Unraveling the Role of Tumor-Infiltrating Immune Cells in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Implications for Antitumor Immune Responses and Immunotherapy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Immune Landscape in HNSCC
3. Mechanisms of Immune Evasion as a Challenge to Therapeutic Effectiveness
3.1. Loss of Human Leukocyte Antigen and Impairment of Antigen Presentation
3.2. Disruption of Immune Cell Infiltration, Secretion of Immunosuppressive Factors, and Recruitment of Suppressor Cells
3.2.1. Innate Immune Cells
Dendritic Cells
Tumor-Associated Macrophages
Neutrophils
Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells
3.2.2. Adaptive Immune Cells
Regulatory T Cells
Regulatory B Cells
3.2.3. Non-Immune Cells
3.2.4. Secretion of Immunosuppressive Factors and Recruitment of Suppressor Cells
3.3. Expression of Immune Checkpoint Molecules
3.4. Metabolic Changes in the Tumor Microenvironment
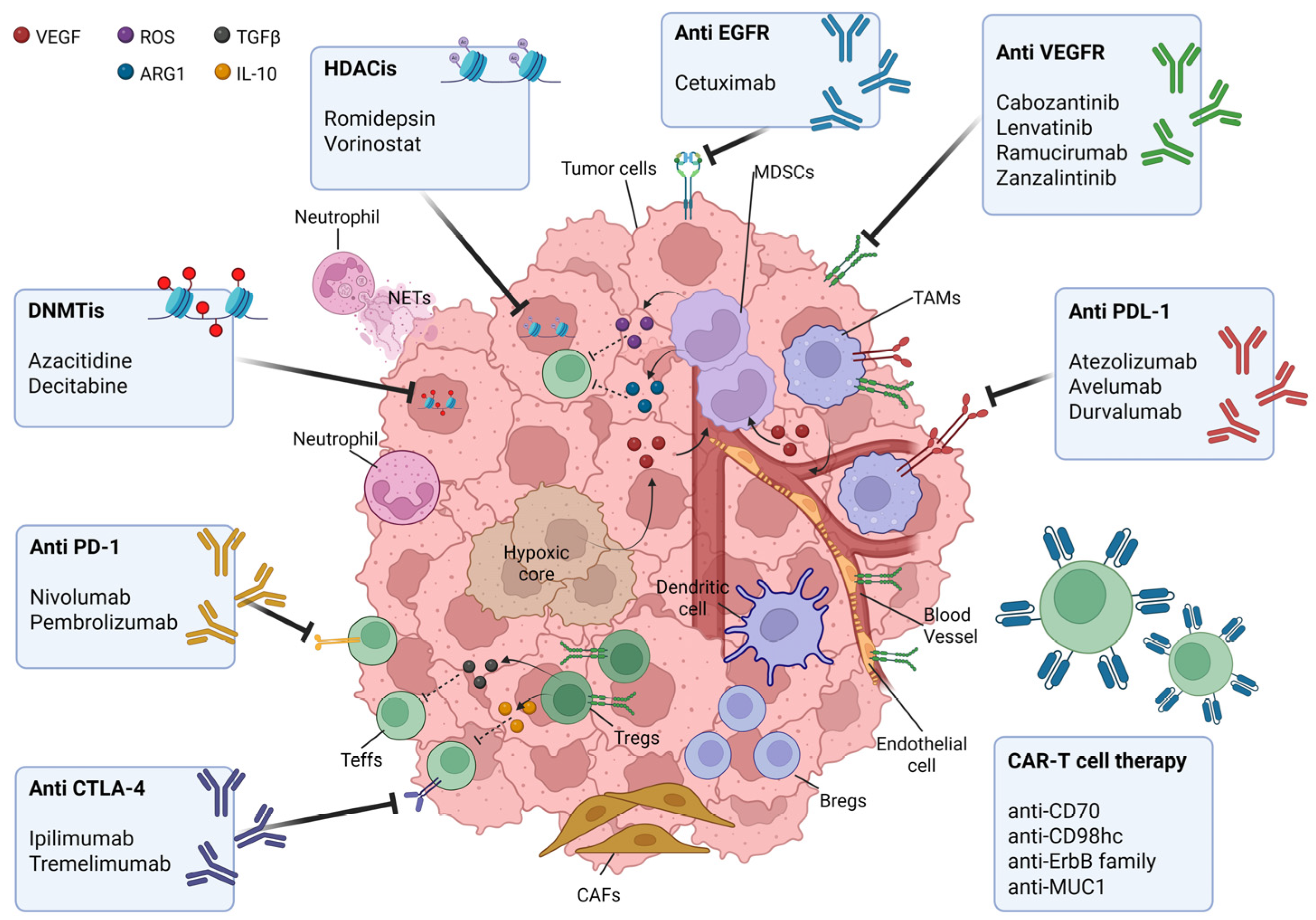
4. Strategies to Counteract Immune Escape Mechanisms in HNSCC Patients
4.1. Chemotherapy
4.2. Immune Checkpoints Inhibitors
4.2.1. PD-1/PDL-1
4.2.2. CTLA-4
4.2.3. New Combination Strategies, Bi-Specific Antibodies, and Antibody–Drug Conjugates
4.3. CAR-T Cell Immunotherapy
4.3.1. ErbB Family
4.3.2. MUC1
4.3.3. CD70
4.3.4. CD98hc
4.4. Targeting Epigenetic Alteration in HNSCC
4.4.1. DNA Methyltransferase Inhibitors (DNMTis)
4.4.2. Histone Methyltransferase and Deacetylase Inhibitors
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 5-FU | 5-fluorouracil |
| ADC | Antibody–drug conjugate |
| ADCCJ | Antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity |
| ARG1 | Arginase 1 |
| B2M | Beta 2 microglobulin |
| Breg | Regulatory B cell |
| CAF | Cancer-associated fibroblast |
| CAR | Chimeric antigen receptor |
| CDC | Complement-dependent cytotoxicity |
| CIITA | Class II major histocompatibility complex transactivator |
| CPS | Combined positive score |
| CRT | Cisplatin-based chemotherapy |
| CTL | Cytotoxic T lymphocyte |
| CTLA-4 | Cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen 4 |
| CXCL | C-X-C motif chemokine ligand |
| DC | Dendritic cell |
| DNMT1 | DNA methyltransferase-1 |
| DNMTis | DNA methyltransferase inhibitors |
| EC | Endothelial cells |
| ECM | Extracellular matrix |
| EFS | Event-free survival |
| EGFR | Epidermal growth factor receptor |
| FDA | Food and Drug Administration |
| GM-CSF | Granulocyte/monocyte-colony stimulating factor |
| HDACis | Histone deacetylase inhibitors |
| LOH | Loss of heterozygosity |
| HLA | Human leukocyte antigen |
| HNSCC | Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma |
| HPV | Human papilloma virus |
| ICP | Immune checkpoint |
| ICPi | Immune checkpoint inhibitors |
| IDO | Indolamine-2,3-dioxygenase |
| IFN | Interferon |
| IgG | Immunoglobulin |
| IL | Interleukin |
| LAG-3 | Lymphocyte-activation gene 3 |
| LAHNC | Locally advanced head and neck carcinoma |
| LncRNAs | Long coding ribonucleic acids |
| LRF | Reducing locoregional failure |
| LRT | Locoregional treatment |
| LSCC | Laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma |
| MDSC | Myeloid-derived suppressor cell |
| MHC | Major histocompatibility complex |
| NETs | Neutrophil extracellular traps |
| NK | Natural killer |
| NLR | Neutrophil-to lymphocyte ratios |
| NO | Nitric oxide |
| OPSCC | Oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma |
| ORR | Overall response rate |
| OS | Overall survival |
| PD-1 | Programmed death receptor 1 |
| PD-L1 | Programmed death ligand 1 |
| PFS | Progression-free survival |
| PGE2 | Prostaglandin E2 |
| PI3KPMN | Phosphatidyl-linositol-3-kinasePre metastatic niches |
| PTEN | Phosphatase and tensin homolog |
| R/M | recurrence and or metastatic |
| RNS | Reactive nitrogen species |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| RT | Radiotherapy |
| TAMs | Tumor-associated macrophages |
| TANs | Tumor-associated neutrophils |
| TCGA | The Cancer Genome Atlas |
| TCR | T cell receptor |
| TGFBR2 | Transforming growth factor beta |
| TGFβ | Transforming growth factor beta |
| TIGIT | T cell immunoglobulin and ITIM domain |
| TIL | Tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte |
| TIM-3 | T cell immunoglobulin and mucin domain-containing protein 3 |
| TME | Tumor microenvironment |
| TNFα | Tumor necrosis factor alpha |
| TP53 | Tumor Protein P53 |
| Treg | Regulatory T cell |
| VEGF | Vascular endothelial growth factor |
| VISTA | V-domain Ig suppressor of T cell activation |
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global Cancer Statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer Statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2022, 72, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashibe, M.; Brennan, P.; Chuang, S.-C.; Boccia, S.; Castellsague, X.; Chen, C.; Curado, M.P.; Dal Maso, L.; Daudt, A.W.; Fabianova, E.; et al. Interaction between Tobacco and Alcohol Use and the Risk of Head and Neck Cancer: Pooled Analysis in the International Head and Neck Cancer Epidemiology Consortium. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2009, 18, 541–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ang, K.K.; Harris, J.; Wheeler, R.; Weber, R.; Rosenthal, D.I.; Nguyen-Tân, P.F.; Westra, W.H.; Chung, C.H.; Jordan, R.C.; Lu, C.; et al. Human Papillomavirus and Survival of Patients with Oropharyngeal Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, E.; Ismaila, N.; Bauman, J.E.; Dabney, R.; Gan, G.; Jordan, R.; Kaufman, M.; Kirtane, K.; McBride, S.M.; Old, M.O.; et al. Immunotherapy and Biomarker Testing in Recurrent and Metastatic Head and Neck Cancers: ASCO Guideline. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 1132–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saddawi-Konefka, R.; Simon, A.B.; Sumner, W.; Sharabi, A.; Mell, L.K.; Cohen, E.E.W. Defining the Role of Immunotherapy in the Curative Treatment of Locoregionally Advanced Head and Neck Cancer: Promises, Challenges, and Opportunities. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 738626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binnewies, M.; Roberts, E.W.; Kersten, K.; Chan, V.; Fearon, D.F.; Merad, M.; Coussens, L.M.; Gabrilovich, D.I.; Ostrand-Rosenberg, S.; Hedrick, C.C.; et al. Understanding the Tumor Immune Microenvironment (TIME) for Effective Therapy. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 541–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorsson, V.; Gibbs, D.L.; Brown, S.D.; Wolf, D.; Bortone, D.S.; Yang, T.-H.O.; Porta-Pardo, E.; Gao, G.; Plaisier, C.L.; Eddy, J.A.; et al. The Immune Landscape of Cancer. Immunity 2018, 48, 812–830.