Preclinical In Vitro Evaluation of Extracellular Vesicles from Human Dental Pulp Stem Cells for the Safe and Selective Modulation of Anaplastic Thyroid Carcinoma
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Distribution, Particle Concentration, and Protein Content of hDPSC-EVs
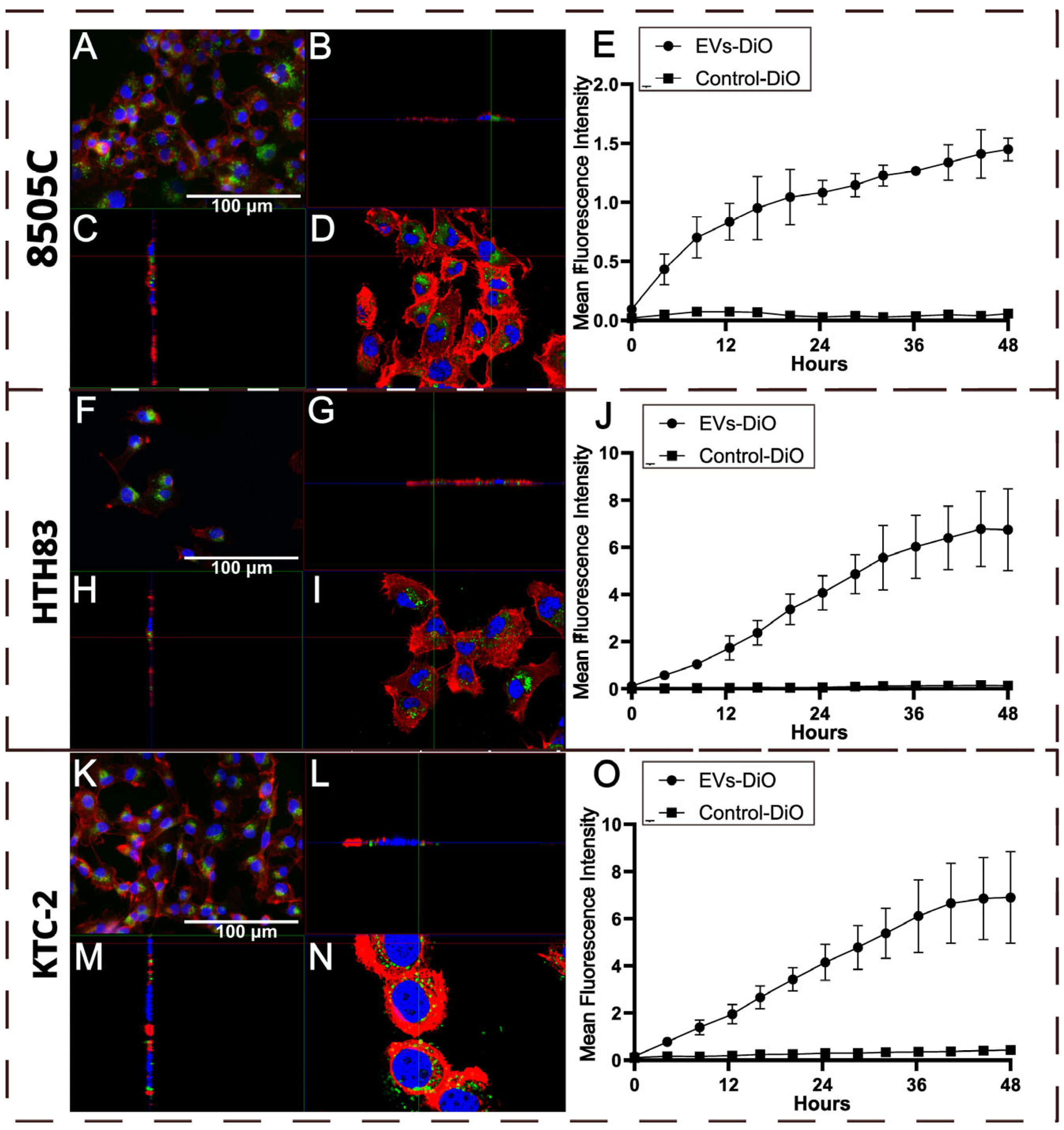
2.2. Uptake of hDPSC-EVs by ATC Cell Lines
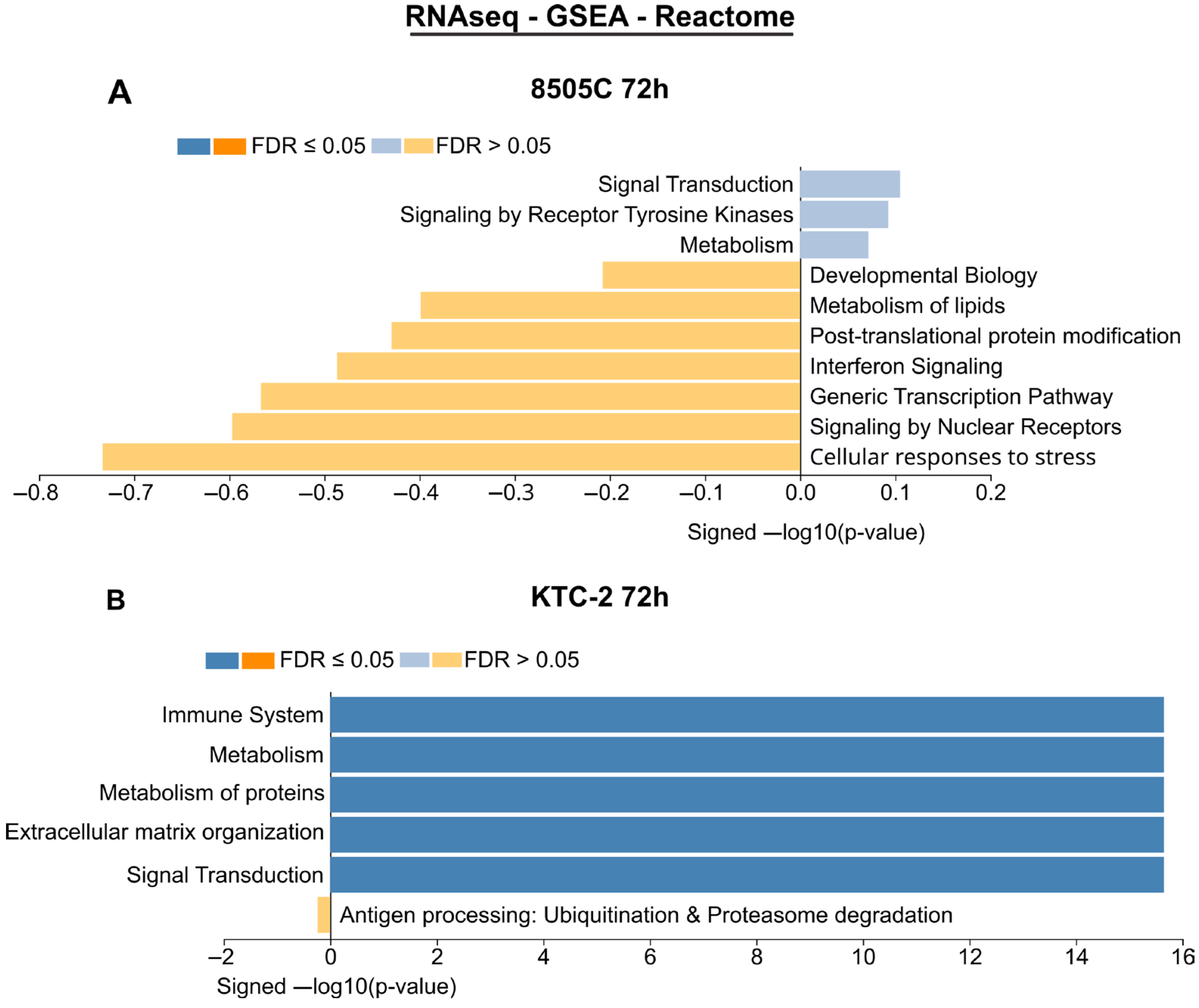
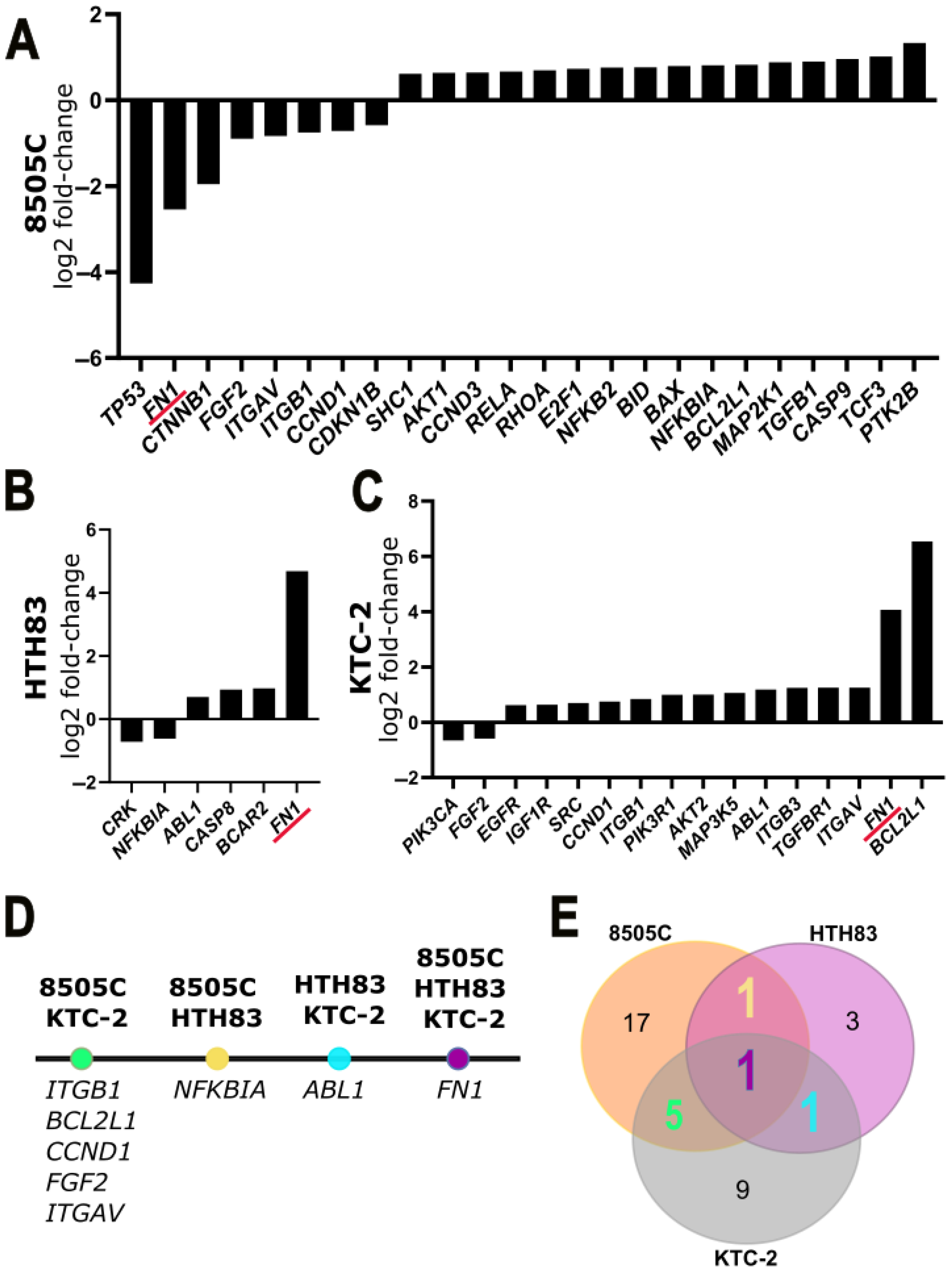
2.3. Transcriptomic Results of RNA Sequencing and qPCR Array
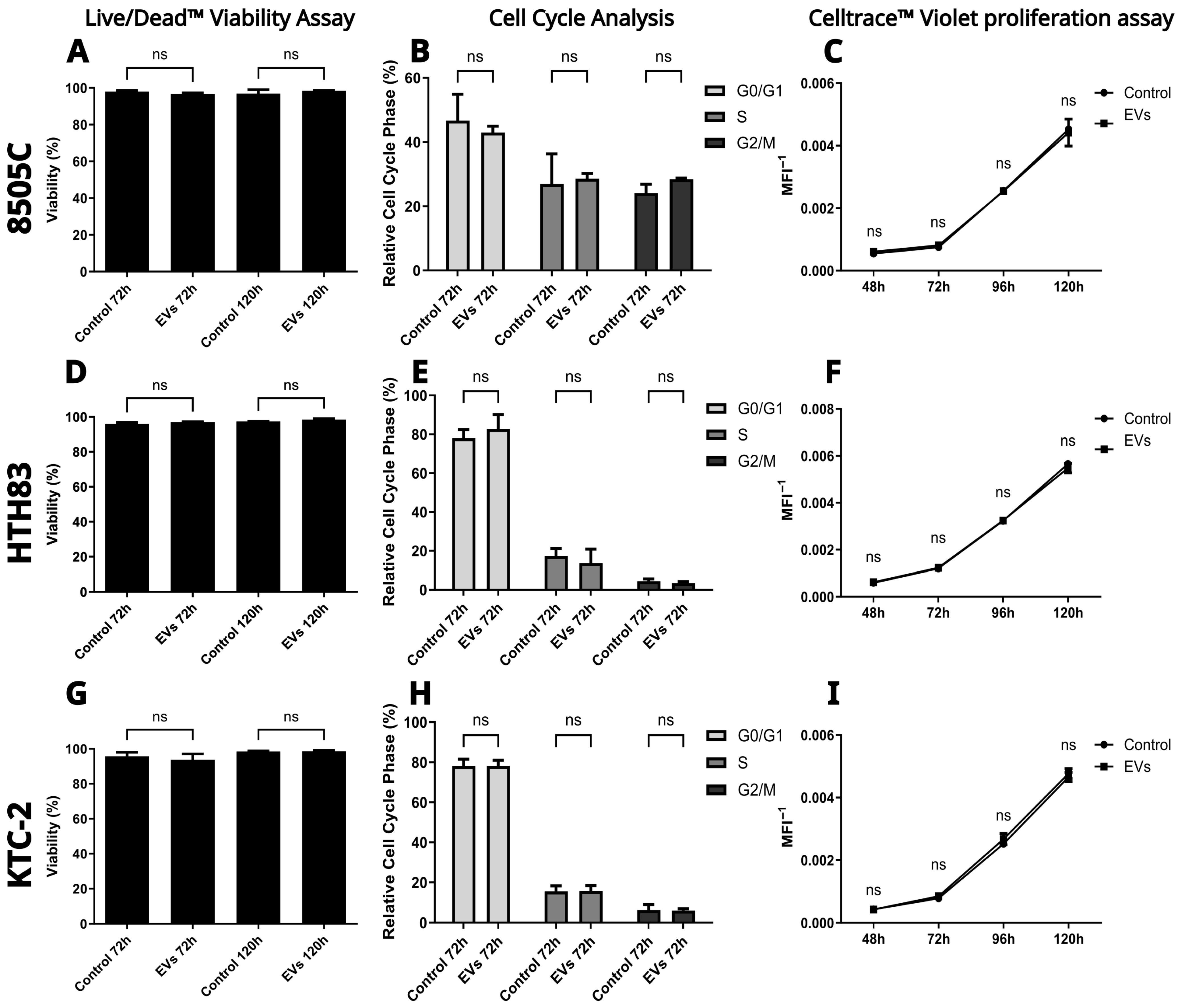
2.4. hDPSC-EVs Do Not Alter Viability, Cell Cycle Progression, or Proliferation in ATC Cell Lines
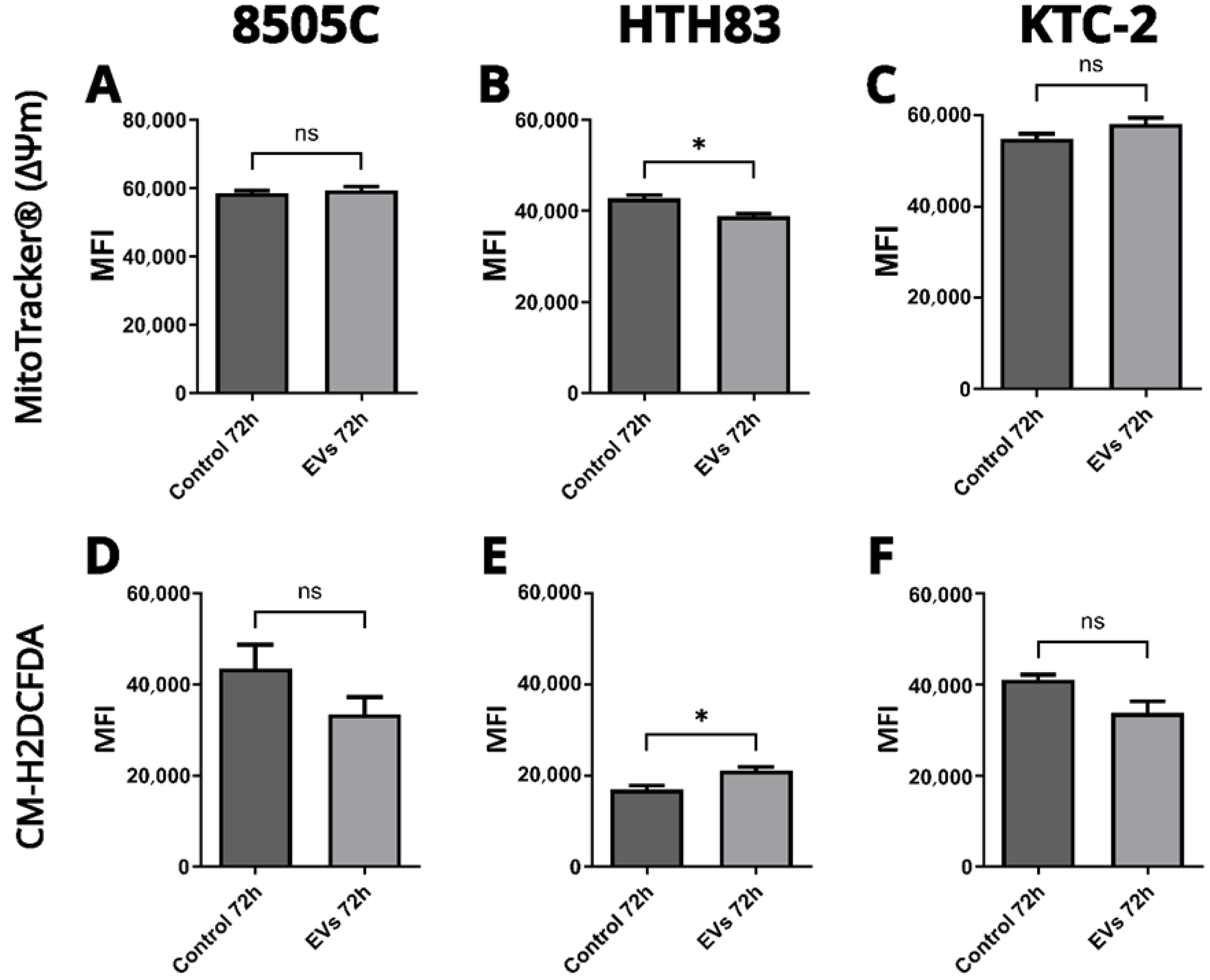
2.5. Effects on Mitochondrial Function and ROS Production
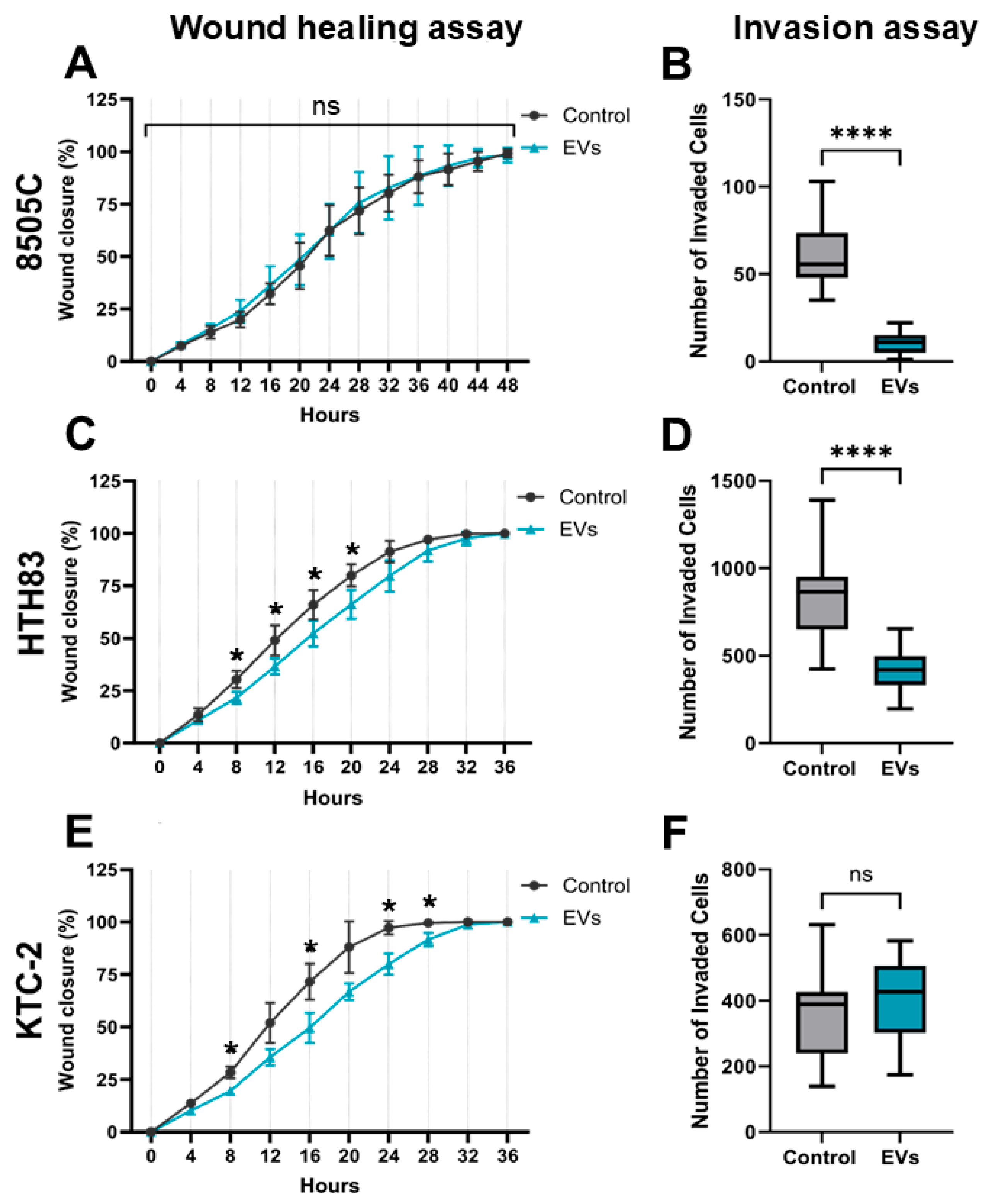
2.6. Inhibition of Migration and Invasion by hDPSC-EVs in ATC Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture Conditions and Treatments
4.2. Human Dental Pulp Stem Cells’ Culture and Characterization
4.3. Conditioned Medium Collection and hDPSC-EV Isolation
4.4. Determination of Size Distribution, Concentration, and Protein Mass-Relative of hDPSC-EVs
4.5. Fluorescent Labeling of EVs
4.6. Uptake Assay by Fluorescence Microscopy and Confocal Microscopy
4.7. Time-Lapse Confocal Microscopy Uptake Assay
4.8. RNA Extraction and Quality Control
4.9. Total RNA Sequencing
4.10. cDNA Synthesis and qPCR Arrays
4.11. Live/Dead™ Viability Assay
4.12. Cell Proliferation Assessment Using the CellTrace™ Violet Assay
4.13. Cell Cycle Assessment
4.14. Cell Metabolism Assessment
4.15. Migration Assessment
4.16. Invasion Assay
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ATC | Anaplastic Thyroid Carcinoma |
| DAPI | 4′,6-Diamidino-2-phenylindole |
| DEG(s) | Differentially Expressed Gene(s) |
| EV(s) | Extracellular Vesicle(s) |
| FBS | Fetal Bovine Serum |
