Identification of Monogenic Causes of Arterial Ischemic Stroke in Children with Arteriopathies by Next-Generation Sequencing
Abstract
1. Introduction
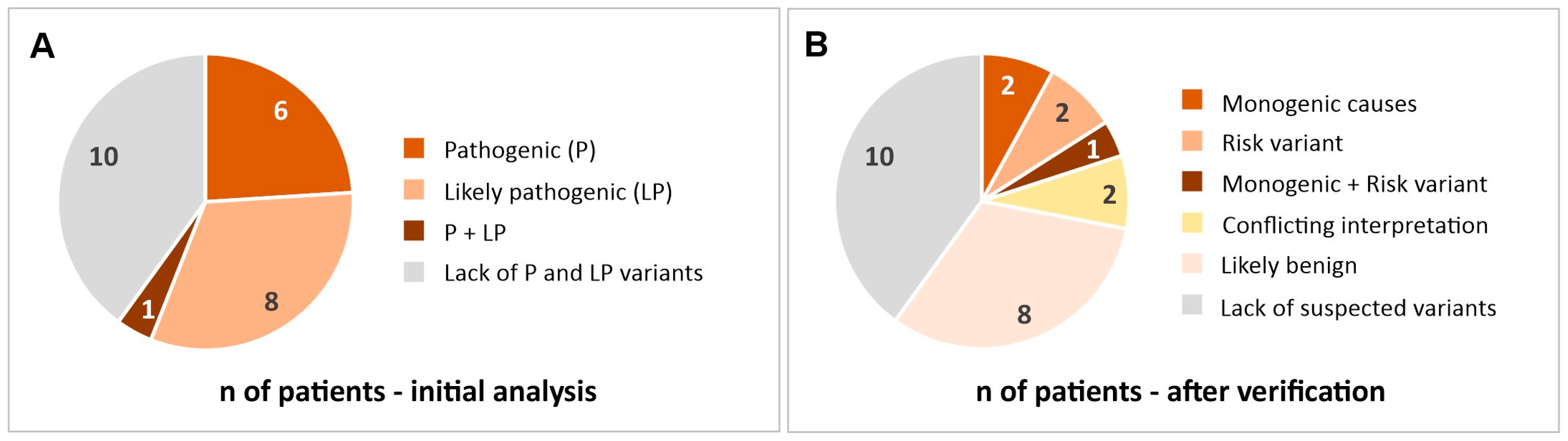
2. Results
2.1. Most Likely Monogenic Causes of Stroke
2.1.1. ELN (Elastin)
2.1.2. SCN5A (Sodium Voltage-Gated Channel, Alpha Subunit 5)
2.1.3. VHL (Von Hippel–Lindau Tumor Suppressor)
2.2. Mutations That Can Be a Risk Factor for Stroke
2.2.1. FV (Coagulation Factor V)
2.2.2. ADAMTS13 (A Disintegrin-like and Metalloprotease with Thrombospondin Type 1 Motif, 13)
2.3. Variants with Conflicting Interpretations
2.3.1. ACAD9 (Acyl-CoA Dehydrogenase Family, Member 9)
2.3.2. ENG (Endoglin)
2.4. Other Variants Found in a Study Group
2.4.1. CBS (Cystathionine Beta-Synthase)
2.4.2. PMM2 (Phosphomannomutase-2)
2.4.3. PKD1 (Polycystin 1)
3. Discussion
Limitations
4. Materials and Methods
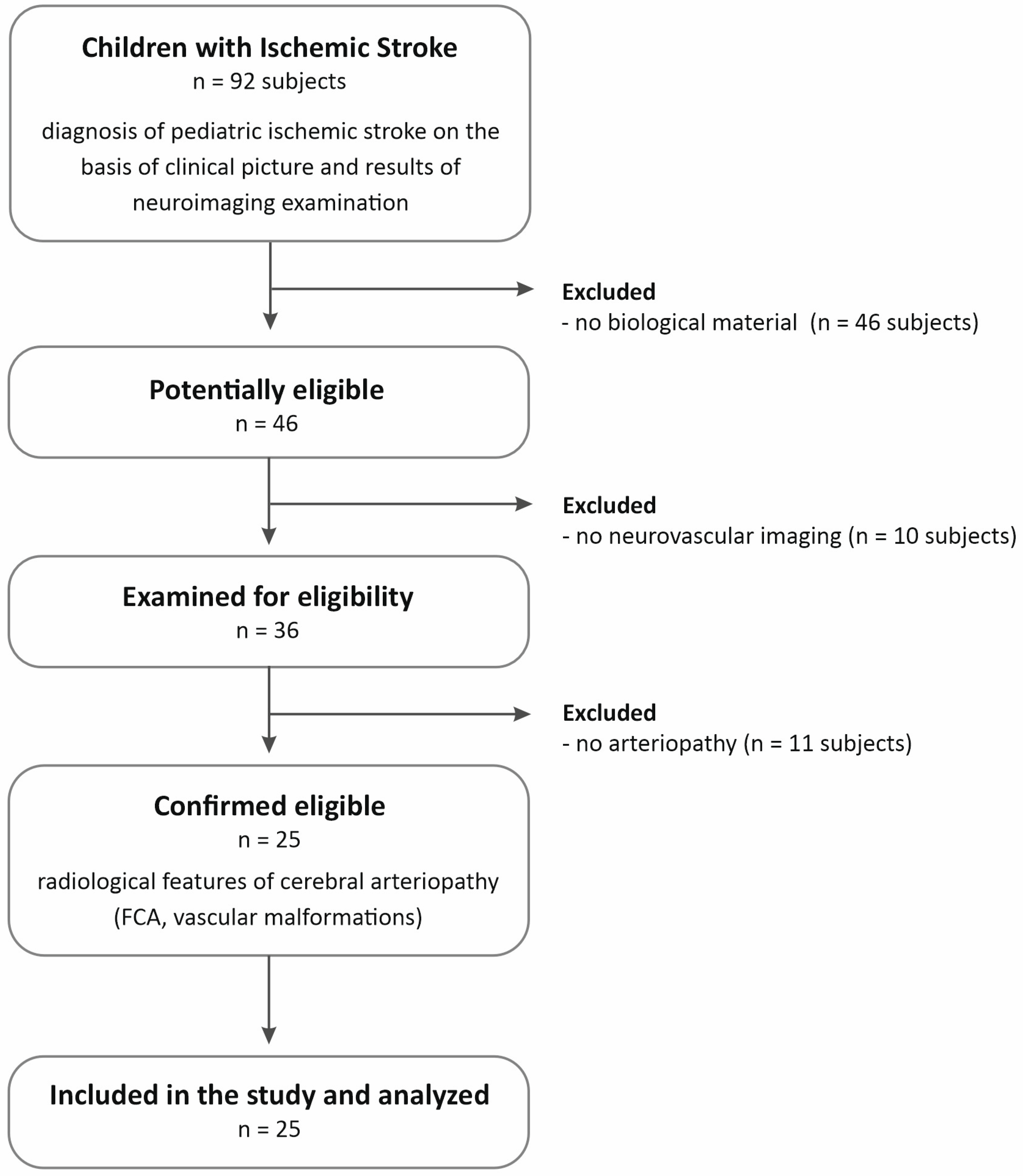
4.1. Patient Cohort
- Age from 29 days of age to the completion of 18 years of age
- Diagnosis of pediatric arterial ischemic stroke (PAIS) based on the clinical picture and results of neuroimaging examination. PAIS was defined as an acute neurological deficit with sudden onset occurring in a child between the 29th day of life and 18 years of age, and the vascular cause of the symptoms observed in the patient is confirmed by neuroimaging studies, and the location of the changes in the neuroimaging studies corresponds to the clinical symptoms.
- Radiological features of cerebral arteriopathy (focal cerebral arteriopathy of childhood (FCA) or other vascular malformations)
- Caucasian origin
- 5.
- Age below 29 days or above 18 years
- 6.
- Lack of neuroimaging studies
- 7.
- No confirmed diagnosis of ischemic stroke
- 8.
- Diagnosis of a CNS pathology other than ischemic stroke (stroke mimics)
- 9.