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knebel, M.; Körner, S.; Kühn, J.P.; Wemmert, S.; Brust, L.; Smola, S.; Wagner, M.; Bohle, R.M.; Morris, L.G.T.; Pandey, A.; et al. Prognostic Impact of Intra- and Peritumoral Immune Cell Subpopulations in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinomas—Comprehensive Analysis of the TCGA-HNSC Cohort and Immunohistochemical Validation on 101 Patients. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1172768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- William, W.N.; Zhao, X.; Bianchi, J.J.; Lin, H.Y.; Cheng, P.; Lee, J.J.; Carter, H.; Alexandrov, L.B.; Abraham, J.P.; Spetzler, D.B.; et al. Immune Evasion in HPV- Head and Neck Precancer-Cancer Transition Is Driven by an Aneuploid Switch Involving Chromosome 9p Loss. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2022655118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Xia, X.; Huang, L.-B.; An, H.; Cao, M.; Kim, G.D.; Chen, H.-N.; Zhang, W.-H.; Shu, Y.; Kong, X.; et al. Pan-Cancer Single-Cell Analysis Reveals the Heterogeneity and Plasticity of Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts in the Tumor Microenvironment. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 6619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obradovic, A.; Graves, D.; Korrer, M.; Wang, Y.; Roy, S.; Naveed, A.; Xu, Y.; Luginbuhl, A.; Curry, J.; Gibson, M.; et al. Immunostimulatory Cancer-Associated Fibroblast Subpopulations Can Predict Immunotherapy Response in Head and Neck Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 28, 2094–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Guo, H.; Zhai, P.; Yan, M.; Liu, C.; Wang, X.; Shi, C.; Li, J.; Tong, T.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Spatial and Single-Cell Transcriptomics Reveal a Cancer-Associated Fibroblast Subset in HNSCC That Restricts Infiltration and Antitumor Activity of CD8+ T Cells. Cancer Res. 2024, 84, 258–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saba, N.F.; Steuer, C.E.; Ekpenyong, A.; McCook-Veal, A.; Magliocca, K.; Patel, M.; Schmitt, N.C.; Stokes, W.; Bates, J.E.; Rudra, S.; et al. Pembrolizumab and Cabozantinib in Recurrent Metastatic Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Phase 2 Trial. Nat. Med. 2023, 29, 880–887, Erratum in Nat. Med. 2024, 30, 2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mastronikolis, N.S.; Spyropoulou, D.; Kyrodimos, E.; Piperigkou, Z.; Giotakis, E.; Delides, A.; Karamanos, N.K. The Interplay between Tumor and Nodal Microenvironments for the Formation of Nodal Premetastatic Niche in Head and Neck Cancer. Am. J. Physiol.-Cell Physiol. 2023, 325, C1516–C1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, C.; Huang, Y.C.; Luo, H.C.; He, J.L.; Wang, R.C.; Yang, F.; Meng, W.R.; Li, L.; Zhu, G.Q. Deciphering the Premetastatic Lymphatic Niche of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. J. Dent. Res. 2025, 220345241307894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmusrati, A.; Wang, J.; Wang, C.-Y. Tumor Microenvironment and Immune Evasion in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Int. J. Oral Sci. 2021, 13, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seliger, B.; Massa, C.; Yang, B.; Bethmann, D.; Kappler, M.; Eckert, A.W.; Wickenhauser, C. Immune Escape Mechanisms and Their Clinical Relevance in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantovani, A.; Sozzani, S.; Locati, M.; Allavena, P.; Sica, A. Macrophage Polarization: Tumor-Associated Macrophages as a Paradigm for Polarized M2 Mononuclear Phagocytes. Trends Immunol. 2002, 23, 549–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Saeed, A.F.U.H.; Liu, Q.; Jiang, Q.; Xu, H.; Xiao, G.G.; Rao, L.; Duo, Y. Macrophages in Immunoregulation and Therapeutics. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, N.; Shomori, K.; Shiomi, T.; Nakabayashi, M.; Takeda, C.; Ryoke, K.; Ito, H. Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts and CD163-Positive Macrophages in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Their Clinicopathological and Prognostic Significance. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2012, 41, 444–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balermpas, P.; Rödel, F.; Liberz, R.; Oppermann, J.; Wagenblast, J.; Ghanaati, S.; Harter, P.N.; Mittelbronn, M.; Weiss, C.; Rödel, C.; et al. Head and Neck Cancer Relapse after Chemoradiotherapy Correlates with CD163+ Macrophages in Primary Tumour and CD11b+ Myeloid Cells in Recurrences. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 111, 1509–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, K.; Hiroi, M.; Shimada, J.; Ohmori, Y. Infiltration of M2 Tumor-Associated Macrophages in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Correlates with Tumor Malignancy. Cancers 2011, 3, 3726–3739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giese, M.A.; Hind, L.E.; Huttenlocher, A. Neutrophil Plasticity in the Tumor Microenvironment. Blood 2019, 133, 2159–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papayannopoulos, V. Neutrophil Extracellular Traps in Immunity and Disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 18, 134–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cools-Lartigue, J.; Spicer, J.; McDonald, B.; Gowing, S.; Chow, S.; Giannias, B.; Bourdeau, F.; Kubes, P.; Ferri, L. Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Sequester Circulating Tumor Cells and Promote Metastasis. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 3446–3458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tohme, S.; Yazdani, H.O.; Al-Khafaji, A.B.; Chidi, A.P.; Loughran, P.; Mowen, K.; Wang, Y.; Simmons, R.L.; Huang, H.; Tsung, A. Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Promote the Development and Progression of Liver Metastases after Surgical Stress. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 1367–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Liu, Y.; Hu, T.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Li, T.; Wang, C.; Dong, Z.; Novakovic, V.A.; Hu, T.; et al. Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Enhance Procoagulant Activity in Patients with Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 145, 1695–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, G.H.; Lin, Y.Q.; Tian, L.; Zhang, T.; Yan, D.M.; Yu, J.H.; Deng, Y.C. Natural Killer Cell Homing and Trafficking in Tissues and Tumors: From Biology to Application. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charap, A.J.; Enokida, T.; Brody, R.; Sfakianos, J.; Miles, B.; Bhardwaj, N.; Horowitz, A. Landscape of Natural Killer Cell Activity in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. J. Immunother. Cancer 2020, 8, e001523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Zheng, L.; Qi, C. Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells (MDSCs) in the Tumor Microenvironment and Their Targeting in Cancer Therapy. Mol. Cancer 2025, 24, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Shi, H.; Zhang, B.; Ou, X.; Ma, Q.; Chen, Y.; Shu, P.; Li, D.; Wang, Y. Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells as Immunosuppressive Regulators and Therapeutic Targets in Cancer. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadrup, S.; Donia, M.; Thor Straten, P. Effector CD4 and CD8 T Cells and Their Role in the Tumor Microenvironment. Cancer Microenviron. 2013, 6, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Church, S.E.; Jensen, S.M.; Antony, P.A.; Restifo, N.P.; Fox, B.A. Tumor-Specific CD4+ T Cells Maintain Effector and Memory Tumor-Specific CD8+ T Cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 2014, 44, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bos, R.; Sherman, L.A. CD4+ T-Cell Help in the Tumor Milieu Is Required for Recruitment and Cytolytic Function of CD8+ T Lymphocytes. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 8368–8377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raskov, H.; Orhan, A.; Christensen, J.P.; Gögenur, I. Cytotoxic CD8+ T Cells in Cancer and Cancer Immunotherapy. Br. J. Cancer 2021, 124, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- So, Y.K.; Byeon, S.-J.; Ku, B.M.; Ko, Y.H.; Ahn, M.-J.; Son, Y.-I.; Chung, M.K. An Increase of CD8+ T Cell Infiltration Following Recurrence Is a Good Prognosticator in HNSCC. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 20059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, G.; Egloff, A.M.; Afeyan, A.B.; Wolff, J.O.; Zeng, Z.; Chernock, R.D.; Zhou, L.; Messier, C.; Lizotte, P.; Pfaff, K.L.; et al. Pre-Existing Tumor-Resident T Cells with Cytotoxic Potential Associate with Response to Neoadjuvant Anti-PD-1 in Head and Neck Cancer. Sci. Immunol. 2023, 8, eadf4968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Xu, L.; Nie, L.; Zhang, C.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, R.; Cao, J.; Tian, L.; Liu, M. B Cells in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Current Opinion and Novel Therapy. Cancer Cell Int. 2024, 24, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, B.; Ma, F.; Tong, F.; Yan, B.; Liu, T.; Xie, H.; Song, L.; Yu, S.; Wei, L. Characteristics of B Lymphocyte Infiltration in HPV+ Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 2021, 112, 1402–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lechner, A.; Schlößer, H.A.; Thelen, M.; Wennhold, K.; Rothschild, S.I.; Gilles, R.; Quaas, A.; Siefer, O.G.; Huebbers, C.U.; Cukuroglu, E.; et al. Tumor-Associated B Cells and Humoral Immune Response in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Oncoimmunology 2019, 8, 1535293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z. The History and Advances in Cancer Immunotherapy: Understanding the Characteristics of Tumor-Infiltrating Immune Cells and Their Therapeutic Implications. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2020, 17, 807–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merlano, M.C.; Denaro, N.; Garrone, O. Immune Escape Mechanisms in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Implication for New Immunotherapy Approach. Curr. Opin. Oncol. 2020, 32, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leen, G.; Stein, J.E.; Robinson, J.; Maldonado Torres, H.; Marsh, S.G.E. The HLA Diversity of the Anthony Nolan Register. HLA 2021, 97, 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, L.G.T. Loss of Human Leukocyte Antigen and Immune Escape in Head and Neck Cancer. Laryngoscope 2024, 134, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Karchin, R. Pan-Cancer HLA Gene-Mediated Tumor Immunogenicity and Immune Evasion. Mol. Cancer Res. 2022, 20, 1272–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhou, C.; Chen, K.; Huang, B.; Liu, Q.; Ye, H. Benchmarking HLA Genotyping and Clarifying HLA Impact on Survival in Tumor Immunotherapy. Mol. Oncol. 2021, 15, 1764–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaafsma, E.; Fugle, C.M.; Wang, X.; Cheng, C. Pan-Cancer Association of HLA Gene Expression with Cancer Prognosis and Immunotherapy Efficacy. Br. J. Cancer 2021, 125, 422–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Y.; Yang, G.; Song, Y.; Zhao, X.; So, C.; Liao, J.; Wang, L.D.; Yang, C.S. DNA Hypermethylation Is a Mechanism for Loss of Expression of the HLA Class I Genes in Human Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinomas. Carcinogenesis 2001, 22, 1615–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollack, B.P.; Sapkota, B.; Cartee, T.V. Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Inhibition Augments the Expression of MHC Class I and II Genes. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 4400–4413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogino, T.; Shigyo, H.; Ishii, H.; Katayama, A.; Miyokawa, N.; Harabuchi, Y.; Ferrone, S. HLA Class I Antigen Down-Regulation in Primary Laryngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Lesions as a Poor Prognostic Marker. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 9281–9289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Cancer Genome Atlas Network. Comprehensive Genomic Characterization of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinomas. Nature 2015, 517, 576–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferris, R.L.; Whiteside, T.L.; Ferrone, S. Immune Escape Associated with Functional Defects in Antigen-Processing Machinery in Head and Neck Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 3890–3895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferris, R.L. Immunology and Immunotherapy of Head and Neck Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 3293–3304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostecki, K.L.; Iida, M.; Crossman, B.E.; Salgia, R.; Harari, P.M.; Bruce, J.Y.; Wheeler, D.L. Immune Escape Strategies in Head and Neck Cancer: Evade, Resist, Inhibit, Recruit. Cancers 2024, 16, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.-Y.; Safdar, J.; Li, Z.-N.; Fang, Q.-G.; Zhang, X.; Xu, Z.-F.; Sun, C.-F. CCR7 Regulates Cell Migration and Invasion through MAPKs in Metastatic Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Head and Neck. Int. J. Oncol. 2014, 45, 2502–2510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guak, H.; Al Habyan, S.; Ma, E.H.; Aldossary, H.; Al-Masri, M.; Won, S.Y.; Ying, T.; Fixman, E.D.; Jones, R.G.; McCaffrey, L.M.; et al. Glycolytic Metabolism Is Essential for CCR7 Oligomerization and Dendritic Cell Migration. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.T.; Knops, A.; Swendseid, B.; Martinez-Outschoom, U.; Harshyne, L.; Philp, N.; Rodeck, U.; Luginbuhl, A.; Cognetti, D.; Johnson, J.; et al. Prognostic Significance of Tumor-Associated Macrophage Content in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Meta-Analysis. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrandino, R.M.; Roof, S.; Garneau, J.; Haidar, Y.; Bates, S.E.; Park, Y.-H.A.; Bauml, J.M.; Genden, E.M.; Miles, B.; Sigel, K. Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio as a Prognostic Indicator for Overall and Cancer-Specific Survival in Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck. Head Neck 2020, 42, 2830–2840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rachidi, S.; Wallace, K.; Wrangle, J.M.; Day, T.A.; Alberg, A.J.; Li, Z. Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio and Overall Survival in All Sites of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Head Neck 2016, 38, E1068–E1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaul, M.E.; Fridlender, Z.G. Tumour-Associated Neutrophils in Patients with Cancer. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 16, 601–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Zhou, J.; Tang, D.; Zhou, L.; Chou, L.; Chou, K.-Y.; Tao, L.; Lu, L.-M. Neutrophil Infiltration Mediated by CXCL5 Accumulation in the Laryngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Microenvironment: A Mechanism by Which Tumour Cells Escape Immune Surveillance. Clin. Immunol. 2017, 175, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Starska-Kowarska, K. The Role of Different Immunocompetent Cell Populations in the Pathogenesis of Head and Neck Cancer—Regulatory Mechanisms of Pro- and Anti-Cancer Activity and Their Impact on Immunotherapy. Cancers 2023, 15, 1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, X.; Fan, H.; Tang, Y.; Wang, S.; Cao, M.; Wang, H.; Dai, L.; Wang, K.; Yu, X.; Wu, J.; et al. Myeloid Derived Suppressor Cells Contribute to the Malignant Progression of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0229089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, X.; Song, S.; Weng, G.; Wen, Y.; Liu, F.; Cao, D.; Liu, Y. Expansion of PMN-Myeloid Derived Suppressor Cells and Their Clinical Relevance in Patients with Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Oral Oncol. 2019, 95, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavrielatou, N.; Vathiotis, I.; Economopoulou, P.; Psyrri, A. The Role of B Cells in Head and Neck Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 5383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeske, S.S.; Brand, M.; Ziebart, A.; Laban, S.; Doescher, J.; Greve, J.; Jackson, E.K.; Hoffmann, T.K.; Brunner, C.; Schuler, P.J. Adenosine-Producing Regulatory B Cells in Head and Neck Cancer. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2020, 69, 1205–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, S.; Dosset, M.; Castro, A.; Carter, H.; Zanetti, M. Transcriptional Analysis Links B Cells and TERT Expression to Favorable Prognosis in Head and Neck Cancer. PNAS Nexus 2023, 2, pgad046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.; New, J.; Vishwakarma, V.; Joshi, R.; Enders, J.; Lin, F.; Dasari, S.; Gutierrez, W.R.; Leef, G.; Ponnurangam, S.; et al. Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts Drive Glycolysis in a Targetable Signaling Loop Implicated in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Progression. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 3769–3782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrido, M.A.; Navarro-Ocón, A.; Ronco-Díaz, V.; Olea, N.; Aptsiauri, N. Loss of Heterozygosity (LOH) Affecting HLA Genes in Breast Cancer: Clinical Relevance and Therapeutic Opportunities. Genes 2024, 15, 1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreescu, M.; Berbec, N.; Tanase, A.D. Assessment of Impact of Human Leukocyte Antigen-Type and Cytokine-Type Responses on Outcomes after Targeted Therapy Currently Used to Treat Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 2731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirico, M.; D’Angelo, A.; Gianni, C.; Casadei, C.; Merloni, F.; De Giorgi, U. Current State and Future Challenges for PI3K Inhibitors in Cancer Therapy. Cancers 2023, 15, 703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, A.W.Y.; Lim, K.P.; Cheong, S.C. Translational Genomics and Recent Advances in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2020, 61, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, X.; Jiang, J.; Pang, X.; Huang, M.; Tang, Y.; Liang, X.; Tang, Y. The Evolving Landscape of PD-1/PD-L1 Pathway in Head and Neck Cancer. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Yang, Q.-C.; Li, Y.-C.; Yang, L.-L.; Liu, J.-F.; Li, H.; Xiao, Y.; Bu, L.-L.; Zhang, W.-F.; Sun, Z.-J. Targeting CMTM6 Suppresses Stem Cell-Like Properties and Enhances Antitumor Immunity in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2020, 8, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.-W.; Wu, L.; Sun, Z.-J. Co-Inhibitory Immune Checkpoints in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Oral Dis. 2018, 24, 120–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manieri, N.A.; Chiang, E.Y.; Grogan, J.L. TIGIT: A Key Inhibitor of the Cancer Immunity Cycle. Trends Immunol. 2017, 38, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Mao, L.; Liu, J.-F.; Chen, L.; Yu, G.-T.; Yang, L.-L.; Wu, H.; Bu, L.-L.; Kulkarni, A.B.; Zhang, W.-F.; et al. Blockade of TIGIT/CD155 Signaling Reverses T-Cell Exhaustion and Enhances Antitumor Capability in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2019, 7, 1700–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; McMichael, E.L.; Shayan, G.; Li, J.; Chen, K.; Srivastava, R.; Kane, L.P.; Lu, B.; Ferris, R.L. Novel Effector Phenotype of Tim-3+ Regulatory T Cells Leads to Enhanced Suppressive Function in Head and Neck Cancer Patients. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 4529–4538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Struckmeier, A.-K.; Gosau, M.; Smeets, R. Immunotherapeutic Strategies beyond the PD-1/PD-L1 Pathway in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma—A Scoping Review on Current Developments in Agents Targeting TIM-3, TIGIT, LAG-3, and VISTA. Oral Oncol. 2025, 161, 107145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Lin, W.-P.; Xiao, Y.; Yang, Q.-C.; Bushabu Fidele, N.; Yu, H.-J.; Sun, Z.