Abstract
4-coumarate-CoA ligase (4CL) plays a crucial role in the phenylpropanoid metabolic pathway and is a key enzyme involved in plant growth and stress responses. Black rot, caused by Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris (Xcc) is a major bacterial disease affecting the production of global cruciferous crop-like cabbage (Brassica oleracea var. capitata). However, the role of 4CL genes in cabbage resistance to black rot remains unclear. In this study, transcriptome sequencing was conducted using resistant cabbage MY and susceptible cabbage LY at 0, 6, 24, and 48 h post-inoculation. KEGG analysis identified the enrichment of the phenylpropanoid biosynthesis pathway, and significant expression changes of 4CL genes were determined through the expression heat map. Further genome-wide analysis revealed 43 Bol4CL gene family members on the cabbage genome distributed across nine chromosomes. Gene structure and protein motif analysis revealed similarities in motifs within the same evolutionary branch, but variations in gene structure. A combination of Bol4CL gene expression profiles and differentially expressed genes (DEGs) from the transcriptome identified Bol4CL41 as a key gene for further study. Inoculation of overexpressed Bol4CL41 T2 generation stably expressed cabbage seedlings demonstrated significantly larger lesion areas compared to wild type cabbage, indicating that Bol4CL41 negatively regulates resistance to black rot in cabbage. The analysis of multi-time point transcriptomes in cabbage and the functional study of the Bol4CL gene family enhance our understanding of the mechanisms underlying plant disease resistance. This provides compelling evidence and experimental support for elucidating the mechanisms of black rot resistance in cabbage.
1. Introduction
Black rot (BR), caused by the bacterial pathogen Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris (Xcc), is a major disease affecting the production of cruciferous crops [1]. Due to the limited availability of resistance sources and a lack of clear understanding of the molecular mechanisms of disease resistance in cabbage, BR inflicts significant damage. Up to now, BR has spread worldwide, especially causing severe damage to cabbage and other cruciferous vegetables in Asia, Europe, and North America, leading to yield reductions exceeding 70% in severe cases [2,3,4,5]. BR is a vascular disease that mainly affects the leaves of the host plant, from the seedling stage to maturity. The pathogen can invade the plant through hydathodes, stomata, and wounds under suitable conditions of temperature and humidity, resulting in localized tissue necrosis. In severe cases, plant growth is stunted, leaves become brittle and dry, and the entire plant may wilt, die, and appear scorched [1,6,7]. Given the detrimental impact of BR on cabbage and other cruciferous vegetables, it is imperative to investigate the mechanisms of plant disease resistance.
The phenylpropanoid metabolic pathway is essential for plant survival, supplying plants with a large number of secondary metabolite precursors that contribute to growth, development, and resistance to external environmental factors [8]. The 4-coumarate-CoA ligase (4CL) is a key enzyme in this pathway, encoded by a multigene family in higher plants, with the number of gene members varying among different species [9]. Since the cloning of the first 4CL gene in 1981 [10], numerous 4CL and 4CL-like genes have been identified across various plant species. For example, in Arabidopsis, four 4CL genes and nine 4CL-like genes have been identified [11], five family members have been found in rice [12], and 20 family members in tobacco [9]. 4CL belongs to the adenosine monophosphate (AMP)-binding protein family [11]. Based on the functions of the proteins encoded by 4CL genes, 4CL can be divided into three subgroups. Class I is mainly involved in regulating the biosynthesis of plant lignin compounds, and Class II mainly regulates flavonoid formation [13]. Class III is 4CL-like, which has different gene functions from the first two subgroups, and lacks the ability to catalyze the formation of CoA esters from substrates [14].
4CL members affect plant growth, the biosynthesis of phenylpropanoid derivatives, and responses to environmental stress, effectively regulating and enhancing plant–environment interactions [15]. The 4CL gene family has been identified as a class of stress resistance genes [16], playing a crucial role when many plants are subjected to abiotic stresses. Ehlting et al. [17] found that overexpressing 4CL can enhance drought tolerance in Arabidopsis. Transcriptional profiling analyses indicated that the expression of 4CL2, 4CL11, and 4CL12 changed significantly in one or both desert poplars in response to salt stress compared to that in P. trichocarpa. It was hypothesized that the evolution of the 4CL genes may have promoted the development of both desert poplars [9]. Me4CL32 gene changes under various abiotic stresses (drought, salt, cold, heat) and hormone stimulation (GA3 and ABA), indicating that Me4CL32 can respond to both environmental stresses and hormonal signals [18]. The 4CL gene family also plays an important role under biotic stresses. After Arabidopsis was infected with downy mildew, the accumulation of AtCL1/2 mRNA was induced after 12 and 24 h, respectively [17]. When tomatoes were infected with Alternaria solani, the transcriptional levels of Sl4CL genes were found to be up-regulated [19]. These data suggest that in plants, 4CL plays a significant role in both biotic and abiotic stress responses.
Cabbage is one of the most important species in the Brassicaceae family [20], but its yield is severely affected by BR. Therefore, investigating the mechanisms of disease resistance in cabbage is of considerable importance. In this study, we analyzed the transcriptome data of extremely resistant and susceptible cabbage varieties at various stages after inoculation, focusing on the key enzyme 4CL in the phenylpropanoid synthesis pathway. We identified members of the 4CL gene family in cabbage and determined their phylogenetic relationships, conserved motifs, chromosomal locations, synteny, and expression profiles of the Bol4CL genes at different stages following inoculation. Notably, we identified Bol4CL41 as a key gene exhibiting differential expression between resistant and susceptible materials, and functional validation revealed that Bol4CL41 negatively regulates cabbage resistance to BR.
2. Results
2.1. Comparison of the Phenotypes of MY and LY After Inoculation
To compare BR resistance between MY and LY, we first inoculated the two materials at the seedling stage. Leaf tissues were collected pre-inoculation (0 h) and at 6, 24, and 48 h post-inoculation (hpi), followed by multi-time point transcriptome sequencing. A resistance assessment at 14 d post-inoculation revealed minimal lesions on MY (Figure 1a), with no disease symptoms observed on the inner leaves. In contrast, LY exhibited systemic disease, characterized by larger and deeper lesions. Statistical analysis of the lesion area (Figure 1b) demonstrated a significantly larger lesion area in LY compared to MY. This makes them excellent research materials for investigating the mechanisms of BR resistance.

Figure 1.
The phenotypes of MY and LY varied greatly after inoculation. (a) Phenotypic differences between MY and LY post-inoculation. (b) Statistical analysis of the lesion area. The data are shown as the means ± SDs, n = 3. Asterisks represent significant differences between two groups according to the Unpaired t test (**** p < 0.0001).
