Effects of Stress and Allopregnanolone on the Expression of Neurotrophins and TrkB Receptor in the Sheep Hippocampus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
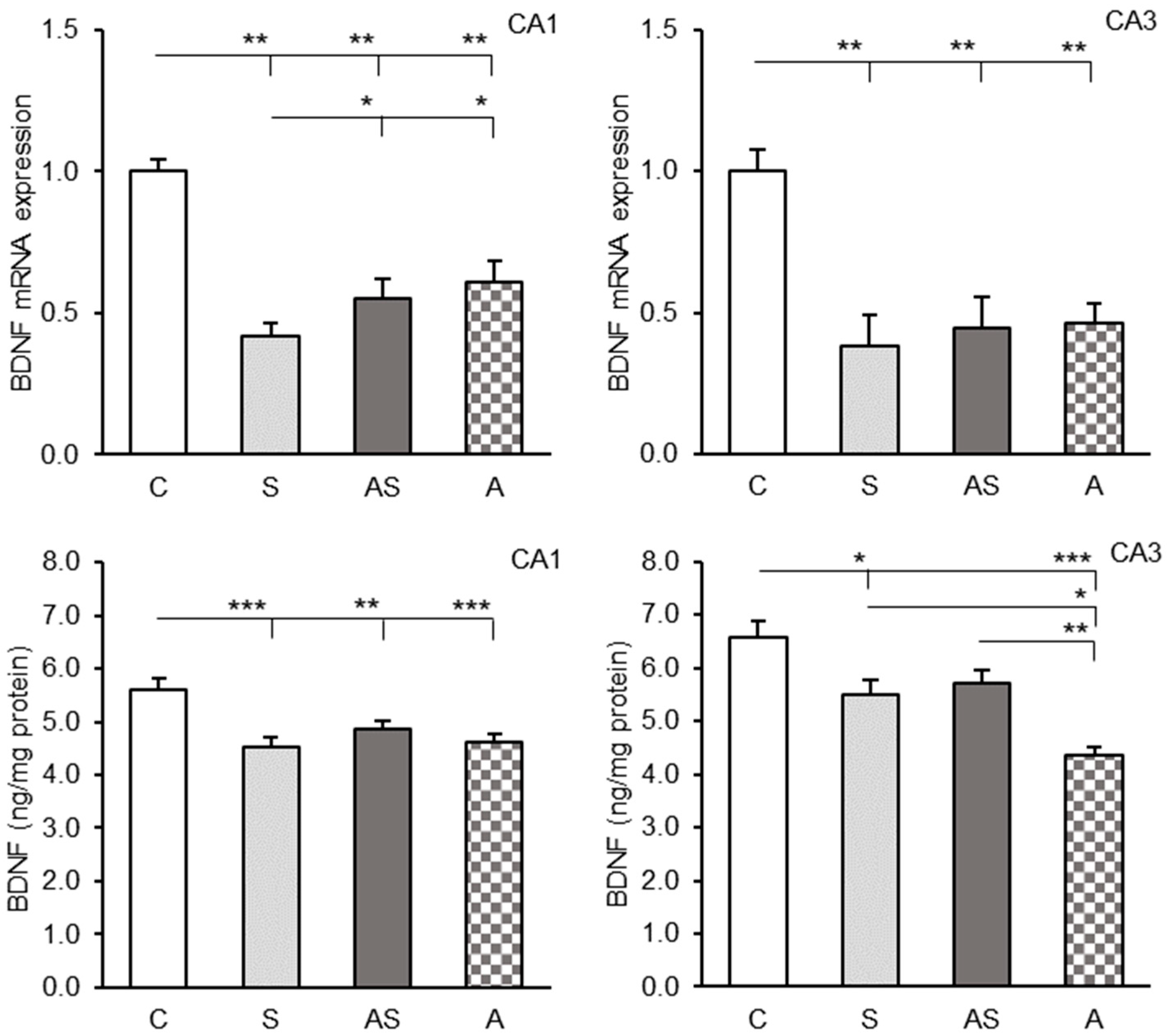
2.1. BDNF Expression in the CA1 and CA3 Regions
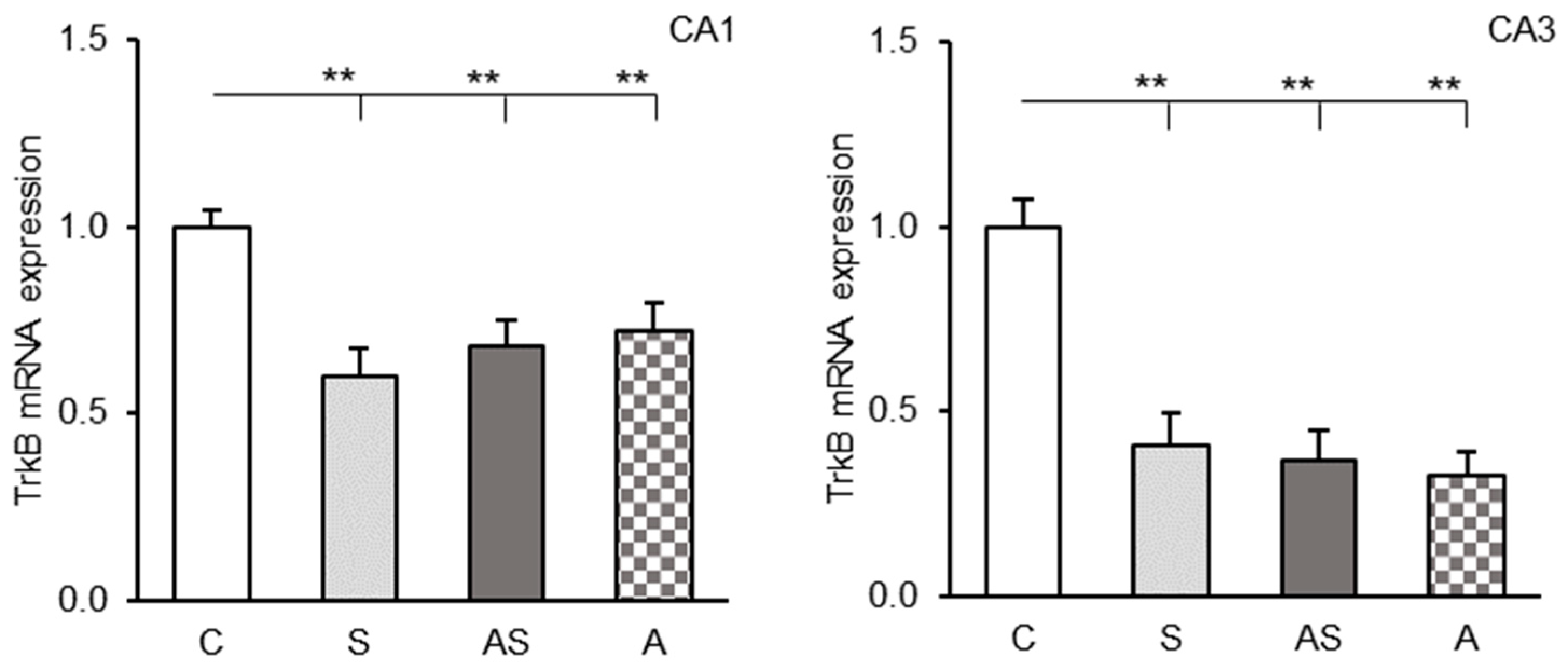
2.2. TrkB mRNA Levels in the CA1 and CA3 Fields
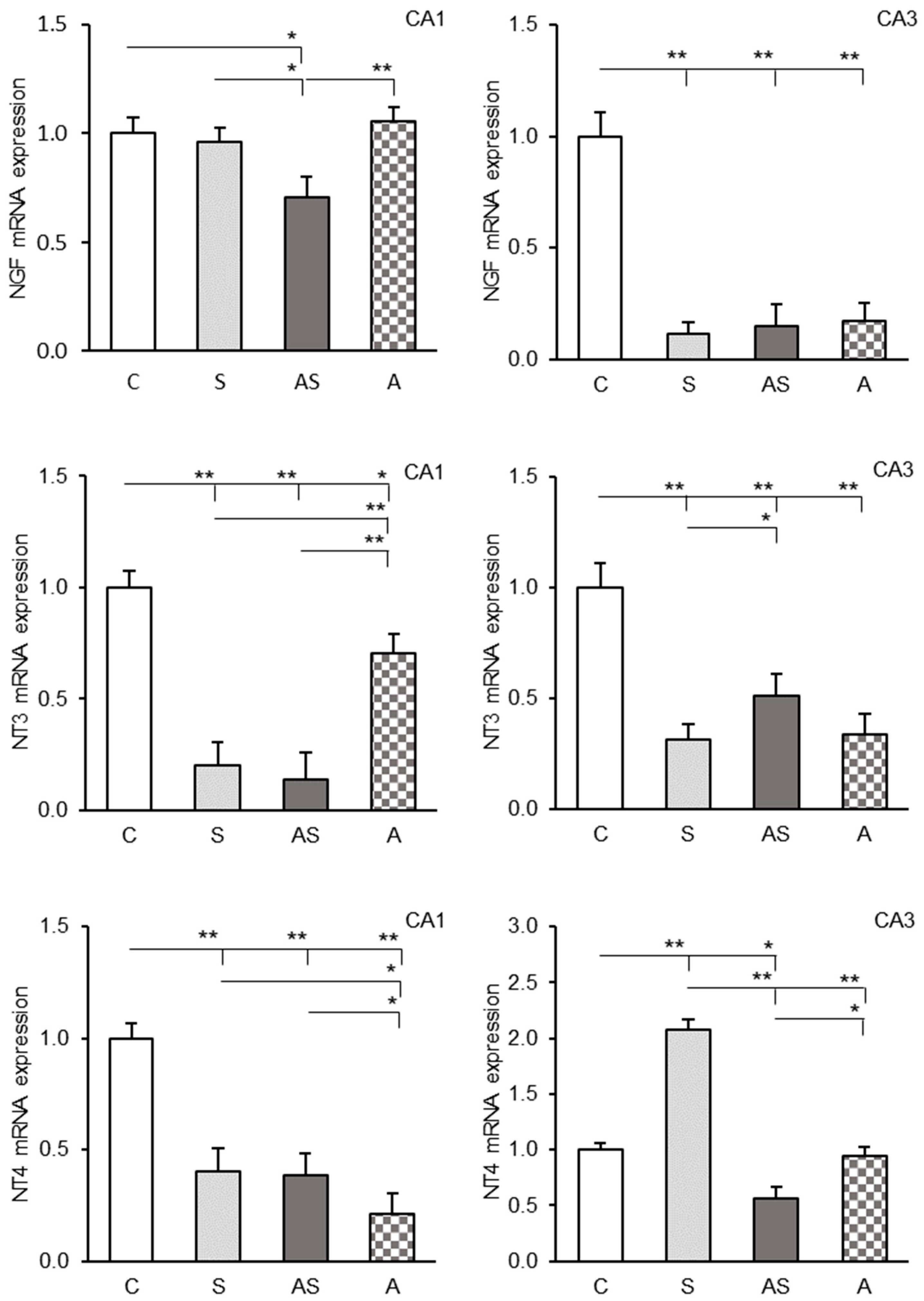
2.3. Expression Profiles of NGF, NT3 and NT4 Transcripts in the CA1 and CA3 Fields
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animal Management
4.2. Brain Surgery
4.3. Experimental Design and Tissue Collection
4.4. Tissue BDNF Concentration Assay
4.5. Neurotrophin mRNA Abundance Assay
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions and Limitations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviation
| ACTH | Adrenocorticoid hormone |
| ALLO | Allopregnanolone |
| AVP | Arginine vasopressin |
| BNST | Bed nucleus of the stria terminalis |
| BDNF | Brain-derived neurotrophic hormone |
| CA | Cornu ammonis (1 and 3) |
| CNS | Central nervous system |
| CRH | Corticotropin-releasing hormone |
| DG | Dentate gyrus |
| GABA | Gamma-aminobutyric acid |
| GAPDH | Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase |
| GR | Glucocorticoid receptors |
| HPA | Hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal |
| LTP | Long-term potentiation |
| MR | Mineralocorticoid receptors |
| NGF | Nerve growth factor |
| NT3 | Neurotrophin 3 |
| NT4 | Neurotrophin 4 |
| P75NTR | P75 neurotrophin receptor |
| PPIC | Peptidylprolyl isomerase C |
| PVN | Paraventricular nucleus |
| RL | Ringer–Locke solution |
| SGZ | Subgranular zone |
| SVZ | Subventricular zone |
| Trk | Tropomyosin receptor kinases |
References
- Compagnone, N.A.; Mellon, S.H. Neurosteroids: Biosynthesis and function of these novel neuromodulators. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 2000, 21, 1–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebner, M.J.; Corol, D.I.; Havlikova, H.; Honour, J.W.; Fry, J.P. Identification of neuroactive steroids and their precursors and metabolites in adult male rat brain. Endocrinology 2006, 147, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellon, S.H.; Griffin, L.D. Neurosteroids: Biochemistry and clinical significance. Trends Endocrinol. Metabol. 2002, 13, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borowicz, K.K.; Piskorska, B.; Banach, M.; Czuczwar, S.J. Neuroprotective actions of neurosteroids. Front. Endocrinol. 2011, 2, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melcangi, R.C.; Panzica, G.C. ALLO: State of the art. Prog. Neurobiol. 2014, 113, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunn, B.G.; Cunningham, L.; Mitchell, S.G.; Swinny, J.D.; Lambert, J.J.; Belelli, D. GABAA receptor-acting neurosteroids: A role in the development and regulation of the stress response. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 2015, 36, 28–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, S.M.; Pinna, G.; Guidotti, A. ALLO: From molecular pathophysiology to therapeutics. A historical perspective. Neurobiol. Stress. 2020, 12, 100215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diviccaro, S.; Cioffi, L.; Falvo, E.; Giatti, S.; Melcangi, R.C. ALLO: An overview on its synthesis and effects. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2022, 34, e12996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Wang, T.; Yao, J.; Brinton, R.D. ALLO promotes neuronal and oligodendrocyte differentiation in vitro and in vivo: Therapeutic implication for Alzheimer’s disease. Neurotherapeutics 2020, 17, 1813–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheibani, V.; Rajizadeh, M.A.; Bejeshk, M.A.; Haghparast, E.; Nozari, M.; Esmaeili-Mahani, S.; Nezhadi, A. The effects of neurosteroid ALLO on synaptic dysfunction in the hippocampus in experimental parkinsonism rats: An electrophysiological and molecular study. Neuropeptides 2022, 92, 102229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dechant, G.; Neumann, H. Neurotrophins. In Molecular and Cellular Biology of Neuroprotection in the CNS; Alzheimer, C., Ed.; AEMB: Mahomet, IL, USA, 2002; Volume 513, pp. 303–324. [Google Scholar]
- Bothwell, M. NGF, BDNF, NT3, and NT4. In Neurotrophic Factors; Lewin, G.R., Carter, B.D., Eds.; Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology 220; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 3–16. [Google Scholar]
- Sasi, M.; Vignoli, B.; Canossa, M.; Blum, R. Neurobiology of local and intercellular BDNF signaling. Pflügers Arch.-Eur. J. Physiol. 2017, 469, 593–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arévalo, J.C.; Deogracias, R. Mechanisms controlling the expression and secretion of BDNF. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leal, G.; Bramham, C.R.; Duarte, C.B. Chapter Eight—BDNF and hippocampal synaptic plasticity. Vitam. Horm. 2017, 104, 153–195. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Traynelis, S.F.; Wollmuth, L.P.; McBain, C.J.; Menniti, F.S.; Vance, K.M.; Ogden, K.K.; Hansen, K.B.; Yuan, H.; Myers, S.J.; Dingledine, R. Glutamate receptor ion channels: Structure, regulation, and function. Pharmacol. Rev. 2010, 62, 405–496. [Google Scholar]
- Schlett, K. Glutamate as a modulator of embryonic and adult neurogenesis. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2006, 6, 949–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattson, M.P. Glutamate and neurotrophic factors in neuronal plasticity and disease. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2008, 1144, 97–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Z.; Wang, Y.; Sun, Z. The relationships between stress, mental disorders, and epigenetic regulation of BDNF. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purdy, R.H.; Morrow, A.L.; Moore, P.H., Jr.; Paul, S.M. Stress-induced elevations of gamma-aminobutyric acid type A receptor-active steroids in the rat brain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 4553–4557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sze, Y.; Gill, A.C.; Brunton, P.J. Sex-dependent changes in neuroactive steroid concentrations in the rat brain following acute swim stress. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2018, 30, e12644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akk, G.; Shu, H.J.; Wang, C.; Steinbach, J.H.; Zorumski, C.F.; Covey, D.F.; Mennerick, S. Neurosteroid access to the GABAA receptor. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 11605–11613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bali, A.; Jaggi, A.S. Multifunctional aspects of ALLO in stress and related disorders. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2014, 48, 64–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misztal, T.; Młotkowska, P.; Marciniak, E.; Misztal, A. Allopregnanolone reduces neuroendocrine response to acute stressful stimuli in sheep. J. Endocrinol. 2020, 244, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chrousos, G.P.; Gold, P.W. The concepts of stress and stress system disorders. Overview of physical and behavioral homeostasis. JAMA 1992, 267, 1244–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodman, R.L. Chapter 47: Neuroendocrine control of the ovine estrous cycle. In The Physiology of Reproduction, 2nd ed.; Knobil, E., Neill, J.D., Eds.; Raven Press, Ltd.: New York, NY, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, M.; Krishnamoorthy, V.R.; Kim, S.; Khurana, S.; LaPorte, H.M. Brainderived neuerotrophic factor and related mechanisms that mediate and influence progesterone-induced neuroprotection. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1286066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrientos, R.M.; Sprunger, D.B.; Campeau, S.; Higgins, E.A.; Watkins, L.R.; Rudy, J.W.; Maier, S.F. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor mRNA downregulation produced by social isolation is blocked by intrahippocampal interleukin-1 receptor antagonist. Neuroscience 2003, 121, 847–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, A.; Bellisario, V.; Capoccia, S.; Tirassa, P.; Calza, A.; Alleva, E.; Cirulli, F. Social deprivation stress is a triggering factor for the emergence of anxiety- and depression-like behaviours and leads to reduced brain BDNF levels in C57BL/6J mice. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2012, 37, 762–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.; Saruta, J.; Sasaguri, K.; Sato, S.; Tsukinoki, K. Allowing animals to bite reverses the effects of immobilization stress on hippocampal neurotrophin expression. Brain Res. 2008, 1195, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshminarasimhan, H.; Chattarji, S. Stress leads to contrasting effects on the levels of brain derived neurotrophic factor in the hippocampus and amygdala. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marmigère, F.; Givalois, L.; Rage, F.; Arancibia, S.; Tapia-Arancibia, L. Rapid induction of BDNF expression in the hippocampus during immobilization stress challenge in adult rats. Hippocampus 2003, 13, 646–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lessmann, V.; Gottmann, K.; Heumann, R. BDNF and NT-4/5 enhance glutamatergic synaptic transmission in cultured hippocampal neurones. NeuroReport 1994, 6, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, N.; Yamada, M.; Numakawa, T.; Ogura, A.; Hatanaka, H. BDNF potentiates spontaneous Ca2+ oscillations in cultured hippocampal neurons. Brain Res. 1997, 778, 318–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funder, J.W. Glucocorticoid and mineralocorticoid receptors: Biology and clinical relevance. Ann. Rev. Med. 1997, 48, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jankord, R.; Herman, J.P. Limbic regulation of hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenocortical function during acute and chronic stress. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2008, 1148, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitchener, P.; Di Blasi, F.; Borrelli, E.; Piazza, P.V. Differences between brain structures in nuclear translocation and DNA binding of the glucocorticoid receptor during stress and the circadian cycle. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2004, 19, 1837–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Revest, J.M.; Le Roux, A.; Roullot-Lacarrière, V.; Kaouane, N.; Vallée, M.; Kasanetz, F.; Rougé-Pont, F.; Tronche, F.; Desmedt, A.; Piazza, P.V. BDNF-TrkB signaling through Erk1/2 MAPK phosphorylation mediates the enhancement of fear memory induced by glucocorticoids. Mol. Psychiatry 2014, 19, 1001–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arango-Lievano, M.; Lambert, W.M.; Bath, K.G.; Garabedian, M.J.; Chao, M.V.; Jeanneteau, F. Neurotrophic-priming of glucocorticoid receptor signaling is essential for neuronal plasticity to stress and antidepressant treatment. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 15737–15742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, A.B.; Montgomery, K.; Bale, T.L.; Thompson, S.M. What the hippocampus tells the HPA axis: Hippocampal output attenuates acute stress responses via disynaptic inhibition of CRF+ PVN neurons. Neurobiol. Stress 2022, 20, 100473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.A.; Makino, S.; Kvetnansky, R.; Post, R.M. Stress and glucocorticoids affect the expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and neurotrophin-3 mRNAs in the hippocampus. J. Neurosci. 1995, 15, 1768–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueyama, T.; Kawai, Y.; Nemoto, K.; Sekimoto, M.; Toné, S.; Senba, E. Immobilization stress reduced the expression of neurotrophins and their receptors in the rat brain. Neurosci. Res. 1997, 28, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drake, C.T.; Milner, T.A.; Patterson, S.L. Ultrastructural localization of full-length trkB immunoreactivity in rat hippocampus suggests multiple roles in modulating activity-dependent synaptic plasticity. J. Neurosci. 