-J. VISTA Blockade Alleviates Immunosuppression of MDSCs in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2023, 125, 111128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aggarwal, V.; Workman, C.J.; Vignali, D.A.A. LAG-3 as the Third Checkpoint Inhibitor. Nat. Immunol. 2023, 24, 1415–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.-W.; Mao, L.; Yu, G.-T.; Bu, L.-L.; Ma, S.-R.; Liu, B.; Gutkind, J.S.; Kulkarni, A.B.; Zhang, W.-F.; Sun, Z.-J. LAG-3 Confers Poor Prognosis and Its Blockade Reshapes Antitumor Response in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Oncoimmunology 2016, 5, e1239005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.H.; Qiu, J.; O’Sullivan, D.; Buck, M.D.; Noguchi, T.; Curtis, J.D.; Chen, Q.; Gindin, M.; Gubin, M.M.; Van Der Windt, G.J.W.; et al. Metabolic Competition in the Tumor Microenvironment Is a Driver of Cancer Progression. Cell 2015, 162, 1229–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Tang, Z.; Huang, H.; Zhou, G.; Cui, C.; Weng, Y.; Liu, W.; Kim, S.; Lee, S.; Perez-Neut, M.; et al. Metabolic Regulation of Gene Expression by Histone Lactylation. Nature 2019, 574, 575–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Pan, X.; Fan, Z.; Xia, J.; Ren, X. Lactate Dehydrogenase B as a Metabolism-Related Marker for Immunotherapy in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cell Signal 2024, 120, 111200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, K.; Zou, J.; Wang, B.; Liu, C.; Khan, M.; Xie, T.; Huang, X.; Shen, P.; Tian, Y.; Yuan, Y. A Metabolism-Related Gene Prognostic Index Bridging Metabolic Signatures and Antitumor Immune Cycling in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 857934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauss, C.; Stone, L.D.; Ghafouri, M.; Quan, D.; Johnson, J.; Fribley, A.M.; Amm, H.M. Overcoming Resistance to Standard-of-Care Therapies for Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinomas. Cells 2024, 13, 1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starska-Kowarska, K. Role of Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cells in Head and Neck Cancer-Regulatory Mechanisms of Tumorigenic and Immune Activity, Chemotherapy Resistance, and Therapeutic Benefits of Stromal Cell-Based Pharmacological Strategies. Cells 2024, 13, 1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchard, P.; Baujat, B.; Holostenco, V.; Bourredjem, A.; Baey, C.; Bourhis, J.; Pignon, J.-P.; MACH-CH Collaborative Group. Meta-Analysis of Chemotherapy in Head and Neck Cancer (MACH-NC): A Comprehensive Analysis by Tumour Site. Radiother. Oncol. 2011, 100, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacas, B.; Carmel, A.; Landais, C.; Wong, S.J.; Licitra, L.; Tobias, J.S.; Burtness, B.; Ghi, M.G.; Cohen, E.E.W.; Grau, C.; et al. Meta-Analysis of Chemotherapy in Head and Neck Cancer (MACH-NC): An Update on 107 Randomized Trials and 19,805 Patients, on Behalf of MACH-NC Group. Radiother. Oncol. 2021, 156, 281–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, A.M.; Weaver, A.N.; Acosta, P.; Harris, L.; Bowles, D.W. Review of Current and Future Medical Treatments in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancers 2024, 16, 3488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chow, L.Q.M. Head and Neck Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Cohen, R.B.; Dimitrios Colevas, A. Platinum/Taxane/Pembrolizumab vs Platinum/5FU/Pembrolizumab in Recurrent/Metastatic Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma (r/m HNSCC). Oral Oncol. 2024, 158, 106997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calais, G.; Alfonsi, M.; Bardet, E.; Sire, C.; Germain, T.; Bergerot, P.; Rhein, B.; Tortochaux, J.; Oudinot, P.; Bertrand, P. Randomized Trial of Radiation Therapy versus Concomitant Chemotherapy and Radiation Therapy for Advanced-Stage Oropharynx Carcinoma. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1999, 91, 2081–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pignon, J.-P.; le Maître, A.; Maillard, E.; Bourhis, J.; MACH-NC Collaborative Group. Meta-Analysis of Chemotherapy in Head and Neck Cancer (MACH-NC): An Update on 93 Randomised Trials and 17,346 Patients. Radiother. Oncol. 2009, 92, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiyota, N.; Tahara, M.; Mizusawa, J.; Kodaira, T.; Fujii, H.; Yamazaki, T.; Mitani, H.; Iwae, S.; Fujimoto, Y.; Onozawa, Y.; et al. Weekly Cisplatin Plus Radiation for Postoperative Head and Neck Cancer (JCOG1008): A Multicenter, Noninferiority, Phase II/III Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 1980–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Chaudhary, M.K.; Thakar, A.; Bhaskar, S.; Sikka, K.; Pramanik, R.; Biswas, A.; Singh, C.A.; Sahoo, R.K.; Deo, S.; et al. 1172TiP—Concurrent Chemotherapy and External Radiation Therapy: An Open Label Non-Inferiority Phase III Randomized Controlled Trial of Weekly versus Three Weekly Cisplatin and Radical Radiotherapy in Locally Advanced Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: CONCERT Trial. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, v473–v474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.A.N.; Dikhit, P.S.; Jose, A.; Mehta, V.; Pai, A.; Kudva, A.; Rao, M. Oral Metronomic Chemotherapy in Advanced and Metastatic Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Need of the Hour. J. Maxillofac. Oral Surg. 2024, 23, 793–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, V.M.; Noronha, V.; Menon, N.; Singh, A.; Ghosh-Laskar, S.; Budrukkar, A.; Bhattacharjee, A.; Swain, M.; Mathrudev, V.; Nawale, K.; et al. Results of Phase III Randomized Trial for Use of Docetaxel as a Radiosensitizer in Patients With Head and Neck Cancer, Unsuitable for Cisplatin-Based Chemoradiation. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 2350–2361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burtness, B.; Harrington, K.J.; Greil, R.; Soulières, D.; Tahara, M.; de Castro, G.; Psyrri, A.; Basté, N.; Neupane, P.; Bratland, Å.; et al. Pembrolizumab Alone or with Chemotherapy versus Cetuximab with Chemotherapy for Recurrent or Metastatic Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck (KEYNOTE-048): A Randomised, Open-Label, Phase 3 Study. Lancet 2019, 394, 1915–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vermorken, J.B.; Mesia, R.; Rivera, F.; Remenar, E.; Kawecki, A.; Rottey, S.; Erfan, J.; Zabolotnyy, D.; Kienzer, H.-R.; Cupissol, D.; et al. Platinum-Based Chemotherapy plus Cetuximab in Head and Neck Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 1116–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehra, R.; Seiwert, T.Y.; Gupta, S.; Weiss, J.; Gluck, I.; Eder, J.P.; Burtness, B.; Tahara, M.; Keam, B.; Kang, H.