“Non-Classical” Platinum Complexes: A Concise Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. “Non-Classical” Platinum Complexes with Cytotoxic Activity
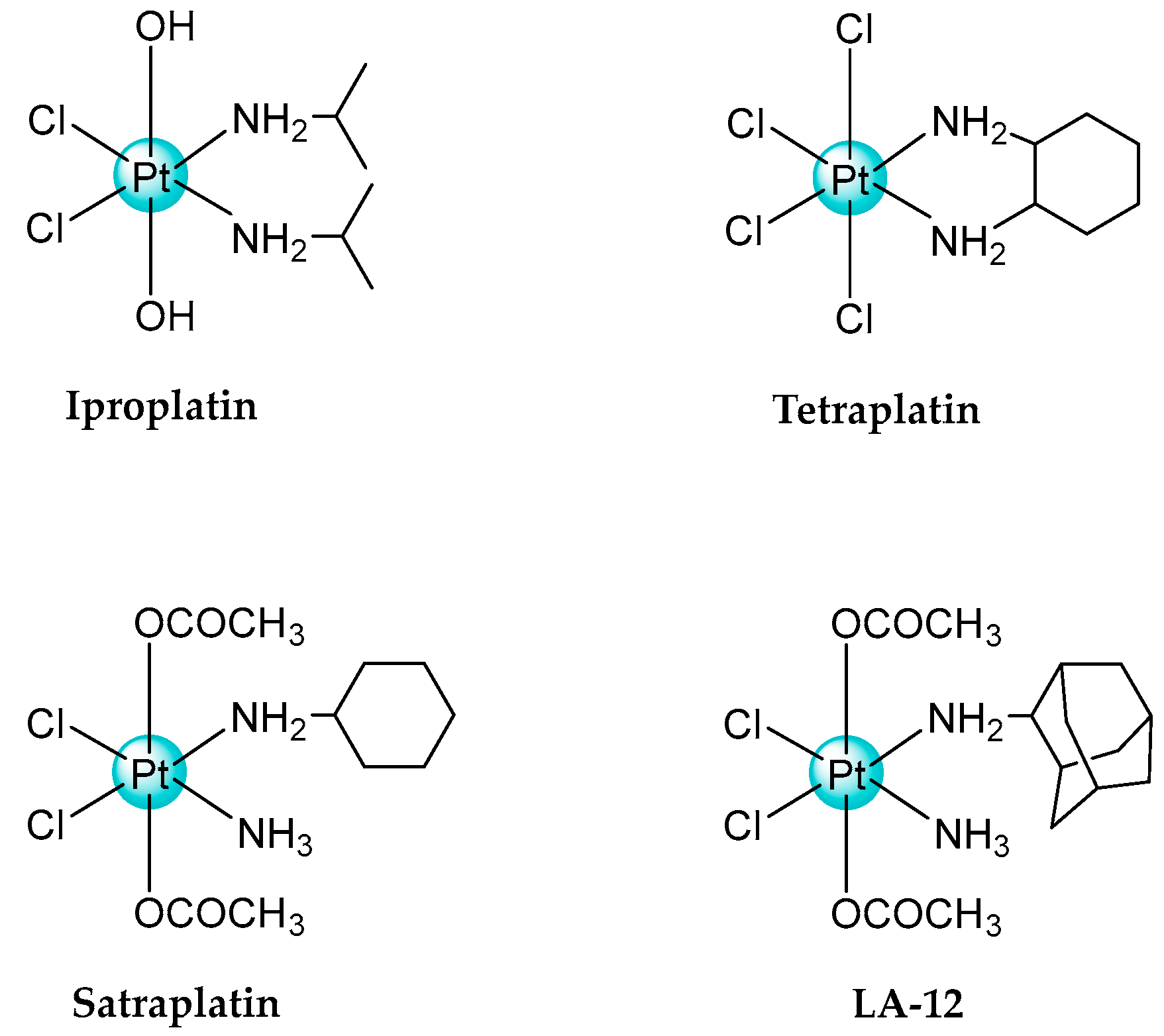
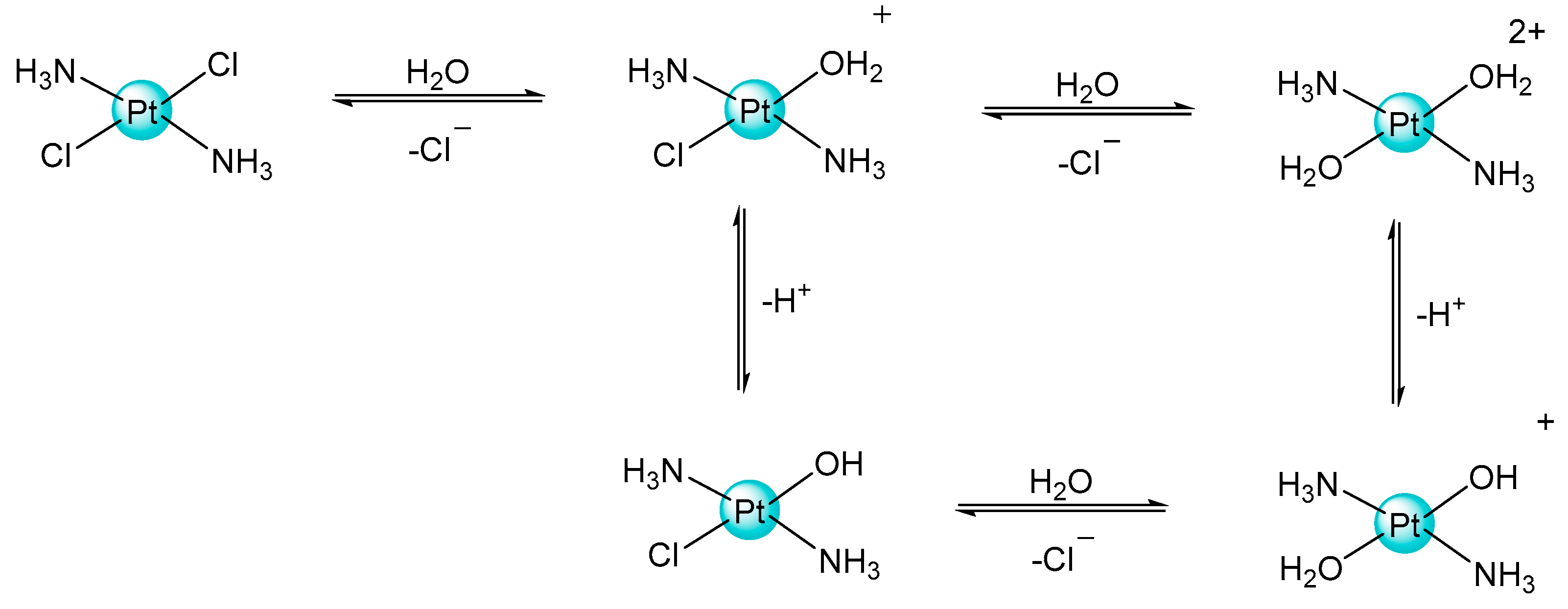
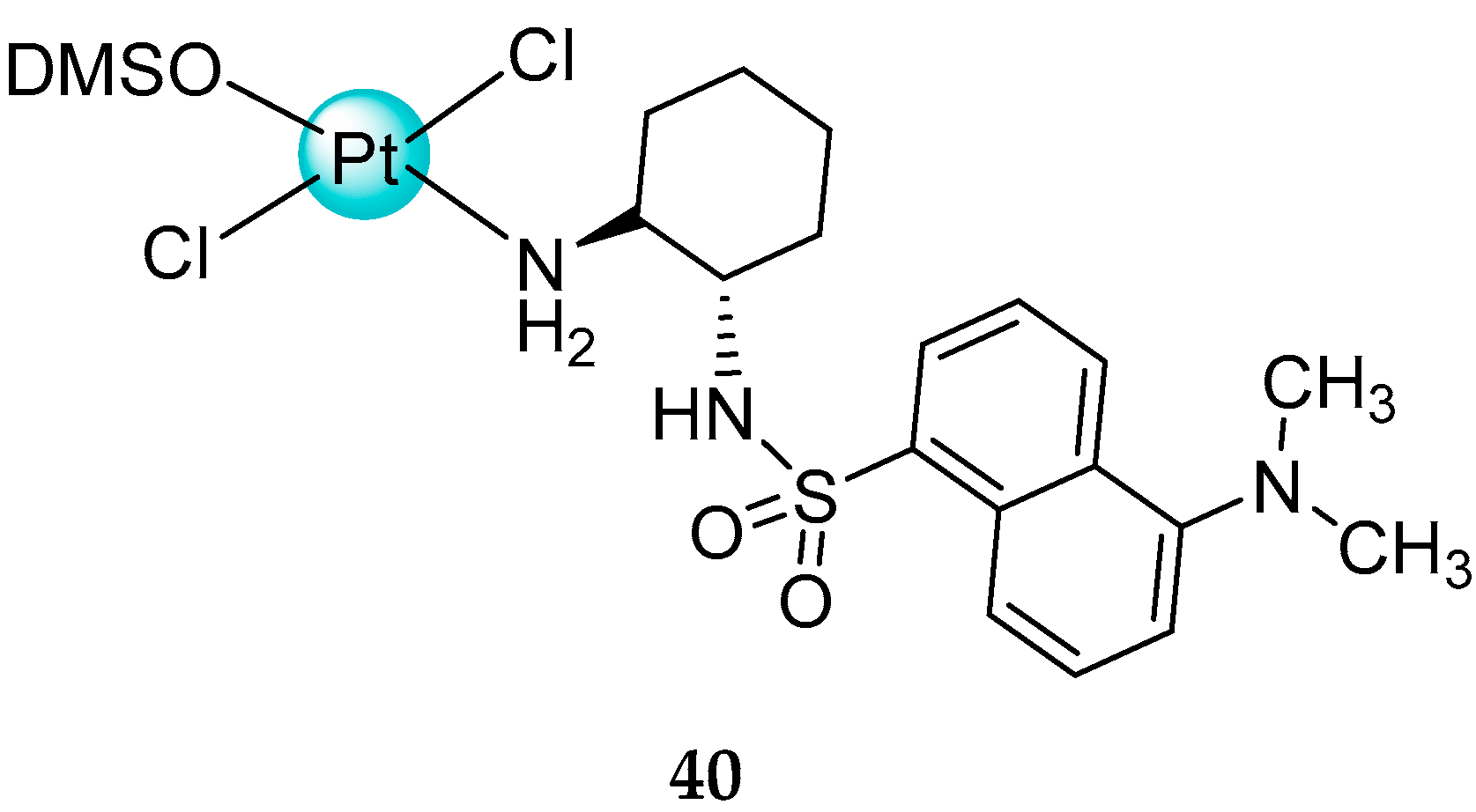
2.1. Pt(IV) Complexes
- -
- Firstly, it is evident that the kinetic inertness of platinum(IV) complexes reduces the probability of adverse reactions in vivo [35]. This phenomenon can be attributed to the increased stability of these complexes exhibit in acidic environments formed as a consequence of bacterial activity (specifically, the synthesis of folic acid for DNA). Consequently, the complexes demonstrate heightened effectiveness against these bacterial cultures [36].
- -
- -
- Finally, Pt(IV) complexes have been demonstrated to retain their efficacy against cancer cells in hypoxic conditions, thus establishing them as promising candidates for the treatment of avascular tumours [38].
- -
- Greater selectivity of the complexes towards tumour cells;
- -
- Improved cellular uptake;
- -
- Greater tolerance of the complexes in biological media.
- (a)
- Ligand-bridge electron transfer is a process in which axial ligands form a bridge between the Pt(IV) centre and the (RA). This process facilitates electron transfer and the release of the second ligand in the axial position. It can thus be concluded that the active square planar Pt(II) species are formed.
- (b)
- Ligand-bridge-H transfer is a process characterized by the transfer of two electrons as a result of a shift in a hydride unit (H) from the RA to the bridging ligand. This process leads to the formation of the RA oxidized form and the loss of the axial ligand in the trans-position.
- (c)
- Enolate b-carbon attack is a process that involves the nucleophilic attack of the enolate b-carbon of AscH on one axial ligand (X). Consequently, the formation of the new C-X bond is observed, accompanied by the release of the second axial ligand.