| FDR | False Discovery Rate |
| GSEA | Gene Set Enrichment Analysis |
| hDPSCs | Human Dental Pulp Stem Cells |
| hDPSC-EV(s) | Extracellular Vesicle(s) Derived from Human Dental Pulp Stem Cells |
| MAPK | Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase |
| MFI | Mean Fluorescence Intensity |
| MSC-EVs | Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles |
| NTA | Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis |
| PBS | Phosphate-Buffered Saline |
| PI | Propidium Iodide |
| qPCR | Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction |
| RNA-seq | RNA Sequencing |
| ROS | Reactive Oxygen Species |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
| ΔΨm | Mitochondrial Membrane Potential |
References
- Molinaro, E.; Romei, C.; Biagini, A.; Sabini, E.; Agate, L.; Mazzeo, S.; Materazzi, G.; Sellari-Franceschini, S.; Ribechini, A.; Torregrossa, L.; et al. Anaplastic Thyroid Carcinoma: From Clinicopathology to Genetics and Advanced Therapies. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2017, 13, 644–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bible, K.C.; Kebebew, E.; Brierley, J.; Brito, J.P.; Cabanillas, M.E.; Clark, T.J.; Di Cristofano, A.; Foote, R.; Giordano, T.; Kasperbauer, J.; et al. 2021 American Thyroid Association Guidelines for Management of Patients with Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer. Thyroid 2021, 31, 337–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Pang, H. Combination of Novel Therapies and New Attempts in Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2023, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Leo, S.; Trevisan, M.; Fugazzola, L. Recent Advances in the Management of Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer. Thyroid Res. 2020, 13, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrari, S.M.; Elia, G.; Ragusa, F.; Ruffilli, I.; La