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Pembrolizumab in Recurrent/Metastatic Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Pooled Analyses after Long-Term Follow-up in KEYNOTE-012. Br. J. Cancer 2018, 119, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, L.Q.M.; Haddad, R.; Gupta, S.; Mahipal, A.; Mehra, R.; Tahara, M.; Berger, R.; Eder, J.P.; Burtness, B.; Lee, S.-H.; et al. Antitumor Activity of Pembrolizumab in Biomarker-Unselected Patients with Recurrent and/or Metastatic Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Results From the Phase Ib KEYNOTE-012 Expansion Cohort. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 3838–3845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrington, K.J.; Burtness, B.; Greil, R.; Soulières, D.; Tahara, M.; de Castro, G.; Psyrri, A.; Brana, I.; Basté, N.; Neupane, P.; et al. Pembrolizumab With or Without Chemotherapy in Recurrent or Metastatic Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Updated Results of the Phase III KEYNOTE-048 Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 790–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, E.E.W.; Soulières, D.; Le Tourneau, C.; Dinis, J.; Licitra, L.; Ahn, M.-J.; Soria, A.; Machiels, J.-P.; Mach, N.; Mehra, R.; et al. Pembrolizumab versus Methotrexate, Docetaxel, or Cetuximab for Recurrent or Metastatic Head-and-Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma (KEYNOTE-040): A Randomised, Open-Label, Phase 3 Study. Lancet 2019, 393, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferris, R.L.; Blumenschein, G.; Fayette, J.; Guigay, J.; Colevas, A.D.; Licitra, L.; Harrington, K.; Kasper, S.; Vokes, E.E.; Even, C.; et al. Nivolumab for Recurrent Squamous-Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1856–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topalian, S.L.; Hodi, F.S.; Brahmer, J.R.; Gettinger, S.N.; Smith, D.C.; McDermott, D.F.; Powderly, J.D.; Carvajal, R.D.; Sosman, J.A.; Atkins, M.B.; et al. Safety, Activity, and Immune Correlates of Anti-PD-1 Antibody in Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 2443–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillison, M.L.; Blumenschein, G.; Fayette, J.; Guigay, J.; Colevas, A.D.; Licitra, L.; Harrington, K.J.; Kasper, S.; Vokes, E.E.; Even, C.; et al. Long-Term Outcomes with Nivolumab as First-Line Treatment in Recurrent or Metastatic Head and Neck Cancer: Subgroup Analysis of CheckMate 141. Oncologist 2022, 27, e194–e198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colevas, A.D.; Bahleda, R.; Braiteh, F.; Balmanoukian, A.; Brana, I.; Chau, N.G.; Sarkar, I.; Molinero, L.; Grossman, W.; Kabbinavar, F.; et al. Safety and Clinical Activity of Atezolizumab in Head and Neck Cancer: Results from a Phase I Trial. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, 2247–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zandberg, D.P.; Algazi, A.P.; Jimeno, A.; Good, J.S.; Fayette, J.; Bouganim, N.; Ready, N.E.; Clement, P.M.; Even, C.; Jang, R.W.; et al. Durvalumab for Recurrent or Metastatic Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Results from a Single-Arm, Phase II Study in Patients with ≥25% Tumour Cell PD-L1 Expression Who Have Progressed on Platinum-Based Chemotherapy. Eur. J. Cancer 2019, 107, 142–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guigay, J.; Lee, K.-W.; Patel, M.R.; Daste, A.; Wong, D.J.; Goel, S.; Gordon, M.S.; Gutierrez, M.; Balmanoukian, A.; Le Tourneau, C.; et al. Avelumab for Platinum-Ineligible/Refractory Recurrent and/or Metastatic Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck: Phase Ib Results from the JAVELIN Solid Tumor Trial. J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9, e002998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, N.Y.; Uppaluri, R.; Westra, W.; Cohen, E.E.; Haddad, R.I.; Temam, S.; Le Tourneau, C.; Chernock, R.; Safina, S.; Klochikhin, A.; et al. Abstract CT285: KEYNOTE-689: A Phase 3 Study of Neoadjuvant and Adjuvant Pembrolizumab plus Standard of Care (SOC) in Locally Advanced (LA) Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma (HNSCC). Cancer Res. 2020, 80, CT285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferris, R.L.; Haddad, R.; Even, C.; Tahara, M.; Dvorkin, M.; Ciuleanu, T.E.; Clement, P.M.; Mesia, R.; Kutukova, S.; Zholudeva, L.; et al. Durvalumab with or without Tremelimumab in Patients with Recurrent or Metastatic Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: EAGLE, a Randomized, Open-Label Phase III Study. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 942–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, R.I.; Harrington, K.; Tahara, M.; Ferris, R.L.; Gillison, M.; Fayette, J.; Daste, A.; Koralewski, P.; Zurawski, B.; Taberna, M.; et al. Nivolumab Plus Ipilimumab Versus EXTREME Regimen as First-Line Treatment for Recurrent/Metastatic Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck: The Final Results of CheckMate 651. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 2166–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferris, R.L.; Moskovitz, J.; Kunning, S.; Ruffin, A.T.; Reeder, C.; Ohr, J.; Gooding, W.E.; Kim, S.; Karlovits, B.J.; Vignali, D.A.A.; et al. Phase I Trial of Cetuximab, Radiotherapy, and Ipilimumab in Locally Advanced Head and Neck Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 28, 1335–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Licitra, L.; Tahara, M.; Harrington, K.; Olivera Hurtado de Mendoza, M.; Guo, Y.; Aksoy, S.; Fang, M.; Żurawski, B.; Csőszi, T.; Klochikhin, M.; et al. Pembrolizumab with or Without Lenvatinib As First-Line Therapy for Recurrent or Metastatic Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma (R/M HNSCC): Phase 3 LEAP-010 Study. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2024, 118, e2–e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saba, N.F.; Chaudhary, R.; Kirtane, K.; Marra, A.; Ekpenyong, A.; McCook-Veal, A.; Schmitt, N.C.; Gross, J.H.; Patel, M.R.; Remick, J.; et al. Pembrolizumab and Cabozantinib in Recurrent and/or Metastatic Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Long-Term Survival Update with a Biomarker Analysis. Clin. Cancer Res. 2024, 30, 4601–4608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forster, M.; Brana, I.; Pousa, A.L.; Doger, B.; Roxburgh, P.; Bajaj, P.; Peguero, J.; Krebs, M.; Carcereny, E.; Patel, G.; et al. Eftilagimod Alpha (Soluble LAG3 Protein) Combined with Pembrolizumab as Second-Line Therapy for Patients with Metastatic Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2024, 30, 3726–3734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Hu, M.; Jin, T.; Teng, K.; Han, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, K.