Extracellular Vesicles Released by Bovine Alphaherpesvirus 1-Infected A549 Cells May Limit Subsequent Infections of the Progeny Virus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
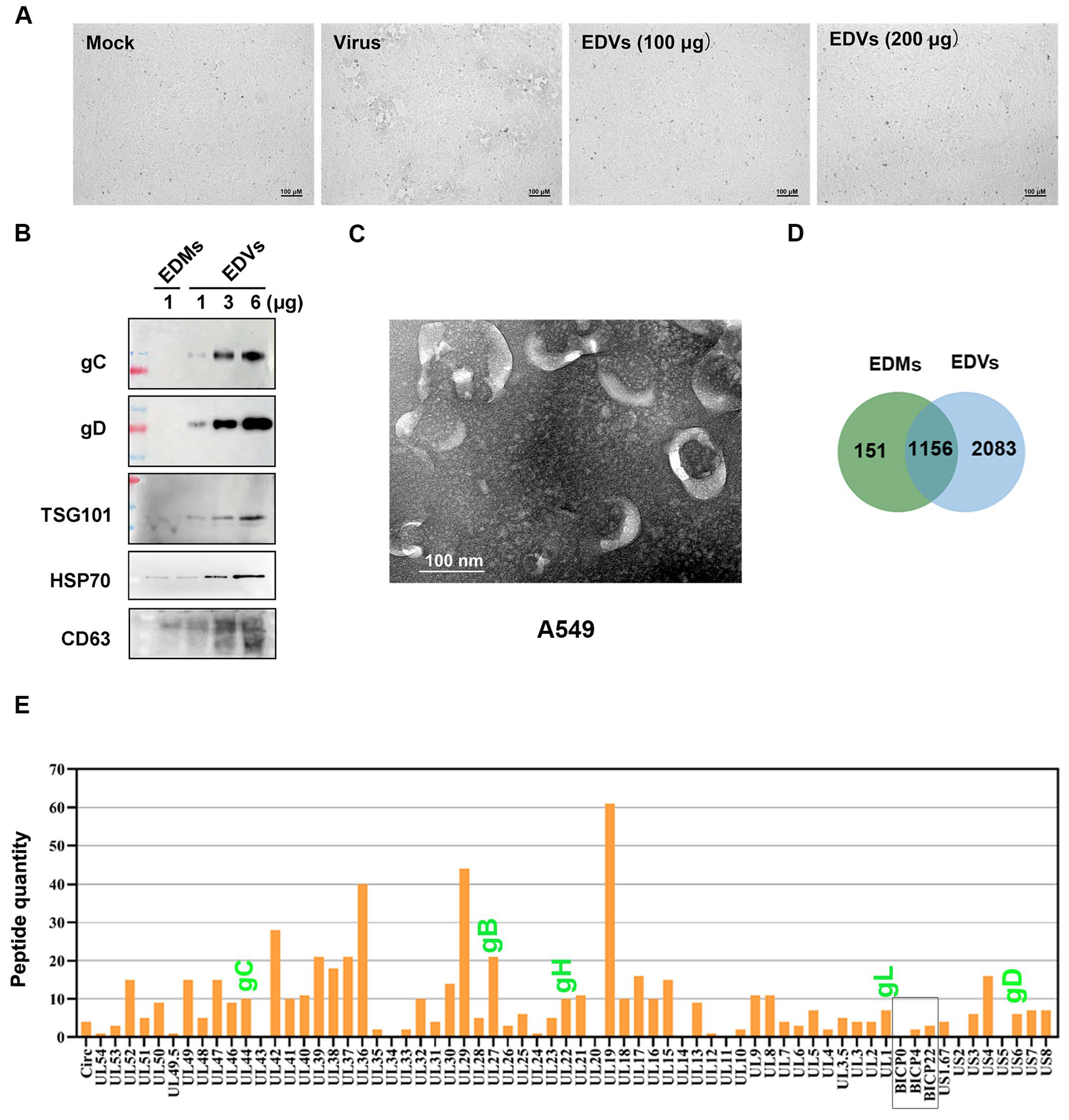
2.1. Extracellular Vesicles (EDVs) Derived from BoAHV-1-Infected A549 Cells Contain a Variety of Viral Proteins
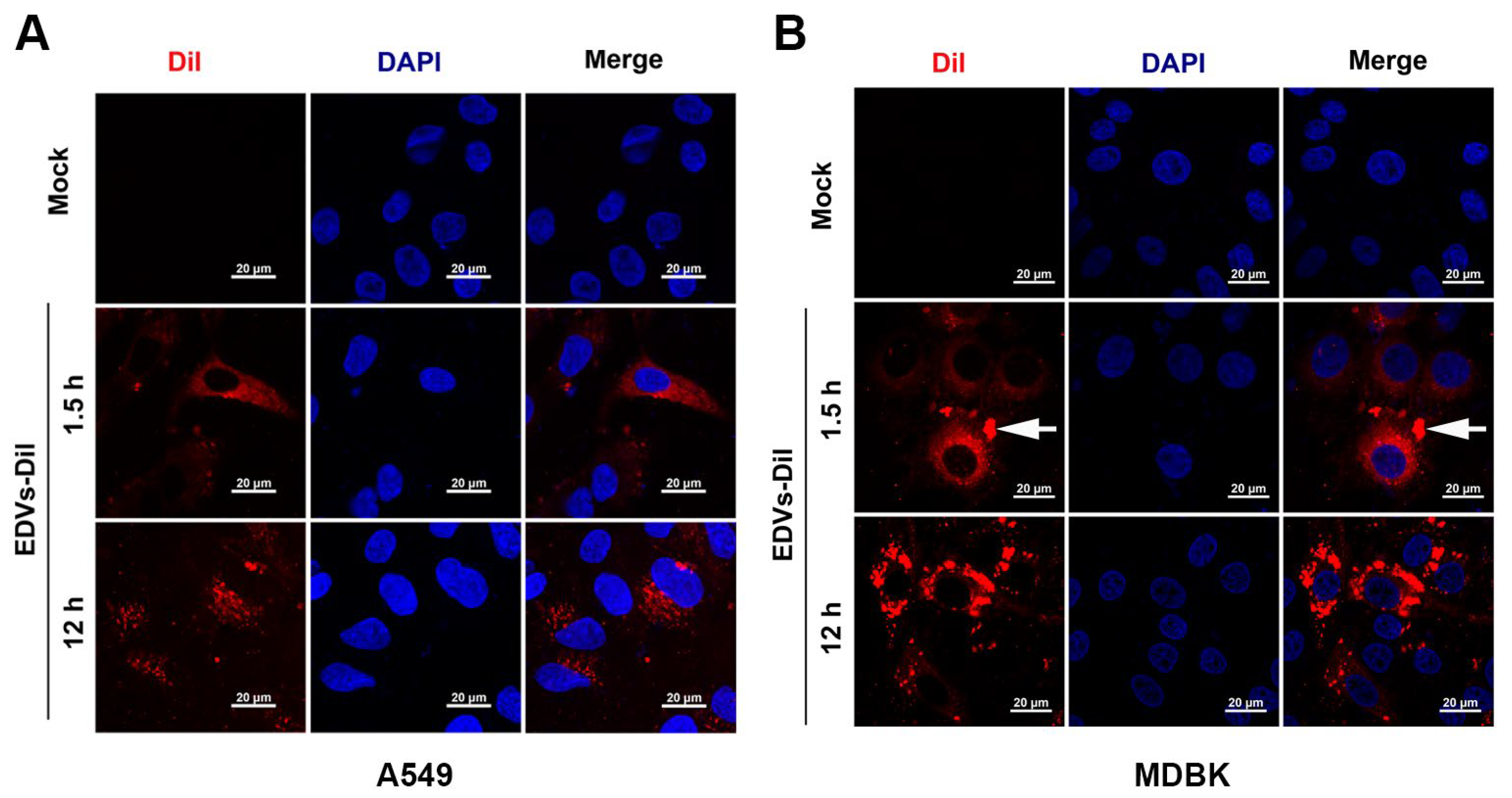
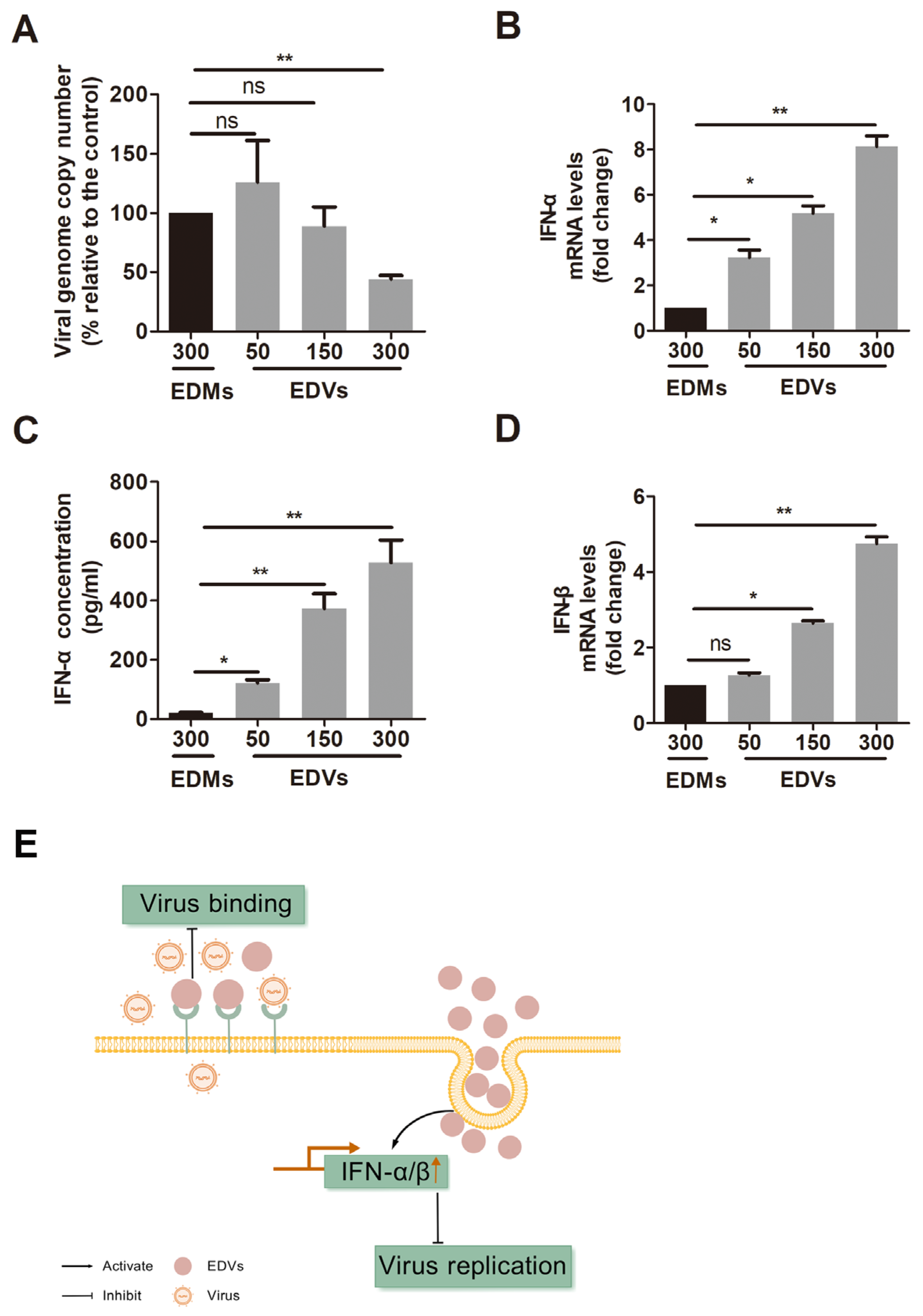
2.2. EDVs Can Be Internalized into Various Target Cells and Induce Production of Type I Interferons Such as INF-α and IFN-β
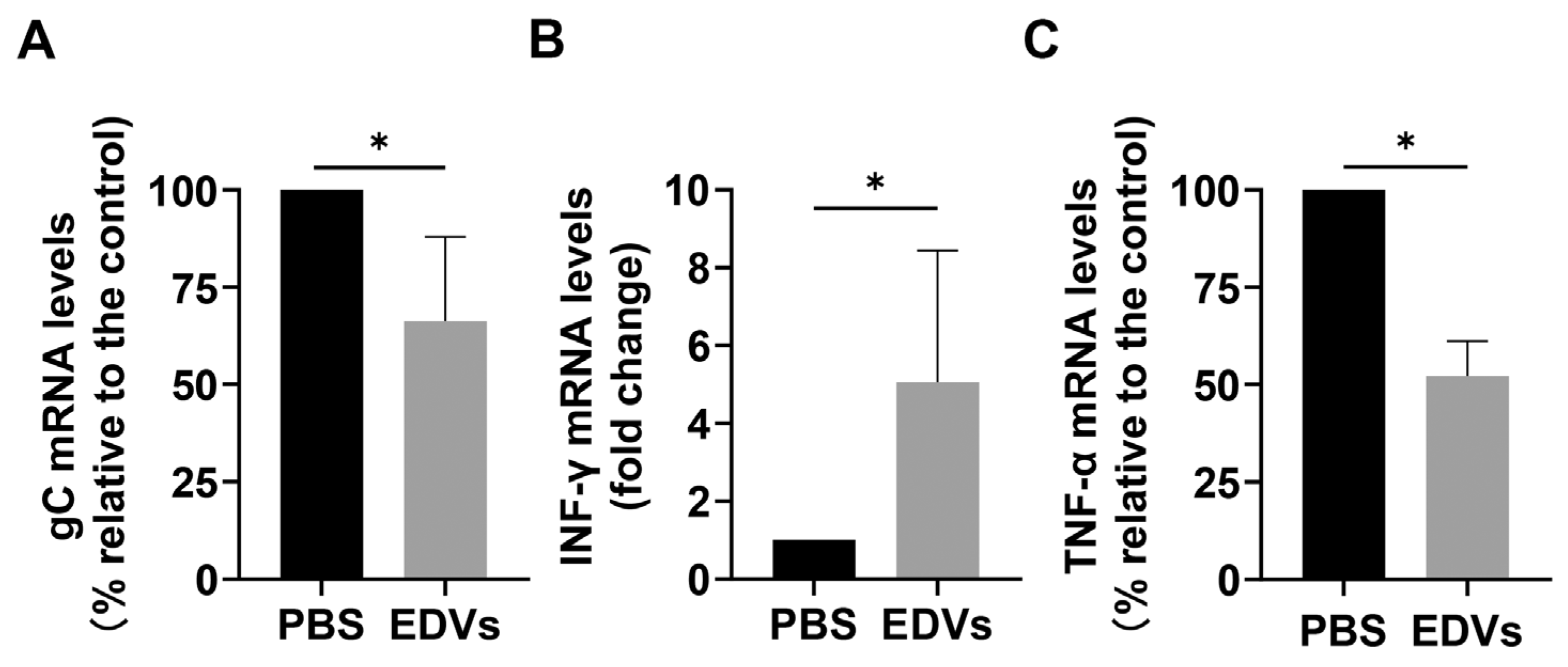
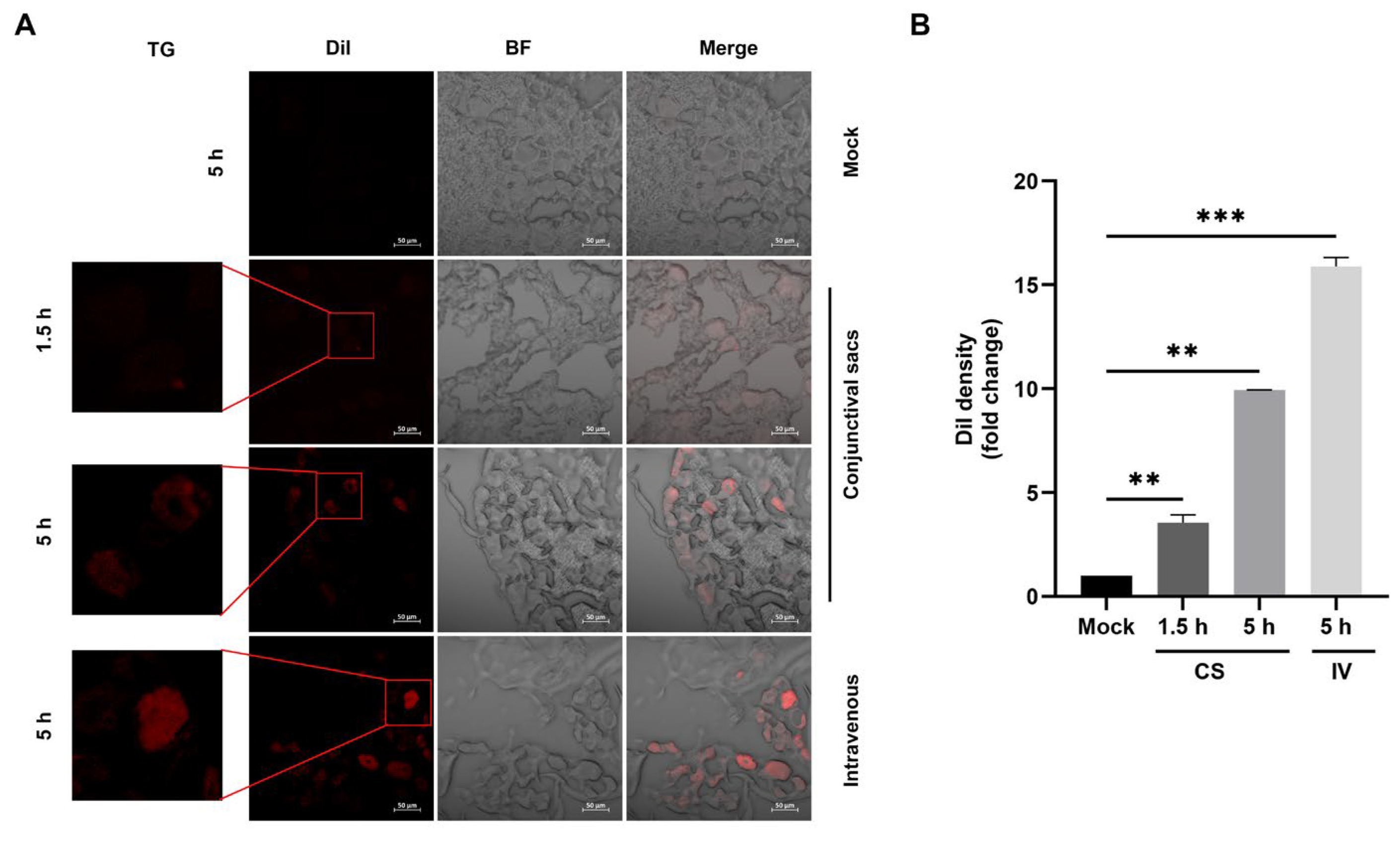
2.3. EDVs Can Be Delivered into TG Neurons and Have the Capacity to Disrupt Virus Productive Infection In Vivo Partially via the Enhanced Induction of INF-γ
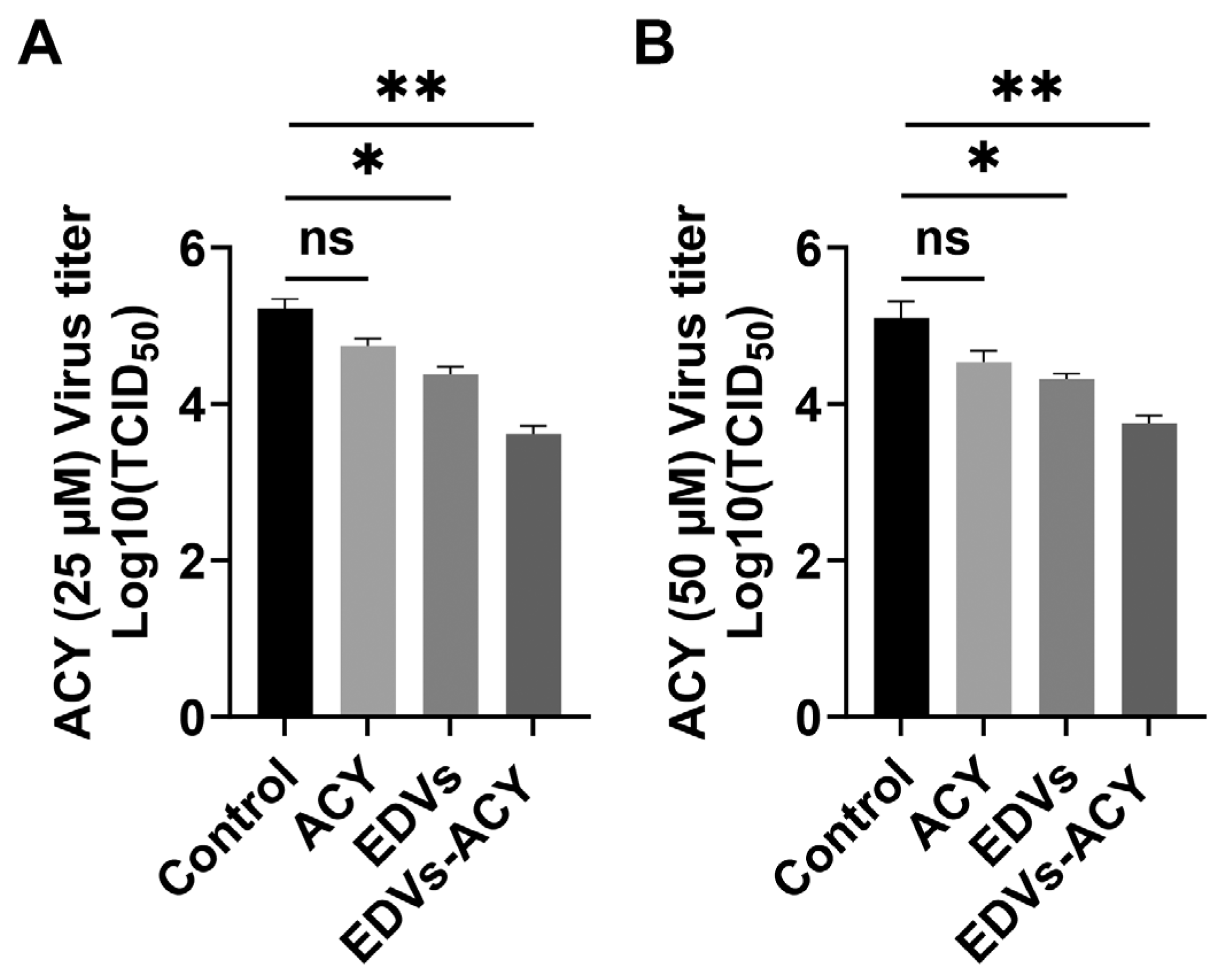
2.4. EDVs Enhance the Antiviral Effects of Acyclovir In Vitro
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cells and Virus
4.2. Antibodies and Chemicals
4.3. Isolation of EVs
4.4. Western Blot Analysis
4.5. Detection of EVs via Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
4.6. Detection of EDV Internalization by Target Cells
4.7. RNA Isolation and Quantification of mRNA via RT-qPCR
4.8. Detection of Released IFN-α with ELISA
4.9. Animal Experiment
4.10. Detection of Internalized Dil-Labeled EDVs in Neurons from the TG
4.11. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tikoo, S.K.; Campos, M.; Babiuk, L.A. Bovine herpesvirus 1 (BHV-1): Biology, pathogenesis, and control. Adv. Virus Res. 1995, 45, 191–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrini, S.; Iscaro, C.; Righi, C. Antibody Responses to Bovine Alphaherpesvirus 1 (BoHV-1) in Passively Immunized Calves. Viruses 2019, 11, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddell, S.G.; Smith, D.B.; Adriaenssens, E.; Alfenas-Zerbini, P.; Dutilh, B.E.; Garcia, M.L.; Junglen, S.; Krupovic, M.; Kuhn, J.H.; Lambert, A.J.; et al. Virus taxonomy and the role of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV). J. Gen. Virol. 2023, 104, 001840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, S.I.; Coats, J.; Neis, R.A.; Navarro, S.M.; Paulsen, D.B.; Feng, J.M. A bovine herpesvirus type 1 mutant virus with truncated glycoprotein E cytoplasmic tail has defective anterograde neuronal transport in rabbit dorsal root ganglia primary neuronal cultures in a microfluidic chamber system. J. Neurovirol. 2010, 16, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rock, D.L.; Beam, S.L.; Mayfield, J.E. Mapping bovine herpesvirus type 1 latency-related RNA in trigeminal ganglia of latently infected rabbits. J. Virol. 