Deciphering the 3D Structural Characterization of Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone in Tenualosa ilisha Using Homology Modeling, Molecular Dynamics, and Docking Approaches
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
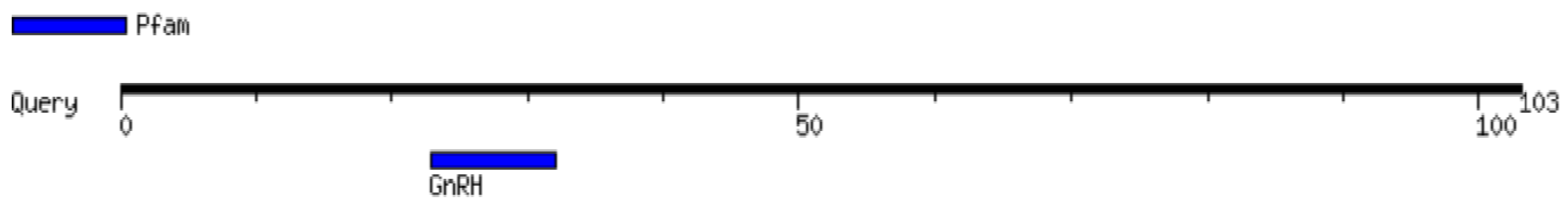
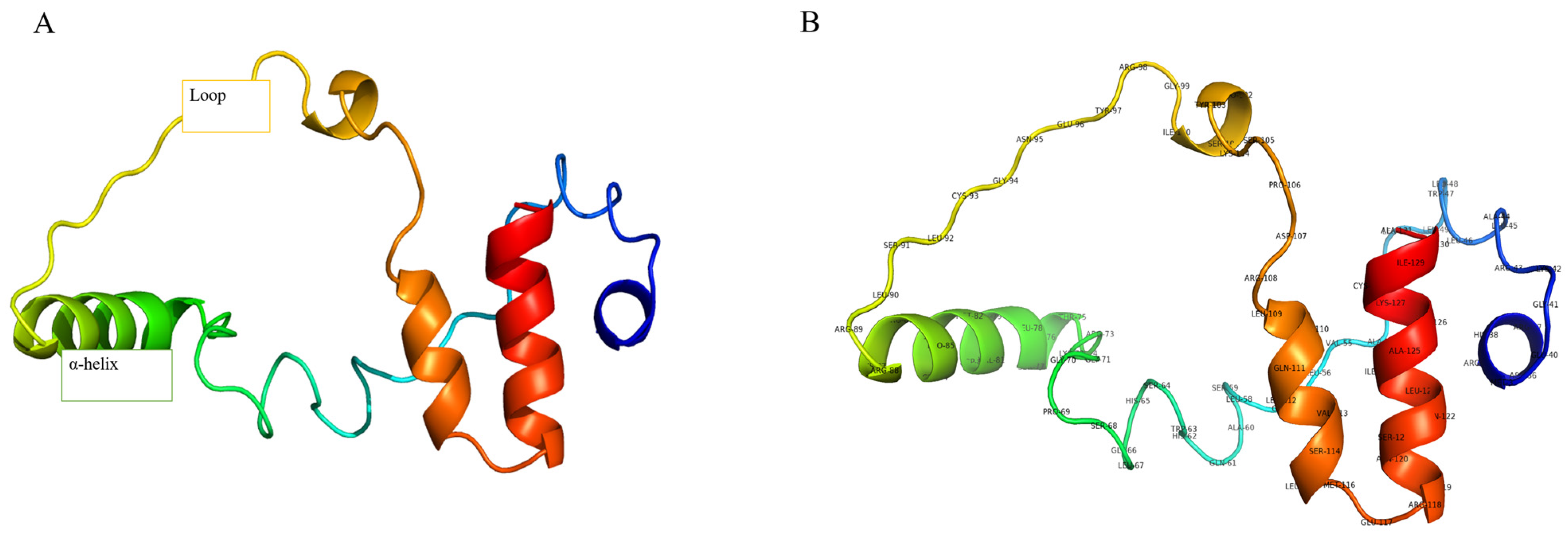
2.1. Gene Annotation and Secondary Structure Examination
2.2. Validation and Refinement of GnRH 3D Structure
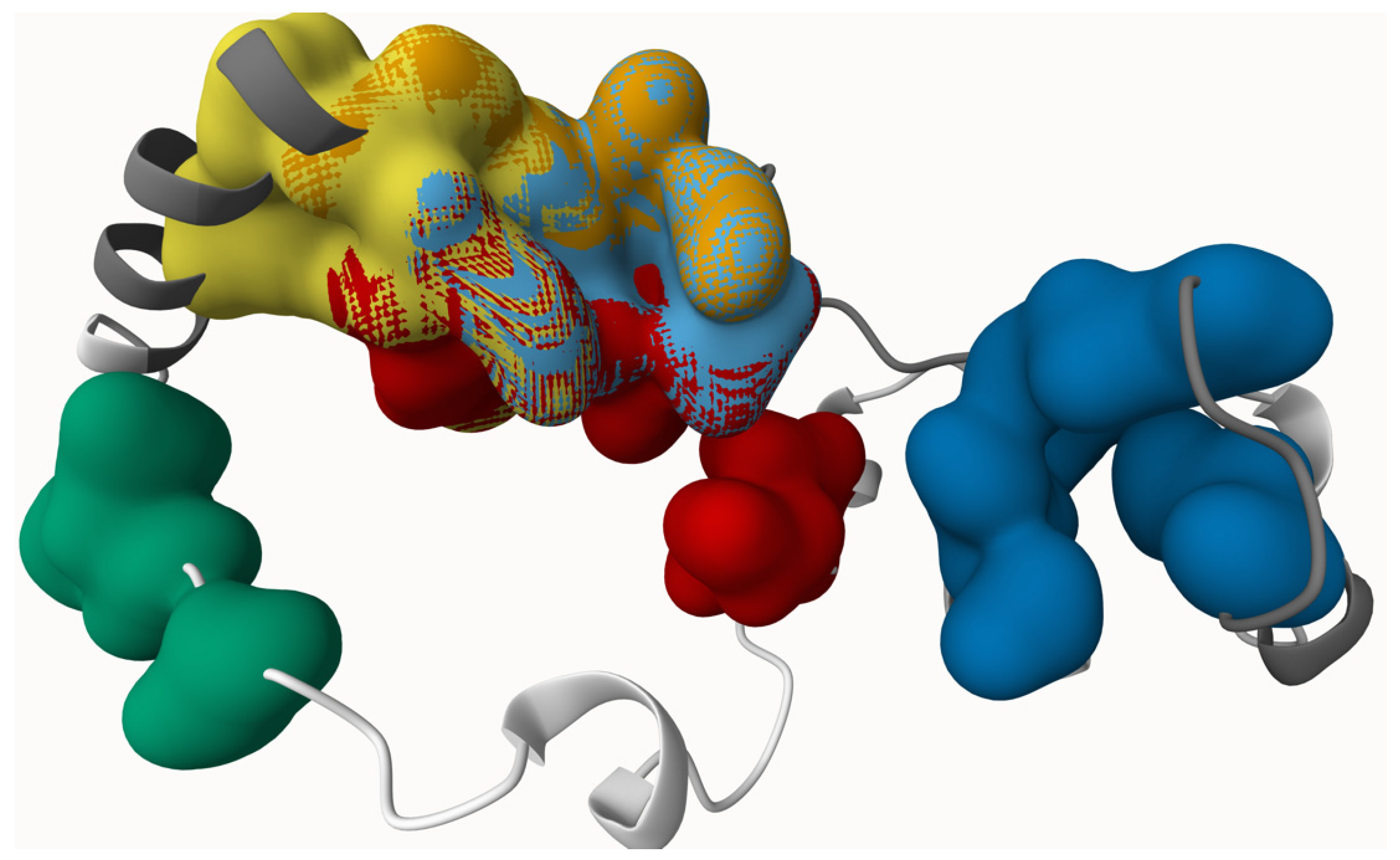
2.3. Protein Binding Site Identification
2.4. In Silico Evaluation of ADME Property, Bioactivity Score, and Toxicity Parameter of Selected Ligands
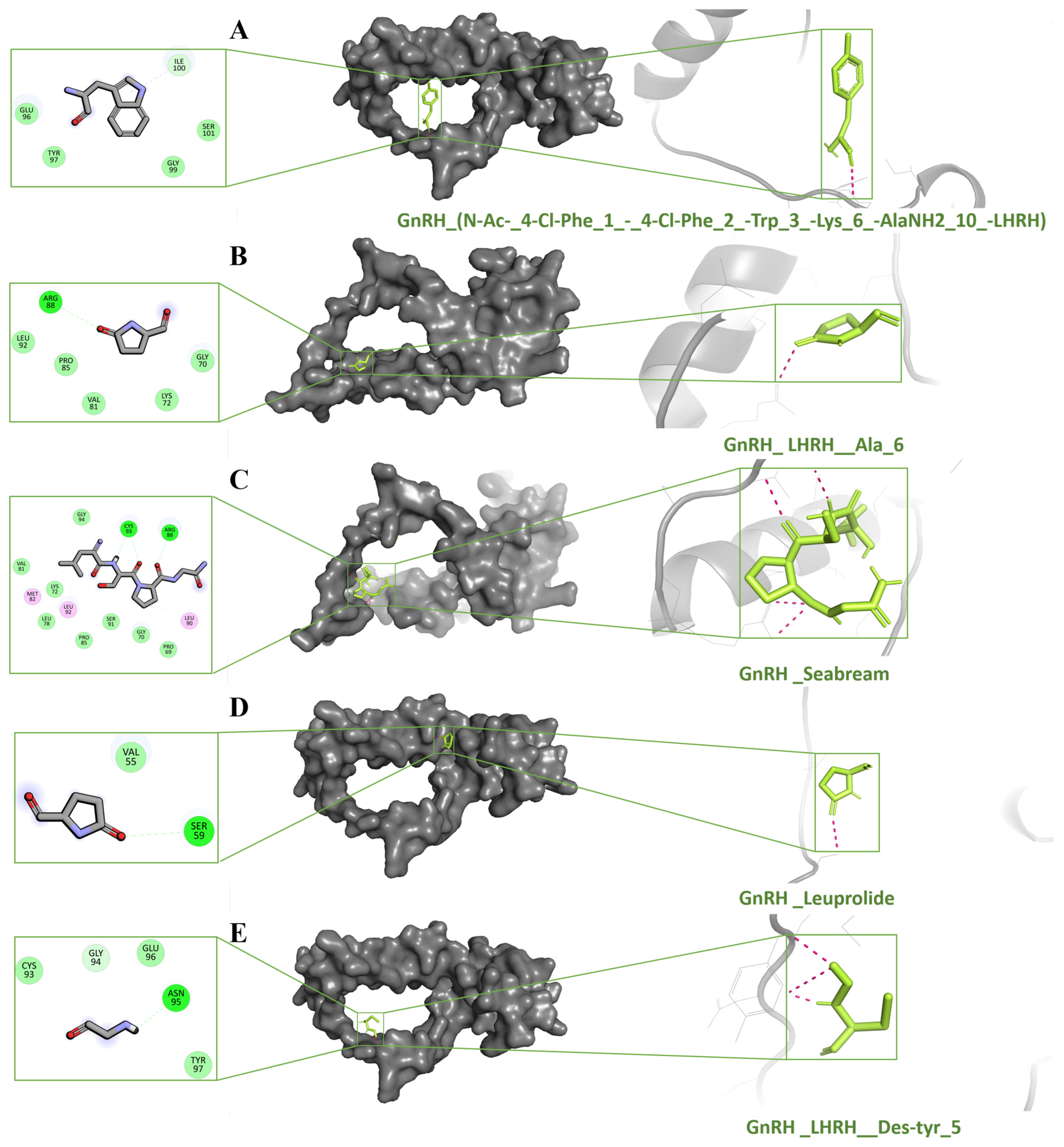
2.5. Molecular Docking Studies
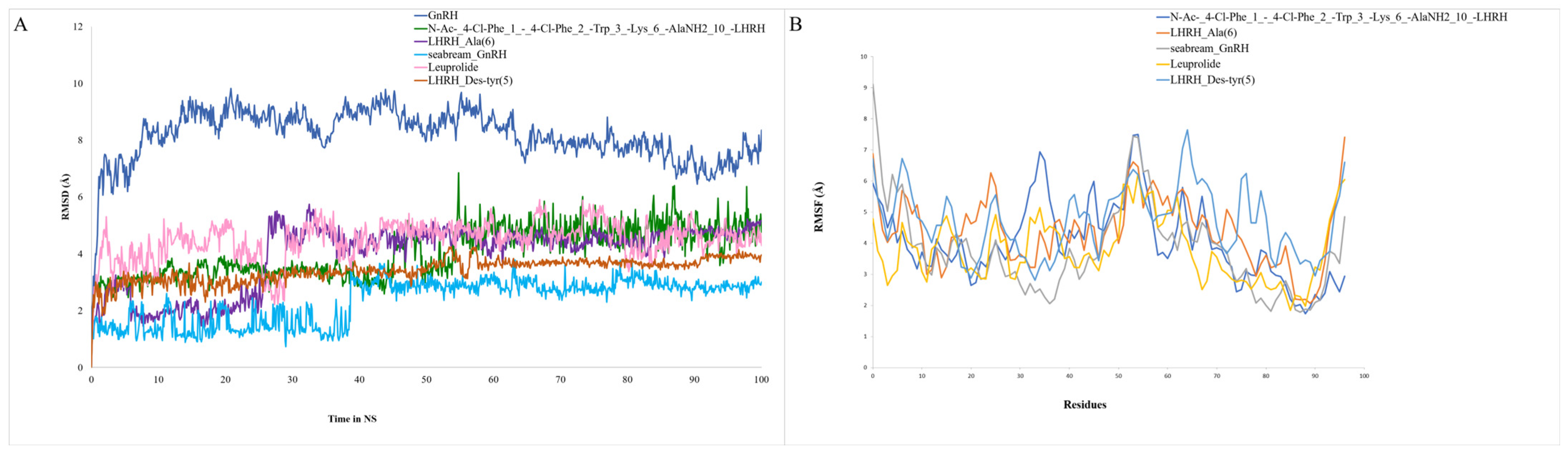
2.6. Analysis of Molecular Dynamic Trajectories
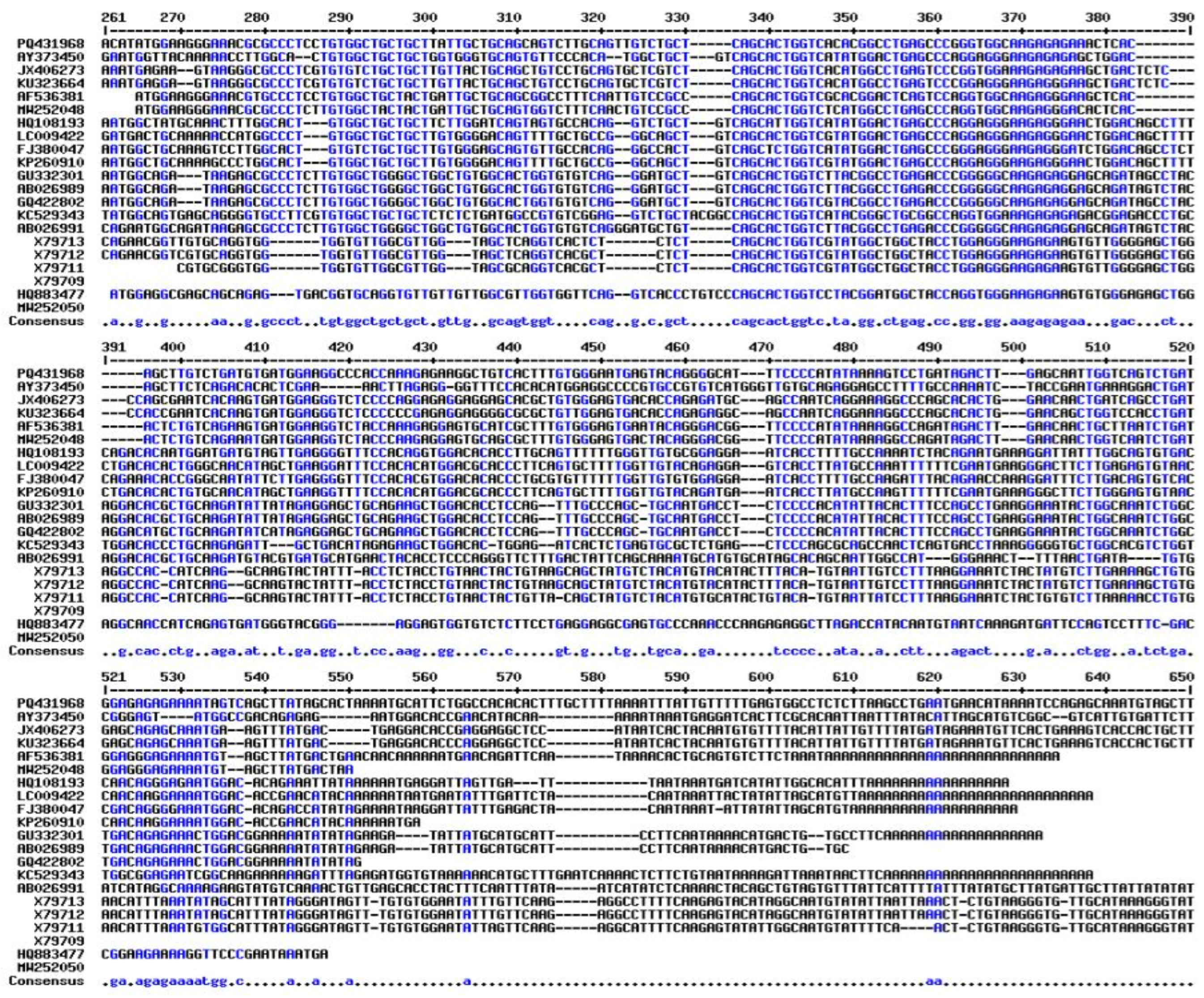
2.7. Evolutionary and Phylogenetic Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Ethics Statement
4.2. Animals and Tissue Collection
4.3. Gene Annotation and Protein Analysis
4.4. Structural Modeling and Validation
4.5. Binding Site Prediction
4.6. Ligand Preparation and Docking
4.7. Molecular Dynamics Simulation (MD)
4.8. Phylogenetic Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rather, M.A.; Bhat, I.A.; Sharma, R. Identification and Characterization of ChickenII-GnRH (CII-GnRH) Gene of Catlacatla (Hamilton, 1822). Eur. J. Exper. Biol. 2015, 5, 53–56. [Google Scholar]
- Rather, M.A.; Bhat, I.A.; Sharma, N.; Sharma, R.; Gireesh-Babu, P.; Chaudhari, A.; Sundaray, J.K. Molecular Characterization, Tissue Distribution of Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH) Beta Subunit and Effect of Kisspeptin-10 on Reproductive Hormonal Profile of Catla Catla (Hamilton, 1822). Aquac. Res. 2016, 47, 2089–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amoss, M.; Burgus, R.; Blackwell, R.; Vale, W.; Fellows, R.; Guillemin, R. Purification, Amino Acid Composition and N-Terminus of the Hypothalamic Luteinizing Hormone Releasing Factor (LRF) of Ovine Origin. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1971, 44, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuo, H.; Baba, Y.; Nair, R.M.G.; Arimura, A.; Schally, A.V. Structure of the Porcine LH-and FSH-Releasing Hormone. I. The Proposed Amino Acid Sequence. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1971, 43, 1334–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vickers, E.D.; Laberge, F.; Adams, B.A.; Hara, T.J.; Sherwood, N.M. Cloning and Localization of Three Forms of Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone, Including the Novel Whitefish Form, in a Salmonid, Coregonus Clupeaformis. Biol. Reprod. 2004, 70, 1136–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kah, O.; Lethimonier, C.; Somoza, G.; Guilgur, L.G.; Vaillant, C.; Lareyre, J.-J. GnRH and GnRH Receptors in Metazoa: A Historical, Comparative, and Evolutive Perspective. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2007, 153, 346–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lethimonier, C.; Madigou, T.; Muñoz-Cueto, J.-A.; Lareyre, J.-J.; Kah, O. Evolutionary Aspects of GnRHs, GnRH Neuronal Systems and GnRH Receptors in Teleost Fish. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2004, 135, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silver, M.R.; Kawauchi, H.; Nozaki, M.; Sower, S.A. Cloning and Analysis of the Lamprey GnRH-III CDNA from Eight Species of Lamprey Representing the Three Families of Petromyzoniformes. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2004, 139, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soga, T.; Ogawa, S.; Millar, R.P.; Sakuma, Y.; Parhar, I.S. Localization of the Three GnRH Types and GnRH Receptors in the Brain of a Cichlid Fish: Insights into Their Neuroendocrine and Neuromodulator Functions. J. Comp. Neurol. 2005, 487, 28–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojilkovic, S.S.; Reinhart, J.; Catt, K.J. Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone Receptors: Structure and Signal Transduction Pathways. Endocr. Rev. 1994, 15, 462–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Conn, P.M. Transcriptional Activation of Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone (GnRH) Receptor Gene by GnRH: Involvement of Multiple Signal Transduction Pathways. Endocrinology 1999, 140, 358–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rather, M.A.; Agarwal, D.; Bhat, T.A.; Khan, I.A.; Zafar, I.; Kumar, S.; Amin, A.; Sundaray, J.K.; Qadri, T. Bioinformatics Approaches and Big Data Analytics Opportunities in Improving Fisheries and Aquaculture. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 233, 123549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, R.; Upadhayay, A.D.; Roy, A.K. In Silico Analysis and Characterization of Fresh Water Fish ATPases and Homology Modelling. Ann. Proteom. Bioinform. 2017, 1, 18–24. [Google Scholar]
- Sahoo, L.; Sahoo, S.; Mohanty, M.; Sankar, M.; Dixit, S.; Das, P.; Rasal, K.D.; Rather, M.A.; Sundaray, J.K. Molecular Characterization, Computational Analysis and Expression Profiling of Dmrt1 Gene in Indian Major Carp, Labeo Rohita (Hamilton 1822). Anim. Biotechnol. 2021, 32, 413–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rather, M.A.; Dutta, S.; Guttula, P.K.; Dhandare, B.C.; Yusufzai, S.I.; Zafar, M.I. Structural Analysis, Molecular Docking and Molecular Dynamics Simulations of G-Protein-Coupled Receptor (Kisspeptin) in Fish. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2020, 38, 2422–2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, H.M.; Sajjad, M.; Ali, M.A.; Gul, R.; Naveed, M.; Aslam, M.S.; Shinwari, K.; Bhinder, M.A.; Ghani, M.U.; Saleem, M. Identification of RdRp Inhibitors against SARS-CoV-2 through E-Pharmacophore-Based Virtual Screening, Molecular Docking and MD Simulations Approaches. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 237, 124169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Z.-L.; Gallagher, R.; Sellar, R.; Coetsee, M.; Millar, R.P. Mutations Remote from the Human Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone (GnRH) Receptor-Binding Sites Specifically Increase Binding Affinity for GnRH II but Not GnRH I: Evidence for Ligand-Selective, Receptor-Active Conformations. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 29796–29803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhandare, B.C.; Rather, M.A.; Bhosale, B.P.; Pawar, R.; Guttula, P.K.; Pagarkar, A.U. Molecular Modeling, Docking and Dynamic Simulations of Growth Hormone Receptor (GHR) of Labeo Rohita. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2022, 40, 3024–3037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parhar, I.; Ogawa, S.; Kitahashi, T. RFamide Peptides as Mediators in Environmental Control of GnRH Neurons. Prog. Neurobiol. 2012, 98, 176–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan Baig, M.; Ahmad, K.; Roy, S.; Mohammad Ashraf, J.; Adil, M.; Haris Siddiqui, M.; Khan, S.; Amjad Kamal, M.; Provazník, I.; Choi, I. Computer Aided Drug Design: Success and Limitations. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2016, 22, 572–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.; Ahmad, I.; Ahmad, I.; Amin, A.; Rather, M.A. Gene Characterization, Molecular Docking and Dynamic Simulations of Insulin-Like Growth Factor Receptor (IGF-1Ra) in Common Carp, Cyprinus Carpio. Proc. Zool. Soc. 2023, 76, 382–396. [Google Scholar]