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, J.; Cheng, Y.; et al. 876P Evaluation of the Safety and Efficacy of Ivonescimab in Combination with Ligufalimab as First-Line (1L) Treatment for PD-L1 Positive Recurrent/Metastasis Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma (R/M HNSCC). Ann. Oncol. 2024, 35, S626–S627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanna, G.J.; Kaczmar, J.; Zandberg, D.P.; Wong, D.J.; Yilmaz, E.; Sherman, E.J.; Calvo, A.H.; Sacco, A.G.; Bohr, D.; Reiners, R.; et al. 922P Dose Expansion Results of the Bifunctional EGFR/TGFβ Inhibitor BCA101 with Pembrolizumab in Patients with Recurrent, Metastatic Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Ann. Oncol. 2023, 34, S582–S583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swiecicki, P.; Yilmaz, E.; Rosenberg, A.J.; Fujisawa, T.; Yang Bruce, J.; Meng, C.; Wozniak, M.; Wang, L.; Gorla, S.R.; Geiger, J.L. Enfortumab Vedotin in the Previously Treated Advanced Head and Neck Cancer (HNC) Cohort of EV-202. JCO 2023, 41, 6017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michel, L.; Jimeno, A.; Sukari, A.; Beck, J.T.; Chiu, J.; Ahern, E.; Hilton, J.; Even, C.; Zanetta, S.; Mekan, S.; et al. Sacituzumab Govitecan in Patients with Relapsed/Refractory Advanced Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Results from the Phase II TROPiCS-03 Basket Study. Clin. Cancer Res. 2025, 31, 832–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Fayette, J.; Salas, S.; Hong, D.S.; Adkins, D.; Dunn, L.; Ciardiello, F.; Cirauqui, B.; William, W.N.; Saba, N.F.; et al. Tisotumab Vedotin in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Updated Analysis from innovaTV 207 Part C. JCO 2024, 42, 6012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Sferruzza, G.; Yang, L.; Zhou, L.; Chen, S. CAR-T and CAR-NK as Cellular Cancer Immunotherapy for Solid Tumors. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2024, 21, 1089–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorós-Pérez, B.; Rivas-Pardo, B.; Gómez del Moral, M.; Subiza, J.L.; Martínez-Naves, E. State of the Art in CAR-T Cell Therapy for Solid Tumors: Is There a Sweeter Future? Cells 2024, 13, 725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Liu, M.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Sharma, A.; Liu, H.; Schmidt-Wolf, I.G.H. Recent Advances and Future Perspectives of CAR-T Cell Therapy in Head and Neck Cancer. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1213716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollock, N.I.; Grandis, J.R. HER2 as a Therapeutic Target in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 526–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Choi, J.Y.; Rah, Y.C.; Ahn, J.-C.; Kim, H.; Jeong, W.-J.; Ahn, S.-H. ErbB3, a Possible Prognostic Factor of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2020, 129, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papa, S.; Adami, A.; Metoudi, M.; Beatson, R.; George, M.S.; Achkova, D.; Williams, E.; Arif, S.; Reid, F.; Elstad, M.; et al. Intratumoral Pan-ErbB Targeted CAR-T for Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Interim Analysis of the T4 Immunotherapy Study. J. Immunother. Cancer 2023, 11, e007162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, Z.; Zhang, K.; Lam, A.K.; Huang, J.; Qiu, F.; Qiao, B.; Zhang, Y. MUC1 as a Target for CAR-T Therapy in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carinoma. Cancer Med. 2019, 9, 640–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Starzer, A.M.; Berghoff, A.S. New Emerging Targets in Cancer Immunotherapy: CD27 (TNFRSF7). ESMO Open 2020, 4, e000629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, Y.P.; Jin, L.; Bennett, K.B.; Wang, D.; Fredenburg, K.M.; Tseng, J.E.; Chang, L.-J.; Huang, J.; Chan, E.K.L. CD70 as a Target for Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cells in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Oral Oncol. 2018, 78, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feral, C.C.; Nishiya, N.; Fenczik, C.A.; Stuhlmann, H.; Slepak, M.; Ginsberg, M.H. CD98hc (SLC3A2) Mediates Integrin Signaling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, Y.; Omori, Y.; Suzuki, S.; Yamada, T. CD98hc as a Marker of Radiotherapy-Resistant Cancer Stem Cells in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Arch. Med. Sci. 2023, 19, 1859–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Digomann, D.; Kurth, I.; Tyutyunnykova, A.; Chen, O.; Löck, S.; Gorodetska, I.; Peitzsch, C.; Skvortsova, I.-I.; Negro, G.; Aschenbrenner, B.; et al. The CD98 Heavy Chain Is a Marker and Regulator of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Radiosensitivity. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 3152–3163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köseer, A.S.; Loureiro, L.R.; Jureczek, J.; Mitwasi, N.; González Soto, K.E.; Aepler, J.; Bartsch, T.; Feldmann, A.; Kunz-Schughart, L.A.; Linge, A.; et al. Validation of CD98hc as a Therapeutic Target for a Combination of Radiation and Immunotherapies in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancers 2022, 14, 1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, K.; Farrukh, H.; Chittepu, V.C.S.R.; Xu, H.; Pan, C.; Zhu, Z. CAR Race to Cancer Immunotherapy: From CAR T, CAR NK to CAR Macrophage Therapy. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 41, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maalej, K.M.; Merhi, M.; Inchakalody, V.P.; Mestiri, S.; Alam, M.; Maccalli, C.; Cherif, H.; Uddin, S.; Steinhoff, M.; Marincola, F.M.; et al. CAR-Cell Therapy in the Era of Solid Tumor Treatment: Current Challenges and Emerging Therapeutic Advances. Mol. Cancer 2023, 22, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Lu, C. Targeting Epigenetic Dysregulations in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. J. Dent. Res. 2025, 104, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Xu, N.; Shibata, H.; Saloura, V.; Uppaluri, R. Epigenetic Modulation of Immunotherapy and Implications in Head and Neck Cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2021, 40, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Chun, C.; Lagunas, A.M.; Crowe, D.L. Lysine Methyltransferase 2D Regulates Immune Response and Metastasis in Head and Neck Cancer. Anticancer. Res. 2024, 44, 3231–3242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fehn, A.; von Witzleben, A.; Grages, A.; Kors, T.A.; Ezić, J.; Betzler, A.C.; Brunner, C.; Schuler, P.J.; Theodoraki, M.