2.2. Functional Annotation of DEGs and Expression of Phenylpropanoid Biosynthesis Genes
Differential expression gene analysis was performed on 10 combinations: R0 vs. S0, R6 vs. S6, R24 vs. S24, R48 vs. S48, R0 vs. R6, R0 vs. R24, R0 vs. R48, S0 vs. S6, S0 vs. S24, and S0 vs. S48, (Figure 2a). A total of 26 differentially expressed genes were common to all 10 groups (Table S1), of which 2 genes (BolC04g001130.2J and BolC06g036850.2J) contained an AMP-binding enzyme domain and exhibited consistent differential expression trends in 8 groups.
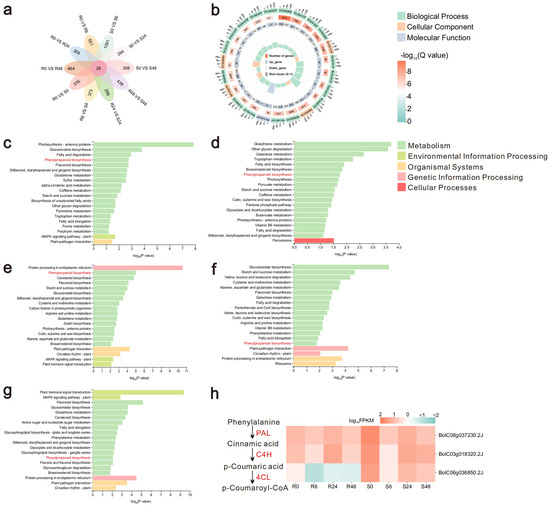
Figure 2.
The phenylpropanoid biosynthesis pathway is differentially expressed in cabbage after inoculation. (a) Flower plot of 10 sets of differentially expressed genes. (b) shows the GO enrichment results for R0 vs. S0. (c–g) represent KEGG enrichment results for R0 vs. S0, R24 vs. S24, R0 vs. R24, S0 vs. S24, and S0 vs. S48, respectively. (h) Expression profiles of key genes in the phenylpropanoid biosynthesis pathway across multiple time points.
To investigate the influence of intrinsic differences between MY and LY on cabbage resistance to BR, we performed GO functional enrichment analysis on DEGs from R0 vs. S0 (Figure 2b). The results showed significant enrichment of GO functions in Biological Process; Biological Process was mainly enriched to respond to external biotic stimulus and glucosinolate biosynthetic process; Cellular Component was mainly enriched in cell periphery, plasma membrane, anchored component of membrane and protein-DNA complex; Molecular Function was enriched for pigment binding. Enrichment results for other groups can be found in Figure S1. To further explore the biological functions of these DEGs, KEGG enrichment analysis was performed (Figure 2c–g and Figure S2). A total of 20 pathways were significantly enriched in each group, including glucosinolate biosynthesis, fatty acid degradation, phenylpropanoid biosynthesis, and flavonoid biosynthesis. The phenylpropanoid biosynthesis pathway was found to be enriched in five groups: R0 vs. S0, R24 vs. S24, R0 vs. R24, S0 vs. S24, and S0 vs. S48 (Figure 2c–g). Different resistant plants have certain variability, and also according to the electron microscope observation of Ma et al. [21], the pathogens gathered on the plant leaves at 24 hpi, and the pathogens proliferated and invaded the plants at 48 hpi, so very critical time nodes are at 0 h, and 24, 48 hpi. Besides that, two of the above genes that were cross-differentially expressed in 10 combinations were in the phenylpropanoid biosynthesis pathway, so we screened three highly expressed genes involved in the phenylpropanoid biosynthesis pathway from the transcriptome data and plotted the expression heat map (Figure 2h). In the phenylpropanoid biosynthesis pathway, the expression of 4CL in MY and LY varied greatly, with lower expression in MY and higher expression in LY. It was hypothesized that 4CL may contribute to the susceptibility of cabbage to disease; therefore, the 4CL gene family in cabbage will be the focus of subsequent research.
2.3. Systematic Identification and Phylogenetic Analysis Reveal Functional Divergence in the Cabbage 4CL Gene Family
A genome-wide analysis identified 43 Bol4CL genes in the cabbage JZS V2.0 genome, which were named Bol4CL1-Bol4CL43 (Table S2). The length of protein ranged from 352 amino acids (AAs) (Bol4CL43) to 1543 (Bol4CL36) amino acids, and the predicted molecular weights varying from 38.36 kDa (Bol4CL43) to 169.61 kDa (Bol4CL36). The theoretical pI varied from 4.64 (Bol4CL36) to 8.91 (Bol4CL27). The subcellular location was predicted, which provided possible clues for functional research. The results of subcellular localization prediction showed that Bol4CLs were mainly located in the cytoplasm (Bol4CL12, Bol4CL16, Bol4CL18, Bol4CL22, Bol4CL24, Bol4CL25, Bol4CL26, Bol4CL29, Bol4CL33, Bol4CL41, Bol4CL42, and Bol4CL43). This suggests that this gene family may play a potentially significant role in the cytoplasm.
In order to determine the evolutionary relationships between Bol4CLs and 4CLs to other species, we performed multiple sequence alignment and generated a NJ phylogenetic tree for 4CLs from Arabidopsis, rice, broccoli, and Chinese cabbage (Figure 3). A gene ID renaming table can be found in Table S3. For this study, we generated a version of the phylogenetic reconstruction that incorporated the 4CL and 4CL-like amino acid sequence data from cabbage, Arabidopsis, rice, broccoli, and Chinese cabbage. In total, all 4CLs from 5 species are clustered into three classes, designated as Class 1, Class 2, and Class 4CL-likes. Class 1 contained three At4CL genes (At4CL1, At4CL2, and At4CL3) and four Os4CL genes (Os4CL1, OsAt4CL3, Os4CL4, and Os4CL5), Class 2 contained At4CL4, Os4CL5, and Bol4CL41, while Class 4CL-likes included all of the 4CL-like genes identified from Arabidopsis (At4CL5, At4CL6, At4CL7, At4CL8, At4CL9, At4CL10, At4CL11, At4CL12, and At4CL13) and mostly derived from the genes of cabbage, broccoli, and Chinese cabbage. Based on evolutionary relationships, Os4CL genes are found only in Classes 1 and 2, while Bol4CL genes are present in Classes 2 and 4CL-likes. Arabidopsis, broccoli, and Chinese cabbage are distributed across Classes 1, 2, and 4CL-likes. There is potential functional similarity among the 4CL genes within the same group; the phylogenetic tree results help predict the functions of Bol4CL genes.