1987, 61, 3827–3831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, R.; Cuddington, B.; Mossman, K. Bovine herpesvirus type 1 as a novel oncolytic virus. Cancer Gene Ther. 2010, 17, 344–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baracuhy, E.M.; Cormier, O.; Davola, M.E.; Collins, S.; Mossman, K. Virus replication is not required for oncolytic bovine herpesvirus-1 immunotherapy. Mol. Ther. Oncol. 2024, 32, 200906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuddington, B.P.; Dyer, A.L.; Workenhe, S.T.; Mossman, K.L. Oncolytic bovine herpesvirus type 1 infects and kills breast tumor cells and breast cancer-initiating cells irrespective of tumor subtype. Cancer Gene Ther. 2013, 20, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, W.; Ding, X.; Li, S.; He, Y.; Zhu, L. Oncolytic Bovine Herpesvirus 1 Inhibits Human Lung Adenocarcinoma A549 Cell Proliferation and Tumor Growth by Inducing DNA Damage. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Bi, J.; Huang, J.; Tang, Y.; Du, S.; Li, P. Exosome: A Review of Its Classification, Isolation Techniques, Storage, Diagnostic and Targeted Therapy Applications. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 6917–6934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Yang, Y.; Li, Y.; Shi, T.; Luan, Y.; Yin, C. Exosome and virus infection. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1154217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robado de Lope, L.; Sanchez-Herrero, E.; Serna-Blasco, R.; Provencio, M.; Romero, A. Cancer as an infective disease: The role of EVs in tumorigenesis. Mol. Oncol. 2023, 17, 390–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaser, M.C.; Buffolo, F.; Halu, A.; Turner, M.E.; Schlotter, F.; Higashi, H.; Pantano, L.; Clift, C.L.; Saddic, L.A.; Atkins, S.K.; et al. Multiomics of Tissue Extracellular Vesicles Identifies Unique Modulators of Atherosclerosis and Calcific Aortic Valve Stenosis. Circulation 2023, 148, 661–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.; Yang, J.; Sun, J.; Qin, G. Extracellular vesicles in cardiovascular disease: Biological functions and therapeutic implications. Pharmacol. Ther. 2022, 233, 108025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giro, O.; Jimenez, A.; Pane, A.; Badimon, L.; Ortega, E.; Chiva-Blanch, G. Extracellular vesicles in atherothrombosis and cardiovascular disease: Friends and foes. Atherosclerosis 2021, 330, 61–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Nader, M.A.; Deep, G. Emergence of Extracellular Vesicles as “Liquid Biopsy” for Neurological Disorders: Boom or Bust. Pharmacol. Rev. 2024, 76, 199–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Han, Q.