Rhein Inhibits Microglia-Mediated Neuroinflammation and Neuronal Damage of Alzheimer’s Disease via Regulating the Glutamine–Aspartate–Arginine–NO Metabolic Pathway
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
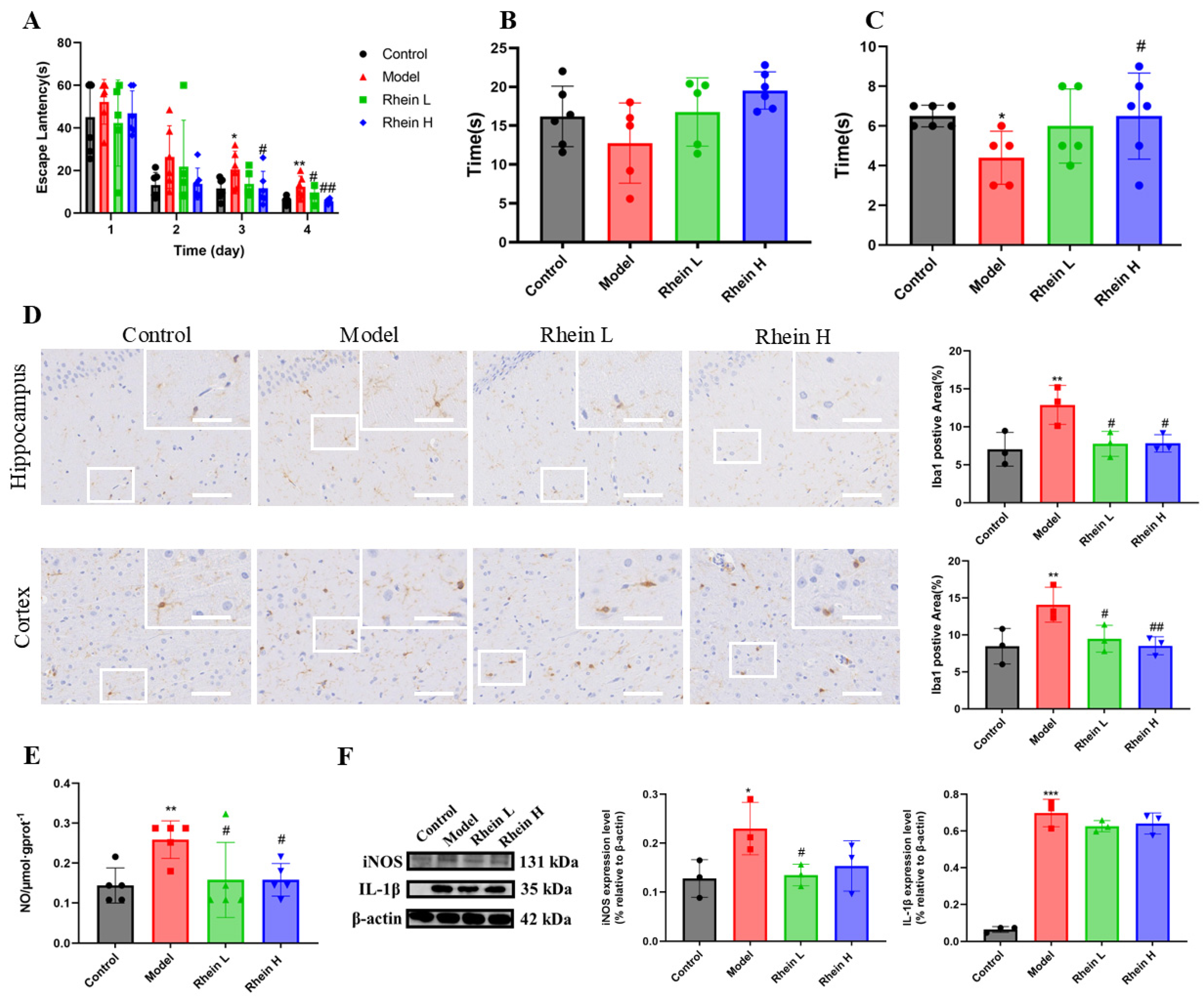
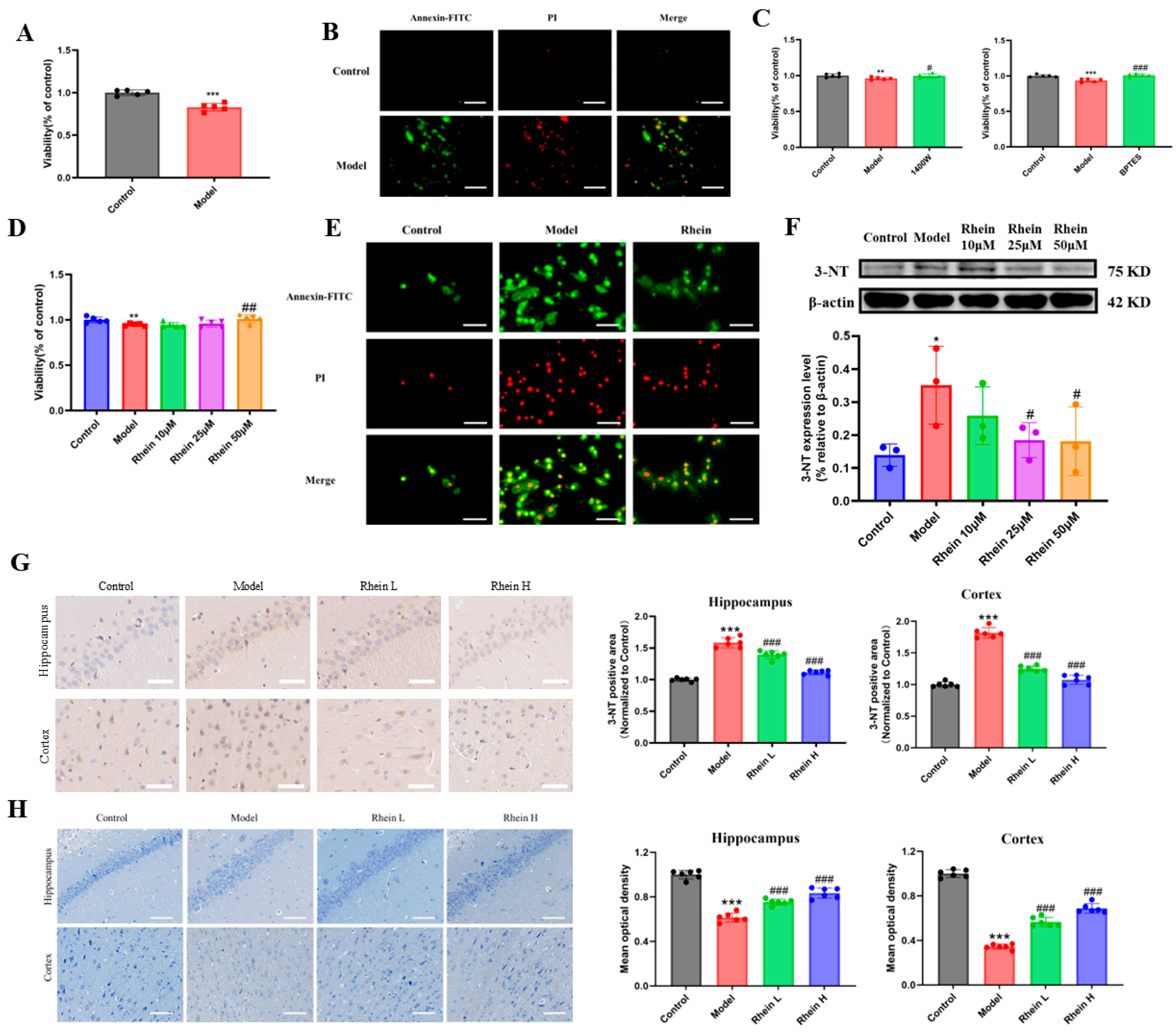
2.1. Effect of Rhein on Activated Microglia-Mediated Neuroinflammation in AD Rat Brain
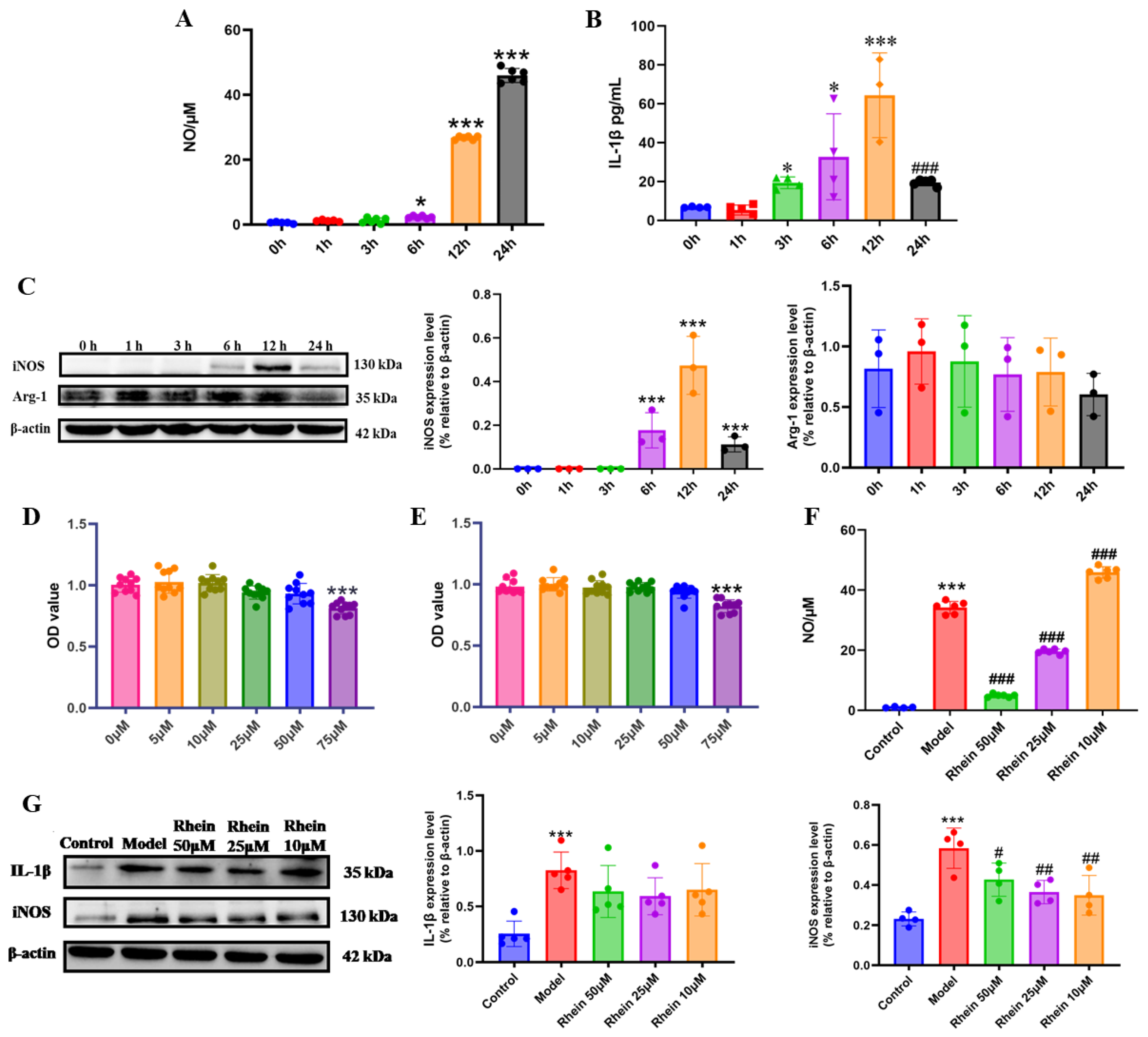
2.2. Rhein Inhibits LPS-Induced Inflammatory Response Mediated by Activated Microglia
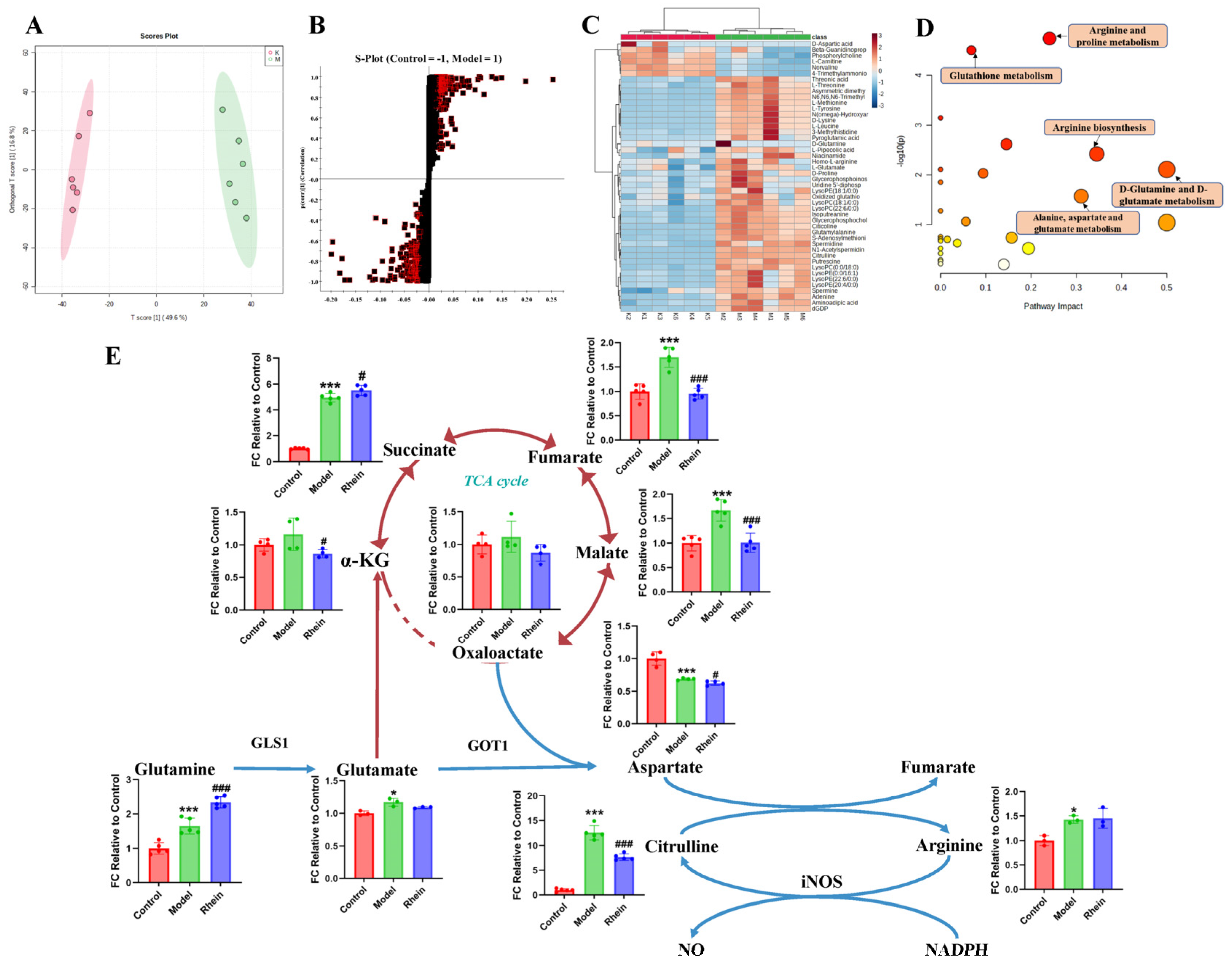
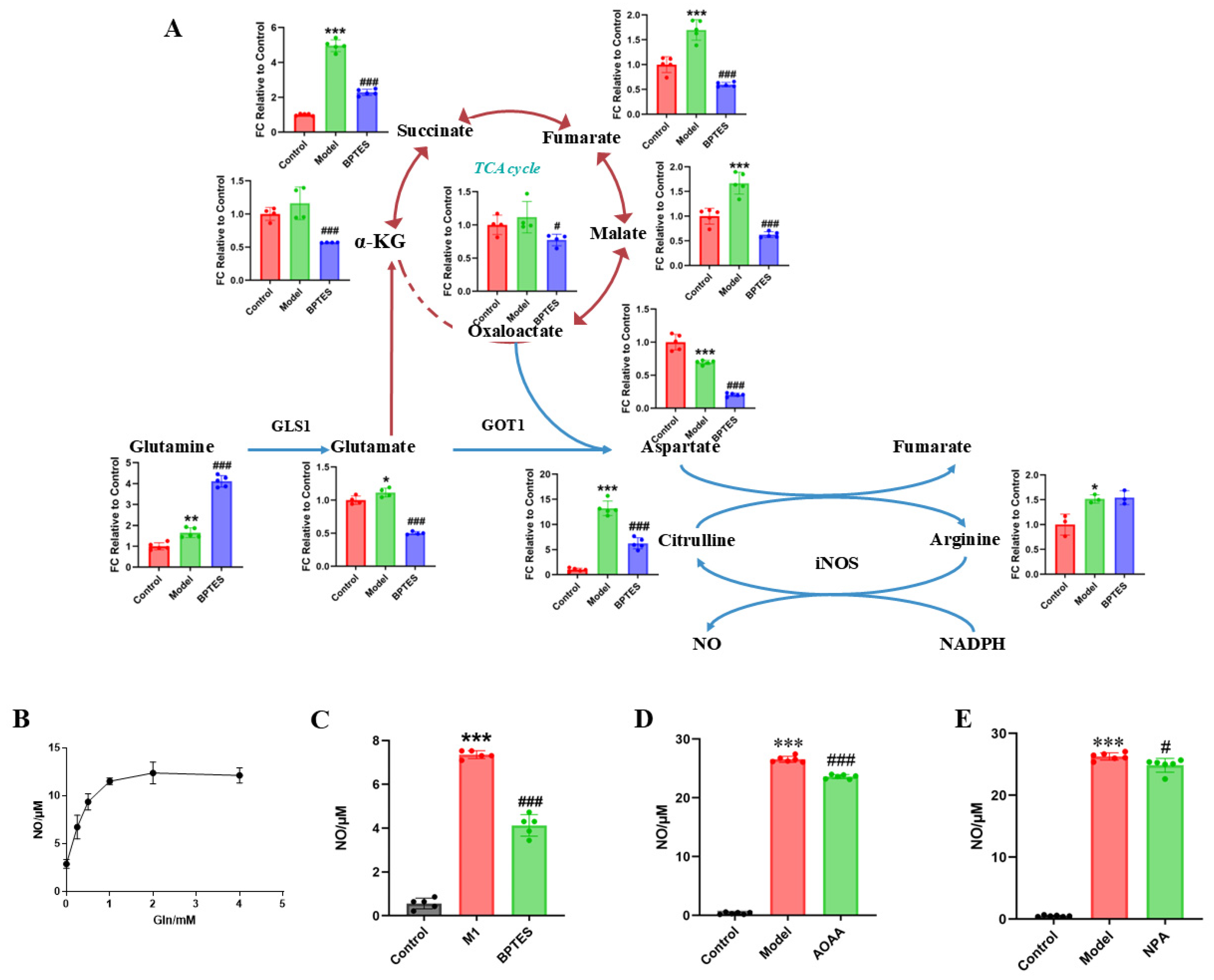
2.3. Regulatory Effect of Rhein on Metabolism of Activated Microglia
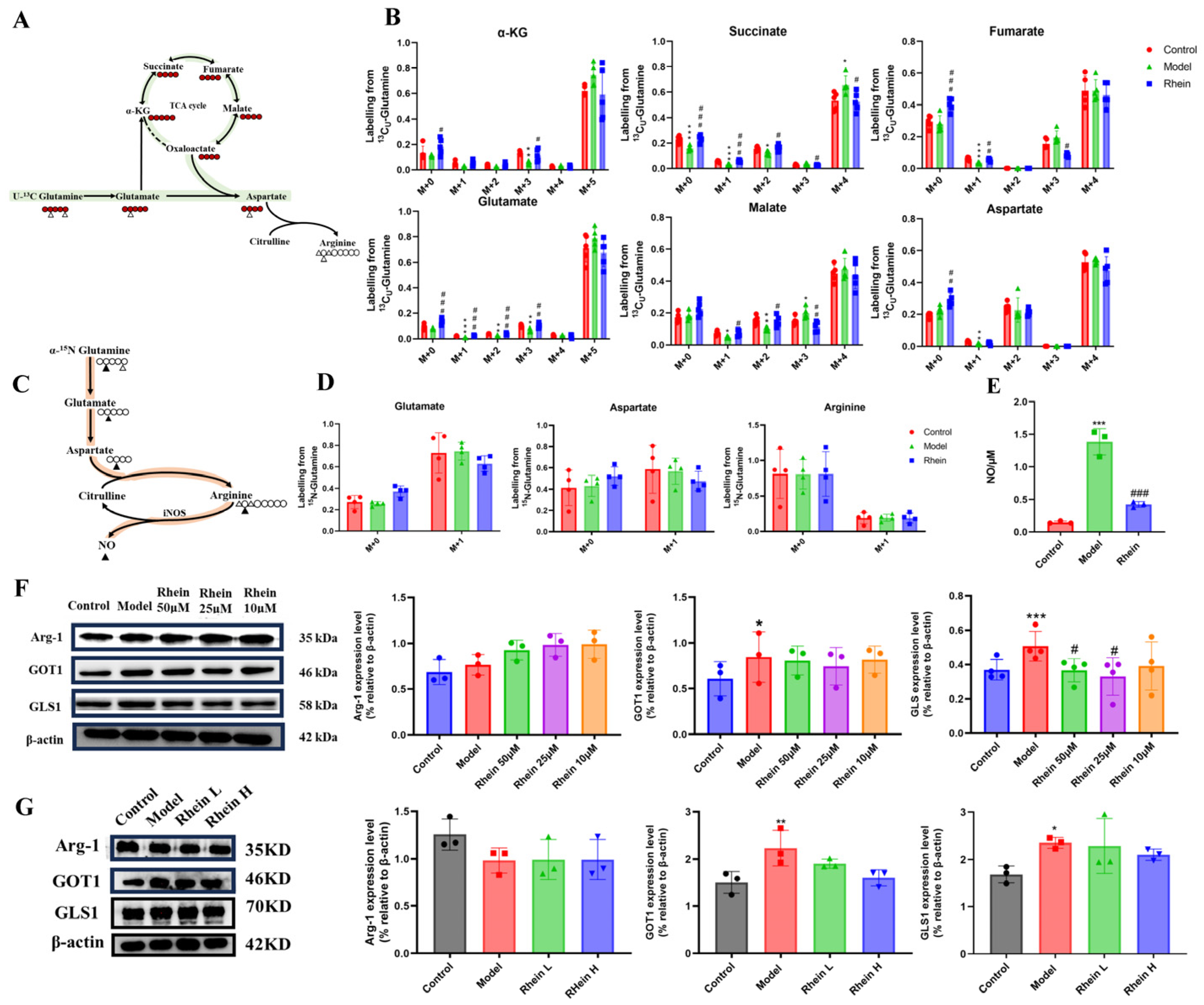
2.4. Regulatory Effect of Rhein on the Glutamine–Aspartate–Arginine Metabolic Pathway in Activated Microglia
2.5. The Glutamine–Aspartate–Arginine–NO Metabolic Pathway Regulates the Inflammatory Factor NO Production in Microglia
2.6. Rhein Alleviates Neuronal Damage by Inhibiting the Glutamine–Aspartate–Arginine–NO Metabolic Pathway
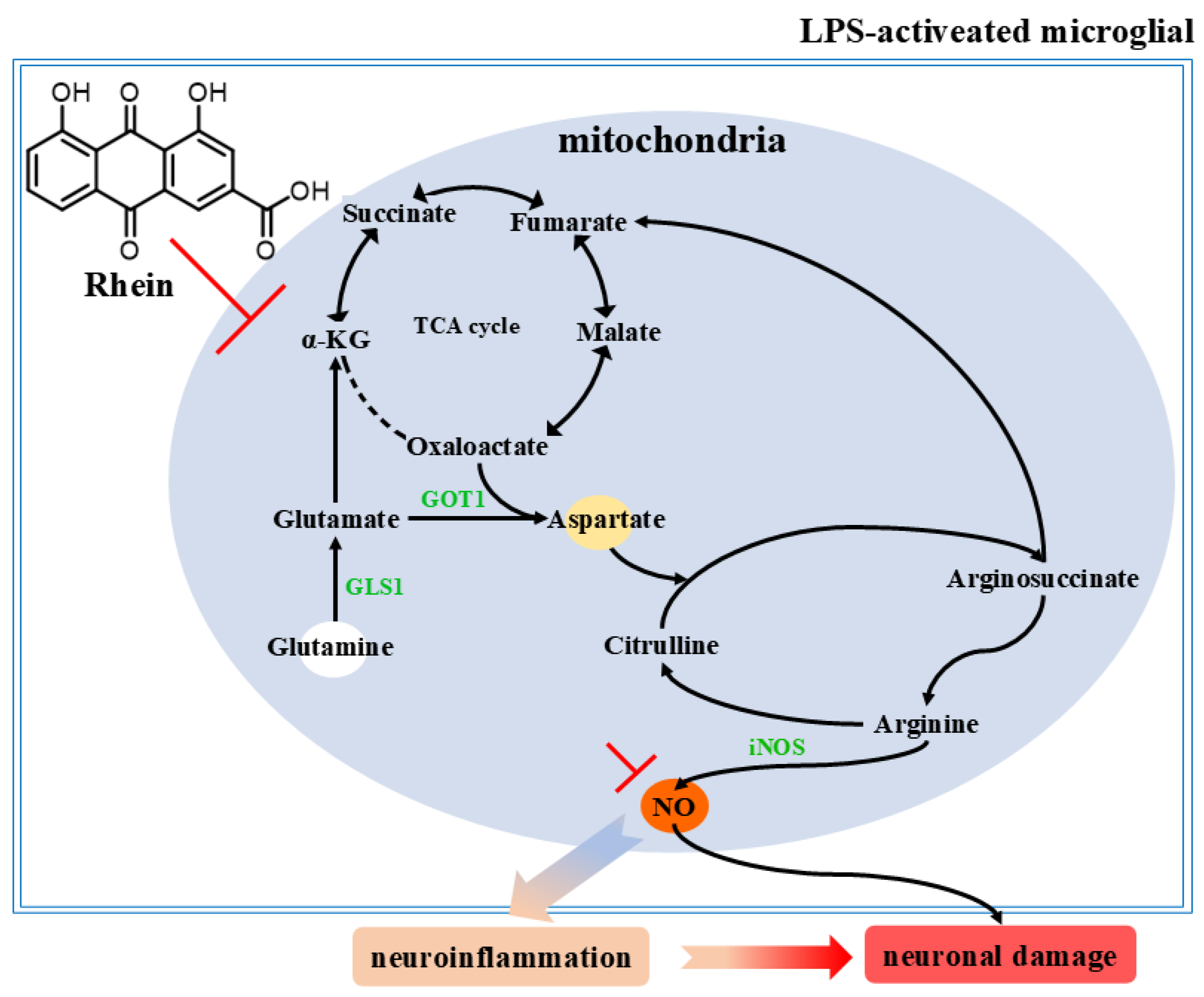
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Reagents
4.2. Animal
4.3. Morris Water Maze
4.4. Immunohistochemistry
4.5. Nissl Staining
4.6. Cells
4.7. Cell Viability Assay
4.8. NO and IL-1β Determination
4.9. Apoptosis Detection
4.10. Western Blotting
4.11. Metabolomics
4.11.1. Sample Preparation
4.11.2. Determination Condition
4.12. Data Analysis and Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Alzheimer’s Association. Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2024, 20, 3708–3821. [Google Scholar]
- Calsolaro, V.; Edison, P. Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease: Current evidence and future directions. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2016, 12, 719–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Block, M.L.; Zecca, L.; Hong, J.S. Microglia-mediated neurotoxicity: Uncovering the molecular mechanisms. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2007, 8, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, F.; Edison, P. Neuroinflammation and microglial activation in Alzheimer disease: Where do we go from here? Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2021, 17, 157–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, M.; Xu, Y.; Pearse, D.D. Cyclic AMP is a key regulator of M1 to M2a phenotypic conversion of microglia in the presence of Th2 cytokines. J. Neuroinflam. 2016, 13, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baik, S.H.; Kang, S.; Lee, W.; Choi, H.; Chung, S.; Kim, J.I.; Mook-Jung, I. A Breakdown in Metabolic Reprogramming Causes Microglia Dysfunction in Alzheimer’s Disease. Cell Metab. 2019, 30, 493–507.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vizuete, A.F.K.; Fróes, F.; Seady, M.; Caurio, A.C.; Junior, O.V.R.; Leite, A.K.O.; Farias, C.P.; Wyse, A.T.; Gonçalves, C.-A. Targeting glycolysis for neuroprotection in early LPS-induced neuroinflammation. Brain Behav. Immun.-Health 2024, 42, 100901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Kasmi, K.C.; Stenmark, K.R. Contribution of metabolic reprogramming to macrophage plasticity and function. Semin. Immunol. 2015, 27, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Li, Y.C.; Liu, X.T.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Y.H.; Zhao, Q.; Gao, W.; Liu, B.; Yang, H.; Li, P. Blockage of citrate export prevents TCA cycle fragmentation via Irg1 inactivation. Cell Rep. 2022, 38, 110391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Luo, G.; Chen, D.; Xiang, Z. A Comprehensive and System Review for the Pharmacological Mechanism of Action of Rhein, an Active Anthraquinone Ingredient. Front. Pharmacol. 2016, 7, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.W.; Chang, C.C.; Chang, T.S.; Li, H.H.; Hung, H.C.; Liu, G.Y.; Lin, C.L. Aβ stimulates microglial activation through antizyme-dependent downregulation of ornithine decarboxylase. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 9733–9745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jha, A.K.; Huang, S.C.; Sergushichev, A.; Lampropoulou, V.; Ivanova, Y.; Loginicheva, E.; Chmielewski, K.; Stewart, K.M.; Ashall, J.; Everts, B.; et al. Network integration of parallel metabolic and transcriptional data reveals metabolic modules that regulate macrophage polarization. Immunity 2015, 42, 419–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heneka, M.T.; Carson, M.J.; El Khoury, J.; Landreth, G.E.; Brosseron, F.; Feinstein, D.L.; Jacobs, A.H.; Wyss-Coray, T.; Vitorica, J.; Ransohoff, R.M.; et al. Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet Neurol. 2015, 14, 388–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Lu, D.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Li, W.; Chen, G. The effects of nitric oxide in alzheimer’s disease. Med. Gas Res. 2023, 14, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Justo, A.F.O.; Toscano, E.C.D.B.; Leite, R.E.P.; Paes, V.R.; Grinberg, L.T.; Pasquallucci, C.A.; Jacob-Filho, W.; Suemoto, C.K. The neural nitric oxide synthase is associated with cognitive decline and alzheimer’s disease pathology. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2023, 19, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, L.J.; Adams, N.A.; Pan, Y.; Price, A.; Wong, M. The mitochondrial permeability transition pore regulates nitric oxide-mediated apoptosis of neurons induced by target deprivation. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 359–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Hagemann, T.L.; Kalwa, H.; Michel, T.; Messing, A.; Feany, M.B. Nitric oxide mediates glial-induced neurodegeneration in Alexander disease. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, P.; Tian, X.; Zhang, W.; Yang, Z.; Zhou, J.; Zheng, J.; Cui, H.; Tang, T.; Luo, J.; Wang, Y. Rhein Suppresses Neuroinflammation via Multiple Signaling Pathways in LPS-Stimulated BV2 Microglia Cells. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2020, 2020, 7210627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Fan, R.; Luo, J.; Tang, T.; Xing, Z.; Xia, Z.; Peng, W.; Wang, W.; Lv, H.; Huang, W.; et al. An ultra high performance liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry method for plasma and cerebrospinal fluid pharmacokinetics of rhein in patients with traumatic brain injury after administration of rhubarb decoction. J. Sep. Sci. 2015, 38, 1100–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Hu, G.; Xu, R.; Qiao, Y.; Wu, H.P.; Ding, X.; Duan, P.; Tu, P.; Lin, Y.J. Rhein lysinate decreases the generation of β-amyloid in the brain tissues of Alzheimer’s disease model mice by inhibiting inflammatory response and oxidative stress. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2013, 15, 756–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Gao, D.; Du, K.; Han, C.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Gao, X. Rhein Ameliorates Cognitive Impairment in an APP/PS1 Transgenic Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease by Relieving Oxidative Stress through Activating the SIRT1/PGC-1α Pathway. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2022, 2022, 2524832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Yang, J.; Yu, W.; Cao, J.; Li, X. Rhein attenuates PTZ-induced epilepsy and exerts neuroprotective activity via inhibition of the TLR4-NFκB signaling pathway. Neurosci. Lett. 2021, 758, 136002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, F.; Sancheti, H.; Patil, I.; Cadenas, E. Energy metabolism and inflammation in brain aging and Alzheimer’s disease. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2016, 100, 108–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.Y.; Liu, L.; Yang, Q.W. Functions and mechanisms of microglia/macrophages in neuroinflammation and neurogenesis after stroke. Prog. Neurobiol. 