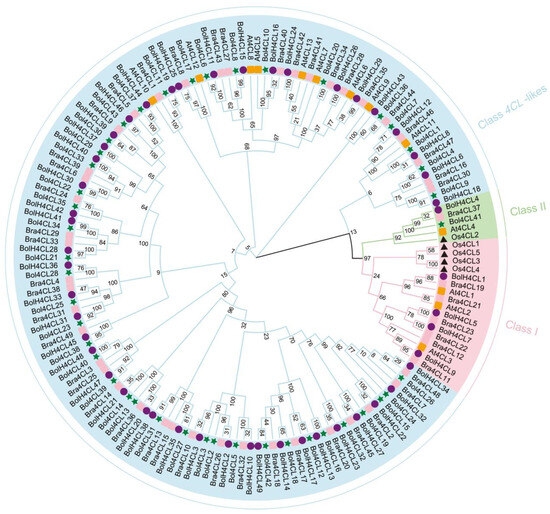
Figure 3.
Phylogenetic analysis representing the relationship between 4CL proteins in cabbage, Arabidopsis, rice, broccoli and Chinese cabbage. The 4CL subgroup is marked with different colors.
2.4. Gene Structure and Conserved Motif of Bol4CLs
To better understand the structural diversity of Bol4CL genes, conserved protein motifs were identified using the MEME online tool. A total of 10 putative conserved motifs were identified within the Bol4CL genes. The number of motifs identified in the Bol4CLs varied considerably, ranging from 4 to 9. Motifs 5 and 6 were present in all Bol4CLs, while motif 1 was found in 42 Bol4CLs and motif 3 in 39. Conserved domains within the same phylogenetic branch exhibited structural similarities (Figure 4a). To better understand the evolution of the Bol4CL gene family, we analyzed the gene structure. The coding sequence (CDS)-intron structure is shown in Figure 4b. Among the 43 Bol4CLs analyzed, the number of CDSs in Bol4CLs is different. Furthermore, differences in the lengths of introns and exons were observed among the members of the Bol4CL family.
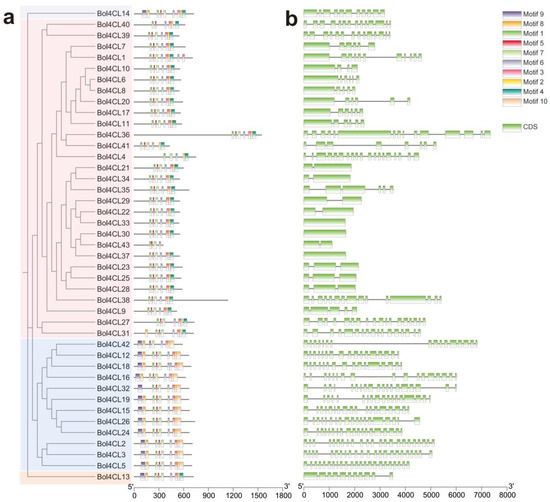
Figure 4.
Phylogenetically alignment conserved motifs and gene structures analysis of Bol4CL genes in cabbage. (a) Different colored boxes indicate the 10 conversed protein motifs of Bol4CL genes. (b) Gene structure analysis of 43 Bol4CL genes.
2.5. Chromosomal Location and Synteny Analysis of Bol4CLs
Synteny analysis can reveal the evolutionary history and functional conservation of gene families. Therefore, we investigated the synteny of Bol4CL genes to explore their functions and regulatory mechanisms in cabbage and other species. Through this analysis, we identified 15 homologous gene pairs among the 43 members of the Bol4CL gene family located on the 9 chromosomes of cabbage, specifically: Bol4CL20/Bol4CL6 and Bol4CL10, Bol4CL20/Bol4CL29, Bol4CL33/Bol4CL29, Bol4CL8 and Bol4CL34/Bol4CL6 and Bol4CL10, Bol4CL26/Bol4CL15, Bol4CL24/Bol4CL26, Bol4CL22/Bol4CL33, Bol4CL25 and Bol4CL41/Bol4CL28, Bol4CL39/Bol4CL40, Bol4CL2/Bol4CL3, Bol4CL16 and Bol4CL18/Bol4CL42, Bol4CL12/Bol4CL42, Bol4CL14/Bol4CL27, Bol4CL12/Bol4CL16, and Bol4CL18, Bol4CL22/Bol4CL29 (Figure 5a). Chromosomal location analysis of the cabbage and rice genomes identified few collinear gene pairs, only five. In contrast, collinearity analysis between cabbage and Arabidopsis identified more collinear gene pairs (Figure 5b). The collinearity between the cabbage and Arabidopsis genomes was significantly higher than that between the cabbage and rice genomes, indicating a close homologous relationship between cabbage and Arabidopsis, with one homologous gene exhibiting one-to-many collinearity. This further reveals the conservation and functional divergence of these 4CL genes across species.
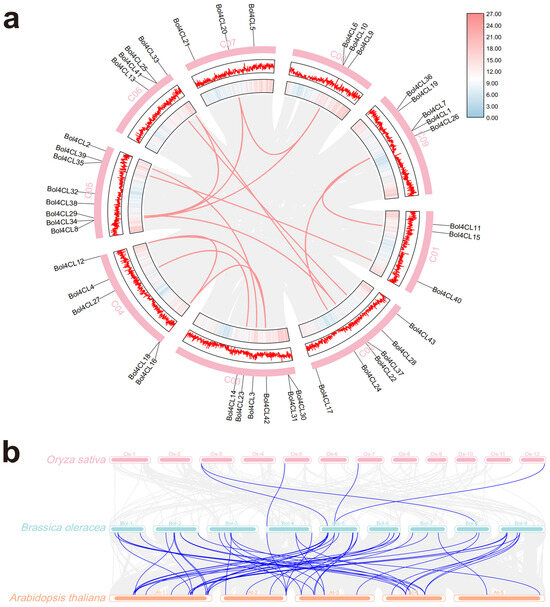
Figure 5.
Synteny analysis of 4CL gene family in different plants. (a) Synteny Circos plot within the cabbage genome. The inner circle displays gene density, with the pink color representing higher gene density. The second circle is a linear gene density plot, with the outermost circle representing the chromosome. The red connecting lines indicate syntenic gene pairs. (b) Synteny plot between cabbage and rice, cabbage and Arabidopsis. The blue connecting lines indicate syntenic gene pairs between the two species.
