Carrageenans and the Carrageenan-Echinochrome Complex as Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Agents
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Characteristics of CRGs
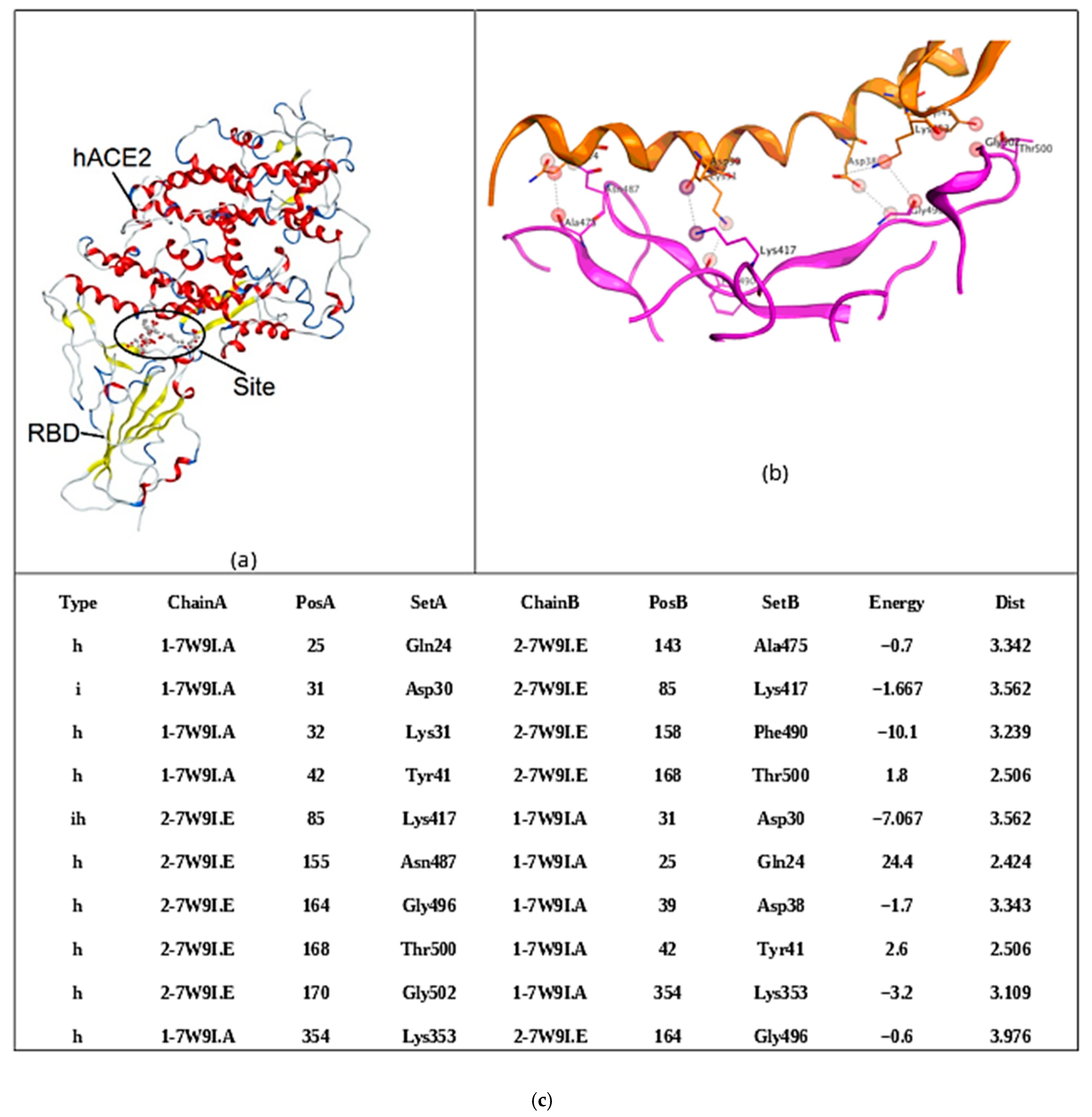
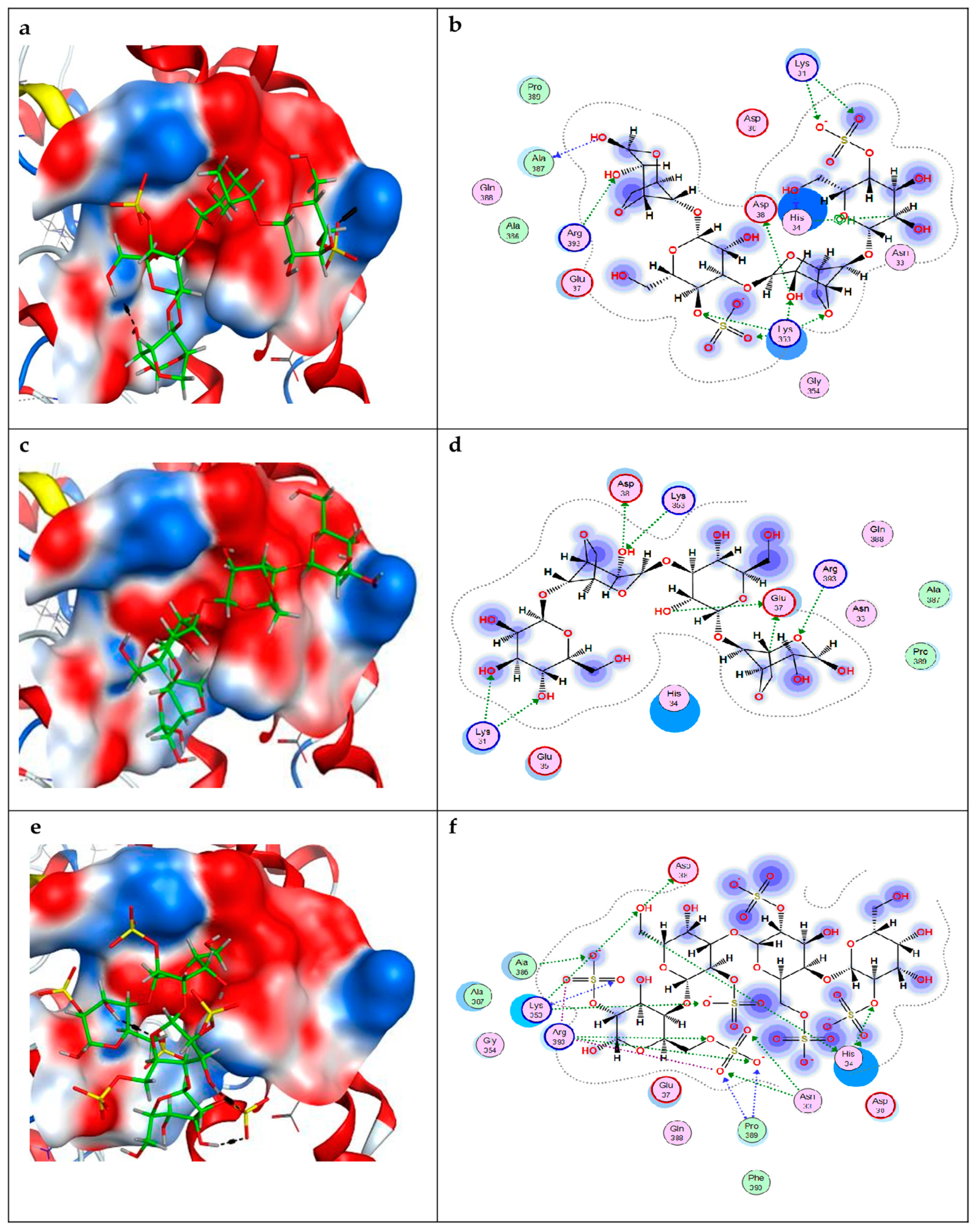
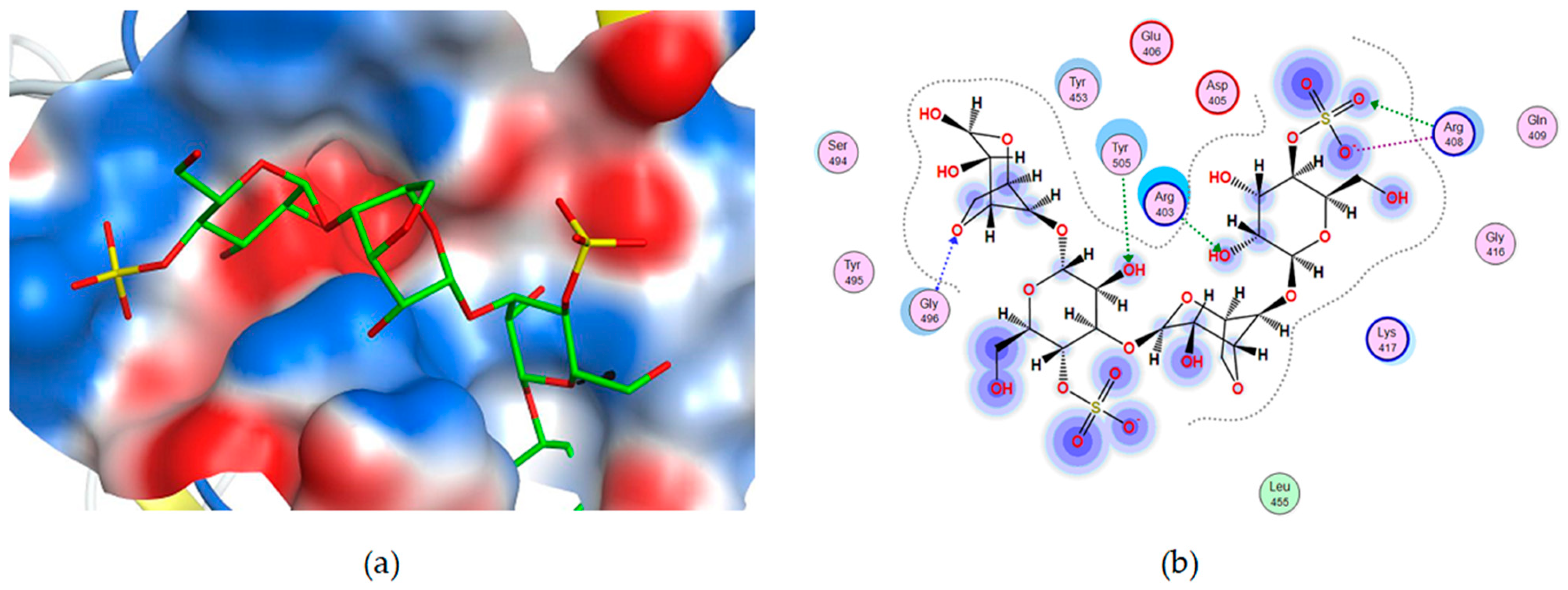
2.2. Molecular Docking of Carrageenan Tetrasaccharides with SARS-CoV-2 RBD and ACE2
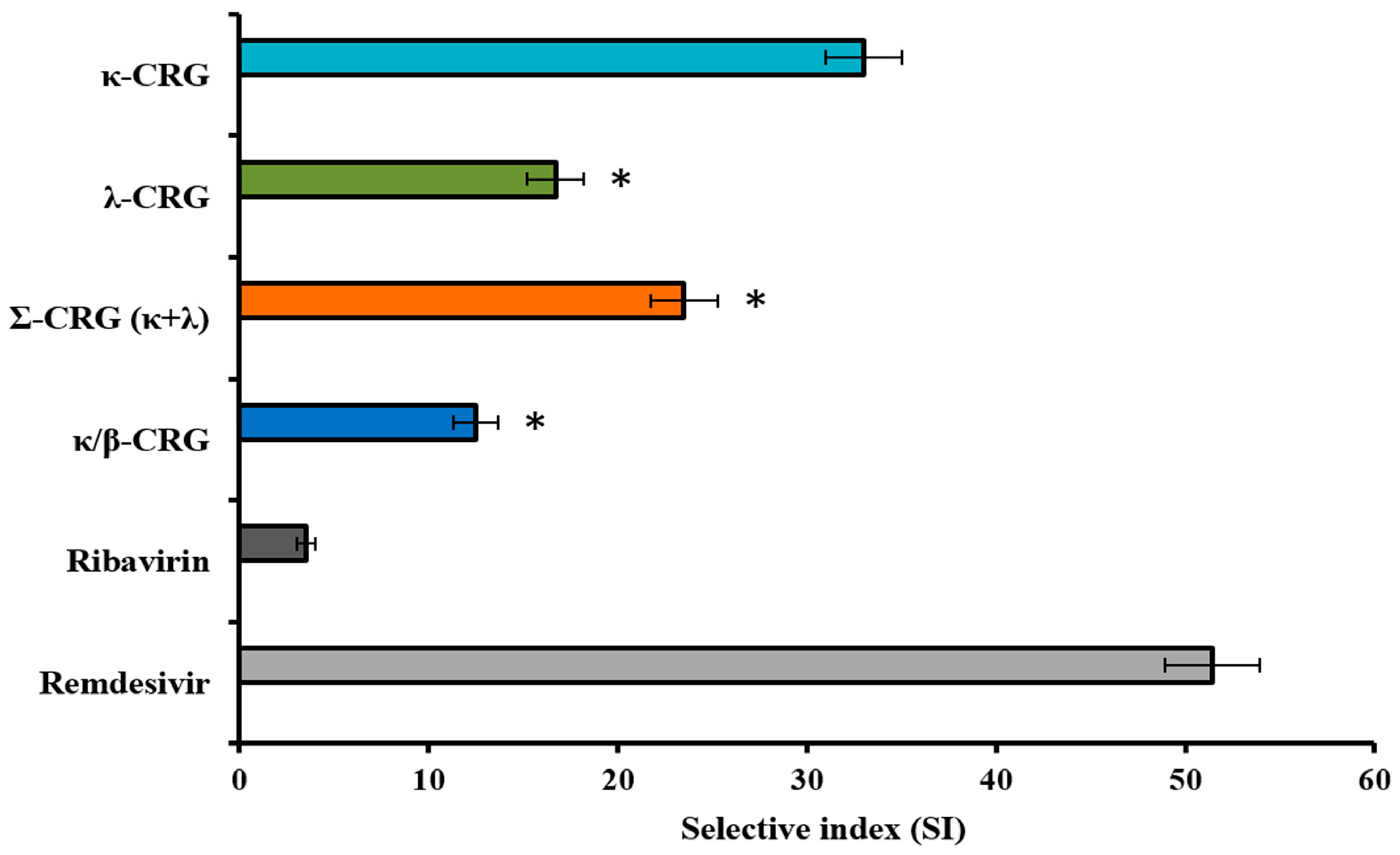
2.3. Cytotoxicity and Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Activity of the Different Types of Carrageenans
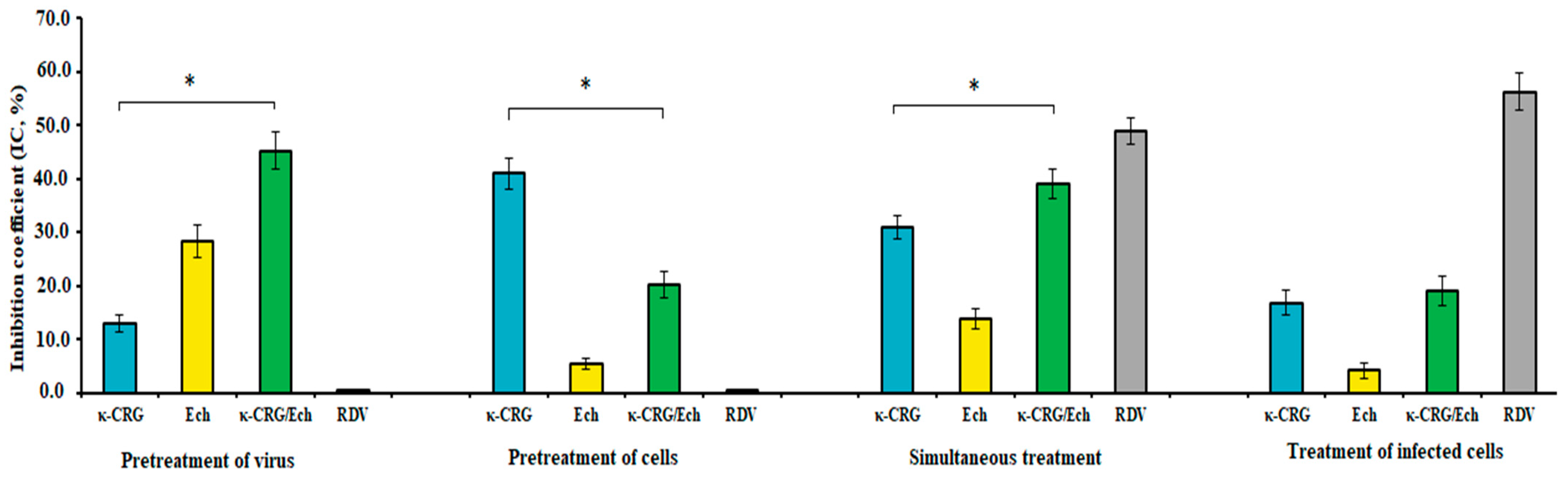
2.4. Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Activity of the κ-CRG/Ech Complex and Its Components
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Algal Material
4.2. Extraction and Characterization of Carrageenans
4.3. Preparation of CRG/Ech Complex
4.4. Molecular Docking
4.5. Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Activity of the Tested Compounds
4.5.1. Virus and Cell Culture
4.5.2. Cytotoxicity of the Tested Compounds
4.5.3. Infectious Viral Titer of SARS-CoV-2
4.5.4. Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Activity of Different Types of CRGs
4.5.5. Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Activity of the κ-CRG/Ech Complex
4.5.6. CPE Inhibition Assay
4.5.7. Virus Replication Level (VRL) Inhibition Assay
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Geahchan, S.; Ehrlich, H.; Rahman, M.A. The Anti-Viral Applications of Marine Resources for COVID-19 Treatment: An Overview. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wise, J. COVID-19: WHO declares end of global health emergency. BMJ 2023, 381, 1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poorolajal, J. The global pandemics are getting more frequent and severe. J. Res. Health Sci. 2021, 21, e00502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenharo, M. WHO declares end to COVID-19’s emergency phase. Nature 2023, 882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmadi, A.; Moghadamtousi, S.Z.; Abubakar, S.; Zandi, K. Antiviral Potential of Algae Polysaccharides Isolated from Marine Sources: A Review. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 825203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yim, S.K.; Kim, K.; Kim, I.H.; Chun, S.H.; Oh, T.H.; Kim, J.U.; Kim, J.U.; Jung, W.H.; Moon, H.S.; Ku, B.S.; et al. Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 Virus Entry by the Crude Polysaccharides of Seaweeds and Abalone Viscera In Vitro. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrew, M.; Jayaraman, G. Marine sulfated polysaccharides as potential antiviral drug candidates to treat Corona Virus disease (COVID-19). Carbohydr. Res. 2021, 505, 108326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Ghosh, K.; Hahn, F.; Wangen, C.; Strojan, H.; Muller, R.; Anand, N.; Ali, I.; Bera, K.; Ray, B. Chemically sulfated polysaccharides from natural sources: Assessment of extraction-sulfation efficiencies, structural features and antiviral activities. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 136, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wang, S.X.; Guan, H.S. The Antiviral Activities and Mechanisms of Marine Polysaccharides: An Overview. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 2795–2816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knutsen, S.H.; Myslabodski, D.E.; Larsen, B.; Usov, A.I. A modified system of nomenclature for red algal Galactans. Bot. Mar. 1994, 37, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falshaw, R.; Bixler, H.J.; Johndro, K. Structure and performance of commercial kappa-2 carrageenan extracts. Pt III. Structure analysis and performance in two dairy applications of extracts from the New Zealand red seaweed. Food Hydrocoll. 2003, 17, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yermak, I.M.; Khotimchenko, Y.S. Chemical properties, biological activities and applications of carrageenan from red algae. In Recent Advances in Marine Biotechnology; Fingerman, M., Nagabhushanam, R., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2003; Volume 9, pp. 207–255. [Google Scholar]
- Krylova, N.V.; Kravchenko, A.O.; Iunikhina, O.V.; Pott, A.B.; Likhatskaya, G.N.; Volod’ko, A.V.; Zaporozhets, T.S.; Shchelkanov, M.Y.; Yermak, I.M. Influence of the Structural Features of Carrageenans from Red Algae of the Far Eastern Seas on Their Antiviral Properties. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jousselin, C.; Pliego-Cortés, H.; Damour, A.; Garcia, M.; Bodet, C.; Robledo, D.; Bourgougnon, N.; Lévêque, N. Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Activity of Polysaccharides Extracted from Halymenia floresii and Solieria chordalis (Rhodophyta). Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, Y.; Shin, H.; Lee, M.K.; Kwon, O.S.; Shin, J.S.; Kim, Y.I.; Kim, C.W.; Lee, H.R.; Kim, M. Antiviral activity of lambda-carrageenan against influenza viruses and severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schütz, D.; Conzelmann, C.; Fois, G.; Groß, R.; Weil, T.; Wettstein, L.; Stenger, S.; Zelikin, A.; Hoffmann, T.K.; Frick, M.; et al. Carrageenan-containing over-the-counter nasal and oral sprays inhibit SARS-CoV-2 infection of airway epithelial cultures. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2021, 320, L750–L756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bovard, D.; van der Toorn, M.; Schlage, W.K.; Constant, S.; Renggli, K.; Peitsch, M.C.; Hoeng, J. Iota-carrageenan extracted from red algae is a potent inhibitor of SARS-CoV-2 infection in reconstituted human airway epithelia. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2022, 29, 101187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, S.; Jonsson, C.B.; Taylor, S.L.; Figueroa, J.M.; Dugour, A.V.; Palacios, C.; Vega, J.C. Iota-carrageenan inhibits SARS-CoV-2 in vitro at concentrations easily achievable by nasal and nebulization formulations. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0259943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueroa, J.M.; Lombardo, M.E.; Dogliotti, A.; Flynn, L.P.; Giugliano, R.; Simonelli, G.; Valentini, R.; Ramos, A.; Romano, P.; Marcote, M.; et al. Efficacy of a Nasal Spray Containing Iota-Carrageenan in the Postexposure Prophylaxis of COVID-19 in Hospital Personnel Dedicated to Patients Care with COVID-19 Disease. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2021, 14, 6277–6286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, W.; Moore, M.J.; Vasilieva, N.; Sui, J.; Wong, S.K.; Berne, M.A.; Somasundaran, M.; Sullivan, J.L.; Luzuriaga, K.; Greenough, T.C.; et al. Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 is a functional receptor for the SARS coronavirus. Nature 2003, 426, 450–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, C.B.; Farzan, M.; Chen, B.; Choe, H. Mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 entry into cells. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2022, 23, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, W.; Zhang, W.; Mitra, D.; McCandless, M.G.; Sharma, P.; Tandon, R.; Zhang, F.; Linhardt, R.J. The structure-activity relationship of the interactions of SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoproteins with glucuronomannan and sulfated galactofucan from Saccharina japonica. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 163, 1649–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, M.A. Antioxidants and viral infections: Host immune response and viral pathogenicity. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2001, 20, 384–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shikov, A.N.; Pozharitskaya, O.N.; Krishtopina, A.S.; Makarov, V.G. Naphthoquinone pigments from sea urchins: Chemistry and pharmacology. Phytochem. Rev. 2018, 17, 509–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.K.; Vasileva, E.A.; Mishchenko, N.P.; Fedoreyev, S.A.; Han, J. Multifaceted Clinical Effects of Echinochrome. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fedoreyev, S.A.; Krylova, N.V.; Mishchenko, N.P.; Vasileva, E.A.; Pislyagin, E.A.; Iunikhina, O.V.; Lavrov, V.F.; Svitich, O.A.; Ebralidze, L.K.; Leonova, G.N. Antiviral and antioxidant properties of echinochrome A. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padmi, H.; Prasedya, E.S.; Kharisma, V.D.; Widyananda, M.H.; Ansori, A.N.M.; Sibero, M.T.; Ullah, E.; Chylichcova, S.; Gumenyuk, O.; Bratishko, N.; et al. Macroalgae Bioactive Compounds for the potential Antiviral of SARS-CoV-2: An In Silico Study. J. Pure Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 16, 1018–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yermak, I.M.; Mischchenko, N.P.; Davydova, V.N.; Glazunov, V.P.; Tarbeeva, D.V.; Kravchenko, A.O.; Pimenova, E.A.; Sorokina, I.V. Carrageenans-Sulfated Polysaccharides from Red Seaweeds as Matrices for the Inclusion of Echinochrome. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krylova, N.V.; Gorbach, V.I.; Iunikhina, O.V.; Pott, A.B.; Glazunov, V.P.; Kravchenko, A.O.; Shchelkanov, M.Y.; Yermak, I.M. Antiherpetic Activity of Carrageenan Complex with Echinochrome A and Its Liposomal Form. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yermak, I.M.; Kim, Y.H.; Titlynov, E.A.; Isakov, V.V.; Solov’eva, T.F. Chemical structure and gel properties of carrageenans from algae belonging to the Gigartinaceae and Tichocarpaceae, collected from the Russian Pacific Coast. J. Appl. Phycol. 