- (d)
- Pt(II)-catalyzed mechanisms are where the reduction of Pt(IV) complex is realized by another Pt(II) complex, the formation of AscH–PtII–X–PtIV–Y dimer, where X and Y are the Pt(IV) axial ligands and the bridging ligand mediates the two electron transfers.
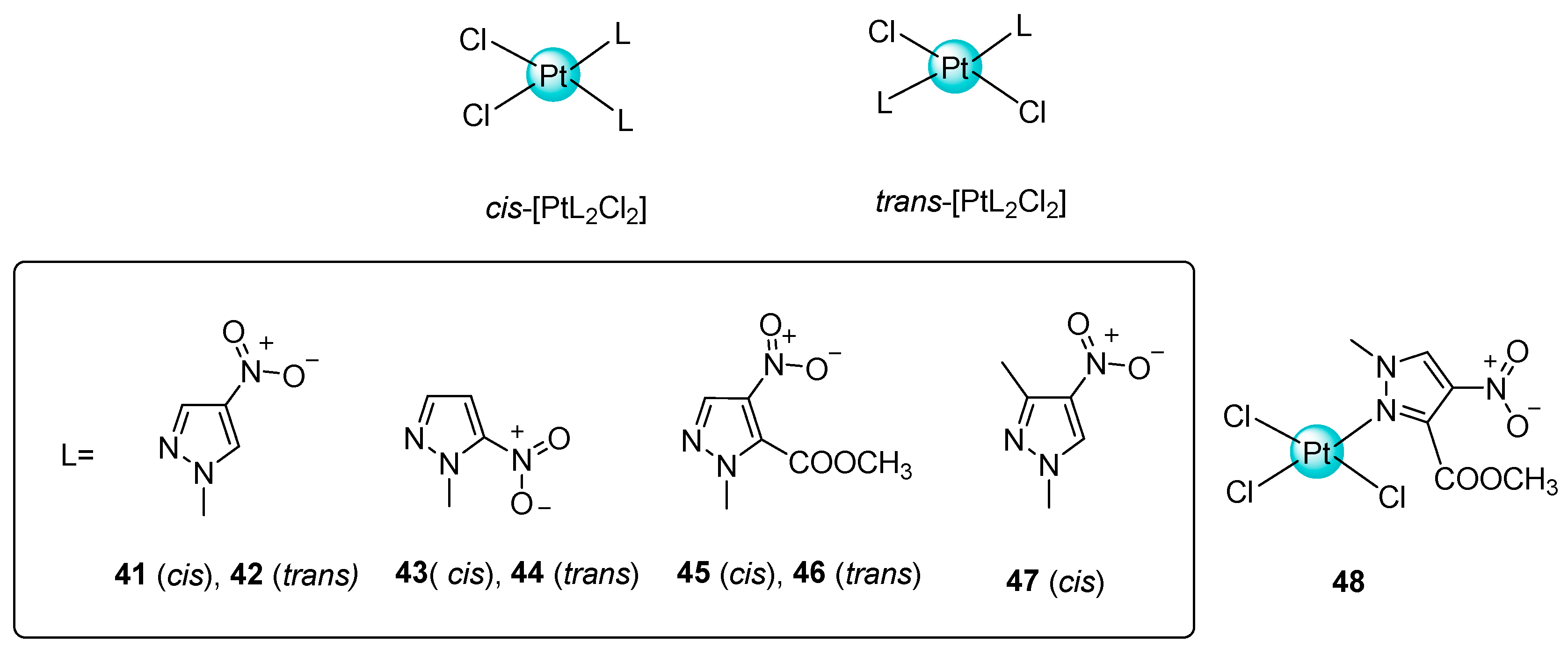
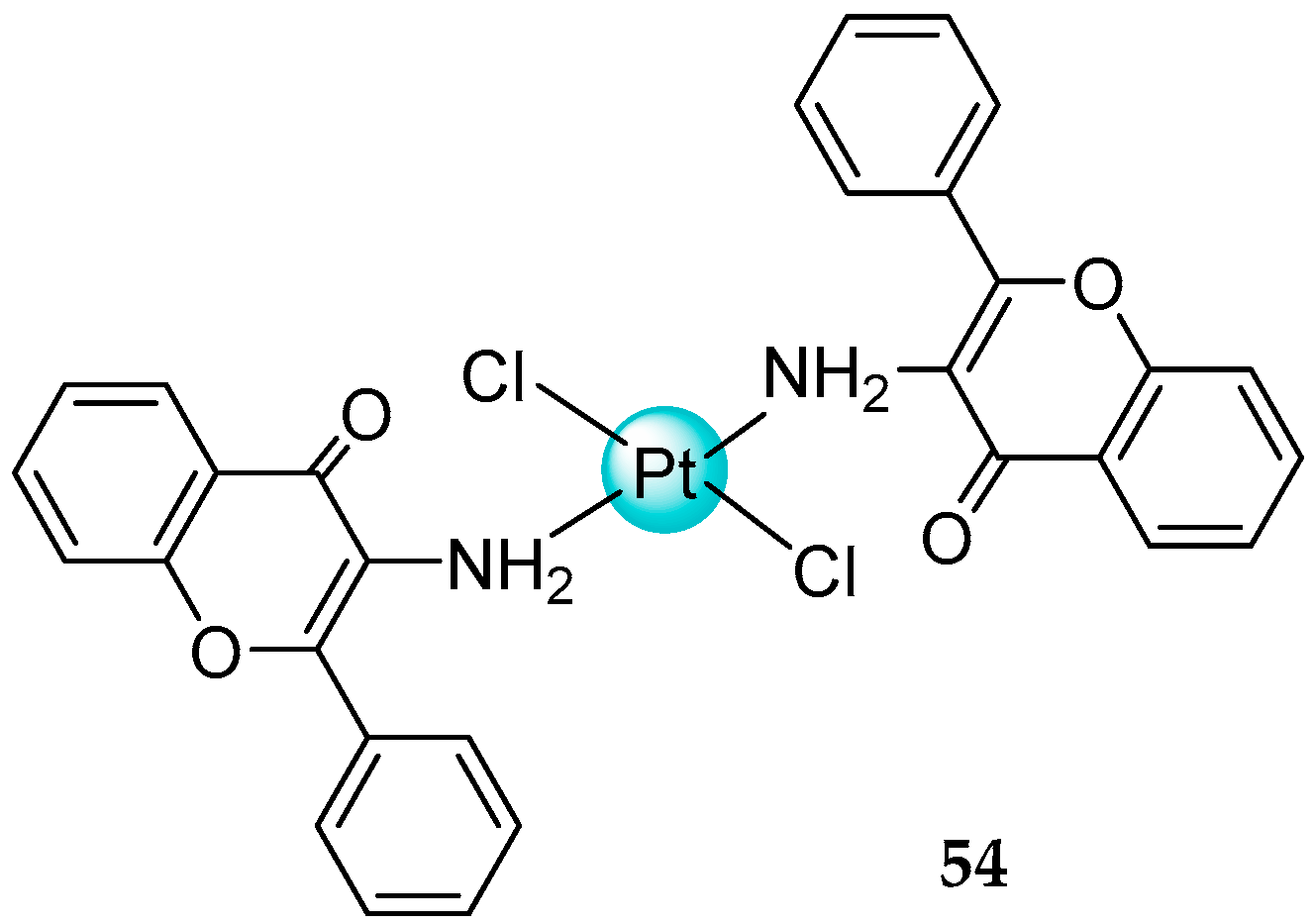
2.2. Trans-Platinum Complexes
- -
- The presence of a substituent in the 1-methylnitrotyrazole ring probably reduces in vitro cytotoxicity of the platinum complexes tested;
- -
- A positive effect on the stability of the Pt complex has the maximum possible distance of the nitro group from the coordination centre of the 1-methylnitrotypyrazole ligand;
- -
- The trans-isomers are more lipophilic and have a higher cytotoxic activity than the corresponding cis-isomers;
- -
- Under hypoxic conditions, the tested compounds were found to be inactive or less active compared to normoxic conditions.
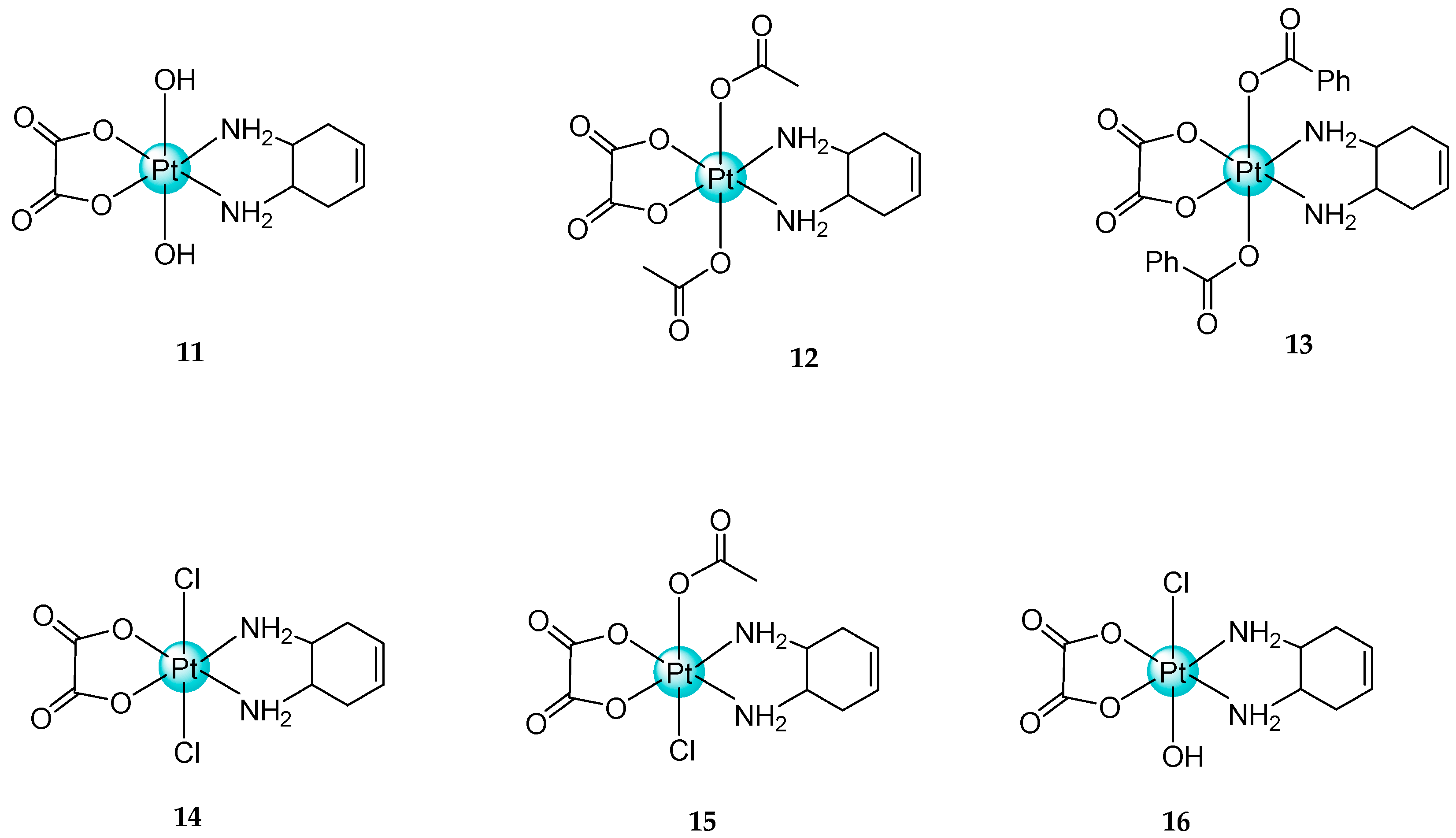
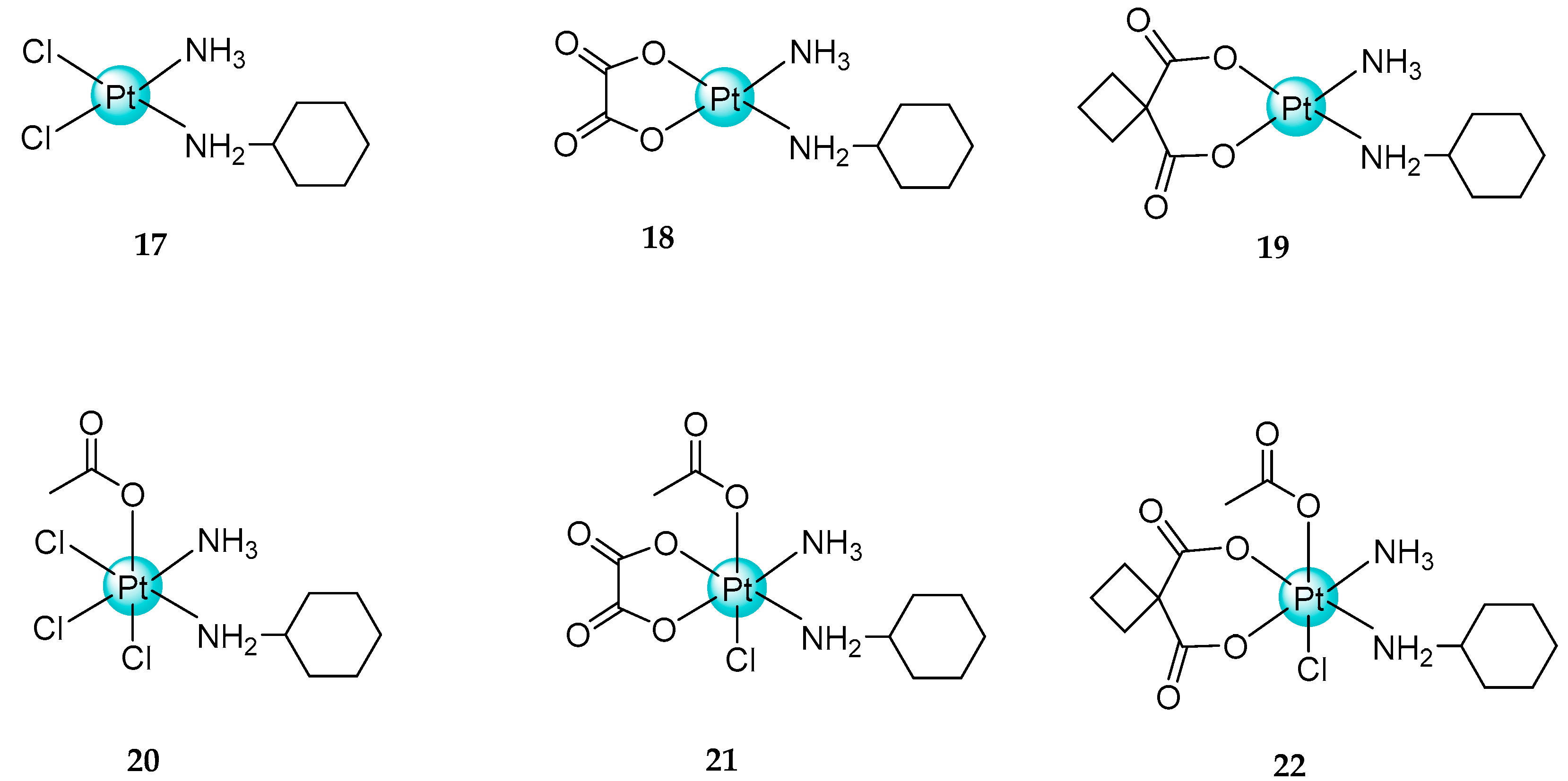
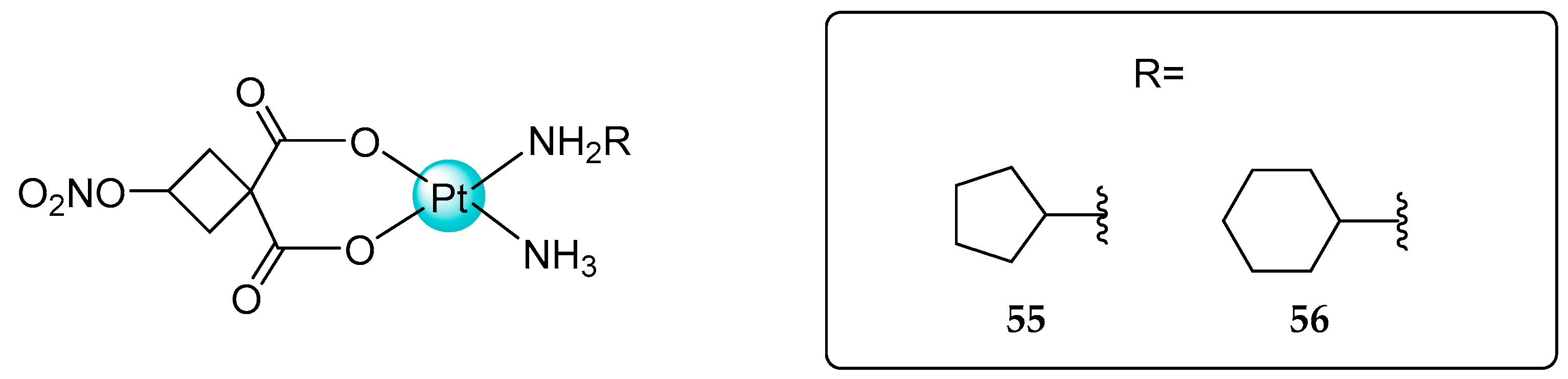
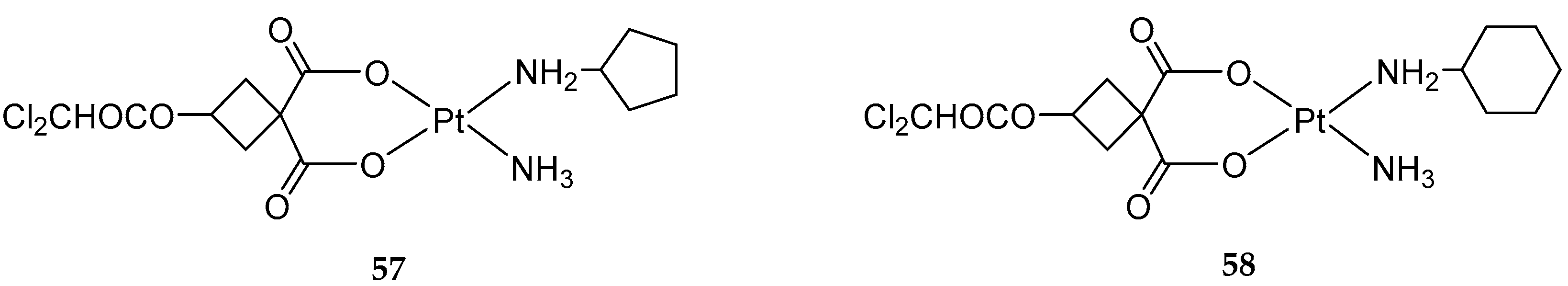
2.3. Mixed Ammine/Amine Platinum Complexes
- (1)
- Water-soluble platinum complexes, which are less toxic and show less antitumor activity;
- (2)
- Water-insoluble platinum complexes, which have low nephrotoxicity.
3. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rosenberg, B.; Van Camp, L.; Krigas, T. Inhibition of cell division in Escherichia coli, by electrolysis products from a platinum electrode. Nature 1965, 205, 698–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alderden, R.A.; Hall, M.D.; Hambley, T.W. The discovery and development of cisplatin. J. Chem. Educ. 2006, 83, 728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S. Cisplatin: The first metal based anticancer drug. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 88, 102925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, J.J.; Lippard, S.J. Synthetic methods for the preparation of platinum anticancer complexes. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 4470–4495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Q.; Ng, K.-Y.; Xu, Z.; Xua, W.; Zhu, G. Advances in technical strategies for monitoring the reduction of platinum(IV) complexes. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2024, 11, 3085–3118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, A.; Di Maio, M.; Chiodini, P.; Rudd, R.; Okamoto, H.; Skarlos, D.; Früh, M.; Qian, W.; Tamura, T.; Samantas, E.; et al. Carboplatin- or cisplatin-based chemotherapy in first-line treatment of small-cell lung cancer: The COCIS meta-analysis of individual patient data. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 1692–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clavel, M.; Vermorken, J.B.; Cognetti, F.; Cappelaere, P.; de Mulder, P.; Schornagel, J.H.; Tueni, E.A.; Verweij, J.; Wildiers, J.; Clerico, M.; et al. Randomized comparison of cisplatin, methotrexate, bleomycin and vincristine (CABO) versus cisplatin and 5-fluorouracil (CF) versus cisplatin (C) in recurrent or metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck: A phase III study of the EORTC Head and Neck Cancer Cooperative Group. Ann. Oncol. 1994, 5, 521–526. [Google Scholar]
- Santabarbara, G.; Maione, P.; Rossi, A.; Gridelli, C. Pharmacotherapeutic options for treating adverse effects of Cisplatin chemotherapy. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2015, 17, 561–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brock, P.R.; Knight, K.R.; Freyer, D.R.; Campbell, K.; Steyger, P.; Blakley, B.; Rassekh, S.; Chang, K.; Fligor, B.; Rajput, K.; et al. Platinum-induced ototoxicity in children: A consensus review on mechanisms, predisposition, and protection, including a new International Society of Pediatric Oncology Boston ototoxicity scale. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 2408–2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McWhinney, S.R.; Goldberg, R.M.; McLeod, H.L. Platinum neurotoxicity pharmacogenetics. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2009, 8, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Panichpisal, K.; Kurtzman, N.; Nugent, K. Cisplatin nephrotoxicity: A review. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2007, 334, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, D.W.; Pouliot, L.M.; Hall, M.D.; Gottesman, M.M. Cisplatin resistance: A cellular selfdefense mechanism resulting from multiple epigenetic and genetic changes. Pharmacol. Rev. 2012, 64, 706–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safirstein, R.; Miller, P.; Guttenplan, J.B. Uptake and metabolism of cisplatin by rat kidney. Kidney Int. 1984, 25, 753–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelland, L. The resurgence of platinum-based cancer chemotherapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2007, 7, 573–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheate, N.J.; Walker, S.; Craig, G.E.; Oun, R. The status of platinum anticancer drugs in the clinic and in clinical trials. Dalton Trans. 2010, 39, 8113–8127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subocz, M.; Popławska, B.; Bielawska, A.; Bielawski, K. Platinum coordination complexes in cancer chemotherapy. Annal. Acad. Med. Siles. 2011, 65, 70–76. [Google Scholar]
- Ciancetta, A.; Coletti, C.; Marrone, A.; Re, N. Activation of carboplatin by chloride ions: A theoretical investigation. Theor. Chem. Acc. 2011, 129, 757–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopacz-Bednarska, A.; Król, T. Selected platinum complexes in standard and modern anticancer therapies. Nowotw. J. Oncol. 2022, 72, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mielcarek, P.; Majdak, E.; Krasińska, E.; Kobierski, J.; Kozaka, J.; Emerich, J. Comparison of quality of life in patients with advanced ovarian cancer treated with intravenous paclitaxel and carboplatin versus cyclophosphamide and cisplatin as first line chemotherapy—A preliminary report. Nowotw. J. Oncol. 2002, 52, 33–36. [Google Scholar]
