Zingerone as a Neuroprotective Agent Against Cognitive Disorders: A Systematic Review of Preclinical Studies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy and Screening
2.2. Inclusion Criteria
- Memory function was measured using associated behavioural parameters such as Morris water maze, Y-Maze and Recognition Memory.
- Anxiety was measured using associated behavioural parameters such as an elevated plus maze, open field test and light/dark choice.
- Depressive-like behaviour was measured using associated parameters such as forced swimming test, shock exposure (tail or foot shock), open space swimming test, sucrose consumption test, etc.
- Neuroinflammation was measured using associated inflammatory markers, factors and pathways, including cytokines, chemokines, nitric oxide, NF-kB, NLRP3 inflammasome and Toll-like receptor-4 (TLR4).
2.3. Exclusion Criteria
2.4. Data Extraction
2.5. Quality Assessment of Included Studies
3. Results
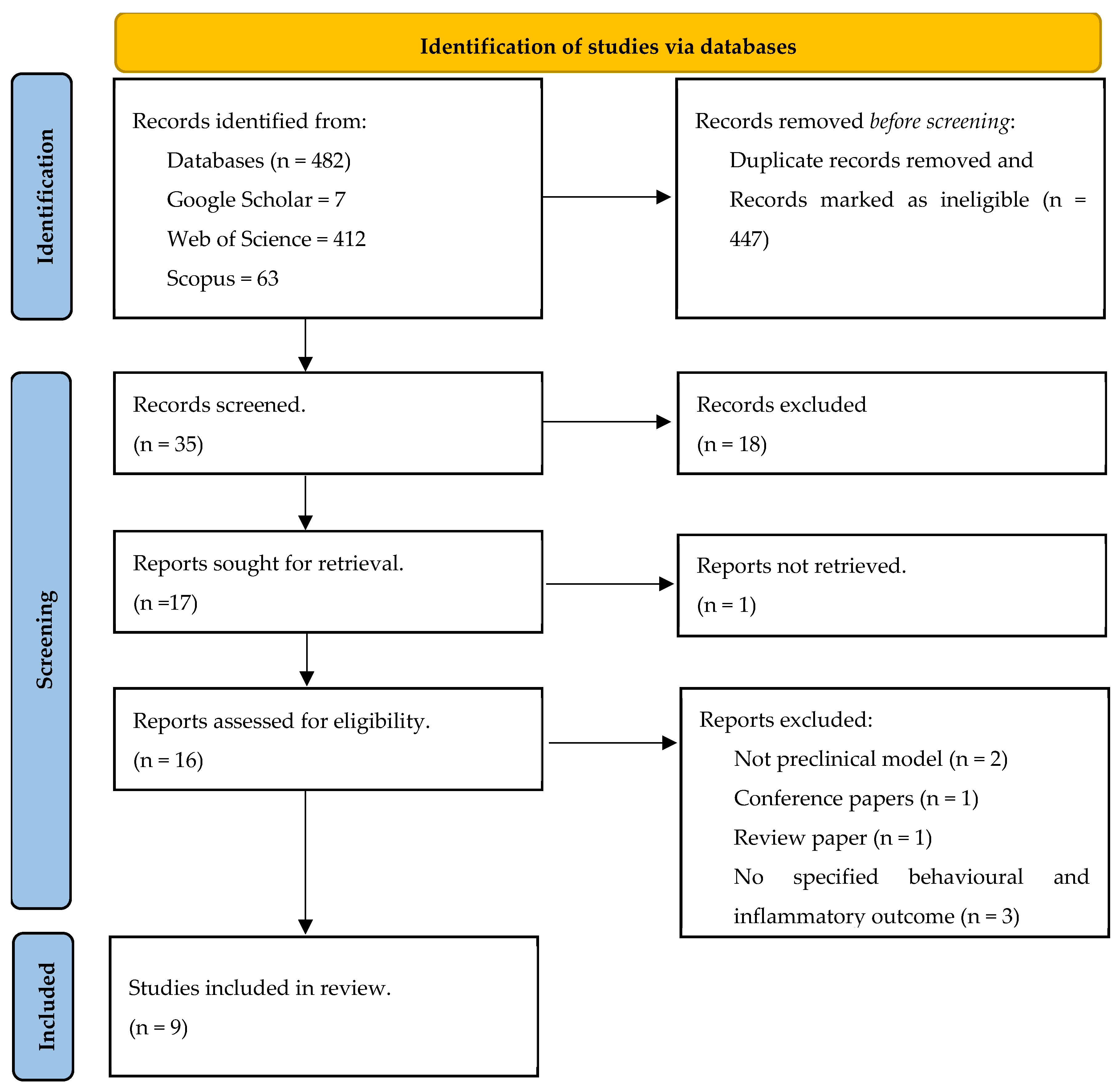
3.1. Article Selection and Study Characteristics
3.2. Quality Assessment of Methods and Experimental Models of Included Studies
3.3. Effect of Zingerone on Neuroinflammatory Markers
3.4. Zingerone and Memory Function
3.5. Effect of Zingerone on Anxiety and Depressive-like Disorders
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Casten, R.; Leiby, B.E.; Kelley, M.; Rovner, B.W. A Randomized Controlled Trial to Test the Efficacy of a Diabetes Behavioral Intervention to Prevent Memory Decline in Older Blacks/African Americans with Diabetes and Mild Cognitive Impairment. Contemp. Clin. Trials 2022, 123, 106977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolphin, H.; Dyer, A.H.; Dukelow, T.; Finucane, C.; Commins, S.; Kennelly, S.P. Safety and Feasibility of Transcutaneous Vagus Nerve Stimulation in Mild Cognitive Impairment: Vinci-Ad Study Protocol. BMC Neurol. 2023, 23, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, T.; Jiang, X.; Xu, N.; Zhao, X.; Xie, X.; Xia, X.; Bian, X.; Liu, H. Risk Factors and Metabolomics of Mild Cognitive Impairment in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2024, 11, 1341290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humphreys, J.; Hernández, M.D.C.V. Impact of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon Exposure on Cognitive Function and Neurodegeneration in Humans: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 1052333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Ranadive, N.; Kinra, M.; Nampoothiri, M.; Arora, D.; Mudgal, J. An Overview on Chemotherapy-Induced Cognitive Impairment and Potential Role of Antidepressants. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2020, 18, 838–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kizilbash, A.H.; Vanderploeg, R.D.; Curtiss, G. The Effects of Depression and Anxiety on Memory Performance. Arch. Clin. Neuropsychol. 2002, 17, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castaneda, A.E.; Tuulio-Henriksson, A.; Marttunen, M.; Suvisaari, J.; Lönnqvist, J. A Review on Cognitive Impairments in Depressive and Anxiety Disorders with a Focus on Young Adults. J. Affect. Disord. 2008, 106, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rock, P.L.; Roiser, J.P.; Riedel, W.J.; Blackwell, A.D. Cognitive Impairment in Depression: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Psychol. Med. 2014, 44, 2029–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Zhang, M.; Hao, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Liu, C. Neuroinflammation Mechanisms of Neuromodulation Therapies for Anxiety and Depression. Transl. Psychiatry 2023, 13, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Bi, W.; Xiao, S.; Lan, X.