- Tello, J.A.; Wu, S.; Rivier, J.E.; Sherwood, N.M. Four Functional GnRH Receptors in Zebrafish: Analysis of Structure, Signaling, Synteny and Phylogeny. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2008, 48, 570–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laskowski, R.A.; MacArthur, M.W.; Moss, D.S.; Thornton, J.M. IUCr PROCHECK: A Program to Check the Stereochemical Quality of Protein Structures. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 1993, 26, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afonine, P.V.; Poon, B.K.; Read, R.J.; Sobolev, O.V.; Terwilliger, T.C.; Urzhumtsev, A.; Adams, P.D. Real-Space Refinement in PHENIX for Cryo-EM and Crystallography. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. D Struct. Biol. 2018, 74, 531–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colovos, C.; Yeates, T.O. Verification of Protein Structures: Patterns of Nonbonded Atomic Interactions. Protein Sci. 1993, 2, 1511–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, K.; Bordoli, L.; Kopp, J.; Schwede, T. The SWISS-MODEL Workspace: A Web-Based Environment for Protein Structure Homology Modelling. Bioinformatics 2006, 22, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, S.; Yin, J.; Zhang, P.; Xuan, X.; Wang, P.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, B.; Yang, M. Cryo-EM Structures and Transport Mechanism of Human P5B Type ATPase ATP13A2. Cell Discov. 2021, 7, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.K.; Kumar, P.; Mahalingam, K. Molecular Genetics of Human Obesity: A Comprehensive Review. Comptes Rendus Biol. 2017, 340, 87–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipinski, C. Poor Aqueous Solubility—An Industry Wide Problem in Drug Discovery. Am. Pharm. Rev. 2002, 5, 82–85. [Google Scholar]
- Veber, D.F.; Johnson, S.R.; Cheng, H.-Y.; Smith, B.R.; Ward, K.W.; Kopple, K.D. Molecular Properties That Influence the Oral Bioavailability of Drug Candidates. J. Med. Chem. 2002, 45, 2615–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, W.; Lorance, E.D.; Gould, I.R. Understanding the solvent contribution to chemical reaction barriers. J. Phys. Chem. A 2019, 123, 10490–10499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trott, O.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock Vina: Improving the Speed and Accuracy of Docking with a New Scoring Function, Efficient Optimization, and Multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadnayak, A.; Nayak, A.; Jena, S.; Sahoo, A.; Panda, P.C.; Ray, A.; Nayak, S. Nitric Oxide Inhibitory Potential of Curcuma Angustifolia Roxb. Essential Oil: An in Silico and in Vitro Analysis. Plant Sci. Today 2024, 11, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betz, S.F.; Lio, F.M.; Gao, Y.; Reinhart, G.J.; Guo, Z.; Mesleh, M.F.; Zhu, Y.-F.; Struthers, R.S. Determination of the Binding Mode of Thienopyrimidinedione Antagonists to the Human Gonadotropin Releasing Hormone Receptor Using Structure− Activity Relationships, Site-Directed Mutagenesis, and Homology Modeling. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 6170–6176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Xu, Z.; Yang, X. Graphene Oxide-Induced Structural Morphology and Colloidal Interaction at Water–Oil Interface. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 363, 119854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitchen, D.B.; Decornez, H.; Furr, J.R.; Bajorath, J. Docking and Scoring in Virtual Screening for Drug Discovery: Methods and Applications. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2004, 3, 935–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollingsworth, S.A.; Dror, R.O. Molecular Dynamics Simulation for All. Neuron 2018, 99, 1129–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Tong, H.H.Y.; Yao, X.; Liu, H.; Li, G. Computational Methods for Unlocking the Secrets of Potassium Channels: Structure, Mechanism, and Drug Design. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Comput. Mol. Sci. 2024, 14, e1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurisso, A.; Daina, A.; Walker, R.C. A Practical Introduction to Molecular Dynamics Simulations: Applications to Homology Modeling. In Homology Modeling: Methods and Protocols; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 137–173. [Google Scholar]
- Ulloa-Aguirre, A.; Zariñán, T.; Jardón-Valadez, E. Misfolded G Protein-Coupled Receptors and Endocrine Disease. Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Prospects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordoli, L.; Kiefer, F.; Arnold, K.; Benkert, P.; Battey, J.; Schwede, T. Protein Structure Homology Modeling Using SWISS-MODEL Workspace. Nat. Protoc. 2009, 4, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jumper, J.; Evans, R.; Pritzel, A.; Green, T.; Figurnov, M.; Ronneberger, O.; Tunyasuvunakool, K.; Bates, R.; Žídek, A.; Potapenko, A.; et al. Highly accurate protein structure prediction with AlphaFold. Nature 2021, 596, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gadnayak, A.; Dehury, B.; Nayak, A.; Jena, S.; Sahoo, A.; Panda, P.C.; Ray, A.; Nayak, S. ‘Mechanistic Insights into 5-Lipoxygenase Inhibition by Active Principles Derived from Essential Oils of Curcuma Species: Molecular Docking, ADMET Analysis and Molecular Dynamic Simulation Study. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0271956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nayak, A.; Gadnayak, A.; Dash, K.T.; Jena, S.; Ray, A.; Nayak, S.; Sahoo, A. Exploring Molecular Docking with MM-GBSA and Molecular Dynamics Simulation to Predict Potent Inhibitors of Cyclooxygenase (COX-2) Enzyme from Terpenoid-Based Active Principles of Zingiber Species. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2023, 41, 10840–10850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
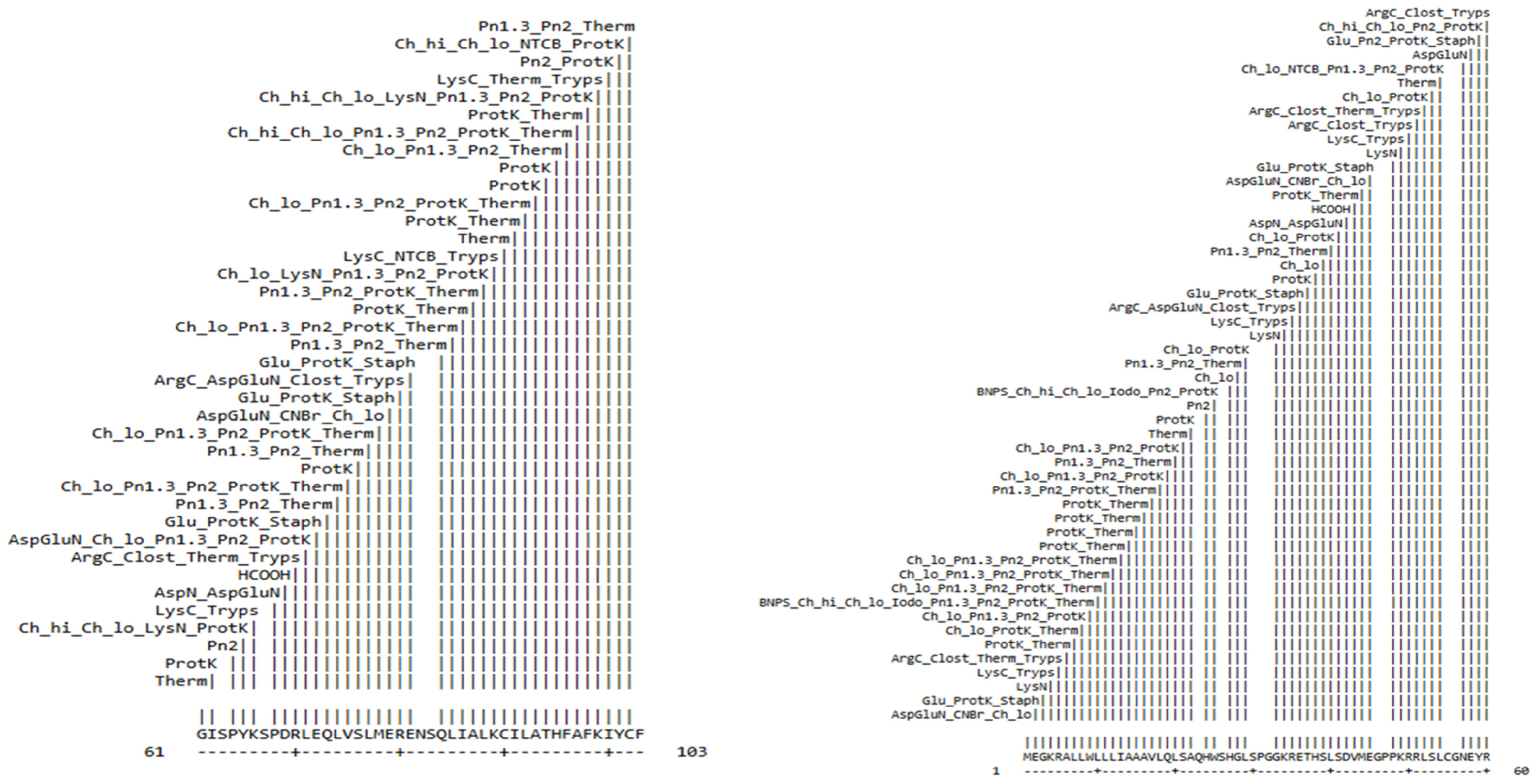


| Position of Cleavage Site | Name of Cleaving Enzyme | Resulting Peptide Sequence | Peptide Length (aa) | Peptide Mass (Da) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Asp-N endopeptidase + N-terminal Glu CNBr Chymotrypsin-low specificity (C-term to [FYWML], not before P) | M | 1 | 149.208 |
| 2 | Glutamyl endopeptidase Proteinase K Staphylococcal peptidase I | E | 1 | 147.131 |
| 3 | LysN | G | 1 | 75.067 |
| 4 | LysC Trypsin | K | 1 | 146.189 |
| 5 | Arg-C proteinase Clostripain Thermolysin Trypsin | R | 1 | 174.203 |
| 6 | Proteinase K Thermolysin | A | 1 | 89.094 |
| 7 | Chymotrypsin-low specificity (C-term to [FYWML], not before P) Proteinase K Thermolysin | L | 1 | 131.175 |