1999, 11, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, L.; Amado, A.M.; Critchley, A.T.; van de Velde, F.; Ribeiro-Claro, P.J.A. Identification of selected seaweed polysaccharides (phycocolloids) by vibrational spectroscopy (FTIR-ATR and FT-Raman). Food Hydrocoll. 2009, 23, 1903–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van De Velde, F.; Knutsen, S.H.; Usov, A.I.; Rollema, H.S.; Cerezo, A.S. 1H and 13C high resolution NMR spectroscopy of carrageenans: Application in research and industry. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2002, 13, 73–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastyuk, S.D.; Barabanova, A.O.; Correc, G.; Nazarenko, E.L.; Davydova, V.N.; Helbert, W.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Yermak, I.M. Analysis of structural heterogeneity of kappa/beta-carrageenan oligosaccharides from Tichocarpus crinitus by negative-ion ESI and tandem MALDI mass spectrometry. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 86, 546–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalitnik, A.A.; Marcov, P.A.; Anastyuk, S.D.; Barabanova, A.O.; Glazunov, V.P.; Popov, S.V.; Ovodov, Y.S.; Yermak, I.M. Gelling polysaccharide from Chondrus armatus and its oligosaccharides: The structural peculiarities and anti-inflammatory activity. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 115, 768–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Correc, G.; Barabanova, A.; Tuvikene, R.; Truus, K.; Yermak, I.; Helbert, W. Comparison of the structures of hybrid κ/β-carrageenans extracted from Furcellaria lumbricalis and Tichocarpus crinitus. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 88, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salih, A.E.M.; Thissera, B.; Yaseen, M.; Hassane, A.S.I.; El-Seedi, H.R.; Sayed, A.M.; Rateb, M.E. Marine Sulfated Polysaccharides as Promising Antiviral Agents: A Comprehensive Report and Modeling Study Focusing on SARS-CoV-2. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sliwoski, G.; Kothiwale, S.; Meiler, J.; Lowe, E.W., Jr. Computational methods in drug discovery. Pharmacol. Rev. 2013, 66, 334–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, C.