- Faivre, S.; Chan, D.; Salinas, R.; Woynarowska, B.; Woynarowski, J.M. DNA strand breaks and apoptosis induced by oxaliplatin in cancer cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2003, 66, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnstone, T.C. The Crystal Structure of Oxaliplatin: A Case of Overlooked Pseudo Symmetry. Polyhedron 2014, 67, 429–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arango, D.; Wilson, A.J.; Shi, Q.; Corner, G.A.; Arañes, M.J.; Nicholas, C.; Lesser, M.; Mariadason, J.M.; Augenlicht, L.H. Molecular mechanisms of action and prediction of response to oxaliplatin in colorectal cancer cells. Br. J. Cancer 2004, 91, 1931–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francesco, A.M.; Ruggiero, A.; Riccardi, R. Cellular and molecular aspects of drugs of the future: Oxaliplatin. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2002, 59, 1914–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misset, J.L. Oxaliplatin in practice. Br. J. Cancer. 1998, 77, 4–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fanelli, M.; Formica, M.; Fusi, V.; Giorgi, L.; Micheloni, M.; Paolic, P. New trends in platinum and palladium complexes as antineoplastic agents. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2015, 310, 41–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.C.; Gong, Y.Q.; Zheng, X.M. Synthesis, characterization and antitumor activity of platinum(II) complexes of mixed ammine/amine with bidentate carboxylates. Synth. React. Inorg. Met.-Org. Chem. 2002, 32, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Štarha, P.; Křikavová, R. Platinum(IV) and platinum(II) anticancer complexes with biologically active releasable ligands. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2024, 501, 215578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravera, M.; Gabano, E.; McGlinchey, M.J.; Osella, D. A view on multi-action Pt(IV) antitumor prodrugs. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2019, 492, 32–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, M.D.; Hambley, T.W. Platinum(IV) antitumour compounds: Their bioinorganic chemistry. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2002, 232, 49–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apps, M.G.; Choi, E.H.; Wheat, N.J. The state-of-play and future of platinum drugs. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2015, 22, R219–R233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnstone, T.C.; Suntharalingam, K.; Lippard, S.J. The next generation of platinum drugs: Targeted Pt(II) agents, nanoparticle delivery, and Pt(IV) prodrugs. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 3436–3486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liaw, B.C.; Tsao, C.-K.; Seng, S.; Jun, T.; Gong, Y.; Galsky, M.D.; Oh, W.K. Biomarker development trial of satraplatin in patients with metastatic castration–resistant prostate cancer. Oncologist 2023, 28, 366–e224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navas, F.; Chocarro-Calvo, A.; Iglesias-Hernandez, P.; Fernandez-Garcia, P.; Morales, V.; Garcia-Martinez, J.M.; Sanz, R.; De la Vieja, A.; Garcia-Jimenez, C.; Garcia-Muñoz, R.A. Promising anticancer prodrugs based on Pt(IV) complexes with bisorganosilane ligands in axial positions. J. Med. Chem. 2024, 67, 6410–6424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novak, J.; Zykova, A.R.; Potemkin, V.A.; Sharutin, V.V.; Sharutina, O.K. Platinum(IV) compounds as potential drugs: A quantitative structure-activity relationship study. BioImpacts 2023, 13, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galanski, M.; Jakupec, M.; Keppler, B. Update of the preclinical situation of anticancer platinum complexes: Novel design strategies and innovative analytical approaches. Curr. Med. Chem. 2005, 1, 2075–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öğütçü, H.; Yetim, N.K.; Özkan, E.H.; Eren, O.; Kaya, G.; Sarı, N.; Ali, D. Nanospheres caped Pt(II) and Pt(IV): Synthesis and evaluation as antimicrobial and antifungal agent. Pol. J. Chem. Technol. 2017, 19, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, E.L.; Bose, R.N. Platinum(II) catalysis and radical intervention in reductions of platinum(IV) antitumor drugs by ascorbic acid. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2003, 95, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, M.D.; Mellor, H.R.; Callaghan, R.; Hambley, T.W. Basis for design and development of platinum(IV) anticancer complexes. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 50, 3403–3411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Jia, C.; Zhang, X.; Liao, X.; Yang, B.; Cong, Y.; Pu, S.; Gao, C. Targeting drug delivery system for platinum(IV)-based antitumor complexes. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 194, 112229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, K.R.; Kutikov, A.; Lippard, S.J. Synthesis, characterization, and cytotoxicity of a series of estrogen-tethered platinum(IV) complexes. Chem. Biol. 2004, 11, 557–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, S.; Barnés, C.M.; Haskel, A.; Short, S.M.; Barnes, K.R.; Lippard, S.J. Conjugated platinum(IV)-peptide complexes for targeting angiogenic tumor vasculature. Bioconjug. Chem. 2008, 19, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
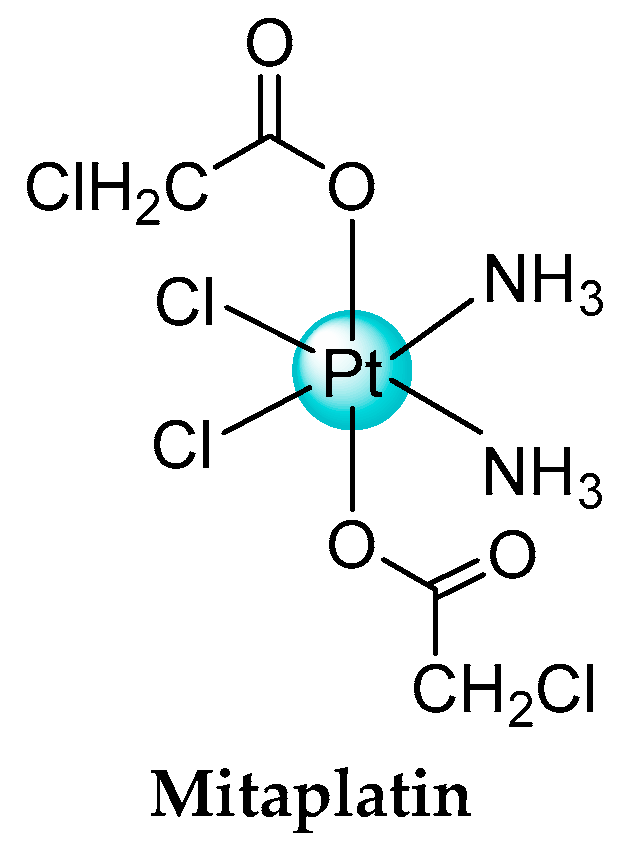
