Quinazoline Derivative kzl052 Suppresses Prostate Cancer by Targeting WRN Helicase to Stabilize DNA Replication Forks
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
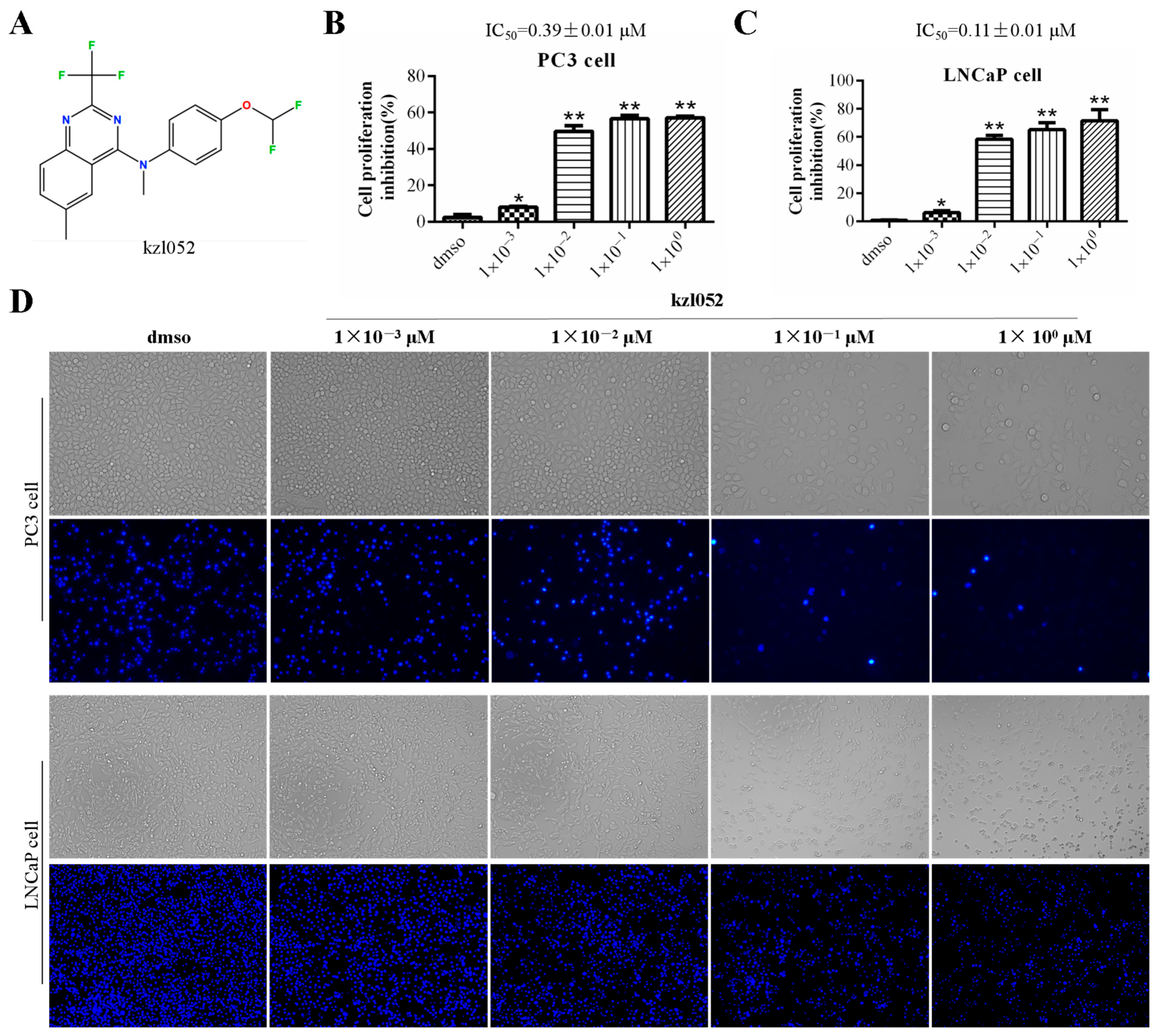
2.1. kzl052 Inhibits the Growth of Prostate Cancer Cells In Vitro
2.2. The Sensitivity of kzl052 Against Prostate Cancer by Targeting WRN
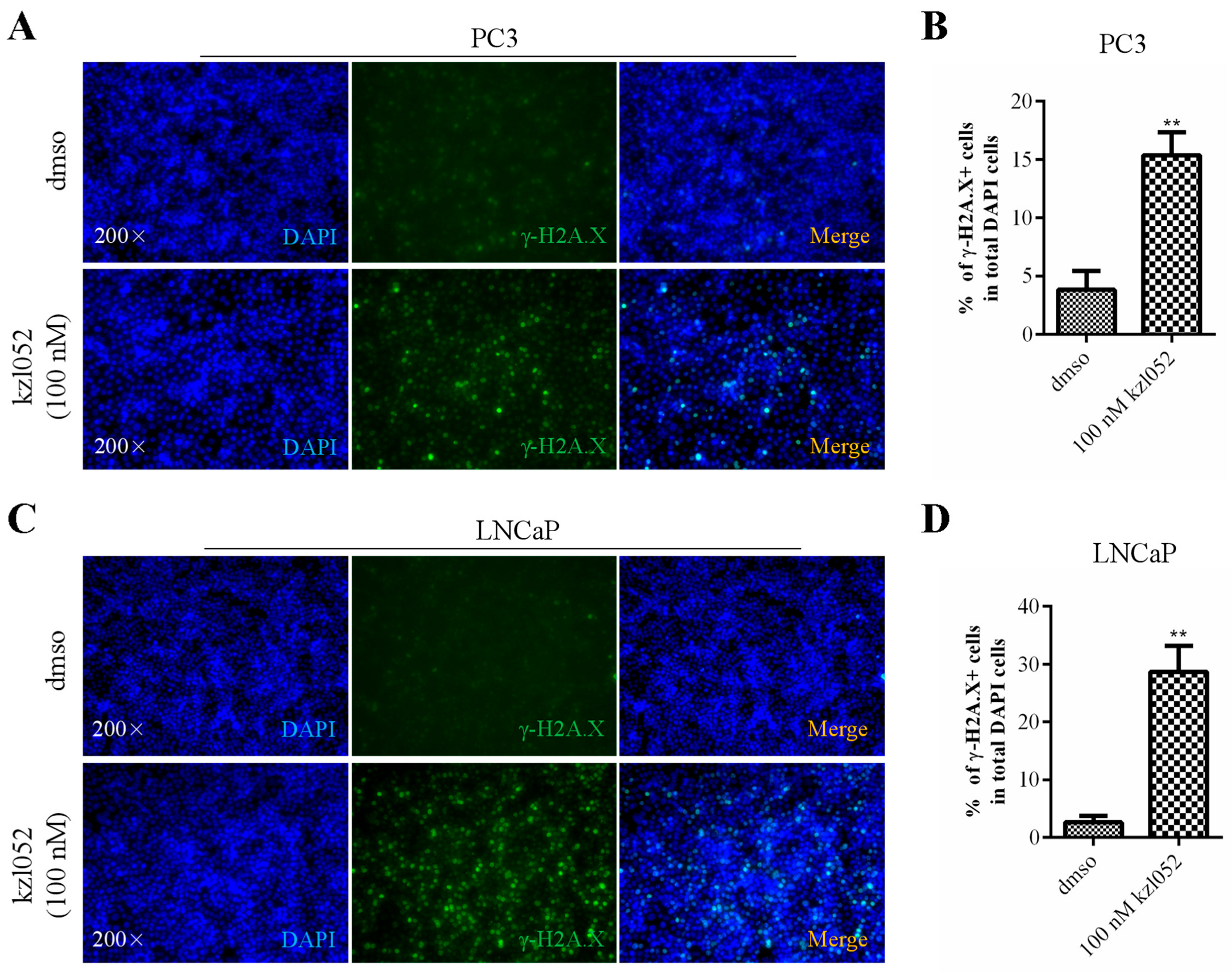
2.3. kzl052 Promotes DNA Damage in PCa Cells
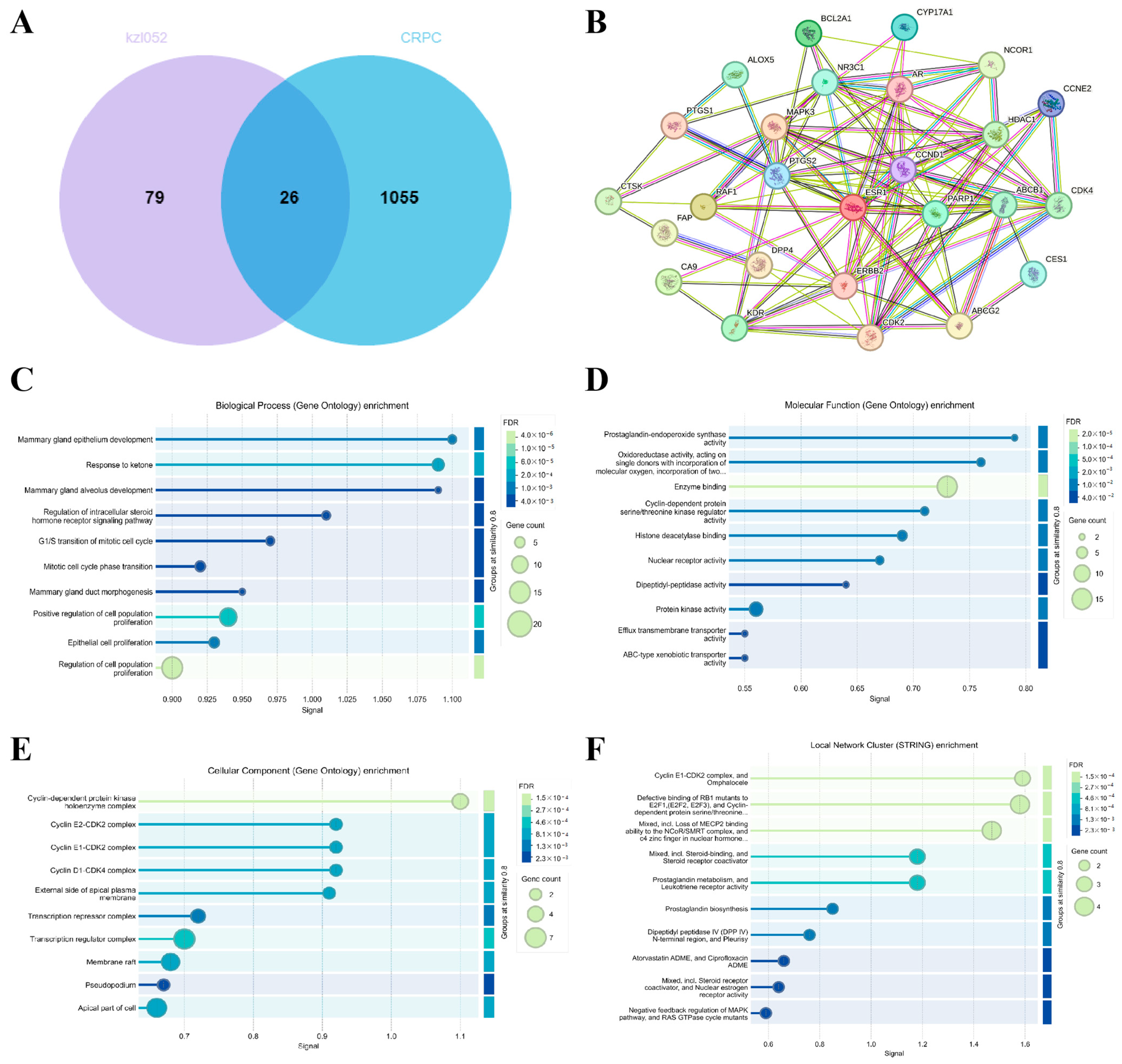
2.4. Signaling Pathway Analysis of kzl052 Inhibiting PCa Progression
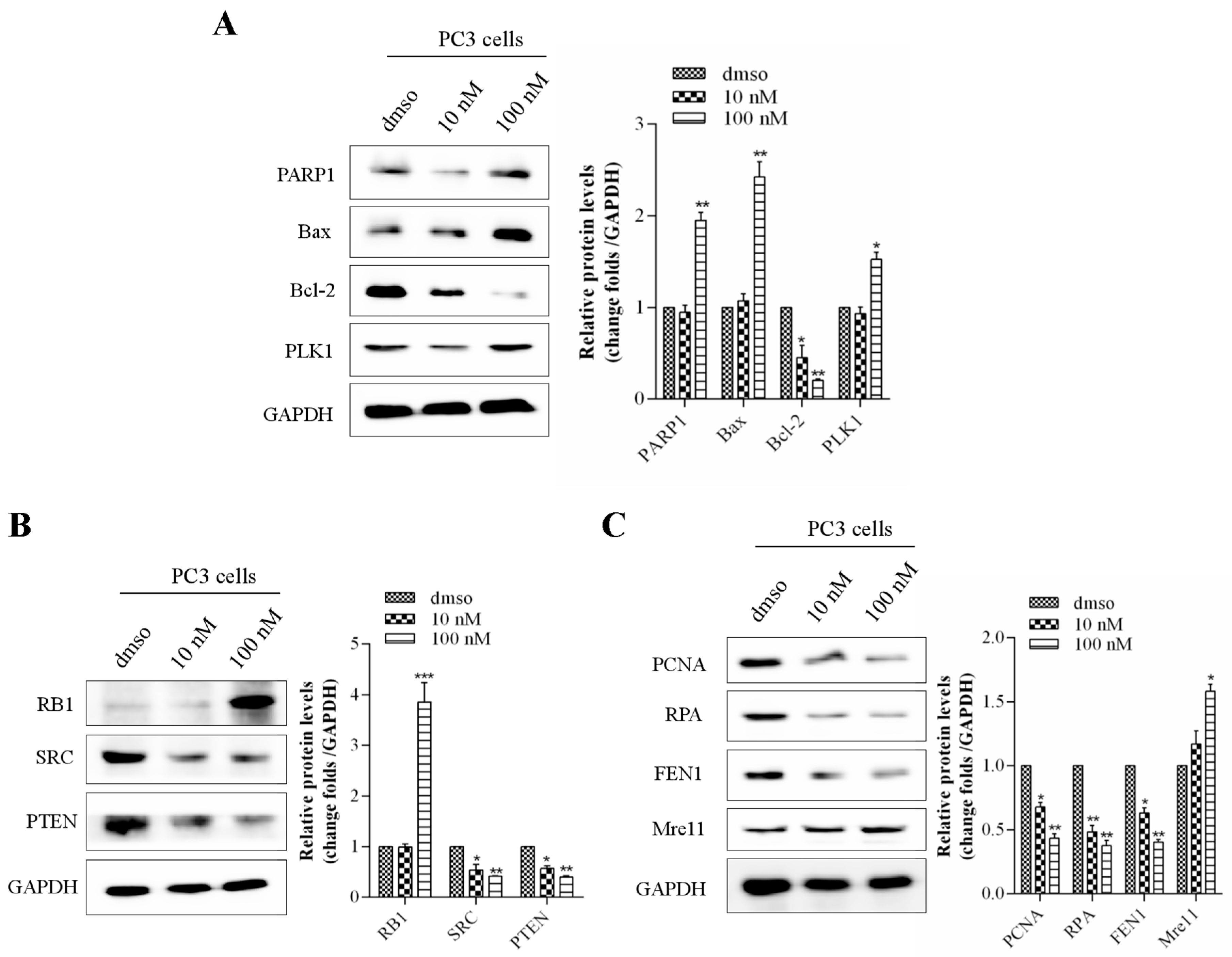
2.5. kzl052 Regulates the Stability of the DNA Replication Fork and RB Pathway
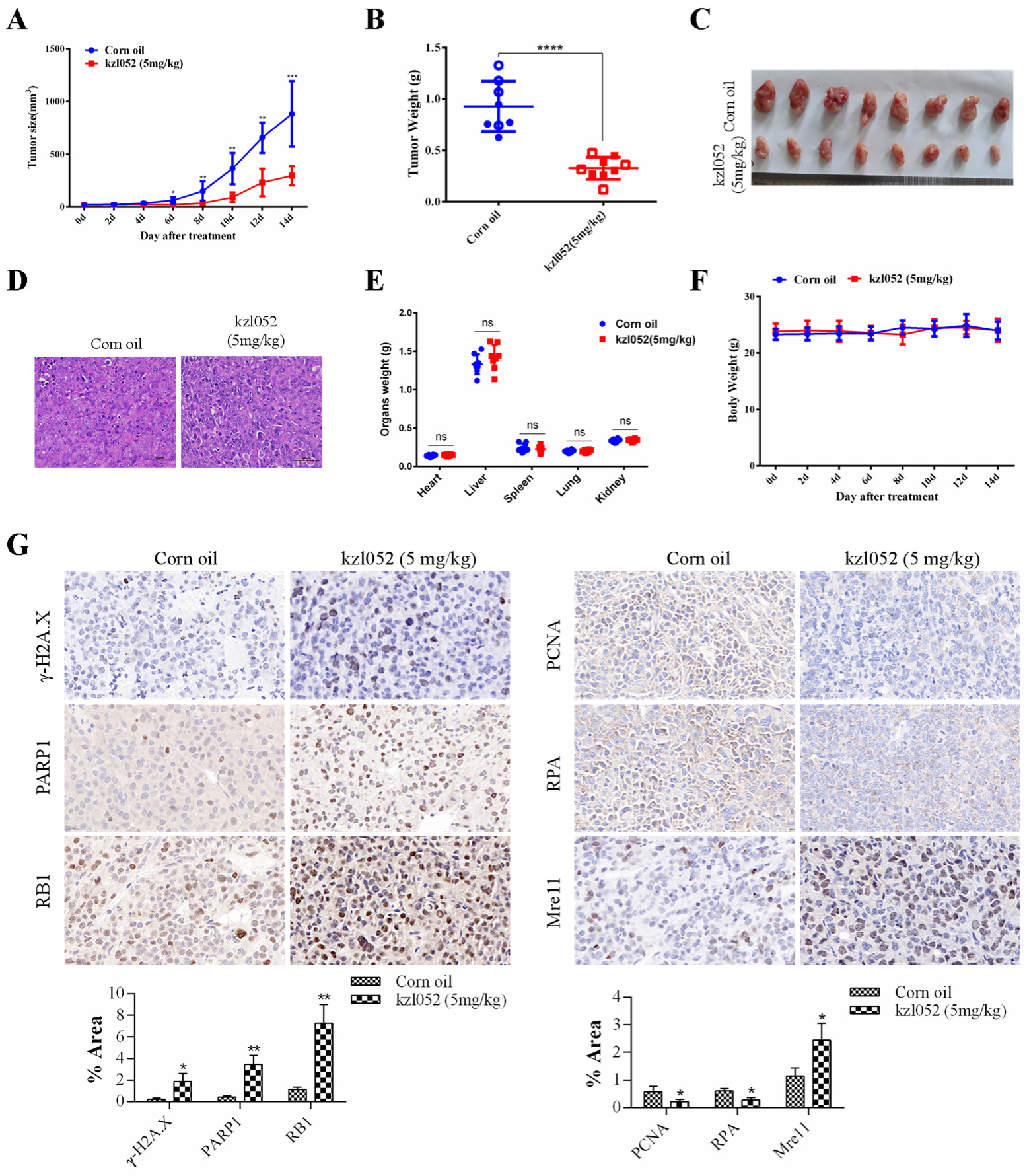
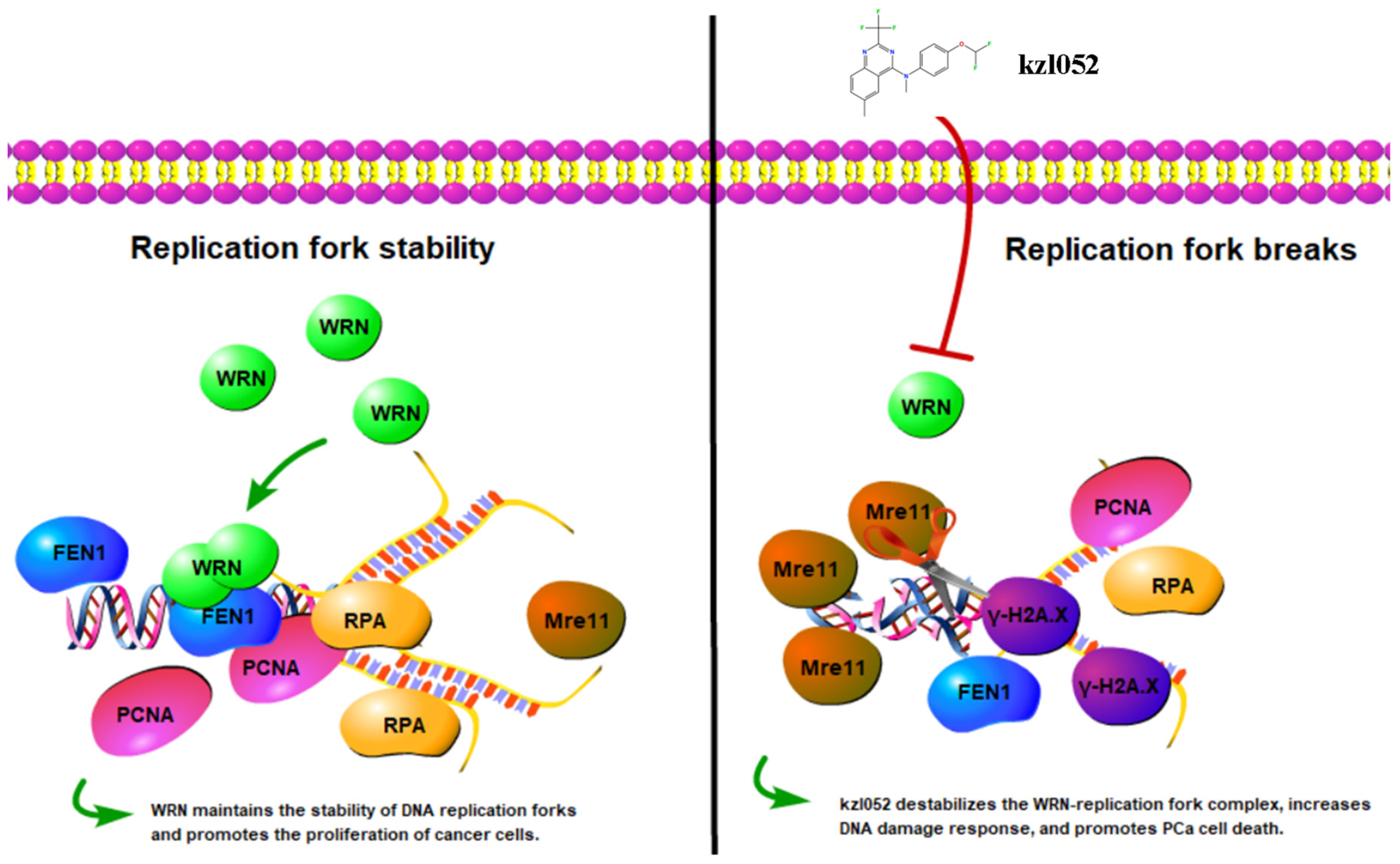
2.6. kzl052 Inhibits the Progression of Prostate Cancer by Regulating DNA Replication Fork Stability
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture and Transfection
4.2. MTT Assay
4.3. Hoechst Staining
4.4. AutoDocking
4.5. Cellular Thermal Shift Assay (CETSA)
4.6. Bioinformatics Analysis
4.7. Western Blot Assay
4.8. Immunofluorescence Assay
4.9. Animal Expriment
4.10. Hematoxylin and Eosin Staining (H&E)
4.11. Immunohistochemical Staining
4.12. Acute Toxicity Analysis
4.13. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CETSA | Cellular Thermal Shift Assay |
| H&E | Hematoxylin and Eosin Staining |
| WRN | Werner |
| PCa | Prostate Cancer |
| CRPC | Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer |
| WS | Werner Syndrome |
| ARG | Arginine |
| GO | Gene Ontology |
| MSI | Microsatellite Instability |
| MSS | Microsatellite Stability |
References
- Bergengren, O.; Pekala, K.R.; Matsoukas, K.; Fainberg, J.; Mungovan, S.F.; Bratt, O.; Bray, F.; Brawley, O.; Luckenbaugh, A.N.; Mucci, L.; et al. 2022 Update on Prostate Cancer Epidemiology and Risk Factors-A Systematic Review. Eur. Urol. 2023, 84, 191–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Mo, M.; Wei, Y.; Wu, J.; Pan, J.; Freedland, S.J.; Zheng, Y.; Ye, D. Epidemiology and genomics of prostate cancer in Asian men. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2021, 18, 282–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brawley, O.W.; Ramalingam, R. The enigma of race and prostate cancer. Cancer 2024, 130, 179–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.; Song, X.L.; Li, X.A.; Chen, M.; Guo, J.; Yang, D.H.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, S.C. Current therapy and drug resistance in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. Drug Resist. Updat. 2023, 68, 100962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makino, T.; Izumi, K.; Mizokami, A. Undesirable Status of Prostate Cancer Cells after Intensive Inhibition of AR Signaling: Post-AR Era of CRPC Treatment. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, F.; Xu, D.; Wang, S.; Wong, C.K.; Martinez-Fundichely, A.; Lee, C.J.; Cohen, S.; Park, J.; Hill, C.E.; Eng, K.; et al. Chromatin profiles classify castration-resistant prostate cancers suggesting therapeutic targets. Science 2022, 376, eabe1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKay, R.R.; Morgans, A.K.; Shore, N.D.; Dunshee, C.; Devgan, G.; Agarwal, N. First-line combination treatment with PARP and androgen receptor-signaling inhibitors in HRR-deficient mCRPC: Applying clinical study findings to clinical practice in the United States. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2024, 126, 102726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiorano, B.A.; Conteduca, V.; Catalano, M.; Antonuzzo, L.; Maiello, E.; De Giorgi, U.; Roviello, G. Personalized medicine for metastatic prostate cancer: The paradigm of PARP inhibitors. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2023, 192, 104157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seed, G.; Beije, N.; Yuan, W.; Bertan, C.; Goodall, J.; Lundberg, A.; Tyler, M.; Figueiredo, I.; Pereira, R.; Baker, C.; et al. Elucidating acquired PARP inhibitor resistance in advanced prostate cancer. Cancer Cell 2024, 42, 2113–2123.