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Y.; Hong, Q.; Xu, S.; Li, Z.; Yang, Y.; Huang, Z.; Cong, Y. Structural basis for SARS-CoV-2 Delta variant recognition of ACE2 receptor and broadly neutralizing antibodies. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caly, L.; Druce, J.D.; Catton, M.G.; Jans, D.A.; Wagstaff, K.M. The FDA-approved drug ivermectin inhibits the replication of SARS-CoV-2 in vitro. Antivir. Res. 2020, 178, 104787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamming, I.; Timens, W.; Bulthuis, M.L.; Lely, A.T.; Navis, G.; van Goor, H. Tissue distribution of ACE2 protein, the functional receptor for SARS coronavirus. A first step in understanding SARS pathogenesis. J. Pathol. 2004, 203, 631–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, P.H.M.; Sodero, A.C.R.; Jofily, P.; Silva, F.P., Jr. Key Topics in Molecular Docking for Drug Design. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aung, T.H. Molecular Docking of Carrageenans for Main Protease (Mpro) and Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 (ACE2) of SARS-CoV-2. Drug Des. 2022, 11, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Q.; Guo, Q.; Xu, W.; Li, Z.; Zhao, T. Specific Inhibitory Effect of κ-Carrageenan Polysaccharide on Swine Pandemic 2009 H1N1 Influenza Virus. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0126577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yermak, I.; Anastyuk, S.; Kravchenko, A.; Helbert, W.; Glazunov, V.; Shulgin, A.; Spirin, P.; Prassolov, V. New Insights into the Structure of Kappa/Beta-Carrageenan: A Novel Potential Inhibitor of HIV-1. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shulgin, A.; Spirin, P.; Lebedev, T.; Kravchenko, A.; Glasunov, V.; Yermak, I.; Prassolov, V. Comparative study of HIV-1 inhibition efficiency by carrageenans from red seaweeds family Gigartinaceae, Tichocarpaceae and Phyllophoraceae. Heliyon 2024, 10, e33407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van De Velde, F.; Lourenço, N.D.; Pinheiro, H.M.; Bakker, M. Carrageenan: A food-grade and biocompatible support for immobilisation techniques. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2002, 344, 815–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yermak, I.M.; Kravchenko, A.O.; Khasina, E.I.; Menchinskaya, E.S.; Pislyagin, E.A.; Sokolova, E.V.; Likhatskaya, G.N.; Aminin, D.L. The Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Carrageenan/Echinochrom Complex at Experimental Endotoxemia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawad, B.; Adhikari, P.; Podgornik, R.; Ching, W.