- Dhar, S.; Lippard, S.J. Mitaplatin, a potent fusion of cisplatin and the orphan drug dichloroacetate. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 22199–22204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ang, W.H.; Khalaila, I.; Allardyce, C.S.; Juillerat-Jeanneret, L.; Dyson, P.J. Rational design of platinum(IV) compounds to overcome glutathione-S-transferase mediated drug resistance. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 1382–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reithofer, M.R.; Valiahdi, S.M.; Galanski, M.; Jakupec, M.A.; Arion, V.B.; Keppler, B.K. Novel endothall-containing platinum(IV) complexes: Synthesis, characterization, and cytotoxic activity. Chem. Biodivers. 2008, 5, 2160–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, R.K.; Marrache, S.; Choi, J.H.; Berding, T.B.; Dhar, S. The prodrug platin-A: Simultaneous release of cisplatin and aspirin. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 1963–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, W.; Crews, B.C.; Marnett, L.J.; Hey-Hawkins, E. Conjugates of cisplatin and cyclooxygenase inhibitors as potent antitumor agents overcoming cisplatin resistance. ChemMedChem 2014, 9, 1150–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, W.; Crews, B.C.; Sárosi, M.B.; Daniel, C.M.; Ghebreselasie, K.; Scholz, M.S.; Marnett, L.J.; Hey-Hawkins, E. Conjugation of cisplatin analogues and cyclooxygenase inhibitors to overcome cisplatin resistance. ChemMedChem 2015, 10, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
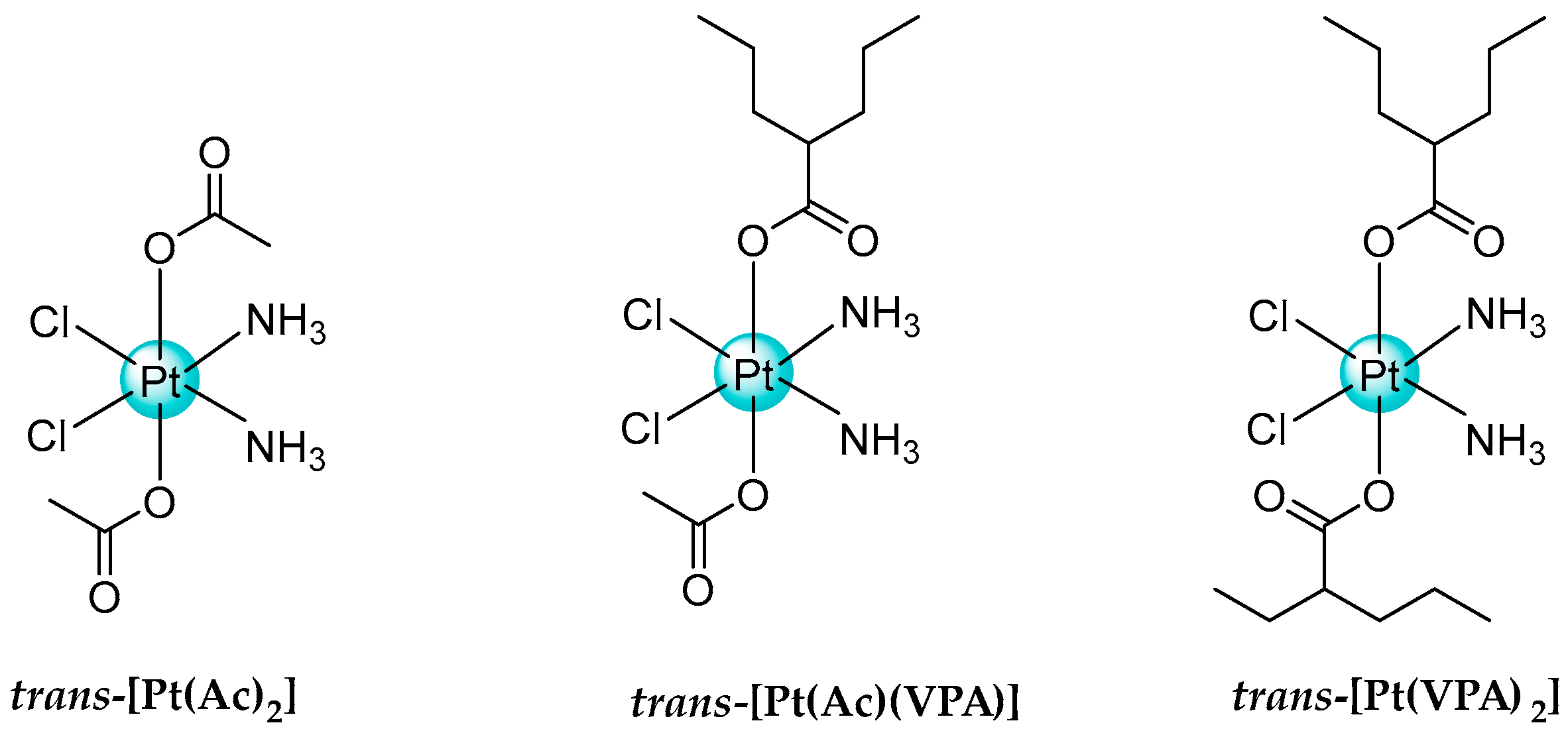
- Novohradsky, V.; Zerzankova, L.; Stepankova, J.; Vrana, O.; Raveendran, R.; Gibson, D.; Kasparkova, J.; Brabec, V. New insights into the molecular and epigenetic effects of antitumor Pt(IV)-valproic acid conjugates in human ovarian cancer cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2015, 95, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
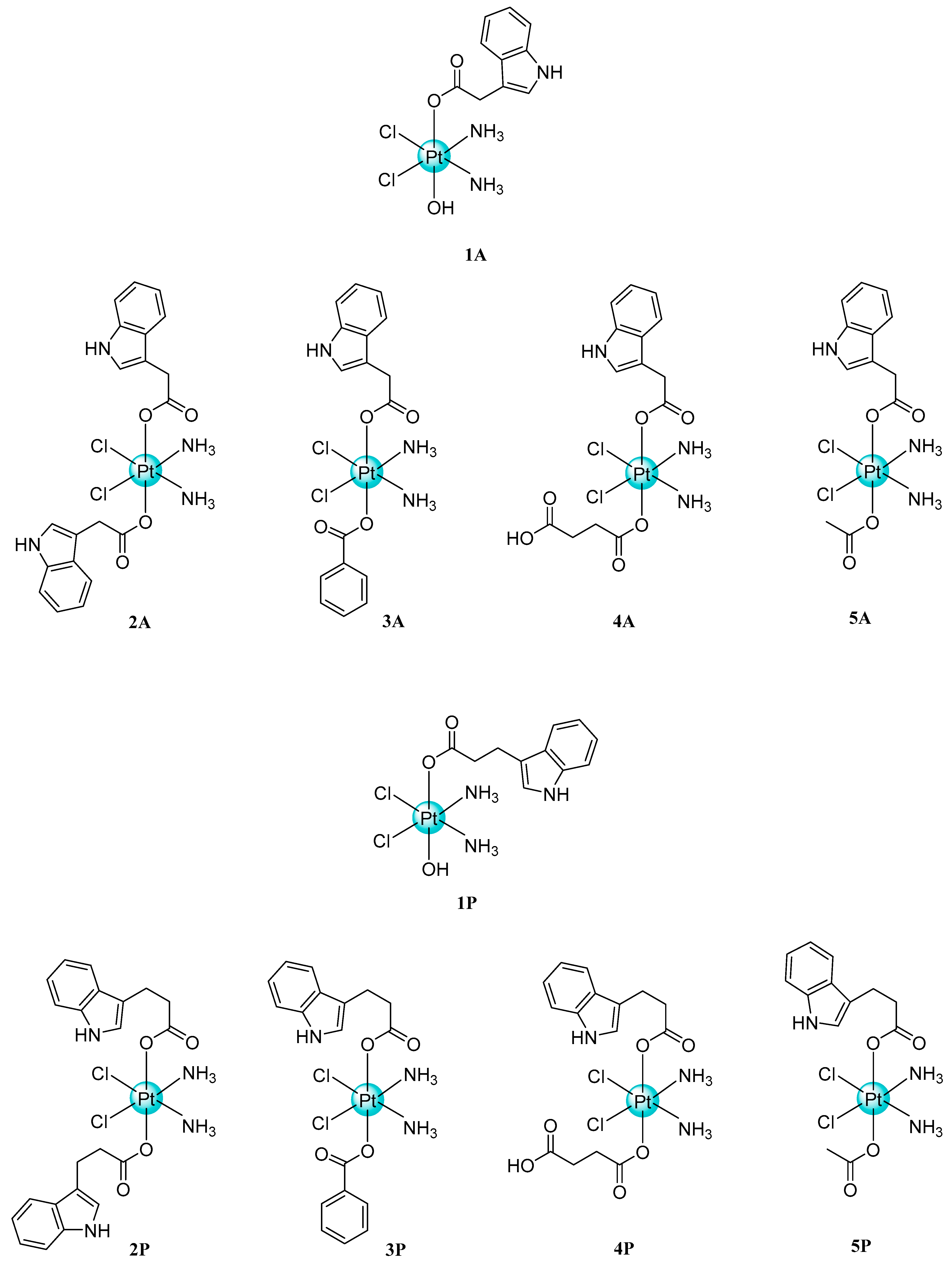
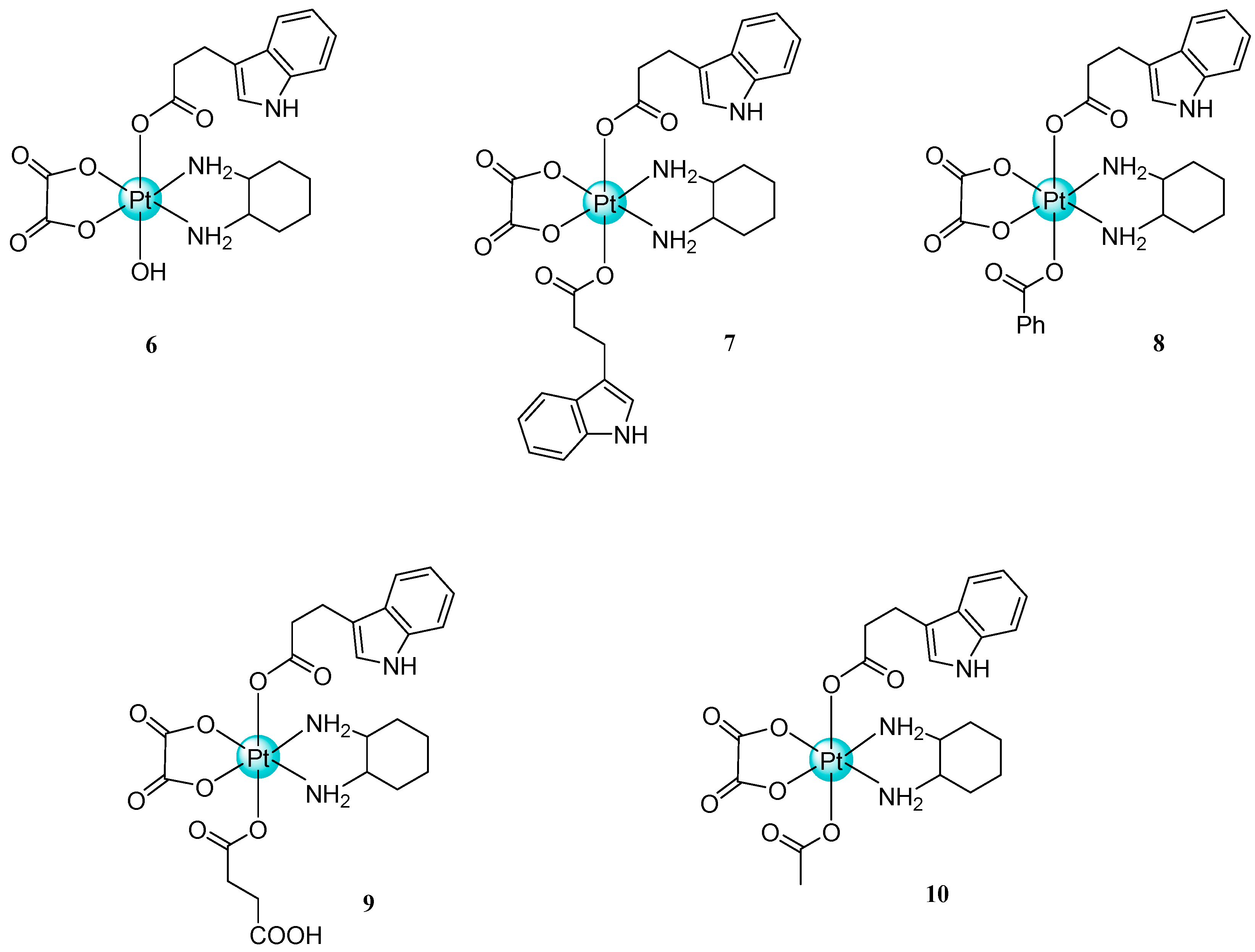
- Tolan, D.; Gandin, V.; Morrison, L.; El-Nahas, A.; Marzano, C.; Montagner, D.; Erxleben, A. Oxidative stress induced by Pt(IV) pro-drugs based on the cisplatin scaffold and indole carboxylic acids in axial position. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 29367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karbownik, M.; Reiter, R.J.; Garcia, J.J.; Cabrera, J.; Burkhardt, S.; Osuna, C.; Lewiński, A. Indole-3-propionic acid, a melatonin-related molecule, protects hepatic microsomal membranes from iron-induced oxidative damage: Relevance to cancer reduction. J. Cell. Biochem. 2001, 81, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karbownik, M.; Stasiak, M.; Zygmunt, A.; Zasada, K.; Lewiński, A. Protective effects of melatonin and indole-3-propionic acid against lipid peroxidation caused by potassium bromate in the rat kidney. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2006, 24, 483–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolan, D.; Almotairy, A.R.Z.; Howe, O.; Devereux, M.; Montagner, D.; Erxleben, A. Cytotoxicity and ROS production of novel Pt(IV) oxaliplatin derivatives with indole propionic acid. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2019, 492, 262–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raveendran, R.; Braude, J.P.; Wexselblatt, E.; Novohradsky, V.; Stuchlikova, O.; Brabec, V.; Gandin, V.; Gibson, D. Pt(IV) derivatives of cisplatin and oxaliplatin with phenylbutyrate axial ligands are potent cytotoxic agents that act by several mechanisms of action. Chem. Sci. 2016, 7, 2381–2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadia, P.; Micoli, K.; Barbanente, A.; Ditaranto, N.; Hoeschele, J.D.; Natile, G.; Marzano, C.; Gandin, V.; Margiotta, N. Platinum(IV) complexes of trans-1,2-diamino-4-cyclohexene: Prodrugs affording an oxaliplatin analogue that overcomes cancer resistance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, C.; Cong, Y.; Pu, S.; Cai, L.; Zhong, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liao, X.; Li, Y.; Yang, B.; Gao, C. Synthesis, characterization, and biological activity of new mixed ammine/amine platinum(IV) complexes. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2020, 34, e5680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höfer, D.; Varbanov, H.P.; Hejl, M.; Jakupec, M.A.; Roller, A.; Galanski, M.; Keppler, B.K. Impact of the equatorial coordination sphere on the rate of reduction, lipophilicity and cytotoxic activity of platinum(IV) complexes. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2017, 174, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartwig, J.F.; Lippard, S.J. DNA binding properties of [Pt(NH3)(C6H11NH2)Cl2], a metabolite of an orally active platinum anticancer drug. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1992, 114, 5646–5654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.; Filotto, C.; Bisanzo, M.; Delaney, S.; Lagasee, D.; Whitworth, J.L.; Jusko, A.; Li, C.; Wood, N.A.; Willingham, J.; et al. Reduction and anticancer activity of platinum(IV) complexes. Inorg. Chem. 1998, 37, 2500–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.K.; Zhang, J.Z.; Aitken, J.B.; Hambley, T.W. Influence of equatorial and axial carboxylato ligands on the kinetic inertness of platinum(IV) complexes in the presence of ascorbate and cysteine and within DLD-1 cancer cells. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 8757–8764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKeage, M.J.; Morgan, S.E.; Boxall, F.E.; Murrer, B.A.; Hard, G.C.; Harrap, K.R. Preclinical toxicology and tissue platinum distribution of novel oral antitumour platinum complexes: Ammine/amine platinum(IV) dicarboxylates. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 1994, 33, 497–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelland, L.R.; Murrer, B.A.; Abel, G.; Giandomenico, C.M.; Mistry, P.; Harrap, K.R. Ammine/amine platinum(IV) dicarboxylates: A novel class of platinum complex exhibiting selective cytotoxicity to intrinsically cisplatin-resistant human ovarian carcinoma cell lines. Cancer Res. 1992, 52, 822–828. [Google Scholar]
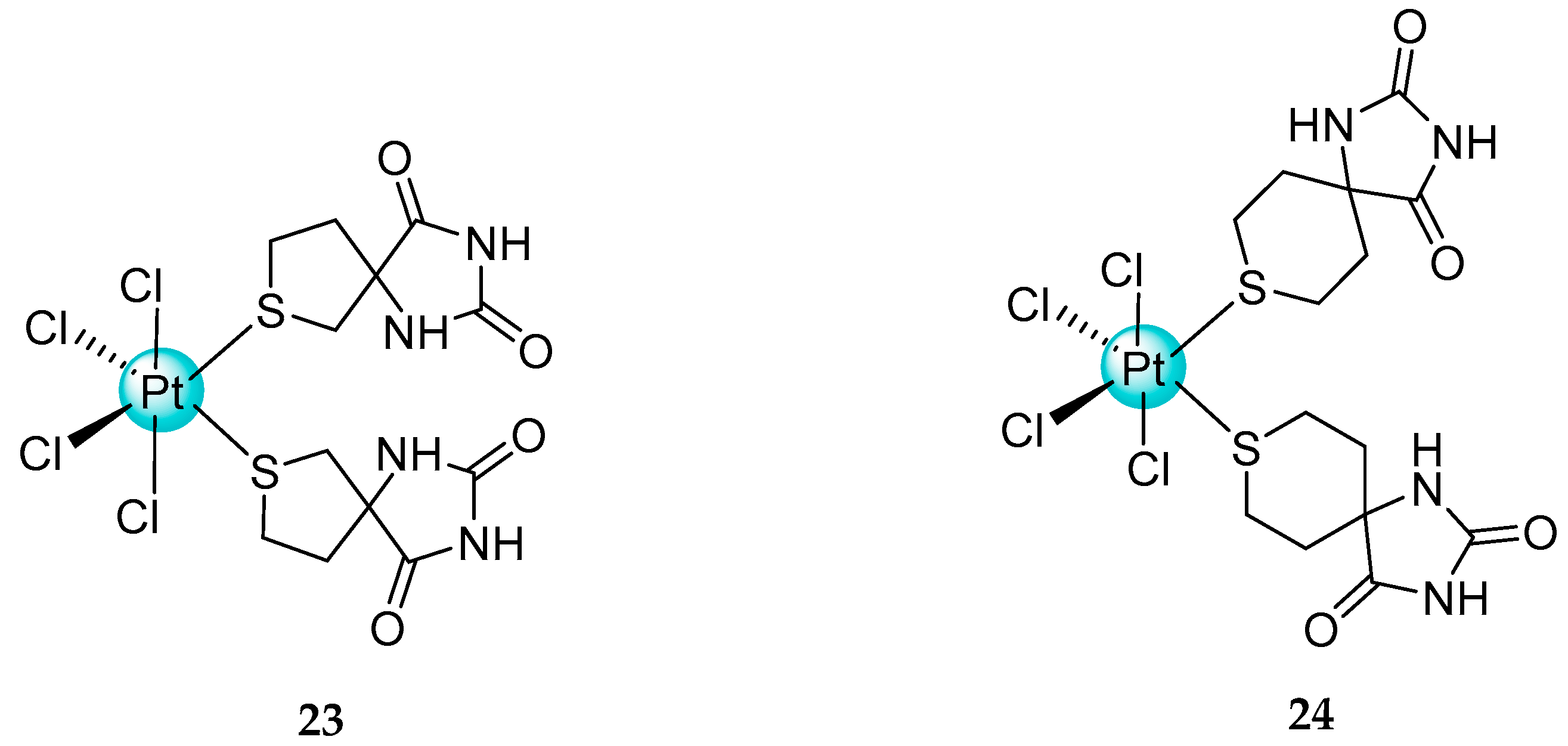