- Lack of biological material
4.2. Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS)
4.3. Definition of Gene Panel and Genetic Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AAC | amino acid change |
| ACAD9 | Acyl-CoA dehydrogenase family, member 9 |
| AD | autosomal dominant |
| ADAMTS13 | A disintegrin-like and metalloprotease with thrombospondin type 1 motif, 13 |
| ADPKD | autosomal dominant Polycystic kidney disease type 1 |
| AR | autosomal recessive |
| CBS | cystathionine beta-synthase |
| CDG-1a | congenital disorders of glycosylation |
| CNS | central nervous system |
| ELN | Elastin |
| ENG | Endoglin |
| FCA | focal cerebral arteriopathy of childhood |
| FV | coagulation factor V |
| HHT | Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia |
| hTTP | Familial thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura |
| LP | likely pathogenic |
| MAF | minor allele frequency |
| MC1DN20 | Mitochondrial complex I deficiency nuclear type 20 |
| MRA | magnetic resonance angiography |
| MRI | magnetic resonance imaging |
| NGS | next-generation sequencing |
| P | pathogenic |
| PKD1 | Polycystin 1 |
| PMM2 | Phosphomannomutase-2 |
| PPH1 | Primary pulmonary hypertension 1 |
| SCN5A | sodium voltage-gated channel, alpha subunit 5 |
| TCD | Transcranial Doppler |
| TIA | transient ischemic attack |
| VHL | Von Hippel–Lindau tumor suppressor |
| VHLS | Von Hippel–Lindau syndrome |
References
- Gao, L.; Lim, M.; Nguyen, D.; Bowe, S.; MacKay, M.T.; Stojanovski, B.; Moodie, M. The incidence of pediatric ischemic stroke: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Stroke 2023, 18, 765–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, S.; Levy, S.M.; Moreno, A.; Zhu, G.; Savitz, S.; Zha, A.; Wu, H. Risk factors for pediatric ischemic stroke and intracranial hemorrhage: A national electronic health record based study. Heliyon 2024, 10, e31124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopyta, I.A.; Emich-Widera, E.; Balcerzyk, A.; Niemiec, P.; Zak, I.; Pilarska, E.; Kaciński, M.; Wendorff, J.; Nowak, T.; Iwanicki, T.; et al. Polymorphisms of genes encoding coagulation factors II, V, VII, and XIII in relation to pediatric ischemic stroke: Family-based and Case-control study. Neurologist 2012, 18, 282–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balcerzyk, A.; Niemiec, P.; Kopyta, I.; Emich-Widera, E.; Pilarska, E.; Pienczk-Ręcławowicz, K.; Kaciński, M.; Wendorff, J.; Żak, I. Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase gene A1298C polymorphism in pediatric stroke--case-control and family-based study. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2014, 24, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balcerzyk, A.; Zak, I.; Niemiec, P.; Kopyta, I.; Emich-Widera, E.; Iwanicki, T.; Pilarska, E.; Pienczk-Recławowicz, K.; Kacinski, M.; Wendorff, J.; et al. APOE gene epsilon polymorphism does not determine predisposition to ischemic stroke in children. Pediatr. Neurol. 2010, 43, 25–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terni, E.; Gianini, N.; Brondi, M.; Montano, V.; Bonuccelli, U.; Mancuso, M. Genetics in ischaemic stroke in young adults. BBA Clin. 2015, 3, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munot, P.; Crow, Y.J.; Ganesan, V. Pediatric stroke: Genetic insight into disease and treatment targets. Lancet Neurol. 2011, 10, 264–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markus, H.S. Stroke genetics. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2011, 20, R124–R131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.C.; Cole, J.W.; Kittner, S.J.; Mitchell, B.D. Genetics of ischemic stroke in young adults. Circ. Cardiovasc. Genet. 2014, 7, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amlie- Lefond, C.; Bernard, T.J.; Sebire, G.; Friedman, N.R.; Heyer, G.; Lerner, N.; deVeber, G.; Fullerton, H. Predictors of cerebral arteriopathy in children with arterial ischemic stroke: Results of the International Pediatric Stroke Study. Circulation 2009, 119, 1417–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafay, M.F.; Shapiro, K.A.; Surmava, A.M.; deVeber, G.A.; Kirton, A.; Fullerton, H.J.; Amlie-Lefond, C.; Weschke, B.; Dlamini, N.; Carpenter, J.L.; et al. Spectrum of cerebral arteriopathies in children with arterial ischemic stroke. Neurology 2020, 94, e2479–e2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beslow, L.A.; Jordan, L.C. Pediatric stroke: The importance of cerebral arteriopathy and vascular malformations. Childs Nerv. Syst. 2010, 26, 1263–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franklin by Genoox. Available online: https://franklin.genoox.com (accessed on 1 May 2024).