-Y. Binding Interactions between Receptor-Binding Domain of Spike Protein and Human Angiotensin Converting Enzyme-2 in Omicron Variant. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2022, 13, 3915–3921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, M.; Woo, H.G. Omicron: A Heavily Mutated SARS-CoV-2 Variant Exhibits Stronger Binding to ACE2 and Potently Escapes Approved COVID-19 Therapeutic Antibodies. Front. Immunol. 2022, 12, 830527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shchelkanov, M.Y.; Sakhuriya, I.B.; Burunova, V.V.; Pavlova, T.V.; Kornilaeva, G.V.; Karamov, E.V.; Eremin, V.F. Dehydrogenase activity of infected cells and biological properties of HIV-1 variants. Biochemistry 1999, 64, 431–436. [Google Scholar]
- Pauwels, R.; Balzarini, J.; Baba, M.; Snoeck, R.; Schols, D.; Herdewijn, P.; Desmyter, J.; De Clercq, E. Rapid and automated tetrazolium-based colorimetric assay for the detection of anti-HIV compounds. J. Virol. Methods 1988, 20, 309–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latha, D.; Hrishikesh, D.; Shiban, G.; Chandrashekar, C.; Bharath, B.R. In silico, in vitro screening of plant extracts for anti-SARS-CoV-2 activity and evaluation of their acute and sub-acute toxicity. Phytomed Plus 2022, 2, 100233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuznetsova, T.A.; Krylova, N.V.; Kokoulin, M.S.; Persiyanova, E.V.; Maistrovskaya, O.S.; Milovankin, P.G.; Belov, Y.A.; Shchelkanov, M.Y. Polysaccharides from Marine Bacteria and Their Anti-SARS-CoV-2Activity. Microbiol. Res. 2025, 16, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
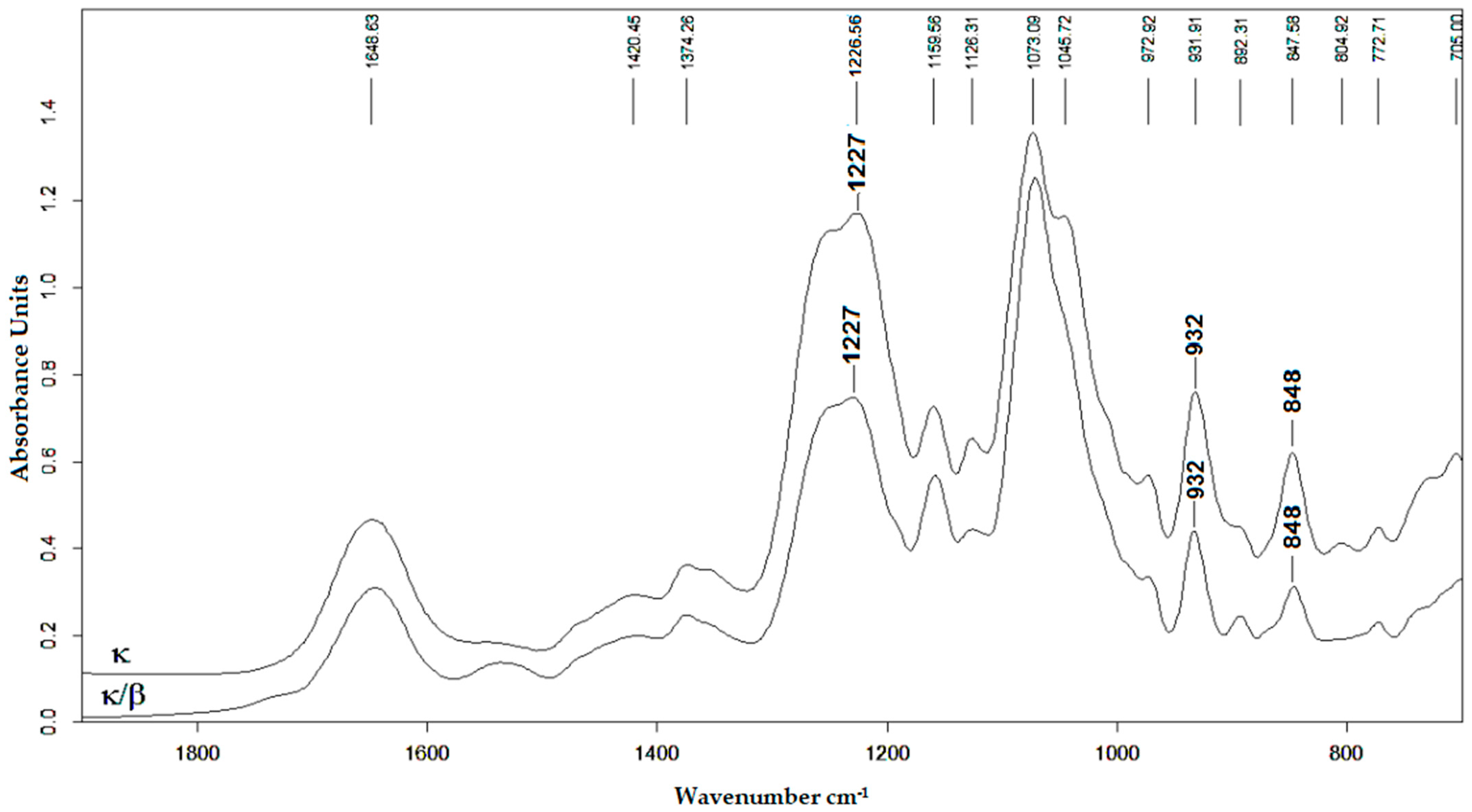
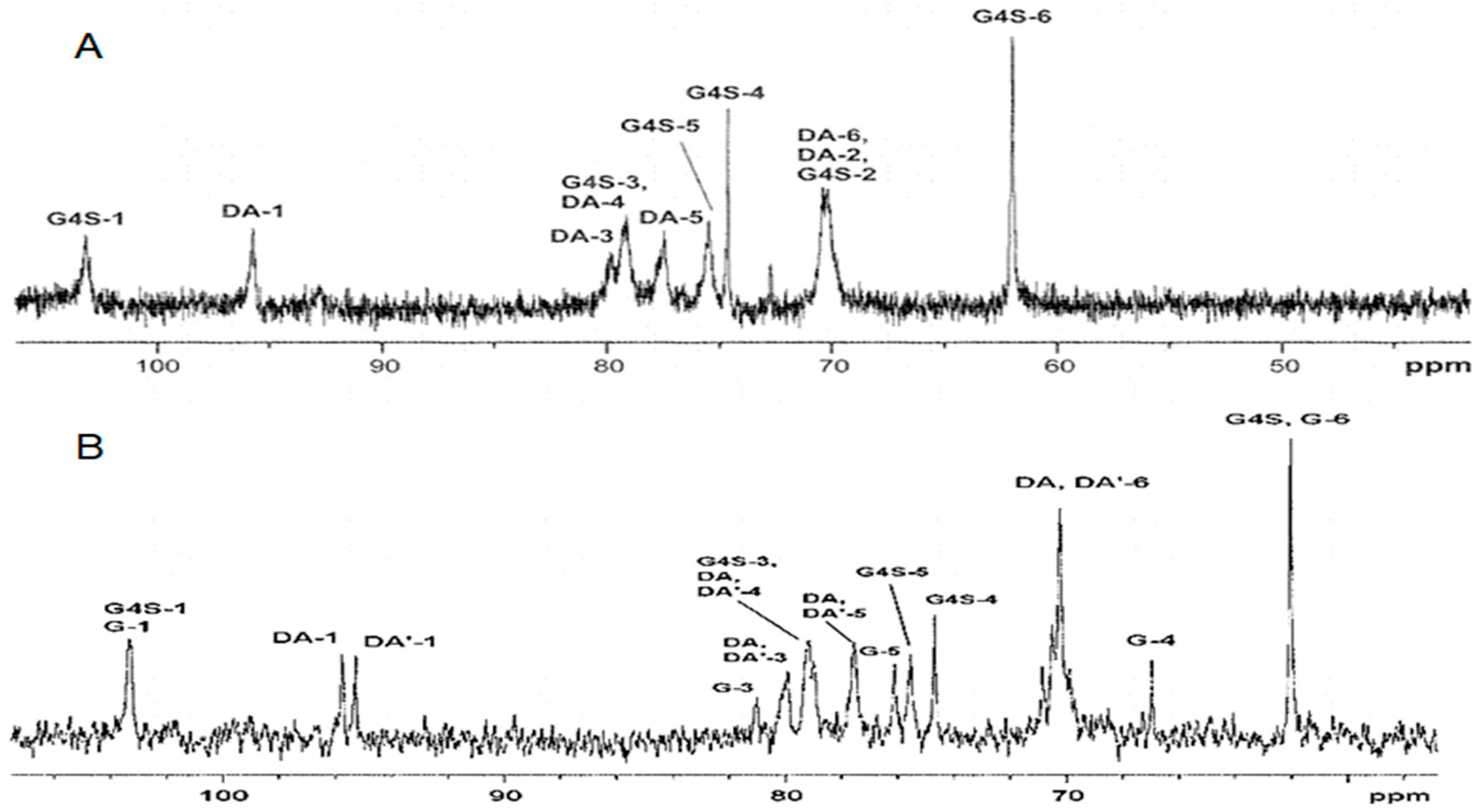
| Type of CRG | The Disaccharide Repeating Units | SO3Na% of Sample Weight | MW, kDa |
|---|---|---|---|
| Σ-CRG (κ + λ) kappa+ lambda | 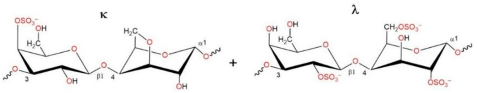 | 27.1 | 328 |
| κ-CRG kappa-type | 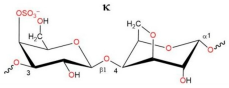 | 22.8 | 542 |
| κ/β kappa/beta-CRG | 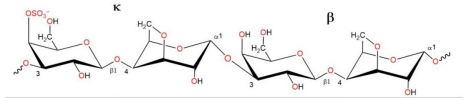 | 18.7 | 229 |
| λ-CRG lambda–type |  | 30.9 | 145 |