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orren, D.K.; Machwe, A. Response to Replication Stress and Maintenance of Genome Stability by WRN, the Werner Syndrome Protein. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 8300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mojumdar, A. Mutations in conserved functional domains of human RecQ helicases are associated with diseases and cancer: A review. Biophys. Chem. 2020, 265, 106433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, J.A.; Gileadi, O. RecQ helicases in DNA repair and cancer targets. Essays Biochem. 2020, 64, 819–830. [Google Scholar]
- Baxter, J.S.; Zatreanu, D.; Pettitt, S.J.; Lord, C.J. Resistance to DNA repair inhibitors in cancer. Mol. Oncol. 2022, 16, 3811–3827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, J.H.; Sellamuthu, K.; Prakash, L.; Prakash, S. WRN exonuclease imparts high fidelity on translesion synthesis by Y family DNA polymerases. Genes Dev. 2024, 38, 213–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paccosi, E.; Guzzon, D.; Proietti-De-Santis, L. Genetic and epigenetic insights into Werner Syndrome. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2025, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picco, G.; Cattaneo, C.M.; van Vliet, E.J.; Crisafulli, G.; Rospo, G.; Consonni, S.; Vieira, S.F.; Rodríguez, I.S.; Cancelliere, C.; Banerjee, R.; et al. Cell Model Network UK Group. Werner Helicase Is a Synthetic-Lethal Vulnerability in Mismatch Repair-Deficient Colorectal Cancer Refractory to Targeted Therapies, Chemotherapy, and Immunotherapy. Cancer Discov. 2021, 11, 1923–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savva, C.; Sadiq, M.; Sheikh, O.; Karim, S.; Trivedi, S.; Green, A.R.; Rakha, E.A.; Madhusudan, S.; Arora, A. Werner Syndrome Protein Expression in Breast Cancer. Clin. Breast Cancer 2021, 21, 57–73.