Investigating Protective Effect of Suspension of Paeoniflorin in Combination with Curcumin Against Acute Liver Injury Based on Inhibition of TLR4/NF-κB/NLRP3 Inflammatory Pathway
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Appearance and Quality of Different Groups of Compound Suspensions
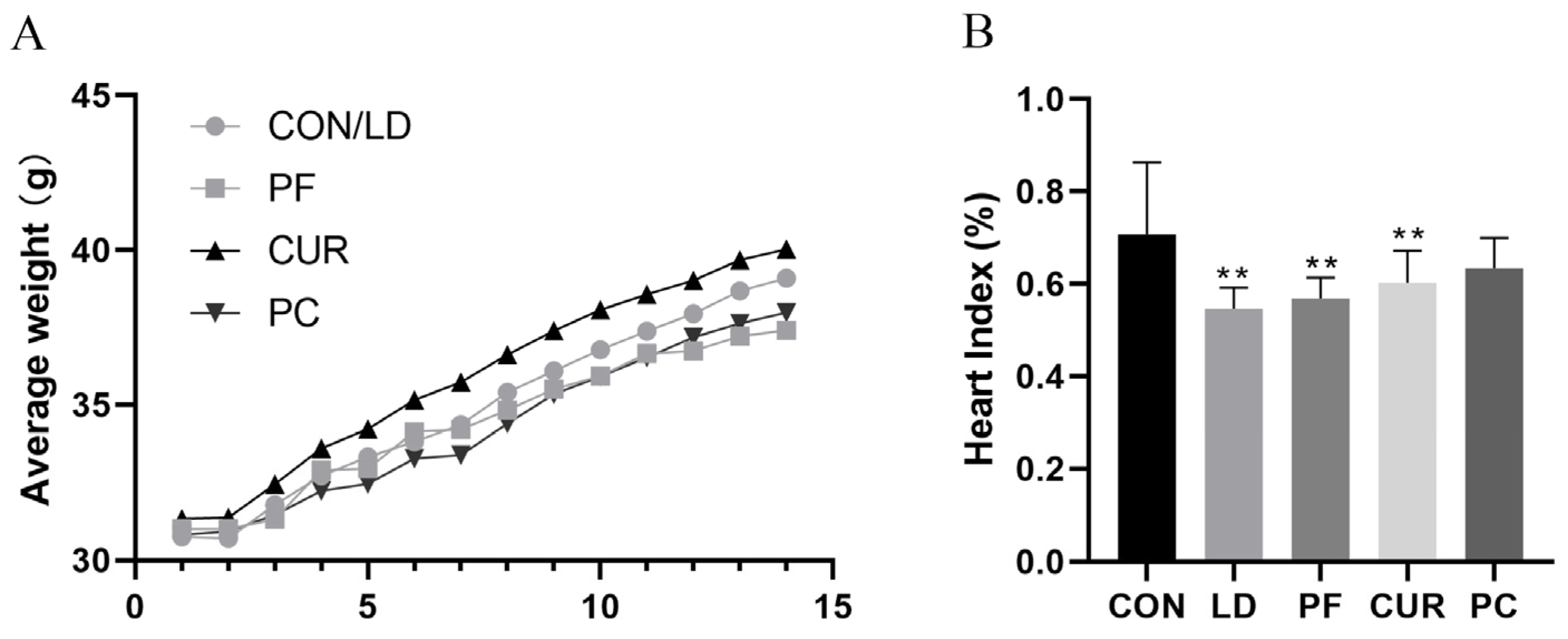
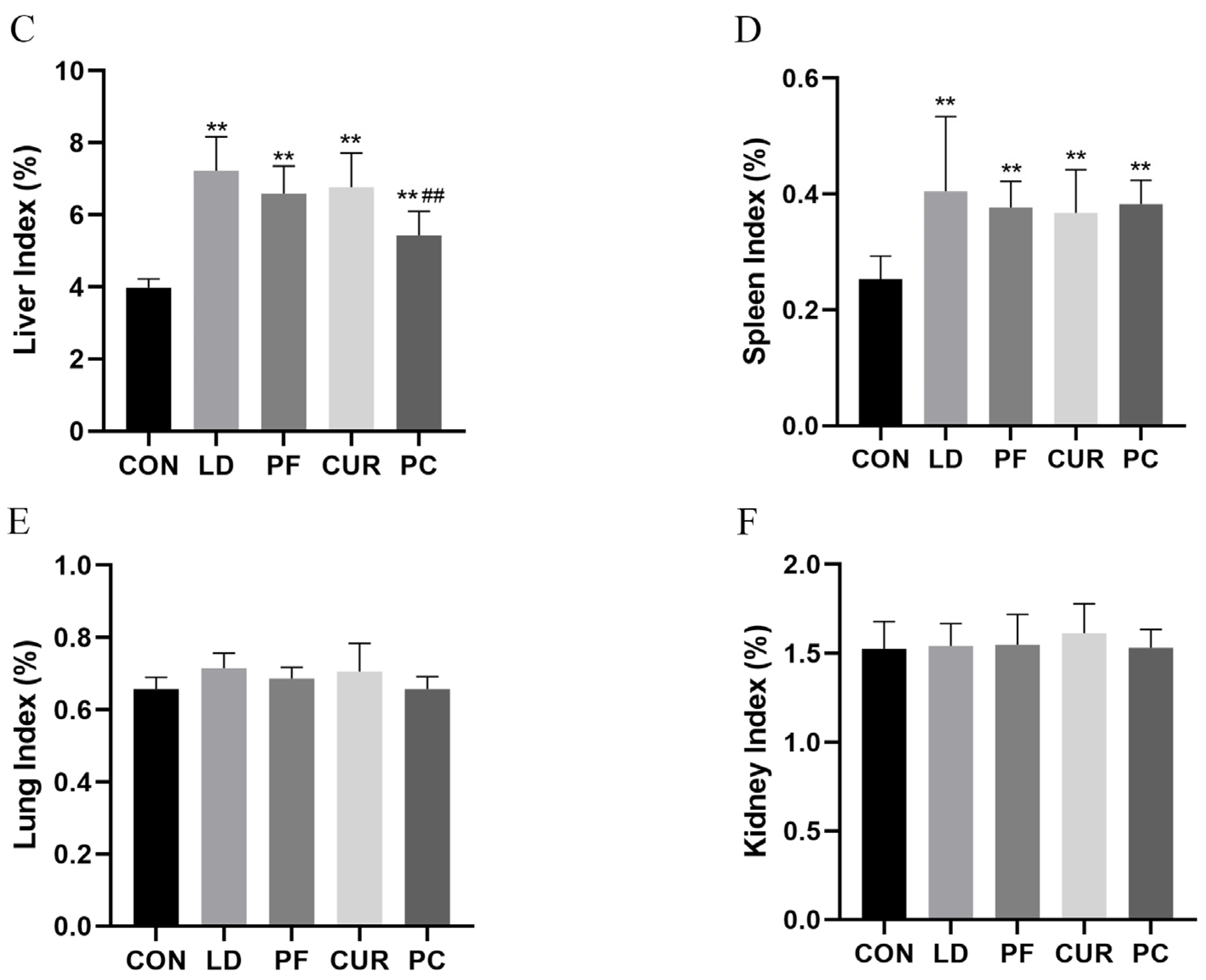
2.2. Protective Effect of Different Suspensions on Body Weight and Organ Index
2.3. The Protective Effect of Different Suspensions on the Liver’s Histopathologic Structure
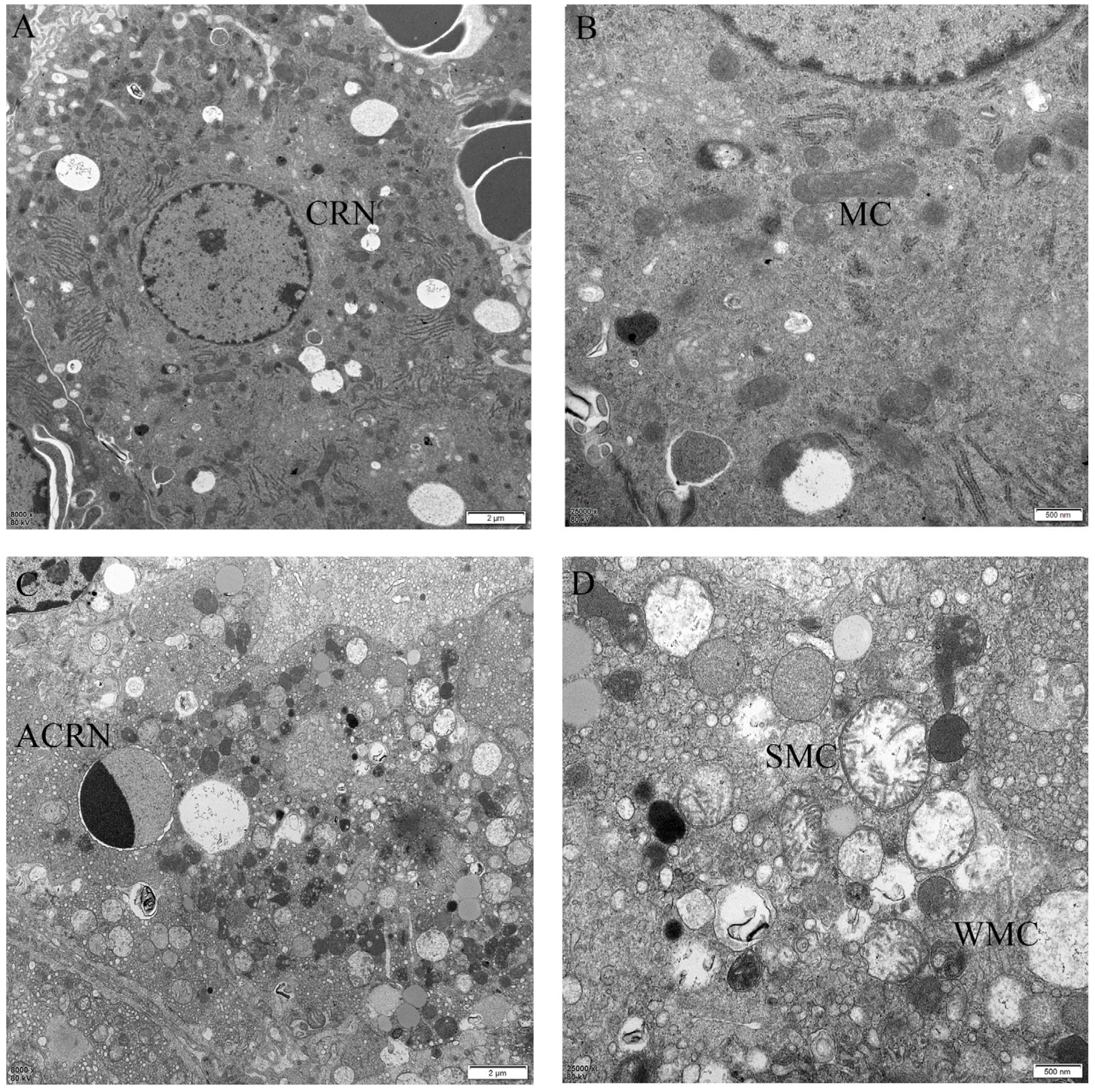
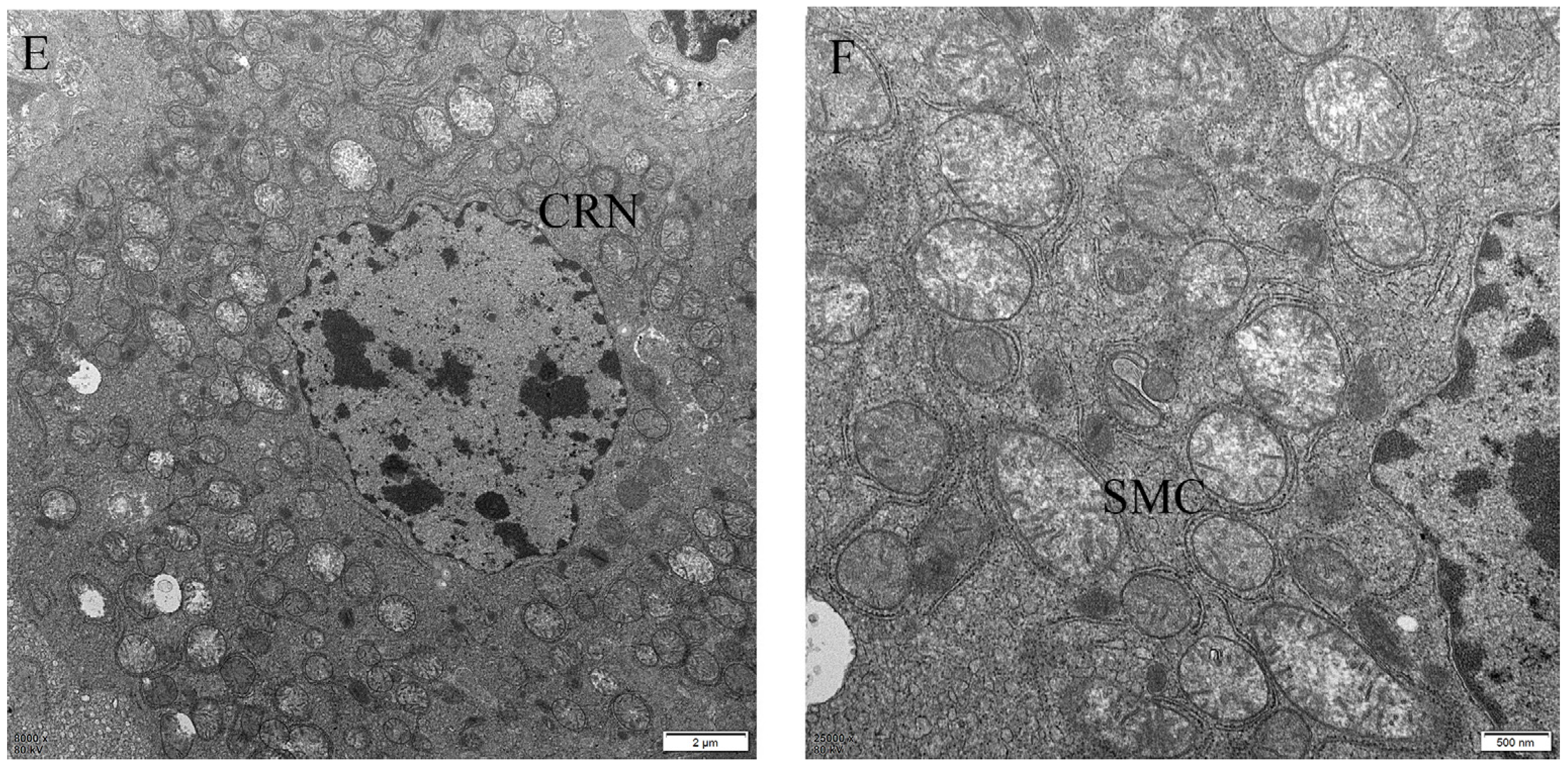
2.4. The Protective Effect of Different Suspensions on the Liver’s Ultrastructure
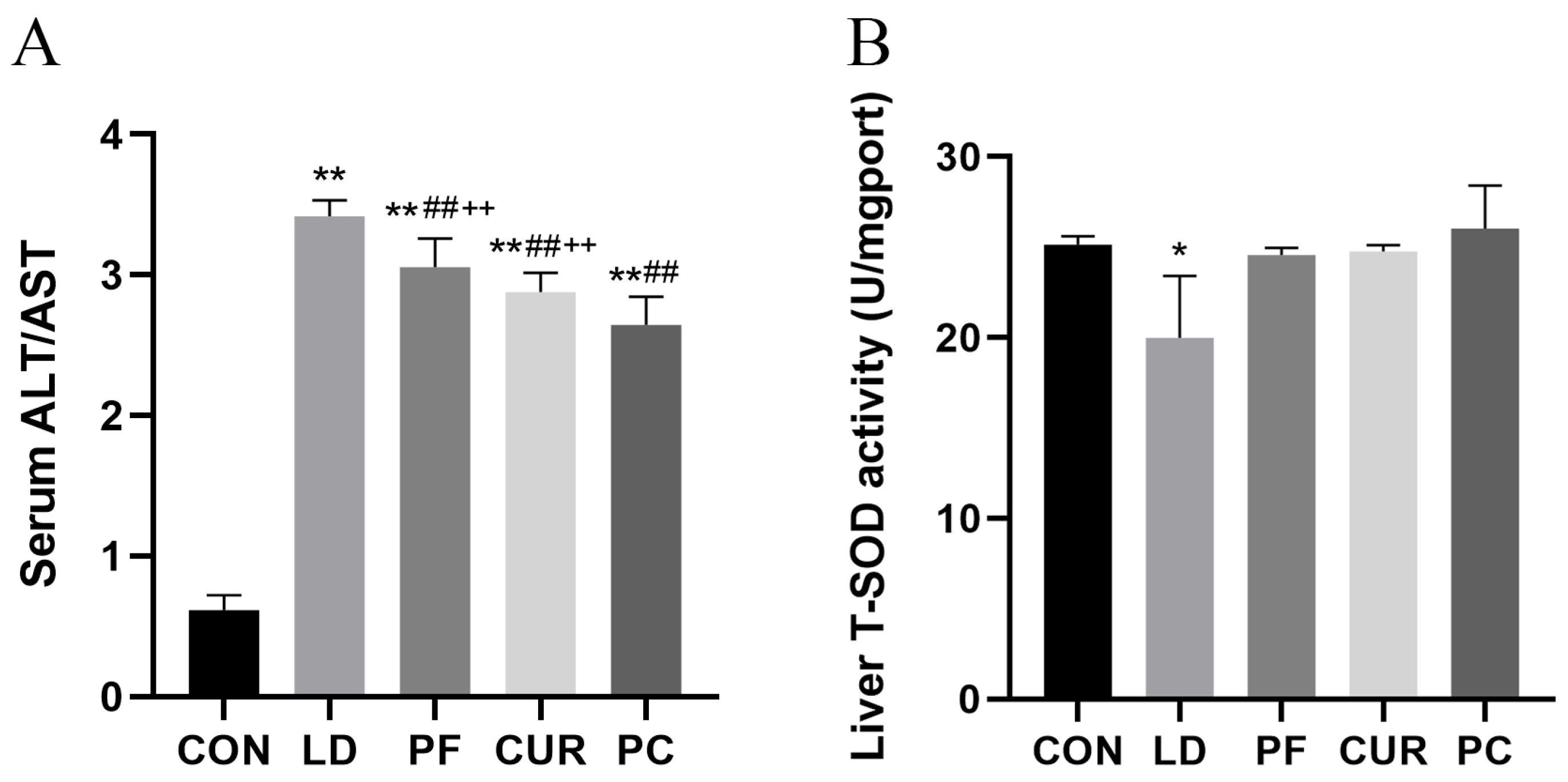
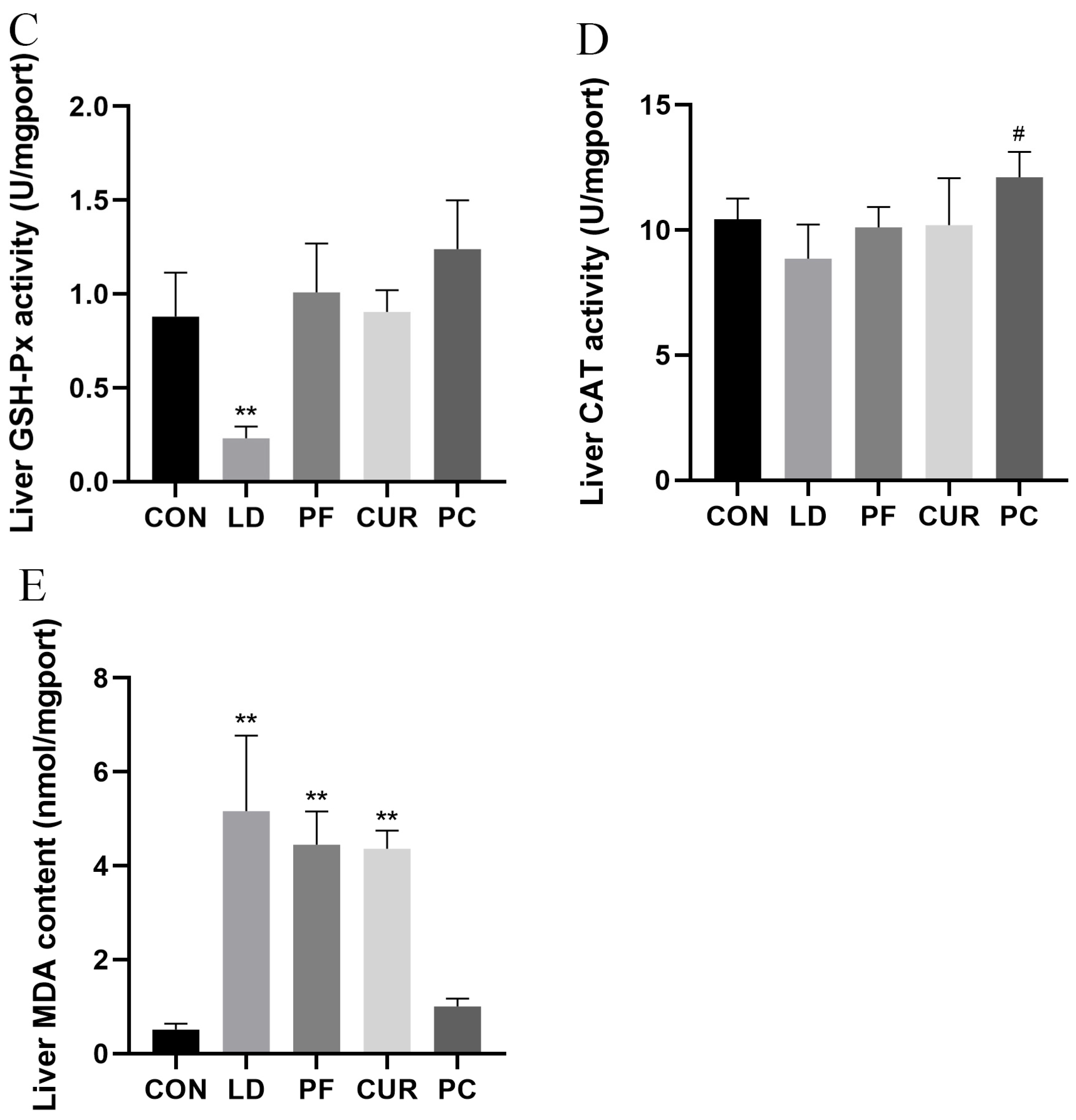
2.5. Protective Effect of Different Suspensions on Biochemical Indices
2.6. Protective Effect of Different Suspensions on Serum Factors
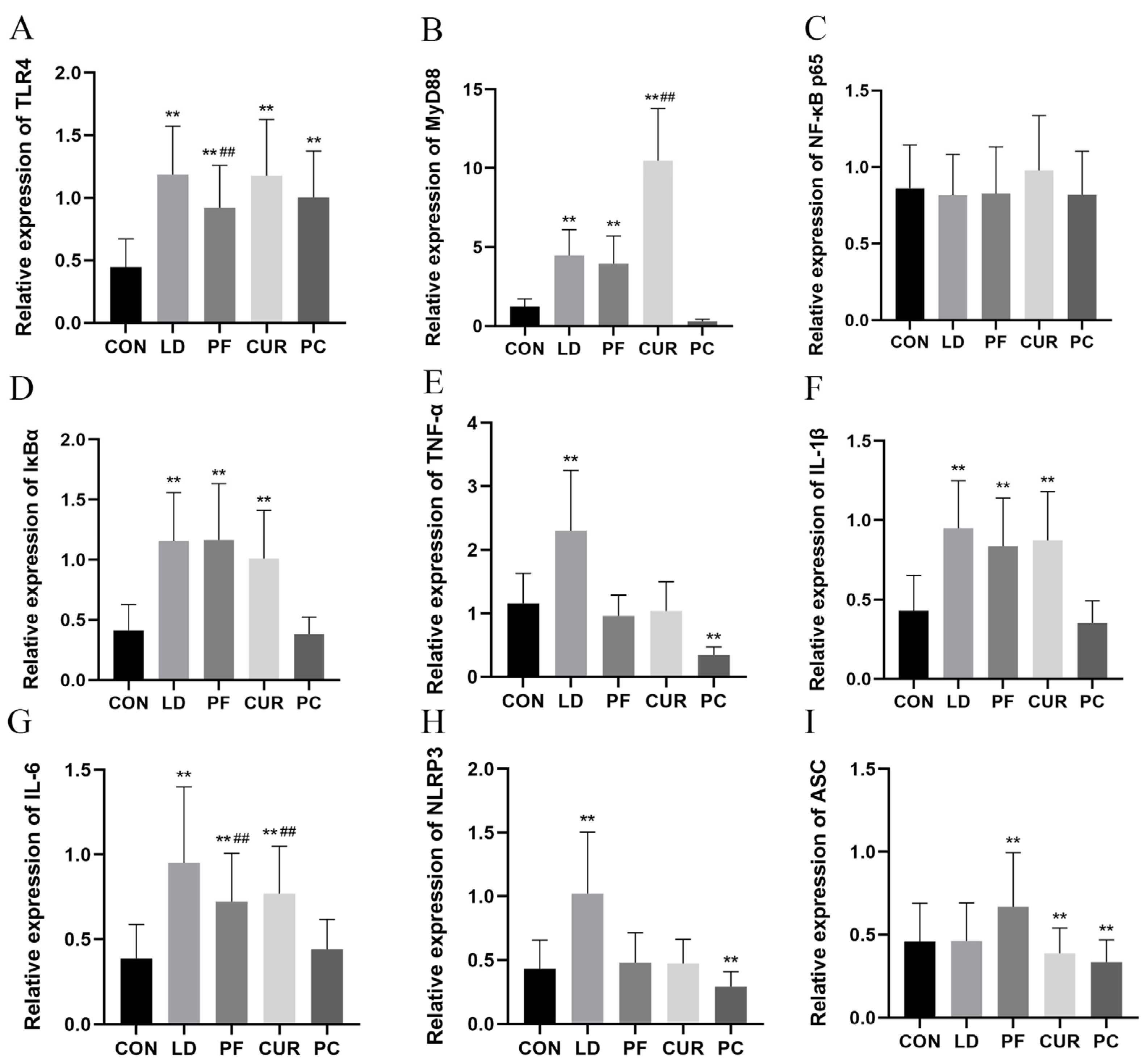
2.7. Protective Effects of Different Suspensions on Liver mRNA Expression
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals
4.2. Preparation Method and Suspension Prescription Screening
4.3. Quality Evaluation of Suspensions
4.4. Animals and Experimental Design
4.5. Sample Collection
4.6. Organ Index
4.7. Histopathologic Observation of Liver
4.8. Ultrastructural Observation of Liver
4.9. Biochemical Test of Serum and Liver
4.10. Serum ELISA Assay
4.11. Liver RNA Extraction and RT-qPCR Assay
4.12. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, L.; Wei, W. Anti-inflammatory and immunoregulatory effects of paeoniflorin and total glucosides of paeony. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 207, 107452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Qiao, L.; Xu, W.; Wang, X.; Li, H.; Xu, W.; Chu, K.; Lin, Y. Paeoniflorin Attenuates Cerebral Ischemia-Induced Injury by Regulating Ca2+/CaMKII/CREB Signaling Pathway. Molecules 2017, 22, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, P.; Xiao, D.; Zhao, Y.; Jia, W.; Ding, L.; Dong, H.; Wei, C.; et al. Paeoniflorin alleviates AngII-induced cardiac hypertrophy in H9c2 cells by regulating oxidative stress and Nrf2 signaling pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 165, 115253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, M.; Chu, Y.; Lei, J.; Yao, Z.; Wang, P.; Chen, Z.; Wang, K.; Sang, X.; Han, X.; Wang, L.; et al. Pharmacological Mechanisms and Clinical Applications of Curcumin: Update. Aging Dis. 2023, 14, 716–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lu, Z.; Wu, H.; Lv, F. Study on the antibiotic activity of microcapsule curcumin against foodborne pathogens. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2009, 136, 71–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Li, M.; Wang, L.; Chen, L.; Goh, B.C. Curcumin in cancer therapy: Exploring molecular mechanisms and overcoming clinical challenges. Cancer Lett. 2023, 570, 216332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wang, H.; Zhao, S.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, C.; Sun, N.; Fan, H. Paeoniflorin ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute liver injury by inhibiting oxidative stress and inflammation via SIRT1/FOXO1a/SOD2 signaling in rats. Phytother. Res. 2022, 36, 2558–2571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, G.; Tirkey, N.; Bharrhan, S.; Chanana, V.; Rishi, P.; Chopra, K. Inhibition of oxidative stress and cytokine activity by curcumin in amelioration of endotoxin-induced experimental hepatoxicity in rodents. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2006, 145, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhao, J.; Ding, Y.; Li, L. A cost-effective method to prepare curcumin nanosuspensions with enhanced oral bioavailability. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2017, 485, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo, Y.; Shibazaki, M.; Yamaguchi, K.; Kai, K.; Sugawara, S.; Takada, H.; Kikuchi, H.; Kumagai, K. Enhancement by galactosamine of lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced tumour necrosis factor production and lethality: Its suppression by LPS pretreatment. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1999, 128, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Kong, L.; Wang, S.; Huang, K.; Wu, J.; Wang, C.; Sun, H.; Liu, K.; Meng, Q. Isoliquiritigenin alleviates LPS/D-GalN-induced acute liver failure by activating the PGC-1α/Nrf2 pathway to reduce oxidative stress and inflammatory response. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 100, 108159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Y.; Zhang, S.; Sun, Z.; Tong, Z.; Ge, Y.; Zhou, L.; Xu, Q.; Zhou, H.; Wang, W. Preclinical validation of silibinin/albumin nanoparticles as an applicable system against acute liver injury. Acta Biomater. 