- Bakalova, A.; Buyukliev, R.; Momekov, G. Synthesis, DFT calculations and cytotoxic investigation of platinum complexes with 3-thiolanespiro-5′-hydantoin and 4-thio-1H-tetrahydropyranespiro-5’-hydantoinhe. J. Mol. Struct. 2015, 1091, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherneva, E.; Bakalova, A.; Michailova, R.; Nikolova-Mladenova, B. Preparation, characterization, theoretical investigation and cytotoxic activity of new mixed ammine/amine platinum complexes with 3-amino-5-methyl-5-phenylhydantoin. Bulg. Chem. Commun. 2017, 49, 89–95. [Google Scholar]
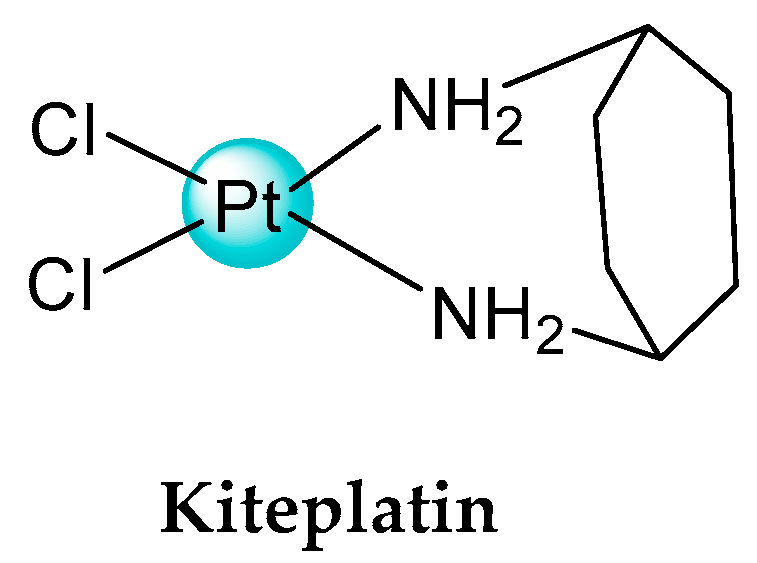
- Savino, S.; Gandin, V.; Hoeschele, J.D.; Marzano, C.; Natile, G.; Margiotta, N. Dual-acting antitumor Pt(IV) prodrugs of kiteplatin with dichloroacetate axial. Dalton Trans. 2018, 47, 7144–7158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Margiotta, N.; Marzano, C.; Gandin, V.; Osella, D.; Ravera, M.; Gabano, E.; Platts, J.A.; Petruzzella, E.; Hoeschele, J.D.; Natile, G. Revisiting [PtCl₂(cis-1,4-DACH)]: An underestimated antitumor drug with potential application to the treatment of oxaliplatin-refractory colorectal cancer. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 7182–7192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
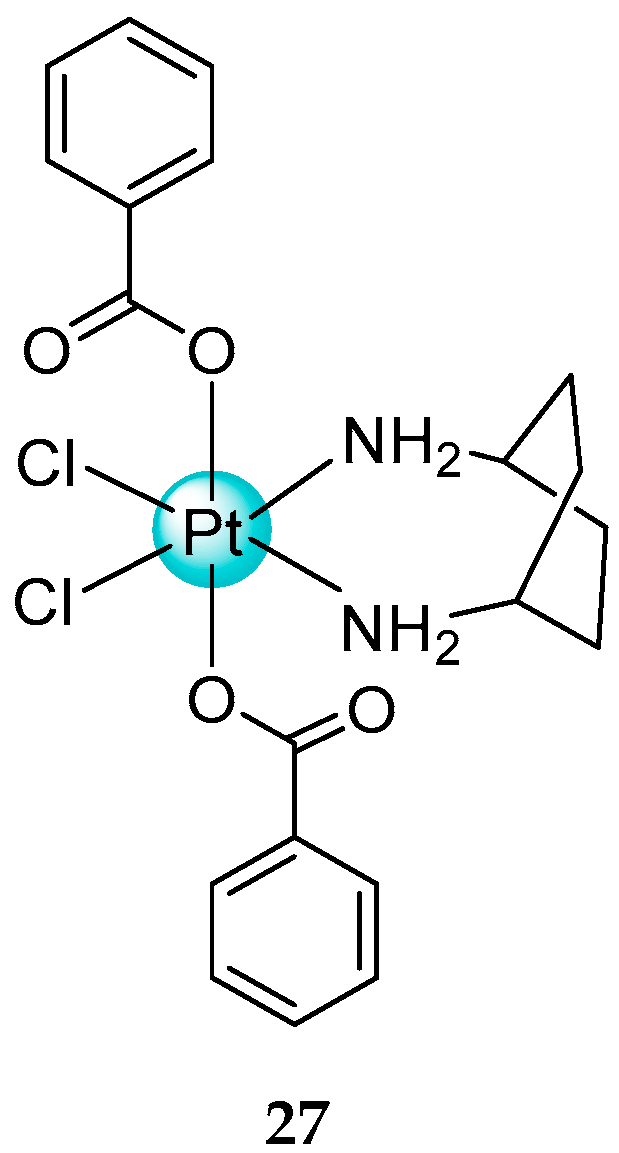
- Barbanente, A.; Gandin, V.; Ceresa, C.; Marzano, C.; Ditaranto, N.; Hoeschele, J.D.; Natile, G.; Arnesano, F.; Pacifico, C.; Intini, F.P.; et al. Improvement of kiteplatin efficacy by a benzoato Pt(IV) prodrug suitable for oral administration. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canil, G.; Braccini, S.; Marzo, T.; Marchetti, L.; Pratesi, A.; Biver, T.; Funaioli, T.; Chiellini, F.; Hoeschele, J.D.; Gabbiani, C. Photocytotoxic Pt(IV) complexes as prospective anticancer agents. Dalton Trans. 2019, 48, 10933–10944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Veer, J.L.; Peters, A.R.; Reedijk, J. Reaction products from platinum(IV) amine compounds and 5’-GMP are mainly bis(5’-GMP) platinum (II) amine adducts. J. Inorg. Biochem. 1986, 26, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.Z.; Wexelblatt, E.; Hambley, T.W.; Gibson, D. Pt(IV) analogs of oxaliplatin that do not follow the expected correlation between electrochemical reduction potential and rate of reduction by ascorbate. Chem. Comm. 2012, 48, 847–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varbanov, H.; Valiahdi, S.M.; Jakupec, M.A.; Galanski, M.; Keppler, B.K. Novel tetracarboxylatoplatinum(IV) complexes as carboplatin prodrugs. Dalton Trans. 2012, 41, 14404–14415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höfer, D.; Varbanov, H.P.; Legin, A.; Jakupec, M.A.; Roller, A.; Galanski, M.S.; Keppler, B.K. Tetracarboxylatoplatinum(IV) complexes featuring monodentate leaving groups–A rational approach toward exploiting the platinum(IV) prodrug strategy. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2015, 153, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemirovski, A.; Kasherman, Y.; Tzaraf, Y.; Gibson, D. Reduction of cis,trans,cis-[PtCl2(OCOCH3)2(NH3)2] by aqueous extracts of cancer cells. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 50, 5554–5556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponte, F.; Scoditti, S.; Mazzone, G.; Sicilia, E. The current status in computational exploration of Pt(IV) prodrug activation by reduction. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2023, 25, 15586–15599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aputen, A.D.; Elias, M.G.; Gilbert, J.; Sakoff, J.A.; Gordon, C.P.; Scott, K.F.; Aldrich-Wright, J.R. Platinum(IV) prodrugs incorporating an indole-based derivative, 5-benzyloxyindole-3-acetic acid in the axial position exhibit prominent anticancer activity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orzechowska, M.; Fabijańska, M.; Ochocki, J.; Małecki, M. Anticancer activity of a trans-platinum(II) complex of 3-aminoflavone to ovarian cancer cells. Ginekol. Pol. 2017, 88, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natile, G.; Coluccia, M. Current status of trans-platinum compounds in cancer therapy. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2001, 216-217, 383–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connors, T.A.; Cleare, M.J.; Harrap, K.R. Structure-activity relationships of the antitumor platinum coordination complexes. Cancer Treat. Rep. 1979, 63, 1499–1502. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, D. Development of non-traditional platinum anticancer agents: Trans-platinum planar amine compounds and polynuclear platinum compounds. Ph.D. Thesis, Virginia Common Wealth University, Richmond, VA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
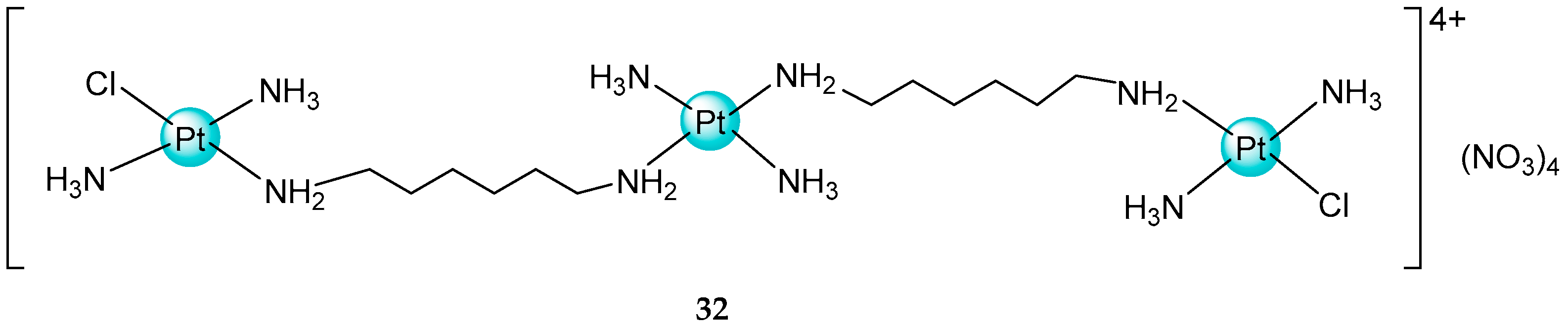
- Farrell, N.P. Multi-platinum anti-cancer agents. Substitution-inert compounds for tumor selectivity and new targets. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 8773–8785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
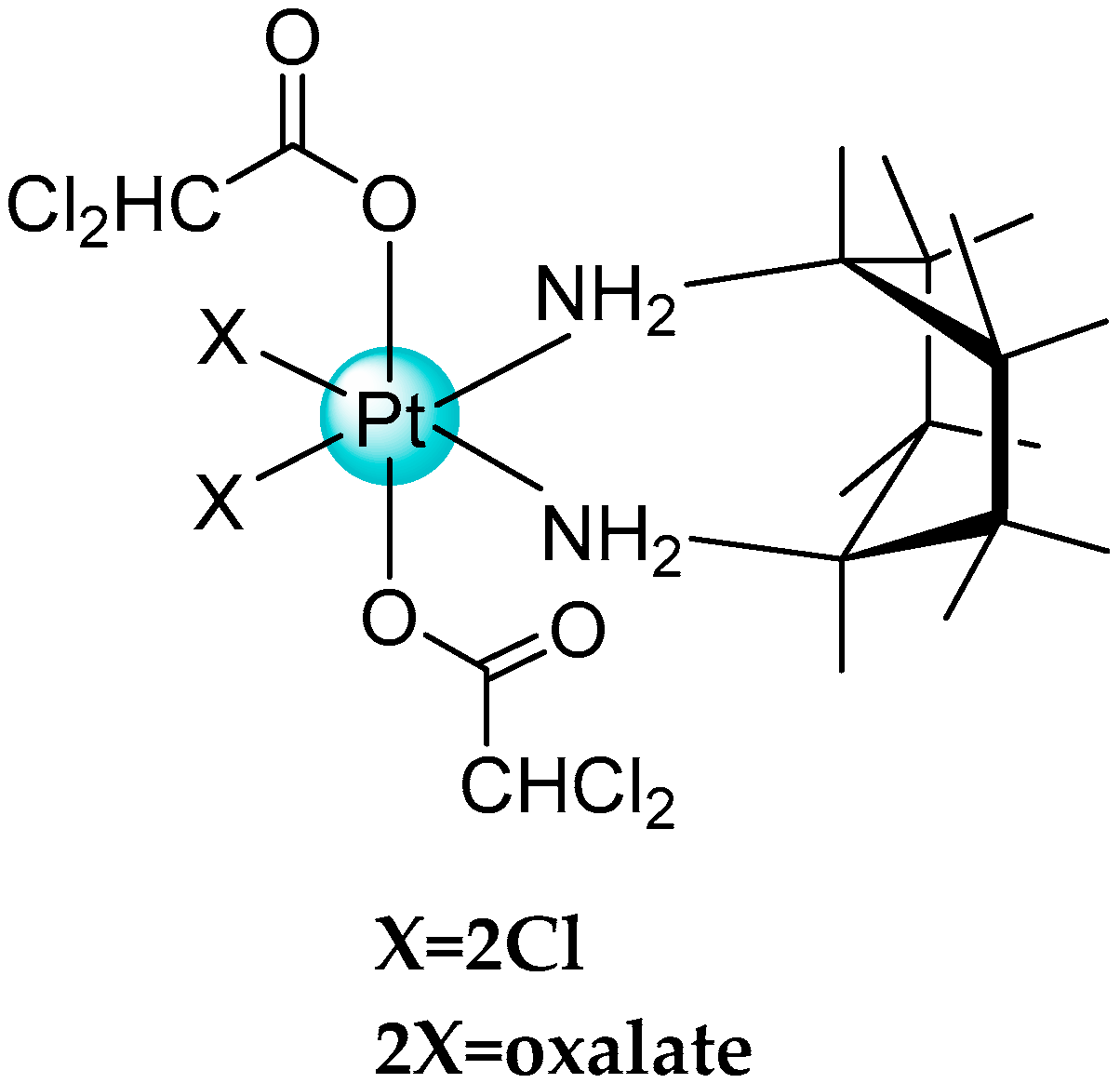
- Kelland, L.R.; Abel, G.; McKeage, M.J.; Jones, M.; Goddard, P.M.; Valenti, M.; Murrer, B.A.; Harrap, K.R. Preclinical antitumor evaluation of bis-acetato-ammine-dichloro-cyclohexylamine platinum(IV): An orally active platinum drug. Cancer Res. 1993, 53, 2581–2586. [Google Scholar]