2.6. Gene Expression Profiles Heatmap of Bol4CL at Different Stages After Inoculation
Studying the expression levels of Bol4CL genes during different inoculation stages in cabbage helps us to understand their role in plant disease resistance. The FPKM values of 43 Bol4CL genes were screened from the transcriptome data, and heat map analysis was used to visualize the expression profiles of these genes during disease resistance in cabbage (Figure 6). The results showed that a total of 35 Bol4CL genes were expressed at all time points after inoculation in both materials. The transcription levels of Bol4CL genes varied among these samples, but interestingly, the expression levels of all Bol4CL genes were significantly lower at the R24 stage than at other stages. It was speculated that Bol4CL genes negatively regulated the resistance to BR in cabbage, and that 24 h after inoculation was a critical period for the colonization and propagation of the bacteria, so that the expression of Bol4CL genes in the resistant material was greatly reduced. Genes such as Bol4CL13, Bol4CL14, and Bol4CL35 showed sustained expression and relatively high expression levels at different stages in both materials. Bol4CL41 gene expression was higher in susceptible material and lower in resistant material, exhibiting a similar expression pattern to Bol4CL2, which is in the same branch. In conclusion, these genes may play a role in negatively regulating BR resistance in cabbage, but further functional validation is needed to confirm this hypothesis.
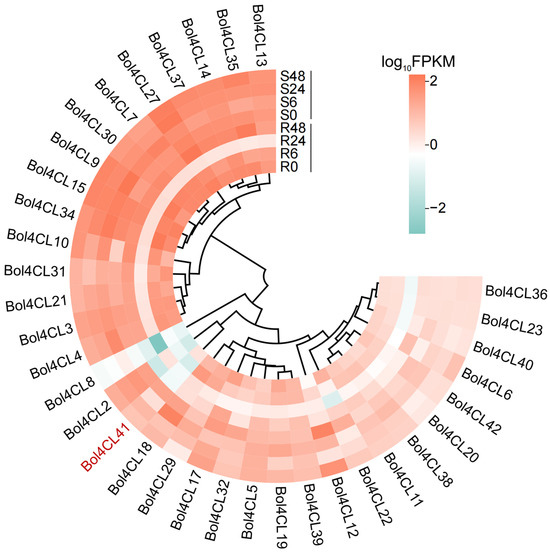
Figure 6.
Expression patterns of Bol4CL genes differentially expressed in cabbage of different multiple time points post-inoculation.
2.7. Bol4CL41 Negatively Regulates BR Resistance in Cabbage
To elucidate the biological functions of Bol4CL41 proteins in cabbage, we generated transgenic plants overexpressing Bol4CL41. Through continuous self-fertilization, homozygous T2 generation plants were ultimately obtained and confirmed the resulting altered gene expression by qRT-PCR (Figure 7a). Two independent transgenic lines exhibiting high levels of Bol4CL41 were selected for further inoculation tests. The seedling phenotype showed that the transgenic lines showed a significantly increased susceptibility to BR compared to the wild type (GL) after inoculation (Figure 7b,c). These results demonstrate that Bol4CL41 negatively regulates BR resistance in cabbage.
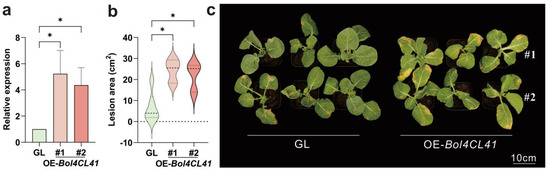
Figure 7.
Bol4CL41 negatively regulates BR resistance in cabbage. (a) Expression of GL, OE-Bol4CL41#1, and OE-Bol4CL41#2. Relative expression of OE-Bol4CL41#1 and OE-Bol4CL41#2 was calculated relative to GL expression, which was designated as 1. The data are shown as the means ± SDs, n = 3. Asterisks represent significant differences across three groups according to Ordinary one-way ANOVA (* p < 0.05). (b) Statistical analysis of the lesion area. The data are shown as the means ± SDs, n = 3. Asterisks represent significant differences across three groups according to Ordinary one-way ANOVA (* p < 0.05). (c) Phenotypic differences between GL, OE-Bol4CL41#1 and OE-Bol4CL41#2.
3. Discussion
Transcriptome analysis has been employed for years to elucidate plant–microbe interactions [22]. Transcriptome sequencing and differential gene expression analysis at various time points following plant infection are valuable for illustrating the dynamic gene responses within the plant, contributing significantly to understanding disease resistance or susceptibility mechanisms. Research into the gene regulation of responses to pathogen attack may reveal the roles of relevant defense genes [23]. Sun et al. [24] performed transcriptome analysis on resistant and susceptible cabbage varieties at 0, 12, 24, 48, and 96 h post-inoculation, discovering enhanced glucosinolate biosynthetic and catabolic pathways. To investigate the differential expression of JAZ genes in cabbage after Xcc infection, Liu et al. [25] analyzed RNA-seq data from resistant and susceptible varieties post-inoculation, identifying both induced and repressed JAZ genes. Transcriptome analysis of cruciferous leaves at 3 and 12 d post-inoculation revealed that 78 and 809 genes up-regulated, and 10 and 169 genes down-regulated, at early and late stages, respectively. Genes related to terpenes, flavonoids, alkaloids, and anthocyanins and phytohormones were up-regulated at the early stage of infection [26]. Tortosa et al. [27] demonstrated that CBP60g and SARD1 contribute to Xcc resistance, as evidenced by transcriptome analysis of broccoli at 3 and 12 dpi and validation in Arabidopsis knockout mutants. Certain metabolic and signaling pathways are consistently activated during plant–pathogen interactions. In this study, we performed transcriptome sequencing on two cabbage varieties at 0, 6, 24, and 48 h post-inoculation. Glucosinolate biosynthesis and flavonoid biosynthesis were identified as enriched KEGG pathway; the results of Sun et al. [24] and Tortosa et al. [26] analyses verified this result. Moreover, previous transcriptome analyses have indicated that the expression of resistance-related genes varies at different time points post-inoculation. Our research confirms this, showing that the expression levels of all Bol4CL genes were lower at R24 compared to other time points. This suggests that the timing of defense activation is crucial for plant survival, so it is necessary to detect the gene dynamics before and after plant inoculation and cross-analysis of multiple time points.
4CL is an important rate-limiting enzyme in the phenylpropane metabolism pathway [28]. The activity levels of 4CL enzymes significantly influence the accumulation of substances such as flavonoids and lignin. Furthermore, 4CLs play a crucial role in plant growth and resistance to external environmental stresses [29]. Therefore, the systematic identification and comprehensive analysis of the 4CL gene family are of great significance for understanding the functions of these family members. The 4CL gene family at the genome-wide level has been reported in various species [30,31,32,33]. However, the 4CL family has not been systematically studied in cabbage, an economically and nutritionally vital crop. In this study, 43 4CL genes were identified in cabbage and named Bol4CL1-43. Cabbage possesses a greater number of 4CL members compared to Arabidopsis [12] and rice [13], likely due to differences in genome size or the evolutionary diversity of these gene families. Phylogenetic reconstruction is a robust tool for resolving gene family evolution [34]. In plants, 4CL genes can be categorized into three subgroups: Class I, II, and the 4CL-like subgroup [10]. Based on the classification of At4CL genes, this study also divided Bol4CL genes into three subgroups. Class I and II contain fewer members, with Bol4CLs, BolH4CLs, and Bra4CLs predominantly clustered in the Class 4CL-like subgroup. Variations between different species may be primarily related to their evolutionary level. Further analysis of conserved motifs and gene structures in Bol4CL proteins indicated that, while conserved motifs within the same subgroup exhibited similarity, the distribution of introns and exons varied considerably. This variation was exemplified by Bol4CL12 and Bol4CL42, both in the same clade, Bol4CL42 displaying an exceptionally long intron sequence. There were differences in the structure and motif types of each member gene, which may cause the functional differences among the subgroups. Analyzing gene collinearity across different species has revealed additional insights into the evolutionary relationship between Bol4CL genes and At4CL, Os4CL genes. This analysis enhances our understanding of the phylogenetic tree and broadens our knowledge base.