Motta, C.; Paparo, S.R.; Patrizio, A.; Vita, R.; Benvenga, S.; Materazzi, G.; et al. Novel Treatments for Anaplastic Thyroid Carcinoma. Gland Surg. 2020, 9, S28–S42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Tan, J.; Wu, B.; Wu, R.; Han, Y.; Wang, C.; Gao, Z.; Jiang, D.; Xia, X. Customizing Cancer Treatment at the Nanoscale: A Focus on Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer Therapy. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2023, 21, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uppalapati, S.S.; Guha, L.; Kumar, H.; Mandoli, A. Nanotechnological Advancements for the Theranostic Intervention in Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer: Current Perspectives and Future Direction. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2024, 24, 245–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Gong, H.; Luo, S.; Cui, Y. The Role of Exosomes and Their Applications in Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Zeng, S.; Gong, Z.; Yan, Y. Exosome-Based Immunotherapy: A Promising Approach for Cancer Treatment. Mol. Cancer 2020, 19, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Z.; Zhang, B.; Wu, C.; Yu, F.; Han, B.; Li, B.; Li, L. Therapeutic Roles of Mesenchymal Stem Cell—Derived Extracellular Vesicles in Cancer. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 14, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Li, N.; Li, Y.; Hou, S.; Zhang, W.; Meng, Z.; Wang, S.; Jia, Q.; Tan, J.; Wang, R.; et al. Engineering a HEK-293T Exosome-Based Delivery Platform for Efficient Tumor-Targeting Chemotherapy/Internal Irradiation Combination Therapy. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2022, 20, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gangadaran, P.; Li, X.J.; Kalimuthu, S.k.; Min, O.J.; Hong, C.M.; Rajendran, R.L.; Lee, H.W.; Zhu, L.; Baek, S.H.; Jeong, S.Y.; et al. New Optical Imaging Reporter-Labeled Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer-Derived Extracellular Vesicles as a Platform for In Vivo Tumor Targeting in a Mouse Model. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, J.; Hou, X.; Hao, J.; Zhang, W.; Shi, Y.; Huang, Y.; Ruan, X.; Zheng, X.; Gao, M. METTL3 Inhibition Induced by M2 Macrophage-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Drives Anti-PD-1 Therapy Resistance via M6A-CD70-Mediated Immune Suppression in Thyroid Cancer. Cell Death Differ. 2023, 30, 2265–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cecchin, R.; Troyer, Z.; Witwer, K.; Morris, K.V. Extracellular Vesicles: The next Generation in Gene Therapy Delivery. Mol. Ther. 2023, 31, 1225–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunartvanichkul, T.; Arayapisit, T.; Sangkhamanee, S.S.; Chaweewannakorn, C.; Iwasaki, K.; Klaihmon, P.; Sritanaudomchai, H. Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes from Human Exfoliated Deciduous Teeth Promote Angiogenesis in Hyperglycemic-Induced Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells. J. Appl. Oral Sci. 2023, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Li, X.; Yin, Y.; He, X.-T.; An, Y.; Tian, B.-M.; Hong, Y.-L.; Wu, L.-A.; Chen, F.-M. The Proangiogenic Effects of Extracellular Vesicles Secreted by Dental Pulp Stem Cells Derived from Periodontally Compromised Teeth. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2020, 11, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umar, S.; Debnath, K.; Leung, K.; Huang, C.-C.; Lu, Y.; Gajendrareddy, P.; Ravindran, S. Immunomodulatory Properties of Naïve and Inflammation-Informed Dental Pulp Stem Cell Derived Extracellular Vesicles. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1447536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landa, I.; Pozdeyev, N.; Korch, C.; Marlow, L.A.; Smallridge, R.C.; Copland, J.A.; Henderson, Y.C.; Lai, S.Y.; Clayman, G.L.; Onoda, N.; et al. Comprehensive Genetic Characterization of Human Thyroid Cancer Cell Lines: A Validated Panel for Preclinical Studies. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 3141–3151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadowski, S.M.; Boufraqech, M.; Zhang, L.; Mehta, A.; Kapur, P.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Shen, M.; Kebebew, E. Torin2 Targets Dysregulated Pathways in Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer and Inhibits Tumor Growth and Metastasis. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 18038–18049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozorg-Ghalati, F.; Hedayati, M. Molecular Biomarkers of Anaplastic Thyroid Carcinoma. Curr. Mol. Med. 2017, 17, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.; Mo, J.; Dong, S.; Liao, Z.; Zhang, B.; Zhu, P. Integrinβ-1 in Disorders and Cancers: Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Targets. Cell Commun. Signal. 2024, 22, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, X.; Liu, C.; Zhang, T.; Zhu, Y.; Dong, X.; Xue, P. Down-regulation of FN1 Inhibits Colorectal Carcinogenesis by Suppressing Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion. J. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 119, 4717–4728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Chen, H.; Jiang, Z.; Lin, Y.; Wang, X.; Xiang, J.; Peng, J. Integrin Subunit Alpha V Promotes Growth, Migration, and Invasion of Gastric Cancer Cells. Pathol.-Res. Pract. 2019, 215, 152531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.K.; Yun, S.J.; Ha, J.M.; Kim, Y.W.; Jin, I.H.; Yun, J.; Shin, H.K.; Song, S.H.