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, J. The Mechanisms of HBV-Induced Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Hepatocell. Carcinoma 2021, 8, 435–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, S.; Wu, S.; Chen, L. Exosomes Modulate the Viral Replication and Host Immune Responses in HBV Infection. Biomed. Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 2103943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, X.; Jia-Yin, Y.; Jun-Yang, H.; Rui, W.; Xiong-Ri, K.; Long-Rui, D.; Liu, J.; Jue-Yu, Z. Comprehensive analysis of lncRNA-mRNA co-expression networks in HPV-driven cervical cancer reveals the pivotal function of LINC00511-PGK1 in tumorigenesis. Comput. Biol. Med. 2023, 159, 106943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadri Nahand, J.; Bokharaei-Salim, F.; Salmaninejad, A.; Nesaei, A.; Mohajeri, F.; Moshtzan, A.; Tabibzadeh, A.; Karimzadeh, M.; Moghoofei, M.; Marjani, A.; et al. microRNAs: Key players in virus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 12188–12225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Huang, C.K.; Yu, H.; Shen, B.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, Y.; Li, Z.; Feng, X.; Zhao, J.; Duan, L.; et al. The role of exosomes in hepatitis, liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2017, 21, 986–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, J.; Yang, L.; Nan, X.; Zhu, S.; Yan, M.; Xiang, S.; Zhang, L.; Li, Q.; Yang, C.; Wang, X.; et al. Extracellular vesicles promote the infection and pathogenicity of Japanese encephalitis virus. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2025, 14, e70033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barberis, E.; Vanella, V.V.; Falasca, M.; Caneapero, V.; Cappellano, G.; Raineri, D.; Ghirimoldi, M.; De Giorgis, V.; Puricelli, C.; Vaschetto, R.; et al. Circulating Exosomes Are Strongly Involved in SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8, 632290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grabowska, K.; Wachalska, M.; Graul, M.; Rychlowski, M.; Bienkowska-Szewczyk, K.; Lipinska, A.D. Alphaherpesvirus gB Homologs Are Targeted to Extracellular Vesicles, but They Differentially Affect MHC Class II Molecules. Viruses 2020, 12, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogrammatzis, C.; Saleh, S.; Deighan, C.; Kalamvoki, M. Diverse Populations of Extracellular Vesicles with Opposite Functions during Herpes Simplex Virus 1 Infection. J. Virol. 2021, 95, e02357-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalamvoki, M.; Deschamps, T. Extracellular vesicles during Herpes Simplex Virus type 1 infection: An inquire. Virol. J. 2016, 13, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, M.; Heydarkhan-Hagvall, S.; Tangruksa, B.; Gonzalez-King Garibotti, H.; Jing, Y.; Maugeri, M.; Kohl, F.; Hultin, L.; Reyahi, A.; Camponeschi, A.; et al. Lipid Nanoparticles Deliver the Therapeutic VEGFA mRNA In Vitro and In Vivo and Transform Extracellular Vesicles for Their Functional Extensions. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, e2206187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Liu, N.; Wu, W.; Li, H.; Lu, W.; Guo, X. Umbilical Cord Blood-Derived M1 Macrophage Exosomes Loaded with Cisplatin Target Ovarian Cancer In Vivo and Reverse Cisplatin Resistance. Mol. Pharm. 2023, 20, 5440–5453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attem, J.; Narayana, R.V.L.; Manukonda, R.; Kaliki, S.; Vemuganti, G.K. Small extracellular vesicles loaded with carboplatin effectively enhance the cytotoxicity of drug-resistant cells from Y79 cells-in vitro. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 173, 116403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Ding, Y.; Huang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, W.; Tang, Q.; An, Y.; Chen, R.; Hu, C. Angiopep-2 Modified Exosomes Load Rifampicin with Potential for Treating Central Nervous System Tuberculosis. Int. J. Nanomed. 2023, 18, 489–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, R.C.; Tan, S.S.; Yeo, R.W.Y.; Choo, A.B.H.; Reiner, A.T.; Su, Y.; Shen, Y.; Fu, Z.Y.; Alexander, L.; Sze, S.K.; et al. MSC secretes at least 3 EV types each with a unique permutation of membrane lipid, protein and RNA. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2016, 5, 29828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greening, D.W.; Xu, R.; Ji, H.; Tauro, B.J.; Simpson, R.J. A protocol for exosome isolation and characterization: Evaluation of ultracentrifugation, density-gradient separation, and immunoaffinity capture methods. Methods Mol. Biol. 2015, 1295, 179–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastenkos, G.; Lee, B.; Pritchard, S.M.; Nicola, A.V. Bovine Herpesvirus 1 Entry by a Low-pH Endosomal Pathway. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e00839-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwyzer, M.; Vlcek, C.; Menekse, O.; Fraefel, C.; Paces, V. Promoter, spliced leader, and coding sequence for BICP4, the largest of the immediate-early proteins of bovine herpesvirus 1. Virology 1993, 197, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toomer, G.; Workman, A.; Harrison, K.S.; Stayton, E.; Hoyt, P.R.; Jones, C. Stress Triggers Expression of Bovine Herpesvirus 1 Infected Cell Protein 4 (bICP4) RNA during Early Stages of Reactivation from Latency in Pharyngeal Tonsil. J. Virol. 2022, 96, e0101022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connolly, S.A.; Jardetzky, T.S.; Longnecker, R. The structural basis of herpesvirus entry. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasika, G.K.; Letchworth, G.J., 3rd. Cellular expression of bovine herpesvirus 1 gD inhibits cell-to-cell spread of two closely related viruses without blocking their primary infection. Virology 1999, 254, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Reske, A.; Pollara, G.; Krummenacher, C.; Chain, B.M.; Katz, D.R. Understanding HSV-1 entry glycoproteins. Rev. Med. Virol. 2007, 17, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, D.; Chen, Z.; Yang, F.; Ye, F.; Lin, S.; He, B.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, J.; Chen, Z.; Lin, X.; et al. Crystal structure of bovine herpesvirus 1 glycoprotein D bound to nectin-1 reveals the basis for its low-affinity binding to the receptor. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaba5147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Q.; Longnecker, R.; Connolly, S.A. Substitution of herpes simplex virus 1 entry glycoproteins with those of saimiriine herpesvirus 1 reveals a gD-gH/gL functional interaction and a region within the gD profusion domain that is critical for fusion. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 6470–6482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalluri, R. The biology and function of extracellular vesicles in immune response and immunity. Immunity 2024, 57, 1752–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deschamps, T.; Kalamvoki, M. Extracellular Vesicles Released by Herpes Simplex Virus 1-Infected Cells Block Virus Replication in Recipient Cells in a STING-Dependent Manner. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e01102-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemaire, M.; Weynants, V.; Godfroid, J.; Schynts, F.; Meyer, G.; Letesson, J.J.; Thiry, E. Effects of bovine herpesvirus type 1 infection in calves with maternal antibodies on immune response and virus latency. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2000, 38, 1885–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abril, C.; Engels, M.; Liman, A.; Hilbe, M.; Albini, S.; Franchini, M.; Suter, M.; Ackermann, M. Both viral and host factors contribute to neurovirulence of bovine herpesviruses 1 and 5 in interferon receptor-deficient mice. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 3644–3653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, R.; Gonzalez-Cano, P.; Brownlie, R.; Griebel, P.J. Induction of interferon and interferon-induced antiviral effector genes following a primary bovine herpesvirus-1 (BHV-1) respiratory infection. J. Gen. Virol. 