Immunomodulatory Mechanisms Underlying Neurological Manifestations in Long COVID: Implications for Immune-Mediated Neurodegeneration
Abstract
1. Introduction
Literature Search Strategies
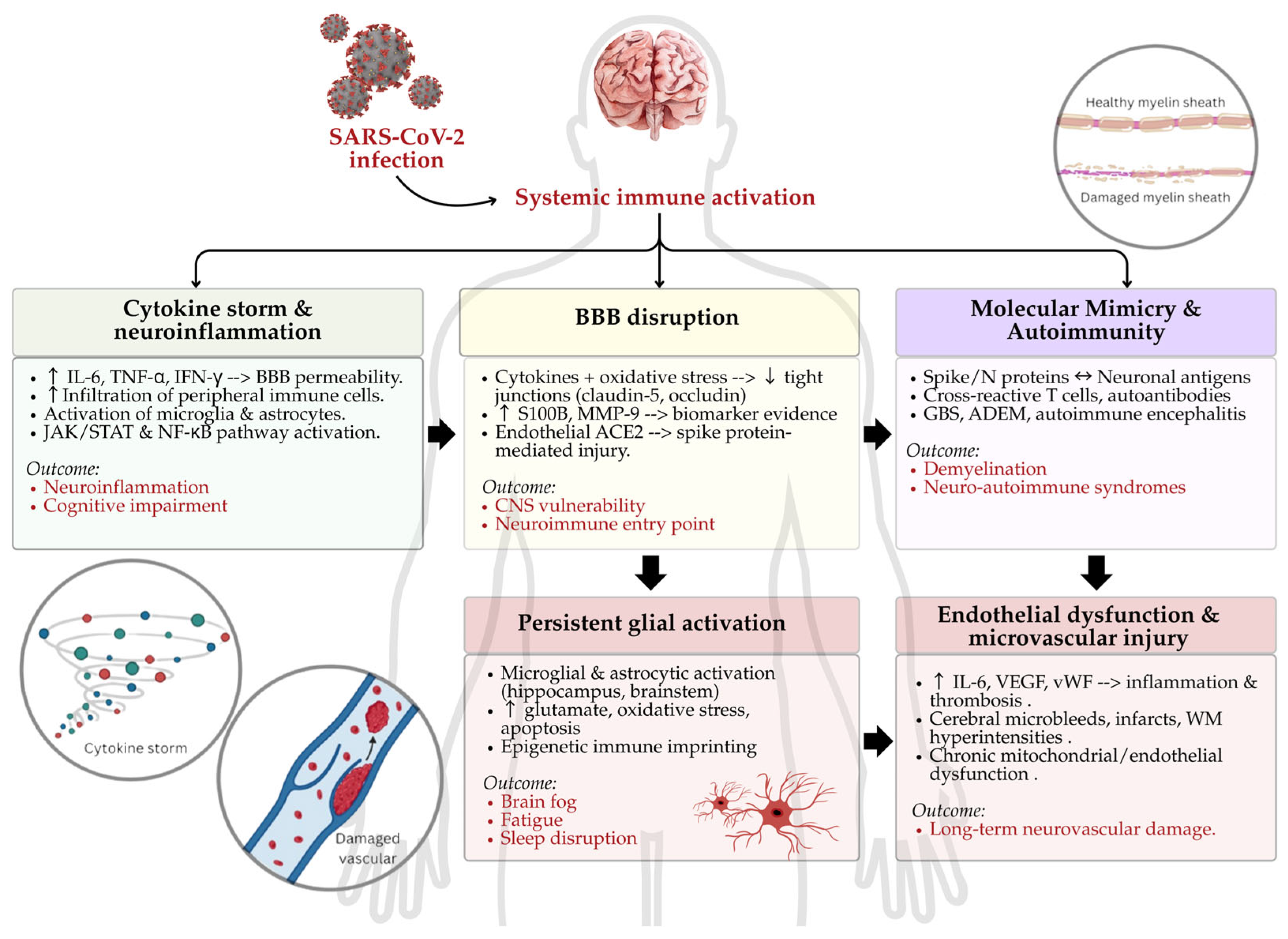
2. Immunopathogenesis of Neuro-COVID: Molecular Mechanisms of Immune-Driven Neural Injury
2.1. Cytokine Storm and Neuroinflammation
2.2. BBB Disruption
2.3. Autoimmunity and Molecular Mimicry
2.4. Persistent Glial Activation and Neuroimmune Reprogramming
2.5. Endothelial Dysfunction and Microvascular Injury
3. Neurological Sequelae of Long COVID: Clinical Presentation and Immunological Correlates
3.1. Cognitive Impairment and Brain Fog
3.2. Neuropathy and Paresthesia
3.3. Mood Disorders and Neuropsychiatric Symptoms
3.4. Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome (POTS)
3.5. Neurodegenerative Syndromes: Parkinsonism and Dementia
3.6. Autoimmune Neurological Disorders
4. Variant-Specific Neuropathogenesis: Immune Signatures and Neurovirulence of SARS-CoV-2 Strains
4.1. D614G Mutation: Elevated Neurovirulence and Inflammatory Reactivity
4.2. Delta Variant: High CNS Entry with Moderate Immune Activation
4.3. Omicron Variant: Altered Neuroinflammatory Profile
4.4. Beta and Alpha Variants: Reduced CNS Penetrance and Lower Inflammatory Impact
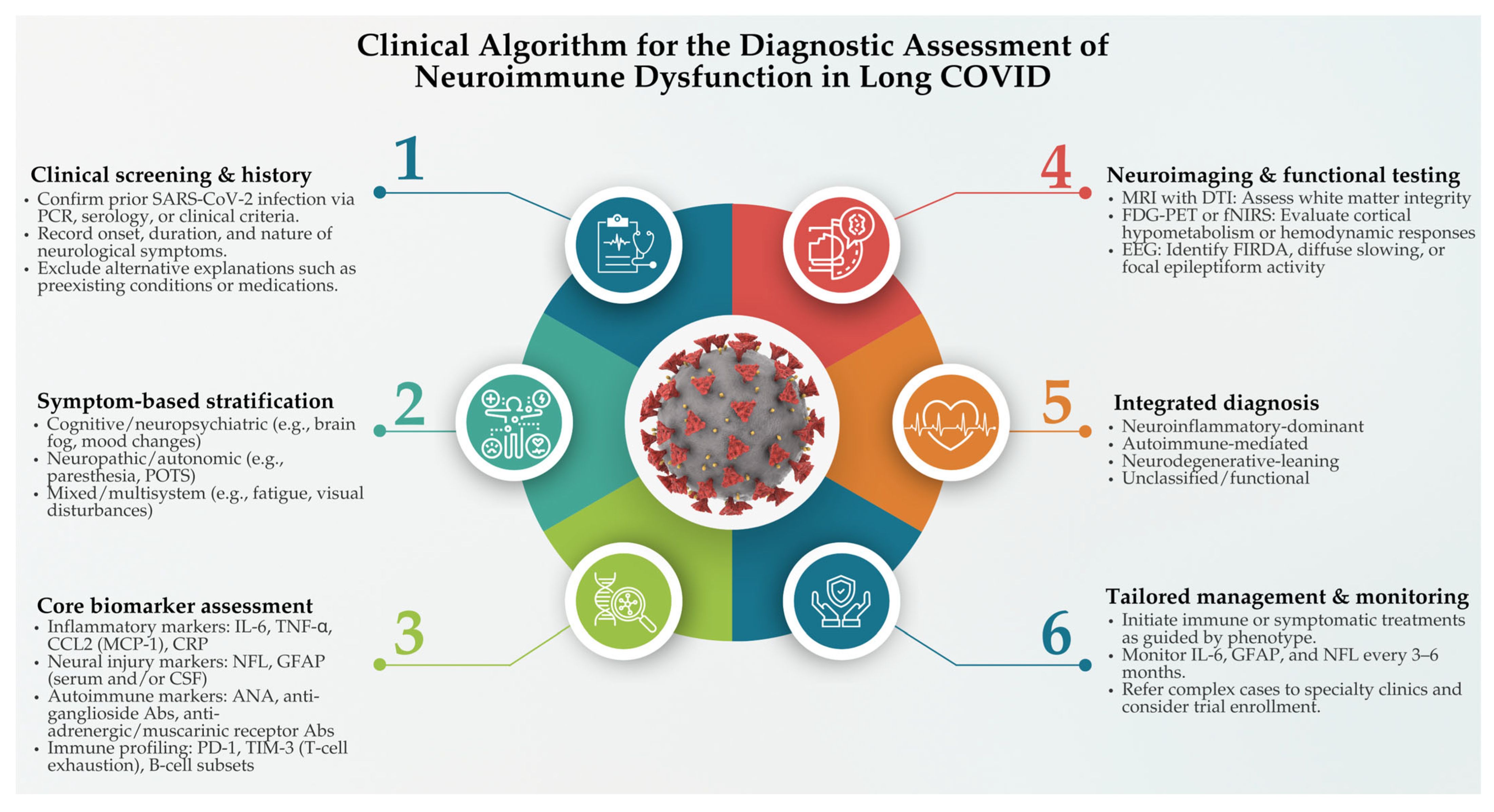
5. Diagnostic and Biomarker-Based Assessment of Neuroimmune Dysfunction in Long COVID
6. Risk Factors for Neuro-COVID: Immune Vulnerability and Susceptibility Determinants
7. Limitations and Future Directions
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACE2 | Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 |
| ADEM | Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis |
| BBB | Blood–brain barrier |
| CCL2 | C-C motif ligand 2 |
| CNS | Central nervous system |
| CRP | C-reactive protein |
| CSF | Cerebrospinal fluid |
| CSVD | Cerebral small vessel disease |
| DTI | Diffusion tensor imaging |
| EEG | Electroencephalography |
| FDG-PET | Fludeoxyglucose-positron emission tomography |
| FIRDA | Frontal intermittent rhythmic delta activity |
| fNIRS | Functional near-infrared spectroscopy |
| GBS | Guillain–Barré syndrome |
| GFAP | Glial fibrillary acidic protein |
| HPA | Hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal |
| HSP70 | Heat shock protein 70 |
| IFN-γ | Interferon-γ |
| IL | Interleukin |
| JAK/STAT | Janus kinase/signal transducer and activator of transcription |
| MCP-1 | Monocytic chemotactic protein 1 |
| MMP | Matrix metalloproteinases |
| MOG | Myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein |
| NFL | Neurofilament light chain |
| NF-κB | Nuclear factor kappa beta |
| NLRP3 | NLR family pyrin domain containing 3 |
| NMDA | N-methyl-D-aspartate |
| PASC | Post-acute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 |
| PET | Positron emission tomography |
| POTS | Postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome |
| PTSD | Post-traumatic stress disorder |
| SARS-CoV-2 | Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 |
| SCFA | Short-chain fatty acids |
| SFN | Small fiber neuropathy |
| TLR7 | Toll-like receptor 7 |
| TMPRSS2 | transmembrane protease, serine 2 |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor-alpha |
| VEGF | Vascular endothelial growth factor |
| vWF | Von Willebrand factor |
References
- Tsilingiris, D.; Vallianou, N.G.; Karampela, I.; Christodoulatos, G.S.; Papavasileiou, G.; Petropoulou, D.; Magkos, F.; Dalamaga, M. Laboratory Findings and Biomarkers in Long COVID: What Do We Know So Far? Insights into Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, Therapeutic Perspectives and Challenges. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choutka, J.; Jansari, V.; Hornig, M.; Iwasaki, A. Unexplained Post-Acute Infection Syndromes. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 911–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization (WHO). A Clinical Case Definition of Post COVID-19 Condition by a Delphi Consensus, 6 October 2021. 2021. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/WHO-2019-nCoV-Post_COVID-19_condition-Clinical_case_definition-2021.1 (accessed on 1 April 2024).
- Mudgal, S.K.; Gaur, R.; Rulaniya, S.; T, L.; Agarwal, R.; Kumar, S.; Varshney, S.; Sharma, S.; Bhattacharya, S.; Kalyani, V. Pooled Prevalence of Long COVID-19 Symptoms at 12 Months and Above Follow-Up Period: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cureus 2023, 15, e36325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boechat, J.L.; Chora, I.; Morais, A.; Delgado, L. The Immune Response to SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19 Immunopathology—Current Perspectives. Pulmonology 2021, 27, 423–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanderkamp, S.G.; Niazy, M.; Stegelmeier, A.A.; Stinson, K.J.; Ricker, N.; Bridle, B.W. Cytokine, Chemokine, and Acute-Phase Protein Profiles in Plasma as Correlative Biomarkers of Clinical Outcomes for Patients with COVID-19. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 15397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- VanElzakker, M.B.; Bues, H.F.; Brusaferri, L.; Kim, M.; Saadi, D.; Ratai, E.M.; Dougherty, D.D.; Loggia, M.L. Neuroinflammation in Post-Acute Sequelae of COVID-19 (PASC) as Assessed by [11C]PBR28 PET Correlates with Vascular Disease Measures. bioRxiv 2023, 119, 713–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, F.; Rovito, R.; Marchetti, G.; Monforte, A.D. SARS-CoV-2 and the Nervous System: Review on Pathogenesis of Nervous System SARS-CoV-2 Damage. In Neurology of COVID-19 [Internet]; Priori, A., Ed.; Milano University Press: Milano, Italy, 2021; Chapter 1. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK579780/ (accessed on 1 April 2024).
- Guerrero, J.I.; Barragán, L.A.; Martínez, J.D.; Montoya, J.P.; Peña, A.; Sobrino, F.E.; Tovar-Spinoza, Z.; Ghotme, K.A. Central and Peripheral Nervous System Involvement by COVID-19: A Systematic Review of the Pathophysiology, Clinical Manifestations, Neuropathology, Neuroimaging, Electrophysiology, and Cerebrospinal Fluid Findings. BMC Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunai, C.; Collie, C.; Michael, B.D. Immune-Mediated Mechanisms of COVID-19 Neuropathology. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 882905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che Mohd Nassir, C.M.N.; Hashim, S.; Wong, K.K.; Abdul Halim, S.; Idris, N.S.; Jayabalan, N.; Guo, D.; Mustapha, M. COVID-19 Infection and Circulating Microparticles—Reviewing Evidence as Microthrombogenic Risk Factor for Cerebral Small Vessel Disease. Mol. Neurobiol. 