2022, 146, 385–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, J.; Fu, S.; Xu, W.; Liu, J.; Yang, Y.; Chen, T.; Zhao, Y.; Li, D.; et al. Ultra-small quercetin-based nanotherapeutics ameliorate acute liver failure by combatting inflammation/cellular senescence cycle. Theranostics 2025, 15, 1035–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.L.; Wu, Y.; Wang, N.; Wang, S.M.; Zhang, B.; Shi, C.G.; Zhang, S.C. Paeoniflorin attenuates hippocampal damage in a rat model of vascular dementia. Exp. Ther. Med. 2016, 12, 3729–3734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, Y.; Luo, J.; Wu, X.; Wei, Z.; Tong, B.; Yu, J.; Wang, T.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Y.; Yuan, X.; et al. Curcumin attenuates collagen-induced inflammatory response through the “gut-brain axis”. J. NeuroInflamm. 2018, 15, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, A.K.; Pal, D.; Pany, D.R.; Mohanty, B. Evaluation of Spinacia oleracea L. leaves mucilage as an innovative suspending agent. J. Adv. Pharm. Technol. Res. 2010, 1, 338–341. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Wu, P.; Ning, Y.; Yan, X.; Zhu, T.; Ma, C.; Liu, A. Sedative and hypnotic effect of freeze-dried paeoniflorin and sini san freeze-dried powder in pentobarbital sodium-induced mice. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2014, 34, 184–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yang, B.; Yu, B. Paeoniflorin Protects against Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Induced by a High-Fat Diet in Mice. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2015, 38, 1005–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Ghany, H.M.; El-Sisy, D.M.; Salem, M.E. A comparative study of effects of curcumin and its nanoparticles on the growth, immunity and heat stress resistance of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 2523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Wu, X.; Wen, Q.; Tang, H.; Zhao, L.; Shi, F.; Li, Y.; Yin, Z.; Zou, Y.; Song, X.; et al. Eriodictyol Alleviated LPS/D-GalN-Induced Acute Liver Injury by Inhibiting Oxidative Stress and Cell Apoptosis via PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, W.; Hwang-Bo, J.; Jeon, H.; Ko, M.; Choi, J.; Jeong, Y.J.; Park, J.H.; Kim, I.; Kim, T.W.; Kim, H.; et