of arabinosyltransferases controls shoot meristem size in tomato. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 784–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Liu, X.; Engstrom, E.M.; Nimchuk, Z.L.; Pruneda-Paz, J.L.; Tarr, P.T.; Yan, A.; Kay, S.A.; Meyerowitz, E.M. Control of plant stem cell function by conserved interacting transcriptional regulators. Nature 2015, 517, 377–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brummell, D.A.; Dal Cin, V.; Crisosto, C.H.; Labavitch, J.M. Cell wall metabolism during maturation, ripening and senescence of peach fruit. J. Exp. Bot. 2004, 55, 2029–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brummell, D.A.; Harpster, M.H. Cell wall metabolism in fruit softening and quality and its manipulation in transgenic plants. Plant Mol. Biol. 2001, 47, 311–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavrova, V.V.; Zinovieva, S.V.; Udalova, Z.V.; Matveeva, E.M. Expression of PR genes in tomato tissues infected by nematode Meloidogyne incognita (Kofoid et White, 1919) Chitwood, 1949. Dokl. Biochem. Biophys. 2017, 476, 306–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, B.; Luo, Q.; Shen, Y.; Wei, L.; Song, X.; Liao, H.; Ni, L.; Shen, T.; Du, X.; Han, J.; et al. Coordinated regulation of vegetative phase change by brassinosteroids and the age pathway in Arabidopsis. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Huang, J. OsNF-YA3 regulates plant growth and osmotic stress tolerance by interacting with SLR1 and SAPK9 in rice. Plant J. 2023, 114, 914–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.; Shen, H.; Gao, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Xie, Q.; Wu, T.; Chen, G.; Hu, Z. Overexpression of SlCRF6 in tomato inhibits leaf development and affects plant morphology. Plant Sci. 2024, 338, 111921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, Z.; Long, T.; Guo, P.; Luo, J.; Nie, X.; Xie, Q.; Chen, G.; Hu, Z. The Nuclear Transcription Factor SlNF-YC9 Regulates the Protrusion of Tomato Fruit Tip. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6511. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136511
Gao Z, Long T, Guo P, Luo J, Nie X, Xie Q, Chen G, Hu Z. The Nuclear Transcription Factor SlNF-YC9 Regulates the Protrusion of Tomato Fruit Tip. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(13):6511. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136511
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Zihan, Ting Long, Pengyu Guo, Junjie Luo, Xiaoqian Nie, Qiaoli Xie, Guoping Chen, and Zongli Hu. 2025. "The Nuclear Transcription Factor SlNF-YC9 Regulates the Protrusion of Tomato Fruit Tip" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 13: 6511. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136511
APA StyleGao, Z., Long, T., Guo, P., Luo, J., Nie, X., Xie, Q., Chen, G., & Hu, Z. (2025). The Nuclear Transcription Factor SlNF-YC9 Regulates the Protrusion of Tomato Fruit Tip. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(13), 6511. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136511