2021, 58, 4188–4215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.; Kc, N.; Paneque, A.; Cole, P.D. Tau, Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein, and Neurofilament Light Chain as Brain Protein Biomarkers in Cerebrospinal Fluid and Blood for Diagnosis of Neurobiological Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 6295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmakaty, I.; Ferih, K.; Karen, O.; Ouda, A.; Elsabagh, A.; Amarah, A.; Malki, M.I. Clinical Implications of COVID-19 Presence in CSF: Systematic Review of Case Reports. Cells 2022, 11, 3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paranga, T.G.; Mitu, I.; Pavel-Tanasa, M.; Rosu, M.F.; Miftode, I.L.; Constantinescu, D.; Obreja, M.; Plesca, C.E.; Miftode, E. Cytokine Storm in COVID-19: Exploring IL-6 Signaling and Cytokine-Microbiome Interactions as Emerging Therapeutic Approaches. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 11411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, M.J.A.; Ribeiro, L.R.; Gouveia, M.I.M.; Marcelino, B.D.R.; Santos, C.S.D.; Lima, K.V.B.; Lima, L.N.G.C. Hyperinflammatory Response in COVID-19: A Systematic Review. Viruses 2023, 15, 553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takata, F.; Nakagawa, S.; Matsumoto, J.; Dohgu, S. Blood-Brain Barrier Dysfunction Amplifies the Development of Neuroinflammation: Understanding of Cellular Events in Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cells for Prevention and Treatment of BBB Dysfunction. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 661838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini-Farsani, Z.; Yadollahi-Farsani, M.; Arab, S.; Forouzanfar, F.; Yadollahi, M.; Asgharzade, S. Prediction and Analysis of microRNAs Involved in COVID-19 Inflammatory Processes Associated with the NF-κB and JAK/STAT Signaling Pathways. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 100, 108071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anjum, A.; Hussain, A. Post-COVID Neurocognitive Disorder and Its Relation with Interleukin: A Hospital-Based Cross-Sectional Study. Indian J. Psychol. Med. 2024, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, H.E.; McCorkell, L.; Vogel, J.M.; Topol, E.J. Long COVID: Major Findings, Mechanisms and Recommendations. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2023, 21, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrucci, R.; Cuffaro, L.; Capozza, A.; Rosci, C.; Maiorana, N.; Groppo, E.; Reitano, M.R.; Poletti, B.; Ticozzi, N.; Tagliabue, L.; et al. Brain Positron Emission Tomography (PET) and Cognitive Abnormalities One Year after COVID-19. J. Neurol. 2023, 270, 1823–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Tan, R.; Mo, Y.; Zhang, J. The Blood-Brain Barrier in Health, Neurological Diseases, and COVID-19. Fundam. Res. 2022, 2, 817–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonetto, V.; Pasetto, L.; Lisi, I.; Carbonara, M.; Zangari, R.; Ferrari, E.; Punzi, V.; Luotti, S.; Bottino, N.; Biagianti, B.; et al. Markers of Blood-Brain Barrier Disruption Increase Early and Persistently in COVID-19 Patients with Neurological Manifestations. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1070379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zingaropoli, M.A.; Pasculli, P.; Barbato, C.; Petrella, C.; Fiore, M.; Dominelli, F.; Latronico, T.; Ciccone, F.; Antonacci, M.; Liuzzi, G.M.; et al. Biomarkers of Neurological Damage: From Acute Stage to Post-Acute Sequelae of COVID-19. Cells 2023, 12, 2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanzadehpanah, H.; Lotfian, E.; Avan, A.; Saki, S.; Nobari, S.; Mahmoodian, R.; Sheykhhasan, M.; Froutagh, M.H.S.; Ghotbani, F.; Jamshidi, R.; et al. Role of SARS-CoV-2 and ACE2 in the Pathophysiology of Peripheral Vascular Diseases. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 166, 115321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyerstedt, S.; Casaro, E.B.; Rangel, É.B. COVID-19: Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 (ACE2) Expression and Tissue Susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2021, 40, 905–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Zhang, J.; Schiavon, C.R.; He, M.; Chen, L.; Shen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, Q.; Cho, Y.; Andrade, L.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein Impairs Endothelial Function via Downregulation of ACE2. bioRxiv 2020, 128, 1323–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteil, V.; Kwon, H.; Prado, P.; Hagelkrüys, A.; Wimmer, R.A.; Stahl, M.; Leopoldi, A.; Garreta, E.; Hurtado Del Pozo, C.; Prosper, F.; et al. Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 Infections in Engineered Human Tissues Using Clinical-Grade Soluble Human ACE2. Cell 2020, 181, 905–913.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vahabi, M.; Ghazanfari, T.; Sepehrnia, S. Molecular Mimicry, Hyperactive Immune System, and SARS-CoV-2 Are Three Prerequisites of the Autoimmune Disease Triangle Following COVID-19 Infection. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2022, 112, 109183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arévalo-Cortés, A.; Rodriguez-Pinto, D.; Aguilar-Ayala, L. Evidence for Molecular Mimicry between SARS-CoV-2 and Human Antigens: Implications for Autoimmunity in COVID-19. Autoimmune Dis. 2024, 2024, 8359683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lake, C.M.; Breen, J.J. Sequence Similarity between SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid and Multiple Sclerosis-Associated Proteins Provides Insight into Viral Neuropathogenesis Following Infection. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutman, E.G.; Fernandes, R.A.; Raposo-Vedovi, J.V.; Salvio, A.L.; Duarte, L.A.; Tardim, C.F.; Costa, V.G.C.; Pereira, V.C.S.R.; Bahia, P.R.V.; da Silva, M.M.; et al. Molecular Mimicry between SARS-CoV-2 Proteins and Human Self-Antigens Related with Autoimmune Central Nervous System (CNS) Disorders. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucchese, G.; Flöel, A. SARS-CoV-2 and Guillain-Barré Syndrome: Molecular Mimicry with Human Heat Shock Proteins as Potential Pathogenic Mechanism. Cell Stress Chaperones 2020, 25, 731–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, H.J.; Clothier, H.J.; Sepulveda Kattan, G.; Boyd, J.H.; Buttery, J.P. Acute Disseminated Encephalomyelitis and Transverse Myelitis Following COVID-19 Vaccination—A Self-Controlled Case Series Analysis. Vaccine 2024, 42, 2212–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Z.; Cao, Y.; Liu, W.; Li, J. The SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Protein and Its Role in Viral Structure, Biological Functions, and a Potential Target for Drug or Vaccine Mitigation. Viruses 2021, 13, 1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabizadeh, F.; Noori, M.; Rahmani, S.; Hosseini, H. Acute Disseminated Encephalomyelitis (ADEM) Following COVID-19 Vaccination: A Systematic Review. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2023, 111, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoian, A.; Bajko, Z.; Stoian, M.; Cioflinc, R.A.; Niculescu, R.; Arbănași, E.M.; Russu, E.; Botoncea, M.; Bălașa, R. The Occurrence of Acute Disseminated Encephalomyelitis in SARS-CoV-2 Infection/Vaccination: Our Experience and a Systematic Review of the Literature. Vaccines 2023, 11, 1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Wei, X.; Pan, H.; Shi, H.; Shi, Y. Unveiling the Intricacies of COVID-19: Autoimmunity, Multi-Organ Manifestations and the Role of Autoantibodies. Scand. J. Immunol. 2024, 99, e13344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, E.L.; Koralnik, I.J.; Liotta, E.M. Therapeutic Approaches to the Neurologic Manifestations of COVID-19. Neurotherapeutics 2022, 19, 1435–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Censi, S.; Bisaccia, G.; Gallina, S.; Tomassini, V.; Uncini, A. Guillain-Barré Syndrome and SARS-CoV-2 Infection: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis on a Debated Issue and Evidence for the ‘Italian Factor’. Eur. J. Neurol. 2024, 31, e16094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palaiodimou, L.; Stefanou, M.I.; Katsanos, A.H.; Fragkou, P.C.; Papadopoulou, M.; Moschovos, C.; Michopoulos, I.; Kokotis, P.; Bakirtzis, C.; Naska, A.; et al. Prevalence, Clinical Characteristics and Outcomes of Guillain-Barré Syndrome Spectrum Associated with COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Eur. J. Neurol. 2021, 28, 3517–3529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pajo, A.T.; Espiritu, A.I.; Apor, A.D.A.O.; Jamora, R.D.G. Neuropathologic Findings of Patients with COVID-19: A Systematic Review. Neurol. Sci. 2021, 42, 1255–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishijima, T.; Nakajima, K. Inflammatory Cytokines TNFα, IL-1β, and IL-6 Are Induced in Endotoxin-Stimulated Microglia through Different Signaling Cascades. Sci. Prog. 2021, 104, 368504211054985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, D.; Biswas, K.; Nag, S.; Ramachandra, S.G.; Das Sarma, J. Microglia Play a Major Role in Direct Viral-Induced Demyelination. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2013, 2013, 510396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Blackall, M.; Sominsky, L.; Spencer, S.J.; Vlahos, R.; Churchill, M.; Bozinovski, S. Increased Hypothalamic Microglial Activation after Viral-Induced Pneumococcal Lung Infection Is Associated with Excess Serum Amyloid A Production. J. Neuroinflamm. 2018, 15, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.L.; Gong, X.X.; Qin, Z.H.; Wang, Y. Molecular Mechanisms of Excitotoxicity and Their Relevance to the Pathogenesis of Neurodegenerative Diseases—An Update. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2025, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.Y.; Whalley, J.P.; Knight, J.C.; Wicker, L.S.; Todd, J.A.; Ferreira, R.C. SARS-CoV-2 Infection Induces a Long-Lived Pro-Inflammatory Transcriptional Profile. Genome Med. 2023, 15, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, S.; Rishi, P.; Chadha, V.D. Understanding the Epigenetic Mechanisms in SARS CoV-2 Infection and Potential Therapeutic Approaches. Virus Res. 2022, 318, 198853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owens, C.D.; Pinto, C.B.; Detwiler, S.; Mukli, P.; Peterfi, A.; Szarvas, Z.; Hoffmeister, J.R.; Galindo, J.; Noori, J.; Kirkpatrick, A.C.; et al. Cerebral Small Vessel Disease Pathology in COVID-19 Patients: A Systematic Review. Ageing Res. Rev. 2023, 88, 101962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boparai, M.S.; Musheyev, B.; Hou, W.; Mehler, M.F.; Duong, T.Q. Brain MRI Findings in Severe COVID-19 Patients: A Meta-Analysis. Front. Neurol. 2023, 14, 1258352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, A.; Song, N.; Sivan, M.; Chowdhury, R.; Burke, M.R. Exploring the Experiences of Cognitive Symptoms in Long COVID: A Mixed-Methods Study in the UK. BMJ Open 2025, 15, e084999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameed, R.; Bahadur, A.R.; Singh, S.B.; Sher, J.; Todua, M.; Moradi, L.M.; Bastakoti, S.; Arslan, M.; Ajmal, H.; Lee, G.Y.; et al. Neurological and Psychiatric Manifestations of Long COVID-19 and Their [18F]FDG PET Findings: A Review. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cull, O.; Al Qadi, L.; Stadler, J.; Martin, M.; El Helou, A.; Wagner, J.; Maillet, D.; Chamard-Witkowski, L. Radiological Markers of Neurological Manifestations of Post-Acute Sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 Infection: A Mini-Review. Front. Neurol. 2023, 14, 1233079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrascu, R.; Dumitru, C.S. Advances in Understanding Inflammation and Tissue Damage: Markers of Persistent Sequelae in COVID-19 Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heming, M.; Li, X.; Räuber, S.; Mausberg, A.K.; Börsch, A.L.; Hartlehnert, M.; Singhal, A.; Lu, I.N.; Fleischer, M.; Szepanowski, F.; et al. Neurological Manifestations of COVID-19 Feature T Cell Exhaustion and Dedifferentiated Monocytes in Cerebrospinal Fluid. Immunity 2021, 54, 164–175.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molnar, T.; Lehoczki, A.; Fekete, M.; Varnai, R.; Zavori, L.; Erdo-Bonyar, S.; Simon, D.; Berki, T.; Csecsei, P.; Ezer, E. Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Long COVID: Mechanisms, Consequences, and Potential Therapeutic Approaches. GeroScience 2024, 46, 5267–5286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, B.Q.; Lai, Q.L.; Li, E.C.; Cai, M.T.; Fang, G.L.; Shen, C.H.; Zhang, Y.X.; Ding, M.P. Myelin Oligodendrocyte Glycoprotein Antibody and N-Methyl-d-Aspartate Receptor Antibody Overlapping Syndrome: Insights from the Recent Case Reports. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2024, 215, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, A.; Mishra, H.P.; Goel, A.; Gupta, A. COVID-19—A Potential Trigger for MOGAD-Associated Optic Neuritis: A Case Report and Literature Review. Ther. Adv. Ophthalmol. 2023, 15, 25158414231199541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, A.; Agrawal, D.K. Role of Gut Microbiota in Long COVID: Impact on Immune Function and Organ System Health. Arch. Microbiol. Immunol. 2025, 9, 38–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oaklander, A.L.; Mills, A.J.; Kelley, M.; Toran, L.S.; Smith, B.; Dalakas, M.C.; Nath, A. Peripheral Neuropathy Evaluations of Patients with Prolonged Long COVID. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2022, 9, e1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bandinelli, F.; Di Carlo, M.; Colantuono, V.A.; Nozzoli, F.; Salaffi, F.; Chiocchetti, B.; Nucci, E.; Mastricci, A.; Gherardi, E.; Manetti, M. Post-COVID-19 Small Fiber Neuropathy as a New Emerging Quality of Life-Threatening Disease: A Systematic Review. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalakas, M.C. Post-COVID Small Fiber Neuropathy, Implications of Innate Immunity, and Challenges on IVIG Therapy. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2024, 11, e200248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandinelli, F.; Nassini, R.; Gherardi, E.; Chiocchetti, B.; Manetti, M.; Cincotta, M.; Nozzoli, F.; Nucci, E.; De Logu, F.; Pimpinelli, N. Small Fiber Neuropathy Associated with Post-COVID-19 and Post-COVID-19 Vaccination Arthritis: A Rare Post-Infective Syndrome or a New-Onset Disease? J. Pers. Med. 2024, 14, 789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslamian, F.; Taleschian-Tabrizi, N.; Izadseresht, B.; Shakouri, S.K.; Gholian, S.; Rahbar, M. Electrophysiologic Findings in Patients with COVID-19 and Quadriparesia in the Northwest of Iran, a Case Series Study and Literature Review. Casp. J. Intern. Med. 2021, 12 (Suppl. 2), S451–S459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandori, W.J.; Padgett, L.E.; Alimadadi, A.; Gutierrez, N.A.; Araujo, D.J.; Huh, C.J.; Olingy, C.E.; Dinh, H.Q.; Wu, R.; Vijayanand, P.; et al. Single-Cell Immune Profiling Reveals Long-Term Changes in Myeloid Cells and Identifies a Novel Subset of CD9+ Monocytes Associated with COVID-19 Hospitalization. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2022, 112, 1053–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caliman-Sturdza, O.A.; Gheorghita, R.; Lobiuc, A. Neuropsychiatric Manifestations of Long COVID-19: A Narrative Review of Clinical Aspects and Therapeutic Approaches. Life 2025, 15, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rengasamy, M.; Marsland, A.; Spada, M.; Hsiung, K.; Kovats, T.; Price, R.B. A Chicken and Egg Scenario in Psychoneuroimmunology: Bidirectional Mechanisms Linking Cytokines and Depression. J. Affect. Disord. Rep. 2021, 6, 100177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iglesias-González, M.; Boigues, M.; Sanagustin, D.; Giralt-López, M.; Cuevas-Esteban, J.; Martínez-Cáceres, E.; Díez-Quevedo, C. Association of Serum Interleukin-6 and C-Reactive Protein with Depressive and Adjustment Disorders in COVID-19 Inpatients. Brain Behav. Immun. Health 2022, 19, 100405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camici, M.; Del Duca, G.; Brita, A.C.; Antinori, A. Connecting Dots of Long COVID-19 Pathogenesis: A Vagus Nerve–Hypothalamic–Pituitary–Adrenal–Mitochondrial Axis Dysfunction. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2024, 14, 1501949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azarias, F.R.; Almeida, G.H.D.R.; de Melo, L.F.; Rici, R.E.G.; Maria, D.A. The Journey of the Default Mode Network: Development, Function, and Impact on Mental Health. Biology 2025, 14, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madden, D.; Stephens, T.M.; Scott, J.; O’Neal Swann, C.; Prather, K.; Hoffmeister, J.; Ding, L.; Dunn, I.F.; Conner, A.K.; Yuan, H. Functional Connectivity of Default Mode Network in Non-Hospitalized Patients with Post-COVID Cognitive Complaints. Front. Neurosci. 2025, 19, 1576393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, S.R.; Fedorowski, A.; Sheldon, R.S. Diagnosis and Management of Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome. CMAJ 2022, 194, E378–E385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kizilbash, S.J.; Ahrens, S.P.; Bruce, B.K.; Chelimsky, G.; Driscoll, S.W.; Harbeck-Weber, C.; Lloyd, R.M.; Mack, K.J.; Nelson, D.E.; Ninis, N.; et al. Adolescent Fatigue, POTS, and Recovery: A Guide for Clinicians. Curr. Probl. Pediatr. Adolesc. Health Care 2014, 44, 108–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, E.; Heindrich, C.; Wittke, K.; Kedor, C.; Rust, R.; Freitag, H.; Sotzny, F.; Krüger, A.; Tölle, M.; Grabowski, P.; et al. Efficacy of Repeated Immunoadsorption in Patients with Post-COVID Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome and Elevated β2-Adrenergic Receptor Autoantibodies: A Prospective Cohort Study. Lancet Reg. Health Eur. 2024, 49, 101161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semmler, A.; Mundorf, A.K.; Kuechler, A.S.; Schulze-Bosse, K.; Heidecke, H.; Schulze-Forster, K.; Schott, M.; Uhrberg, M.; Weinhold, S.; Lackner, K.J.; et al. Chronic Fatigue and Dysautonomia Following COVID-19 Vaccination Is Distinguished from Normal Vaccination Response by Altered Blood Markers. Vaccines 2023, 11, 1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunning, W.T.; Kramer, P.M.; Cichocki, J.A.; Karabin, B.L.; Khuder, S.A.; Grubb, B.P. Platelet Storage Pool Deficiency and Elevated Inflammatory Biomarkers Are Prevalent in Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome. Cells 2022, 11, 774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunning, W.T., 3rd; Stepkowski, S.M.; Kramer, P.M.; Karabin, B.L.; Grubb, B.P. Inflammatory Biomarkers in Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome with Elevated G-Protein-Coupled Receptor Autoantibodies. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brock, M.V.; Bosmans, F. A Multi-Hit Model of Long COVID Pathophysiology: The Interaction between Immune Triggers and Nervous System Signaling. Trans. Am. Clin. Climatol. Assoc. 2024, 134, 149–164. [Google Scholar]
- El-Rhermoul, F.Z.; Fedorowski, A.; Eardley, P.; Taraborrelli, P.; Panagopoulos, D.; Sutton, R.; Lim, P.B.; Dani, M. Autoimmunity in Long COVID and POTS. Oxf. Open Immunol. 2023, 4, iqad002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Bi, K.; Zhou, L.; Wang, J.; Huang, L.; Sun, Y.; Peng, G.; Wu, W. Advances in Blood Biomarkers for Alzheimer’s Disease: Ultra-Sensitive Detection Technologies and Impact on Clinical Diagnosis. Degener. Neurol. Neuromuscul. Dis. 2024, 14, 85–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabresi, P.; Mechelli, A.; Natale, G.; Volpicelli-Daley, L.; Di Lazzaro, G.; Ghiglieri, V. Alpha-Synuclein in Parkinson’s Disease and Other Synucleinopathies: From Overt Neurodegeneration Back to Early Synaptic Dysfunction. Cell Death Dis. 2023, 14, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Kim, T.W.; Han, Y.; Nair, M.S.; Harschnitz, O.; Zhu, J.; Wang, P.; Koo, S.Y.; Lacko, L.A.; Chandar, V.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Infection Causes Dopaminergic Neuron Senescence. Cell Stem Cell 2024, 31, 196–211.