al. A Comparative Study of the Hepatoprotective Effect of Centella asiatica Extract (CA-HE50) on Lipopolysaccharide/d-galactosamine-Induced Acute Liver Injury in C57BL/6 Mice. Nutrients 2021, 13, 4090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Yang, N.; Ni, S.; Li, W.; Xu, L.; Dong, P.; Lu, M. Pretreatment of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) ameliorates D-GalN/LPS induced acute liver failure through TLR4 signaling pathway. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2014, 7, 6626–6634. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.; Mo, C.; Zeng, T.; Lai, Y.; Zhou, C.; Xie, S.; Chen, L.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Huang, S.; et al. Lupeol ameliorates LPS/D-GalN induced acute hepatic damage by suppressing inflammation and oxidative stress through TGFβ1-Nrf2 signal pathway. Aging 2021, 13, 6592–6605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baratta, J.L.; Ngo, A.; Lopez, B.; Kasabwalla, N.; Longmuir, K.J.; Robertson, R.T. Cellular organization of normal mouse liver: A histological, quantitative immunocytochemical, and fine structural analysis. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2009, 131, 713–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Jiang, W.; Zhou, A.L.; Zhao, M.; Jiang, D.R. Inhibitory effect of oxymatrine on hepatocyte apoptosis via TLR4/PI3K/Akt/GSK-3β signaling pathway. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 3839–3849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Cui, M.; Xu, D.; Hong, D.; Xia, Y.; Xu, C.; Li, R.; Zhang, X.; Lou, Y.; He, Q.; et al. Liver-specific deletion of Eva1a/Tmem166 aggravates acute liver injury by impairing autophagy. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, P.X.; Lecoeur, H.; Zorn, E.; Dauguet, C.; Mignotte, B.; Gougeon, M.L. Alterations in mitochondrial structure and function are early events of dexamethasone-induced thymocyte apoptosis. J. Cell Biol. 1995, 130, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannini, E.G.; Testa, R.; Savarino, V. Liver enzyme alteration: A guide for clinicians. CMAJ 2005, 172, 367–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Ji, Q.; She, C.Y.; Cheng, Y.; Zhou, J.R.; Wu, Q.M. Ophiopogonin D ameliorates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in high-fat diet-induced obese mice by improving