Assessment of Abuse Potential of Three Indazole-Carboxamide Synthetic Cannabinoids 5F-ADB, MDMB-4en-PINACA and ADB-4en-PINACA
Abstract
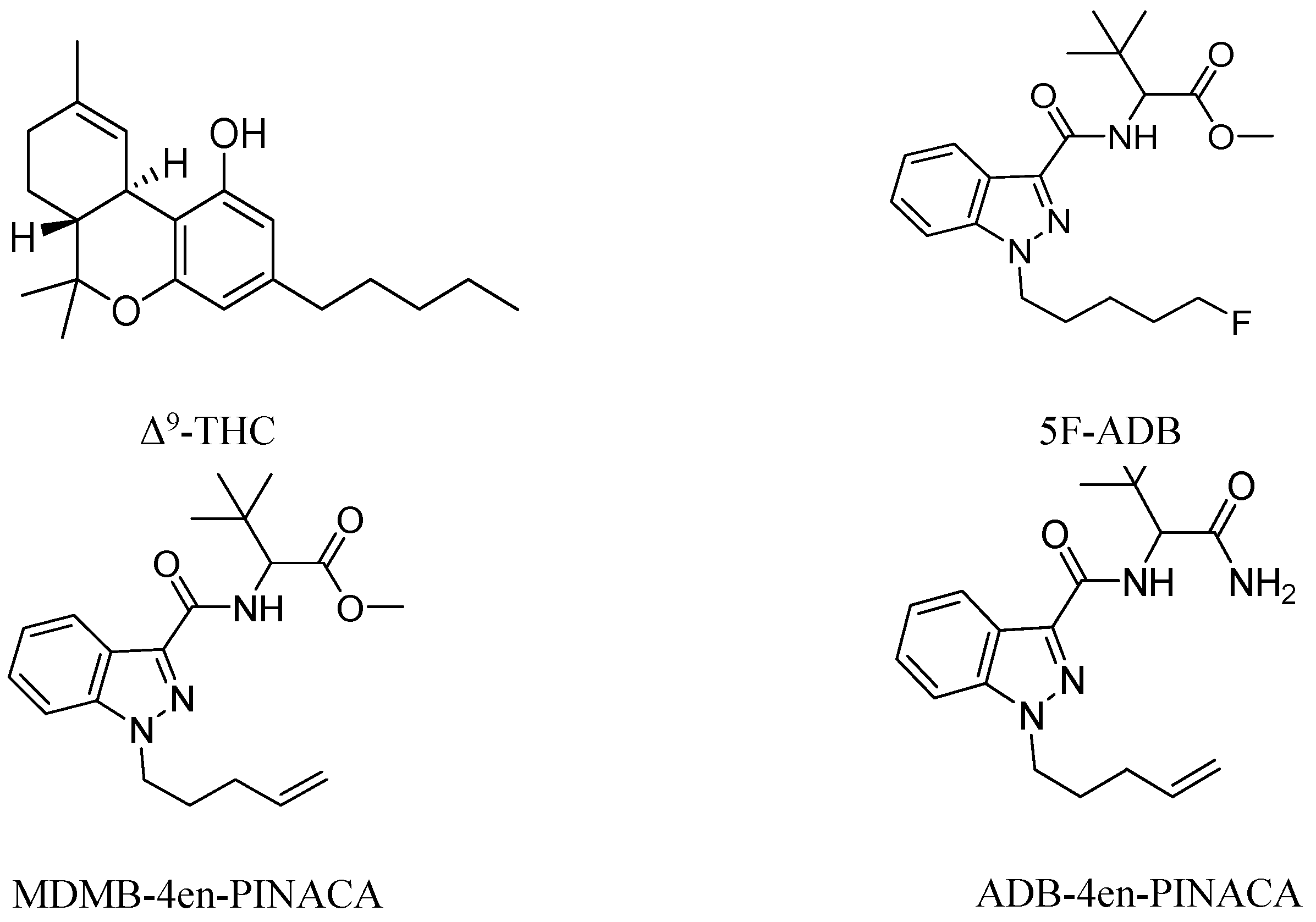
1. Introduction
2. Results
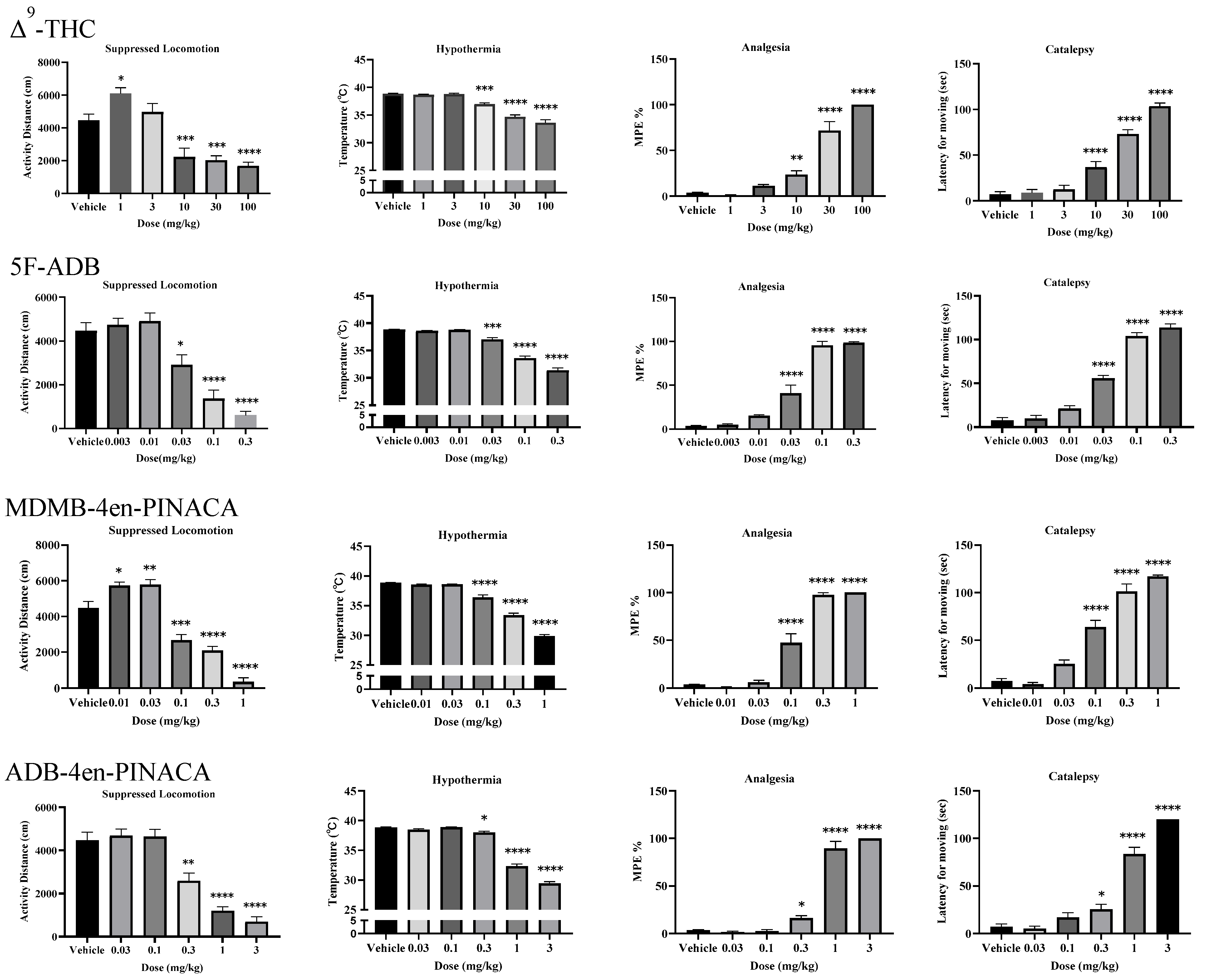
2.1. Three SCs Induced Tetrad Effects
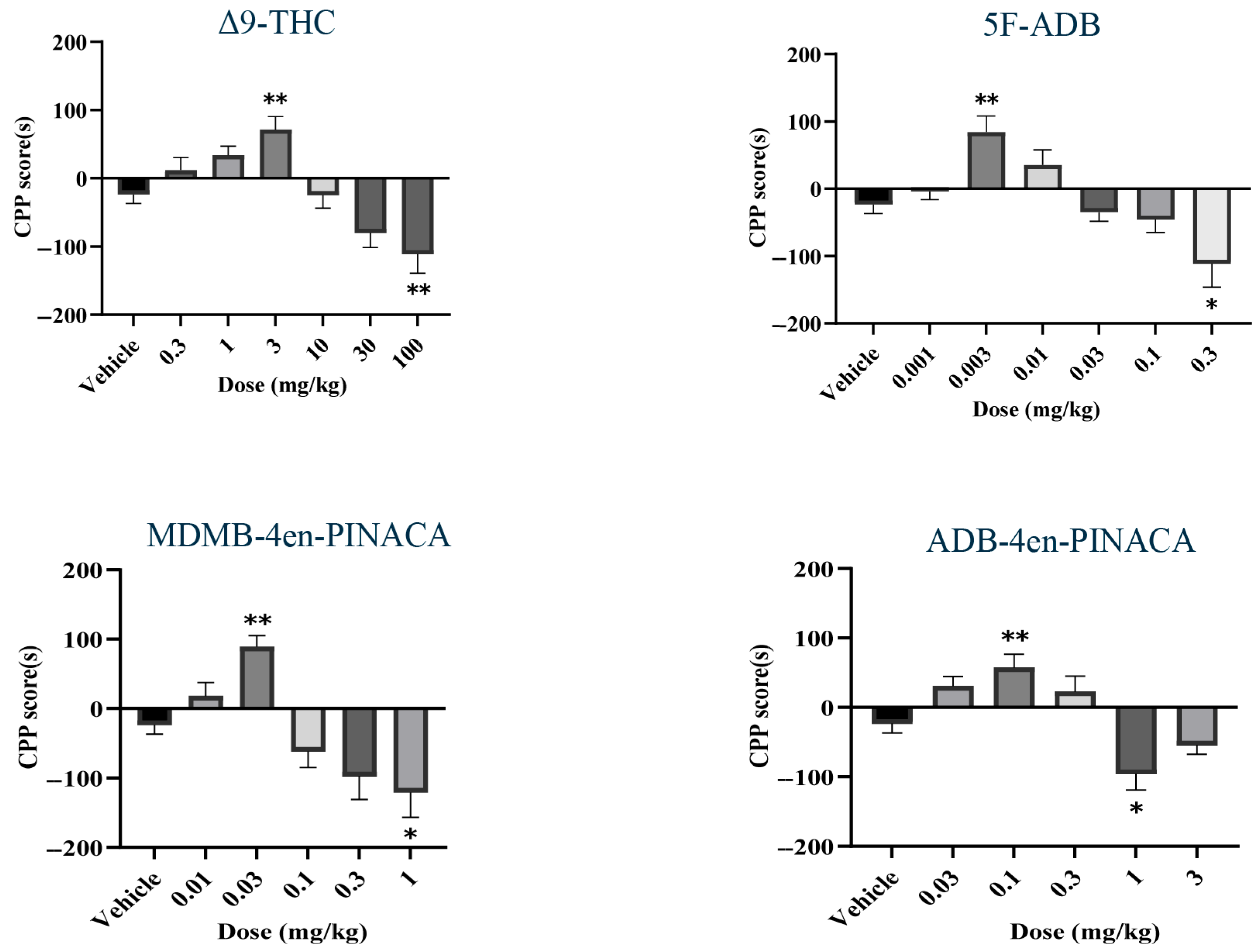
2.2. Drug-Induced CPP
2.3. Evaluation of Drug Withdrawal
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Drugs
4.3. Tetrad Assay
4.3.1. Locomotor Activity
4.3.2. Body Temperature
4.3.3. Analgesia
4.3.4. Catalepsy
4.4. CPP Paradigm
4.4.1. The Pre-Conditioning Test (Day 1)
4.4.2. Drug Conditioning (Days 2–11)
4.4.3. The Post-Conditioning Test (Day 12)
4.5. Precipitated Withdrawal Assay
4.6. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wilson, C.D.; Hiranita, T.; Fantegrossi, W.E. Cannabimimetic Effects of Abused Indazole-Carboxamide Synthetic Cannabinoid Receptor Agonists Ab-Pinaca, 5f-Ab-Pinaca and 5f-Adb-Pinaca in Mice: Tolerance, Dependence and Withdrawal. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2022, 236, 109468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatch, M.B.; Tourigny, A.; Shetty, R.A.; Forster, M.J. Behavioral Pharmacology of Five Novel Synthetic Cannabinoids. Behav. Pharmacol. 2022, 33, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, G.; Kuzma, M.; Mayer, M.; Petrus, K.; Tóth, D. Fatal Overdose with the Cannabinoid Receptor Agonists Mdmb-4en-Pinaca and 4f-Abutinaca: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. Toxics 2023, 11, 673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Errico, S.; Zanon, M.; Radaelli, D.; Concato, M.; Padovano, M.; Scopetti, M.; Frati, P.; Fineschi, V. Acute Kidney Injury (Aki) in Young Synthetic Cannabinoids Abusers. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lapoint, J.; James, L.P.; Moran, C.L.; Nelson, L.S.; Hoffman, R.S.; Moran, J.H. Severe Toxicity Following Synthetic Cannabinoid Ingestion. Clin. Toxicol. 2011, 49, 760–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malik, K.; Kommana, S.; Paul, J.; Krakauer, M. Synthetic Cannabinoid Induced Ocular Self-Injury. Orbit 2021, 40, 326–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermanns-Clausen, M.; Kneisel, S.; Szabo, B.; Auwärter, V. Acute Toxicity Due to the Confirmed Consumption of Synthetic Cannabinoids: Clinical and Laboratory Findings. Addiction 2013, 108, 534–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alon, M.H.; Saint-Fleur, M.O. Synthetic Cannabinoid Induced Acute Respiratory Depression: Case Series and Literature Review. Respir. Med. Case Rep. 2017, 22, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pineda Garcia, J.C.; Li, R.S.; Kikura-Hanajiri, R.; Tanaka, Y.; Ishii, Y. Timeframe Analysis of Novel Synthetic Cannabinoids Effects: A Study on Behavioral Response and Endogenous Cannabinoids Disruption. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 3083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaunitz, F.; Andresen-Streichert, H. Correction To: Analytical Findings in a Non-Fatal Intoxication with the Synthetic Cannabinoid 5f-Adb (5f-Mdmb-Pinaca): A Case Report. Int. J. Leg. Med. 2023, 137, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groth, O.; Roider, G.; Angerer, V.; Schäper, J.; Graw, M.; Musshoff, F.; Auwärter, V. “Spice”-Related Deaths in and around Munich, Germany: A Retrospective Look at the Role of Synthetic Cannabinoid Receptor Agonists in Our Post-Mortem Cases over a Seven-Year Period (2014–2020). Int. J. Leg. Med. 2023, 137, 1059–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boland, D.M.; Reidy, L.J.; Seither, J.M.; Radtke, J.M.; Lew, E.O. Forty-Three Fatalities Involving the Synthetic Cannabinoid, 5-Fluoro-Adb: Forensic Pathology and Toxicology Implications. J. Forensic Sci. 2020, 65, 170–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabanlong, C.V.; Russell, L.N.; Fantegrossi, W.E.; Prather, P.L. Metabolites of Synthetic Cannabinoid 5f-Mdmb-Pinaca Retain Affinity, Act as High Efficacy Agonists and Exhibit Atypical Pharmacodynamic Properties at Cb1 Receptors. Toxicol. Sci. 2022, 187, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banister, S.D.; Longworth, M.; Kevin, R.; Sachdev, S.; Santiago, M.; Stuart, J.; Mack, J.B.; Glass, M.; McGregor, I.S.; Connor, M.; et al. Pharmacology of Valinate and Tert-Leucinate Synthetic Cannabinoids 5f-Ambica, 5f-Amb, 5f-Adb, Amb-Fubinaca, Mdmb-Fubinaca, Mdmb-Chmica, and Their Analogues. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2016, 7, 1241–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lie, W.; Cheong, E.J.Y.; Goh, E.M.L.; Moy, H.Y.; Cannaert, A.; Stove, C.P.; Chan, E.C.Y. Diagnosing Intake and Rationalizing Toxicities Associated with 5f-Mdmb-Pinaca and 4f-Mdmb-Binaca Abuse. Arch. Toxicol. 2021, 95, 489–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonides, L.H.; Cannaert, A.; Norman, C.; Vives, L.; Harrison, A.; Costello, A.; Daeid, N.N.; Stove, C.P.; Sutcliffe, O.B.; McKenzie, C. Enantiospecific Synthesis, Chiral Separation, and Biological Activity of Four Indazole-3-Carboxamide-Type Synthetic Cannabinoid Receptor Agonists and Their Detection in Seized Drug Samples. Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatch, M.B.; Forster, M.J. Cannabinoid-Like Effects of Five Novel Carboxamide Synthetic Cannabinoids. Neurotoxicology 2019, 70, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asaoka, N.; Kawai, H.; Nishitani, N.; Kinoshita, H.; Shibui, N.; Nagayasu, K.; Shirakawa, H.; Kaneko, S. A New Designer Drug 5f-Adb Activates Midbrain Dopaminergic Neurons but Not Serotonergic Neurons. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2016, 41, 813–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannaert, A.; Sparkes, E.; Pike, E.; Luo, J.L.; Fang, A.; Kevin, R.C.; Ellison, R.; Gerona, R.; Banister, S.D.; Stove, C.P. Synthesis and in Vitro Cannabinoid Receptor 1 Activity of Recently Detected Synthetic Cannabinoids 4f-Mdmb-Bica, 5f-Mpp-Pica, Mmb-4en-Pica, Cumyl-Cbmica, Adb-Binaca, App-Binaca, 4f-Mdmb-Binaca, Mdmb-4en-Pinaca, a-Chminaca, 5f-Ab-P7aica, 5f-Mdmb-P7aica, and 5f-Ap7aica. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2020, 11, 4434–4446. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, K.; Qin, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Xin, G.; Shi, B.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Lu, J. Metabolic Profiles and Screening Tactics for Mdmb-4en-Pinaca in Human Urine and Serum Samples. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2022, 220, 114985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction and Europol. EMCDDA Technical Report on the New Psychoactive Substance Methyl 3,3-dimethyl-2-{[1-(pent-4-en-1-yl)-1H-indazole-3-carbonyl]amino}butanoate (MDMB-4en-PINACA); EMCDDA: Lisbon, Portugal, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Krotulski, A.J.; Cannaert, A.; Stove, C.; Logan, B.K. The Next Generation of Synthetic Cannabinoids: Detection, Activity, and Potential Toxicity of Pent-4en and but-3en Analogues Including Mdmb-4en-Pinaca. Drug Test. Anal. 2021, 13, 427–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grafinger, K.E.; Cannaert, A.; Ametovski, A.; Sparkes, E.; Cairns, E.; Banister, S.D.; Auwärter, V.; Stove, C.P. Systematic Evaluation of a Panel of 30 Synthetic Cannabinoid Receptor Agonists Structurally Related to Mmb-4en-Pica, Mdmb-4en-Pinaca, Adb-4en-Pinaca, and Mmb-4cn-Butinaca Using a Combination of Binding and Different Cb(1) Receptor Activation Assays-Part Ii: Structure Activity Relationship Assessment Via a Β-Arrestin Recruitment Assay. Drug Test. Anal. 2021, 13, 1402–1411. [Google Scholar]