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayat, A.H.; Azimi, H.; Hassani Moghaddam, M.; Ebrahimi, V.; Fathi, M.; Vakili, K.; Mahmoudiasl, G.R.; Forouzesh, M.; Boroujeni, M.E.; Nariman, Z.; et al. COVID-19 Causes Neuronal Degeneration and Reduces Neurogenesis in Human Hippocampus. Apoptosis 2022, 27, 852–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palermo, G.; Giannoni, S.; Bellini, G.; Siciliano, G.; Ceravolo, R. Dopamine Transporter Imaging, Current Status of a Potential Biomarker: A Comprehensive Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavallieri, F.; Fioravanti, V.; Bove, F.; Del Prete, E.; Meoni, S.; Grisanti, S.; Zedde, M.; Pascarella, R.; Moro, E.; Valzania, F. COVID-19 and Parkinsonism: A Critical Appraisal. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadidchi, R.; Al-Ani, Y.; Piskun, H.; Pakan, R.; Duong, K.S.; Jamil, H.; Wang, S.H.; Henry, S.; Maurer, C.W.; Duong, T.Q. Impact of COVID-19 on Long-Term Outcomes in Parkinson’s Disease. Eur. J. Neurol. 2025, 32, e70013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bougea, A.; Georgakopoulou, V.E.; Palkopoulou, M.; Efthymiopoulou, E.; Angelopoulou, E.; Spandidos, D.A.; Zikos, P. New-Onset Non-Motor Symptoms in Patients with Parkinson’s Disease and Post-COVID-19 Syndrome: A Prospective Cross-Sectional Study. Med. Int. 2023, 3, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khieukhajee, J.; Rojana-Udomsart, A.; Srisarakorn, P.; Wongsurit, T.; Aungsumart, S. Cognitive Impairment and Risk Factors in Post-COVID-19 Hospitalized Patients. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Disord. Extra 2023, 13, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roh, J.H.; Jung, I.; Suh, Y.; Kim, M.-H. A Potential Association between COVID-19 Vaccination and Development of Alzheimer’s Disease. QJM 2024, 117, 709–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hicks, B.; Read, S.; Hu, B.; Wittenberg, R.; Grahamslaw, A.; Karim, A.; Martin, E.; Nuzum, E.; Reichental, J.; Russell, A.; et al. A Cohort Study of the Impact of COVID-19 on the Quality of Life of People Newly Diagnosed with Dementia and Their Family Carers. Alzheimer’s Dement. Transl. Res. Clin. Interv. 2022, 8, e12236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakker, E.D.; van Maurik, I.S.; Zwan, M.D.; Gillissen, F.; van der Veere, P.J.; Bouwman, F.H.; Pijnenburg, Y.A.L.; van der Flier, W.M. Impact of COVID-19 Pandemic on Mortality Rate in Memory Clinic Patients. Alzheimer’s Dement. Diagn. Assess. Dis. Monit. 2024, 16, e12541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finsterer, J. SARS-CoV-2 Triggered Relapse of Multiple Sclerosis. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2022, 215, 107210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borra, R.; Patel, N.T.; Shaikh, R.; Parmar, M.S.; Borra, S. A Case of Transverse Myelitis Secondary to COVID-19 Infection. Cureus 2022, 14, e32297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mok, C.C.; Cheung, C.C.L.; Chan, K.L.; Tse, S.M.; To, C.H. Effect of SARS-CoV-2 Infection on Disease Flares in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Case-Control Study. Rheumatology 2024, 63, 3390–3396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cervia-Hasler, C.; Brüningk, S.C.; Hoch, T.; Fan, B.; Muzio, G.; Thompson, R.C.; Ceglarek, L.; Meledin, R.; Westermann, P.; Emmenegger, M.; et al. Persistent Complement Dysregulation with Signs of Thromboinflammation in Active Long COVID. Science 2024, 383, eadg7942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franke, C.; Boesl, F.; Goereci, Y.; Gerhard, A.; Schweitzer, F.; Schroeder, M.; Foverskov-Rasmussen, H.; Heine, J.; Quitschau, A.; Kandil, F.I.; et al. Association of Cerebrospinal Fluid Brain-Binding Autoantibodies with Cognitive Impairment in Post-COVID-19 Syndrome. Brain Behav. Immun. 2023, 109, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarius, S.; Pache, F.; Körtvelyessy, P.; Jelčić, I.; Stettner, M.; Franciotta, D.; Keller, E.; Neumann, B.; Ringelstein, M.; Senel, M.; et al. Cerebrospinal Fluid Findings in COVID-19: A Multicenter Study of 150 Lumbar Punctures in 127 Patients. J. Neuroinflamm. 2022, 19, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiriveedi, M.; Sto Domingo, F.G.; Longley, S.; Patel, S.; Baddam, S.; Chimakurthy, A. Post-COVID-19 Guillain-Barré Syndrome with GM1 and GD1b Antibodies: A Case Study and Literature Review. Am. J. Case Rep. 2025, 26, e947416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.; Wang, Z.; Abdel-Mohsen, M.; Chen, X.; Montaner, L.J. Tissue Injury and Leukocyte Changes in Post-Acute Sequelae of SARS-CoV-2: Review of 2833 Post-Acute Patient Outcomes per Immune Dysregulation and Microbial Translocation in Long COVID. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2023, 113, 236–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, L.; Rissmann, M.; Benavides, F.F.W.; Leijten, L.; van Run, P.; Begeman, L.; Veldhuis Kroeze, E.J.B.; Lendemeijer, B.; Smeenk, H.; de Vrij, F.M.S.; et al. In Vitro and In Vivo Differences in Neurovirulence between D614G, Delta and Omicron BA.1 SARS-CoV-2 Variants. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2022, 10, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, L.L.Y.; Anderson, D.E.; Cheng, H.S.; Ivan, F.X.; Chen, S.; Kang, A.E.Z.; Foo, R.; Gamage, A.M.; Tiew, P.Y.; Koh, M.S.; et al. The Establishment of COPD Organoids to Study Host-Pathogen Interaction Reveals Enhanced Viral Fitness of SARS-CoV-2 in Bronchi. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 7635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benavides, F.F.W.; Veldhuis Kroeze, E.J.B.; Leijten, L.; Schmitz, K.S.; van Run, P.; Kuiken, T.; de Vries, R.D.; Bauer, L.; van Riel, D. Neuroinvasive and Neurovirulent Potential of SARS-CoV-2 in the Acute and Post-Acute Phase of Intranasally Inoculated Ferrets. PLoS ONE 2025, 20, e0311449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plantone, D.; Stufano, A.; Righi, D.; Locci, S.; Iavicoli, I.; Lovreglio, P.; De Stefano, N. Neurofilament Light Chain and Glial Fibrillary Acid Protein Levels Are Elevated in Post-Mild COVID-19 or Asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 Cases. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 6429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ao, Z.; Ouyang, M.J.; Olukitibi, T.A.; Yao, X. SARS-CoV-2 Delta Spike Protein Enhances the Viral Fusogenicity and Inflammatory Cytokine Production. iScience 2022, 25, 104759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messlinger, K.; Neuhuber, W.; May, A. Activation of the Trigeminal System as a Likely Target of SARS-CoV-2 May Contribute to Anosmia in COVID-19. Cephalalgia 2022, 42, 176–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stangis, M.; Adesse, D.; Sharma, B.; Castro, E.; Kumar, K.; Kumar, N.; Minevich, M.; Toborek, M. The S1 Subunits of SARS-CoV-2 Variants Differentially Trigger the IL-6 Signaling Pathway in Human Brain Endothelial Cells and Downstream Impact on Microglia Activation. NeuroImmune Pharmacol. Ther. 2024, 3, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Parra, H.; Reyes-Hernández, O.D.; Figueroa-González, G.; González-Del Carmen, M.; González-Torres, M.; Peña-Corona, S.I.; Florán, B.; Cortés, H.; Leyva-Gómez, G. Alteration of the Blood-Brain Barrier by COVID-19 and Its Implication in the Permeation of Drugs into the Brain. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1125109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhou, L.; Bao, L.; Liu, J.; Zhu, H.; Lv, Q.; Liu, R.; Chen, W.; Tong, W.; Wei, Q.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Crosses the Blood-Brain Barrier Accompanied with Basement Membrane Disruption without Tight Junctions Alteration. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, W.; Montano, M.; Corley, M.J.; Helmy, E.; Kobayashi, H.; Kinisu, M.; Suryawanshi, R.; Luo, X.; Royer, L.A.; Roan, N.R.; et al. Neuropilin-1 Mediates SARS-CoV-2 Infection of Astrocytes in Brain Organoids, Inducing Inflammation Leading to Dysfunction and Death of Neurons. mBio 2022, 13, e0230822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proust, A.; Queval, C.J.; Harvey, R.; Adams, L.; Bennett, M.; Wilkinson, R.J. Differential Effects of SARS-CoV-2 Variants on Central Nervous System Cells and Blood-Brain Barrier Functions. J. Neuroinflamm. 2023, 20, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albornoz, E.A.; Amarilla, A.A.; Modhiran, N.; Parker, S.; Li, X.X.; Wijesundara, D.K.; Aguado, J.; Zamora, A.P.; McMillan, C.L.D.; Liang, B.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Drives NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation in Human Microglia through Spike Protein. Mol. Psychiatry 2023, 28, 2878–2893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckman, D.; Bonillas, A.; Diniz, G.B.; Ott, S.; Roh, J.W.; Elizaldi, S.R.; Schmidt, B.A.; Sammak, R.L.; Van Rompay, K.K.A.; Iyer, S.S.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Infects Neurons and Induces Neuroinflammation in a Non-Human Primate Model of COVID-19. Cell Rep. 2022, 41, 111573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Mi, Z.; Liu, Z.; Rong, P. SARS-CoV-2: Pathogenesis, Therapeutics, Variants, and Vaccines. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1334152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Narayan, R.K.; Kumari, C.; Faiq, M.A.; Kulandhasamy, M.; Kant, K.; Pareek, V. SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry Receptor ACE2 Mediated Endothelial Dysfunction Leads to Vascular Thrombosis in COVID-19 Patients. Med. Hypotheses 2020, 145, 110320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, S.N.; Padiyath, S.; Chandrababu, K.; Raj, L.; Chakrapani P.S., B.; Ninan, G.A.; Sivadasan, A.; Jacobs, A.R.; Li, Y.W.; Bhaskar, A. Neurological, Psychological, Psychosocial Complications of Long-COVID and Their Management. Neurol. Sci. 2025, 46, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.; Zhu, M.; Chen, M.; Li, X.; Feng, X. The Role of Macrophage Plasticity in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Biomark. Res. 2024, 12, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dansereau, M.A.; Midavaine, É.; Bégin-Lavallée, V.; Belkouch, M.; Beaudet, N.; Longpré, J.M.; Mélik-Parsadaniantz, S.; Sarret, P. Mechanistic Insights into the Role of the Chemokine CCL2/CCR2 Axis in Dorsal Root Ganglia to Peripheral Inflammation and Pain Hypersensitivity. J. Neuroinflamm. 2021, 18, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tilikete, C.; Zamali, I.; Meddeb, Z.; Kharroubi, G.; Marzouki, S.; Dhaouadi, T.; Ben Hmid, A.; Samoud, S.; Galai, Y.; Charfeddine, S.; et al. Exploring the Landscape of Symptom-Specific Inflammatory Cytokines in Post-COVID Syndrome Patients. BMC Infect. Dis. 2024, 24, 1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muri, J.; Cecchinato, V.; Cavalli, A.; Shanbhag, A.A.; Matkovic, M.; Biggiogero, M.; Maida, P.A.; Moritz, J.; Toscano, C.; Ghovehoud, E.; et al. Autoantibodies against Chemokines Post-SARS-CoV-2 Infection Correlate with Disease Course. Nat. Immunol. 2023, 24, 604–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pachner, A.R.; Pike, S.; Smith, A.D.; Gilli, F. CXCL13 as a Biomarker: Background and Utility in Multiple Sclerosis. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Haile, K.; Gedefaw, L.; Lau, B.W.-M.; Jin, L.; Yip, S.P.; Huang, C.-L. Blood Biomarkers as Prognostic Indicators for Neurological Injury in COVID-19 Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comeau, D.; Martin, M.; Robichaud, G.A.; Chamard-Witkowski, L. Neurological Manifestations of Post-Acute Sequelae of COVID-19: Which Liquid Biomarker Should We Use? Front. Neurol. 2023, 14, 1233192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peluso, M.J.; Sans, H.M.; Forman, C.A.; Nylander, A.; Ho, H.; Lu, S.; Goldberg, S.A.; Hoh, R.; Tai, V.; Munter, S.E.; et al. Plasma Markers of Neurologic Injury and Inflammation in People with Self-Reported Neurologic Postacute Sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2022, 9, e200003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frontera, J.A.; Yang, D.; Lewis, A.; Patel, P.; Medicherla, C.; Arena, V.; Fang, T.; Andino, A.; Snyder, T.; Madhavan, M.; et al. A Prospective Study of Long-Term Outcomes among Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients with and without Neurological Complications. J. Neurol. Sci. 2021, 426, 117486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greene, C.; Connolly, R.; Brennan, D.; Laffan, A.; O’Keeffe, E.; Zaporojan, L.; O’Callaghan, J.; Thomson, B.; Connolly, E.; Argue, R.; et al. Blood–Brain Barrier Disruption and Sustained Systemic Inflammation in Individuals with Long COVID-Associated Cognitive Impairment. Nat. Neurosci. 2024, 27, 421–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, D.L.; Imberti, L.; Quaresima, V.; Fiorini, C.; NIAID COVID-19 Consortium; Gildersleeve, J.C. Abnormal Antibodies to Self-Carbohydrates in SARS-CoV-2-Infected Patients. PNAS Nexus 2022, 1, pgac062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dani, M.; Dirksen, A.; Taraborrelli, P.; Torocastro, M.; Panagopoulos, D.; Sutton, R.; Lim, P.B. Autonomic Dysfunction in ‘Long COVID’: Rationale, Physiology and Management Strategies. Clin. Med. 2021, 21, e63–e67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anft, M.; Wiemers, L.; Rosiewicz, K.S.; Doevelaar, A.; Skrzypczyk, S.; Kurek, J.; Kaliszczyk, S.; Seidel, M.; Stervbo, U.; Seibert, F.S.; et al. Effect of Immunoadsorption on Clinical Presentation and Immune Alterations in COVID-19-Induced and/or Aggravated ME/CFS. Mol. Ther. 2025, 33, 2886–2899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korobova, Z.R.; Arsentieva, N.A.; Liubimova, N.E.; Batsunov, O.K.; Butenko, A.A.; Kokoeva, A.E.; Kucherenko, N.G.; Kashchenko, V.A.; Boeva, E.V.; Norka, A.O.; et al. B Cell Dynamics and Transitional B Cells in Long COVID. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemente, L.; La Rocca, M.; Quaranta, N.; Iannuzzi, L.; Vecchio, E.; Brunetti, A.; Gentile, E.; Dibattista, M.; Lobasso, S.; Bevilacqua, V.; et al. Prefrontal Dysfunction in Post-COVID-19 Hyposmia: An EEG/fNIRS Study. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1240831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sáez-Landete, I.; Gómez-Domínguez, A.; Estrella-León, B.; Díaz-Cid, A.; Fedirchyk, O.; Escribano-Muñoz, M.; Pedrera-Mazarro, A.; Martín-Palomeque, G.; Garcia-Ribas, G.; Rodríguez-Jorge, F.; et al. Retrospective Analysis of EEG in Patients with COVID-19: EEG Recording in Acute and Follow-Up Phases. Clin. EEG Neurosci. 2022, 53, 215–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberto, K.T.; Espiritu, A.I.; Fernandez, M.L.L.; Gutierrez, J.C. Electroencephalographic Findings in COVID-19 Patients: A Systematic Review. Seizure 2020, 82, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.Y.; Wu, J.J.; Zhu, Y.; Zheng, M.X.; Hua, X.Y.; Xu, J.G. Investigating Autonomic Dysfunction in Post-COVID-19 Syndrome from Skin to Brain: A Case-Control Study Using EMG-SSR and fNIRS. Brain Res. Bull. 2025, 220, 111158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Jiang, C.; Lin, X.; Yang, Y. Point-of-Care Detection of Cytokines in Cytokine Storm Management and Beyond: Significance and Challenges. View 2021, 2, 20210003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalra, R.S.; Dhanjal, J.K.; Meena, A.S.; Kalel, V.C.; Dahiya, S.; Singh, B.; Dewanjee, S.; Kandimalla, R. COVID-19, Neuropathology, and Aging: SARS-CoV-2 Neurological Infection, Mechanism, and Associated Complications. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2021, 13, 662786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gritsenko, A.; Green, J.P.; Brough, D.; Lopez-Castejon, G. Mechanisms of NLRP3 Priming in Inflammaging and Age-Related Diseases. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2020, 55, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjadj, J.; Yatim, N.; Barnabei, L.; Corneau, A.; Boussier, J.; Smith, N.; Péré, H.; Charbit, B.; Bondet, V.; Chenevier-Gobeaux, C.; et al. Impaired Type I Interferon Activity and Inflammatory Responses in Severe COVID-19 Patients. Science 2020, 369, 718–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owens, C.D.; Pinto, C.B.; Szarvas, Z.; Muranyi, M.; Pinaffi-Langley, A.C.d.C.; Peterfi, A.; Mukli, P.; Detwiler, S.; Olay, L.; Kaposzta, Z.; et al. COVID-19 Exacerbates Neurovascular Uncoupling and Contributes to Endothelial Dysfunction in Patients with Mild Cognitive Impairment. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huerne, K.; Filion, K.B.; Grad, R.; Ernst, P.; Gershon, A.S.; Eisenberg, M.J. Epidemiological and Clinical Perspectives of Long COVID Syndrome. Am. J. Med. Open 2023, 9, 100033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, F.; Tomasoni, D.; Falcinella, C.; Barbanotti, D.; Castoldi, R.; Mulè, G.; Augello, M.; Mondatore, D.; Allegrini, M.; Cona, A.; et al. Female Gender Is Associated with Long COVID Syndrome: A Prospective Cohort Study. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2022, 28, 611.e9–611.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairweather, D.; Beetler, D.J.; McCabe, E.J.; Lieberman, S.M. Mechanisms Underlying Sex Differences in Autoimmunity. J. Clin. Investig. 2024, 134, e180076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moulton, V.R. Sex Hormones in Acquired Immunity and Autoimmune Disease. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte-Silva, M.; Oliveira, C.N.S.; Fuzo, C.; Silva-Neto, P.V.; Toro, D.M.; Pimentel, V.E.; Pérez, M.M.; Fraga-Silva, T.F.C.; Carvalho, J.C.S.; Neto, F.M.S.; et al. Divergent Androgenic Modulation of SARS-CoV-2 Infection Cooperates with Dysregulated Immune Response to Dictate Worse COVID-19 Outcomes in Men. Brain Behav. Immun. 2023, 114, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miles, M.A.; Huttmann, T.D.; Liong, S.; Liong, F.; O’Leary, J.J.; Brooks, D.A.; Selemidis, S. Exploring the Contribution of TLR7 to Sex-Based Disparities in Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV)-Induced Inflammation and Immunity. Viruses 2025, 17, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, J.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Q.; Xu, S. Neurological Risks of COVID-19 in Women: The Complex Immunology Underpinning Sex Differences. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1281310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guilmot, A.; Maldonado Slootjes, S.; Bissay, V.; Dubuisson, N.; de Broglie, C.; Gille, M. SARS-CoV-2-Associated Guillain-Barré Syndrome in Four Patients: What Do We Know About Pathophysiology? Acta Neurol. Belg. 2022, 122, 703–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhkhari, M.; Caidi, H.; Sadki, K. HLA Alleles Associated with COVID-19 Susceptibility and Severity in Different Populations: A Systematic Review. Egypt. J. Med. Hum. Genet. 2023, 24, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Augusto, D.G.; Murdolo, L.D.; Chatzileontiadou, D.S.M.; Sabatino, J.J., Jr.; Yusufali, T.; Peyser, N.D.; Butcher, X.; Kizer, K.; Guthrie, K.; Murray, V.W.; et al. A Common Allele of HLA Is Associated with Asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Nature 2023, 620, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozak, K.; Pavlyshyn, H.; Kamyshnyi, O.; Shevchuk, O.; Korda, M.; Vari, S.G. The Influence of Genetic Polymorphisms on Cytokine Profiles in Pediatric COVID-19: A Pilot Study. Front. Pediatr. 2025, 13, 1523627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchynskyi, M.; Kamyshna, I.; Halabitska, I.; Petakh, P.; Oksenych, V.; Kamyshnyi, O. Genetic Predictors of Paxlovid Treatment Response: The Role of IFNAR2, OAS1, OAS3, and ACE2 in COVID-19 Clinical Course. J. Pers. Med. 2025, 15, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhariwal, R.; Dave, K.; Jain, M. Omics-Based Analysis of Mitochondrial Dysfunction and BBB Integrity in Post-COVID-19 Sequelae. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 31016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasquarelli-do-Nascimento, G.; Braz-de-Melo, H.A.; Faria, S.S.; Santos, I.O.; Kobinger, G.P.; Magalhães, K.G. Hypercoagulopathy and Adipose Tissue Exacerbated Inflammation May Explain Higher Mortality in COVID-19 Patients with Obesity. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niesen, M.; Trotta, N.; Noel, A.; Coolen, T.; Fayad, G.; Leurkin-Sterk, G.; Delpierre, I.; Henrard, S.; Sadeghi, N.; Goffard, J.C.; et al. Structural and Metabolic Brain Abnormalities in COVID-19 Patients with Sudden Loss of Smell. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2021, 48, 1890–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peluso, M.J.; Ryder, D.; Flavell, R.; Wang, Y.; Levi, J.; LaFranchi, B.H.; Deveau, T.M.; Buck, A.M.; Munter, S.E.; Asare, K.A.; et al. Multimodal Molecular Imaging Reveals Tissue-Based T Cell Activation and Viral RNA Persistence for Up to 2 Years Following COVID-19. medRxiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMillan, P.; Turner, A.J.; Uhal, B.D. Mechanisms of Gut-Related Viral Persistence in Long COVID. Viruses 2024, 16, 1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fekete, R.; Simats, A.; Bíró, E.; Pósfai, B.; Cserép, C.; Schwarcz, A.D.; Szabadits, E.; Környei, Z.; Tóth, K.; Fichó, E.; et al. Microglia Dysfunction, Neurovascular Inflammation and Focal Neuropathologies Are Linked to IL-1- and IL-6-Related Systemic Inflammation in COVID-19. Nat. Neurosci. 2025, 28, 558–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Li, Y.; Pan, L.; Sha, J.; Bailey, M.; Faure-Kumar, E.; Williams, C.K.; Wohlschlegel, J.; Magaki, S.; Niu, C.; et al. Brain-Wide Alterations Revealed by Spatial Transcriptomics and Proteomics in COVID-19 Infection. Nat. Aging 2024, 4, 1598–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizera, J.; Genzor, S.; Sova, M.; Stanke, L.; Burget, R.; Jakubec, P.; Vykopal, M.; Pobeha, P.; Zapletalová, J. The Effectiveness of Glucocorticoid Treatment in Post-COVID-19 Pulmonary Involvement. Pneumonia 2024, 16, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakimi, P.; Zaboli, K.A.; Golbabapour-Samakoush, M.; Azizimohammadi, S.; Soleimani, F.; Salmani, M.H.; Teimoori-Toolabi, L. HLA Polymorphisms and COVID-19 Susceptibility and Severity: Insights from an Iranian Patients Cohort. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2025, 29, e70570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z. Integrative Genome-Wide Association Studies of COVID-19 Susceptibility and Hospitalization Reveal Risk Loci for Long COVID. medRxiv 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, N.K.; Tailang, M.; Jain, H.K.; Chandrasekaran, B.; Sahoo, B.M.; Subramanian, A.; Thangavel, N.; Aldahish, A.; Chidambaram, K.; Alagusundaram, M.; et al. Therapeutic Implications of Current Janus Kinase Inhibitors as Anti-COVID Agents: A Review. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1135145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrente-López, A.; Hermosilla, J.; Navas, N.; Cuadros-Rodríguez, L.; Cabeza, J.; Salmerón-García, A. The Relevance of Monoclonal Antibodies in the Treatment of COVID-19. Vaccines 2021, 9, 557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamariz, L.; Bast, E.; Klimas, N.; Palacio, A. Low-Dose Naltrexone Improves Post-COVID-19 Condition Symptoms. Clin. Ther. 2024, 46, e101–e106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordelli, E.; Soda, P.; Citter, S.; Schiavon, E.; Salvatore, C.; Fazzini, D.; Clementi, G.; Cellina, M.; Cozzi, A.; Bortolotto, C.; et al. Machine Learning Predicts Pulmonary Long COVID Sequelae Using Clinical Data. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2024, 24, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zabidi, N.Z.; Liew, H.L.; Farouk, I.A.; Puniyamurti, A.; Yip, A.J.W.; Wijesinghe, V.N.; Low, Z.Y.; Tang, J.W.; Chow, V.T.K.; Lal, S.K. Evolution of SARS-CoV-2 Variants: Implications on Immune Escape, Vaccination, Therapeutic and Diagnostic Strategies. Viruses 2023, 15, 944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carabelli, A.M.; Peacock, T.P.; Thorne, L.G.; Harvey, W.T.; Hughes, J.; COVID-19 Genomics UK Consortium; Peacock, S.J.; Barclay, W.S.; de Silva, T.I.; Towers, G.J.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 variant biology: Immune escape, transmission and fitness. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2023, 21, 162–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Condition | Neurological Symptoms | Immune Biomarkers |
|---|---|---|
| Cognitive dysfunction | Brain fog and memory loss | IL-6, GFAP, NFL, and TNF-α |
| Peripheral neuropathy | Numbness and tingling | IL-8, TNF-α, and autoantibodies |
| Depression and anxiety | Sleep disturbance and fatigue | IL-1β, IFN-γ, and CRP |
| Postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome (POTS) | Tachycardia and orthostatic intolerance | IL-6, MCP-1, and CD30 |
| Parkinsonism | Tremors and rigidity | α-synuclein, IL-1β, and sTNFRs |
| Guillain–Barré syndrome (GBS) | Muscle weakness and paralysis | Anti-ganglioside antibodies and IL-12 |
| Variant | Key Spike Mutations | Neuroinvasive Potential | Immune Signature | CNS Cell Tropism | Clinical Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D614G [99,100,101,102] | D614G | High (olfactory and cortical) | CXCL10, IFN-β, and IL-6 | Neurons and microglia | Anosmia, brain fog, and encephalitis |
| Delta [103,104,105,106,107] | L452R and T478K | Moderate–High | IL-1β and MCP-1 | Astrocytes and pericytes | Headache and encephalopathy |
| Omicron (BA.1–XBB) [19,108,109,110] | Multiple S1/S2 | Low direct and high indirect | IL-6, CXCL8, and HSP70 | Astrocytes and pericytes | Cognitive dysfunction and fatigue |
| Alpha [109,111,112,113] | N501Y and P681H | Low | IL-12 and IFN-γ | Endothelial cells | Mild anosmia and fatigue |
| Beta [109,111,112,113] | E484K and K417N | High (olfactory and cortical) | IL-18 and TNF-α | Glial cells | Neurovascular symptoms |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hein, Z.M.; Thazin; Kumar, S.; Che Ramli, M.D.; Che Mohd Nassir, C.M.N. Immunomodulatory Mechanisms Underlying Neurological Manifestations in Long COVID: Implications for Immune-Mediated Neurodegeneration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6214. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136214
Hein ZM, Thazin, Kumar S, Che Ramli MD, Che Mohd Nassir CMN. Immunomodulatory Mechanisms Underlying Neurological Manifestations in Long COVID: Implications for Immune-Mediated Neurodegeneration. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(13):6214. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136214
Chicago/Turabian StyleHein, Zaw Myo, Thazin, Suresh Kumar, Muhammad Danial Che Ramli, and Che Mohd Nasril Che Mohd Nassir. 2025. "Immunomodulatory Mechanisms Underlying Neurological Manifestations in Long COVID: Implications for Immune-Mediated Neurodegeneration" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 13: 6214. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136214
APA StyleHein, Z. M., Thazin, Kumar, S., Che Ramli, M. D., & Che Mohd Nassir, C. M. N. (2025). Immunomodulatory Mechanisms Underlying Neurological Manifestations in Long COVID: Implications for Immune-Mediated Neurodegeneration. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(13), 6214. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136214