Increasing studies have shown that 4CLs play critical roles in the biotic stress responses of plants [35,36]. Analysis of gene expression patterns in plants under biotic stress can provide valuable insights into gene function. Differentially expressed genes may be candidate genes involved in the plant’s stress response. We constructed a clustered heatmap to analyze the expression profiles of 43 Bol4CL genes in MY and LY at different time points post-inoculation with Xcc. The results revealed that Bol4CL41 and Bol4CL2 exhibited higher expression levels in the susceptible material and lower levels in the resistant material, suggesting that Bol4CL2 and Bol4CL41 may play a role in negatively regulating BR resistance in cabbage. Furthermore, Bol4CL41 was identified as a differentially expressed gene across all 10 groups in the transcriptome analysis, making it a key gene for further investigation.
The transcriptional activation of 4CLs has been demonstrated in cultured cells of various plants, including soybean, parsley, and Arabidopsis, following treatment [35,36,37]. In addition, this activation has been observed in soybean and parsley inoculated with Phytophthora sojae and in potato infected with Phytophthora infestans [37,38,39]. In Arabidopsis, a transient accumulation of 4CL mRNA was detected after infiltrating leaves with an avirulent strain of the bacterial pathogen, Pseudomonas syringae pv. maculicola [40]. Our transcriptome analysis of the Bol4CL gene family at different time points after inoculation with MY and LY (Table S4) revealed that the expression of most genes in the Bol4CL gene family was up-regulated in LY compared to MY, with only a small number of genes being down-regulated. Specifically, the expression levels of the Bol4CL2, Bol4CL18, Bol4CL41, and Bol4CL42 genes increased at every time point (Figure 8). To investigate whether Bol4CL41 plays a role in cabbage resistance to BR, we first overexpressed Bol4CL41 and transformed it into cabbage. Following continuous self-pollination and selection, we obtained T2 generation overexpressing cabbage seedlings. After inoculation, we found that two lines of OE-Bol4CL41 cabbage exhibited larger lesion areas compared to wild type cabbage. These results indicate that the Bol4CL41 gene negatively regulates cabbage resistance to BR.
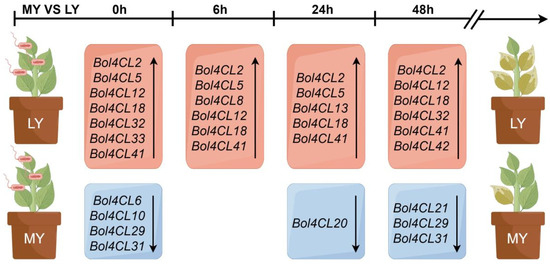
Figure 8.
Differential up- and down-regulation of the Bol4CL gene family in R0 vs. S0, R6 vs. S6, R24 vs. S24, and R48 vs. S48 contributes to differences in resistance levels to MY and LY.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials, Growth Conditions, and Inoculation Method
The cabbage inbred lines were obtained from the Institute of Vegetables and Flowers, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (IVF-CAAS), Beijing, China. Both MY and LY were bred through resistance identification and systematic selection. MY is a highly resistant line, while LY is highly susceptible. Seedlings were grown in a greenhouse at 24–28 °C with 60–70% relative humidity for one month, watered 3–4 times per week, and inoculated when 4–5 true leaves had grown.
The inoculation strain used was Xcc race 1-typed strain WHI3811 [41], provided by Dr. Joann G. Vicente, University of Warwick, UK. Xcc was cultured in nutrient broth (NB) medium containing 5 g of peptone, 3 g of beef extract, and 5 g of NaCl per liter of distilled water, with a pH of 6.5–6.8 [42], with shaking at 28 °C and 200 rpm/min for approximately 16 h until it reached the logarithmic phase, after which it was adjusted to a concentration of 1 × 108 cfu/mL with an appropriate amount of sterile water (OD600 = 0.2).
With slight modifications based on the spray inoculation method of Kong et al. (2021) [43], seedlings were sprayed with a fine mist of water and covered with plastic film for 14 h, maintaining an indoor temperature of 15–18 °C and indoor relative humidity above 90%, with relative humidity inside the film maintained above 95%. After the leaf margins were spatulated with water using a medical throat sprayer, the bacterial liquid was evenly sprayed on the cabbage leaves until it covered the leaves in the form of fine water droplets and covered the plastic film. After 24 h, the plastic film was removed while a room temperature of 26–28 °C was maintained.
4.2. RNA-Seq and Transcriptome Analysis of Cabbage in Response to BR
MY and LY leaf samples were taken before inoculation (0 h) and 6, 24, and 48 h after inoculation, and quickly placed in liquid nitrogen and stored at −80 °C until RNA extraction. RNA extraction and sequencing were performed by Personalbio Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China).
Following sequencing, the samples yield image files that are converted using the sequencing platform’s software of Personalbio Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China) to generate FASTQ raw data, which is the initial output. The sequencing data contains some joints and low-quality reads, which can significantly interfere with subsequent analysis, so it is necessary to further filter the sequencing data. The criteria for data filtering include the following: removing the junction at the 3′ end by Cutadapt 1.18, removing sequences with at least a 10 bp overlap with the known junction (AGATCGGAAG), allowing for 20% base mismatches. The reads with an average quality score lower than Q20 are removed.
Filtered reads were compared to the cabbage reference genome of Brassicaceae Database (BRAD, http://www.brassicadb.cn/#/, accessed on 27 February 2025) using HISAT2 (http://ccb.jhu.edu/software/hisat2/index.shtml, accessed on 27 February 2025) software. The read count value on each gene was counted using HTSeq2.0 [44] as the raw expression of the gene. Reads counts were positively correlated with the true expression levels of the genes, as well as with gene length and sequencing depth. To ensure comparability of gene expression levels across different genes and samples, Fragments Per Kilobase of transcript per Million reads mapped (FPKM) was used to normalize the expression. Differential expression analysis and gene selection are subsequently performed using DESeq2 (https://bioconductor.org/packages/release/bioc/html/DESeq2.html, accessed on 27 February 2025) [45], with differentially expressed genes identified based on the criteria of |log2FoldChange| > 1 and a significance threshold of p value < 0.05.