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, J.; Lu, D.; Wei, W.; Wang, Y.; Li, H.; et al. Neuroinflammation Induced by Lipopolysaccharide Causes Cognitive Impairment in Mice. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.H.; Tu, J.L.; Li, X.H.; Hua, Q.; Liu, W.Z.; Liu, Y.; Pan, B.X.; Hu, P.; Zhang, W.H. Neuroinflammation Induces Anxiety- and Depressive-Like Behavior by Modulating Neuronal Plasticity in the Basolateral Amygdala. Brain Behav. Immun. 2021, 91, 505–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.L.; Han, Q.Q.; Gong, W.Q.; Pan, D.H.; Wang, L.Z.; Hu, W.; Yang, M.; Li, B.; Yu, J.; Liu, Q. Microglial Activation Mediates Chronic Mild Stress-Induced Depressive- and Anxiety-Like Behavior in Adult Rats. J. Neuroinflamm. 2018, 15, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitaoka, S. Inflammation in the Brain and Periphery Found in Animal Models of Depression and Its Behavioral Relevance. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2022, 148, 262–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fourrier, C.; Singhal, G.; Baune, B.T. Neuroinflammation and Cognition across Psychiatric Conditions. CNS Spectr. 2019, 24, 4–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Lin, E.; Xiao, R.; Li, Z.; Liu, B.; Wang, J. Structural Characteristic, Strong Antioxidant, and Anti-Gastric Cancer Investigations on an Oleoresin from Ginger (Zingiber Officinale Var. Roscoe). Foods 2024, 13, 1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, B.; Rehman, M.U.; Amin, I.; Arif, A.; Rasool, S.; Bhat, S.A.; Afzal, I.; Hussain, I.; Bilal, S.; Mir, M. A Review on Pharmacological Properties of Zingerone (4-(4-Hydroxy-3-Methoxyphenyl)-2-Butanone). Sci. World J. 2015, 2015, 816364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamsabadi, S.; Nazer, Y.; Ghasemi, J.; Mahzoon, E.; Rahimi, V.B.; Ajiboye, B.O.; Askari, V.R. Promising Influences of Zingerone against Natural and Chemical Toxins: A Comprehensive and Mechanistic Review. Toxicon 2023, 233, 107247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, X.; Liu, H.; Yuwen, Q.; Wang, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, X.; Sun, J. Protective Effects of Zingerone on High Cholesterol Diet-Induced Atherosclerosis through Lipid Regulatory Signaling Pathway. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2021, 40, 1732–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wali, A.F.; Rehman, M.U.; Raish, M.; Kazi, M.; Rao, P.G.M.; Alnemer, O.; Ahmad, P.; Ahmad, A. Zingerone [4-(3-Methoxy-4-Hydroxyphenyl)-Butan-2] Attenuates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammation and Protects Rats from Sepsis Associated Multi Organ Damage. Molecules 2020, 25, 5127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.K.; Chung, S.W.; Kim, D.H.; Kim, J.M.; Lee, E.K.; Kim, J.Y.; Ha, Y.M.; Kim, Y.H.; No, J.K.; Chung, H.S.; et al. Modulation of Age-Related Nf-Kappab Activation by Dietary Zingerone Via Mapk Pathway. Exp. Gerontol. 2010, 45, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyaya, K.; Sharma, P.K.; Akhtar, A.; Sah, S.P. Protective Effects of Zingerone against Depression-Like Behavior and Biochemical Changes in Chronic Stressed Rats: Antioxidant Effects. J. Med. Food 2022, 25, 576–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molavinia, S.; Nikravesh, M.; Pashmforoosh, M.; Vardanjani, H.R.; Khodayar, M.J. Zingerone Alleviates Morphine Tolerance and Dependence in Mice by Reducing Oxidative Stress-Mediated Nlrp3 Inflammasome Activation. Neurochem. Res. 2023, 49, 415–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Q.; Zhu, J.Z.; Bao, X.Y.; Zhu, P.C.; Tong, Q.; Huang, Y.Y.; Zhang, Q.H.; Zhang, K.J.; Zheng, G.Q.; Wang, Y. A Preclinical Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Astragaloside Iv for Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.S.; Bae, W.Y.; Park, C.; Jeong, J.W. Zingerone Activates Vmat2 During Mpp+-Induced Cell Death. Phytother. Res. 2015, 29, 1783–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emeka, A.G.; Augustine, O.; Chidinma, O.E.; Nto, N.J. Zingerone Improves Memory Impairment in Wistar Rats Exposed to Cadmium Via Modulation of Redox Imbalance. J. Krishna Inst. Med. Sci. Univ. 2023, 12, 3–16. [Google Scholar]