- Sakamaki, Y.; Mirsadeghi, H.A.; Fereidoonnezhad, M.; Mirzaei, F.; Dehkordi, Z.M.; Chamyani, S.; Alshami, M.; Abedanzadeh, S.; Shahsavari, H.R.; Beyzavi, M.H. Trans-Platinum(II) thionate complexes: Synthesis, structural characterization, and in vitro biological assessment as potent anticancer agents. ChemPlusChem 2019, 84, 1525–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero, E.; Miranda, S.; Lüttenberg, S.; Fröhlich, N.; Koenen, J.-M.; Mohr, F.; Cerrada, E.; Laguna, M.; Mendía, A. Trans-thionate derivatives of Pt(II) and Pd(II) with water-soluble phosphane PTA and DAPTA ligands: Antiproliferative activity against human ovarian cancer cell lines. Inorg. Chem. 2013, 52, 6635–6647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coluccia, M.; Natile, G. Trans-platinum complexes in cancer therapy. Anti-Cancer Agents Med. Chem. 2007, 7, 111–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheena, M.A.; Farrell, N.P. Towards antitumor active trans-platinum compounds. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2009, 2009, 1293–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, N.; Ha, T.T.; Souchard, J.P.; Wimmer, F.L.; Cros, S.; Johnson, N.P. Cytostatic trans-platinum(II) complexes. J. Med. Chem. 1989, 32, 2240–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, S.M.; Lippard, S.J. Cisplatin: From DNA damage to cancer chemotherapy. Prog. Nucleic Acid Res. Mol. Biol. 2001, 67, 93–130. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Grabner, S.; Modec, B.; Bukovec, N.; Bukovec, P.; Čemažar, M.; Kranjc, S.; Serša, G.; Sčančar, J. Cytotoxic trans-platinum(II) complex with 3-hydroxymethylpyridine: Synthesis, X-ray structure and biological activity evaluation. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2016, 161, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Beusichem, M.; Farrell, N. Activation of the trans-geometry in platinum antitumor complexes. Synthesis, characterization, and biological activity of complexes with the planar ligands pyridine, N-methylimidazole, thiazole, and quinoline. Crystal and molecular structure of trans-dichlorobis(thiazole)platinum(II). Inorg. Chem. 1992, 31, 634–639. [Google Scholar]
- Fojo, T.; Farrell, N.; Ortuzar, W.; Tanimura, H.; Weinstein, J.; Myers, T.G. Identification of non-cross-resistant platinum compounds with novel cytotoxicity profiles using the NCI anticancer drug screen and clustered image map visualizations. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2005, 53, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakić, G.M.; Grgurić-Šipka, S.; Kaluderović, G.N.; Gómez-Ruiz, S.; Bjelogrlić, S.K.; Radulović, S.S.; Tešić, Ž.L. Novel trans-dichloridoplatinum(II) complexes with 3- and 4-acetylpyridine: Synthesis, characterization, DFT calculations and cytotoxicity. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 44, 1921–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipovic, L.; Arandelovic, S.; Gligorijevic, N.; Krivokuca, A.; Jankovic, R.; Srdic-Rajic, T.; Rakic, G.; Tesic, Z.; Radulovic, S. Biological evaluation of trans-dichloridoplatinum(II) complexes with 3- and 4-acetylpyridine in comparison to cisplatin. Radiol. Oncol. 2013, 47, 346–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bakalova, A.; Buyukliev, R.; Varbanov, H.; Momekov, G. Design, synthesis and comparative cytotoxic investigation of platinum(II) complexes with some derivatives of 5-methyl-5-(4-pyridyl)hydantoin. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2014, 423, 46–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coluccia, M.; Nassi, A.; Loseto, F.; Boccarelli, A.; Mariggio, M.A.; Giordano, D.; Intini, F.P.; Caputo, P.; Natile, G. A Trans-platinum complex showing higher antitumor activity than the cis-congeners. J. Med. Chem. 1993, 36, 510–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coluccia, M.; Nassi, A.; Boccarelli, A.; Giordano, D.; Cardellicchio, N.; Locker, D.; Leng, M.; Sivo, M.; Intini, F.P.; Natile, G. In vitro and in vivo antitumour activity and cellular pharmacological properties of new platinum-iminoether complexes with different configuration at the iminoether ligands. J. Inorg. Biochem. 1999, 77, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coluccia, M.; Boccarelli, A.; Mariggio, M.A.; Cardellicchio, N.; Caputo, P.; Intini, F.P.; Natile, G. Platinum(II) complexes containing iminoethers: A trans platinum antitumor agent. Chem. Biol. Interact. 1995, 98, 251–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brabec, V.; Vrana, O.; Novakova, O.; Kleinwachter, V.; Intini, F.P.; Coluccia, M.; Natile, G. DNA adducts of antitumor trans-[PtCl2(E-iminoether)2]. Nucleic Acids Res. 1996, 24, 336–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Leng, M.; Locker, D.; Giraud-Panis, M.J.; Schwartz, A.; Intini, F.P.; Natile, G.; Pisano, C.; Boccarelli, A.; Giordano, D.; Coluccia, M. Replacement of an NH3 by an iminoether in transplatin makes an antitumor drug from an inactive compound. Mol. Pharmacol. 2000, 58, 1525–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.; Isab, A.A.; Ali, S. Structural and mechanistic aspects of platinum anticancer agents. Transit. Met. Chem. 2006, 31, 1003–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Intini, F.P.; Natile, G.; Sletten, E. Kinetic study of the reaction between an antitumor 15N labeled trans-platinum iminoether complex and GMP by [1H, 15N] HMQC NM. J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. 2002, 18, 3489–3495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, C.; Díaz-García, C.V.; Agudo-López, A.; del Solar, V.; Cabrera, S.; Agulló-Ortuño, M.T.; Navarro-Ranninger, C.; Alemán, J.; López-Martín, J.A. Evaluation of novel trans-sulfonamide platinum complexes against tumor cell lines. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 76, 360e368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, P.M.; Jackman, J.; Bae, I.; Myers, T.G.; Fan, S.; Mutoh, M.; Scudiero, D.A.; Monks, A.; Sausville, E.A.; Weinstein, J.N.; et al. Characterization of the p53 tumor suppressor pathway in cell lines of the National Cancer Institute anticancer drug screen and correlations with the growth-inhibitory potency of 123 anticancer agents. Cancer Res. 1997, 57, 4285–4300. [Google Scholar]