-N.; Hoffmann, T.K.; et al. 5-Aza-2′-Deoxycytidin (Decitabine) Increases Cancer-Testis Antigen Expression in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Modifies Immune Checkpoint Expression, Especially in CD39-Positive CD8 and CD4 T Cells. Neoplasia 2025, 59, 101086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.-C.; Wang, W.-Y.; Zhou, J.-J.; Wu, L.; Zhang, M.-J.; Yang, Q.-C.; Deng, W.-W.; Sun, Z.-J. Inhibition of DNMT1 Potentiates Antitumor Immunity in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2022, 111, 109113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Yang, J.; Wu, D.; Yu, S.; Liu, J.; Hu, T.; Luo, J.; Zhou, H. DNMT1-Targeting Remodeling Global DNA Hypomethylation for Enhanced Tumor Suppression and Circumvented Toxicity in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Mol. Cancer 2024, 23, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calanca, N.; Francisco, A.L.N.; Bizinelli, D.; Kuasne, H.; Barros Filho, M.C.; Flores, B.C.T.; Pinto, C.A.L.; Rainho, C.A.; Soares, M.B.P.; Marchi, F.A.; et al. DNA Methylation-Based Depiction of the Immune Microenvironment and Immune-Associated Long Non-Coding RNAs in Oral Cavity Squamous Cell Carcinomas. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 167, 115559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Mudianto, T.; Ma, X.; Riley, R.; Uppaluri, R. Targeting EZH2 Enhances Antigen Presentation, Antitumor Immunity and Circumvents Anti-PD-1 Resistance in Head and Neck Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 290–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, C.P.; Wu, Q.V.; Voutsinas, J.; Fromm, J.R.; Jiang, X.; Pillarisetty, V.G.; Lee, S.M.; Santana-Davila, R.; Goulart, B.; Baik, C.S.; et al. A Phase II Trial of Pembrolizumab and Vorinostat in Recurrent Metastatic Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinomas and Salivary Gland Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 837–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Drugs | Target | Type | Fc Engineering | Half-Life (Days) | ADCC/ADCP Activity | Unique Mechanism/Features | Key Trials in HNSCC | Approval in HNSCC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pembrolizumab | PD-1 | Humanized IgG4κ | Hinge-stabilized (S228P) to prevent Fab-arm exchange | ~26 | no | Targets PD-1; strong correlation with PD-L1 CPS ≥ 20 for efficacy | KEYNOTE-048, KEYNOTE-040 | FDA-approved: 1L (CPS ≥ 1) or 2L+ |
| Nivolumab | PD-1 | Human IgG4κ | Hinge-stabilized (S228P) | ~25 | no | Binds PD-1 with higher affinity than pembrolizumab; no PD-L1 CPS requirement for 2L+ approval | CheckMate 141 | FDA-approved: 2L+ (post-platinum) |
| Atezolizumab | PDL-1 | Humanized IgG1κ | Fc null (N298A mutation) to eliminate effector function | ~27 | no | Blocks PD-L1 binding to both PD-1 and B7-1 (CD80); may enhance T-cell priming | IMvoke, CITYSCAPE | Investigational |
| Avelumab | PD-L1 | Human IgG1λ | Wild-type Fc | ~6 | yes | Retains ADCC activity; may kill PD-L1⁺ Tregs or tumor cells | JAVELIN Head & Neck 100 | Investigational |
| Durvalumab | PD-L1 | Human IgG1κ | Fc silenced (L234F, L235E, P331S) | ~18 | no | Engineered to minimize FcγR binding; often paired with tremelimumab (CTLA-4) in combos | HAWK, KESTREL | Investigational |
| Ipilimumab | CTLA-4 | Human IgG1κ | Wild-type Fc | ~15 | Yes (theoretical) | Targets CTLA-4 on T-cells; depletes Tregs via ADCC in TME | CheckMate 651 (combo with nivo) | Not approved (investigational) |
| Trememilumab | CTLA-4 | Human IgG2λ | No Fc effector function (IgG2 subclass) | ~22 | no | IgG2 limits Fc-mediated effects; focuses on CTLA-4 blockade without T-cell depletion | KESTREL, EAGLE | Investigational |
| Drugs | Target | Trial-Phase | Key Trial Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lenvatinib + Pembrolizumab | VEGFR1-3, FGFR | LEAP-010—Phase 3 | ORR: 46% (1L CPS ≥ 1); PFS: 6.3 mo; no OS benefit. |
| Cabozantinib + Pembrolizumab | VEGFR 1-3, MET, KIT, AXL, FLT3 | Phase 2 | ORR 52%, PFS 12.8 mo |
| Zanzalitinib (XL092) + Pembrolizumab | MET, VEGFR2, AXL, MER | STELLAR 305—Phase 2/3 | Trial ongoing |
| Eftilagimod Alpha (IMP321) + Pembrolizumab | LAG-3 (MHC II agonist) | TACTI-002 Part C—Phase 2 | ORR: 30%; PFS 2.3 mo; 12-mo OS rate 46%. |
| Petosemtamab (MCLA-158) + Pembrolizumab | EGFR × LGR5 bispecific | Phase 2 | ORR: 30% in EGFR-resistant HNSCC |
| Ivonescimab (AK112) | PD-1 × VEGF-A bispecific | Phase 2 | ORR: 40%; PFS 5 mo |
| Ligufalimab (AK117) | CD47 (SIRPα inhibitor) | Phase 2 | Combined with Ivonescimab ORR: 65%. PFS 7.1 mo |
| BCA101 | EGFR × TGF-β bispecific | Phase 1 | ORR: 48% in EGFR + HNSCC |
| SI-B001 | EGFR × PD-L1 bispecific | Phase 1/2 | ORR: 30% |
| Enfortumab Vedotin | Nectin-4 (ADC) | Phase 2 | ORR 23.9%, PFS 3.94 mo, OS 5.98 mo |
| Sacituzumab Govitecan | Trop-2 (ADC) | Phase 2 | ORR 16%, PFS 4.1 mo, OS 9 mo |
| Tisotumab vedotin | Tissue factor (ADC) | Phase 2 | ORR 32.5% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arriola Benítez, P.C.; Fusco, M.; Amorin, R.; Picón, C.R.; Piccioni, F.; Victoria, L.; Rizzo, M.M.; Malvicini, M. Unraveling the Role of Tumor-Infiltrating Immune Cells in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Implications for Antitumor Immune Responses and Immunotherapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6337. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136337
Arriola Benítez PC, Fusco M, Amorin R, Picón CR, Piccioni F, Victoria L, Rizzo MM, Malvicini M. Unraveling the Role of Tumor-Infiltrating Immune Cells in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Implications for Antitumor Immune Responses and Immunotherapy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(13):6337. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136337
Chicago/Turabian StyleArriola Benítez, Paula Constanza, Mariel Fusco, Ricardo Amorin, Carlos Rafael Picón, Flavia Piccioni, Lucia Victoria, Manglio Miguel Rizzo, and Mariana Malvicini. 2025. "Unraveling the Role of Tumor-Infiltrating Immune Cells in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Implications for Antitumor Immune Responses and Immunotherapy" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 13: 6337. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136337
APA StyleArriola Benítez, P. C., Fusco, M., Amorin, R., Picón, C. R., Piccioni, F., Victoria, L., Rizzo, M. M., & Malvicini, M. (2025). Unraveling the Role of Tumor-Infiltrating Immune Cells in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Implications for Antitumor Immune Responses and Immunotherapy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(13), 6337. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136337