| Compounds | CC50 (µg/mL) | Pretreatment of Virus | Pretreatment of Cells | Simultaneous Treatment | Treatment of Infected Cells | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IC50 (µg/mL) | SI | IC50 (µg/mL) | SI | IC50 (µg/mL) | SI | IC50 (µg/mL) | SI | ||
| κ-CRG | >2000 | 75 ± 9 | 27 ± 3 * | 28 ± 3 | 71 ± 9 * | 62 ± 6 | 32 ± 3 * | 90 ± 9 | 22 ± 3 |
| Ech | 142 ± 6 | 4 ± 0.5 | 35 ± 4 * | 89 ± 9 | 1.6 ± 0.2 * | 41 ± 5 | 3.5 ± 0.4 * | 92 ± 9 | 1.5 ± 0.2 * |
| κ-CRG/Ech | >1000 | 13 ± 2 | 77 ± 8 | 49 ± 5 | 20 ± 2 | 24 ± 3 | 42 ± 4 | 43 ± 5 | 23 ± 3 |
| Ribavirin | 730 ± 80 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 207 ± 25 | 3.5 ± 0.4 | 158 ± 17 | 4.6 ± 0.5 |
| Remdesivir | 72 ± 9 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1.4 ± 0.1 | 51 ± 6 | 0.6 ± 0.1 | 120 ± 13 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Krylova, N.V.; Kravchenko, A.O.; Likhatskaya, G.N.; Iunikhina, O.V.; Glazunov, V.P.; Zaporozhets, T.S.; Shchelkanov, M.Y.; Yermak, I.M. Carrageenans and the Carrageenan-Echinochrome Complex as Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Agents. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6175. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136175
Krylova NV, Kravchenko AO, Likhatskaya GN, Iunikhina OV, Glazunov VP, Zaporozhets TS, Shchelkanov MY, Yermak IM. Carrageenans and the Carrageenan-Echinochrome Complex as Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Agents. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(13):6175. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136175
Chicago/Turabian StyleKrylova, Natalya V., Anna O. Kravchenko, Galina N. Likhatskaya, Olga V. Iunikhina, Valery P. Glazunov, Tatyana S. Zaporozhets, Mikhail Y. Shchelkanov, and Irina M. Yermak. 2025. "Carrageenans and the Carrageenan-Echinochrome Complex as Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Agents" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 13: 6175. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136175
APA StyleKrylova, N. V., Kravchenko, A. O., Likhatskaya, G. N., Iunikhina, O. V., Glazunov, V. P., Zaporozhets, T. S., Shchelkanov, M. Y., & Yermak, I. M. (2025). Carrageenans and the Carrageenan-Echinochrome Complex as Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Agents. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(13), 6175. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136175