GO (http://geneontology.org/, accessed on 27 February 2025) and KEGG (http://www.kegg.jp/, accessed on 27 February 2025) annotations were used for classification. GO and KEGG enrichment analyses were performed using topGO (https://bioconductor.org/packages/release/bioc/html/topGO.html, accessed on 27 February 2025) [39] and clusterProfiler (https://bioconductor.org/packages/release/bioc/html/clusterProfiler.html, accessed on 27 February 2025) [46], respectively. The p value was calculated using the hypergeometric distribution method (the significance threshold for enrichment was p value < 0.05) and corrected by FDR to obtain Q value. Generally, functions with Q value < 0.05 were regarded as significant enrichment. To identify GO term and KEGG pathway compared with the whole genomic background, the major biological functions exercised by the differential genes were identified. The KEGG enrichment maps were selected from R0 vs. S0 time points, and −log10(p value) > 1.3 was considered as significant enrichment; the 23 GO terms with the smallest Q value in R0 vs. S0 time points were selected for the enrichment maps. Both the GO enrichment plot and the multi-time point expression heatmap of the phenylpropanoid biosynthesis pathway were generated using ChiPlot (https://www.chiplot.online/, accessed on 27 February 2025), with −log10(Q value) > 1.3 considered significantly enriched.
4.3. Genome-Wide Identification of 4CL in Different Species
The sequences of the rice Os4CL family genes were obtained from the Rice Annotation Project Database (RAP-DB, https://rapdb.dna.affrc.go.jp/, accessed on 27 February 2025), and Arabidopsis At4CL family gene sequences were sourced from The Arabidopsis Information Resource (TAIR, https://www.arabidopsis.org/, accessed on 27 February 2025). Bol4CL (cabbage), BolH4CL (broccoli), and Bra4CL (Chinese cabbage) family gene sequences were sourced from BRAD (http://www.brassicadb.cn/#/, accessed on 27 February 2025). Initially, InterPro (https://www.ebi.ac.uk/interpro/search/, accessed on 27 February 2025) was used to identify the PFAM ID for the 4CL gene family as PF00501. Subsequently, the Hidden Markov Model (HMM) (https://www.ebi.ac.uk/interpro/download/Pfam/, accessed on 27 February 2025) was employed, along with TBtools-II (https://github.com/CJ-Chen/TBtools-II, accessed on 27 February 2025) [30] to perform the initial screening of family members. Sequences were extracted using the NCBI CD-Search Tool (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Structure/bwrpsb/bwrpsb.cgi, accessed on 27 February 2025), and genes with an E-value ≤ 1 × 10−5 and a bitscore ≥ 200 were selected for secondary screening, ultimately defining the family members.
4.4. Construction of Phylogenetic Trees and Analysis of Protein Characteristics
ClustalW alignment was performed in MEGA7 (https://www.megasoftware.net/, accessed on 27 February 2025), and a phylogenetic tree was constructed using the Neighbor-Joining (NJ) method, with 1000 bootstrap replications used to assess tree topology and reliability. Evolview (https://evolgenius.info/helpsite/qst1.html, accessed on 27 February 2025) was used to visualize the phylogenetic tree.
Using the ExPASy ProtParam online tool (https://web.expasy.org/protparam/, accessed on 27 February 2025), the relative molecular weight (MW), theoretical isoelectric point (pI), instability index, aliphatic index, and grand average of hydropathicity (GRAVY) protein characteristics of Bol4CL were predicted. Using the WoLF PSORT online website (https://psort.hgc.jp/, accessed on 27 February 2025), a subcellular localization prediction for the Bol4CL protein was performed. The specific chromosomal location of the gene from the BRAD was obtained (http://www.brassicadb.cn/#/, accessed on 27 February 2025).
4.5. Gene Structural Analysis of Bol4CL Genes
To effectively analyze gene structures and motifs, the full-length protein sequences of Bol4CL were uploaded to the online website MEME Suite 5.5.7 (https://meme-suite.org., accessed on 27 February 2025) to search for conserved motifs by finding motif numbers set to up to 10 in sequences. Gene structure annotations in GFF3 format for cabbage were downloaded from the BRAD (http://www.brassicadb.cn/#/, accessed on 27 February 2025). Next, the TBtools-II software [30] was used for the visualization of motifs and gene structures.
4.6. Chromosome Location and Synteny Analysis
To investigate the genomic synteny among cabbage, rice, and Arabidopsis, synteny analyses were performed using the One Step McScanX-Super Fast module in TBtools software [47]. The genome sequence files and gene structure annotation files for the three species were imported into the software, with E value set to 1 × 10−5 and the blast hit count set to 10. Following completion of the synteny analysis, the Multiple Synteny Plot module in TBtools [48] was used to further visualize the results. Visualization of the cabbage genome Circos plot was performed using the Advanced Circos module.
4.7. Construction Gene Expression Profiles Heatmap
To study the expression profiles of Bol4CL genes across different varieties and various post-inoculation time points, we excavated the transcriptomic data. The transcript abundances were calculated and quantified for each sample using FPKM. Finally, the average FPKM values were log-transformed and used to generate a heatmap using ChiPlot (https://www.chiplot.online/, accessed on 27 February 2025).
4.8. Vector Construction, Transgenic Plant Generation and Inoculation Treatments
The overexpression vector pBWA(V)BS-Bol4CL41 was constructed by inserting the full coding sequence (CDS) of the Bol4CL41 gene into the transformed vector pBWA(V)BS. For cabbage transformation, the resulting recombinant vector was introduced into cabbage (GL) through the agrobacterium (GV3101)-mediated transformation. Homozygous T2 transgenic lines were selected according to their resistance to Basta, and positive lines were identified by qRT-PCR using cDNA. Afterwards, resistance identification was conducted on the T2 transgenic positive lines.
4.9. Disease Mechanism Diagram Drawing, Resistance Evaluation and Data Analysis
The disease mechanism diagram was created using Figdraw (https://www.figdraw.com/static/index.html#/, accessed on 28 February 2025). The lesion area was calculated using ImageJ V1.8.0.112 software (National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD, USA). The data were first calculated in Excel (Beijing Jinshan Office Software Co., Ltd., Beijing, China). Subsequently, the data were statistically analyzed using GraphPad Prism 9.0 software (GraphPad Software Inc., La Jolla, CA, USA). Differences between the two materials were assessed using a t-test, with a significance threshold set at p < 0.05 and p < 0.01 for highly significant differences.