- Griffioen, P.; de Jonge, R.; van Zelst, B.D.; Montserrate Brouns, R.; Lindemans, J. Detection and allele-frequencies of the 833T>C, 844ins68 and a novel mutation in the cystathionine beta-synthase gene. Clin. Chim. Acta 2005, 354, 191–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remme, C.A. Cardiac sodium channelopathy associated with SCN5A mutations: Electrophysiological, molecular and genetic aspects. J. Physiol. 2013, 591, 4099–4116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nordstrom-O’Brien, M.; van der Luijt, R.B.; van Rooijen, E.; van den Ouweland, A.M.; Majoor-Krakauer, D.F.; Lolkema, M.P.; van Brussel, A.; Voest, E.E.; Giles, R.H. Genetic analysis of von Hippel-Lindau disease. Hum. Mutat. 2010, 31, 521–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Leeuwaarde, R.; Ahmad, S.; van Nesselrooij, B.; Zandee, W.; Giles, H. Von Hippel-Lindau Syndrome. In Gene Reviews®; Adam, M., Feldman, J., Mirzaa, G.M., Pagon, R.A., Wallace, S.E., Amemiya, A., Eds.; University of Washington: Seattle, WA, USA; pp. 1993–2024.
- Ben-Skowronek, I.; Kozaczuk, S. Von Hippel-Lindau Syndrome. Horm. Res. Paediatr. 2015, 84, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Cott, E.M.; Soderberg, B.L.; Laposata, M. Hypercoagulability test strategies in the protein C and protein S pathway. Clin. Lab. Med. 2002, 22, 391–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Taylor, A.K.; Huang, X.; Luo, B.; Spector, E.B.; Fang, P.; Richards, C.S.; ACMG Laboratory Quality Assurance Committee. Venous thromboembolism laboratory testing (factor V Leiden and factor II c.*97G>A), 2018 update: A technical standard of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics (ACMG). Genet. Med. 2018, 20, 1489–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kujovich, J.L. Factor V Leiden thrombophilia. Genet. Med. 2011, 13, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katneni, U.K.; Holcomb, D.D.; Hernandez, N.E.; Hamasaki-Katagiri, N.; Hunt, R.C.; Bar, H.; Ibla, J.C.; Kimchi-Sarfaty, C. In silico features of ADAMTS13 contributing to plasmatic ADAMTS13 levels in neonates with congenital heart disease. Thromb. Res. 2020, 193, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borogovac, A.; George, J.N. Stroke and myocardial infarction in hereditary thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura: Similarities to sickle cell anemia. Blood Adv. 2019, 3, 3973–3976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fidalgo, T.; Martinho, P.; Pinto, C.S.; Oliveira, A.C.; Salvado, R.; Borràs, N.; Coucelo, M.; Manco, L.; Maia, T.; Mendes, M.J.; et al. Combined study of ADAMTS13 and complement genes in the diagnosis of thrombotic microangiopathies using next-generation sequencing. Res. Pract. Thromb. Haemost. 2017, 1, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leinøe, E.; Zetterberg, E.; Kinalis, S.; Østrup, O.; Kampmann, P.; Norström, E.; Andersson, N.; Klintman, J.; Qvortrup, K.; Nielsen, F.C.; et al. Application of whole-exome sequencing to direct the specific functional testing and diagnosis of rare inherited bleeding disorders in patients from the Öresund Region, Scandinavia. Br. J. Haematol. 2017, 179, 308–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilinca, A.; Martinez-Majander, N.; Samuelsson, S.; Piccinelli, P.; Truvé, K.; Cole, J.; Kittner, S.; Soller, M.; Kristoffersson, U.; Tatlisumak, T.; et al. Whole-Exome Sequencing in 22 Young Ischemic Stroke Patients with Familial Clustering of Stroke. Stroke 2020, 51, 1056–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pousada, G.; Baloira, A.; Fontán, D.; Núñez, M.; Valverde, D. Mutational and clinical analysis of the ENG gene in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension. BMC Genet. 2016, 17, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfarr, N.; Fischer, C.; Ehlken, N.; Becker-Grünig, T.; López-González, V.; Gorenflo, M.; Hager, A.; Hinderhofer, K.; Miera, O.; Nagel, C.; et al. Hemodynamic and genetic analysis in children with idiopathic, heritable, and congenital heart disease associated pulmonary arterial hypertension. Respir. Res. 2013, 14, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.J.; Lee, D.H.; Yoo, H.W.; Koo, S.K.; Park, E.S.; Park, J.W.; Lim, H.G.; Jung, S.C. Identification and functional analysis of cystathionine beta-synthase gene mutations in patients with homocystinuria. J. Hum. Genet. 