2016, 142, 23–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinelli, J.B.; Yoon, H.; Ringel, A.E.; Jeanfavre, S.; Clish, C.B.; Haigis, M.C. Metabolic recycling of ammonia via glutamate dehydrogenase supports breast cancer biomass. Science 2017, 358, 941–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Qin, C.; Hu, Z.W.; Zhou, L.Q.; Yu, H.H.; Chen, M.; Bosco, D.B.; Wang, W.; Wu, L.J.; Tian, D.S. Microglia reprogram metabolic profiles for phenotype and function changes in central nervous system. Neurobiol. Dis. 2021, 152, 105290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancini, A.; Tantucci, M.; Mazzocchetti, P.; de Iure, A.; Durante, V. Microglial activation and the nitric oxide/cGMP/PKG pathway underlie enhanced neuronal vulnerability to mitochondrial dysfunction in experimental multiple sclerosis. Neurobiol. Dis. 2018, 113, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radi, R. Oxygen radicals, nitric oxide, and peroxynitrite: Redox pathways in molecular medicine. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 5839–5848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Yao, H.; Liu, W.; Ya, B.; Cheng, H.; Xing, Z.; Wu, Y. Microglia Polarization in Alzheimer’s Disease: Mechanisms and a Potential Therapeutic Target. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2021, 13, 772717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Le, W. Differential Roles of M1 and M2 Microglia in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 53, 1181–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Zheng, J.; Xu, S.; Fang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zeng, J.; Shao, A.; Shi, L.; Lu, J.; Mei, S.; et al. Mer regulates microglial/macrophage M1/M2 polarization and alleviates neuroinflammation following traumatic brain injury. J. Neuroinflamm. 