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, S.; Tong, J.; Jha, A.; Risnik, D.; Lizardo, D.; Lu, X.; Goel, A.; Opresko, P.L.; Yu, J.; Zhang, L. Synthetical lethality of Werner helicase and mismatch repair deficiency is mediated by p53 and PUMA in colon cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2211775119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallmyr, A.; Tomkinson, A.E.; Rassool, F.V. Up-regulation of WRN and DNA ligase IIIalpha in chronic myeloid leukemia: Consequences for the repair of DNA double-strand breaks. Blood 2008, 112, 1413–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Kaku, H.; Huang, P.; Xu, K.; Yang, K.; Zhang, J.; Li, M.; Xie, L.; Wang, X.; Sakai, A.; et al. Single nucleotide polymorphism WRN Leu1074Phe is associated with prostate cancer susceptibility in Chinese subjects. Acta Med. Okayama 2011, 65, 315–323. [Google Scholar]
- Febres-Aldana, C.A.; Krishnamurthy, K.; Delgado, R.; Kochiyil, J.; Poppiti, R.; Medina, A.M. Prostatic carcinoma with neuroendocrine differentiation harboring the EWSR1-FEV fusion transcript in a man with the WRN G327X germline mutation: A new variant of prostatic carcinoma or a member of the Ewing sarcoma family of tumors? Pathol. Res. Pract. 2020, 216, 152758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Liang, G.; Cheng, S.; Wei, J.; Li, H.; Liu, X.; You, C.; Mao, M.; Ahmad, M.; et al. Quinazoline derivatives inhibit cell growth of prostate cancer as a WRN helicase dependent manner by regulating DNA damage repair and microsatellite instability. Bioorg. Chem. 2024, 153, 107963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Yu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, K.; Peng, X.; Xu, G.; Chen, C.; Meng, X.; Zeng, X.; Wu, H.; et al. Discovery of novel quinazoline derivatives containing trifluoromethyl against cell proliferation by targeting werner helicase. Mol. Divers. 