1999, 19, 8009–8026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, D.R.; Miller, F.D. Neurotrophin signal transduction in the nervous system. Curr. Opin.Neurobiol. 2000, 10, 381–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miranda, M.; Morici, J.F.; Zanoni, M.B.; Bekinschtein, P. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor: A key molecule for memory in the healthy and the pathological brain. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McEwen, B.S. Stress and hippocampal plasticity. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 1999, 22, 105–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyer, M.M.; Shaw, G.A.; Goswamee, P.; Dyer, S.K.; Burns, C.M.; Soriano, E.; Sanchez, C.S.; Rowson, S.A.; McQuiston, A.R.; Neigh, G.N. Chronic adolescent stress causes sustained impairment of cognitive flexibility and hippocampal synaptic strength in female rats. Neurobiol. Stress 2021, 14, 100303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radecki, D.T.; Brown, L.M.; Martinez, J.; Teyler, T.J. BDNF protects against stress-induced impairments in spatial learning and memory and LTP. Hippocampus 2005, 15, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, H.G.; Dickinson-Anson, H.; Gage, F.H. Neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus of the adult rat: Age-related decrease of neuronal progenitor proliferation. J. Neurosci. 1996, 16, 2027–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eriksson, P.S.; Perfilieva, E.; Bjork-Eriksson, T.; Alborn, A.-M.; Nordborg, C.; Peterson, D.A.; Gage, F.H. Neurogenesis in the adult human hippocampus. Nat. Med. 1998, 4, 1313–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lévy, F.; Batailler, M.; Meurisse, M.; Migaud, M. Adult Neurogenesis in Sheep: Characterization and Contribution to Reproduction and Behavior. Front. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirescu, C.; Gould, E. Stress and adult neurogenesis. Hippocampus 2006, 16, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bath, K.G.; Mandairon, N.; Jing, D.; Rajagopal, R.; Kapoor, R.; Chen, Z.Y.; Khan, T.; Proenca, C.C.; Kraemer, R.; Cleland, T.A.; et al. Variant brain-derived neurotrophic factor (Val66Met) alters adult olfactory bulb neurogenesis and spontaneous olfactory discrimination. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 2383–2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergami, M.; Rimondini, R.; Santi, S.; Blum, R.; Gotz, M.; Canossa, M. Deletion of TrkB in adult progenitors alters newborn neuron integration into hippocampal circuits and increases anxiety-like behavior. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 15570–15575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molendijk, M.L.; Bus, B.A.; Spinhoven, P.; Penninx, B.W.; Kenis, G.; Prickaerts, J.; Voshaar, R.O.; Elzinga, B.M. Serum levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in major depressive disorder: State-trait issues, clinical features and pharmacological treatment. Mol. Psych. 2010, 16, 1088–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duman, R.S.; Aghajanian, G.K.; Sanacora, G.; Krystal, J.H. Synaptic plasticity and depression: New insights from stress and rapid-acting antidepressants. Nat. Med. 2016, 22, 238–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunton, P.J. Neuroactive steroids and stress axis regulation: Pregnancy and beyond. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2016, 160, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelkey, K.A.; Chittajallu, R.; Craig, M.T.; Tricoire, L.; Wester, J.C.; McBain, C.J. Hippocampal GABAergic inhibitory interneurons. Physiol. Rev. 2017, 97, 1619–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naert, G.; Maurice, T.; Tapia-Arancibia, L.; Givalois, L. Neuroactive steroids modulate HPA axis activity and cerebral brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) protein levels in adult male rats. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2007, 32, 1062–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, G.; Hojo, Y.; Kato, A.; Komatsuzaki, Y.; Horie, S.; Soma, M.; Kim, J.; Kawato, S. Rapid nongenomic modulation by neurosteroids of dendritic spines in the hippocampus: Androgen, oestrogen and corticosteroid. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2018, 30, e12561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strzetelski, J. IZ PIB–INRA Feeding Recommendations for Ruminants and Feed Tables; IZ PIB-INRA: Krakow, Poland, 2014. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Traczyk, W.; Przekop, F. Methods of investigation of the function of the hypothalamus and hypophysis in chronic experiments in sheep. Acta Physiol. Pol. 1963, 14, 217–226. [Google Scholar]
- Welento, J.; Szteyn, S.; Milart, Z. Observations on the stereotaxic configuration of the hypothalamus nuclei in the sheep. Anat. Anz. 1969, 124, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Misztal, T.; Górski, K.; Tomaszewska-Zaremba, D.; Fülöp, F.; Romanowicz, K. Effects of a structural analogue of salsolinol, 1-MeDIQ, on pituitary prolactin release and dopaminergic activity in the mediobasal hypothalamus in nursing sheep. Brain Res. 2010, 1307, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misztal, T.; Kowalczyk, P.; Młotkowska, P.; Marciniak, E. The effect of ALLO on enzymatic activity of the DNA base excision repair pathway in the sheep hippocampus and amygdala under natural and stressful conditions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roszkowicz-Ostrowska, K.; Młotkowska, P.; Kowalczyk, P.; Marciniak, E.; Barszcz, M.; Misztal, T. Central stimulatory effect of kynurenic acid on BDNF-TrkB signaling and BER enzymatic activity in the hippocampal CA1 field in sheep. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfaffl, M.W.; Horgan, G.W.; Dempfle, L. Relative Expression Software Tool (REST) for group-wise comparison and statistical analysis of relative expression results in real-time PCR. Nucl. Acids Res. 2002, 30, e36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfaffl, M.W.; Tichopad, A.; Prgomet, C.; Neuvians, T.P. Determination of stable housekeeping genes, differentially regulated target genes and sample integrity: BestKeeper—Excel-based tool using pair-wise correlations. Biotechno. Lett. 2004, 26, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Młotkowska, P.; Marciniak, E.; Roszkowicz-Ostrowska, K.; Misztal, T. Effects of allopregnanolone on central reproductive functions in sheep under natural and stressful conditions. Theriogenology 2020, 158, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Gene | Primers (5′–3′) | Genbank Acc. No. | Amplicon Size |
|---|---|---|---|
| BDNF | F: CGTTGGCTGACACTTTTGAA R: CGCAGCATCCAGGTAATTTT | XM_012143442.1 | 188 |
| NGF | F: CAGTCCAAGGGGCTGGAT R: AGTGTGGCCAGGACAGAAAG | XM_004002369.5 | 101 |
| NT3 | F: TGCCACGATCTTACAGGTGA R: TGCCTGGATCAGCTTGATTA | XM_004006944.5 | 151 |
| NT4 | F: CCTGAGATGTCACGAAGGAC R: TGAACACCTGTCAGCACCTC | XM_027978595.3 | 112 |
| TRKB | F: TGTCTGAGCTGATCCTGGTG R: TATCTGCAGGTTTGCCAGTG | XM_012117231.2 | 155 |
| GAPDH | F: GGGTCATCATCTCTGCACCT R: GGTCATAAGTCCCTCCACGA | NM_001190390.1 | 131 |
| PPIC | F: TGGAAAAGTCGTGCCCAAGA R: TGCTTATACCACCAGTGCCA | XM_004008676.1 | 158 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Misztal, T.; Młotkowska, P.; Marciniak, E.; Barszcz, M.; Osuch, B.; Gajewska, A.; Misztal, A. Effects of Stress and Allopregnanolone on the Expression of Neurotrophins and TrkB Receptor in the Sheep Hippocampus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6190. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136190
Misztal T, Młotkowska P, Marciniak E, Barszcz M, Osuch B, Gajewska A, Misztal A. Effects of Stress and Allopregnanolone on the Expression of Neurotrophins and TrkB Receptor in the Sheep Hippocampus. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(13):6190. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136190
Chicago/Turabian StyleMisztal, Tomasz, Patrycja Młotkowska, Elżbieta Marciniak, Marcin Barszcz, Bartosz Osuch, Alina Gajewska, and Anna Misztal. 2025. "Effects of Stress and Allopregnanolone on the Expression of Neurotrophins and TrkB Receptor in the Sheep Hippocampus" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 13: 6190. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136190
APA StyleMisztal, T., Młotkowska, P., Marciniak, E., Barszcz, M., Osuch, B., Gajewska, A., & Misztal, A. (2025). Effects of Stress and Allopregnanolone on the Expression of Neurotrophins and TrkB Receptor in the Sheep Hippocampus. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(13), 6190. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136190