- Chopra, D.; Chadha, V.D.; Dhawan, D.K. Understanding the Role of Zingerone on Biochemical and Behavioral Changes in Rat Brain Inflicted with C6 Glioma Cells. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2023, 37, e23477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadhav, G.B.; Sable, R.R. Gramine and Zingerone Mitigates Neuroinflammation Related Depressive Behaviour Induced by Chronic Unpredictable Mild Stress in Rat. Res. J. Pharm. Technol. 2023, 16, 3067–3074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleki, M.; Moosavi, M.; Zeidooni, L.; Azadnasab, R.; Khodayar, M.J. Zingerone Neuroprotective Effects in a Rat Model of Manic-Like Behavior Induced by Ketamine. Learn. Motiv. 2023, 84, 101934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, S.; Wali, A.F.; Rashid, S.M.; Alsaffar, R.M.; Ahmad, A.; Jan, B.L.; Paray, B.A.; Alqahtani, S.M.A.; Arafah, A.; Rehman, M.U. Zingerone Targets Status Epilepticus by Blocking Hippocampal Neurodegeneration Via Regulation of Redox Imbalance, Inflammation and Apoptosis. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, S.; Gur, C.; Kucukler, S.; Akaras, N.; Kandemir, F.M. Zingerone Attenuates Sciatic Nerve Damage Caused by Sodium Arsenite by Inhibiting Nf-Κb, Caspase-3, and Atf-6/Chop Pathways and Activating the Akt-2/Foxo1 Pathway. Iran. J. Basic. Med. Sci. 2024, 27, 485–491. [Google Scholar]
- Piirainen, S.; Youssef, A.; Song, C.; Kalueff, A.V.; Landreth, G.E.; Malm, T.; Tian, L. Psychosocial Stress on Neuroinflammation and Cognitive Dysfunctions in Alzheimer’s Disease: The Emerging Role for Microglia? Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2017, 77, 148–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, S.W.; Kim, Y.K. The Role of Neuroinflammation and Neurovascular Dysfunction in Major Depressive Disorder. J. Inflamm. Res. 2018, 11, 179–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castanon, N.; Luheshi, G.; Layé, S. Role of Neuroinflammation in the Emotional and Cognitive Alterations Displayed by Animal Models of Obesity. Front. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, M.; Mei, X.L.; Zhao, Y.N. Sepsis and Cerebral Dysfunction: Bbb Damage, Neuroinflammation, Oxidative Stress, Apoptosis and Autophagy as Key Mediators and the Potential Therapeutic Approaches. Neurotox. Res. 2021, 39, 489–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Gan, L.; Ren, L.; Lin, Y.; Ma, C.; Lin, X. Factors Influencing the Blood-Brain Barrier Permeability. Brain Res. 2022, 1788, 147937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabab, T.; Khanabdali, R.; Moghadamtousi, S.Z.; Kadir, H.A.; Mohan, G. Neuroinflammation Pathways: A General Review. Int. J. Neurosci. 2017, 127, 624–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blamire, A.M.; Anthony, D.C.; Rajagopalan, B.; Sibson, N.R.; Perry, V.H.; Styles, P. Interleukin-1β-Induced Changes in Blood–Brain Barrier Permeability, Apparent Diffusion Coefficient, and Cerebral Blood Volume in the Rat Brain: A Magnetic Resonance Study. J. Neurosci. 2000, 20, 8153–8159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, T.; Leng, B. Cynaropicrin Averts the Oxidative Stress and Neuroinflammation in Ischemic/Reperfusion Injury through the Modulation of Nf-Kb. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2023, 195, 5424–5438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Ansari, V.A.; Mahmood, T.; Ahsan, F.; Wasim, R. Neurodegeneration: Microglia: Nf-Kappab Signaling Pathways. Drug Res. 2022, 72, 496–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ljubisavljevic, S.; Stojanovic, I. Neuroinflammation and Demyelination from the Point of Nitrosative Stress as a New Target for Neuroprotection. Rev. Neurosci. 2015, 26, 49–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourgognon, J.M.; Spiers, J.G.; Robinson, S.W.; Scheiblich, H.; Glynn, P.; Ortori, C.; Bradley, S.J.; Tobin, A.B.; Steinert, J.R. Inhibition of Neuroinflammatory Nitric Oxide Signaling Suppresses Glycation and Prevents Neuronal Dysfunction in Mouse Prion Disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2009579118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrabi, S.M.; Sharma, N.S.; Karan, A.; Shahriar, S.M.S.; Cordon, B.; Ma, B.; Xie, J. Nitric Oxide: Physiological Functions, Delivery, and Biomedical Applications. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, e2303259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, Y.; Kelley, N.; He, Y. Role of the Nlrp3 Inflammasome in Neurodegenerative Diseases and Therapeutic Implications. Neural Regen. Res. 2020, 15, 1249–1250. [Google Scholar]
- Cassel, S.L.; Joly, S.; Sutterwala, F.S. The Nlrp3 Inflammasome: A Sensor of Immune Danger Signals. Semin. Immunol. 2009, 21, 194–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dourado, N.S.; Souza, C.D.S.; De Almeida, M.M.A.; Da Silva, A.B.; Santos, B.L.D.; Silva, V.D.A.; De Assis, A.M.; Da Silva, J.S.; Souza, D.O.; De Fatima Dias Costa, M.; et al. Neuroimmunomodulatory and Neuroprotective Effects of the Flavonoid Apigenin in In Vitro Models of Neuroinflammation Associated with Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2020, 12, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-J.; Ren, L.; Qian, X.; Zhai, L.; Sun, M.; Miao, Z.; Li, J.; Xu, X. Loss of Ahi1 Impairs Neurotransmitter Release and Causes Depressive Behaviors in Mice. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e93640. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, K.Y.; Mao, Q.Q.; Ip, S.P.; Choi, R.C.; Dong, T.T.; Lau, D.T.; Tsim, K.W. A Standardized Chinese Herbal Decoction, Kai-Xin-San, Restores Decreased Levels of Neurotransmitters and Neurotrophic Factors in the Brain of Chronic Stress-Induced Depressive Rats. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2012, 2012, 149256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Study | Zingerone Intervention (Dose, Route of Administration and Duration of Experiment) | Experimental Model | Evaluated Parameters | Main Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Choi et al. [24] | 10 mg/kg/day intraperitoneal, 10 days | 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine mouse model (20 mg/kg, i.p. injection). Male C57BL/6 mice (10 weeks old). | IBA-1 and GFAP expression | No significant changes in IBA-1 and GFAP expression |
| Anyanwu et al. [25] | 200 mg/kg/day oral administration, 21 days | Cadmium-induced model (5 mg/kg, oral administration). Male Wistar rats. | Behaviour—Y-Maze | A significant increase in spatial activity, evident by an increase in time spent in the novel arm, number of arm entries, alternation and percentage alternation |
| Chopra et al. [26] | 100 mg/kg/day oral administration, 42 days | Brain-inflicted glioma cells in Male Wistar rats. Intracerebroventricular injection of C6 glioma cells (1 × 105/10 µL. | Y-Maze Passive avoidance test Novel object Recognition test Elevated plus maze | Improved exploration behaviour, improved learning and memory ability, anti-anxiety-like behaviour |