2017, 98, 1831–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Mayet, F.S.; Sawant, L.; Wijesekera, N.; Jones, C. Progesterone increases the incidence of bovine herpesvirus 1 reactivation from latency and stimulates productive infection. Virus Res. 2020, 276, 197803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Ren, L.; Li, S.; Li, W.; Zheng, X.; Yang, Y.; Fu, W.; Yi, J.; Wang, J.; Du, G. The biology, function, and applications of exosomes in cancer. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2021, 11, 2783–2797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Andaloussi, S.; Lee, Y.; Lakhal-Littleton, S.; Li, J.; Seow, Y.; Gardiner, C.; Alvarez-Erviti, L.; Sargent, I.L.; Wood, M.J. Exosome-mediated delivery of siRNA in vitro and in vivo. Nat. Protoc. 2012, 7, 2112–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.S.; Haney, M.J.; Zhao, Y.; Mahajan, V.; Deygen, I.; Klyachko, N.L.; Inskoe, E.; Piroyan, A.; Sokolsky, M.; Okolie, O.; et al. Development of exosome-encapsulated paclitaxel to overcome MDR in cancer cells. Nanomedicine 2016, 12, 655–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, C.; Li, R.; Chen, H.; Chen, D.; Li, W. Exosomes in HIV infection. Curr. Opin. HIV AIDS 2021, 16, 262–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Shennawy, L.; Hoffmann, A.D.; Dashzeveg, N.K.; McAndrews, K.M.; Mehl, P.J.; Cornish, D.; Yu, Z.; Tokars, V.L.; Nicolaescu, V.; Tomatsidou, A.; et al. Circulating ACE2-expressing extracellular vesicles block broad strains of SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geraghty, R.J.; Krummenacher, C.; Cohen, G.H.; Eisenberg, R.J.; Spear, P.G. Entry of alphaherpesviruses mediated by poliovirus receptor-related protein 1 and poliovirus receptor. Science 1998, 280, 1618–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, Y.; Koike, M.; Moriishi, E.; Kawabata, A.; Tang, H.; Oyaizu, H.; Uchiyama, Y.; Yamanishi, K. Human herpesvirus-6 induces MVB formation, and virus egress occurs by an exosomal release pathway. Traffic 2008, 9, 1728–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meckes, D.G., Jr.; Gunawardena, H.P.; Dekroon, R.M.; Heaton, P.R.; Edwards, R.H.; Ozgur, S.; Griffith, J.D.; Damania, B.; Raab-Traub, N. Modulation of B-cell exosome proteins by gamma herpesvirus infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, E2925–E2933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meckes, D.G., Jr.; Shair, K.H.; Marquitz, A.R.; Kung, C.P.; Edwards, R.H.; Raab-Traub, N. Human tumor virus utilizes exosomes for intercellular communication. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 20370–20375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalamvoki, M. HSV-1 virions and related particles: Biogenesis and implications in the infection. J. Virol. 2025, 99, e0107624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Yu, Y.; Jiang, X.; Yuan, W.; Zhu, G. First report of bovine herpesvirus 1 isolation from bull semen samples in China. Acta Virol. 