lipid metabolism, oxidative stress and inflammatory response. Exp. Ther. Med. 2023, 26, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wang, S.; Li, X.; Jiang, L.; Wang, X.; Kou, R.; Wang, Q.; Xu, L.; Zhao, N.; Xie, K. Diallyl sulfide protects against lipopolysaccharide/d-galactosamine-induced acute liver injury by inhibiting oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis in mice. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 120, 500–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Jiang, Y.; Qin, Y.; Liu, J.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, K.; Wang, X.; Liu, G. Linoleic Acid Alleviates Lipopolysaccharide Induced Acute Liver Injury via Activation of Nrf2. Physiol. Res. 2024, 73, 381–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raetz, C.R.; Whitfield, C. Lipopolysaccharide endotoxins. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2002, 71, 635–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erridge, C.; Bennett-Guerrero, E.; Poxton, I.R. Structure and function of lipopolysaccharides. Microbes Infect. 2002, 4, 837–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banchereau, J.; Steinman, R.M. Dendritic cells and the control of immunity. Nature 1998, 392, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, H.W.; Cavacini, L. Structure and function of immunoglobulins. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 125, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, M.J.; Liu, Z.G. Crosstalk of reactive oxygen species and NF-κB signaling. Cell Res. 2011, 21, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, T.; Akira, S. The role of pattern-recognition receptors in innate immunity: Update on Toll-like receptors. Nat. Immunol. 2010, 11, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, T. The nuclear factor NF-kappaB pathway in inflammation. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2009, 1, 001651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Kong, Y.; Chen, H.; Xia, J.; Zhao, J.; Zhou, Y. Unraveling the priming phase of NLRP3 inflammasome activation: Molecular insights and clinical relevance. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2025, 146, 113821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paik, S.; Kim, J.K.; Silwal, P.; Sasakawa, C.; Jo, E.K. An update on the regulatory mechanisms of NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2021, 18, 1141–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharif, O.; Bolshakov, V.N.; Raines, S.; Newham, P.; Perkins, N.D. Transcriptional profiling of the LPS induced NF-kappaB response in macrophages. BMC Immunol. 2007, 8, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.C. Non-canonical NF-κB signaling pathway. Cell Res. 2011, 21, 71–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Dou, W.; Zhang, E.; Sun, A.; Ding, L.; Wei, X.; Chou, G.; Mani, S.; Wang, Z. Paeoniflorin abrogates DSS-induced colitis via a TLR4-dependent pathway. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2014, 306, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.X.; Gong, X.H.; Zhang, H.; Peng, C. A review on the pharmacokinetics of paeoniflorin and its anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 130, 110505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Yin, L.; Yang, W.; Wu, Z.; Niu, J. Antioxidant effects of Paeoniflorin and relevant molecular mechanisms as related to a variety of diseases: A review. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 176, 116772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, F.; Ye, B.; Cao, J.; Cai, X.; Lin, L.; Huang, S.; Huang, W.; Huang, Z. Curcumin Represses NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation via TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB and P2 × 7R Signaling in PMA-Induced Macrophages. Front. Pharmacol. 2016, 7, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.Y.; Chun, Y.S.; Kim, J.K.; Lee, J.O.; Ku, S.K.; Shim, S.M. Curcumin Attenuates Sarcopenia in Chronic Forced Exercise Executed Aged Mice by Regulating Muscle Degradation and Protein Synthesis with Antioxidant and Anti-inflammatory Effects. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 6214–6228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taneja, R.; Nahata, M.C.; Scarim, J.; Pande, P.G.; Scarim, A.; Hoddinott, G.; Fourie, C.L.; Jew, R.K.; Schaaf, H.S.; Garcia-Prats, A.J.; et al. Stable sugar and sugar-free suspensions of pretomanid. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 2022, 26, 1112–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.R.; Yang, Y.Q.; Ruan, D.D.; Que, Y.M.; Gao, H.; Yang, Y.Z.; Zhao, H.J. Paeoniflorin Attenuates APAP-Induced Liver Injury via Intervening the Crosstalk Between Hepatocyte Pyroptosis and NETs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Ma, X.; Wang, J.; Zhu, Y.; Li, R.; Wang, J.; He, X.; Shan, L.; Wang, R.; Wang, L.; et al. Paeoniflorin alleviates liver fibrosis by inhibiting HIF-1α through mTOR-dependent pathway. Fitoterapia 2014, 99, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Dai, C.; Liu, Q.; Li, J.; Qiu, J. Curcumin Attenuates on Carbon Tetrachloride-Induced Acute Liver Injury in Mice via Modulation of the Nrf2/HO-1 and TGF-β1/Smad3 Pathway. Molecules 2018, 23, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Liu, T.; Wang, Z.; Shen, W.; Yuan, X.; Xie, J.; Zhang, Y. Role of Curcumin in Chronic Liver Diseases: A Comprehensive Review. Drug Des. Devel Ther. 2025, 19, 3395–3406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, W.; Song, E.; Song, Y. Co-administration of lipopolysaccharide and D-galactosamine induces genotoxicity in mouse liver. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Killilea, M.; Kerr, D.M.; Mallard, B.M.; Roche, M.; Wheatley, A.M. Exacerbated LPS/GalN-Induced Liver Injury in the Stress-Sensitive Wistar Kyoto Rat Is Associated with Changes in the Endocannabinoid System. Molecules 2020, 25, 3834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yang, J.; Liang, C.; Yang, W.; Zhu, Q.; Luo, H.; Liu, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J. Potential Protective Effect of Riboflavin Against Pathological Changes in the Main Organs of Male Mice Induced by Fluoride Exposure. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2022, 200, 1262–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Groups | 1 h | 2 h | 3 h | 6 h | 1 Day | 2 Days | 3 Days | 4 Days | 5 Days | 6 Days | 7 Days | N |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.00 | 0.98 | 0.96 | 0.94 | 0.88 | 0.70 | 0.56 | 0.36 | 0.20 | 0.12 | 0.10 | 10 |
| 2 | 1.00 | 0.98 | 0.96 | 0.92 | 0.88 | 0.44 | 0.28 | 0.12 | 0.08 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 13 |
| 3 | 1.00 | 0.98 | 0.96 | 0.94 | 0.82 | 0.59 | 0.51 | 0.39 | 0.31 | 0.24 | 0.18 | 9 |
| 4 | 1.00 | 0.96 | 0.96 | 0.96 | 0.92 | 0.88 | 0.84 | 0.84 | 0.78 | 0.76 | 0.75 | 10 |
| 5 | 1.00 | 0.96 | 0.96 | 0.94 | 0.90 | 0.85 | 0.83 | 0.83 | 0.81 | 0.77 | 0.77 | 9 |
| 6 | 1.00 | 0.98 | 0.98 | 0.96 | 0.90 | 0.82 | 0.76 | 0.75 | 0.75 | 0.73 | 0.73 | 8 |
| 7 | 1.00 | 0.96 | 0.96 | 0.96 | 0.94 | 0.94 | 0.90 | 0.88 | 0.88 | 0.87 | 0.85 | 12 |