| 8 | Chymotrypsin-low specificity (C-term to [FYWML], not before P) Pepsin (pH 1.3) Pepsin (pH > 2) Proteinase K | L | 1 | 131.175 |
| 9 | BNPS-Skatole Chymotrypsin-high specificity (C-term to [FYW], not before P) Chymotrypsin-low specificity (C-term to [FYWML], not before P) Iodosobenzoic acid Pepsin (pH 1.3) Pepsin (pH > 2) Proteinase K Thermolysin | W | 1 | 204.228 |
| 10 | Chymotrypsin-low specificity (C-term to [FYWML], not before P) Pepsin (pH 1.3) Pepsin (pH > 2) Proteinase K Thermolysin | L | 1 | 131.175 |
| 11 | Chymotrypsin-low specificity (C-term to [FYWML], not before P) Pepsin (pH 1.3) Pepsin (pH > 2) Proteinase K Thermolysin | L | 1 | 131.175 |
| 12 | Chymotrypsin-low specificity (C-term to [FYWML], not before P) Pepsin (pH 1.3) Pepsin (pH > 2) Proteinase K Thermolysin | L | 1 | 137.175 |
| 13 | Proteinase K Thermolysin | I | 1 | 131.175 |
| 14 | Proteinase K Thermolysin | A | 1 | 89.094 |
| 15 | Proteinase K Thermolysin | A | 1 | 89.094 |
| 16 | Proteinase K Thermolysin | A | 1 | 89.094 |
| 17 | Pepsin (pH 1.3) Pepsin (pH > 2) Proteinase K Thermolysin | V | 1 | 117.148 |
| 18 | Chymotrypsin-low specificity (C-term to [FYWML], not before P) Pepsin (pH 1.3) Pepsin (pH > 2) Proteinase K | L | 1 | 131.175 |
| 19 | Pepsin (pH 1.3) Pepsin (pH > 2) Thermolysin | Q | 1 | 146.146 |
| 20 | Chymotrypsin-low specificity (C-term to [FYWML], not before P) Pepsin (pH 1.3) Pepsin (pH > 2) Proteinase K | L | 1 | 131.175 |
| 21 | Thermolysin | S | 1 | 105.093 |
| 22 | Proteinase K | A | 1 | 89.094 |
| 24 | Pepsin (pH > 2) | Q H | 2 | 283.287 |
| 25 | BNPS-Skatole Chymotrypsin-high specificity (C-term to [FYW], not before P) Chymotrypsin-low specificity (C-term to [FYWML], not before P) Iodosobenzoic acid Pepsin (pH > 2) Proteinase K | W | 1 | 204.228 |
| 27 | Chymotrypsin-low specificity (C-term to [FYWML], not before P) | SH | 2 | 242.235 |
| 28 | Pepsin (pH 1.3) Pepsin (pH > 2) Thermolysin | G | 1 | 75.067 |
| 29 | Chymotrypsin-low specificity (C-term to [FYWML], not before P) Proteinase K | L | 1 | 131.175 |
| 33 | LysN | SPGG | 4 | 316.314 |
| 34 | LysC Trypsin | K | 1 | 146.189 |
| 35 | Arg-C proteinase Asp-N endopeptidase + N-terminal Glu Clostripain Trypsin | R | 1 | 174.203 |
| 36 | Glutamyl endopeptidase Proteinase K Staphylococcal peptidase I | E | 1 | 147.131 |
| 37 | Proteinase K | T | 1 | 119.120 |
| 38 | Chymotrypsin-low specificity (C-term to [FYWML], not before P) | H | 1 | 155.156 |
| 39 | Pepsin (pH 1.3) Pepsin (pH > 2) Thermolysin | S | 1 | 105.093 |
| 40 | Chymotrypsin-low specificity (C-term to [FYWML], not before P) Proteinase K | L | 1 | 131.175 |
| 41 | Asp-N endopeptidase Asp-N endopeptidase + N-terminal Glu | S | 1 | 105.093 |
| 42 | Formic acid | D | 1 | 133.104 |
| 43 | Proteinase K Thermolysin | V | 1 | 117.148 |
| 44 | Asp-N endopeptidase + N-terminal Glu CNBr Chymotrypsin-low specificity (C-term to [FYWML], not before P) | M | 1 | 149.208 |
| 45 | Glutamyl endopeptidase Proteinase K Staphylococcal peptidase I | E | 1 | 147.131 |
| 48 | LysN | GPP | 3 | 269.301 |
| 49 | LysC Trypsin | K | 1 | 146.189 |
| 50 | Arg-C proteinase Clostripain Trypsin | R | 1 | 154.203 |
| 51 | Arg-C proteinase Clostripain Thermolysin Trypsin | R | 1 | 174.203 |
| 52 | Chymotrypsin-low specificity (C-term to [FYWML], not before P) Proteinase K | L | 1 | 131.175 |
| 53 | Thermolysin | S | 1 | 105.093 |
| 54 | Chymotrypsin-low specificity (C-term to [FYWML], not before P) NTCB (2-nitro-5-thiocyanobenzoic acid) Pepsin (pH 1.3) Pepsin (pH > 2) Proteinase K | L | 1 | 131.175 |