2017, 61, 483–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karger, A.; Bettin, B.; Granzow, H.; Mettenleiter, T.C. Simple and rapid purification of alphaherpesviruses by chromatography on a cation exchange membrane. J. Virol. Methods 1998, 70, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanotti, S.; Magri, F.; Poggetti, F.; Ripolone, M.; Velardo, D.; Fortunato, F.; Ciscato, P.; Moggio, M.; Corti, S.; Comi, G.P.; et al. Immunofluorescence signal intensity measurements as a semi-quantitative tool to assess sarcoglycan complex expression in muscle biopsy. Eur. J. Histochem. 2022, 66, 3418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Gene Name | Intensity EDMs | Intensity EDVs | Protein Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Circ | 1471470 | circ protein | |
| UL54 | 1782460 | UL54 protein GN = UL54 | |
| UL53 | 338753 | glycoprotein K GN = UL53 | |
| UL52 | 1431790 | component of DNA helicase/primase complex GN = UL52 | |
| UL51 | 919147 | virion protein GN = UL51 | |
| UL50 | 15733500 | deoxyuridine triphosphatase GN = UL50 | |
| UL49.5 | 3110740 | virion protein (membrane) GN = UL49.5 | |
| UL49 | 31395000 | virion protein (tegument) GN = UL49 | |
| UL48 | 12708800 | alpha-TIF protein GN = UL48 | |
| UL47 | 11379300 | virion protein (tegument GN = UL47 | |
| UL46 | 6599390 | virion protein (tegument) GN = UL46 | |
| UL44 | 10158900 | glycoprotein C GN = UL44 | |
| UL42 | 43852900 | 261308000 | processivity factor for DNA polymerase GN = UL42 |
| UL41 | 4411390 | virion host shutoff factor (tegument) GN = UL41 | |
| UL40 | 15975900 | ribonucleotide reductase small subunit GN = UL40 | |
| UL39 | 8403990 | ribonucleotide reductase large subunit GN = UL39 | |
| UL38 | 41214900 | capsid protein GN = UL38 | |
| UL37 | 811350 | 2325140 | virion protein (tegument) GN = UL37 |
| UL36 | 4044840 | very large virion protein (tegument) GN = UL36 | |
| UL35 | 7290220 | capsid protein GN = UL35 | |
| UL33 | 133690 | UL33 protein GN = UL33 | |
| UL32 | 3502420 | UL32 protein GN = UL32 | |
| UL31 | 3071340 | UL31 protein GN = UL31 | |
| UL30 | 1724140 | DNA polymerase GN = UL30 | |
| UL29 | 116502000 | major DNA binding protein GN = UL29 | |
| UL28 | 1123390 | ICP18.5 assembly protein GN = UL28 | |
| UL27 | 489268 | 2577140 | glycoprotein B GN = UL27 |
| UL26 | 1916690 | serine protease (capsid) GN = UL26 | |
| UL25 | 537027 | UL25 protein GN = UL25 | |
| UL24 | 325064 | virion protein GN = UL24 | |
| UL23 | 1908770 | thymidine kinase GN = UL23 | |
| UL22 | 1593410 | glycoprotein H GN = UL22 | |
| UL21 | 12896500 | virion protein GN = UL21 | |
| UL19 | 63436600 | major capsid protein GN = UL19 | |
| UL18 | 32282100 | capsid protein GN = UL18 | |