5. Conclusions
Following our analysis of multi-time point transcriptomic data, we identified the 4CL gene family as a key focus. We identified 43 Bol4CL genes within the cabbage genome and subsequently analyzed their evolutionary relationships, conserved motifs, gene structures, chromosomal location, and synteny. These analyses provide valuable insights into the functions of this gene family. Gene expression profiles showed that Bol4CL2 and Bol4CL41 were differentially expressed between MY and LY, with Bol4CL41 being a differentially expressed gene among the 10 groups analyzed in the transcriptome analysis. Therefore, a stable genetic transformation line of OE-Bol4CL41 cabbage was constructed. Inoculation of T2 generation seedlings demonstrated that OE-Bol4CL41 plants were more susceptible to Xcc compared to wild type cabbages. These findings indicate that Bol4CL41 negatively regulates resistance to BR in cabbage, providing compelling evidence and experimental support for elucidating the mechanisms underlying BR resistance.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/ijms26136179/s1.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.M., Z.F., J.Y. and H.L.; methodology, H.M. and S.D.; validation, H.M., S.D., Y.Z. (Yulun Zhang) and T.Z.; formal analysis, H.M., S.D. and C.K.; investigation, H.M., S.D., Y.Z. (Yulun Zhang) and T.Z.; writing—original draft, H.M.; writing—review and editing, H.M., C.K., M.L., V.T., A.M.A., Z.H. and H.L.; visualization, H.M.; supervision, J.J., Y.W., Y.Z. (Yangyong Zhang), L.Y., Z.F., J.Y., Z.H. and H.L.; project administration, J.J., Y.W., Y.Z. (Yangyong Zhang), M.Z., L.Y., A.M.A., J.Y., Z.H. and H.L.; funding acquisition, Y.Z. (Yangyong Zhang), V.T., Z.H. and H.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the National Key R&D Program of China (2023YFE0111400), the Science and Technology Innovation Program of the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (CAAS-ASTIP-IVFCAAS), the China Agriculture Research System of MOF and MARA (CARS-23), and the Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (LY22C150002). The work was also partly supported by the Russian Ministry of Science and Higher Education (No. 075-15-2023-582).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All data supporting the findings of this study are available in the paper and its Supplementary Materials published online.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to all lab members for their useful suggestions, support, and encouragement.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Vicente, J.; Holub, E. Anthomonas campestris pv. campestris (cause of black rot of crucifers) in the genomic era is still a worldwide threat to brassica crops. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2013, 14, 2–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, P.H. Black rot: Continuing threat to world crucifers. Plant Dis. 1980, 64, 736–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, B.; Vicente, J.; Manandhar, H.; Roberts, S. Occurrence and diversity of Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris in vegetable Brassica fields in Nepal. Plant Dis. 2010, 94, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fargier, E.; Saux, M.; Manceau, C. A multilocus sequence analysis of Xanthomonas campestris reveals a complex structure within crucifer-attacking pathovars of this species. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2011, 34, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, D.; Rathaur, P.; Vicente, J. Characterization, genetic diversity and distribution of Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris races causing black rot disease in cruciferous crops of india. Plant Pathol. 2016, 65, 1411–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Li, C.; Si, J.; Ren, X.; Song, H. Research progress on physiological race division and disease resistance identification of cabbage black rot. Veg. China 2011, 1, 6–10. [Google Scholar]
- Alvarez, A.M.; Benedict, A.A.; Mizumoto, C.Y.; Hunter, J.E.; Gabriel, D.W. Serological, pathological and genetic diversity among strains of Xanthomonas campestris infecting crucifers. Phytopathology 1994, 84, 1449–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, N.; Lin, H. Contribution of phenylpropanoid metabolism to plant development and plant–environment interactions. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2021, 63, 180–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Ma, T.; Luo, W.; Xu, J.; Liu, J.; Wan, D. Identification of 4CL genes in desert poplars and their changes in expression in response to salt stress. Genes 2015, 6, 901–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragg, H.; Kuhn, D.N.; Hahlbrock, K. Coordinated regulation of 4-coumarate:CoA ligase and phenylalanine ammonia-lyase mRNAs in cultured plant cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1981, 256, 10061–10065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raes, J.; Rohde, A.; Christensen, J.H.; Van, Y.; Boerjan, W. Genome-wide characterization of the lignification toolbox in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2003, 133, 1051–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Li, Y.; Feng, S.; Zou, W.; Guo, K.; Fan, C.; Si, S.; Peng, L. Analysis of five rice 4-coumarate:coenzyme A ligase enzyme activity and stress response for potential roles in lignin and flavonoid biosynthesis in rice. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 430, 1151–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavhale, S.G.; Kalunke, R.M.; Giri, A.P. Structural, functional and evolutionary diversity of 4-coumarate-CoA ligase in plants. Planta 2018, 248, 1063–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Ellis, B.E. 4-Coumarate:CoA ligase gene family in Rubus idaeus: cDNA structures, evolution, and expression. Plant Mol. Biol. 2003, 51, 327–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Zuo, D.; Zhang, X.; Li, H.; Ye, H.; Zhang, N.; Li, M.; Dang, M.; Geng, F.; Zhou, H.; et al. Genome-wide identification analysis of the 4-Coumarate: CoA ligase (4CL) gene family expression profiles in Juglans regia and its wild relatives J. Mandshurica resistance and salt stress. BMC Plant Biol. 2024, 24, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gális, I.; Šimek, P.; Narisawa, T.; Sasaki, M.; Horiguchi, T.; Fukuda, H.; Matsuoka, K. A novel R2R3 MYB transcription factor NtMYBJS1 is a methyl jasmonate-dependent regulator of phenylpropanoid-conjugate biosynthesis in tobacco. Plant J. 2006, 46, 573–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehlting, J.; Büttner, D.; Wang, Q.; Douglas, C.J.; Somssich, I.E.; Kombrink, E. Three 4-coumarate:coenzyme A ligases in Arabidopsis thaliana represent two evolutionarily divergent classes in angiosperms. Plant J. 1999, 19, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, F.; Xiang, C.; Wang, C.; Zang, Y.; Liu, L.; Wu, S.; Wang, C.; Cai, J.; Wang, D.; Min, Y. Identification of the 4CL family in cassava (Manihot esculenta Crantz) and expression pattern analysis of the Me4CL32 gene. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2024, 735, 150731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinde, B.A.; Dholakia, B.B.; Hussain, K.; Panda, S.; Meir, S.; Rogachev, I.; Aharoni, A.; Giri, A.P.; Kamble, A.C. Dynamic metabolic reprogramming of steroidal glycol-alkaloid and phenylpropanoid biosynthesis may impart early blight resistance in wild tomato (Solanum arcanum Peralta). Plant Mol. Biol. 2017, 95, 411–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, R.K.; Shen, Y.; Wang, J.; Sheng, X.; Zhao, Z.; Yu, H.; Gu, H. Advances in Multi-Omics Approaches for Molecular Breeding of Black Rot Resistance in Brassica oleracea L. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 2, 742553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Kong, C.; Deng, S.; Zhao, T.; Ji, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhuang, M.; Yang, L.; Marina, L.; et al. Resistance screening of cabbage to black rot and inheritance pattern analysis. Sci. Hortic. 2025, 345, 114129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, C.; Passo, V.H.D.; Fang, Z.; Yang, L.; Zhuang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Vicente, J.G.; Lv, H. Complete Genome Sequence of Strain WHRI 3811 Race 1 of Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris, the causal agent of black rot of cruciferous Vegetables. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2019, 32, 1571–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohta, H.; Hattori, T. Bacteria sensitive to nutrient broth medium in terrestrial environments. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 1980, 26, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, C.; Chen, G.; Yang, L.; Zhuang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ji, J.; Fang, Z.; Lv, H. Germplasm screening and inheritance analysis of resistance to cabbage black rot in a worldwide collection of cabbage (Brassica oleracea var. capitata) resources. Sci. Hortic. 2021, 288, 110234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putri, G.H.; Anders, S.; Pyl, P.T.; Pimanda, J.E.; Zanini, F. Analysing high-throughput sequencing data in Python with HTSeq 2.0. Bioinformatics 2022, 38, 2943–2945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 5, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexa, A.; Rahnenführer, J. Gene set enrichment analysis with topGO. Bioconduct. Improv. 2009, 27, 776. [Google Scholar]
- Alexa, A.; Rahnenführer, J.; Lengauer, T. Improved scoring of functional groups from gene expression data by decorrelating GO graph structure. Bioinformatics 2006, 22, 1600–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Wang, L.; Han, Y.; He, Q. clusterProfiler: An R package for comparing biological themes among gene clusters. Omics J. Integr. Biol. 2012, 16, 284–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wu, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Zeng, Z.; Xu, J.; Liu, Y.; Feng, J.; Chen, H.; He, Y.; et al. TBtools-II: A “one for all, all for one” bioinformatics platform for biological big-data mining. Mol. Plant 2023, 16, 1733–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wulf, A.; Manthey, K.; Doll, J.; Perlick, A.M.; Linke, B.; Bekel, T.; Meyer, F.; Franken, P.; Küster, H.; Krajinski, F. Transcriptional Changes in Response to Arbuscular Mycorrhiza Development in the Model Plant Medicago truncatula. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2003, 16, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Shukla, N.; Kabadwal, B.C.; Tewari, A.K.; Kumar, J. Review on Plant-Trichoderma-Pathogen Interaction. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. App. Sci. 2018, 7, 2382–2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Zhang, E.; Liu, Y.; Xu, Z.; Hui, M.; Zhang, X.; Cai, M. Transcriptome analysis of two lines of Brassica oleracea in response to early infection with Xanthomonas campestris pv. Campestris. Can. J. Plant Pathol. 2021, 43, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhao, C.; Yang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Fang, Z.; Lv, H. Genome-Wide Identification, Expression Profile of the TIFY Gene Family in Brassica oleracea var. capitata, and Their Divergent Response to Various Pathogen Infections and Phytohormone Treatments. Genes 2020, 11, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tortosa, M.; Cartea, M.E.; Rodríguez, V.M.; Velasco, P. ‘Omic’ profiling of B. oleracea challenged with Xanthomonas campestris pv. Campestris. Acta Hortic. 2018, 1202, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tortosa, M.; Cartea, M.E.; Velasco, P.; Soengas, P.; Rodriguez, V.M. Calcium-signaling proteins mediate the plant transcriptomic response during a well-established Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris infection. Hortic. Res. 2019, 6, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Z.; Nan, X.; Li, W.; Mao, J.; Chen, B. Comprehensive genomic identification and expression analysis 4CL gene family in apple. Gene 2023, 858, 147197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, G.; Pan, X.; Xu, F.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, S.; Jiang, X.; Lu, H. Divergent and Overlapping Function of Five 4-Coumarate/Coenzyme A Ligases from Populus tomentosa. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 2015, 33, 841–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhlmann, A.; Ebel, J. Molecular cloning and expression of 4-coumarate:coenzyme A ligase, an enzyme involved in the resistance response of soybean (Glycine max L.) against pathogen attack. Plant Physiol. 1993, 102, 1147–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voo, K.S.; Whetten, R.W.; O’Malley, D.M.; Sederoff, R.R. 4-coumarate:coenzyme a ligase from loblolly pine xylem. Isolation, characterization, and complementary DNA cloning. Plant Physiol. 1995, 108, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Kawaoka, A.; Tsai, C.J.; Lung, J.; Osakabe, K.; Ebinuma, H.; Chiang, V.L. Compartmentalized expression of two structurally and functionally distinct 4-coumarate:CoA ligase genes in aspen (Populus tremuloides). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 5407–5412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harding, S.A.; Leshkevich, J.; Chiang, V.L.; Tsai, C.J. Differential substrate inhibition couples kinetically distinct 4-coumarate: Coenzyme a ligases with spatially distinct metabolic roles in quaking aspen. Plant Physiol. 2002, 128, 428–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Jin, Z.; Ding, Y.; Guo, M. Characterization of HSP70 family in watermelon (Citrullus lanatus): Identification, structure, evolution, and potential function in response to ABA, cold and drought stress. Front. Genet. 2023, 14, 1201535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, C.; Hoffmann, H.; Schulz, W.; Hahlbrock, K. Structure and elicitor or u.v.-light-stimulated expression of two 4-coumarate: CoA ligase genes in parsley. EMBO J. 1987, 6, 1189–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trezzini, G.F.; Horrichs, A.; Somssich, I.E. Isolation of putative defense-related genes from Arabidopsis thaliana and expression in fungal elicitor-treated cells. Plant Mol. Biol. 1993, 21, 385–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker-André, M.; Schulze-Lefert, P.; Hahlbrock, K. Structural comparison, modes of expression, and putative cis-acting elements of the two 4-coumarate: CoA ligase genes in potato. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 8551–8559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmelzer, E.; Kruger-Lebus, S.; Hahlbrock, K. Temporal and Spatial Patterns of Gene Expression around Sites of Attempted Fungal Infection in Parsley Leaves. Plant Cell 1989, 1, 993–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Ellard, M.; Wanner, L.A.; Davis, K.R.; Douglas, C.J. The Arabidopsis thaliana 4-coumarate:CoA ligase (4CL) gene: Stress and developmentally regulated expression and nucleotide sequence of its cDNA. Plant Mol. Biol. 1995, 28, 871–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).