| 57 | Asp-N endopeptidase + N-terminal Glu | CGN | 3 | 192.310 |
| 58 | Glutamyl endopeptidase Pepsin (pH > 2) Proteinase K Staphylococcal peptidase I | E | 1 | 147.131 |
| 59 | Chymotrypsin-high specificity (C-term to [FYW], not before P) Chymotrypsin-low specificity (C-term to [FYWML], not before P) Pepsin (pH > 2) Proteinase K | Y | 1 | 181.191 |
| 60 | Arg-C proteinase Clostripain Trypsin | R | 1 | 174.203 |
| 61 | Thermolysin | G | 1 | 75.067 |
| 62 | Proteinase K | I | 1 | 171.175 |
| 64 | Pepsin (pH > 2) | SP | 2 | 202.210 |
| 65 | Chymotrypsin-high specificity (C-term to [FYW], not before P) Chymotrypsin-low specificity (C-term to [FYWML], not before P) LysN Proteinase K | Y | 1 | 181.191 |
| 66 | LysC Trypsin | K | 1 | 146.189 |
| 68 | Asp-N endopeptidase Asp-N endopeptidase + N-terminal Glu | SP | 2 | 202.210 |
| 69 | Formic acid | D | 1 | 133.104 |
| 70 | Arg-C proteinase Clostripain Thermolysin Trypsin | R | 1 | 174.203 |
| 71 | Asp-N endopeptidase + N-terminal Glu Chymotrypsin-low specificity (C-term to [FYWML], not before P) Pepsin (pH 1.3) Pepsin (pH > 2) Proteinase K | L | 1 | 131.138 |
| 72 | Glutamyl endopeptidase Proteinase K Staphylococcal peptidase I | E | 1 | 147.131 |
| 73 | Pepsin (pH 1.3) Pepsin (pH > 2) Thermolysin | Q | 1 | 146.146 |
| 74 | Chymotrypsin-low specificity (C-term to [FYWML], not before P) Pepsin (pH 1.3) Pepsin (pH > 2) Proteinase K Thermolysin | L | 1 | 131.175 |
| 75 | Proteinase K | V | 1 | 117.148 |
| 76 | Pepsin (pH 1.3) Pepsin (pH > 2) Thermolysin | S | 1 | 105.093 |
| 77 | Chymotrypsin-low specificity (C-term to [FYWML], not before P) Pepsin (pH 1.3) Pepsin (pH > 2) Proteinase K Thermolysin | L | 1 | 131.175 |
| 78 | Asp-N endopeptidase + N-terminal Glu CNBr Chymotrypsin-low specificity (C-term to [FYWML], not before P) | M | 1 | 149.208 |
| 79 | Glutamyl endopeptidase Proteinase K Staphylococcal peptidase I | E | 1 | 149.131 |
| 80 | Arg-C proteinase Asp-N endopeptidase + N-terminal Glu Clostripain Trypsin | R | 1 | 174.203 |
| 81 | Glutamyl endopeptidase Proteinase K Staphylococcal peptidase I | E | 1 | 147.131 |
| 84 | Pepsin (pH 1.3) Pepsin (pH > 2) Thermolysin | NSQ | 3 | 347.328 |
| 85 | Chymotrypsin-low specificity (C-term to [FYWML], not before P) Pepsin (pH 1.3) Pepsin (pH > 2) Proteinase K Thermolysin | L | 1 | 131.175 |
| 86 | Proteinase K Thermolysin | I | 1 | 131.175 |
| 87 | Pepsin (pH 1.3) Pepsin (pH > 2) Proteinase K Thermolysin | A | 1 | 89.094 |
| 88 | Chymotrypsin-low specificity (C-term to [FYWML], not before P) LysN Pepsin (pH 1.3) Pepsin (pH > 2) Proteinase K | L | 1 | 131.0175 |
| 89 | LysC NTCB (2-nitro-5-thiocyanobenzoic acid) Trypsin | K | 1 | 146.189 |
| 90 | Thermolysin | C | 1 | 121.154 |
| 91 | Proteinase K Thermolysin | I | 1 | 131.175 |
| 92 | Chymotrypsin-low specificity (C-term to [FYWML], not before P) Pepsin (pH 1.3) Pepsin (pH > 2) Proteinase K Thermolysin | L | 1 | 131.175 |
| 93 | Proteinase K | A | 1 | 89.094 |
| 94 | Proteinase K | T | 1 | 191.120 |
| 95 | Chymotrypsin-low specificity (C-term to [FYWML], not before P) Pepsin (pH 1.3) Pepsin (pH > 2) Thermolysin | H | 1 | 155.156 |
| 96 | Chymotrypsin-high specificity (C-term to [FYW], not before P) Chymotrypsin-low specificity (C-term to [FYWML], not before P) Pepsin (pH 1.3) Pepsin (pH > 2) Proteinase K Thermolysin | F | 1 | 165.189 |
| 97 | Proteinase K Thermolysin | A | 1 | 89.094 |
| 98 | Chymotrypsin-high specificity (C-term to [FYW], not before P) Chymotrypsin-low specificity (C-term to [FYWML], not before P) LysN Pepsin (pH 1.3) Pepsin (pH > 2) Proteinase K | F | 1 | 165.192 |