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, J.S.; et al. Selective Activation of Akt1 by Mammalian Target of Rapamycin Complex 2 Regulates Cancer Cell Migration, Invasion, and Metastasis. Oncogene 2011, 30, 2954–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, W.; Chen, L.; Feng, C.; Liang, T. CircMYLK Promotes the Growth, Migration, Invasion, and Survival of Bladder Cancer Cells by Upregulating CCND3 Level via Competitively Binding to MiR-34a. Drug Dev. Res. 2021, 82, 1206–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.-X.; Lu, J.-M.; Mo, R.-J.; He, H.-C.; Xie, J.; Jiang, F.-N.; Lin, Z.-Y.; Chen, Y.-R.; Wu, Y.-D.; Luo, H.-W.; et al. E2F1 Promotes Tumor Cell Invasion and Migration through Regulating CD147 in Prostate Cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2016, 48, 1650–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Shen, Z. FN1 Promotes Thyroid Carcinoma Cell Proliferation and Metastasis by Activating the NF-Κb Pathway. Protein Pept. Lett. 2023, 30, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gule, M.K.; Chen, Y.; Sano, D.; Frederick, M.J.; Zhou, G.; Zhao, M.; Milas, Z.L.; Galer, C.E.; Henderson, Y.C.; Jasser, S.A.; et al. Targeted Therapy of VEGFR2 and EGFR Significantly Inhibits Growth of Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer in an Orthotopic Murine Model. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 2281–2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Tang, J.; Zhuang, X.; Zhuang, Y.; Cheng, W.; Chen, W.; Yao, H.; Zhang, S. MiR-196a Promotes Pancreatic Cancer Progression by Targeting Nuclear Factor Kappa-B-Inhibitor Alpha. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e87897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuda, M.; Tanaka, S. Roles for Crk in Cancer Metastasis and Invasion. Genes Cancer 2012, 3, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, M.R.; Alievi, A.L.; da Costa, V.R.; Kerkis, I.; Araldi, R.P. Exploring the Therapeutic Potential of Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Human Immature Dental Pulp Cells on Papillary Thyroid Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 8178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ying, H.; Lin, F.; Ding, R.; Wang, W.; Hong, W. Extracellular Vesicles Carrying MiR-193a Derived from Mesenchymal Stem Cells Impede Cell Proliferation, Migration and Invasion of Colon Cancer by Downregulating FAK. Exp. Cell Res. 2020, 394, 112144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Jiang, L.; Liu, Q. MiR-18a-5p Derived from Mesenchymal Stem Cells-Extracellular Vesicles Inhibits Ovarian Cancer Cell Proliferation, Migration, Invasion, and Chemotherapy Resistance. J. Transl. Med. 2022, 20, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Wu, F. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Transfer MiR-598 to Inhibit the Growth and Metastasis of Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer by Targeting THBS2. Cell Death Discov. 2023, 9, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerkis, I.; Kerkis, A.; Dozortsev, D.; Stukart-Parsons, G.C.; Gomes Massironi, S.M.; Pereira, L.V.; Caplan, A.I.; Cerruti, H.F. Isolation and Characterization of a Population of Immature Dental Pulp Stem Cells Expressing OCT-4 and Other Embryonic Stem Cell Markers. Cells Tissues Organs 2007, 184, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, R.L.; Paudel, S.; Gangadaran, P.; Oh, J.M.; Oh, E.J.; Hong, C.M.; Lee, S.; Chung, H.Y.; Lee, J.; Ahn, B.-C. Extracellular Vesicles Act as Nano-Transporters of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors to Revert Iodine Avidity in Thyroid Cancer. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pijuan, J.; Barceló, C.; Moreno, D.F.; Maiques, O.; Sisó, P.; Marti, R.M.; Macià, A.; Panosa, A. In Vitro Cell Migration, Invasion, and Adhesion Assays: From Cell Imaging to Data Analysis. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2019, 7, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alievi, A.L.; Teixeira, M.R.; da Costa, V.R.; Kerkis, I.; Araldi, R.P. Preclinical In Vitro Evaluation of Extracellular Vesicles from Human Dental Pulp Stem Cells for the Safe and Selective Modulation of Anaplastic Thyroid Carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6443. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136443
Alievi AL, Teixeira MR, da Costa VR, Kerkis I, Araldi RP. Preclinical In Vitro Evaluation of Extracellular Vesicles from Human Dental Pulp Stem Cells for the Safe and Selective Modulation of Anaplastic Thyroid Carcinoma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(13):6443. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136443
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlievi, Anderson Lucas, Michelli Ramires Teixeira, Vitor Rodrigues da Costa, Irina Kerkis, and Rodrigo Pinheiro Araldi. 2025. "Preclinical In Vitro Evaluation of Extracellular Vesicles from Human Dental Pulp Stem Cells for the Safe and Selective Modulation of Anaplastic Thyroid Carcinoma" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 13: 6443. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136443
APA StyleAlievi, A. L., Teixeira, M. R., da Costa, V. R., Kerkis, I., & Araldi, R. P. (2025). Preclinical In Vitro Evaluation of Extracellular Vesicles from Human Dental Pulp Stem Cells for the Safe and Selective Modulation of Anaplastic Thyroid Carcinoma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(13), 6443. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136443