2005, 50, 648–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruger, W.D.; Cox, D.R. A yeast assay for functional detection of mutations in the human cystathionine β-synthase gene. Hum. Mol. Genet. 1995, 4, 1155–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, P.J.; Furie, K.L.; Kistler, J.P.; Barron, M.; Picard, E.H.; Mandell, R.; Shih, V.E. Stroke in young patients with hyperhomocysteinemia due to cystathionine beta-synthase deficiency. Neurology 2003, 60, 275–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, M.Y.; Bignell, M.; Schwichtenberg, K.; Hanson, N.Q. High prevalence of a mutation in the cystathionine beta-synthase gene. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1996, 59, 1262–1267. [Google Scholar]
- Piedade, A.; Francisco, R.; Jaeken, J.; Sarkhail, P.; Brasil, S.; Ferreira, C.; Rijoff, T.; Pascoal, C.; Gil, A.; Lourenço, A.; et al. Epidemiology of congenital disorders of glycosylation (CDG)—Overview and perspectives. J. Rare Dis. 2022, 1, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, T.; Kawano, H.; Muto, S.; Muramoto, N.; Takano, T.; Lu, Y.; Eguchi, H.; Wada, H.; Okazaki, Y.; Ide, H.; et al. PKD1 mutation is a biomarker for autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, R.; McConnell, R.; Whittacker, J.; Kirkpatrick, P.; Bradley, J.; Sandford, R. Identification of mutations in the repeated part of the autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease type 1 gene, PKD1, by long-range PCR. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1999, 65, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jelsig, A.M.; Urban, Z.; Hucthagowder, V.; Nissen, H.; Ousager, L.B. Novel ELN mutation in a family with supravalvular aortic stenosis and intracranial aneurysm. Eur. J. Med. Genet. 2017, 60, 110–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreau, A.; Janin, A.; Millat, G.; Chevalier, P. Cardiac voltage-gated sodium channel mutations associated with left atrial dysfunction and stroke in children. EP Eur. 2018, 20, 1692–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baruteau, A.; Kyndt, F.; Behr, E.; Vink, A.S.; Lachaud, M.; Joong, A.; Schott, J.J.; Horie, M.; Denjoy, I.; Crotti, L.; et al. SCN5A mutations in 442 neonates and children: Genotype–phenotype correlation and identification of higher-risk subgroups. Eur. Heart J. 2018, 39, 2879–2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butman, J.A.; Linehan, W.M.; Lonser, R.R. Neurologic manifestations of von Hippel-Lindau disease. JAMA 2008, 300, 1334–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankovic, M.; Petrovic, B.; Novakovic, I.; Brankovic, S.; Radosavljevic, N.; Nikolic, D. The Genetic Basis of Strokes in Pediatric Populations and Insight into New Therapeutic Options. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Toland, A.; Boak, B.; Atkinson, D.; Ensing, G.; Morris, C.; Keating, M. Elastin point mutations cause an obstructive vascular disease, supravalvular aortic stenosis. Hum. Mol. Genet. 1997, 6, 1021–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.D.; Meng, L.; Liu, P.; Miyake, C.Y.; Worley, K.C.; Bi, W.; Lalani, S.R. Clinical exome sequencing uncovers a high frequency of Mendelian disorders in infants with stroke: A retrospective analysis. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part A 2022, 188, 3184–3190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilinca, A.; Puschmann, A.; Putaala, J.; de Leeuw, F.E.; Cole, J.; Kittner, S.; Kristoffersson, U.; Lindgren, A.G. Updated Stroke Gene Panels: Rapid evolution of knowledge on monogenic causes of stroke. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2023, 31, 239–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilarska, E.; Kopyta, I.; Szurowska, E.; Radoń-Proskura, J.; Irga-Jaworska, N.; Kozera, G.; Sabiniewicz, R.; Emich-Widera, E.; Wojczal, J. Polish recommendations for diagnosis and therapy of paediatric stroke. Neurol. Neurochir. Pol. 2023, 57, 243–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medley, T.L.; Miteff, C.; Andrews, I.; Ware, T.; Cheung, M.; Monagle, P.; Mandelstam, S.; Wray, A.; Pridmore, C.; Troedson, C.; et al. Australian Clinical Consensus Guideline: The diagnosis and acute management of childhood stroke. Int. J. Stroke 2019, 14, 94–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferriero, D.M.; Fullerton, H.J.; Bernard, T.J.; Billinghurst, L.; Daniels, S.R.; DeBaun, M.R.; deVeber, G.; Ichord, R.N.; Jordan, L.C.; Massicotte, P.; et al. Management of Stroke in Neonates and Children: A Scientific Statement from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 2019, 50, e51–e96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chojdak-Łukasiewicz, J.; Dziadkowiak, E.; Budrewicz, S. Monogenic Causes of Strokes. Genes 2021, 12, 1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCrea, N.; Fullerton, H.J.; Ganesan, V. Genetic and Environmental Associations with Pediatric Cerebral Arteriopathy. Stroke 2019, 50, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hausman-Kedem, M.; Herring, R.; Torres, M.D.; Santoro, J.D.; Kaseka, M.L.; Vargas, C.; Amico, G.; Bertamino, M.; Nagesh, D.; Tilley, J.; et al. The Genetic Landscape of Ischemic Stroke in Children—Current Knowledge and Future Perspectives. Semin. Pediatr. Neurol. 2022, 44, 100999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doig, D.; Davagnanam, I.; Taranath, A.; Zlatareva, D.; Alwis, A.; Siddiqui, A.; Mankad, K. Monogenetic Stroke Syndromes in Children and Young Adults. AJR. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2020, 215, 695–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, S.; Freeman, R.; Noronha, A.; Jamil, H.; Chavez, E.; Carmichael, J.; Ruiz, K.M.; Miller, C.; Benke, S.; Perrot, R.; et al. Applying data science methodologies with artificial intelligence variant reinterpretation to map and estimate genetic disorder prevalence utilizing clinical data. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2024, 194, e63505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, S.; Aziz, N.; Bale, S.; Bick, D.; Das, S.; Gastier-Foster, J.; Grody, W.; Hegde, M.; Lyon, E.; Spector, E.; et al. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: A joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet. Med. 2015, 17, 405–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landrum, M.J.; Lee, J.M.; Benson, M.; Brown, G.R.; Chao, C.; Chitipiralla, S.; Gu, B.; Hart, J.; Hoffman, D.; Jang, W.; et al. ClinVar: Improving access to variant interpretations and supporting evidence. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D1062–D1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karczewski, K.J.; Francioli, L.C.; Tiao, G.; Cummings, B.B.; Alföldi, J.; Wang, Q.; Collins, R.L.; Laricchia, K.M.; Ganna, A.; Birnbaum, D.P.; et al. The mutational constraint spectrum quantified from variation in 141,456 humans. Nature 2020, 581, 434–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Mean (Min.–Max.) | |
|---|---|
| Age at stroke onset (in months) | 83.9 (1–214) |
| n (%) | |
| Sex | male 13 (52) female 12 (48) |
| Imaging methods used in the acute phase of stroke: | |
| only MRI, MRA | 15 (60) |
| angiography + MRI, MRA | 3 (12) |
| only TCD | 3 (12) |
| TCD + MRI | 4 (16) |
| Other vascular diseases | 1 (4)—TIA 2 weeks before stroke |
| Diseases located in a vasculature beyond the CNS | 1 (4)—congenital heart defect (common atrioventricular canal) |
| Neurodevelopmental disorders before stroke | 4 (16) |
| Recurrence of stroke | 1 (4) |
| Cardiovascular diseases in the child’s family | 2 (8) |
| The Number of Each Variant Type | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pathogenic | Likely pathogenic | Uncertain | Likely benign | Benign |
| 7 * | 9 * | 175 | 145 | 7450 |
| No. | Gene | Genotype | Mutation | MAF (gnomAD) | Phenotype Generally Associated (Inheritance) | Phenotypic Features | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| c.DNA | AAC | ||||||
| 1 | ELN (LP) | Het | c.1577-2A>T | - | 0.000 | Supravalvular Aortic Stenosis (AD) Autosomal Dominant Cutis Laxa (AD) | - arteriopathy, with multiple pulmonary and systemic arterial stenoses - loose and/or wrinkled skin, in some cases multiple vascular anomalies including coarctation of the aorta, multiple peripheral pulmonary stenoses, including stenoses in very small vessels |
| 2 | SCN5A (P) | Het | c.655C>T | p.R219* | 0.000 | Brugada syndrome (AD) Sick Sinus Syndrome 1 (AR) | - ventricular arrhythmias and sudden cardiac death - sinus node dysfunction, syncope, presyncope, dizziness, and fatigue |