- Antonides, L.H.; Cannaert, A.; Norman, C.; NicDáeid, N.; Sutcliffe, O.B.; Stove, C.P.; McKenzie, C. Shape Matters: The Application of Activity-Based in Vitro Bioassays and Chiral Profiling to the Pharmacological Evaluation of Synthetic Cannabinoid Receptor Agonists in Drug-Infused Papers Seized in Prisons. Drug Test. Anal. 2021, 13, 628–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grafinger, K.E.; Vandeputte, M.M.; Cannaert, A.; Ametovski, A.; Sparkes, E.; Cairns, E.; Juchli, P.O.; Haschimi, B.; Pulver, B.; Banister, S.D.; et al. Systematic Evaluation of a Panel of 30 Synthetic Cannabinoid Receptor Agonists Structurally Related to Mmb-4en-Pica, Mdmb-4en-Pinaca, Adb-4en-Pinaca, and Mmb-4cn-Butinaca Using a Combination of Binding and Different Cb1 Receptor Activation Assays. Part Iii: The G Protein Pathway and Critical Comparison of Different Assays. Drug Test. Anal. 2021, 13, 1412–1429. [Google Scholar]
- Marusich, J.A.; Gamage, T.F.; Zhang, Y.; Akinfiresoye, L.R.; Wiley, J.L. In Vitro and in Vivo Pharmacology of Nine Novel Synthetic Cannabinoid Receptor Agonists. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2022, 220, 173467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kronstrand, R.; Norman, C.; Vikingsson, S.; Biemans, A.; Crespo, B.V.; Edwards, D.; Fletcher, D.; Gilbert, N.; Persson, M.; Reid, R.; et al. The Metabolism of the Synthetic Cannabinoids Adb-Butinaca and Adb-4en-Pinaca and Their Detection in Forensic Toxicology Casework and Infused Papers Seized in Prisons. Drug Test. Anal. 2022, 14, 634–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pike, E.; Grafinger, K.E.; Cannaert, A.; Ametovski, A.; Luo, J.L.; Sparkes, E.; Cairns, E.A.; Ellison, R.; Gerona, R.; Stove, C.P.; et al. Systematic Evaluation of a Panel of 30 Synthetic Cannabinoid Receptor Agonists Structurally Related to Mmb-4en-Pica, Mdmb-4en-Pinaca, Adb-4en-Pinaca, and Mmb-4cn-Butinaca Using a Combination of Binding and Different Cb(1) Receptor Activation Assays: Part I-Synthesis, Analytical Characterization, and Binding Affinity for Human Cb(1) Receptors. Drug Test. Anal. 2021, 13, 1383–1401. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, S.M.; Kolieb, E.; Imbaby, S.; Hagras, A.M.; Arafat, H.E.K.; Kamel, E.M.; Abdelshakour, M.A.; Ali, M.I.M. Acute Toxic Effects of New Synthetic Cannabinoid on Brain: Neurobehavioral and Histological: Preclinical Studies. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2023, 370, 110306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S. Effects of the Synthetic Cannabinoid MDMB-4en-PINACA on Zebrafish Behavior and Metabolomic Alterations Associated with Neurotransmitter Systems. Master’s Thesis, China Pharmaceutical University, Nanjing, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, F.; Wang, X.; Tan, S.; Shi, Y.; Xie, B.; Xiang, P.; Cong, B.; Ma, C.; Wen, D. Differential Cannabinoid-Like Effects and Pharmacokinetics of Adb-Bica, Adb-Binaca, Adb-4en-Pinaca and Mdmb-4en-Pinaca in Mice: A Comparative Study. Addict. Biol. 2024, 29, e13372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Counts, C.J.; Spadaro, A.V.; Cerbini, T.A.; Krotulski, A.J.; Walton, S.E.; Greller, H.A.; Nelson, L.S.; Ruck, B.E.; Hung, O.; Logan, B.; et al. An Outbreak of Synthetic Cannabinoid-Adulterated Tianeptine Products in New Jersey—Case Series. J. Med. Toxicol. 2025, 21, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Han, L.; Yi, L.; Liu, J.; Qiu, S.; Gu, J.; Bai, H.; Li, J.; Wurita, A.; Hasegawa, K. Newly Emerging Synthetic Cannabinoid Adb-4en-Pinaca: Its Identification and Quantification in an Authentic Human Hair Sample by Gc-Ms/Ms. Forensic Toxicol. 2023, 41, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metna-Laurent, M.; Mondésir, M.; Grel, A.; Vallée, M.; Piazza, P.V. Cannabinoid-Induced Tetrad in Mice. Curr. Protoc. Neurosci. 2017, 80, 9.59.1–9.59.10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiley, J.L.; Compton, D.R.; Dai, D.; Lainton, J.A.; Phillips, M.; Huffman, J.W.; Martin, B.R. Structure-Activity Relationships of Indole- and Pyrrole-Derived Cannabinoids1. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1998, 285, 995–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banister, S.D.; Stuart, J.; Kevin, R.C.; Edington, A.; Longworth, M.; Wilkinson, S.M.; Beinat, C.; Buchanan, A.S.; Hibbs, D.E.; Glass, M.; et al. Effects of Bioisosteric Fluorine in Synthetic Cannabinoid Designer Drugs Jwh-018, Am-2201, Ur-144, Xlr-11, Pb-22, 5f-Pb-22, Apica, and Sts-135. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2015, 6, 1445–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCain, K.R.; Jones, J.O.; Chilbert, K.T.; Patton, A.L.; James, L.P.; Moran, J.H. Impaired Driving Associated with the Synthetic Cannabinoid 5f-Adb. J. Forensic. Sci. Criminol. 2018, 6, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Drews, E.; Schneider, M.; Koch, M. Effects of the Cannabinoid Receptor Agonist Win 55,212-2 on Operant Behavior and Locomotor Activity in Rats. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2005, 80, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barceló, B.; Pichini, S.; López-Corominas, V.; Gomila, I.; Yates, C.; Busardò, F.P.; Pellegrini, M. Acute Intoxication Caused by Synthetic Cannabinoids 5f-Adb and Mmb-2201: A Case Series. Forensic. Sci. Int. 2017, 273, e10–e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepore, M.; Vorel, S.R.; Lowinson, J.; Gardner, E.L. Conditioned Place Preference Induced by Delta 9-Tetrahydrocannabinol: Comparison with Cocaine, Morphine, and Food Reward. Life Sci. 1995, 56, 2073–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Xu, D.; Qiao, Y.; Kuai, L.; Luo, X.; Di, B.; Xu, P. Assessment of Pharmacological Effects and Abuse Potential of 5f-Edmb-Pica, Cumyl-Pegaclone, and Nm-2201 in Mice. Psychopharmacology 2025, 242, 533–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Kuai, L.; Shi, X.; Qiao, Y.; Li, K.; Xu, D.; Di, B.; Yan, F.; Xu, P. Pharmaco-Toxicological Effects of the Synthetic Cannabinoids 4f-Abutinaca, Sdb-005, and Jwh-018 in Mice. In Vitro and In Vivo Studies. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2025, 996, 177586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, H.J.; Lee, K.W.; Song, M.J.; Hyeon, Y.J.; Hwang, J.Y.; Jang, C.G.; Ahn, J.I.; Jeon, S.H.; Kim, H.U.; Kim, Y.H.; et al. Dependence Potential of the Synthetic Cannabinoids Jwh-073, Jwh-081, and Jwh-210: In Vivo and in Vitro Approaches. Biomol. Ther. 2014, 22, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musa, A.; Simola, N.; Piras, G.; Caria, F.; Onaivi, E.S.; De Luca, M.A. Neurochemical and Behavioral Characterization after Acute and Repeated Exposure to Novel Synthetic Cannabinoid Agonist 5-Mdmb-Pica. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Foll, B.; Wiggins, M.; Goldberg, S.R. Nicotine Pre-Exposure Does Not Potentiate the Locomotor or Rewarding Effects of Delta-9-Tetrahydrocannabinol in Rats. Behav. Pharmacol. 2006, 17, 195–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tampus, R.; Yoon, S.S.; de la Peña, J.B.; Botanas, C.J.; Kim, H.J.; Seo, J.W.; Jeong, E.J.; Jang, C.G.; Cheong, J.H. Assessment of the Abuse Liability of Synthetic Cannabinoid Agonists Jwh-030, Jwh-175, and Jwh-176. Biomol. Ther. 2015, 23, 590–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, S.M.; Seo, S.; Park, D.; Kim, S.; Lamichhane, S.; Han, K.-M.; Kim, Y.-H.; Lee, S.; Hong, J.T.; Cha, H.J.; et al. Cannabinoid Receptor Type 1 Regulates Drug Reward Behavior Via Glutamate Decarboxylase 67 Transcription. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, U.S.; Winkelmann, P.R.; Pilhatsch, M.; Nees, J.A.; Spanagel, R.; Schulz, K. Withdrawal Phenomena and Dependence Syndrome after the Consumption of “Spice Gold”. Dtsch. Arztebl. Int. 2009, 106, 464–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlosburg, J.E.; Carlson, B.L.; Ramesh, D.; Abdullah, R.A.; Long, J.Z.; Cravatt, B.F.; Lichtman, A.H. Inhibitors of Endocannabinoid-Metabolizing Enzymes Reduce Precipitated Withdrawal Responses in Thc-Dependent Mice. Aaps. J. 2009, 11, 342–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, A.M.; Siegele, P.B.; Foss, J.D.; Tuma, R.F.; Ward, S.J. Single and Combined Effects of Plant-Derived and Synthetic Cannabinoids on Cognition and Cannabinoid-Associated Withdrawal Signs in Mice. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 176, 1552–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trexler, K.R.; Nass, S.R.; Crowe, M.S.; Gross, J.D.; Jones, M.S.; McKitrick, A.W.; Siderovski, D.P.; Kinsey, S.G. Novel Behavioral Assays of Spontaneous and Precipitated Thc Withdrawal in Mice. Drug Alcohol. Depend. 2018, 191, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darmani, N.A.; Pandya, D.K. Involvement of Other Neurotransmitters in Behaviors Induced by the Cannabinoid Cb1 Receptor Antagonist Sr 141716a in Naive Mice. J. Neural. Transm. 2000, 107, 931–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canazza, I.; Ossato, A.; Trapella, C.; Fantinati, A.; De Luca, M.A.; Margiani, G.; Vincenzi, F.; Rimondo, C.; Di Rosa, F.; Gregori, A.; et al. Effect of the Novel Synthetic Cannabinoids Akb48 and 5f-Akb48 on "Tetrad", Sensorimotor, Neurological and Neurochemical Responses in Mice. In Vitro and in Vivo Pharmacological Studies. Psychopharmacology 2016, 233, 3685–3709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillis, E.P.; Eastman, K.J.; Hill, M.D.; Donnelly, D.J.; Meanwell, N.A. Applications of Fluorine in Medicinal Chemistry. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 8315–8359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.F.; Galaj, E.; Bi, G.H.; Zhang, C.; He, Y.; Zhan, J.; Bauman, M.H.; Gardner, E.L.; Xi, Z.X. Different Receptor Mechanisms Underlying Phytocannabinoid- Versus Synthetic Cannabinoid-Induced Tetrad Effects: Opposite Roles of Cb(1)/Cb(2) Versus Gpr55 Receptors. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 177, 1865–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trexler, K.R.; Vanegas, S.O.; Poklis, J.L.; Kinsey, S.G. The Short-Acting Synthetic Cannabinoid Ab-Fubinaca Induces Physical Dependence in Mice. Drug Alcohol. Depend. 2020, 214, 108179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Drug | Suppressed Locomotion | Hypothermia | Analgesia | Catalepsy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ED50 (95%CI) (mg/kg) | ED50 (95%CI) (mg/kg) | ED50 (95%CI) (mg/kg) | ED50 (95%CI) (mg/kg) | |