| 99 | LysC Thermolysin Trypsin | K | 1 | 146.189 |
| 100 | Pepsin (pH > 2) Proteinase K | I | 1 | 131.175 |
| 101 | Chymotrypsin-high specificity (C-term to [FYW], not before P) Chymotrypsin-low specificity (C-term to [FYWML], not before P) NTCB (2-nitro-5-thiocyanobenzoic acid) Proteinase K | Y | 1 | 181.191 |
| 102 | Pepsin (pH 1.3) Pepsin (pH > 2) Thermolysin | C | 1 | 121.154 |
| 103 | end of sequence | F | 1 | 165.192 |
| Sl.No. | Species Name | Family | Gene Name | Accessions Name | Peptides |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Tenualosa ilisha | Clupeidae | GnRH1 | PQ431968 | QHWSHGLSPG |
| 2 | Alosa sapidissima | Clupeidae | GnRH1 | AF536381 | QHWSHGLSPG |
| 3 | Sardinops melanostictus | Clupeidae | GnRH1 | MW252048 | QHWSHGLSPG |
| 4 | Engraulis japonicus | Engraulidae | GnRH1 | JX406273 | QHWSHGLSPG |
| 5 | Engraulis encrasicolus | Engraulidae | GnRH1 | KU323664 | QHWSHGLSPG |
| 6 | Anguilla anguilla | Anguillidae | GnRH1 | GU332301 | QHWSYGLRPG |
| 7 | Anguilla marmorata | Anguillidae | mGnRH | GQ422802 | QHWSYGLRPG |
| 8 | Anguilla japonica | Anguillidae | mGnRH | AB026989 | QHWSYGLRPG |
| 9 | Acipenser sinensis | Acipenseridae | GnRH1 | KC529343 | QHWSYGLRPG |
| 10 | Mugil cephalus | Mugilidae | GnRH1 | AY373450 | QHWSYGLSPG |
| 11 | Chrysiptera cyanea | Pomacentridae | GnRH1 | LC009422 | QHWSYGLSPG |
| 12 | Amphiprion sebae | Pomacentridae | GnRH1 | KP260910 | QHWSYGLSPG |
| 13 | Amphiprion melanopus | Pomacentridae | GnRH1 | HQ883477 | QHWSYGWLPG |
| 14 | Salmo trutta | Salmonidae | GnRH1 | X79713 | QHWSYGWLPG |
| 15 | Salmo salar | Salmonidae | GnRH1 | X79709 | QHWSYGWLPG |
| 16 | Salmo fontinalis | Salmonidae | GnRH1 | X79712 | QHWSYGWLPG |
| Amino Acids Make up the Pocket | Grid Center | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| X | Y | Z | ||
| 1 | LEU109, GLN111, LEU112, LEU58, TRP63, SER64, SER68, PRO69, GLY70, GLY71, LYS72, ARG73 | 25.7012 | 48.0389 | 17.753 |
| 2 | HIS65, GLY66, SER68, PRO69, LYS72, ARG73, GLU74, VAL81 | 23.5412 | 46.6843 | 7.1108 |
| 3 | SER59, HIS62, HIS65, GLY66, GLU74, | 29.1709 | 52.7545 | 5.1961 |
| 4 | LEU58, SER59, HIS62, SER64, HIS65, ARG73 | 28.3709 | 54.1002 | 12.4156 |
| 5 | SER91, LEU92, CYS93, ASN95 | 7.4175 | 45.3487 | 24.4984 |
| 6 | LEU123, LYS127, ALA131, HIS38, LEU46, ALA52, ALA53, ALA54 | 43.5678 | 60.8414 | 24.49 |
| Sl.No. | Compounds | MW (<500) | TPSA (≤140) | nOHNH (≤5) | nON (≤5) | WLOGP (≤5.88) | Nrotb (≤10) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Seabream | 413.18 | 130.46 | 5 | 5 | −5.21 | 7 |
| 2 | LHRH, Lys(6)- | 453.41 | 100.65 | 7 | 6 | −4.65 | 4 |
| 3 | LHRH, leu(6)-leu(N-alpha-Me)(7)-N-Et-pronh2(9)- | 423.42 | 122.75 | 4 | 4 | −1.86 | 4 |
| 4 | LHRH, his(6)-N-Et-pronh2(9)- | 433.38 | 160.22 | 6 | 5 | −3.28 | 4 |
| 5 | LHRH, his(5)-trp(7)-tyr(8)- | 436.3 | 154.7 | 6 | 5 | −3.56 | 8 |
| 6 | LHRH, gln(1)-des-his(2)-phe(6)-N-Et-pronh2(9)- | 457.44 | 126.08 | 4 | 5 | 0.06 | 4 |
| 7 | LHRH, Des-tyr(5)- | 319.12 | 125.3 | 4 | 3 | −5.58 | 5 |
| 8 | LHRH (2–10), Trp(6)- | 400.35 | 158.24 | 6 | 4 | −2.11 | 9 |
| 9 | Leuprolide | 409.4 | 131.54 | 5 | 4 | −2.2 | 4 |
| 10 | H-Pyr-His-Trp-Ser-Tyr-Gly-OH | 259.77 | 196.83 | 1 | 1 | −2.35 | 3 |
| 11 | Gppt-LHRH | 418.6 | 179.55 | 7 | 5 | −1.96 | 5 |
| 12 | GnRH antagonist 2 | 207.57 | 150.43 | 2 | 1 | 2.71 | 1 |
| 13 | Ac-Abu-Phe(4-F)-Trp-Asp(1)-Gln-D-Arg-Leu-D-Lys-Pro-N(1)Gly-OH | 473.41 | 177.09 | 4 | 7 | −4.14 | 3 |