| Jadhav et al. [27] | 250 mg/kg, 21 days oral administration | Chronic upredictable mild stress rats. Wistar rats. | Sucrose preference test Forced swimming test IL-6, TNF-α | Improved anti-depressant activity Reduced IL-6 and TNF-α |
| Maleki et al. [28] | 50 mg/kg, 14 days, oral administration | Ketamine-induced manic-like behaviour. Ketamine (25 mg/kg, i.p.). Male Wistar Rats. | NO TNF-α | Reduced NO levels Reduced TNF-α levels |
| Molavinia et al. [22] | 50, 100 and 200 mg, oral gavage, 7 days | Morphine (10 mg/kg, i.p.)-induced oxidative stress and inflammasome in mice brain. Adult male NMRI mice. | IL-1β NLRP3 | Reduced IL-1β levels Inhibited NLRP3 inflammasome |
| Rashid et al. [29] | 25 and 50 mg/kg, oral administration for 15 days | Lithium (3 m/Eq/kg, i.p.) and Pilocarpine (10 mg/kg i.p.)-induced status epilepticus in mice. Male Swiss Albino mice. | Morris water maze NF-kB IL-1β IL-6 TNF-α | Reduced escape latency, increase time spent in target quadrant and improved memory and learning. Reduced NF-kB, IL-1β, IL-6 and TNF-α levels |
| Upadhyaya et al. [21] | 25, 50 and 100 mg/kg oral gavage for 28 days | Stress-induced depressive-like behaviour in male Wistar rats. | Morris water maze Forced swimming test Sucrose preference test | Increased sucrose consumption Increased immobility time Zingerone did not exhibit any effect on memory function |
| Yilmaz et al. [30] | 25 and 50 mg/kg oral administration for 14 days | Sodium arsenite-induced sciatic nerve damage and neuroinflammation in male Sprague Dawley rat brain. Sodium arsenite (10 mg/kg). | NF-kB IL-1β TNF-α nNOS | Reduced expression and downregulation of NF-kB, IL-1β TNF-α and nNOS |
| Study | A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Choi et al. [24] | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 5 |
| Anyanwu et [25] | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 5 |
| Chopra et al. [26] | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 6 |
| Jadhav et al. [27] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 8 |
| Molavinia et al. [22] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 7 |
| Maleki et al. [28] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 7 |
| Rashid et al. [29] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 7 |
| Upadhyaya et al. [21] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 7 |
| Yilmaz et al. [30] | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Olasehinde, T.A.; Olaokun, O.O. Zingerone as a Neuroprotective Agent Against Cognitive Disorders: A Systematic Review of Preclinical Studies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6111. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136111
Olasehinde TA, Olaokun OO. Zingerone as a Neuroprotective Agent Against Cognitive Disorders: A Systematic Review of Preclinical Studies. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(13):6111. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136111
Chicago/Turabian StyleOlasehinde, Tosin A., and Oyinlola O. Olaokun. 2025. "Zingerone as a Neuroprotective Agent Against Cognitive Disorders: A Systematic Review of Preclinical Studies" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 13: 6111. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136111
APA StyleOlasehinde, T. A., & Olaokun, O. O. (2025). Zingerone as a Neuroprotective Agent Against Cognitive Disorders: A Systematic Review of Preclinical Studies. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(13), 6111. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136111