| 3 | VHL (LP) FV (P) | Het Het | c.439A>G c.1601G>A | p.I147V p.R534Q | 0.000 0.025 | Von Hippel–Lindau syndrome (VHLS) (AD) Factor V deficiency (AR) Thrombophilia due to activated protein C resistance (AD) | - familial cancer syndrome predisposing to a variety of malignant and benign neoplasms, e.g., pheochromocytoma developing in the adrenal gland or paraganglia and causing chronic hypertension, which can result in cardiomyopathy, myocardial infarction and heart failure, arrhythmia, stroke, and sudden cardiac death - prolonged bleeding, hemorrhagic diathesis tendency to thrombosis |
| 4 | FV (P) | Het | c.1601G>A | p.R534Q | 0.025 | Factor V deficiency (AR) Thrombophilia due to activated protein C resistance (AD) | - prolonged bleeding, hemorrhagic diathesis tendency to thrombosis |
| 5 | ADAMTS13 (P) ACAD9 (P) | Het Het | c.1370C>T c.976G>A | p.P457L p.A326T | 0.002 0.02 | Familial thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (AR) Mitochondrial complex I deficiency, nuclear type 20 (AR) | - microangiopathic mechanical hemolytic anemia, severe thrombocytopenia, visceral ischemia - cardiorespiratory depression, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, encephalopathy, severe lactic acidosis |
| No. | Gene | Genotype | Mutation | MAF (gnomAD) | Phenotype Generally Associated (Inheritance) | Phenotypic Features | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| c.DNA | AAC | ||||||
| 1 | ENG (P) | Het | c.1633G>A | p.G545S | 0.000 | Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (AD) Primary Pulmonary Hypertension in association with HHT | - telangiectases and arteriovenous malformations of skin, mucosa, and viscera (lung, liver, brain) - increased pulmonary vascular resistance and sustained elevation of mean pulmonary arterial pressure, right ventricular hypertrophy and right heart failure |
| 2 | PMM2 (P) | Het | c.422G>A | p.R141H | 0.006 | Congenital disorders of glycosylation (AR) | - severe encephalopathy with axial hypotonia, abnormal eye movement, pronounced psychomotor retardation, peripheral neuropathy, cerebellar hypoplasia, retinitis pigmentosa, peculiar distribution of subcutaneous fat, nipple retraction, hypogonadism, cardiomyopathy |
| 3 | PKD1 (LP) | Het | c.971G>T | p.R324L | 0.004 | Polycystic Kidney Disease type 1 (AD) | - renal cysts, liver cysts, intracranial aneurysm, and hypertension |
| 4 | CBS (LP) | Het | c.832_833ins68 | p.I278Tfs*16 | 0.1 a | Classic homocystinuria (AR) | - myopia, ectopia lentis, intellectual disability, skeletal anomalies, and thromboembolic events |
| 5 | ACAD9 (P) | Het | c.976G>A | p.A326T | 0.02 | Mitochondrial complex I deficiency, nuclear type 20 (AR) | - cardiorespiratory depression, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, encephalopathy, and severe lactic acidosis |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Balcerzyk-Matić, A.; Kopyta, I.; Kruszniewska-Rajs, C.; Niemiec, P.; Gola, J. Identification of Monogenic Causes of Arterial Ischemic Stroke in Children with Arteriopathies by Next-Generation Sequencing. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6228. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136228
Balcerzyk-Matić A, Kopyta I, Kruszniewska-Rajs C, Niemiec P, Gola J. Identification of Monogenic Causes of Arterial Ischemic Stroke in Children with Arteriopathies by Next-Generation Sequencing. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(13):6228. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136228
Chicago/Turabian StyleBalcerzyk-Matić, Anna, Ilona Kopyta, Celina Kruszniewska-Rajs, Paweł Niemiec, and Joanna Gola. 2025. "Identification of Monogenic Causes of Arterial Ischemic Stroke in Children with Arteriopathies by Next-Generation Sequencing" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 13: 6228. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136228
APA StyleBalcerzyk-Matić, A., Kopyta, I., Kruszniewska-Rajs, C., Niemiec, P., & Gola, J. (2025). Identification of Monogenic Causes of Arterial Ischemic Stroke in Children with Arteriopathies by Next-Generation Sequencing. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(13), 6228. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136228