| Δ9-THC | 4.30 (3.07–6.98) | 14.48 (10.05–23.21) | 20.08 (15.76–25.84) | 21.19 (15.27–45.27) |
| 5F-ADB | 0.03 (0.02–0.10) | 0.07 (0.05–0.11) | 0.04 (0.03–0.05) | 0.03 (0.03–0.04) |
| MDMB-4en-PINACA | 0.08 (0.06–0.21) | 0.29 (0.21–0.80) | 0.11 (0.09–0.13) | 0.09 (0.02–0.14) |
| ADB-4en-PINACA | 0.28 (0.20–0.46) | 0.77 (0.68–0.86) | 0.52 (0.40–0.63) | 0.77 (0.59–1.41) |
| Drug | Administration Doses (mg/kg), i.p. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Day 1 | Day 2 | Day 3 | Day 4 | Day 5 | |
| Vehicle | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Δ9-THC | 1 | 3 | 10 | 30 | 100 |
| 5F-ADB | 0.003 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.1 | 0.3 |
| MDMB-4en-PINACA | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 1 |
| ADB-4en-PINACA | 0.03 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 1 | 3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qiao, Y.; Shi, X.; Li, K.; Kuai, L.; Li, X.; Di, B.; Xu, P. Assessment of Abuse Potential of Three Indazole-Carboxamide Synthetic Cannabinoids 5F-ADB, MDMB-4en-PINACA and ADB-4en-PINACA. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6409. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136409
Qiao Y, Shi X, Li K, Kuai L, Li X, Di B, Xu P. Assessment of Abuse Potential of Three Indazole-Carboxamide Synthetic Cannabinoids 5F-ADB, MDMB-4en-PINACA and ADB-4en-PINACA. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(13):6409. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136409
Chicago/Turabian StyleQiao, Yanling, Xuesong Shi, Kaixi Li, Lixin Kuai, Xiangyu Li, Bin Di, and Peng Xu. 2025. "Assessment of Abuse Potential of Three Indazole-Carboxamide Synthetic Cannabinoids 5F-ADB, MDMB-4en-PINACA and ADB-4en-PINACA" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 13: 6409. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136409
APA StyleQiao, Y., Shi, X., Li, K., Kuai, L., Li, X., Di, B., & Xu, P. (2025). Assessment of Abuse Potential of Three Indazole-Carboxamide Synthetic Cannabinoids 5F-ADB, MDMB-4en-PINACA and ADB-4en-PINACA. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(13), 6409. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136409





