Micro- and Nanoplastics as Disruptors of the Endocrine System—A Review of the Threats and Consequences Associated with Plastic Exposure
Abstract
1. Introduction
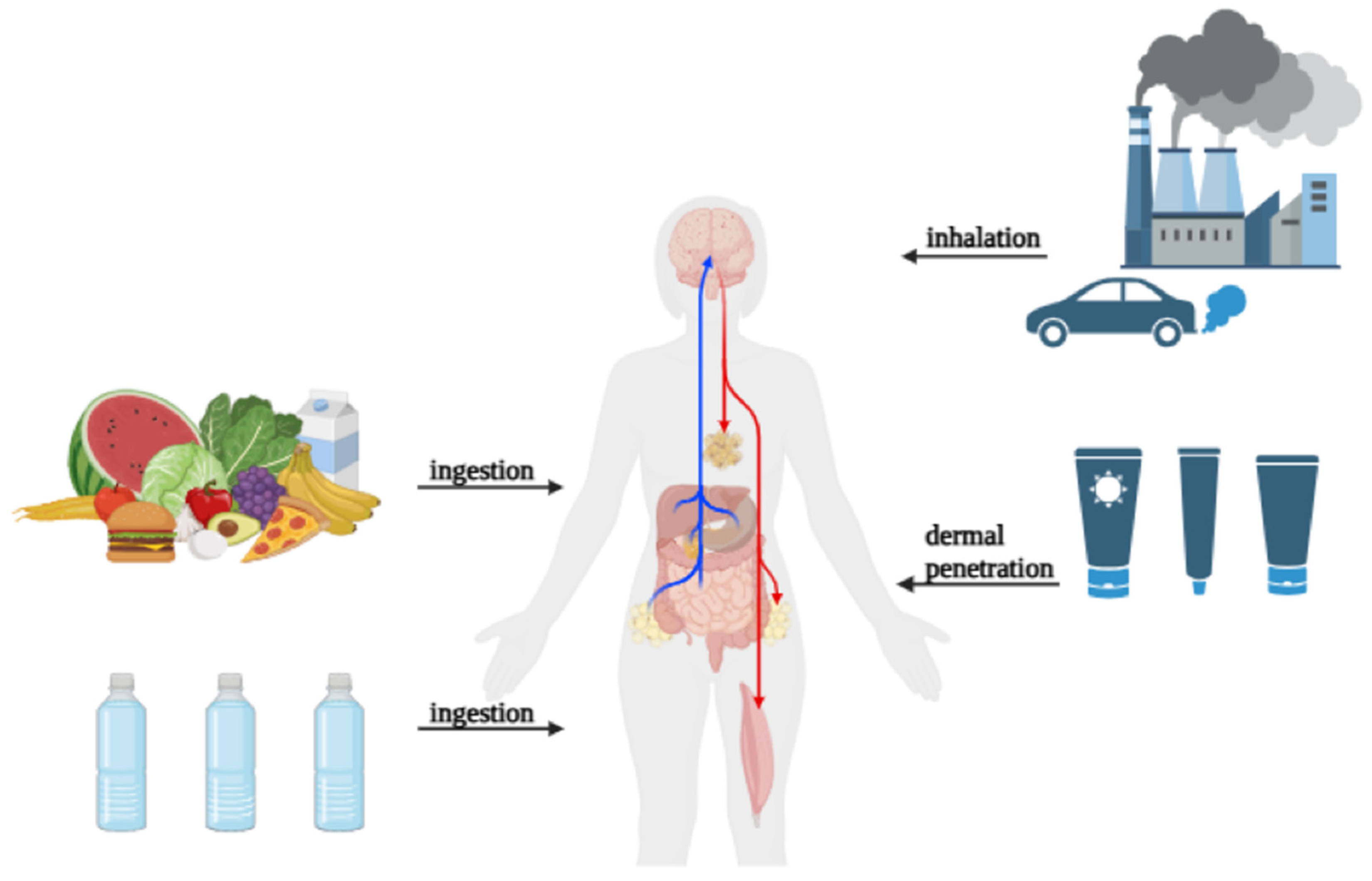
2. Routes of Exposure to Micro- and Nanoplastics in Humans
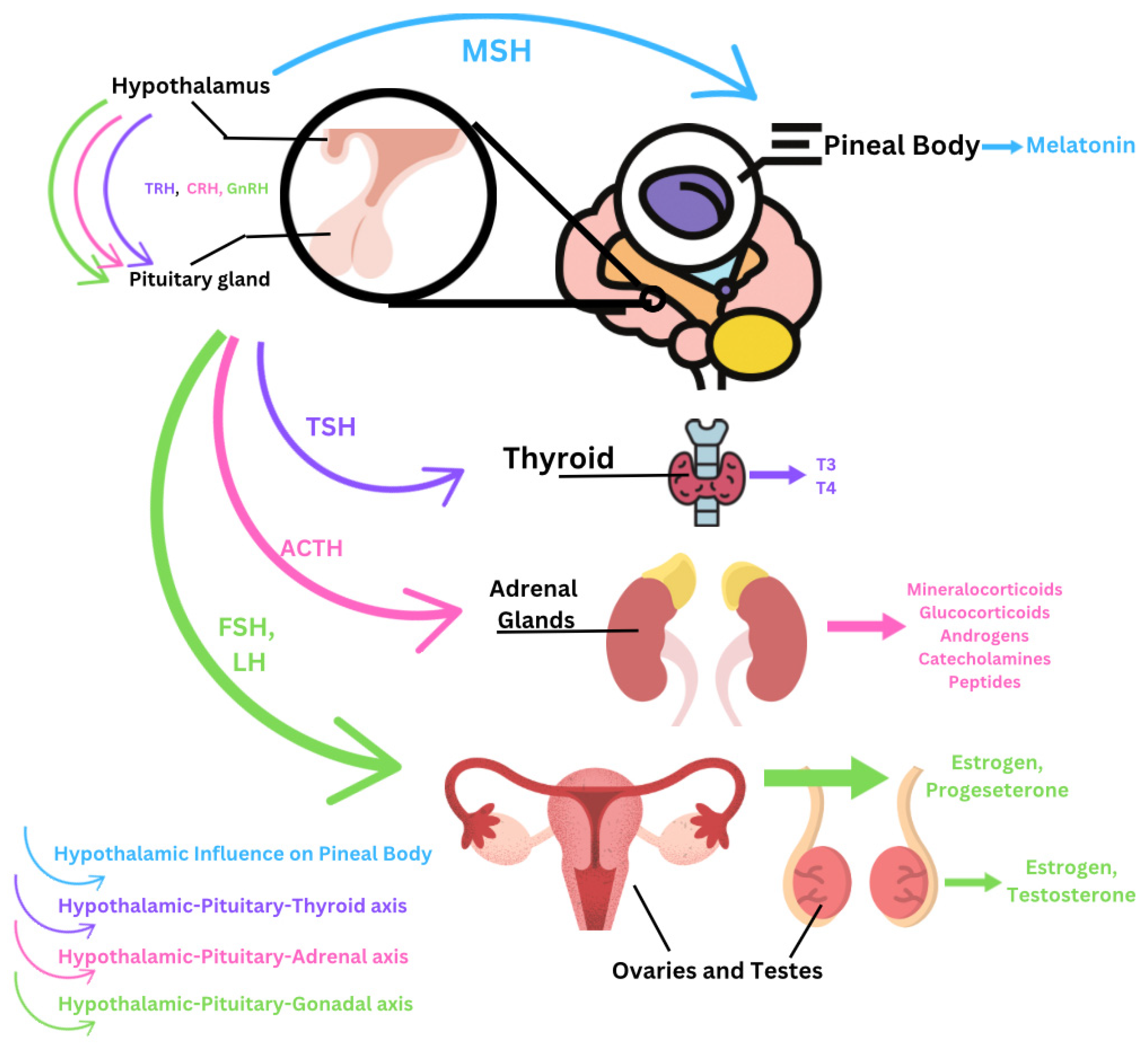
3. Accumulation of Micro- and Nanoplastics Within the Endocrine System
3.1. Hypothalamus
3.2. Pituitary Gland
3.3. Thyroid Gland
3.4. Parathyroids
3.5. Adrenal Glands
3.6. Pineal Body
3.7. Ovaries
3.8. Testes
4. Current Challenges and Limitations and Research Directions for Future Studies
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACTH | adrenocorticotropic hormone |
| ADH | antidiuretic hormone |
| AMH | anti-Mullerian hormone |
| BPA | bisphenol A |
| BTB | blood–testes barrier |
| CaSRs | calcium-sensing receptors |
| CAT | catalase |
| COCs | cumulus–oocyte complexes |
| CRH | corticotropin-releasing hormone |
| deio2 | deiodinase type 2 |
| EDCs | endocrine-disrupting chemicals |
| FSH | follicle-stimulating hormone |
| GH | growth hormone |
| GHRH | growth-hormone-releasing hormone |
| GnRH | gonadotropin-releasing hormone |
| GPx | glutathione peroxidase |
| GSH | glutathione |
| HPG | hypothalamic–pituitary–gonadal |
| HPA | hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal |
| HPT | hypothalamic–pituitary–thyroid |
| LH | luteinizing hormone |
| MDA | malondialdehyde |
| MNPs | micro- and nanoplastics |
| MP | microplastic |
| MPs | microplastics |
| MSH | melanocyte-stimulating hormone |
| NIS | sodium–iodine symporter |
| NP | PS nanoplastic–polystyrene |
| NPs | nanoplastics |
| Nrf2 | nuclear factor erythroid-2-related factor 2 |
| PBDEs | polybrominated diphenyl ethers |
| PCBs | polychlorinated biphenyls |
| PE | polyethylene |
| PP | polypropylene |
| PRL | prolactin |
| PS | polystyrene |
| PTH | parathyroid hormone |
| ROS | reactive oxygen species |
| SCTD | subclinical thyroid disease |
| SOD | superoxide dismutase |
| SOD2 | superoxide dismutase |
| T3 | triiodothyronine |
| T4 | thyroxine |
| TBT | tributyltin |
| TDCs | thyroid-disrupting chemicals |
| TRH | thyrotropin-releasing hormone |
| TSH | thyroid-stimulating hormone |
| nkx2.1 | NK2 homeobox 1 |
References
- da Silva Brito, W.A.; Mutter, F.; Wende, K.; Cecchini, A.L.; Schmidt, A.; Bekeschus, S. Consequences of nano and microplastic exposure in rodent models: The known and unknown. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2022, 19, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ullah, S.; Ahmad, S.; Guo, X.; Ullah, S.; Ullah, S.; Nabi, G.; Wanghe, K. A review of the endocrine disrupting effects of micro and nano plastic and their associated chemicals in mammals. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 13, 1084236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Martínez-Pinna, J.; Sempere-Navarro, R.; Medina-Gali, R.M.; Fuentes, E.; Quesada, I.; Sargis, R.M.; Trasande, L.; Nadal, A. Endocrine disruptors in plastics alter β-cell physiology and increase the risk of diabetes mellitus. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2023, 324, E488–E505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Liang, B.; Zhong, Y.; Huang, Y.; Lin, X.; Liu, J.; Lin, L.; Hu, M.; Jiang, J.; Dai, M.; Wang, B.; et al. Underestimated health risks: Polystyrene micro- and nanoplastics jointly induce intestinal barrier dysfunction by ROS-mediated epithelial cell apoptosis. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2021, 18, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Prüst, M.; Meijer, J.; Westerink, R.H.S. The plastic brain: Neurotoxicity of micro- and nanoplastics. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2020, 17, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Okamura, T.; Hamaguchi, M.; Hasegawa, Y.; Hashimoto, Y.; Majima, S.; Senmaru, T.; Ushigome, E.; Nakanishi, N.; Asano, M.; Yamazaki, M.; et al. Oral Exposure to Polystyrene Microplastics of Mice on a Normal or High-Fat Diet and Intestinal and Metabolic Outcomes. Environ. Health Perspect. 2023, 131, 27006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Martin, L.M.A.; Gan, N.; Wang, E.; Merrill, M.; Xu, W. Materials, surfaces, and interfacial phenomena in nanoplastics toxicology research. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 292 Pt B, 118442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Rehse, S.; Kloas, W.; Zarfl, C. Microplastics Reduce Short-Term Effects of Environmental Contaminants. Part I: Effects of Bisphenol A on Freshwater Zooplankton Are Lower in Presence of Polyamide Particles. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Amereh, F.; Babaei, M.; Eslami, A.; Fazelipour, S.; Rafiee, M. The emerging risk of exposure to nano(micro)plastics on endocrine disturbance and reproductive toxicity: From a hypothetical scenario to a global public health challenge. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 261, 114158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zurub, R.E.; Cariaco, Y.; Wade, M.G.; Bainbridge, S.A. Microplastics exposure: Implications for human fertility, pregnancy and child health. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 14, 1330396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Street, M.E.; Bernasconi, S. Microplastics, environment and child health. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2021, 47, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Niu, H.; Liu, S.; Jiang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Li, Y.; He, L.; Xing, M.; Li, X.; Wu, L.; Chen, Z.; et al. Are Microplastics Toxic? A Review from Eco-Toxicity to Effects on the Gut Microbiota. Metabolites 2023, 13, 739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yee, M.S.; Hii, L.W.; Looi, C.K.; Lim, W.M.; Wong, S.F.; Kok, Y.Y.; Tan, B.K.; Wong, C.Y.; Leong, C.O. Impact of Microplastics and Nanoplastics on Human Health. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Thuróczy, J. Editorial: Endocrine disruptors affecting the human and companion animal endocrine functions—Similarities and indicators in ONE Health concept. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1324986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Liu, M.; Liu, J.; Xiong, F.; Xu, K.; Pu, Y.; Huang, J.; Zhang, J.; Pu, Y.; Sun, R.; Cheng, K. Research advances of microplastics and potential health risks of microplastics on terrestrial higher mammals: A bibliometric analysis and literature review. Environ. Geochem. Health 2023, 45, 2803–2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Osman, A.I.; Hosny, M.; Eltaweil, A.S.; Omar, S.; Elgarahy, A.M.; Farghali, M.; Yap, P.S.; Wu, Y.S.; Nagandran, S.; Batumalaie, K.; et al. Microplastic sources, formation, toxicity and remediation: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2023, 21, 2129–2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Amobonye, A.; Bhagwat, P.; Raveendran, S.; Singh, S.; Pillai, S. Environmental Impacts of Microplastics and Nanoplastics: A Current Overview. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 768297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dube, E.; Okuthe, G.E. Plastics and Micro/Nano-Plastics (MNPs) in the Environment: Occurrence, Impact, and Toxicity. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 6667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aves, A.R.; Revell, L.E.; Gaw, S.; Ruffell, H.; Schuddeboom, A.; Wotherspoon, N.E.; LaRue, M.; McDonald, A.J. First evidence of microplastics in Antarctic snow. Cryosphere 2022, 16, 2127–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habumugisha, T.; Zhang, Z.; Uwizewe, C.; Yan, C.; Ndayishimiye, J.C.; Rehman, A.; Zhang, X. Toxicological review of micro- and nano-plastics in aquatic environments: Risks to ecosystems, food web dynamics and human health. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 278, 116426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, R.; Joshi, V.; Sahoo, G.C.; Jindal, N.; Tiwari, R.R.; Rana, S. Review of mechanisms and impacts of nanoplastic toxicity in aquatic organisms and potential impacts on human health. Toxicol. Rep. 2025, 14, 102013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subaramaniyam, U.; Allimuthu, R.S.; Vappu, S.; Ramalingam, D.; Balan, R.; Paital, B.; Panda, N.; Rath, P.K.; Ramalingam, N.; Sahoo, D.K. Effects of microplastics, pesticides and nano-materials on fish health, oxidative stress and antioxidant defense mechanism. Front. Physiol. 2023, 14, 1217666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madesh, S.; Gopi, S.; Sau, A.; Rajagopal, R.; Namasivayam, S.K.R.; Arockiaraj, J. Chemical contaminants and environmental stressors induced teratogenic effect in aquatic ecosystem—A comprehensive review. Toxicol. Rep. 2024, 13, 101819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, T.W.; Tochetto, G.; de Medeiros Lima, S.V.; de Oliveira, P.V.; Schossler, H.J.; de Oliveira, C.R.S.; da Silva Júnior, A.H. Nanoplastics and microplastics in agricultural systems: Effects on plants and implications for human consumption. Microplastics 2025, 4, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M.; Wang, X.; Ren, T.; Wang, J.; Shan, J. Microplastics contamination in food and beverages: Direct exposure to humans. J. Food Sci. 2021, 86, 2816–2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziani, K.; Ioniță-Mîndrican, C.B.; Mititelu, M.; Neacșu, S.M.; Negrei, C.; Moroșan, E.; Drăgănescu, D.; Preda, O.T. Microplastics: A Real Global Threat for Environment and Food Safety: A State of the Art Review. Nutrients 2023, 15, 617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, T.; Liu, Y.; Lyu, H.; He, Y.; Sun, H.; Tang, J.; Xing, B. Plastic takeaway food containers may cause human intestinal damage in routine life usage: Microplastics formation and cytotoxic effect. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 475, 134866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, F.; Cai, H.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, Q.; Shi, H. Microplastics in take-out food containers. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 399, 122969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Hu, X.; Tang, H.; Lu, K.; Li, H.; Liu, S.; Xing, B.; Ji, R. Steam disinfection releases micro(nano)plastics from silicone-rubber baby teats as examined by optical photothermal infrared microspectroscopy. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2022, 17, 76–85, Erratum in Nat. Nanotechnol. 2022, 17, 672. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41565-022-01155-8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Shi, Y.; Yang, L.; Xiao, L.; Kehoe, D.K.; Gun’ko, Y.K.; Boland, J.J.; Wang, J. Microplastic release from the degradation of polypropylene feeding bottles during infant formula preparation. Nat. Food 2020, 1, 746–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaston, E.; Woo, M.; Steele, C.; Sukumaran, S.; Anderson, S. Microplastics Differ Between Indoor and Outdoor Air Masses: Insights from Multiple Microscopy Methodologies. Appl. Spectrosc. 2020, 74, 1079–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dris, R.; Gasperi, J.; Mirande, C.; Mandin, C.; Guerrouache, M.; Langlois, V.; Tassin, B. A first overview of textile fibers, including microplastics, in indoor and outdoor environments. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 221, 453–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhou, N.; Chen, Y.; Ling, Z.; Xiang, P. Microplastics in the human body: A comprehensive review of exposure, distribution, migration mechanisms, and toxicity. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 946, 174215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Tu, C.; Li, R.; Wu, D.; Yang, J.; Xia, Y.; Peijnenburg, W.J.G.M.; Luo, Y. A systematic review of the impacts of exposure to micro- and nano-plastics on human tissue accumulation and health. Eco Environ. Health 2023, 2, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Tao, L.; Wang, Q.; Wang, F.; Li, G.; Song, M. Potential Health Impact of Microplastics: A Review of Environmental Distribution, Human Exposure, and Toxic Effects. Environ. Health 2023, 1, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giustra, M.; Sinesi, G.; Spena, F.; De Santes, B.; Morelli, L.; Barbieri, L.; Garbujo, S.; Galli, P.; Prosperi, D.; Colombo, M. Microplastics in Cosmetics: Open Questions and Sustainable Opportunities. ChemSusChem 2024, 17, e202401065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucur (Popa.), R.M.; Rădulescu, C.; Dulama, I.D.; Stîrbescu, R.M.; Bucurică, I.A.; Bănică, A.L.; Stănescu, S.G. Potential health risk of microplastic exposures from skin-cleansing products. Toxics 2025, 13, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Yuan, M.; Chen, Y.; Jin, X.; Shangguan, J.; Cui, J.; Chang, S.; Guo, M.; Wang, Y. The neglected potential source of microplastics from daily necessities: A study on protective mobile phone cases. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 441, 129911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enyoh, C.E.; Shafea, L.; Verla, A.W.; Verla, E.N.; Qingyue, W.; Chowdhury, T.; Paredes, M. Microplastics Exposure Routes and Toxicity Studies to Ecosystems: An Overview. Environ. Anal. Health Toxicol. 2020, 35, e2020004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auguet, T.; Bertran, L.; Barrientos-Riosalido, A.; Fabregat, B.; Villar, B.; Aguilar, C.; Sabench, F. Are Ingested or Inhaled Microplastics Involved in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease? Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 13495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhang, C.; Chen, J.; Ma, S.; Sun, Z.; Wang, Z. Microplastics May Be a Significant Cause of Male Infertility. Am. J. Men’s Health 2022, 16, 15579883221096549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sarasamma, S.; Audira, G.; Siregar, P.; Malhotra, N.; Lai, Y.H.; Liang, S.T.; Chen, J.R.; Chen, K.H.; Hsiao, C.D. Nanoplastics Cause Neurobehavioral Impairments, Reproductive and Oxidative Damages, and Biomarker Responses in Zebrafish: Throwing up Alarms of Wide Spread Health Risk of Exposure. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Jewett, E.; Arnott, G.; Connolly, L.; Vasudevan, N.; Kevei, E. Microplastics and Their Impact on Reproduction-Can we Learn From the C. elegans Model? Front. Toxicol. 2022, 4, 748912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Urli, S.; Corte Pause, F.; Crociati, M.; Baufeld, A.; Monaci, M.; Stradaioli, G. Impact of Microplastics and Nanoplastics on Livestock Health: An Emerging Risk for Reproductive Efficiency. Animals 2023, 13, 1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kannan, K.; Vimalkumar, K. A Review of Human Exposure to Microplastics and Insights Into Microplastics as Obesogens. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 724989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Arriagada, A.A.; Albornoz, E.; Opazo, M.C.; Becerra, A.; Vidal, G.; Fardella, C.; Michea, L.; Carrasco, N.; Simon, F.; Elorza, A.A.; et al. Excess iodide induces an acute inhibition of the sodium/iodide symporter in thyroid male rat cells by increasing reactive oxygen species. Endocrinology 2015, 156, 1540–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serrano-Nascimento, C.; Nunes, M.T. Perchlorate, nitrate, and thiocyanate: Environmental relevant NIS-inhibitors pollutants and their impact on thyroid function and human health. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 995503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curran, P.G.; DeGroot, L.J. The effect of hepatic enzyme-inducing drugs on thyroid hormones and the thyroid gland. Endocr. Rev. 1991, 12, 135–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhao, L.; Wei, L.; Li, L. DEHP reduces thyroid hormones via interacting with hormone synthesis-related proteins, deiodinases, transthyretin, receptors, and hepatic enzymes in rats. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2015, 22, 12711–12719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manolis, A.A.; Manolis, T.A.; Melita, H.; Manolis, A.S. Subclinical thyroid dysfunction and cardiovascular consequences: An alarming wake-up call? Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 2020, 30, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, N.; Katsouli, J.; Marczylo, E.L.; Gant, T.W.; Wright, S.; Bernardino de la Serna, J. The potential impacts of micro-and-nano plastics on various organ systems in humans. EBioMedicine 2024, 99, 104901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.; Jose, A.; Sharma, S. Physiology, Parathyroid Hormone. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Loupy, A.; Ramakrishnan, S.K.; Wootla, B.; Chambrey, R.; de la Faille, R.; Bourgeois, S.; Bruneval, P.; Mandet, C.; Christensen, E.I.; Faure, H.; et al. PTH-independent regulation of blood calcium concentration by the calcium-sensing receptor. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 3355–3367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goltzman, D.; Mannstadt, M.; Marcocci, C. Physiology of the Calcium-Parathyroid Hormone-Vitamin D Axis. Front. Horm. Res. 2018, 50, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, R.; Thompson, J.R. The regulation of parathyroid hormone secretion and synthesis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 22, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tennakoon, S.; Aggarwal, A.; Kállay, E. The calcium-sensing receptor and the hallmarks of cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1863 Pt B, 1398–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babić Leko, M.; Pleić, N.; Gunjača, I.; Zemunik, T. Environmental Factors That Affect Parathyroid Hormone and Calcitonin Levels. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 23, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, L.; Zhu, X.; Shrubsole, M.J.; Fan, H.; Chen, J.; Dong, J.; Hao, C.M.; Dai, Q. Renal function, bisphenol A, and alkylphenols: Results from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES 2003–2006). Environ. Health Perspect. 2011, 119, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langeveld, M.; Hollak, C.E.M. Bone health in patients with inborn errors of metabolism. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2018, 19, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerman, L.; Anastasopoulou, C.; McKeon, B. Osteomalacia; Aventura Hospital and Medical Center: Aventura, FL, USA; Jefferson Einstein Medical Center: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Megha, R.; Wehrle, C.J.; Kashyap, S.; Leslie, S.W. Anatomy, Abdomen and pelvis: Adrenal glands (suprarenal glands). In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482264/ (accessed on 30 April 2025).