- Agudo-López, A.; Prieto-García, E.; Alemán, J.; Pérez, C.; Díaz-García, C.V.; Parrilla-Rubio, L.; Cabrera, S.; Navarro-Ranninger, C.; Cortés-Funes, H.; López-Martín, J.A.; et al. Mechanistic added value of a trans-sulfonamide-platinum complex in human melanoma cell lines and synergism with cisplatin. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasparkova, J.; Marini, V.; Najajreh, Y.; Gibson, D.; Brabec, V. DNA binding mode of the cis and trans geometries of new antitumor nonclassical platinum complexes containing piperidine, piperazine or 4-picoline ligand in cell-free media. Relations to their activity in cancer cell lines. Biochemistry 2003, 42, 6321–6332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasparkova, J.; Novakova, O.; Marini, V.; Najajreh, Y.; Gibson, D.; Perez, J.-M.; Brabec, V. Activation of trans-geometry in bifunctional mononuclear platinum complexes by a piperidine ligand. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 47516–47525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, N.P.; Butour, J.-L.; Villani, G.; Wimmer, F.L.; Defais, M.; Pierson, V.; Brabec, V. Metal antitumor compounds: The mechanism of action of platinum complexes. Prog. Clin. Biochem. Med. 1989, 10, 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Khazanov, E.; Barenholz, Y.; Gibson, D.; Najajreh, Y. Novel apoptosis-inducing trans-platinum piperidine derivatives: Synthesis and biological characterization. J. Med. Chem. 2002, 45, 5196–5204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najajreh, Y.; Perez, J.M.; Navarro-Ranninger, C.; Gibson, D. Novel soluble cationic trans-diaminedichloroplatinum(II) complexes that are active against cisplatin resistant ovarian cancer cell lines. J. Med. Chem. 2002, 45, 5189–5195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrell, N.; Kelland, L.R.; Roberts, J.D.; Van Beusichem, M. Activation of the trans geometry in platinum antitumor complexes: A survey of the cytotoxicity of trans complexes containing planar ligands in murine L1210 and human tumor panels and studies on their mechanism of action. Cancer Res. 1992, 52, 5065–5072. [Google Scholar]
- Dalbies, R.; Payet, D.; Leng, M. DNA double helix promotes a linkage isomerization reaction in trans-diamminedichloroplatinum(II)-modified DNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 8147–8151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, M.; Schwartz, A.; Giraud-Panis, M.J. Platinum-Based Drugs in Cancer Therapy; Kelland, L.R., Farrell, N.P., Eds.; Humana Press Inc.: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2000; pp. 63–85. [Google Scholar]
- Dalbies, R.; Boudvillain, M.; Leng, M. Linkage isomerization reaction of intrastrand cross-links in trans-diamminedichloroplatinum(II)-modified single-stranded oligonucleotides. Nucleic Acids Res. 1995, 23, 949–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Regiec, A.; Wojciechowski, P.; Mastalarz, H. Experimental and theoretical spectroscopic and electronic properties enriched with NBO analysis for 1-methyl-3-nitropyrazole and 1-methyl-5-nitropyrazole. J. Mol. Struct. 2014, 1075, 234–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regiec, A.; Mastalarz, H.; Wojciechowski, P. Theoretical anharmonic Raman and infrared spectra with vibrational assignments and NBO analysis for 1-methyl-4-nitropyrazole. J. Mol. Struct. 2014, 1061, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papesch, V.; Dodson, R.M. Isomeric Pyrazolo [4,3-d]pyrimidinedione. J. Org. Chem. 1965, 30, 199–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regiec, A.; Mastalarz, H.; Mastalarz, A.; Kochel, A. Methylation of 4-nitro-3(5)-pyrazolecarboxylic acid. Tetrahedron Lett. 2009, 50, 2624–2627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fereidoonnezhad, M.; Shahsavari, H.R.; Lotfi, E.; Babaghasabha, M.; Fakhri, M.; Faghih, Z.; Faghih, Z.M.; Beyzavi, H. (Benzyl isocyanide)gold(I) pyrimidine-2-thiolate complex: Synthesis and biological activity. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2018, 32, e4200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fereidoonnezhad, M.; Shahsavari, H.R.; Abedanzadeh, S.; Nezafati, A.; Khazali, A.; Mastrorilli, P.; Babaghasabha, M.; Webb, J.; Faghih, Z.; Faghih, Z.; et al. Synthesis, structural characterization, biological evaluation and molecular docking studies of new platinum(II) complexes containing isocyanides. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 8681–8692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalinde, E.; Lara, R.; López, I.P.; Moreno, M.T.; Alfaro-Arnedo, E.; Pichel, J.G.; Piñeiro-Hermida, S. Benzothiazole-based cycloplatinated chromophores: Synthetic, optical, and biological studies. Chem. Eur. J. 2018, 24, 2440–2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babak, M.V.; Pfaffeneder-Kmen, M.; Meier-Menches, S.M.; Legina, M.S.; Theiner, S.; Licona, C.; Orvain, C.; Hejl, M.; Hanif, M.; Jakupec, M.A.; et al. Rollover cyclometalated bipyridine platinum Complexes as potent anticancer agents: Impact of the ancillary ligands on the mode of action. Inorg. Chem. 2018, 57, 2851–2864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fereidoonnezhad, M.; Shahsavari, H.R.; Abedanzadeh, S.; Behchenari, B.; Hossein-Abadi, M.; Faghih, Z.; Beyzavi, M.H. Cycloplatinated(II) complexes bearing 1,1’-bis(diphenylphosphino)ferrocene ligand: Biological evaluation and molecular docking studies. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 2385–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fereidoonnezhad, M.; Niazi, M.; Ahmadipour, Z.; Mirzaee, T.; Faghih, Z.; Faghih, Z.; Shahsavari, H.R. Cyclometalated platinum(II) complexes comprising 2-(diphenylphosphino)pyridine and various thiolate ligands: Synthesis, spectroscopic characterization, and biological activity. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2017, 2017, 2247–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabijańska, M.; Studzian, K.; Szmigiero, L.; Rybarczyk-Pirek, A.J.; Pfitzner, A.; Cebula-Obrzut, B.; Smolewski, P.; Zynera, E.; Ochocki, J. Trans-Platinum(II) complex of 3-aminoflavone–synthesis, X-ray crystal structure and biological activities in vitro. Dalton Trans. 2015, 44, 938–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravishankar, D.; Rajora, A.K.; Greco, F.; Osborn, H.M. Flavonoids as prospective compounds for anticancer therapy. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2013, 45, 2821–2831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kośmider, B.; Osiecka, R. Flavonoid compounds: A review of anticancer properties and interactions with cis-diamminedichloroplatinum(II). Drug Dev. Res. 2004, 63, 200–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souiei, S.; Bousejra-Elgarah, F.; Belkacem, M.A.; Znati, M.; Bouajila, J.; Jannet, H.B. New flavonoid glycosides conjugates: Synthesis, characterization, and evaluation of their cytotoxic activities. Turk. J. Chem. 2019, 43, 404–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reedijk, J. Metal-ligand exchange kinetics in platinum and ruthenium complexes. Platinum Met. Rev. 2008, 52, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miguel, P.J.S.; Roitzsch, M.; Yin, L.; Lax, P.M.; Holland, L.; Krizanovic, O.; Lutterbeck, M.; Schürmann, M.; Fusch, E.C.; Lippert, B. On the many roles of NH3 ligands in mono- and multinuclear complexes of platinum. Dalton Trans. 2009, 10774–10786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Gou, S.; Xu, G. Synthesis and biological evaluation of mixed ammine/amine platinum(II) complexes with dicarboxylate containing organic nitrate as ligand. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2014, 409, 310–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stacpoole, P.W.; Kerr, D.S.; Barnes, C.; Bunch, S.T.; Carney, P.R.; Fennell, E.M.; Felitsyn, N.M.; Gilmore, R.L.; Greer, M.; Henderson, G.N.; et al. Controlled clinical trials of dichloroacetate for treatment of congenital lactic acidosis in children. Padiatrics 2006, 117, 1519–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, J.Y.; Huggins, G.S.; Debidda, M.; Munshi, N.C.; De Vivo, I. Dichloroacetate induces apoptosis in endometrial cancer cells. Gynecol. Oncol. 2008, 109, 394–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhok, B.M.; Yeluri, S.; Perry, S.L.; Hughes, T.A.; Jayne, D.G. Dichloroacetate induces apoptosis and cell-cycle arrest in colorectal cancer cells. Br. J. Cancer 2010, 102, 1746–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, H. Cancer patients opt for unapproved drug. Nature 2007, 446, 474–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coglan, A. Cheap, ‘safe’ drug kills most cancers. New Sci. 2007, 193, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Su, J.; Jiang, J.; Li, X.; Ye, Q.; Zhou, H.; Chen, J.; Li, Y. Two mixed NH3/amine platinum (II) anticancer complexes featuring a dichloroacetate moiety in the leaving group. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakalova, A.; Nikolova-Mladenova, B.; Buyukliev, R.; Cherneva, E.; Momekov, G.; Ivanov, D. Synthesis, DFT calculations and characterisation of new mixed Pt(II) complexes with 3-thiolanespiro-5’-hydantoin and 4-thio-1H-tetrahydropyranspiro-5′-hydantoin. Chem. Pap. 2016, 70, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakalova, A.; Buyukliev, R.; Cherneva, E. New Pt(II) complexes with 3′-methyl-tetrahydro-4H-thiopyranspiro-5’-hydantoin: Synthesis, theoretical and cytotoxic investigation. Med. Chem. Res. 2020, 29, 2218–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherneva, E.; Atanasova, M.; Šmelcerović, Ž.; Tomović, K.; Buyukliev, R.; Šmelcerović, A.; Bakalova, A. 3′-Aminothiocyclohexanespiro-5′-hydantoin and its Pt(II) complex-Synthesis, cytotoxicity and xanthine oxidase inhibitory activity. Inorganics 2022, 10, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakalova, A.; Buyukliev, R.; Nikolova, R.; Shivachev, B.; Mahaylova, R.; Konstantinov, S. Synthesis, spectroscopic properties, crystal structure and biological evaluation of new platinum complexes with 5-methyl-5-(2-thiomethyl)ethyl hydantoin. Anti-Cancer Agents Med. Chem. 2019, 19, 1243–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.; Dou, P.Y.; Wang, K. Synthesis, antitumor activity and acute toxicity of diammine/diaminocyclohexane platinum(II) complexes with oxygen-ligating leaving group. J. Inorg. Biochem. 1997, 65, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.C.; Shen, Y. Synthesis, cytotoxicity, and DNA-binding levels of ammine/cyclohexylamine platinum(II) complexes with dicarboxylates. Synth. React. Inorg. Met.-Org. Nano-Met. Chem. 2006, 36, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhao, X. Synthesis, cytotoxicity and DNA-binding levels of ammine/propylamine platinum(II) complexes with carboxylates. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 42, 286–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Gou, S.; Yin, R.; Jiang, P. Synthesis, antiproliferative activity and DNA binding study of mixed ammine/cyclohexylamine platinum(II) complexes with 1-(substituted benzyl)azetidine-3,3-dicarboxylates. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 46, 5146–5153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





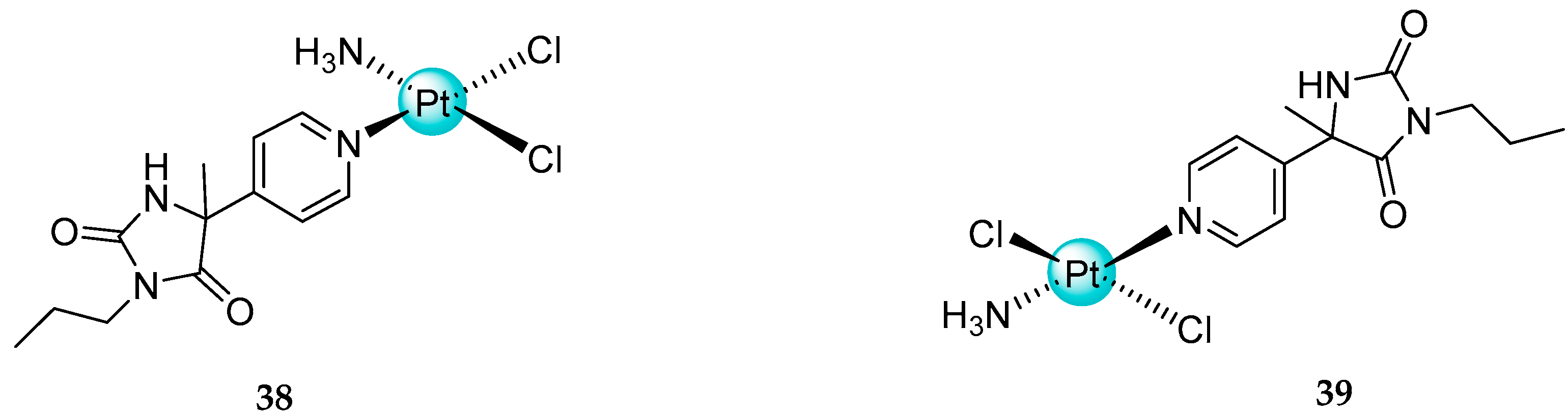



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bakalova, A.; Ruseva, N.; Cherneva, E. “Non-Classical” Platinum Complexes: A Concise Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6270. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136270
Bakalova A, Ruseva N, Cherneva E. “Non-Classical” Platinum Complexes: A Concise Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(13):6270. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136270
Chicago/Turabian StyleBakalova, Adriana, Nina Ruseva, and Emiliya Cherneva. 2025. "“Non-Classical” Platinum Complexes: A Concise Review" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 13: 6270. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136270
APA StyleBakalova, A., Ruseva, N., & Cherneva, E. (2025). “Non-Classical” Platinum Complexes: A Concise Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(13), 6270. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136270