2021, 18, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, H.C.; Yu, Y.C.; Sung, Y.; Han, J.M. Glutamine reliance in cell metabolism. Exp. Mol. Med. 2020, 52, 1496–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Qiu, Y.; Kurland, I.J.; Drlica, K.; Subbian, S.; Tyagi, S.; Shi, L. Glutamine Is Required for M1-like Polarization of Macrophages in Response to Mycobacterium tuberculosis Infection. mBio 2022, 13, e0127422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrer-Sueta, G.; Campolo, N.; Trujillo, M.; Bartesaghi, S.; Carballal, S.; Romero, N.; Alvarez, B.; Radi, R. Biochemistry of Peroxynitrite and Protein Tyrosine Nitration. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 1338–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, J.D.; Diotallevi, M.; Nicol, T.; McNeill, E.; Shaw, A.; Chuaiphichai, S.; Hale, A.; Starr, A.; Nandi, M.; Stylianou, E.; et al. Nitric Oxide Modulates Metabolic Remodeling in Inflammatory Macrophages through TCA Cycle Regulation and Itaconate Accumulation. Cell Rep. 2019, 28, 218–230.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szabó, C.; Ischiropoulos, H.; Radi, R. Peroxynitrite: Biochemistry, pathophysiology and development of therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2007, 6, 662–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryu, J.K.; Nagai, A.; Kim, J.; Lee, M.C.; McLarnon, J.G.; Kim, S.U. Microglial activation and cell death induced by the mitochondrial toxin 3-nitropropionic acid: In vitro and in vivo studies. Neurobiol. Dis. 2003, 12, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, B.; Liu, Q.; Fang, L.; Gou, S. Blood-Brain Barrier Permeable and NO-Releasing Multifunctional Nanoparticles for Alzheimer’s Disease Treatment: Targeting NO/cGMP/CREB Signaling Pathways. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 13853–13872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Pan, K.; Gao, Y.; Li, J.; Zang, Y.; Li, X. Deconvoluting nitric oxide-protein interactions with spatially resolved multiplex imaging. Chem. Sci. 2024, 15, 6562–6571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandookwala, M.; Thakkar, D.; Sengupta, P. Advancements in the Analytical Quantification of Nitroxidative Stress Biomarker 3-Nitrotyrosine in Biological Matrices. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2020, 50, 265–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Yuan, Q.; Chen, F.; Pang, J.; Pan, C.; Xu, F.; Chen, Y. Fundamental Mechanisms of the Cell Death Caused by Nitrosative Stress. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 742483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- George Paxinos, C.W. The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates: Hard Cover Edition; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, C.; Li, Q.; Liu, X.; He, B.; Sui, Z.; Xu, H.; Yin, Y.; Liu, R.; Bi, K. Determination of catecholamines and their metabolites in rat urine by ultra-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry for the study of identifying potential markers for Alzheimer’s disease. J. Mass Spectrom. 2015, 50, 354–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, W.; Zhu, H.; Wu, J.; Liao, S.; Cheng, G.; Li, X. Rhein attenuates angiotensin II-induced cardiac remodeling by modulating AMPK-FGF23 signaling. J. Transl. Med. 2022, 20, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, D.; Luo, G.; Ma, T.; Wang, Y.; Lu, L.; Gao, X. Stepwise Coordination-Driven Metal-Phenolic Nanoparticle as a Neuroprotection Enhancer for Alzheimer’s Disease Therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 524–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Gagnon, S.; Eckle, T.; Borchers, C.H. Metabolomic analysis of key central carbon metabolism carboxylic acids as their 3-nitrophenylhydrazones by UPLC/ESI-MS. Electrophoresis 2013, 34, 2891–2900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, N.; Zia, R.; King, A.; Patel, V.C.; Wendon, J.; McPhail, M.J.W.; Coen, M.; Plumb, R.S.; Wilson, I.D.; Nicholson, J.K. High-Speed Quantitative UPLC-MS Analysis of Multiple Amines in Human Plasma and Serum via Precolumn Derivatization with 6-Aminoquinolyl-N-hydroxysuccinimidyl Carbamate: Application to Acetaminophen-Induced Liver Failure. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 2478–2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Antibody | Source | Dilute | Company |