- Abichandani, V.K. Hypercortisolism and type 2 diabetes: The sinister duo! Clin. Diabetol. 2024, 13, 243–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, A.L.; Pranckevicius, N.A.; Nurse, C.A.; Scott, G.R. Regulation of catecholamine release from the adrenal medulla is altered in deer mice (Peromyscus maniculatus) native to high altitudes. Am. J. Physiol.-Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2019, 317, R407–R417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayavel, S.; Govindaraju, B.; Michael, J.R.; Viswanathan, B. Impacts of micro and nanoplastics on human health. Bull. Natl. Res. Cent. 2024, 48, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faye, C.; Mcgowan, J.C.; Denny, C.A.; David, D.J. Neurobiological Mechanisms of Stress Resilience and Implications for the Aged Population. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2018, 16, 234–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anne, B.; Raphael, R. Endocrine Disruptor Chemicals; MDText.com, Inc.: South Dartmouth, MA, USA, 2021. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK569327/ (accessed on 30 April 2025).
- Pazderska, A.; Pearce, S.H. Adrenal insufficiency—Recognition and management. Clin. Med. 2017, 17, 258–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arendt, J.; Aulinas, A. Physiology of the Pineal Gland and Melatonin. [Updated 2022 Oct 30]; MDText.com, Inc.: South Dartmouth, MA, USA, 2000. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK550972/# (accessed on 30 April 2025).
- El Gazzar, W.B.; Sliem, R.E.; Bayoumi, H.; Nasr, H.E.; Shabanah, M.; Elalfy, A.; Radwaan, S.E.; Gebba, M.A.; Mansour, H.M.; Badr, A.M.; et al. Melatonin Alleviates Intestinal Barrier Damaging Effects Induced by Polyethylene Microplastics in Albino Rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yan, Q.; Xu, C.; Liu, Q.; Shen, Y.; Xu, J.; Wang, G.; Zhao, P. Melatonin attenuates polystyrene microplastics induced motor neurodevelopmental defect in zebrafish (Danio rerio) by activating nrf2-isl2a Axis. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 241, 113754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Liang, B.; Li, Z.; Zhong, Y.; Wang, B.; Zhang, B.; Du, J.; Ye, R.; Xian, H.; Min, W.; et al. Polystyrene nanoplastic exposure induces excessive mitophagy by activating AMPK/ULK1 pathway in differentiated SH-SY5Y cells and dopaminergic neurons in vivo. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2023, 20, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wan, S.; Wang, X.; Chen, W.; Wang, M.; Zhao, J.; Xu, Z.; Wang, R.; Mi, C.; Zheng, Z.; Zhang, H. Exposure to high dose of polystyrene nanoplastics causes trophoblast cell apoptosis and induces miscarriage. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2024, 21, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Khan, A.; Jia, Z. Recent insights into uptake, toxicity, and molecular targets of microplastics and nanoplastics relevant to human health impacts. iScience. 2023, 26, 106061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Landrigan, P.J.; Raps, H.; Cropper, M.; Bald, C.; Brunner, M.; Canonizado, E.M.; Charles, D.; Chiles, T.C.; Donohue, M.J.; Enck, J.; et al. The Minderoo-Monaco Commission on Plastics and Human Health. Ann. Glob. Health 2023, 89, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Geng, Y.; Liu, Z.; Hu, R.; Huang, Y.; Li, F.; Ma, W.; Wu, X.; Dong, H.; Song, K.; Xu, X.; et al. Toxicity of microplastics and nanoplastics: Invisible killers of female fertility and offspring health. Front. Physiol. 2023, 14, 1254886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kloc, M. Seahorse Male Pregnancy as a Model System to Study Pregnancy, Immune Adaptations, and Environmental Effects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- López de Las Hazas, M.C.; Boughanem, H.; Dávalos, A. Untoward Effects of Micro- and Nanoplastics: An Expert Review of Their Biological Impact and Epigenetic Effects. Adv. Nutr. 2022, 13, 1310–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Canosa, L.F.; Bertucci, J.I. The effect of environmental stressors on growth in fish and its endocrine control. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1109461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Venditti, M.; Ben Hadj Hassine, M.; Messaoudi, I.; Minucci, S. The simultaneous administration of microplastics and cadmium alters rat testicular activity and changes the expression of PTMA, DAAM1 and PREP. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2023, 11, 1145702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Brun, N.R.; van Hage, P.; Hunting, E.R.; Haramis, A.G.; Vink, S.C.; Vijver, M.G.; Schaaf, M.J.M.; Tudorache, C. Polystyrene nanoplastics disrupt glucose metabolism and cortisol levels with a possible link to behavioural changes in larval zebrafish. Commun Biol. 2019, 2, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
| Type of Plastic | Common Uses | Environmental Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Polyethylene (PE) | Plastic bags, bottles | Very resistant to degradation, widespread in oceans and soils |
| Polypropylene (PP) | Food containers, straws, bottle caps | Floats in water, slowly degrades under UV exposure |
| Polystyrene (PS) | Disposable cutlery, insulation materials | Brittle material, which breaks into small particles |
| Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) | Pipes, medical devices, flooring | Releases harmful additives |
| Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) | Beverage bottles, clothing fibers | Recyclable but persistent, common in marine environments |
| Polycarbonate (PC) | Electronic devices, eyewear lenses, water bottles | Can leach BPA and forms small, durable fragments |
| Effects on Ovaries | Description |
|---|---|
| Reproductive impact | Reduced ovarian weight, fewer follicles, decreased fertility, impaired oocyte maturation |
| Oxidative stress | Increased ROS and MDA, decreased antioxidant activity (SOD, CAT, GPx), granulosa cell apoptosis |
| Fibrosis | Accumulation of collagen and fibronectin in ovaries, ovarian and uterine tissue fibrosis |
| Hormonal imbalance | Increased LH, FSH, and T, decreased estradiol and AMH, disrupted menstrual cycle, potential masculinization |
| Follicular development | Delayed follicle growth, increased atresia, zona pellucida breakdown in various species |
| Effects on Testes | Details |
|---|---|
| Reproductive function | Reduced sperm quality, abnormal spermatogenesis, decreased sperm count, impaired motility. |
| Oxidative stress | Increased ROS and MDA, decreased antioxidant activity (SOD, CAT, GPx), testicular inflammation, cell death. |
| Hormonal disruption | Reduced testosterone production, dysregulated HPG axis, antiandrogenic effects, altered sperm phenotype |
| Structural damage | Seminiferous tubule degeneration, disrupted BTB, shrunken germ cells, reduced testicular weight. |
| Inflammatory response | Increased TNF-alpha, IL-1beta, and IL-6, activation of apoptotic factors (caspase-3), DNA damage in testes |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tyc, H.J.; Kłodnicka, K.; Teresińska, B.; Karpiński, R.; Flieger, J.; Baj, J. Micro- and Nanoplastics as Disruptors of the Endocrine System—A Review of the Threats and Consequences Associated with Plastic Exposure. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6156. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136156
Tyc HJ, Kłodnicka K, Teresińska B, Karpiński R, Flieger J, Baj J. Micro- and Nanoplastics as Disruptors of the Endocrine System—A Review of the Threats and Consequences Associated with Plastic Exposure. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(13):6156. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136156
Chicago/Turabian StyleTyc, Hanna J., Karolina Kłodnicka, Barbara Teresińska, Robert Karpiński, Jolanta Flieger, and Jacek Baj. 2025. "Micro- and Nanoplastics as Disruptors of the Endocrine System—A Review of the Threats and Consequences Associated with Plastic Exposure" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 13: 6156. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136156
APA StyleTyc, H. J., Kłodnicka, K., Teresińska, B., Karpiński, R., Flieger, J., & Baj, J. (2025). Micro- and Nanoplastics as Disruptors of the Endocrine System—A Review of the Threats and Consequences Associated with Plastic Exposure. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(13), 6156. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136156