| 14 | Ac-Abu-Phe(4-Cl)-Trp-Asp-D-Cys(1)-D-Arg-D-Leu-D-Cys(1)-Pro-Ala-NH2 | 468.89 | 193.39 | 4 | 4 | 0.35 | 3 |
| 15 | N-Ac-(4-Cl-Phe)(1)-(4-Cl-Phe)(2)-Trp(3)-Lys(6)-AlaNH2(10)-LHRH | 371.19 | 142.45 | 5 | 4 | −2.45 | 7 |
| 16 | 3-ylpropanoyl amino-4-(2R,5S,8S,20R)-8-(2R)-2-(2S)-1-amino-1-oxopropan-2-ylcarbamoylpyrr | 436.88 | 115.16 | 5 | 8 | −2.6 | 3 |
| Sl.No. | Ligand | CID | Binding Affinity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | N-Ac-(4-Cl-Phe)(1)-(4-Cl-Phe)(2)-Trp(3)-Lys(6)-AlaNH2(10)-LHRH | 25078179 | −7.5 |
| 2 | LHRH_LYS(6) | 162695 | −6.7 |
| 3 | Seabream_GnRH | 118856782 | −5.9 |
| 4 | Leuprolide | 657181 | −5.8 |
| 5 | LHRH_Des-tyr(5) | 3081503 | −5.6 |
| 6 | LHRH, leu(6)-leu(N-alpha-Me)(7)-N-Et-pronh2(9) | 173522 | −5.5 |
| 7 | H-Pyr-His-Trp-Ser-Tyr-Gly-OH | 13054089 | −5.5 |
| 8 | Gppt-LHRH | 16132140 | −5.4 |
| 9 | LHRH, his(6)-N-Et-pronh2(9) | 164329 | −5.4 |
| 10 | GnRH antagonist 2 | 91755013 | −5.3 |
| 11 | LHRH, his(5)-trp(7)-tyr(8)- | 16130955 | −5.3 |
| 12 | LHRH, gln(1)-des-his(2)-phe(6)-N-Et-pronh2(9) | 25079029 | −5.2 |
| 13 | LHRH (2–10), Trp(6) | 25079046 | −5.2 |
| 14 | Ac-Abu-Phe(4-Cl)-Trp-Asp-D-Cys(1)-D-Arg-D-Leu-D-Cys(1)-Pro-Ala-NH2 | 44378909 | −5 |
| 15 | Ac-Abu-Phe(4-F)-Trp-Asp(1)-Gln-D-Arg-Leu-D-Lys-Pro-N(1)Gly-OH | 44378908 | −4.9 |
| 16 | (3S)-3-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-acetamidobutanoyl]amino]-3-(4-chlorophenyl)propanoyl]amino]-3-pyridin-3-ylpropanoyl]amino]-4-[[(2R,5S,8S,20R)-8-[(2R)-2-[[(2S)-1-amino-1-oxopropan-2-yl]carbamoyl]pyrr | 44378966 | −4.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Panda, S.P.; Das, B.K.; Gadnayak, A.; Nandy, S.K.; Kumar, V.; Pradhan, S.P.; Raut, S.S.; Chakrabarty, R.; Kunui, A.; Sahoo, A.K. Deciphering the 3D Structural Characterization of Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone in Tenualosa ilisha Using Homology Modeling, Molecular Dynamics, and Docking Approaches. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6098. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136098
Panda SP, Das BK, Gadnayak A, Nandy SK, Kumar V, Pradhan SP, Raut SS, Chakrabarty R, Kunui A, Sahoo AK. Deciphering the 3D Structural Characterization of Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone in Tenualosa ilisha Using Homology Modeling, Molecular Dynamics, and Docking Approaches. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(13):6098. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136098
Chicago/Turabian StylePanda, Soumya Prasad, Basanta Kumar Das, Ayushman Gadnayak, Saurav Kumar Nandy, Vikash Kumar, Smruti Priyambada Pradhan, Subhashree Subhasmita Raut, Ratul Chakrabarty, Arghya Kunui, and Amiya Kumar Sahoo. 2025. "Deciphering the 3D Structural Characterization of Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone in Tenualosa ilisha Using Homology Modeling, Molecular Dynamics, and Docking Approaches" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 13: 6098. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136098
APA StylePanda, S. P., Das, B. K., Gadnayak, A., Nandy, S. K., Kumar, V., Pradhan, S. P., Raut, S. S., Chakrabarty, R., Kunui, A., & Sahoo, A. K. (2025). Deciphering the 3D Structural Characterization of Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone in Tenualosa ilisha Using Homology Modeling, Molecular Dynamics, and Docking Approaches. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(13), 6098. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136098