2025, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djerir, B.; Maréchal, A. Detection of γ-H2A.X for Rapid Assessment of Genotoxic Agent-induced Double-strand DNA Breaks by Immunofluorescence. Methods Mol. Biol. 2025, 2919, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chappidi, N.; Quail, T.; Doll, S.; Vogel, L.T.; Aleksandrov, R.; Felekyan, S.; Kühnemuth, R.; Stoynov, S.; Seidel, C.A.M.; Brugués, J.; et al. PARP1-DNA co-condensation drives DNA repair site assembly to prevent disjunction of broken DNA ends. Cell 2024, 187, 945–961.e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahi, M.S.; Islam, M.S.; Jerin, I.; Jahangir, C.A.; Hasan, M.M.; Hoque, K.M.F.; Reza, M.A. Differential expression of Bax-Bcl-2 and PARP-1 confirms apoptosis of EAC cells in Swiss albino mice by Morus laevigata. J. Food Biochem. 2020, 44, e13342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.; Liu, M.; Han, D.; Li, M.; Toure, A.A.; Wang, Z.; Besschetnova, A.; Patalano, S.; Macoska, J.A.; Gao, S.; et al. RB1 loss in castration-resistant prostate cancer confers vulnerability to LSD1 inhibition. Oncogene 2022, 41, 852–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Zhang, J.; Liu, X.; Li, M.; Wang, D.; Kang, Z.; Yu, J.; Chen, J.; Pan, H.; Wang, H.; et al. PTEN loss promotes Warburg effect and prostate cancer cell growth by inducing FBP1 degradation. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 911466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heng, P.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Liu, C.; Zhao, X.; Fan, J.; Xu, C. Identification of evodiamine as a suppressor of prostate cancer progression by reducing AR transcriptional activity via targeting Src. Endocrine 2022, 75, 635–645. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, L.; Bi, T.; Wang, L.; Xiao, W. DNA-damage tolerance through PCNA ubiquitination and sumoylation. Biochem. J. 2020, 477, 2655–2677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, X.