| UL15 | 3017310 | UL15 protein GN = UL15 | |
| UL17 | 5378610 | UL17 protein GN = UL17 | |
| UL16 | 12515300 | virion protein GN = UL16 | |
| UL13 | 1919140 | virion serine/threonine protein kinase GN = UL13 | |
| UL12 | 1651800 | deoxyribonuclease GN = UL12 | |
| UL10 | 122819 | glycoprotein M GN = UL10 | |
| UL9 | 6760560 | replication origin binding protein GN = UL9 | |
| UL8 | 2961340 | component of DNA helicase/primase complex GN = UL8 | |
| UL7 | 1563210 | UL7 protein GN = UL7 | |
| UL6 | 497820 | UL6 protein GN = UL6 | |
| UL5 | 2552160 | 1823880 | component of DNA helicase/primase complex GN = UL5 |
| UL4 | 2357470 | virion protein GN = UL4 | |
| UL3.5 | 6871300 | UL3.5 protein GN = UL3.5 | |
| UL3 | 2245320 | phosphoprotein GN = UL3 | |
| UL2 | 1734430 | uracil DNA glycosylase GN = UL2 | |
| UL1 | 1779770 | glycoprotein L GN = UL1 | |
| BICP4 | 302473 | immediate-early transactivator protein (cell nucleus) GN = BICP4 | |
| BICP22 | 1552040 | immediate-early and late transrepressor protein (cell nucleus) GN = BICP22 | |
| US1.67 | 4648000 | US1.67 protein GN = US1.67 | |
| US3 | 1863100 | virion serine/threonine protein kinase GN = US3 | |
| US4 | 761729 | 45762600 | glycoprotein G GN = US4 |
| US6 | 3996870 | glycoprotein D GN = US6 | |
| US7 | 4721730 | glycoprotein I GN = US7 | |
| US8 | 2426910 | glycoprotein E GN = US8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, Y.; Yang, H.; Huang, Y.; Goreham, R.V.; Ding, X.; Zhu, L. Extracellular Vesicles Released by Bovine Alphaherpesvirus 1-Infected A549 Cells May Limit Subsequent Infections of the Progeny Virus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6181. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136181
Luo Y, Yang H, Huang Y, Goreham RV, Ding X, Zhu L. Extracellular Vesicles Released by Bovine Alphaherpesvirus 1-Infected A549 Cells May Limit Subsequent Infections of the Progeny Virus. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(13):6181. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136181
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Yuanshan, Hao Yang, Yike Huang, Renee V. Goreham, Xiuyan Ding, and Liqian Zhu. 2025. "Extracellular Vesicles Released by Bovine Alphaherpesvirus 1-Infected A549 Cells May Limit Subsequent Infections of the Progeny Virus" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 13: 6181. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136181
APA StyleLuo, Y., Yang, H., Huang, Y., Goreham, R. V., Ding, X., & Zhu, L. (2025). Extracellular Vesicles Released by Bovine Alphaherpesvirus 1-Infected A549 Cells May Limit Subsequent Infections of the Progeny Virus. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(13), 6181. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136181