|---|---|---|---|
| iNOS | Rabbit | 1/2000 | (Proteintech Group, Inc., Rosemont, IL, USA) |
| Arg-1 | Rabbit | 1/10,000 | |
| GLS1 | Rabbit | 1/5000 | |
| GOT | Rabbit | 1/2000 | |
| IL-1β | Rabbit | 1/1000 | |
| Beta-Actin Antibody | Mouse | 1/10,000 | |
| HRP-anti-rabbit IgG | Goat | 1/2000 | |
| HRP-anti-mouse IgG | Goat | 1/2000 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chi, B.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Tian, M.; Wang, Y.; Gao, X. Rhein Inhibits Microglia-Mediated Neuroinflammation and Neuronal Damage of Alzheimer’s Disease via Regulating the Glutamine–Aspartate–Arginine–NO Metabolic Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6404. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136404
Chi B, Zhang Z, Zhang Z, Zhang H, Tian M, Wang Y, Gao X. Rhein Inhibits Microglia-Mediated Neuroinflammation and Neuronal Damage of Alzheimer’s Disease via Regulating the Glutamine–Aspartate–Arginine–NO Metabolic Pathway. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(13):6404. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136404
Chicago/Turabian StyleChi, Bingqing, Zhengyi Zhang, Zhixin Zhang, Han Zhang, Mengjun Tian, Ying Wang, and Xiaoyan Gao. 2025. "Rhein Inhibits Microglia-Mediated Neuroinflammation and Neuronal Damage of Alzheimer’s Disease via Regulating the Glutamine–Aspartate–Arginine–NO Metabolic Pathway" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 13: 6404. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136404
APA StyleChi, B., Zhang, Z., Zhang, Z., Zhang, H., Tian, M., Wang, Y., & Gao, X. (2025). Rhein Inhibits Microglia-Mediated Neuroinflammation and Neuronal Damage of Alzheimer’s Disease via Regulating the Glutamine–Aspartate–Arginine–NO Metabolic Pathway. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(13), 6404. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136404