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, D.; Shi, J.; Zhao, H.; Xie, C.; Wang, Y.; Xu, J.; Zhang, X.; Cai, G.; et al. Proper RPA acetylation promotes accurate DNA replication and repair. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, 5565–5583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yong, C.; Fu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Guo, Z.; Liu, S.B.; Hu, Z. Inhibition of FEN1 promotes DNA damage and enhances chemotherapeutic response in prostate cancer cells. Med. Oncol. 2023, 40, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vertemara, J.; Tisi, R. Dynamic Properties of the DNA Damage Response Mre11/Rad50 Complex. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 12377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryu, J.S.; Koo, H.S. Roles of Caenorhabditis elegans WRN Helicase in DNA Damage Responses, and a Comparison with Its Mammalian Homolog: A Mini-Review. Gerontology 2016, 62, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, E.M.; Shibue, T.; McFarland, J.M.; Gaeta, B.; Ghandi, M.; Dumont, N.; Gonzalez, A.; McPartlan, J.S.; Li, T.; Zhang, Y.; et al. WRN helicase is a synthetic lethal target in microsatellite unstable cancers. Nature 2019, 568, 551–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, S.; Hamon, J.; de Kanter, R.; Scheufler, C.; Andraos-Rey, R.; Barbe, S.; Bechter, E.; Blank, J.; Bordas, V.; Dammassa, E.; et al. Discovery of WRN inhibitor HRO761 with synthetic lethality in MSI cancers. Nature 2024, 629, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.; Majumdar, A.G.; Patro, B.S. Non-enzymatic function of WRN RECQL helicase regulates removal of topoisomerase-I-DNA covalent complexes and triggers NF-κB signaling in cancer. Aging Cell 2022, 21, e13625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.; Hyun, K.; Lee, J.; Joo, D.; Kulikowicz, T.; Bohr, V.A.; Kim, J.; Hohng, S. Werner syndrome protein works as a dimer for unwinding and replication fork regression. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, 337–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noto, A.; Valenzisi, P.; Di Feo, F.; Fratini, F.; Kulikowicz, T.; Sommers, J.A.; Perdichizzi, B.; Semproni, M.; Palermo, V.; Crescenzi, M.; et al. Phosphorylation-dependent WRN-RPA interaction promotes recovery of stalled forks at secondary DNA structure. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackay, H.L.; Stone, H.R.; Ronson, G.E.; Ellis, K.; Lanz, A.; Aghabi, Y.; Walker, A.K.; Starowicz, K.; Garvin, A.J.; Van Eijk, P.; et al. USP50 suppresses alternative RecQ helicase use and deleterious DNA2 activity during replication. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 8102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maresca, C.; Dello Stritto, A.; D’Angelo, C.; Petti, E.; Rizzo, A.; Vertecchi, E.; Berardinelli, F.; Bonanni, L.; Sgura, A.; Antoccia, A.; et al. PARP1 allows proper telomere replication through TRF1 poly (ADP-ribosyl)ation and helicase recruitment. Commun. Biol. 2023, 6, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Datta, A.; Brosh, R.M., Jr. WRN rescues replication forks compromised by a BRCA2 deficiency: Predictions for how inhibition of a helicase that suppresses premature aging tilts the balance to fork demise and chromosomal instability in cancer. Bioessays 2022, 44, e2200057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Datta, A.; Biswas, K.; Sommers, J.A.; Thompson, H.; Awate, S.; Nicolae, C.M.; Thakar, T.; Moldovan, G.L.; Shoemaker, R.H.; Sharan, S.K.; et al. WRN helicase safeguards deprotected replication forks in BRCA2-mutated cancer cells. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ketola, K.; Kaljunen, H.; Taavitsainen, S.; Kaarijärvi, R.; Järvelä, E.; Rodríguez-Martín, B.; Haase, K.; Woodcock, D.J.; Tubio, J.; Wedge, D.C.; et al. Subclone Eradication Analysis Identifies Targets for Enhanced Cancer Therapy and Reveals L1 Retrotransposition as a Dynamic Source of Cancer Heterogeneity. Cancer Res. 2021, 81, 4901–4909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Cell Lines | IC50 Values (μM) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| kzl052 | Docetaxel | NSC 617145 | |