| 8 | 1.00 | 0.98 | 0.98 | 0.98 | 0.98 | 0.94 | 0.92 | 0.90 | 0.90 | 0.88 | 0.88 | 8 |
| 9 | 1.00 | 0.96 | 0.96 | 0.96 | 0.94 | 0.94 | 0.92 | 0.92 | 0.91 | 0.91 | 0.91 | 8 |
| Groups | CMC-Na/g | Tween 80/mL | Citric Acid/g | Sodium Benzoate/g |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.125 | 0.250 | 0.300 | 0.075 |
| 2 | 0.125 | 0.500 | 0.200 | 0.025 |
| 3 | 0.125 | 0.750 | 0.250 | 0.125 |
| 4 | 0.187 | 0.250 | 0.250 | 0.025 |
| 5 | 0.187 | 0.500 | 0.300 | 0.125 |
| 6 | 0.187 | 0.750 | 0.200 | 0.075 |
| 7 | 0.250 | 0.250 | 0.200 | 0.125 |
| 8 | 0.250 | 0.500 | 0.250 | 0.075 |
| 9 | 0.250 | 0.750 | 0.300 | 0.025 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, H.; Xu, F.; Zhang, W.; Fu, H.; Yin, L.; Amevor, F.K.; Lin, J.; et al. Investigating Protective Effect of Suspension of Paeoniflorin in Combination with Curcumin Against Acute Liver Injury Based on Inhibition of TLR4/NF-κB/NLRP3 Inflammatory Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6324. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136324
Wu Z, Zhao Y, Wang Y, Li H, Xu F, Zhang W, Fu H, Yin L, Amevor FK, Lin J, et al. Investigating Protective Effect of Suspension of Paeoniflorin in Combination with Curcumin Against Acute Liver Injury Based on Inhibition of TLR4/NF-κB/NLRP3 Inflammatory Pathway. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(13):6324. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136324
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Zhengkun, Yinquan Zhao, Yang Wang, Haohuan Li, Funeng Xu, Wei Zhang, Hualin Fu, Lizi Yin, Felix Kwame Amevor, Juchun Lin, and et al. 2025. "Investigating Protective Effect of Suspension of Paeoniflorin in Combination with Curcumin Against Acute Liver Injury Based on Inhibition of TLR4/NF-κB/NLRP3 Inflammatory Pathway" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 13: 6324. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136324
APA StyleWu, Z., Zhao, Y., Wang, Y., Li, H., Xu, F., Zhang, W., Fu, H., Yin, L., Amevor, F. K., Lin, J., Li, D., & Shu, G. (2025). Investigating Protective Effect of Suspension of Paeoniflorin in Combination with Curcumin Against Acute Liver Injury Based on Inhibition of TLR4/NF-κB/NLRP3 Inflammatory Pathway. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(13), 6324. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136324