| LX2 | 3.12 ± 0.09 * | 0.41 ± 0.11 | 1.81 ± 0.27 |
| HK2 | 0.92 ± 0.24 *** | 0.11 ± 0.01 | 5.64 ± 0.96 |
| Concentration | Number | Volume | Survival Number | Death Number | Survival Rate | Mortality Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 mg/kg | 4 | 100 μL | 4 | 0 | 100% | 0 |
| 50 mg/kg | 4 | 100 μL | 4 | 0 | 100% | 0 |
| 100 mg/kg | 4 | 100 μL | 4 | 0 | 100% | 0 |
| 200 mg/kg | 4 | 100 μL | 4 | 0 | 100% | 0 |
| 500 mg/kg | 4 | 100 μL | 1 | 3 | 25% | 75% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, J.; Yu, G.; Cheng, S.; Hu, L.; Zan, N.; Xu, B.; Cao, Y.; Luo, H. Quinazoline Derivative kzl052 Suppresses Prostate Cancer by Targeting WRN Helicase to Stabilize DNA Replication Forks. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6093. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136093
Yu J, Yu G, Cheng S, Hu L, Zan N, Xu B, Cao Y, Luo H. Quinazoline Derivative kzl052 Suppresses Prostate Cancer by Targeting WRN Helicase to Stabilize DNA Replication Forks. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(13):6093. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136093
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Jia, Gang Yu, Sha Cheng, Liangliang Hu, Ningning Zan, Bixue Xu, Ying Cao, and Heng Luo. 2025. "Quinazoline Derivative kzl052 Suppresses Prostate Cancer by Targeting WRN Helicase to Stabilize DNA Replication Forks" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 13: 6093. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136093
APA StyleYu, J., Yu, G., Cheng, S., Hu, L., Zan, N., Xu, B., Cao, Y., & Luo, H. (2025). Quinazoline Derivative kzl052 Suppresses Prostate Cancer by Targeting WRN Helicase to Stabilize DNA Replication Forks. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(13), 6093. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136093






